一、背景
在一个页面中需要渲染长列表,且每一项高度不固定。若一次性将数据渲染到 DOM 中,会带来以下问题:
- 首次加载卡顿:大量 DOM 节点创建耗时;
- 交互卡顿:新增、编辑等操作触发频繁重排(reflow)与重绘(repaint);
- 内存占用高:浏览器需维护大量未可视的节点;
- 跳转困难:用户需快速定位到某个特定表格(如通过左侧树节点点击),但目标区域可能尚未渲染。
因此,我们需要一种既能减少初始渲染量 ,又能支持高效滚动与精准跳转的方案。通常大家都会想到分页、懒加载、虚拟滚动。这里分页并不适用项目场景,所以对比下懒加载与虚拟滚动。
二、方案对比:懒加载 vs 虚拟滚动
| 特性 | 懒加载(Lazy Loading) | 虚拟滚动(Virtual Scrolling) |
|---|---|---|
| 核心目标 | 延迟加载资源,减少首屏时间 | 仅渲染可视区域,提升滚动性能 |
| 优化对象 | 图片、数据、组件等资源 | DOM 节点数量(列表项) |
| 适用场景 | 图片瀑布流、路由懒加载、分页列表 | 超长列表、动态高度表格、聊天记录等 |
| DOM 节点数 | 最终仍可能渲染全部节点(只是延迟) | 始终保持少量节点,动态复用 |
| 滚动性能 | 无直接优化,滚动仍可能卡顿 | 显著提升流畅度,避免回流重绘 |
| 实现复杂度 | 简单(如 Intersection Observer) |
较高(需管理滚动、高度测量、复用逻辑) |
✅ 结论 :
我们不仅需要减少初始加载压力,更需保障滚动流畅性 和高频 DOM 操作(如编辑)的响应速度 。
虚拟滚动通过限制 DOM 节点数量,从根本上降低了重排重绘成本,是更优解。
三、解决方案:使用 vue-virtual-scroller(Vue 3)
1、安装与注册
TypeScript
# vue2中
npm i vue-virtual-scroller
# Vue 3 项目需安装 @next 版本
npm install vue-virtual-scroller@next
TypeScript
// main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueVirtualScroller from 'vue-virtual-scroller'
import 'vue-virtual-scroller/dist/vue-virtual-scroller.css'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(VueVirtualScroller)
app.mount('#app')2、核心组件:DynamicScroller + DynamicScrollerItem
适用于不定高度的列表项(如动态行数的表格)。
✅ 模板代码
html
<template>
<DynamicScroller
ref="dynamicScrollerRef"
class="scroller"<!-- 必须有固定高度比如100vh,如果没有设置高度,滚动容器无法工作 -->
:items="renderedList"<!-- 要渲染的数据列表 -->
:min-item-size="200" <!-- 列表项预估高度(px) -->
key-field="processId" <!-- 唯一标识字段 -->
v-slot="{ item, index, active }"
>
<DynamicScrollerItem
:item="item"<!-- 列表项 -->
:active="active"<!-- 当前是否处于活跃状态 -->
:size-dependencies="[item.children.length"<!-- 声明影响 item 高度的依赖项 -->
:data-index="index"<!-- 用于定位快速 -->
>
<!-- 自定义列表项 -->
<a-table
:columns="columns"
:key="`table-${item.processId}`"
:data-source="item.children"
style="margin-top: 10px;"
:pagination="false"
bordered
:data-process-id="item.processId"
>
<template #title>
<!-- 表格标题内容 -->
</template>
<template #bodyCell="{ column, text, record }">
<!-- 单元格自定义渲染 -->
</template>
</a-table>
</DynamicScrollerItem>
</DynamicScroller>
</template>✅ 逻辑
TypeScript
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, nextTick } from 'vue'
interface ChildItem {
index: number;
product: string;
test1: string;
// ...其他字段
}
interface ParentItem {
processId: string;
processName: string;
children: ChildItem[];
// ...其他字段
}
const dynamicScrollerRef = ref()
const renderedList = ref<ParentItem[]>([])
const columns = [
{ title: '序号', dataIndex: 'index', width: 50 },
{ title: '产品', dataIndex: 'product', width: 100 },
// ...其他列
]
// 模拟数据加载
const fetchData = async () => {
const res = await api.getProcessData()
renderedList.value = res.data
}
// 跳转到指定 processId 的表格
const scrollToProcess = (operationId: string) => {
const idx = renderedList.value.findIndex(p => p.processId === operationId)
if (idx >= 0) {
nextTick(() => {
dynamicScrollerRef.value?.scrollToItem(idx, { align: 'center' })
})
}
}
</script>✅ 样式要求
css
.scroller {
height: calc(100vh - 100px); /* 必须设置固定高度 */
}✅ 关键属性详解
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
:min-item-size |
初始布局占位高度(单位 px)。建议设为非全屏状态下的平均表格高度。 |
key-field |
数据项的唯一 ID 字段,用于稳定追踪 item 身份。 |
:size-dependencies |
极其重要! 声明影响高度的依赖项。例如: [item.children.length, fullScreenTableId === item.processId] 当这些值变化时,组件会自动重新测量高度。 |
scrollToItem(index, { align }) |
官方提供的跳转方法,支持 'start'、'center'、'end' 对齐方式,即使目标未渲染也能精准跳转。 |
✅ 效果
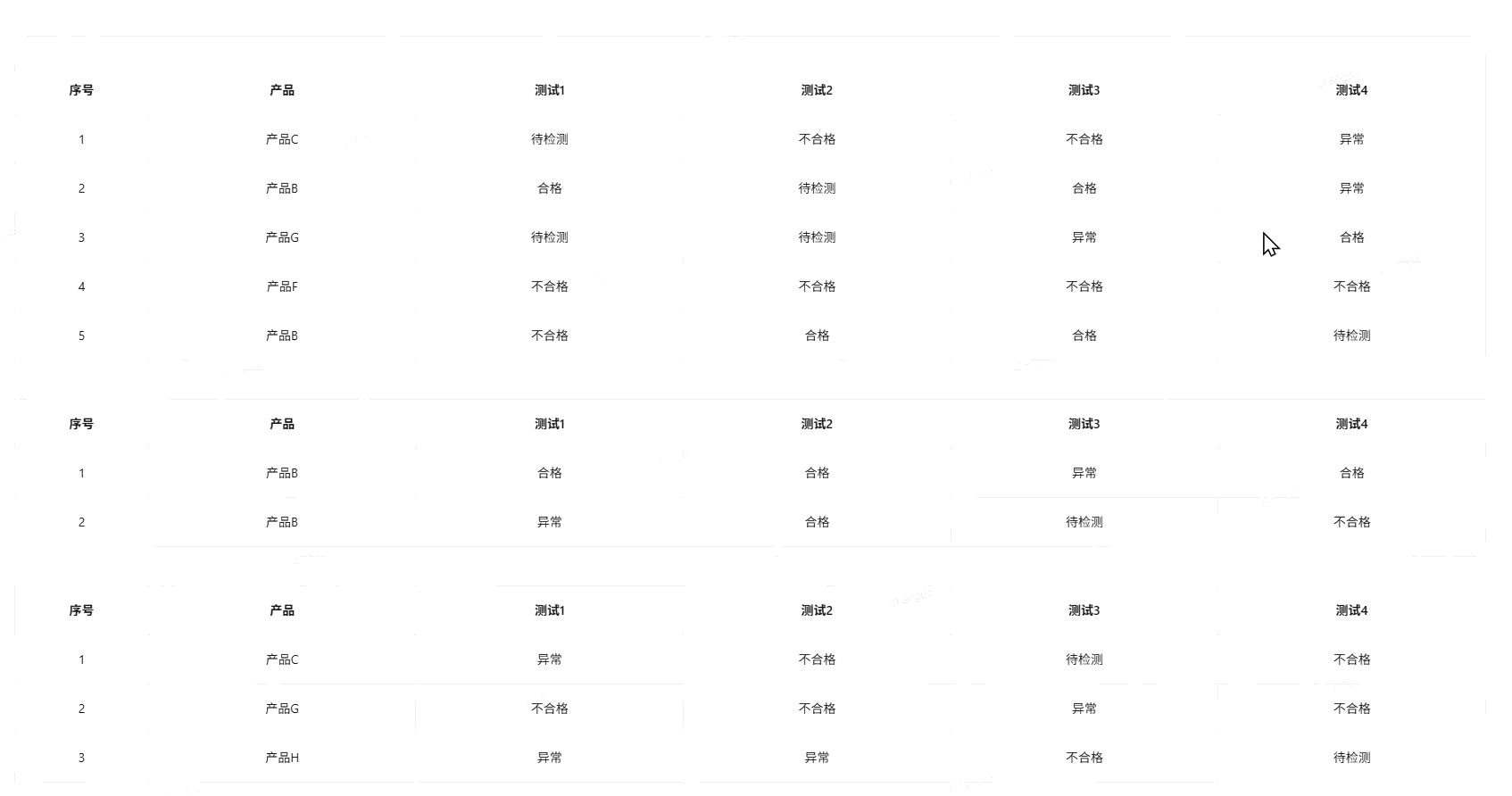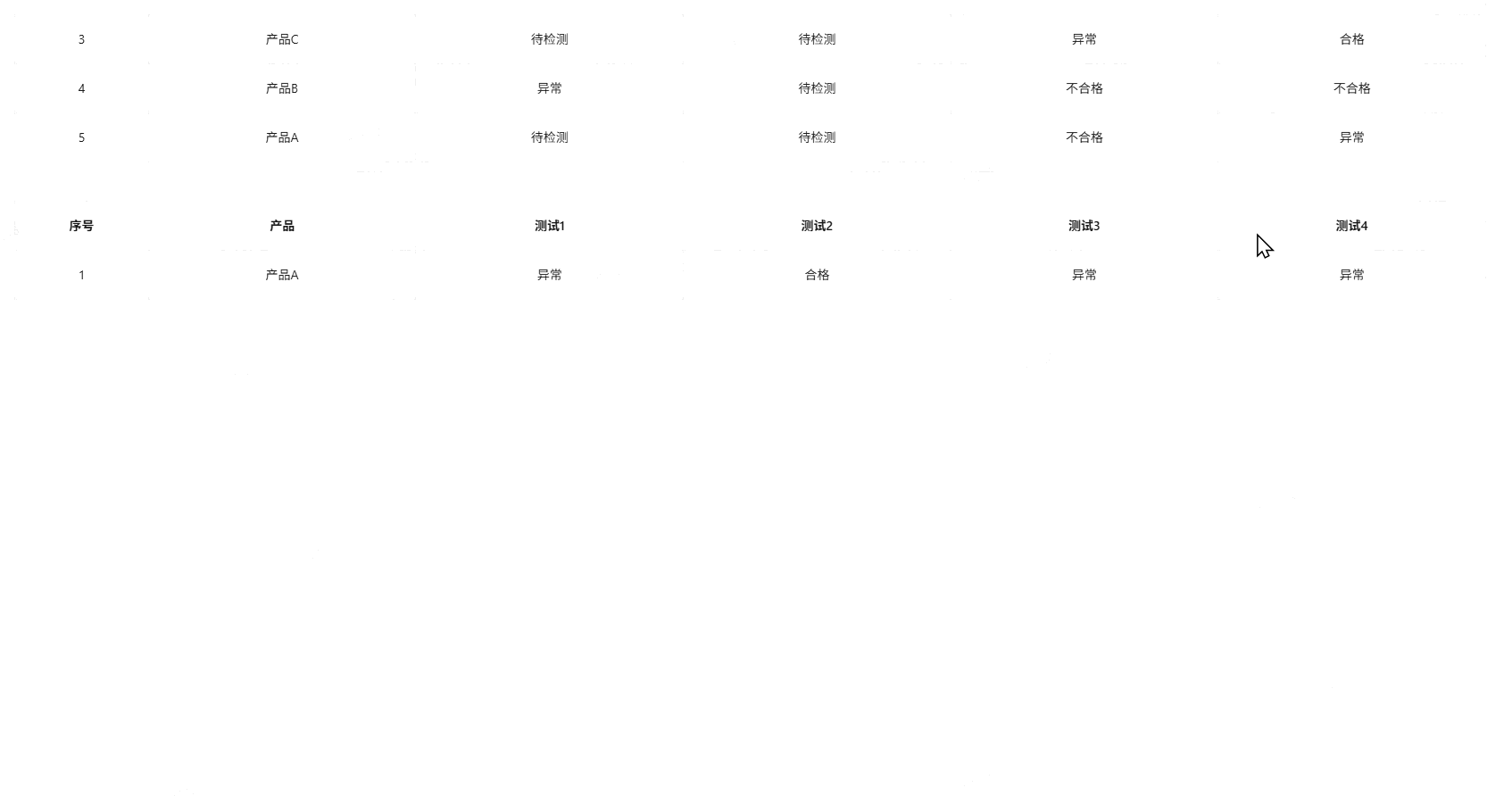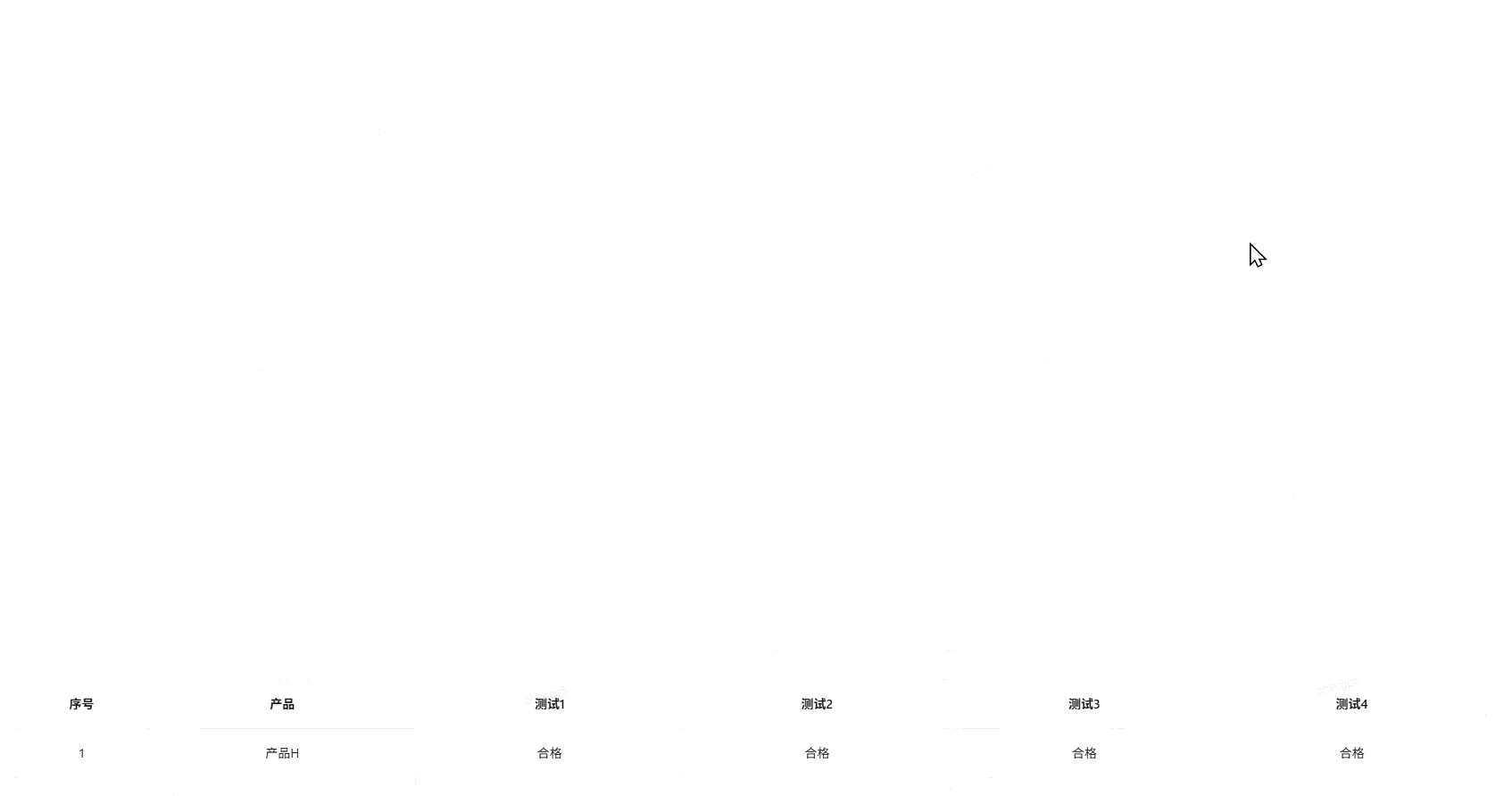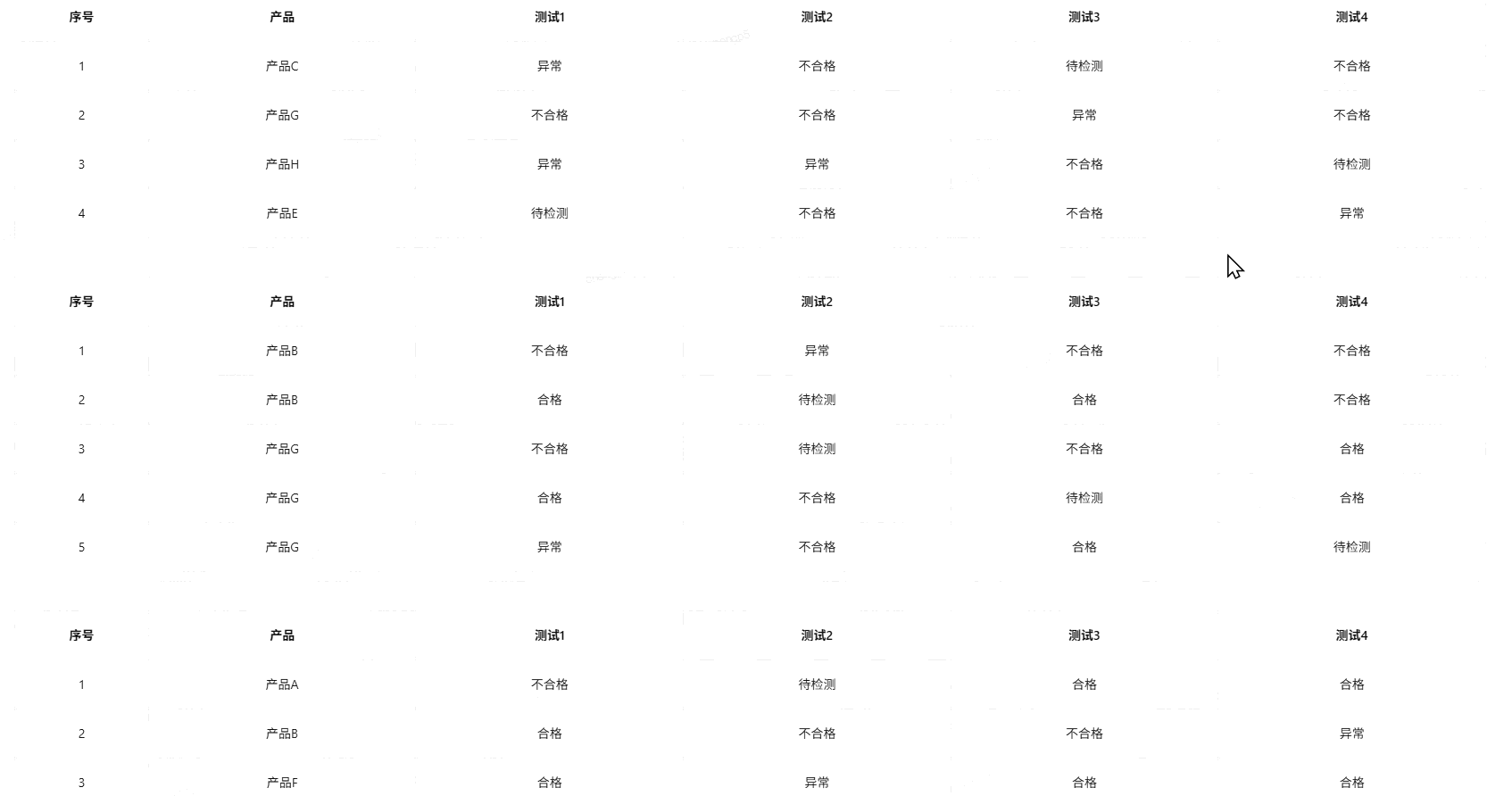
3、附加需求:精准跳转到指定表格
早期尝试使用
document.querySelector().scrollIntoView()失败,原因在于:❌ 未渲染的 DOM 不存在 → 查询返回
null→ 跳转失效。正确做法✅ :使用
DynamicScroller内置的scrollToItem方法。scrollToItem(index, { align = 'start' | 'center' | 'end' })
TypeScript
const scrollToProcess = (operationId: string) => {
const idx = renderedList.value.findIndex(p => p.processId === operationId)
if (idx !== -1) {
nextTick(() => {
dynamicScrollerRef.value?.scrollToItem(idx, { align: 'center' })
})
}
}💡 优势:
- 无需等待 DOM 渲染;
- 自动触发目标项的渲染与测量;
- 基于真实布局计算滚动位置,精准可靠。
四、总结
- 虚拟滚动 是处理大量动态高度列表/表格的最佳实践;
vue-virtual-scroller@next提供了完善的DynamicScroller组件,支持:- 不定高度自动测量;
- 高效 DOM 复用;
- 内置
scrollToItem跳转能力;
- 避免误区 :不要依赖原生
scrollIntoView,应使用组件提供的跳转 API。
🌟 经验之谈 :
曾经以为"跳转"需要手动实现,写了一大堆滚动计算和预加载逻辑,结果发现库本身已完美支持。善用官方 API,少造轮子,多查文档!
没用vue-virtual-scroller之前,使用手动实现,代码直接多了两三倍...
手动实现
1、模板部分
html
<div @scroll="handleScroll" :style="{ height: 'calc(100vh - 100px)', overflowY: 'auto' }" >
<a-table :columns="columns" v-for="(item) in renderedProcessList" :key="`table-${item.processId}`" v-memo="[item, fullScreenTableId]" :data-source="item.children"
style="margin-top: 10px;" :pagination="false" :data-process-id="item.processId">
<!-- ........省略 -->
</a-table>
</div>2、逻辑部分
总体思路:实现一个动态缓冲区 的虚拟列表滚动。核心思想是:仅渲染当前可视区域附近的固定条数数据(如40条),并在上下滚动时动态加载更多数据,同时回收不可见的数据。
(1)定义虚拟列表相关变量
javascript
const fullDataCache = ref([]); // 完整数据缓存
const renderedProcessList = ref([]); // 当前渲染的数据(40条)
const startIndex = ref(0); // 当前渲染数据的起始索引
const endIndex = ref(0); // 当前渲染数据的结束索引
const bufferSize = 40; // 缓冲区大小,即同时渲染的数据条数
const scrollSize = 20; // 向上向下滚动加载数据条数
const shouldHandleScroll = ref(true); //控制跳转时是否触发向上向下滚动(2)首先是初始化时候,不要一下子渲染后端返回的全部数据。而是接收这部分数据但是只渲染固定条数的数据。
javascript
//初始化,全量更新,但只渲染部分数据
const queryProcessList = async (lineId) => {
const res = await controlPlanApi.queryData(lineId);
fullDataCache.value = res.data;
startIndex.value = 0;
endIndex.value = Math.min(bufferSize, fullDataCache.value.length);
renderedProcessList.value = fullDataCache.value.slice(startIndex.value, endIndex.value); // 初始化渲染前40条数据
};(3)接下来就是考虑上下滚动如何加载数据的问题。我的思路是,当滚动到距离顶部/底部10%的距离时,就动态替换原有的渲染数组索引。
|---------------|------------------------------|------------------------------|
| 原有的渲染数组索引 | 向上滚动 | 向下滚动 |
| startIndex | newStartIndex=startIndex-20 | newStartIndex=newEndIndex-40 |
| endIndex | newEndIndex=newStartIndex+40 | newEndIndex=endIndex+20 |
javascript
// 滚动处理函数
const handleScroll = (event) => {
if (!shouldHandleScroll.value) return;
const container = event.target;
const scrollTop = container.scrollTop;//距离顶部滚动的距离
const scrollHeight = container.scrollHeight; // 总高度
//当向下滚动距离底部小于10%时,加载当前数组索引的后面20个数据。
if(scrollTop/scrollHeight > 0.9 && endIndex.value < fullDataCache.value.length){
const newEnd = Math.min(fullDataCache.value.length, endIndex.value + scrollSize);//newEnd=旧的+20
const newStart = Math.max(0, newEnd - bufferSize);//新开始索引 = newEnd-40
startIndex.value = newStart;
endIndex.value = newEnd;
renderedProcessList.value = fullDataCache.value.slice(newStart, newEnd);
// console.log("向下滚动",newStart, newEnd);
}else if(scrollTop/scrollHeight < 0.1 && startIndex.value > 0){
//当向上滚动距离顶部小于10%距离时,加载当前数组索引的前面20个数据。
const newStart = Math.max(0, startIndex.value - scrollSize);//newStart = 旧start - 20
const newEnd = Math.min(newStart + bufferSize, fullDataCache.value.length);//newEnd = newStart + 40
startIndex.value = newStart;
endIndex.value = newEnd;
renderedProcessList.value = fullDataCache.value.slice(newStart, newEnd);
// console.log("向上滚动",newStart, newEnd);
}
};(4)实现指定跳转
javascript
// 跳转
const scrollToProcess = (id) => {
const targetIndex = fullDataCache.value.findIndex(process => process.processId === id);
if (targetIndex === -1) return;
const newStart = Math.max(0, targetIndex - 20);
const newEnd = Math.min(fullDataCache.value.length, newStart + bufferSize);
// 更新当前渲染数据
startIndex.value = newStart;
endIndex.value = newEnd;
renderedProcessList.value = fullDataCache.value.slice(newStart, newEnd);
// console.log("跳转",newStart, newEnd, targetIndex);
nextTick(() => {
const targetElement = document.querySelector(`[data-process-id="${id}"]`);
if (targetElement) {
// 滚动到目标元素位置
targetElement.scrollIntoView({
behavior: 'smooth',
block: 'center'
});
}
});
};