目录
一.HttpRequest子模块
1.1.设计思路
1.1.1.基本思路
首先,我们既然说了这是HTTP请求,那么我们必须知道HTTP请求长什么样子吧

可以看到,这里就是有很多东西需要我们去存储
- 请求方法
- URL(资源请求路径)
- 协议版本
- 请求报头里面的键值对
- 有效载荷
cpp
// 请求方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等)
std::string _method;
// HTTP协议版本(如HTTP/1.1)
std::string _version;
// 请求正文内容
std::string _body;
// 存储HTTP请求头部的键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers;有人可能好奇,嗯?URL呢?别急,我们下面就说
1.1.2.URL的特殊情况
但是,在HTTP请求中,请求行(request line)的第二个部分就是请求的URL(或路径)。
我们常说的URL可能是下面这个东西

例如,一个完整的URL可能是:http://www.example.com:80**/search?q=hello & b=nnnn**
然而,当客户端发起HTTP请求时,并不会将这个完整的URL原封不动地发送给服务器。
但是,在HTTP请求中,我们通常只发送路径和查询字符串,而不是完整的URL(协议、主机、端口等由请求头中的Host字段等其他部分提供)。
例如,一个完整的URL可能是:http://www.example.com:80**/search?q=hello & b=nnnn**
在HTTP请求中,请求行会写为:GET /search?q=hello & b=nnnn HTTP/1.1
在这个例子里面HTTP请求报文里面的URL字段应该是/search?q=hello & b=nnnn
我们把这个
此外,我们还需要搞清楚两个东西
- 资源请求路径:HTTP请求里面的URL中从第一个斜杠(/)开始到查询字符串开始(问号?)之前的部分,或者如果没有查询字符串,则是到URL路径结束的部分。始终以/开头,表示服务器上的资源位置以?开头
- 查询字符串:HTTP请求里面的URL中从问号(
?)开始到URL结束(不考虑片段标识符#之后的部分)的内容。它包含以键值对形式传递的参数。参数格式为key=value,多个参数用&连接,在服务器端被解析为键值对集合
所以,在这个例子中,
-
资源请求路径:/search
-
查询字符串:q=hello & b=nnnn,但是这不是最终体,然后查询字符串会被解析成键值对存入哈希表里面。
例如:
URL: http://www.example.com:8080/api/v1/users?name=John\&age=20
HTTP请求报文里面的URL是/api/v1/users?name=John&age=20
- 资源请求路径: "/api/v1/users"
- 查询字符串部分会被解析成:_params = {"name":"John", "age":"20"}
另外,有时URL中可能还包含锚点(fragment),例如 #section1,但在HTTP请求中,锚点不会发送到服务器,所以这里不考虑。
因此,对于URL这个部分,我们不直接存储HTTP请求里面的URL,而是去存储资源请求路径和查询字符串。
cpp
// 请求的资源路径
std::string _path;
// 存储URL查询参数的键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _params;1.1.3.Content-Length字段
Content-Length: 15000首部字段 Content-Length 表明了实体主体部分的大小(单位是字 节)。
对实体主体进行内容编码传输时,不能再使用 Content-Length 首部字段。
cpp
// 获取请求正文的长度,通过读取Content-Length头部字段
size_t ContentLength() const
{
// Content-Length: 1234\r\n
bool ret = HasHeader("Content-Length");
if (ret == false) {
return 0;
}
std::string clen = GetHeader("Content-Length");
return std::stol(clen);
}1.2.代码概览
那么,我们很快就能写出下面这个
cpp
class HttpRequest {
public:
// 请求方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等)
std::string _method;
// 请求的资源路径
std::string _path;
// HTTP协议版本(如HTTP/1.1)
std::string _version;
// 请求正文内容
std::string _body;
// 存储从路径正则匹配中提取的数据
std::smatch _matches;
// 存储HTTP请求头部的键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers;
// 存储URL查询参数的键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _params;
public:
// 构造函数,初始化协议版本为HTTP/1.1
HttpRequest();
// 重置请求对象,清空所有字段内容
void ReSet();
// 插入一个头部字段到_headers映射中
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &val);
// 判断指定的头部字段是否存在
bool HasHeader(const std::string &key) const;
// 获取指定头部字段的值,如果不存在则返回空字符串
std::string GetHeader(const std::string &key) const;
// 插入一个查询参数到_params映射中
void SetParam(const std::string &key, const std::string &val);
// 判断指定的查询参数是否存在
bool HasParam(const std::string &key) const;
// 获取指定查询参数的值,如果不存在则返回空字符串
std::string GetParam(const std::string &key) const;
// 获取请求正文的长度,通过读取Content-Length头部字段
size_t ContentLength() const;
// 判断是否是短链接(非keep-alive连接)
bool Close() const;
};我们也很快就能写出来
cpp
#pragma once
#include<regex>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include"util.hpp"
class HttpRequest {
public:
// 请求方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等)
std::string _method;
// 请求的资源路径
std::string _path;
// HTTP协议版本(如HTTP/1.1)
std::string _version;
// 请求正文内容
std::string _body;
// 存储从路径正则匹配中提取的数据
std::smatch _matches;
// 存储HTTP请求头部的键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers;
// 存储URL查询参数的键值对
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _params;
public:
// 构造函数,初始化协议版本为HTTP/1.1
HttpRequest():_version("HTTP/1.1") {}
// 重置请求对象,清空所有字段内容
void ReSet() {
_method.clear();
_path.clear();
_version = "HTTP/1.1";
_body.clear();
std::smatch match;
_matches.swap(match);
_headers.clear();
_params.clear();
}
// 插入一个头部字段到_headers映射中
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &val)
{
_headers.insert(std::make_pair(key, val));
}
// 判断指定的头部字段是否存在
bool HasHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end()) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 获取指定头部字段的值,如果不存在则返回空字符串
std::string GetHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end()) {
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
// 插入一个查询参数到_params映射中
void SetParam(const std::string &key, const std::string &val)
{
_params.insert(std::make_pair(key, val));
}
// 判断指定的查询参数是否存在
bool HasParam(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _params.find(key);
if (it == _params.end()) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 获取指定查询参数的值,如果不存在则返回空字符串
std::string GetParam(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _params.find(key);
if (it == _params.end()) {
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
// 获取请求正文的长度,通过读取Content-Length头部字段
size_t ContentLength() const
{
// Content-Length: 1234\r\n
bool ret = HasHeader("Content-Length");
if (ret == false) {
return 0;
}
std::string clen = GetHeader("Content-Length");
return std::stol(clen);
}
// 判断是否是短链接(非keep-alive连接)
bool Close() const
{
// 存在Connection字段,并且Connection字段的值是keep-alive,就说明是长连接,否则都是短连接
if (HasHeader("Connection") == true && GetHeader("Connection") == "keep-alive") {
return false;
}
return true;
}
};这里很多接口我都没有去讲解,因为我觉得一点必要都没有,很简单!
1.3.代码测试
我们直接写一个main.cpp来进行测试
cpp
#include "httprequest.hpp"
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// 创建一个HttpRequest对象
HttpRequest req;
// 1. 设置请求方法、路径和版本
req._method = "GET";
req._path = "/api/users/123";
req._version = "HTTP/1.1";
std::cout << "=== HTTP请求对象示例 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "请求方法: " << req._method << std::endl;
std::cout << "资源路径: " << req._path << std::endl;
std::cout << "协议版本: " << req._version << std::endl;
// 2. 设置请求头部字段
req.SetHeader("Host", "example.com");
req.SetHeader("User-Agent", "MyHttpClient/1.0");
req.SetHeader("Accept", "application/json");
req.SetHeader("Content-Length", "1024");
req.SetHeader("Connection", "keep-alive");
std::cout << "\n=== 请求头部字段 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Host: " << req.GetHeader("Host") << std::endl;
std::cout << "User-Agent: " << req.GetHeader("User-Agent") << std::endl;
std::cout << "Accept: " << req.GetHeader("Accept") << std::endl;
// 3. 检查头部字段是否存在
std::cout << "\n=== 头部字段检查 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否包含Content-Type: " << (req.HasHeader("Content-Type") ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否包含Content-Length: " << (req.HasHeader("Content-Length") ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
// 4. 设置查询参数(模拟URL: /api/users/123?name=John&age=30)
req.SetParam("name", "John");
req.SetParam("age", "30");
req.SetParam("city", "New York");
std::cout << "\n=== 查询参数 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "name: " << req.GetParam("name") << std::endl;
std::cout << "age: " << req.GetParam("age") << std::endl;
std::cout << "city: " << req.GetParam("city") << std::endl;
// 5. 检查查询参数是否存在
std::cout << "\n=== 查询参数检查 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否包含name参数: " << (req.HasParam("name") ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否包含country参数: " << (req.HasParam("country") ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
// 6. 获取请求正文长度
std::cout << "\n=== 请求正文信息 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Content-Length: " << req.ContentLength() << std::endl;
// 7. 判断连接类型
std::cout << "\n=== 连接类型 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否为短连接: " << (req.Close() ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
// 8. 测试路径正则匹配数据(这里只是演示,实际匹配需要在服务器中完成)
std::cout << "\n=== 路径正则匹配数据 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "当前路径: " << req._path << std::endl;
std::cout << "_matches对象已准备就绪(实际匹配在服务器路由中进行)" << std::endl;
// 9. 重置请求对象
std::cout << "\n=== 重置请求对象 ===" << std::endl;
req.ReSet();
std::cout << "重置后方法: " << (req._method.empty() ? "空" : req._method) << std::endl;
std::cout << "重置后路径: " << (req._path.empty() ? "空" : req._path) << std::endl;
std::cout << "重置后默认版本: " << req._version << std::endl;
return 0;
}

二.HttpResponse子模块
2.1.设计思路
2.1.1.基本设计
既然,我们这里说要封装HTTP响应,那么我们必须了解一下HTTP响应的格式吧!!

那么根据上面的报文格式,我们也很快就能写出下面3个成员变量
至于状态码描述,我们早就准备好了,就放在util.hpp里面,我们需要使用的话就根据状态码去获取对应状态码描述即可
cpp
int _statu; // HTTP响应状态码(如200、404、500等)
std::string _body; // 响应正文内容
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers; // 响应头部字段键值对至于协议版本呢!我们响应默认就是HTTP/1.1.
2.1.2.重定向的引入
重定向相关状态码------3xx
首先重定向一般和状态码3XX挂钩
3XX 响应结果表明浏览器需要执行某些特殊的处理以正确处理请 求。
301 Moved Permanently

永久性重定向。
该状态码表示请求的资源已被分配了新的 URI,以后 应使用资源现在所指的 URI。
也就是说,如果已经把资源对应的 URI 保存为书签了,这时应该按 Location 首部字段提示的 URI 重新保存。
像下方给出的请求 URI,当指定资源路径的最后忘记添加斜杠"/",就 会产生 301 状态码。
bash
http://example.com/sample302 Found
临时性重定向。
该状态码表示请求的资源已被分配了新的 URI,希望 用户(本次)能使用新的 URI 访问。
和 301 Moved Permanently 状态码相似,但 302 状态码代表的资源不 是被永久移动,只是临时性质的。
换句话说,已移动的资源对应的 URI 将来还有可能发生改变。
比如,用户把 URI 保存成书签,但不会 像 301 状态码出现时那样去更新书签,而是仍旧保留返回 302 状态码 的页面对应的 URI。
303 See Other
该状态码表示由于请求对应的资源存在着另一个 URI,应使用 GET 方法定向获取请求的资源。
303 状态码和 302 Found 状态码有着相同的功能,但 303 状态码明确 表示客户端应当采用 GET 方法获取资源,这点与 302 状态码有区 别。
比如,当使用 POST 方法访问 CGI 程序,其执行后的处理结果是希望客户端能以 GET 方法重定向到另一个 URI 上去时,返回 303 状态码。
虽然 302 Found 状态码也可以实现相同的功能,但这里使用 303 状态码是最理想的。
我们采用的是 HTTP/1.1,而许多 HTTP/1.1 版以前的浏览器不能正确理解 303 状态码。
虽然 RFC 1945 和 RFC 2068 规范不允许客户端在重定向时改变请求的方法,但是很多现存的浏览器将 302 响应视为 303 响应,并且使用 GET 方式访问在 Location 中规定的 URI,而无视原先请求的方法。所以说这里使用 303 是最理想的。
当 301、302、303 响应状态码返回时,几乎所有的浏览器都会把 POST 改成 GET,并删除请求报文内的主体,之后请求会自动再次 发送。
301、302 标准是禁止将 POST 方法改变成 GET 方法的,但实际使 用时大家都会这么做。
304 Not Modified

该状态码表示客户端发送附带条件的请求时,服务器端允许请求访 问资源,但未满足条件的情况。
304 状态码返回时,不包含任何响应的主体部分。
304 虽然被划分在 3XX 类别中,但是和重定向没有关 系。
附带条件的请求是指采用 GET 方法的请求报文中包含 If-Match,If-Modified Since,If-None-Match,If-Range,If-Unmodified-Since 中任一首部。
307 Temporary Redirect
临时重定向。该状态码与 302 Found 有着相同的含义。
尽管 302 标准禁止 POST 变换成 GET,但实际使用时大家并不遵守。
307 会遵照浏览器标准,不会从 POST 变成 GET。但是,对于处理响应时的行为,每种浏览器有可能出现不同的情况。
2.1.3.设计重定向相关
首先我们需要两个成员变量来存储重定向的相关信息
cpp
bool _redirect_flag; // 重定向标志,true表示需要重定向
std::string _redirect_url; // 重定向目标URL(当_redirect_flag为true时有效)其余
cpp
// 设置重定向响应
// 参数url:重定向目标URL
// 参数statu:重定向状态码,默认为302(临时重定向)
// 常见重定向状态码:301永久重定向,302临时重定向
void SetRedirect(const std::string &url, int statu = 302) {
_statu = statu; // 设置重定向状态码
_redirect_flag = true; // 设置重定向标志
_redirect_url = url; // 设置重定向目标URL
}2.1.4.其余细节
Content-Type字段
例如,在 HTTP 首部中以 Content-Type 这个字段来表示报文主体的 对象类型。
Content-Type: text/html就以上述示例来看,首部字段名为 Content-Type,字符串 text/html 是 字段值。
作为响应,我们必须先设置好一个字段,就是Content-Type,来表示报文主体的 对象类型。
cpp
// 设置响应正文内容,并可指定Content-Type类型
// 参数body:响应正文内容
// 参数type:Content-Type类型,默认为"text/html"
void SetContent(const std::string &body, const std::string &type = "text/html")
{
_body = body; // 存储响应正文
SetHeader("Content-Type", type); // 设置Content-Type头部
}长短连接的判断
cpp
// 判断是否是短链接(非keep-alive连接)
// 返回值:true表示短链接(需要关闭连接),false表示长连接(保持连接)
bool Close()
{
// 没有Connection字段,或者有Connection但是值是close,则都是短链接
// 有Connection字段且值为keep-alive,则是长连接
if (HasHeader("Connection") == true && GetHeader("Connection") == "keep-alive") {
return false; // 长连接,不需要关闭
}
return true; // 短链接,需要关闭
}这个其实还是很简单的
2.2.完整代码

cpp
#pragma once
#include<regex>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include"util.hpp"
class HttpResponse {
public:
int _statu; // HTTP响应状态码(如200、404、500等)
bool _redirect_flag; // 重定向标志,true表示需要重定向
std::string _body; // 响应正文内容
std::string _redirect_url; // 重定向目标URL(当_redirect_flag为true时有效)
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers; // 响应头部字段键值对
public:
// 默认构造函数,初始化状态码为200,重定向标志为false
HttpResponse():_redirect_flag(false), _statu(200) {}
// 带状态码的构造函数,初始化指定状态码,重定向标志为false
HttpResponse(int statu):_redirect_flag(false), _statu(statu) {}
// 重置响应对象,将所有字段恢复到初始状态
void ReSet() {
_statu = 200; // 重置状态码为200
_redirect_flag = false; // 重置重定向标志
_body.clear(); // 清空响应正文
_redirect_url.clear(); // 清空重定向URL
_headers.clear(); // 清空所有头部字段
}
// 插入一个响应头部字段到_headers映射中
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &val)
{
_headers.insert(std::make_pair(key, val));
}
// 判断指定的响应头部字段是否存在
bool HasHeader(const std::string &key)
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end()) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 获取指定响应头部字段的值,如果不存在则返回空字符串
std::string GetHeader(const std::string &key)
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end()) {
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
// 设置响应正文内容,并可指定Content-Type类型
// 参数body:响应正文内容
// 参数type:Content-Type类型,默认为"text/html"
void SetContent(const std::string &body, const std::string &type = "text/html") {
_body = body; // 存储响应正文
SetHeader("Content-Type", type); // 设置Content-Type头部
}
// 设置重定向响应
// 参数url:重定向目标URL
// 参数statu:重定向状态码,默认为302(临时重定向)
// 常见重定向状态码:301永久重定向,302临时重定向
void SetRedirect(const std::string &url, int statu = 302) {
_statu = statu; // 设置重定向状态码
_redirect_flag = true; // 设置重定向标志
_redirect_url = url; // 设置重定向目标URL
}
// 判断是否是短链接(非keep-alive连接)
// 返回值:true表示短链接(需要关闭连接),false表示长连接(保持连接)
bool Close() {
// 没有Connection字段,或者有Connection但是值是close,则都是短链接
// // 存在Connection字段,并且Connection字段的值是keep-alive,就说明是长连接,否则都是短连接
if (HasHeader("Connection") == true && GetHeader("Connection") == "keep-alive") {
return false; // 长连接,不需要关闭
}
return true; // 短链接,需要关闭
}
};2.3.代码测试
cpp
#include "httpresponse.hpp"
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// 创建一个HttpResponse对象
HttpResponse rsp;
std::cout << "=== HTTP响应对象示例 ===" << std::endl;
// 1. 检查初始状态
std::cout << "\n=== 初始状态 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "状态码: " << rsp._statu << std::endl;
std::cout << "重定向标志: " << (rsp._redirect_flag ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
// 2. 设置响应正文
rsp.SetContent("<html><body><h1>Hello, World!</h1></body></html>");
std::cout << "\n=== 设置响应正文后 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "响应正文长度: " << rsp._body.length() << " 字节" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Content-Type: " << rsp.GetHeader("Content-Type") << std::endl;
// 3. 添加其他响应头部
rsp.SetHeader("Server", "MyHttpServer/1.0");
rsp.SetHeader("Date", "Mon, 27 Jul 2009 12:28:53 GMT");
rsp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(rsp._body.length()));
rsp.SetHeader("Connection", "keep-alive");
std::cout << "\n=== 响应头部字段 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Server: " << rsp.GetHeader("Server") << std::endl;
std::cout << "Date: " << rsp.GetHeader("Date") << std::endl;
std::cout << "Content-Length: " << rsp.GetHeader("Content-Length") << std::endl;
std::cout << "Connection: " << rsp.GetHeader("Connection") << std::endl;
// 4. 检查头部字段是否存在
std::cout << "\n=== 头部字段检查 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否包含Server字段: " << (rsp.HasHeader("Server") ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否包含Cache-Control字段: " << (rsp.HasHeader("Cache-Control") ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
// 5. 判断连接类型
std::cout << "\n=== 连接类型 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "是否为短连接: " << (rsp.Close() ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
// 6. 测试重定向功能
std::cout << "\n=== 测试重定向 ===" << std::endl;
HttpResponse redirect_rsp;
redirect_rsp.SetRedirect("https://example.com/new-location", 301);
std::cout << "重定向状态码: " << redirect_rsp._statu << std::endl;
std::cout << "重定向标志: " << (redirect_rsp._redirect_flag ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
std::cout << "重定向URL: " << redirect_rsp._redirect_url << std::endl;
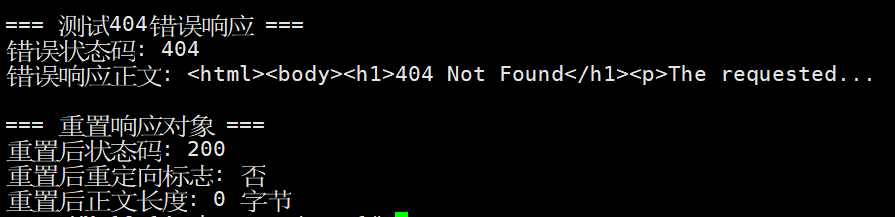
// 7. 测试404错误响应
std::cout << "\n=== 测试404错误响应 ===" << std::endl;
HttpResponse error_rsp(404);
error_rsp.SetContent("<html><body><h1>404 Not Found</h1><p>The requested resource was not found.</p></body></html>");
error_rsp.SetHeader("Server", "MyHttpServer/1.0");
std::cout << "错误状态码: " << error_rsp._statu << std::endl;
std::cout << "错误响应正文: " << error_rsp._body.substr(0, 50) << "..." << std::endl;
// 8. 重置响应对象
std::cout << "\n=== 重置响应对象 ===" << std::endl;
rsp.ReSet();
std::cout << "重置后状态码: " << rsp._statu << std::endl;
std::cout << "重置后重定向标志: " << (rsp._redirect_flag ? "是" : "否") << std::endl;
std::cout << "重置后正文长度: " << rsp._body.length() << " 字节" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
没有一点问题!!