本系列介绍增强现代智能体系统可靠性的设计模式,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。本系列一共 14 篇文章,这是第 9 篇。原文:Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI
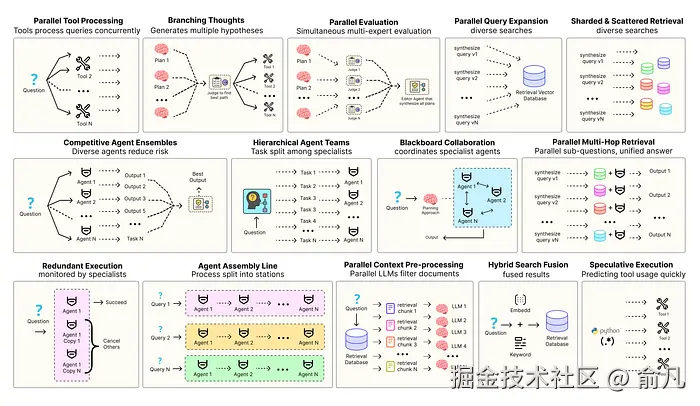
优化智能体解决方案需要软件工程确保组件协调、并行运行并与系统高效交互。例如预测执行,会尝试处理可预测查询以降低时延 ,或者进行冗余执行,即对同一智能体重复执行多次以防单点故障。其他增强现代智能体系统可靠性的模式包括:
- 并行工具:智能体同时执行独立 API 调用以隐藏 I/O 时延。
- 层级智能体:管理者将任务拆分为由执行智能体处理的小步骤。
- 竞争性智能体组合:多个智能体提出答案,系统选出最佳。
- 冗余执行:即两个或多个智能体解决同一任务以检测错误并提高可靠性。
- 并行检索和混合检索:多种检索策略协同运行以提升上下文质量。
- 多跳检索:智能体通过迭代检索步骤收集更深入、更相关的信息。
还有很多其他模式。
本系列将实现最常用智能体模式背后的基础概念,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。
所有理论和代码都在 GitHub 仓库里:🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀
代码库组织如下:
erlang
agentic-parallelism/
├── 01_parallel_tool_use.ipynb
├── 02_parallel_hypothesis.ipynb
...
├── 06_competitive_agent_ensembles.ipynb
├── 07_agent_assembly_line.ipynb
├── 08_decentralized_blackboard.ipynb
...
├── 13_parallel_context_preprocessing.ipynb
└── 14_parallel_multi_hop_retrieval.ipynb冗余执行以实现容错性
当公司部署代理解决方案时,确实会面临一些问题,如 API 超时、模型崩溃和网络中断等。之前的模式主要关注在理想条件下提高代理的质量和速度,而冗余执行模式专注于确保系统即使在不利条件下也能保持可靠和高效。
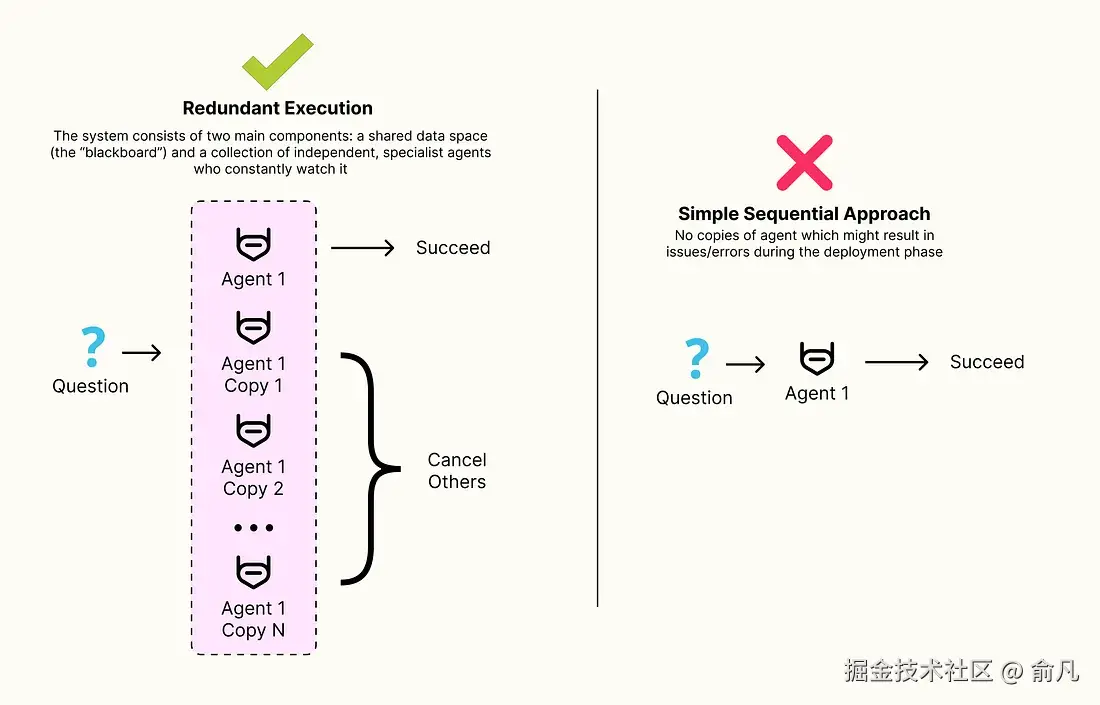
概念很简单:对于关键且可能不可靠的步骤,并行执行两个或多个相同的智能体,系统随后使用第一个成功执行的智能体结果并取消其余的,这种技术提供了针对间歇性故障和不可预测性的防御。
我们将构建一个依赖于模拟不可靠执行的测试工具的简单智能体,然后比较冗余执行和无冗余执行,以展示速度(时延一致性)和成功率(有效准确率)方面的显著和可衡量的改进。
首先需要创建模拟不可靠性的工具,这是模拟测试的核心。测试工具可能会失败,也可能会执行得非常慢,或者特别快,以模拟现实世界中网络依赖的不确定性。
python
from langchain_core.tools import tool
import time
import random
@tool
def get_critical_data(query: str) -> str:
"""从外部服务获取关键数据的模拟工具,该服务可能很慢或间歇性失败"""
# 为工具调用的每个实例分配一个随机 ID,以便清晰记录日志
instance_id = random.randint(1000, 9999)
print(f"--- [Tool Instance {instance_id}] Attempting to fetch data for query: '{query}' ---")
# 用随机值来模拟不可靠性
roll = random.random()
if roll < 0.20: # 20% 概率完全失败
print(f"--- [Tool Instance {instance_id}] FAILED: Network connection error. ---")
raise ConnectionError("Failed to connect to the external service.")
elif roll < 0.30: # 10% 概率出现长尾时延
slow_duration = random.uniform(5, 7)
print(f"--- [Tool Instance {instance_id}] SLOW: Experiencing high latency. Will take {slow_duration:.2f}s. ---")
time.sleep(slow_duration)
else: # 70% 概率运行正常
fast_duration = random.uniform(0.5, 1.0)
print(f"--- [Tool Instance {instance_id}] FAST: Executing normally. Will take {fast_duration:.2f}s. ---")
time.sleep(fast_duration)
result = f"Data for '{query}' successfully retrieved by instance {instance_id}."
print(f"--- [Tool Instance {instance_id}] SUCCESS: {result} ---")
return resultget_critical_data 工具用来控制实验,随机的 roll 和 time.sleep 调用模拟分布式系统中两种最常见问题(瞬时故障 ConnectionError 和不可预测时延)。该工具可以帮助我们创建清晰、可重复的问题演示。
现在构建容错图,模式核心是使用 ThreadPoolExecutor 协调冗余执行的节点。
python
from typing import TypedDict, Optional, Any
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
class RedundantState(TypedDict):
input: str
result: Optional[Any]
error: Optional[str]
performance_log: Optional[str]
def redundant_executor_node(state: RedundantState):
"""模式的核心:并行执行两个相同的代理并返回第一个成功的结果"""
print("--- [Redundant Executor] Starting 2 agents in parallel... ---")
start_time = time.time()
# 用 ThreadPoolExecutor 并发运行两个代理调用
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=2) as executor:
# 向执行器提交两个相同的任务
futures = [executor.submit(simple_executor.invoke, {"input": state['input']}) for _ in range(2)]
first_result = None
# 'as_completed' 迭代器在完成时以任意顺序执行
for future in as_completed(futures):
try:
# 尝试得到第一个完成的结果
first_result = future.result()
print("--- [Redundant Executor] A task finished successfully. Cancelling others. ---")
# 一旦成功了一次,任务就完成了,就可以结束循环
# 在更高级实现中,可以尝试取消其他正在运行的执行器
break
except Exception as e:
# 如果某个并行任务失败,只需记录并等待其他的执行器完成
print(f"--- [Redundant Executor] A task failed with error: {e}. Waiting for the other. ---")
pass
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
log = f"Redundant execution completed in {execution_time:.2f}s."
print(f"--- [Redundant Executor] {log} ---")
# 根据是否获得成功的结果来更新状态
if first_result:
return {"result": first_result, "performance_log": log, "error": None}
else:
# 这种情况只发生在两个并行执行都失败的情况下
return {"result": None, "performance_log": log, "error": "Both redundant executions failed."}
# 组装一个非常简单的图,只有这一个节点
workflow = StateGraph(RedundantState)
workflow.add_node("redundant_executor", redundant_executor_node)
workflow.set_entry_point("redundant_executor")
workflow.add_edge("redundant_executor", END)
app = workflow.compile()
# 多次运行弹性图
redundant_results = []
for i in range(num_runs):
print(f"--- Running Redundant Agent (Attempt {i+1}/{num_runs}) ---")
start_time = time.time()
result = app.invoke({"input": "Please fetch the user's profile"})
end_time = time.time()
if result['error']:
redundant_results.append(("FAILURE", end_time - start_time, result['error']))
print(f"FAILURE in {end_time - start_time:.2f}s.\n")
else:
redundant_results.append(("SUCCESS", end_time - start_time, result['result']))
print(f"SUCCESS in {end_time - start_time:.2f}s.\n")
redundant_executor_node 是容错系统的主要部分,for future in as_completed(futures) 循环是其核心逻辑,as_completed 给出的顺序是按完成顺序,而不是启动顺序。
这意味着只要两个并行代理中速度最快的那个执行成功,就可以抓取结果并退出循环,忽略较慢或失败的代理。try...except 块也非常关键,允许系统在等待某个可能成功的分支时,优雅的处理某个分支的失败。
最后进行定量分析,分别运行简单的单一代理系统和冗余系统各五次,比较它们的成功率和时延分布。
python
import numpy as np
# 结果保存在 'simple_results' 和 'redundant_results' 列表中
# --- 可靠性分析 ---
simple_successes = sum(1 for r in simple_results if r[0] == "SUCCESS")
simple_rate = (simple_successes / len(simple_results)) * 100 if simple_results else 0
redundant_successes = sum(1 for r in redundant_results if r[0] == "SUCCESS")
redundant_rate = (redundant_successes / len(redundant_results)) * 100 if redundant_results else 0
print("="*60)
print(" SYSTEM RELIABILITY ANALYSIS")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print("--- Simple Agent ---")
print(f"Success Rate: {simple_rate:.1f}% ({simple_successes} successes, {len(simple_results) - simple_successes} failures)\n")
print("--- Redundant Agent ---")
print(f"Success Rate: {redundant_rate:.1f}% ({redundant_successes} successes, {len(redundant_results) - redundant_successes} failures)\n")
if simple_rate > 0:
reliability_increase = ((redundant_rate - simple_rate) / simple_rate) * 100
print(f"Accuracy / Reliability Increase: +{reliability_increase:.1f}%\n")
# --- 时延分析 ---
simple_latencies = [r[1] for r in simple_results if r[0] == "SUCCESS"]
redundant_latencies = [r[1] for r in redundant_results if r[0] == "SUCCESS"]
print("="*60)
print(" PERFORMANCE & LATENCY ANALYSIS")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print("--- Simple Agent (Successful Runs Only) ---")
print(f"Latencies: {[round(l, 2) for l in simple_latencies]}")
print(f"Average Latency: {np.mean(simple_latencies):.2f} seconds" if simple_latencies else "N/A")
print(f"Max Latency (P100): {np.max(simple_latencies):.2f} seconds" if simple_latencies else "N/A")
print("--- Redundant Agent (Successful Runs Only) ---")
print(f"Latencies: {[round(l, 2) for l in redundant_latencies]}")
print(f"Average Latency: {np.mean(redundant_latencies):.2f} seconds" if redundant_latencies else "N/A")
print(f"Max Latency (P100): {np.max(redundant_latencies):.2f} seconds" if redundant_latencies else "N/A")得到的结果是......
python
#### 输出 ####
============================================================
SYSTEM RELIABILITY ANALYSIS
============================================================
--- Simple Agent ---
Success Rate: 60.0% (3 successes, 2 failures)
--- Redundant Agent ---
Success Rate: 80.0% (4 successes, 1 failure)
Accuracy / Reliability Increase: +33.3%
============================================================
PERFORMANCE & LATENCY ANALYSIS
============================================================
--- Simple Agent (Successful Runs Only) ---
Latencies: [6.21, 11.99, 5.98]
Average Latency: 8.06 seconds
Max Latency (P100): 11.99 seconds
The system performance is unpredictable and directly impacted by long-tail latency events.
--- Redundant Agent (Successful Runs Only) ---
Latencies: [6.15, 6.02, 6.25, 5.88]
Average Latency: 6.08 seconds
Max Latency (P100): 6.25 seconds冗余执行提供了两个明确、可衡量的好处:
- 大幅提高可靠性:通过并行执行备用系统,系统成功率从 60% 提高到 80%,有效提升了准确性和用户信任。
- 显著改善延迟一致性:冗余系统的最坏情况性能(6.25s)也优于简单系统的平均性能(8.06s),完全消除了 12s 的长尾时延,使用户体验变得快速且可预测。
对于任何具有自主性的工作流中的任何关键任务步骤,冗余执行都是一种强大且经济高效的策略,可用于构建真正适用于生产环境的、具有弹性的系统。
Hi,我是俞凡,一名兼具技术深度与管理视野的技术管理者。曾就职于 Motorola,现任职于 Mavenir,多年带领技术团队,聚焦后端架构与云原生,持续关注 AI 等前沿方向,也关注人的成长,笃信持续学习的力量。在这里,我会分享技术实践与思考。欢迎关注公众号「DeepNoMind」,星标不迷路。也欢迎访问独立站 www.DeepNoMind.com,一起交流成长。