
01 引言
前面用了两节内容介绍了基于Netty的TCP的Socket的相关内容。这一节开始我们介绍基于Netty的WebSocket的相关内容,我们同样可以安好服务端和客户端的方式分别介绍。本节我们介绍WebSocket的服务端。
02 示例代码
java
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WebSocketServer {
@Getter
private ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>(){
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65535));
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/testWs"));
// 自定义的handler,处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new WebBusinessHandler(channelGroup));
}
});
// 配置完成,开始绑定server,通过调用sync同步方法阻塞直到绑定成功
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9090).sync();
log.info("Server started and listen on:{}",channelFuture.channel().localAddress());
// 对关闭通道进行监听
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
}2.1 引导类
引导类同样是io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap,和TCP协议的服务端一样,但是细节不同。
java
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);保活的配置一般会有心跳的代替,所以一般也就没有要设置了。线程组可以根据需要设置,一个接收任务,一个处理任务分工协作。
2.2 编解码器
java
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65535));
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/testWs"));
// 自定义的handler,处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new WebBusinessHandler(channelGroup));编解码同样是WebSocket中的重要配置类。WebSocket握手阶段需要遵守HTTP协议,自然少不了请求请求的解码以及响应的解码。Netty框架本身就提供了这样的编解码器:
io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestDecoder:请求解码器io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseEncoder:响应编码器
配置这样的编解码器自然没有问题。然而Netty框架还提供了更加简便的二合一编解码器:
io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec
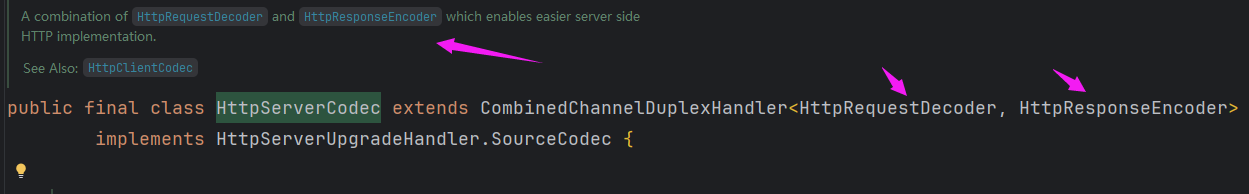
注释中已经说明HttpServerCodec是HttpRequestDecoder和HttpResponseEncoder的结合。所以我们直接用它即可。
解码之后的数据分成两部分:
HttpMessage:包含HTTP请求的通用信息LastHttpContent:最新具有标记的HttpContent
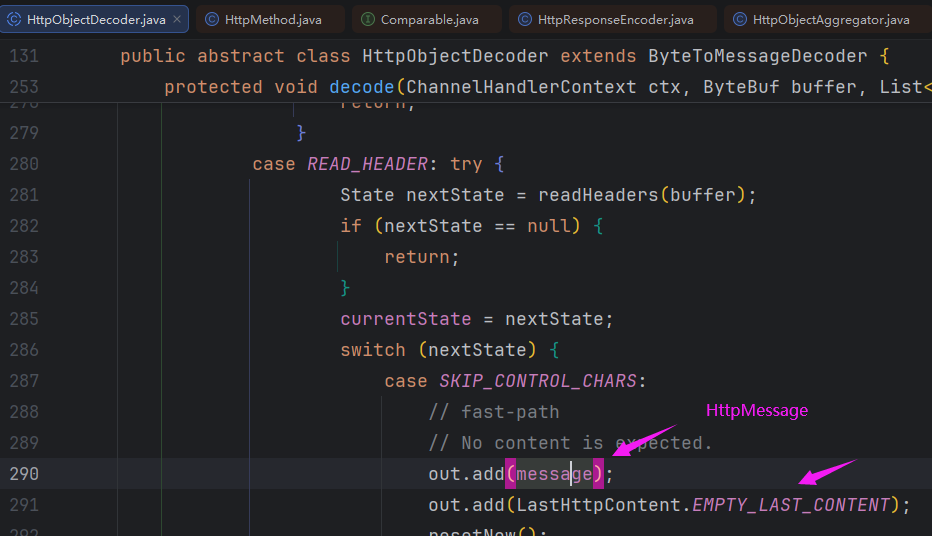
io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator是一个HTTP聚合器,可以将HttpMessage和HttpContent聚合成FullHttpRequest或FullHttpResponse。
案例也给除了用在HttpServerCodec之后。
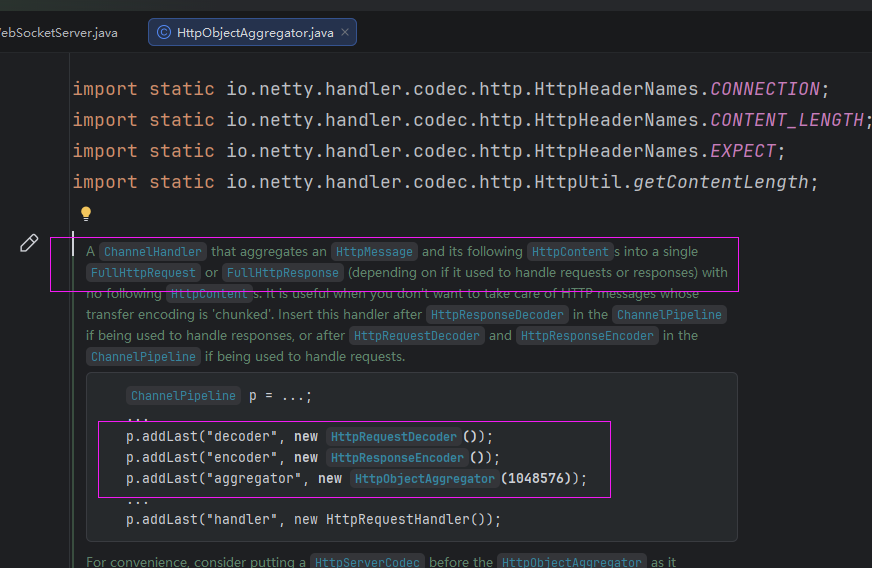
io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler专门处理WebSocket握手和帧,参数表示WebSocket路径。
这里所说的帧就是WebSocketFrame,主要常用的帧:
TextWebSocketFrame:处理文本PingWebSocketFrame:握手请求PongWebSocketFrame:握手响应BinaryWebSocketFrame:处理二进制
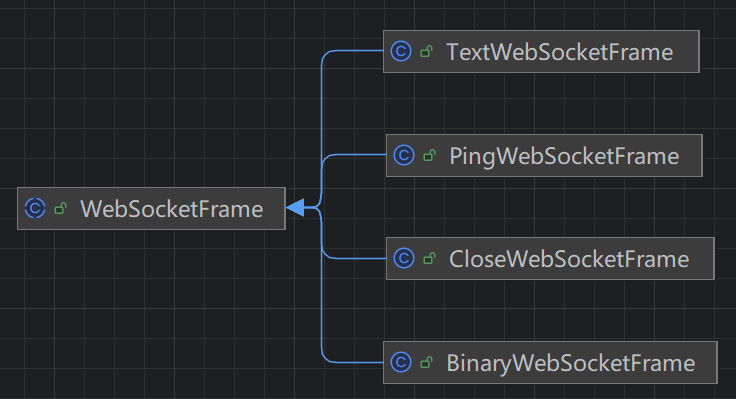
我们常用的是TextWebSocketFrame文本帧。
2.3 自定义处理器
java
@Slf4j
public class WebBusinessHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
private ChannelGroup channelGroup;
public WebBusinessHandler(ChannelGroup channelGroup) {
this.channelGroup = channelGroup;
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 建立客户端
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
log.info("客户端建立连接:channelId={}", channel.id());
channelGroup.add(channel);
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 断开链接
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
log.info("客户端断开连接:channelId={}", channel.id());
channelGroup.remove(channel);
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
// 接受消息
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
log.info("收到来自通道channelId[{}]发送的消息:{}", channel.id(), msg.text());
// 广播通知所有的客户端
channelGroup.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("收到来自channelId[" + channel.id() + "]发送的消息:" + msg.text() + "123_"));
}
}里面的方法和TCP协议的一致。但是要说明的就是里面的参数
io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup
这是一个Channel的通道组,用来管理所有的通道,包括通道的新增、剔除以及消息的发送。
SimpleChannelInboundHandler的泛型我们限制为TextWebSocketFrame,否则获取到的消息就是FullHttpRequest类型。
消息发送时,同样使用的TextWebSocketFrame文本帧。
2.4 其他编解码
在HttpServerCodec和HttpObjectAggregator之间还可以加入两个处理器:
ObjectEncoderChunkedWriteHandler
ObjectEncoder是为了将Java对象序列化成ByteBuf。
ChunkedWriteHandler增加了对异步写入大型数据流的支持,既不会花费大量内存,也不会获得OutOfMemoryError。
2.5 绑定端口
java
// 配置完成,开始绑定server,通过调用sync同步方法阻塞直到绑定成功
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9090).sync();
log.info("Server started and listen on:{}",channelFuture.channel().localAddress());
// 对关闭通道进行监听
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();这个之前已经讲过,这里不在赘述。
03 测试
测试的之后,我们采用在线WebSocketk客户端:
https://webfem.com/tools/ws/index.html
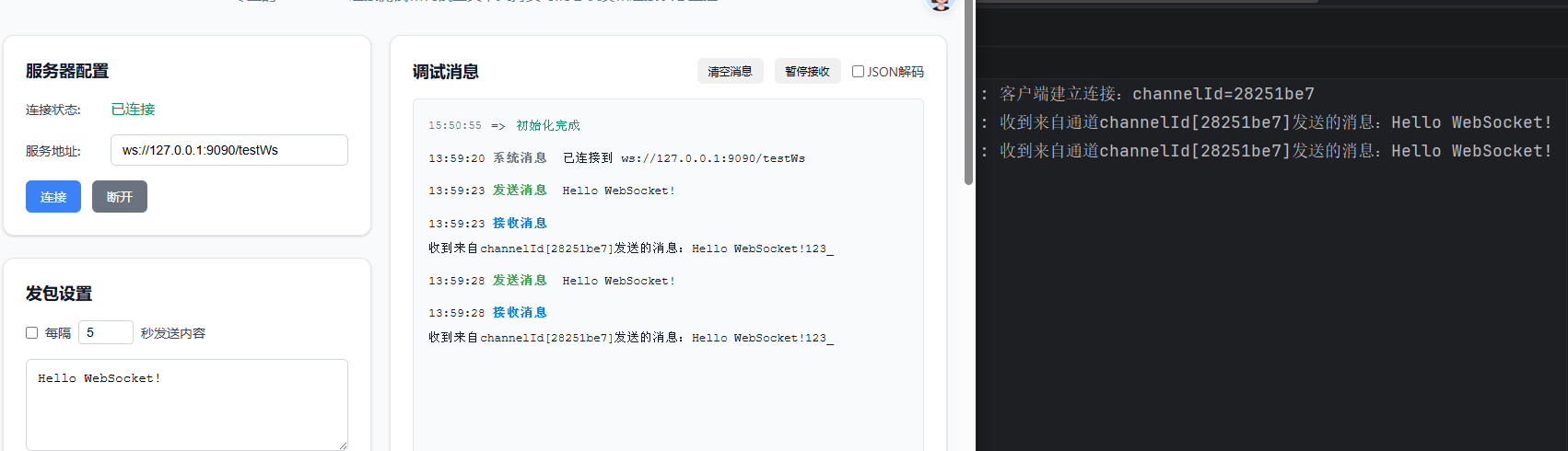
3.1 试错01
因为我们之前在自定义处理器的泛型是TextWebSocketFrame,我们改成Object,看看默认的类型到底是什么?发送数据我们也采用直接发送的形式,看看能否成功?
java
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.info("msg类型:{}", msg.getClass());
// 接受消息
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
log.info("收到来自通道channelId[{}]发送的消息:{}", channel.id(), msg);
// 广播通知所有的客户端
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("收到来自channelId[" + channel.id() + "]发送的消息:" + msg + "123_");
}
我们可以看到,发出去的消息没有响应。打印Msg类型确实是io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame。服务端像客户端发送的消息客户端也没有收到。
3.2 试错02
我们知道编解码是顺序执行的。有没有和我一样,有这样的疑问:
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler有没有可能不受顺序的影响,因为它是一个路径,我们改变一下试试。
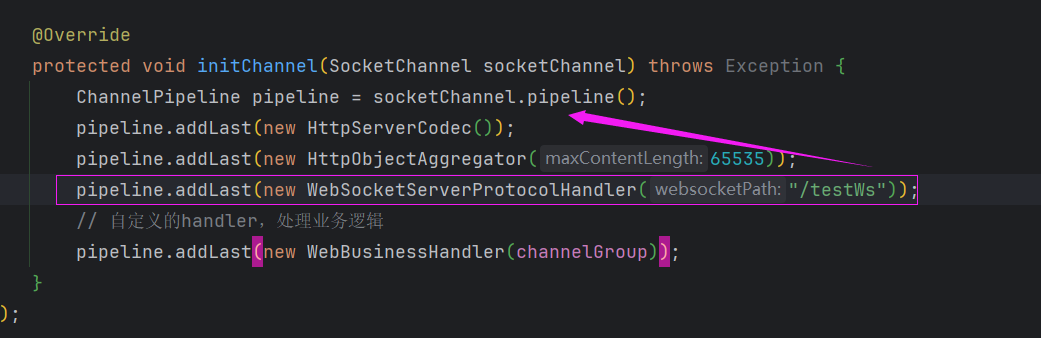
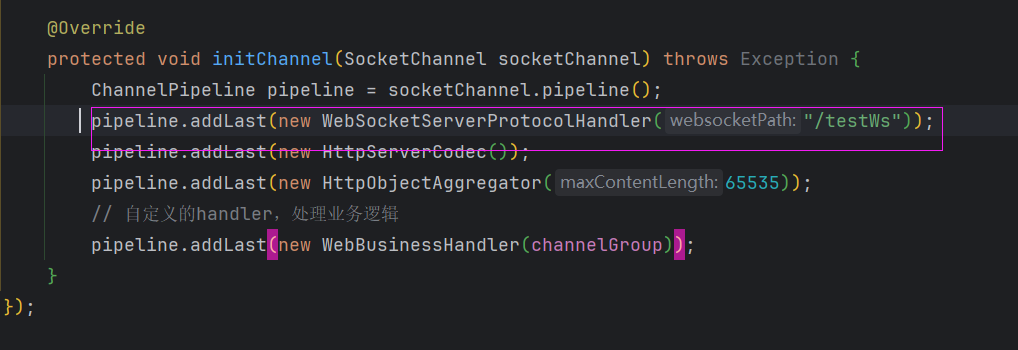
效果:
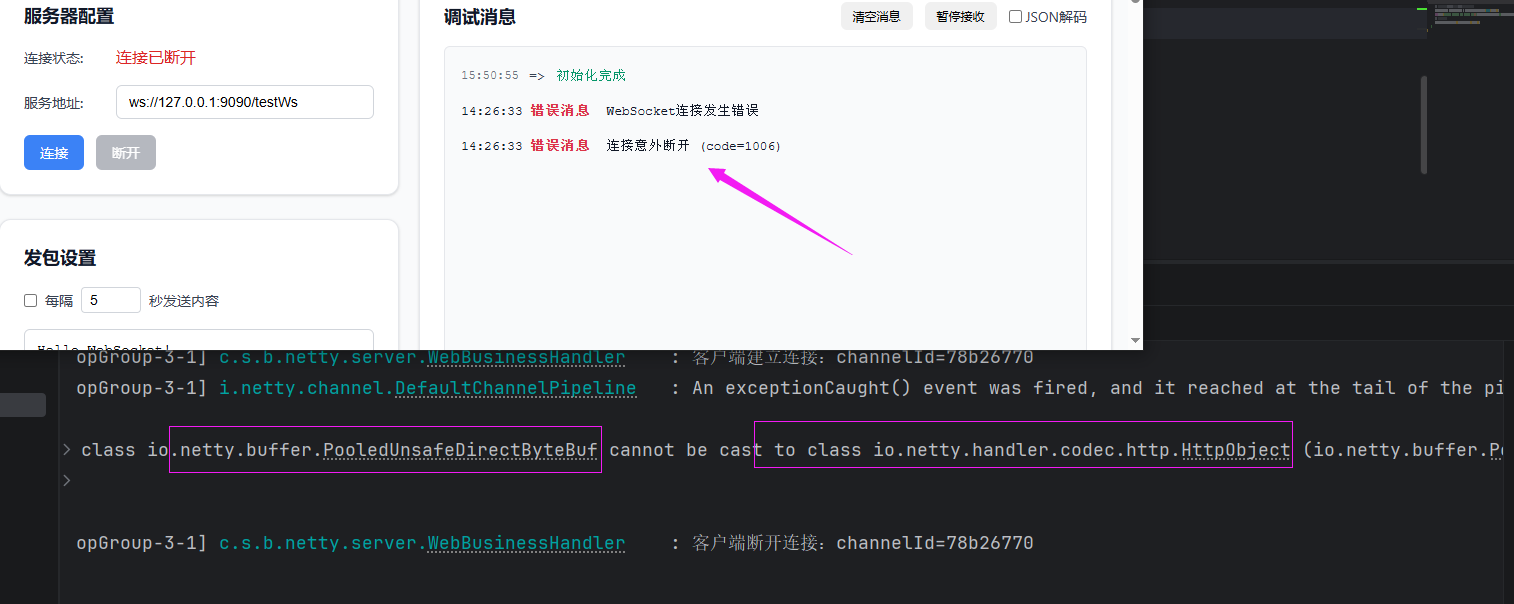
结果肯定是不行的,从报错信息来看,WebSocketServerProtocolHandler不仅提供了连接的路径,还对ByteBuf做了一定的转化。顺序不可妄动。
04 小结
到这里WebSocket的服务端的内容就差不多了,本节的客户端采用了网上在线工具。下一节我们将通过两种方式手搓客户端连接我们的WebSocket服务。