What is Generative AI? ¶
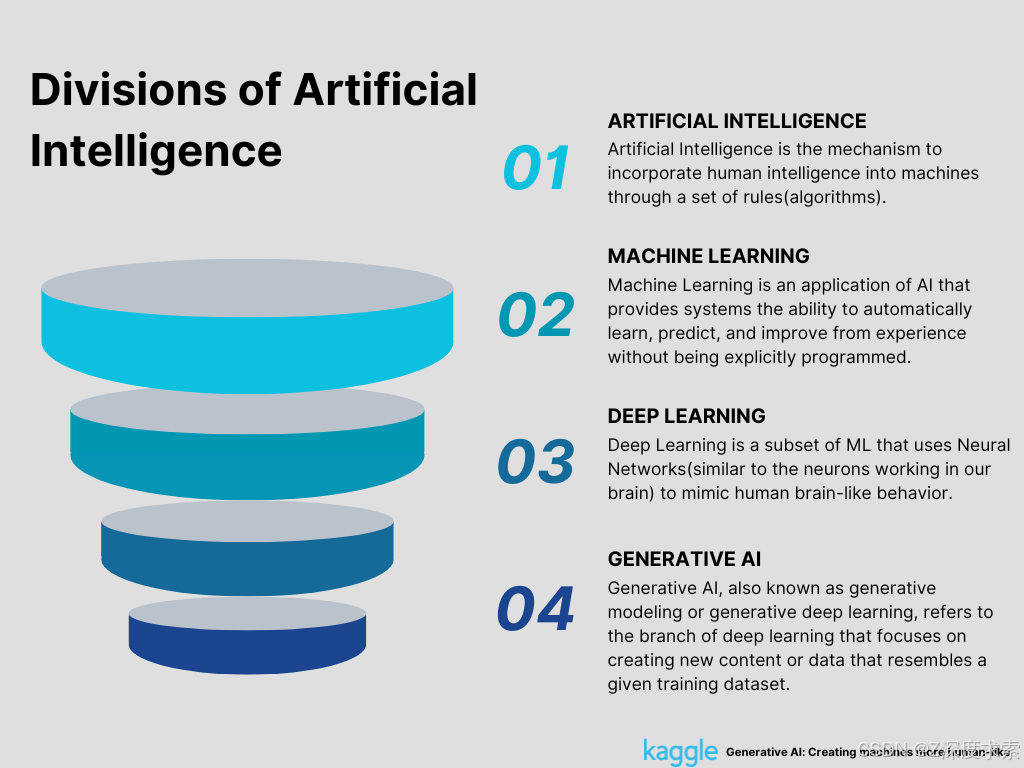
Figure 1: Divisions of AI (Created by Author)
Welcome to the era of machine learning and deep learning in 2023!
Exploring the state of machine learning today and how it affects various fields is crucial as we move forward into the future. Machine learning's potential for growth is very encouraging. Algorithms have advanced significantly, becoming simpler, more approachable to understand, and more potent than before. Machine learning is dramatically altering our lives, from the emergence of deep learning and generative AI to ground-breaking uses in healthcare, finance, transportation, and retail. Let's embark on a journey through the impact, learnings, newest trends, predictions, and issues to uncover the huge potential of machine learning in the present and the future.
Over the past few years, deep learning has developed, and its algorithms are now widely used in a variety of industries. It utilizes artificial intelligence neural networks (ANNs) to carry out intricate computations on vast volumes of data, basing its operation on the structure and operation of the human brain. Generative AI, also referred to as creative AI or art AI is one of these potent toolkits that makes use of deep neural networks. It recognizes patterns and structures within the existing data to produce unique and original content that may include text, visual, audio, code, 3D models, or other types of data. For training, generative AI models can use a variety of learning strategies, such as unsupervised or semi-supervised learning. As a result, businesses are now able to quickly build foundational models using a vast amount of unlabeled data. The idea of foundation models is not new; well-known CNNs like Resnet-50 were initially introduced in 2015. DeepMind's Alpha Code (GoogleLab), ChatGPT, GPT-4, DALL-E, Google Bard, Bing AI, Github Copilot, Synthesia, MidJourney, Jasper, and Stable Diffusion are some of the top generative AI technologies. And ChatGPT evolved into OpenAI's most widely used product to date, launching ChatGPT Plus, a pilot paid subscription, in March 2023.
The vast majority of well-liked generative AI technologies focus on the creation of images. Text input is used by generative AI systems as the foundation for creating graphics in two, three, and even four dimensions. It can produce incredibly accurate portraits of people. You may be surprised to learn that generative AI cannot draw hands, despite its achievements. And it is the most challenging setback in AI. Making avatars is one of the most popular applications of AI picture production and TikTok is among the most well-liked platforms for sharing examples of generative AI. You can even become a superhero, a royal king or queen, or a mermaid with the use of generative AI technologies. The AI-generated QR code, which replaces the outdated black and white QR code with visually attractive ones, is another new trend. Hugging Face has made a free AI QR code generator available for this purpose. Investment in generative AI has already reached over two billion dollars, up 425 percent from 2020. Additionally, generative AI is widely regarded as the most advanced technology over the next 50 years, with many scientists and experts even referring to it as an age-reversing technology!
Generative AI's Evolution
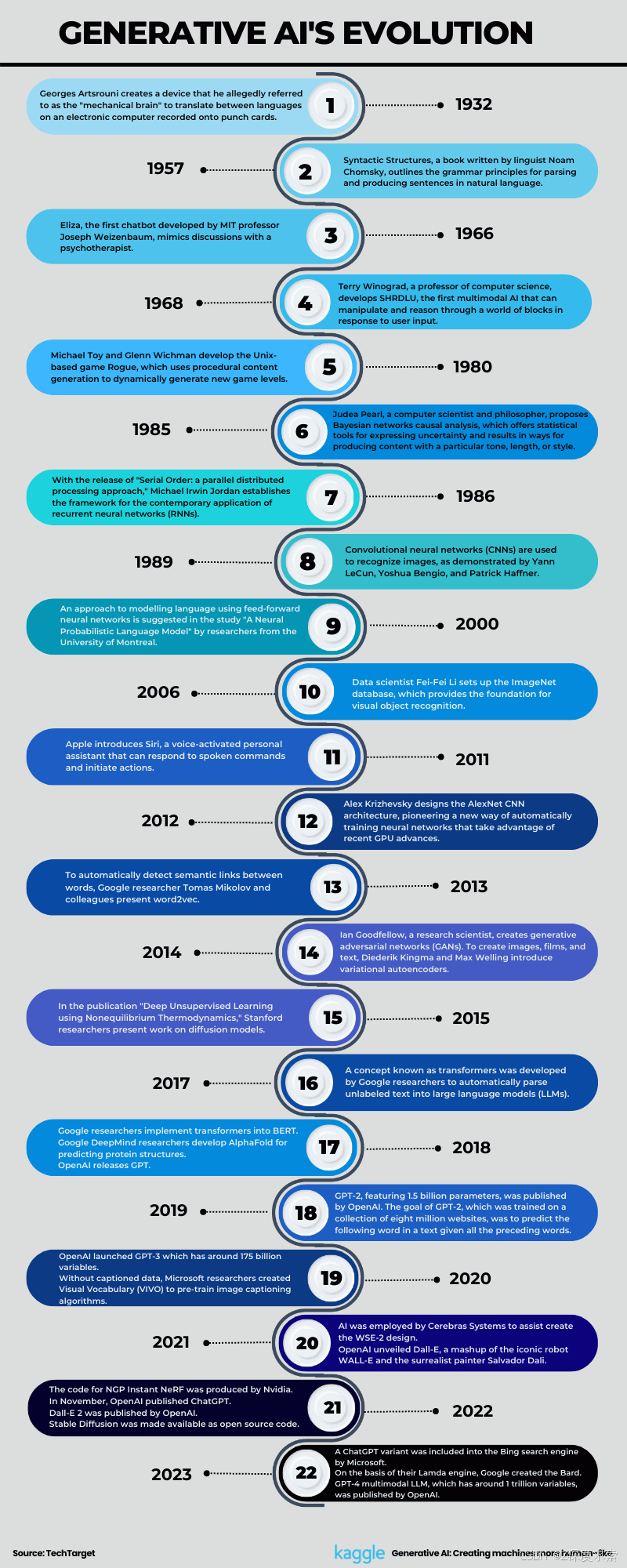
Figure 2: Generative AI's Evolution (Created by Author)
Key requirements of Generative AI
The following essential conditions must be met by generative models to be widely used in practical applications:
- High-generation quality is needed for numerous applications, particularly those that deal directly with those using it.
- A strong generative model should be able to effectively record variations without compromising generation performance if the training data includes a complicated or significant amount of variability.
- Easy and quick generation is necessary for many interactive applications, including real-time photo editing.
Key concepts of Generative AI
- GAN - Generative Adversarial Network pits two neural networks against one another in the context of a zero-sum game. GANs are made to create new, synthetic data that closely resembles the distribution of current data. Here, the two neural networks are a generator and a discriminator. The Generator attempts to deceive the Discriminator by creating artificial samples of data (such as an image, audio, etc.). On the other hand, the Discriminator tries to tell the difference between genuine and fraudulent samples.
- VAE - Variational Auto-Encoders is a subclass of deep generative networks that share the same encoder (inference) and decoder (generative) components as the traditional auto-encoder. It is an autoencoder whose distribution of encodings is regulated during training to guarantee that its latent space has favorable attributes allowing us to produce some new information.
- LLM - Large Language Models are artificial intelligence systems that are based on transformer architecture; built to comprehend and produce human language. In order to grasp the patterns and laws of language, these models are trained to function by learning the statistical correlations between words and phrases in a huge corpus of text.
- NLP - Natural Language Processing is a branch of artificial intelligence that integrates computational linguistics with statistical, machine learning, and deep learning models. With these technologies, computers can completely "understand" what is said or written, including the speaker's or writer's intents and feelings, and interpret human language in the form of text or audio data.
- RNN - Recurrent neural networks are a particular type of artificial neural network that are mostly utilized in NLP and speech recognition. It operates on the idea of preserving a layer's output and using that information to anticipate that layer's output from the input. RNN's Hidden state, which retains some details about a sequence, is its primary and most significant characteristic.
- Autoencoders -- It is an unsupervised neural network that first learns how to minimize and encode information before teaching itself how to decode the compressed and encoded data and rebuild it into a form that is as close to the original input as practical. By developing the ability to disregard data noise, it minimizes the dimensions of the data.
- Autoregressive models -- In order to increase the likelihood of training data, autoregressive models provide an attainable explicit density model. This makes it simple to estimate the likelihood of data observation and to provide an evaluation measure for the generative model using these approaches. It uses a regression model to estimate the value of the following time step after learning from a large number of timed steps and measurements from earlier activities.
- Diffusion models - The diffusion model is a type of generative model that learns to recover the data by reversing the noising process after first erasing the training data by adding Gaussian noise one at a time. The Diffusion Model may be used to produce data after training by simply subjecting randomly sampled noise to the mastered denoising procedure, yielding innovative and varied high-resolution pictures that are similar to the initial data.
- Transformer models - Transformer models are a subset of deep learning models that are frequently used in NLP and other generative AI applications. They are trained to learn the connections between the words in a phrase or line of text. They accomplish this learning by employing a technique known as self-attention, which enables the model to evaluate the relative weights of various words in a sequence according to their context. These models provide the essential benefit of processing input sequences concurrently, outperforming RNNs for many NLP applications.
- Data augmentation - Modifying or "augmenting" a dataset with new data is known as data augmentation. The incorporation of this supplementary data, which may be anything from photographs to text, helps machine learning algorithms perform better. By making modified replicas of an existing dataset using previously collected data, it artificially expands the training set. The dataset may be slightly modified, or new data points may be produced using deep learning.
- Flow-based models - Flow-based models define an invertible transformation between the input and output areas to directly represent the data distribution. They provide effective density estimates in addition to data production. To describe complicated data distributions, they use normalizing fluxes, a series of invertible transformations. These changes make it possible to compute likelihoods and sample data quickly.
- DeepDream - With the help of a convolutional neural network, the potent computer vision system DeepDream can identify and improve certain patterns in photos. DeepDream over-interprets and intensifies the patterns it notices in a picture, much like a toddler watching clouds and attempting to make sense of random shapes and formations.
- Transfer learning - Transfer learning is a machine learning (ML) technique that leverages a trained model created for one job to complete another that is similar but unrelated. Transfer learning accelerates training and lowers the cost of creating a new model from scratch. Computer vision, natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and natural language creation are just a few of the generative AI applications that might benefit from transfer learning.
- GPT - Generative Pre-trained Transformers are a class of neural network models that make use of the transformer architecture. They are sometimes referred to as GPT. They are all-purpose language models capable of writing code, summarizing text, extracting information from documents, and producing original content. Applications with GPT models may produce text and material (including photos, music, and more) that is human-like and can converse with users.
- Fine-tuning - A machine learning model is fine-tuned to improve its performance on a particular task or dataset by changing its hyperparameters or pre-trained weights. When compared to the first pre-training, fine-tuning takes far less data and computing effort. Larger models sometimes perform worse than well-tuned models do.
- Zero-shot learning - A machine learning paradigm known as "zero-shot learning" uses semantic data or connections between known and new classes, which is frequently represented as attribute vectors or knowledge graphs, to categorize or recognize novel categories or instances without the need for training examples.
- Hallucination - The primary reason for hallucination is that the LLM employs its internal "knowledge" (what it has been developed on), which is irrelevant to the user inquiry. This results in the LLM producing the incorrect output.
- Prompt engineering - The secret to endless universes is AI prompt engineering, which employs prompts to acquire the desired outcome from an AI tool. For the text we want the model to produce, the prompt gives context. The prompts we design might be anything from straightforward instructions to intricate texts.
- Foundation models - A foundation model is a system based on deep learning that has been trained using very sizable data sets downloaded from the internet. Because they contain hundreds of billions of hyperparameters that have been trained using hundreds of terabytes of data, these models can cost millions of dollars to develop.
- BERT - Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers is a deep learning algorithm created by Google AI Research that makes use of unsupervised learning to better comprehend natural language inquiries. The model learns bidirectional representations of text data using a transformer architecture, which enables it to comprehend the context of words inside a phrase or paragraph.
- Perceptron - Perceptrons are a component of artificial neural networks that are utilized for a variety of classification applications. Input values (Input nodes), weights and bias, net sum, and an activation function are the four essential factors that make up this single-layer neural network.
Generative AI Tools
Below are 10 different tools that can be used for different output generation.
Table 1: Generative AI Tools (Created by Author)
Generative AI learnings in the past two years
The Machine learning community has taken great strides in researching and testing generative AI during the last few years. The ML community has obtained invaluable observations via intensive study and experimentation that have impacted our knowledge of generative AI and its possible applications.
-
Generative AI depends primarily on the training data it is given, any biases or constraints in the data may be mirrored in the results that are produced. To ensure fairness, minimize biases, and prevent the amplification of already-existing social inequities, the ML community has acknowledged the significance of varied and representative training data.
-
The generative AI community places a strong emphasis on the value of ongoing experimentation and teamwork. The discipline has advanced significantly thanks to the dynamic process of exploration, feedback, and information exchange, which has also sparked more discoveries.
-
The ML community is becoming more and more conscious of the ethical issues surrounding the usage of generative AI as it advances. Deepfakes, false information, and possible abuse of AI-generated material are just a few of the issues that have sparked conversations and initiatives to create ethical standards and protections.
-
Researchers have studied generative modeling strategies that include numerous models cooperating to provide consistent and varied information. In order to provide more varied outputs, collective generation approaches like ensemble methods and mixture models have been used.
-
Generative AI's capacity to unleash creativity is one of the most important lessons the ML community has learned from working with it. In the past several years, generative AI has demonstrated its ability to create fresh and distinctive material, presenting new opportunities for artistic expression and fostering creative solutions in industries like design, music, and the arts.
-
In generative models, the application of attention techniques, such as self-attention, is expanding and gaining popularity. Model quality and coherence are increased as a result of attention processes, which allow models to recognize long-range relationships in the data.
-
A growing area of focus is user-centric design and dynamic interfaces. Users may direct and influence the output of generative models in accordance with their preferences by using techniques like conditional generation, style transfer, and immersive fine-tuning.
-
It is still difficult to make generative models consistently and securely generate outputs given a variety of inputs and circumstances. Instead of producing unrealistic or absurd results, the ML community has concentrated on enhancing generative models' resilience and generalization abilities to provide high-quality outputs.
-
Few-shot and one-shot learning approaches have advanced as a result of the search for data productivity and efficient use of data in generative models. Researchers have investigated strategies for training generative models with less data while generating good results. To help generative models learn fast from a small number of instances, strategies including transfer learning, meta-learning, and using additional sources have been researched by the ML community.
-
Researchers have investigated methods for interpolating in generative models' latent space. This makes it possible for seamless transitions and mixing between various produced outputs, enabling the development of fresh and ongoing variants.
-
The training and performance of generative models have benefited from the increased use of reinforcement learning and self-supervised learning. With the use of these methodologies, models may be trained using various paradigms that allow them to learn from samples they have created themselves or interact with the environment to increase the quality of their creation.
-
The capacity of generative models to transfer a style, a trait, or an attribute from one area of expertise to another has been a lucrative field of research. By facilitating seamless synthesis and modification of material across many styles and fields, this learning has cleared the path for improvements in integrating representations across domains.
-
Using generative models in conjunction with user feedback loops has been shown to be effective in raising the standard and level of user satisfaction with produced outputs. The potential for AI and humans to work together has been shown through iterative procedures incorporating human input and fine-tuning.
-
Large-scale datasets like GPT-3, which are used for pretraining generative models, have shown to be an effective starting point for many downstream applications. Transfer learning enables the models to make use of the pretraining phase's knowledge and experience to enhance performance on certain tasks with fewer datasets.
-
In order to provide outputs that are more detailed and descriptive, multimodal and hybrid generative models have been designed to produce material that spans many modalities. This has uses in speech synthesis, text-to-image conversion, and picture captioning, among others.
-
Due to their intricate architectural designs, generative models' interpretability and explainability continue to be difficult to achieve. In order to help consumers believe and comprehend the outputs produced by generative models, the machine-learning community has been focusing on building approaches to clarify and comprehend the decision-making procedures of these models.
-
Generative AI has found use in a variety of fields, including design, healthcare, and entertainment. The ML community has seen firsthand how generative AI has transformed conventional methods, automated chores, and encouraged creativity, boosting economic development and bettering people's lives.
-
Collaborations involving generative AI artists, researchers, and subject matter specialists have advanced our knowledge of generative AI. Innovative applications and imaginative investigation in a variety of domains have been made possible by the fusion of technical proficiency with domain knowledge.
It's crucial to keep in mind that generative AI is constantly expanding and new knowledge is always being discovered as research advances.
Let's now look into the impact of generative AI.
Impact of Generative AI
In recent years, generative AI has had a significant influence on society. Generative AI has revolutionized several fields by harnessing the potential of machine learning and neural networks.
-
Generative AI has made it possible to provide users with personalized user experiences by adapting content, recommendations, and goods to their tastes. This degree of customization transforms how companies connect with their consumers by enhancing user satisfaction increasing client loyalty, and fostering engagement and entertainment.
-
Automating tedious, time-consuming operations is essential for increasing productivity and efficiency. Generative AI is useful in this situation. With the use of automation, organizations may better allocate resources, reorganize workflows, lessen human error, and provide services more quickly and accurately.
-
Creative sectors have undergone a transformation thanks to generative AI, which has pushed the limits of human creativity. Today, generative models are used by designers and artists to create original and distinctive material, opening up new avenues for artistic expression and extending the boundaries of human artistic potential.
-
Businesses may use data to their advantage by identifying patterns, insights, and forecasts using generative AI. Analytics powered by AI aid businesses in decision-making based on data, process improvement, and trend detection.
-
By removing obstacles and ensuring equality, generative AI helps to advance accessibility and inclusion. Systems for language translation driven by AI allow for cross-cultural and linguistic communication. Additionally, AI-generated audio explanations and subtitles for material improve accessibility for people with vision or hearing impairments.
-
The healthcare sector has benefited greatly from generative AI, which has revolutionized medical investigation, diagnosis, and therapy. AI models help with medical imaging, drug development, illness diagnosis, and personalized treatment planning by analyzing enormous volumes of medical data; this improves patient outcomes and lowers healthcare costs.
-
By maximizing resource use, minimizing waste, and allowing improved energy management, generative AI supports environmental sustainability. AI-driven production models reduce waste, maximize efficiency, and optimize energy use. Additionally, generative AI helps with route optimization and congestion reduction in the transportation sector, promoting sustainable development in the future.
Visualizing the Global Impact of AI
1. How innovation boosts employment growth while creating new jobs?
Almost, 60% of today's workforce operates in professions that weren't around in 1940. This suggests that the development of new jobs driven by technology accounts for more than 85% of the increase in employment over the past 80 years.
Clerical and administrative work, management, and professional work are among the jobs that have emerged and are rapidly growing. Whereas, agriculture, technicians, and transportation still have a long way to go.
Innovations in the field of IT gave rise to new professions including web designers, software programmers, and digital marketers. The increase in overall revenue had adverse effects on the demand for employees in the service sector like education, health care, and food services, which further increased the demand for labor.
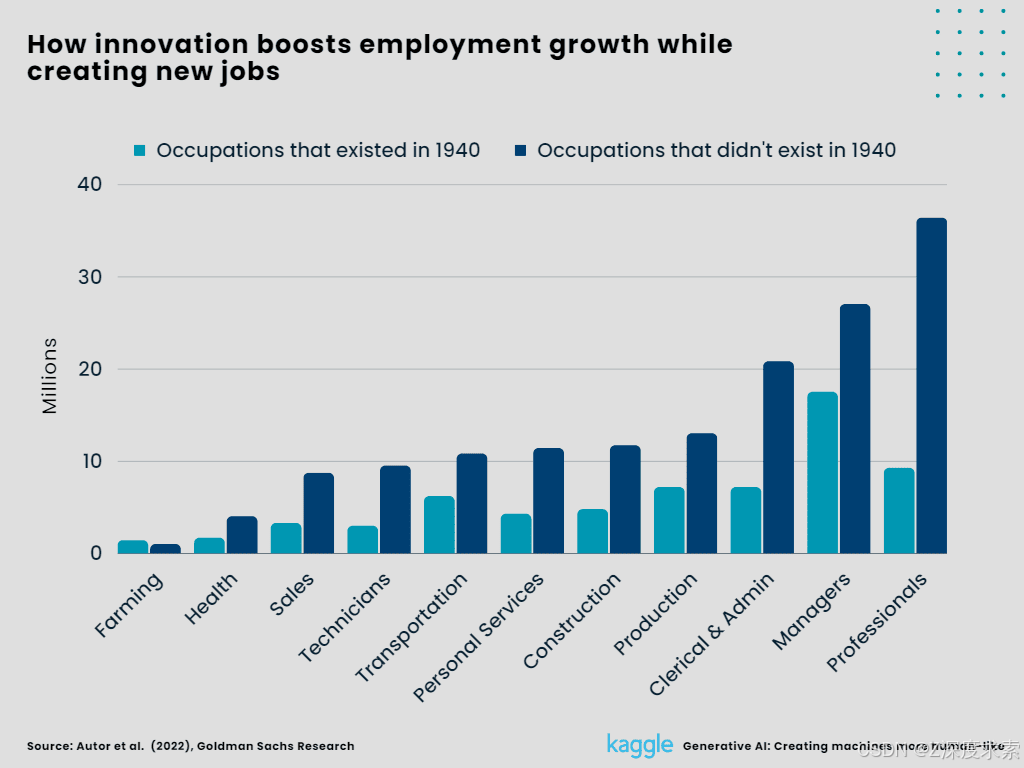
Figure 3: How innovation boosts employment growth while creating new jobs? (Created by Author)
2. Percentage of what the NLP community members think about AI.
American researchers conducted a poll on specialists in natural language processing to find out what they assumed about AI. Even though over 90% said that AI's overall effects in the past and future have been positive, they aren't discounting its potential or its dangers. While 36% believe AI might result in a nuclear-level disaster, 73% anticipate that it will soon bring about dramatic changes in society. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is viewed as a serious issue by 58% of experts, and another 58% believe that recent advancements are accelerating the development of AGI.
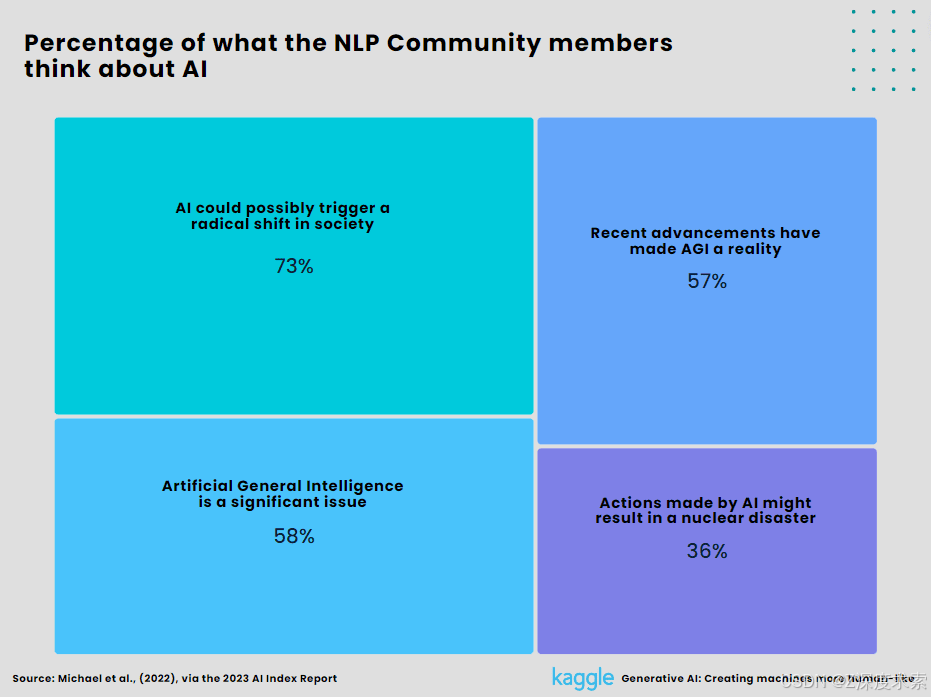
Figure 4:
Percentage of what the NLP community members think about AI (Created by Author)
3. Global views on AI ranging from favorable to unfavorable.
In a study done by the international research organization IPSOS, 78% of Chinese participants said that there are more advantages to employing artificial intelligence than disadvantages. Only 35% of Americans believe AI has a net advantage, with France having the lowest perception at 31%. According to IPSOS, males are generally more supportive of AI than women. China, Saudi Arabia, India, Peru, and Malaysia are the top five nations with favorable reviews. However, France, Canada, the Netherlands, the United States, and Australia are the top five nations with unfavorable reviews.
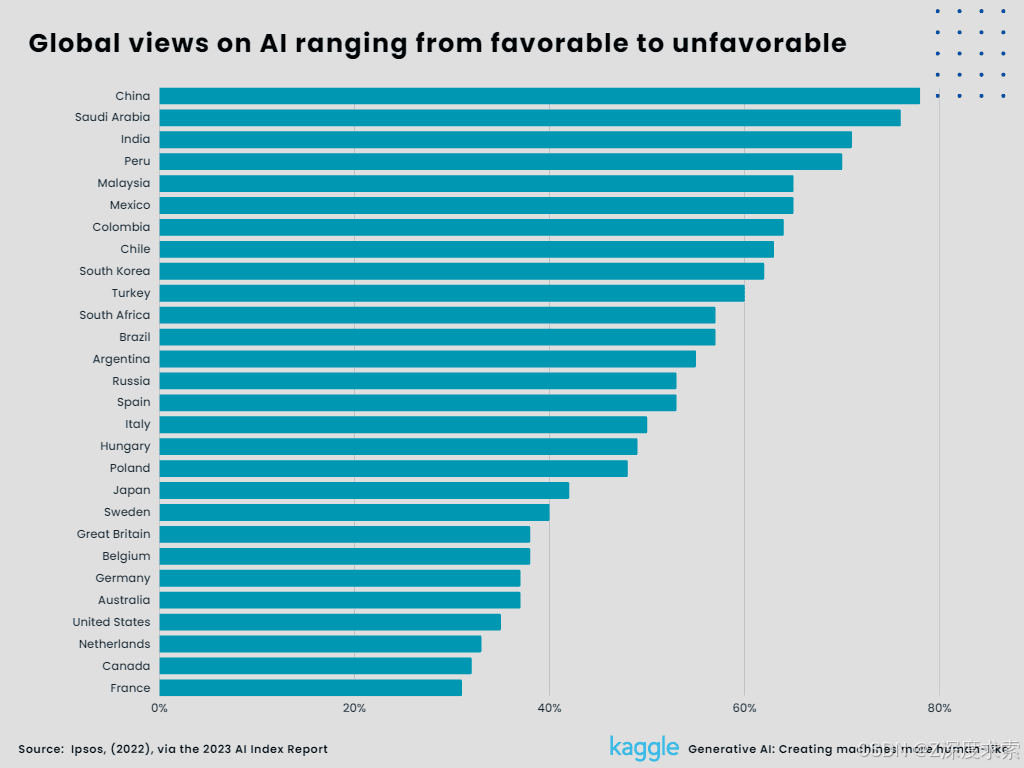
Figure 5:
Global views on AI ranging from favorable to unfavorable (Created by Author)
4. AI has the potential to partially replace few professions.
A Goldman Sachs analysis claims that 300 million full-time jobs in the US and Europe might be replaced by AI or one-fourth of all work duties.
9% to 47% of employment might be eliminated by AI, according to University of Oxford research, with technical, legal, and administrative work being most at risk.
16% of American occupations are predicted to be eliminated by AI by 2025, particularly those that require monotonous, or low-skill labor.
Although there is still much to learn regarding how generative AI can impact the global economy and community, and it will take some time for the consequences to manifest, there are strong indications that they might be significant.
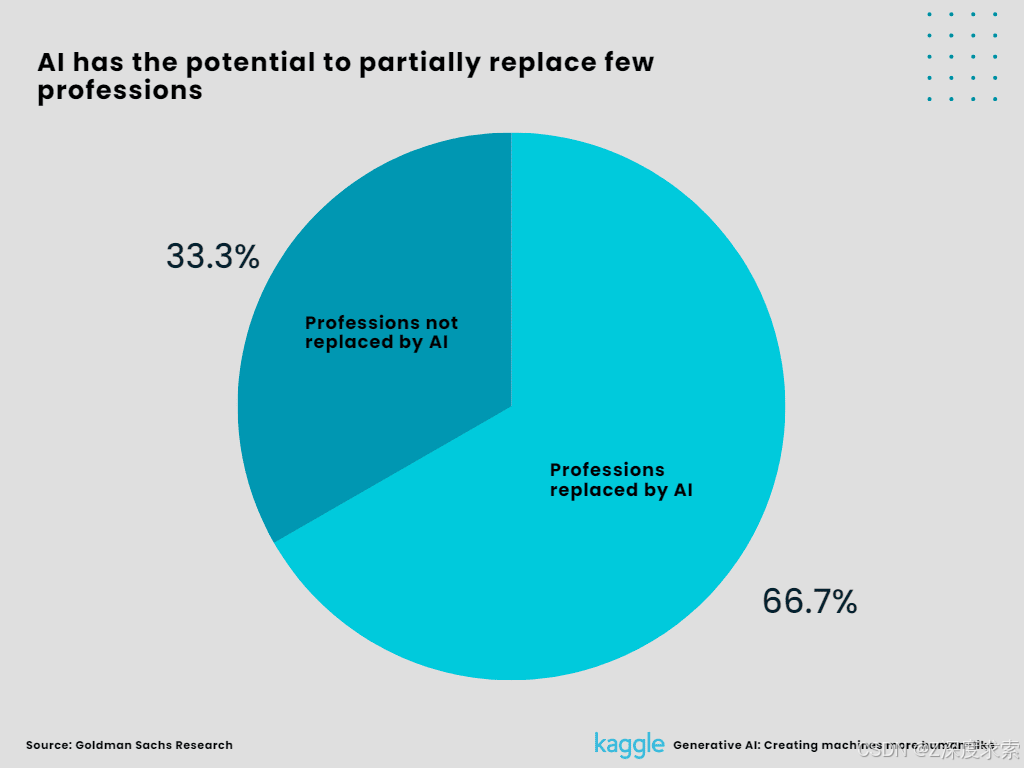
Figure 6:
AI has the potential to partially replace few professions (Created by Author)
5. Several laws associated with AI have started to catch up.
Only one law relating to AI was approved in 2016 compared to 37 in 2022 across 127 nations, according to Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence. A total of 123 laws have been approved by nations since 2016, most of them in the last few years. Spain ranked second with five regulations, and the Philippines came in third with four. The United States topped the list with nine laws.
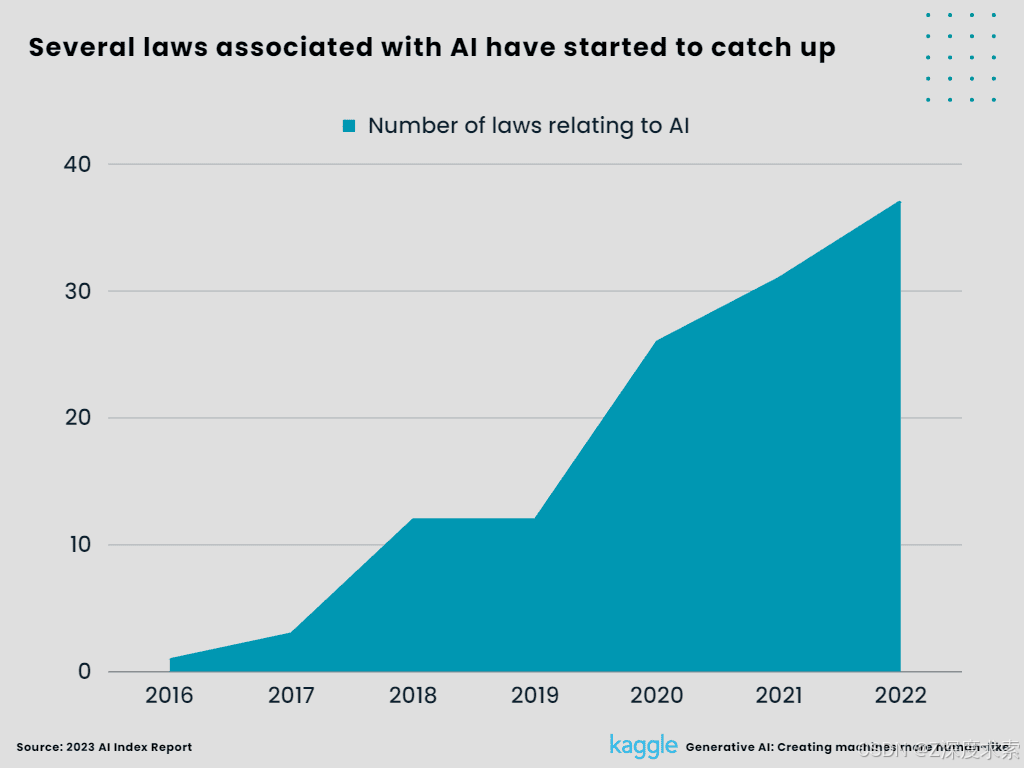
Figure 7:
Several laws associated with AI have started to catch up (Created by Author)
6. CO2 emissions of different machine learning models.
Given their enormous environmental effect, generative AI models---in particular LLMs like GPT-3---have raised serious concerns. Stanford University's AI Index Report 2023 states that in 2022, GPT-3 produced 500 times as much carbon dioxide as a round-trip flight between New York and San Francisco. Similar emissions from other AI models, such as ChatGPT, are also mentioned in the paper. The International Energy Agency estimates that approximately 1% of the world's electrical consumption and greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to data centers, while the global IT industry is responsible for 1.8% to 3.9% of all emissions.
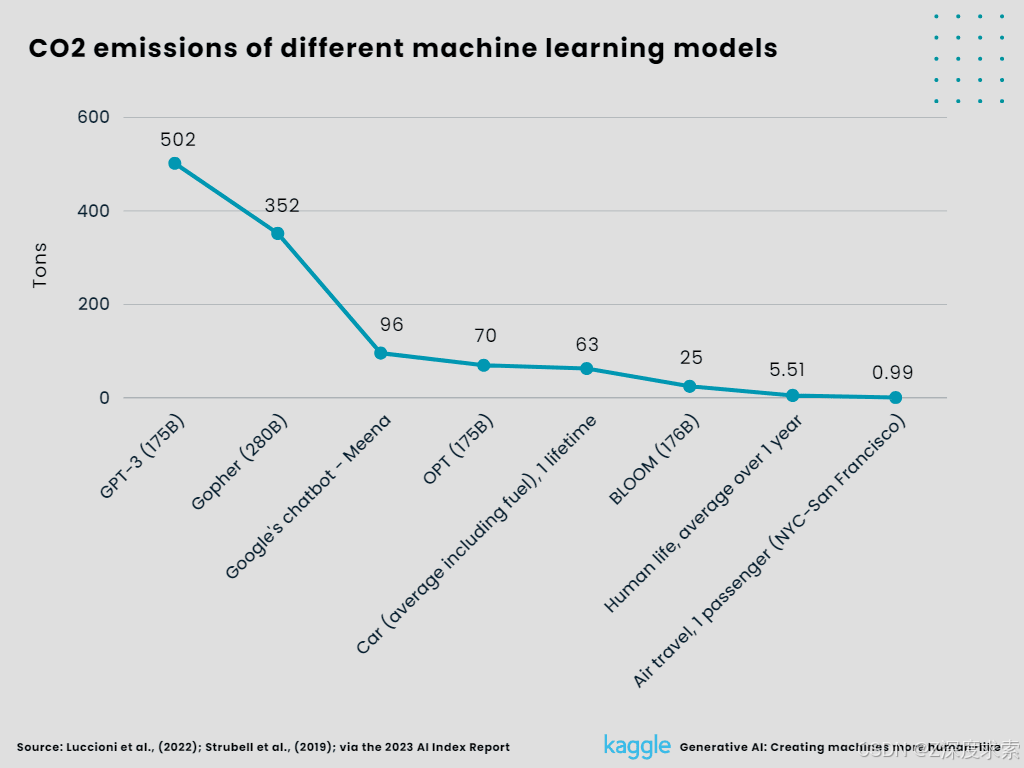
Figure 8:
CO2 emissions of different machine learning models (Created by Author)
7. AI-related disputes and occurrences from 2016 to 2023.
The archive for AI, Algorithmic, and Automation Incidents and Controversies (AIAAIC) reports that the number of reported concerns is nine times more in 2022 than it was in 2016. That can be attributed to both a rise in AI usage and a rising consciousness of its improper application. The graph only depicts the number of incidents till July 2023, but by year's end, it is expected that this figure would have increased thrice. The AI Incident Database, which also allows any user to report AI-related issues online, was used to compile the occurrences up to July 2023.
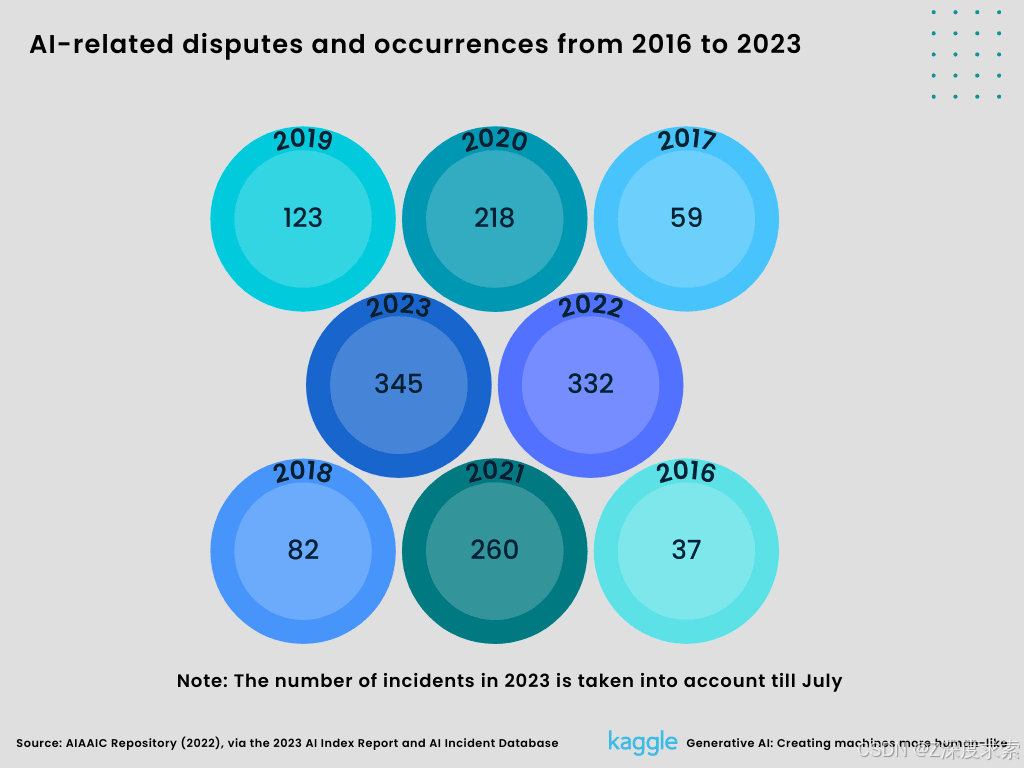
Figure 9:
AI-related disputes and occurrences from 2016 to 2023 (Created by Author)
8. Total Global Investments in AI from 2016 to 2022.
Global investments (minority stakes, mergers and acquisitions, public offers, and private investments) fell for the first time in a decade, down roughly a third from 276.14 billion dollars in 2021 to 189.6 billion dollars in 2022, but the total has still climbed 13-fold over the previous ten years. The Nuance Communications deal, in which Microsoft purchased the computer software business for 19.7 billion dollars, was the largest investment of the year. Government expenditure is growing, at least in the United States, per the study, which is good news for AI research.
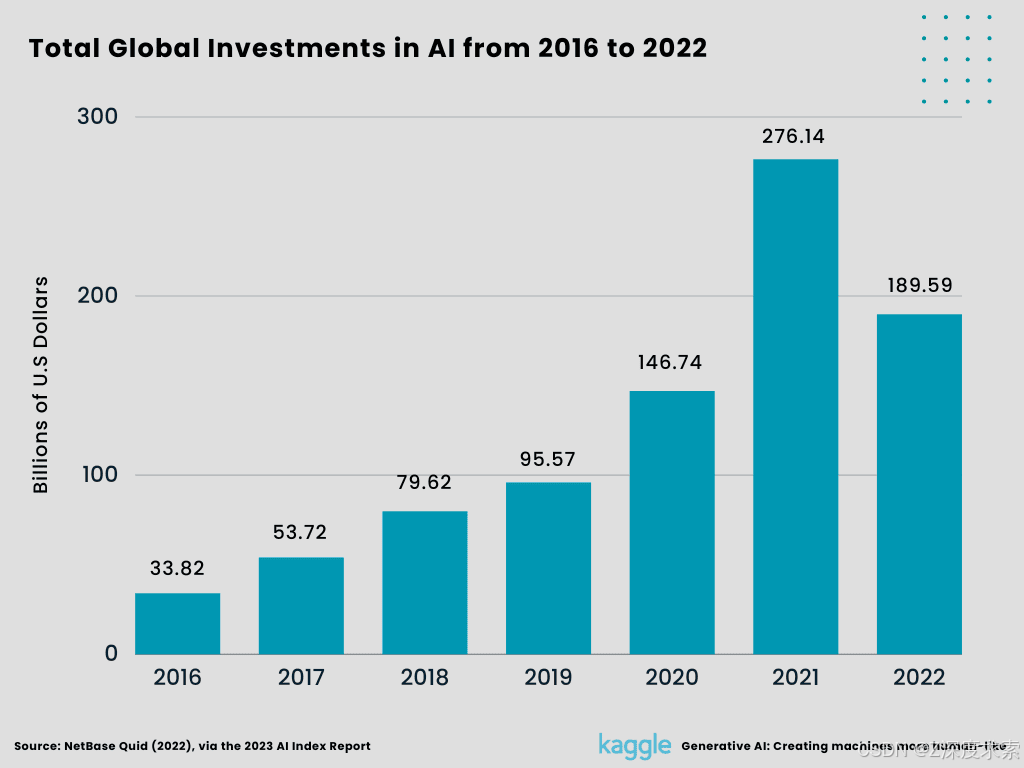
Figure 10:
Total Global Investments in AI from 2016 to 2022 (Created by Author)
9. Global perspectives on how AI will affect careers.
Around 22,816 people under the age of 75 from 31 countries except India, were interviewed online between May 26 -- June 9, 2023. 57% of workers believe AI will alter the way they perform their existing jobs, while 36% believe it will replace them entirely. With variances of up to 50 points, the percentages of workers anticipating each sort of change are high in Southeast Asia and low in Northern Europe. They are also significantly greater among young workers than the rest of the workforce.
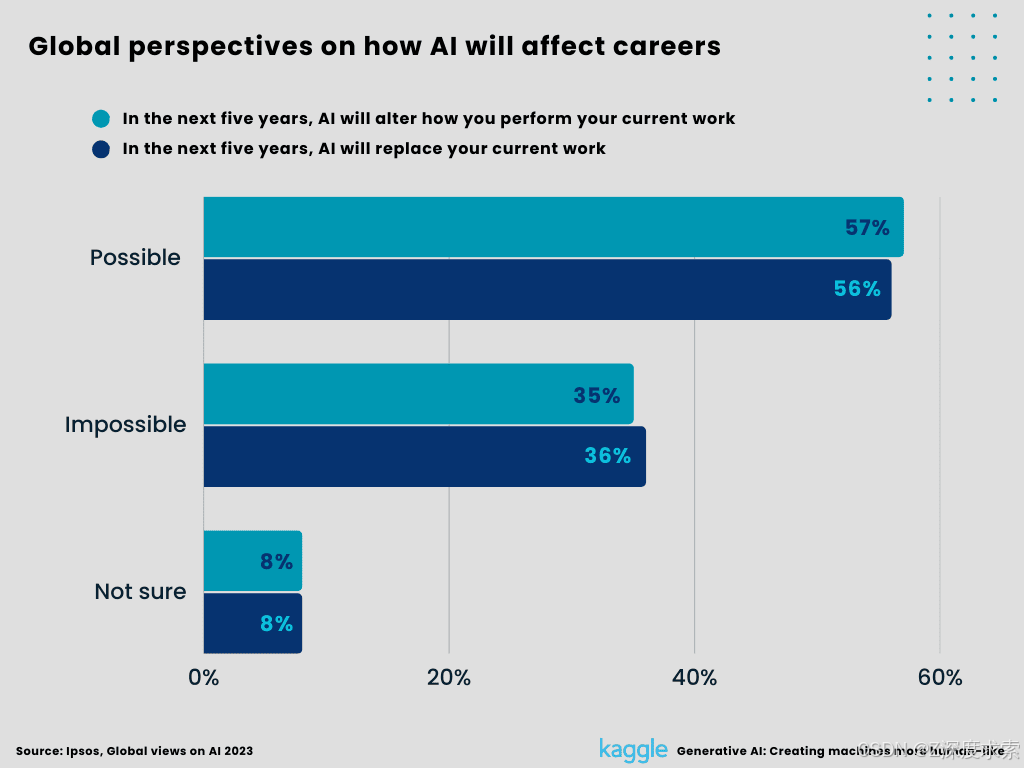
Figure 11:
Global perspectives on how AI will affect careers (Created by Author)
10. Public views on how the usage of AI will change the following fields.
Over half of people worldwide anticipate that greater use of AI will expand their productivity and entertainment options. Only thirty percent of people, or slightly more, believe it will boost the economy of their nation, their work, and their health. 38% of people believe it will worsen the job market than improve it. Once more, optimism about AI is substantially stronger in low-income countries than in high-income ones, and among young, college-educated adults than among older, less-educated adults. While there is much more to discover and learn about how generative AI might affect the world's economy and society, and it is going to take a while for the effects to become apparent, there are strong signs that they could have potential.
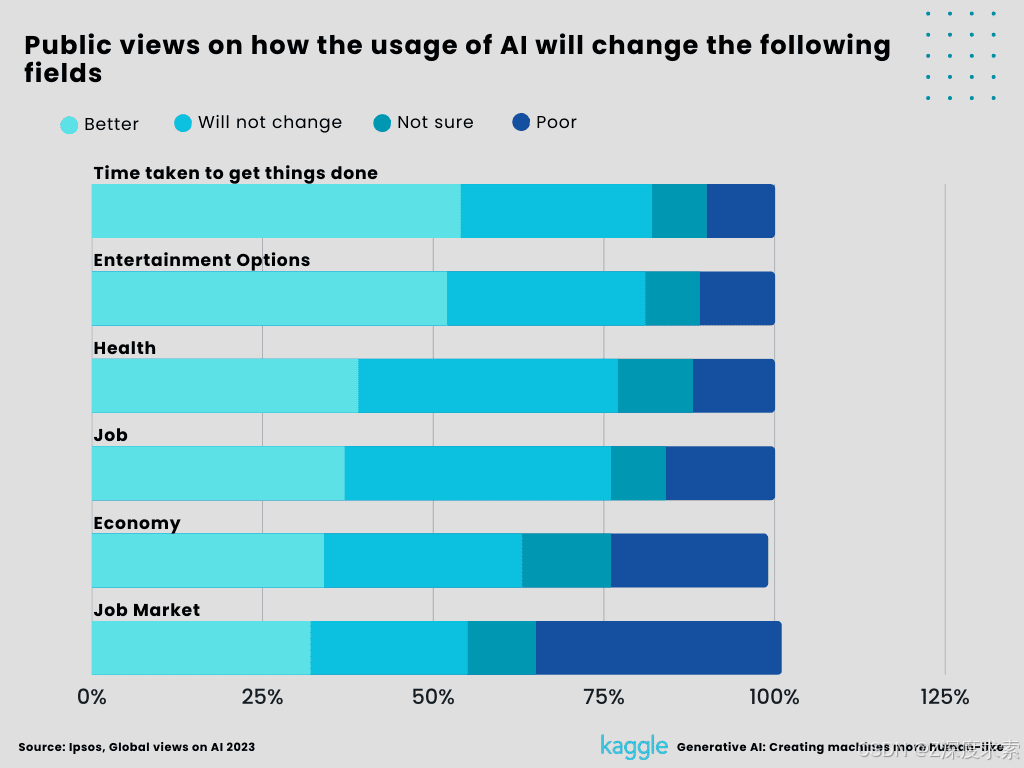
Figure 12:
Public views on how the usage of AI will change the following fields (Created by Author)
Industry-Specific Applications
| Education | Fashion & Design | Finance & Investment | Gaming & Entertainment | Healthcare | Language & Communication | Manufacturing | Marketing & Advertising | Travel & Transportation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized lessons | Clothing Design | Fraud detection | Procedural content generation | Creating realistic copies of medical records for research | Real-Time translation | Product design and Optimization | Targeted advertising | Itinerary generation |
| Course design | Turning sketches into color images | Risk management | Player behavior analysis | Disease detection | Transcription services | Process planning and Automation | Dynamic content generation | Identity verification |
| Content creation for courses | Generating representative fashion models | Trading | AI behavior and Personality for NPCs | Drug discovery and development | Creative writing | Predictive maintenance | AI-generated Ad | Destination recommendations |
| Lesson plan generation | Trend forecasting | Data privacy protection | Realistic characters | Virtual screening | Text generation | AI-enabled supply chain monitoring | AI-powered social media content | AI-generated virtual guides |
| Intelligent tutoring systems | Color palette generation | Investment research | User interface design | Side-effect prediction | Grammar and Plagiarism checking | Demand forecasting | Content curation | Virtual reality experiences |
| Virtual classrooms | Virtual fitting | Personalized marketing | Game testing | Medical imaging | Paraphrasing tools | Human-Robot collaboration | AI-driven customer analytics | Language translation |
| Simulations labs | Consumer Behavior Analysis | Virtual customer support | Interactive fiction | Clinical trial design | Language practice and Exercises | Cost analysis and estimation | Marketing performance analysis | Food and Dining recommendations |
| Restoring old learning materials | Bespoke Tailoring | Compliance monitoring | Game levels and Maps | Virtual medical assistants | Speech synthesis | Energy efficiency and Sustainability | AI-driven testing and Experimentation | AI-generated travel articles and Blogs |
| Plagiarism detection | Personalized Styling | Market prediction | AI-generated narratives | Personalized medicines | Image captioning | Quality control and Inspection | Voice and Conversational marketing | Fraud detection |
| Research assistance | Sustainable Material Selection | Transaction monitoring | Quest and Mission generation | Clinical documentation | Multimodal communication | Yield optimization | Influencer identification | Public transportation assistance |
Table 2: Industry-Specific Applications (Created by Author)
Recent developments and news
2021
-
The Covid-19 epidemic had a favorable effect on the market as a result of the rise in demand for generative AI among businesses to better serve their customers' needs and create unique experiences, including customized audio playlists, customized news sources, and customized product recommendations, which are fueling the market's expansion.
-
In 2021, the market for generative AI was estimated to be worth 7.9 billion USD. By 2030, it is expected to be worth 110.8 billion USD, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate of 34.3%.
-
In order to enable more grounded representation learning, the unique visual and language representational training technique known as ALBEF (Align Before Fuse) was introduced that aligns picture and textual representations before fusing them.
-
On January 5, 2021, OpenAI unveiled DALL-E, an AI system that can generate pictures from text captions. Using a 12 billion variable model trained on word-image pairings, it can produce original and imaginative visuals that correspond to the provided text.
-
On January 5, 2021, OpenAI also published CLIP, an AI system that is capable of learning via any natural language supervision. By training from text-image combinations on the internet, it can accomplish a variety of visual tasks.
-
On January 5th, 2021, OpenAI released CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining), their first multimodal product. Similar to GPT-2 and GPT-3's zero-shot capabilities, it swiftly learns visual ideas using natural language supervision and can be used with any visual classification benchmark.
-
SXIQ was purchased by IBM in November 2021 with the goal of supporting IBM's hybrid cloud and AI strategy by empowering companies to upgrade and enhance complex crucial applications across many platforms and cloud services.
-
SEER is a self-supervised computer vision model which contains a billion parameters and can learn from any unrelated collections of online photos, was released by Meta AI.
-
Vertex AI, which takes around 80% fewer blocks of code to build a model than competing platforms, was made generally available by Google in May during the Google I/O event.
-
Initially designed for text-based jobs, the ViT (Vision Transformer) is a visual representation that is built on the same architecture as transformers. The "image patches" used by this model to analyze pictures are then used to forecast the class labels associated with every patch.
-
GitHub Copilot, an AI pair programmer for developing better code, was introduced by OpenAI and Microsoft on October 29, 2021.
2022
-
In order to improve, coordinate, and enhance purchasing tasks, the General Services Administration (GSA) in the United States started using generative AI and machine learning in August 2022.
-
Additionally, OpenAI utilized GPT-3 as the foundation for the April 2022 release of the DALL-E 2 AI system.
-
A Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) architecture called BLIP (Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training) provides cutting-edge performance on a variety of vision-language tasks, such as image captioning, image-text retrieval, and visual question answering (VQA).
-
On July 11, 2022, Shutterstock increased its agreement with OpenAI to develop generative AI tools for creating content. Customers of Shutterstock will now have access to OpenAI's generative models for producing unique photos, videos, and audio snippets as a result of the cooperation.
-
In 2022, Google DeepMind unveiled Alpha Code, a powerful AI tool for writing computer code. With self-supervised training and an encoder-decoder architecture, it can compete at the level of a human in solving programming challenges.
-
OPT (Open pre-trained transformers) is a collection of decoder-only pre-trained transformers, released on May 3rd, 2022, with parameters ranging from 125M to 175B. OPT is sometimes challenging to duplicate without sizable investment and is sometimes not accessible through APIs. When compared to GPT-3, OPT-175B is proven to be equivalent, despite having been produced with just a one-seventh of its ecological impact.
-
On July 12, 2022, OpenAI launched MidJourney, an AI program that can alter visuals in response to written commands.
-
Merkur Insurance and Mostly AI established cooperation in November 2022 to employ artificial intelligence to create synthetic data for innovations based on data.
-
Sparrow, a conversation agent developed by DeepMind on September 2022, lessens the likelihood of giving risky or improper responses. Sparrow converses with users, responds to their questions, and uses Google to look for additional information online to strengthen its arguments.
-
Shutterstock and OpenAI collaborated to release an image generator using DALL-E 2 from OpenAI. (Although the Shutterstock-OpenAI agreement first surfaced in 2021, the image maker didn't really debut until the latter half of 2022.) In addition to OpenAI, Shutterstock has created license arrangements with companies like Meta, Nvidia, LG, and others in order to create generative AI tools and models for text, photos, and 3D models.
-
Rephrase.ai revealed that the company has funded USD 10.6 million in a round in September 2022, an investment round led by Red Venture, Silver Lake, and 8VC.
2023
-
By merging the capabilities of PaLM-2 and its generative audio model AudioLM, Google has unveiled AudioPaLM, a new multimodal language model for speech understanding and generation.
-
Version 5.2 of Midjourney's AI-driven image synthesis model has been released, and it now features a new "zoom-out" function that allows for preserving a central synthesized image while automatically building up a bigger environment around it, emulating zooming out with a camera lens.
-
A new AI model from Stability AI called SDXL 0.9 can produce more attractive and intricately composed graphics in response to text-based instructions than earlier models.
-
Google unveiled LaMDA in March, which is a conversational AI model that can have more in-depth and genuine interactions with users. The first generative AI native search engine was Neeva, while Google caught up with their Bard chatbot.
-
Microsoft has released new "plug-ins" for Microsoft 365 Copilot, which is a generative AI service that helps in productivity and creativity. In the future, plug-ins might be used to improve operations like processing reimbursement requests or streamlining a business' supply chain.
-
RoboCat, a system developed on top of Gato by DeepMind, and released in June 2023, is a new robotics controller that can learn a new task in as short as 100 steps.
-
"In April 2023, the European Union proposed new copyright regulations for generative AI that would require companies to disclose any copyrighted material used to develop these tools." (Hughes, 2023)
-
A generative AI collectibles campaign that was jointly developed by Alethea AI and Polygon in January 2023 enables training, quick development, and trade of AI characters as NFTs on Polygon.
-
Nvidia launched innovative metaverse technologies in January 2023 for businesses, including omniverse portals and a suite of creative AI tools.
-
In January 2023, Nvidia debuted a new generative AI model that can produce synthetic proteins for applications in medicine and other sectors in collaboration with the pharmaceutical business Evozyne. Nvidia's BioNeMo architecture serves as the foundation for this novel protein transformer variational auto-encoder (ProT-VAE).
-
Chinese tech businesses began working to create their own AI world in January 2023 with official support. Through IDEA, a research facility owned and supported by the Chinese Communist Party, local governments in China are making independent investments in a number of initiatives.
-
Grammarly, a writing assistant powered by artificial intelligence with headquarters in the United States, announced the release of GrammarlyGo in March 2023. This new feature enables users to write, edit, and customize content.
-
AWS, a U.S based provider of software service management, introduced Amazon Bedrock and a number of generative AI services in April 2023. These services can be used to generate and summarize text, create chatbots, and categorize photos based on a given prompt.
-
American healthcare software provider Epic Systems and Microsoft Corp., a technology business, worked in April 2023 to integrate AI and LLMs tools into Epic's electronic medical records software. Through this cooperation, healthcare practitioners will be assisted in boosting productivity while lowering administrative expenses.
-
On July 12, 2023, Kakao Brain, an AI division of the South Korean internet company Kakao, released Karlo 2.0, an AI-powered application that can generate graphics based on prompts. Using a GAN with 1.5 billion variables, it can produce realistic and varied pictures from natural language descriptions or drawings.
News
-
GPT-4, Open AI's most recent text-generation model, has been made generally available through its API.
-
As the initial buzz wears off, ChatGPT experiences a 9.7% traffic decline and a 5.7% decline in unique visitors in June.
-
The world's interest may have been piqued by ChatGPT. However, the Google-owned research facility DeepMind asserts that its upcoming LLM; Gemini, would be on par with or perhaps superior to OpenAI's.
-
Developers will be able to sell AI models created using OpenAI's AI technology on a marketplace that will soon be available.
-
The market for generative AI was worth 10.3 billion US dollars, and it is projected to increase at a compound annual growth rate of 32.2% to reach 54 billion US dollars in five years.
-
To stop ChatGPT and other generative AI tools from being used and to create alternatives, the South Korean steel company POSCO collaborated with Samsung Electronics and LG Electronics.
-
In the generative AI space, six businesses---OpenAI, Hugging Face, Lightricks, Jasper, Glean, and Stability AI---have attained unicorn status and are each valued at over 1 billion dollars.
-
The MBUX infotainment system from Mercedes-Benz will now include OpenAI's ChatGPT language model. This will improve user experience by enabling more organic and sophisticated interactions between drivers and passengers and the system.
-
Hugging Face has approximately 200K models and 36K datasets, making it one of the GitHub open-source projects with the quickest growth.
-
"The more powerful the AI, the more energy it takes. If chatbots become as popular as search engines, the energy costs of deploying the AIs could add up. The good news is that AI can run on renewable energy by bringing the computation to where green energy is more abundant." (Kate Saenko, associate professor of computer science at Boston University, wrote in an article at The Conversation, 2023.)
Technology predictions
-
The demand for prompt engineers will rise as organizations increasingly accept and use AI tools, which is being marked as the future of work.
-
A survey found that in 2022, 63% of marketers used AI for email marketing, 58% for advertising, and 57% for data analysis. We might anticipate an increase in those figures in 2023 as AI technology becomes more widely used.
-
Content produced by AI will soon become the new norm. Natural language processing (NLP) enables AI to produce content more quickly, accurately, and consistently than humans.
-
As massive data sources for audio machine learning, music streaming services like Spotify or Apple Music will surely lead to more AI-generated music. To make it easier for artists to create new music, Spotify has already developed certain AI-based tools, such as the open-source audio-to-MIDI software Basic Pitch.
-
Robots with synthetic muscles are capable of carrying greater weight and producing a greater amount of mechanical power than those powered by human muscles.
-
The transition from smartphones to wearable augmented reality (AR) glasses is expected to begin before 2026 and significantly increase speed once the implementation of 5G is finished.
-
With an ever-expanding data pool at their disposal, hackers will be able to create highly tailored spear phishing lures, ranging from free and open-source material like job openings to sensitive information disclosed in data breaches.
-
By the end of 2023, 66% of organizations will have already acquired at least two cloud providers. By doing this, businesses won't become overly entwined with a single environment.
-
The industry's adoption of cloud-native technologies and innovation are anticipated to be further boosted by recent breakthroughs in edge computing and 5G.
-
API-based options are what email security will look like in the future, as opposed to secure email gateways (SEGs), which isolate email security from internal networks.
-
By 2025, generative AI models are expected to be the source of at least 30% of all recently discovered materials and drugs, according to Gartner.
-
Augmented intelligence, which is the next AI trend for 2023, is aimed at improving cognitive productivity through the combination of automated machines and humans. The banking and insurance services, healthcare, travel, and business industries will all see a significant increase in this AI trend.
-
By using touchless fingerprinting to conduct remote biometric identity verification in 2023, organizations using current biometric database technology will be able to safely perform operations like opening banking accounts and verifying transactions.
-
Security keys and credentials that are FIDO2-compliant relieve end users from privacy obligations, demonstrating that a password-less era is within reach.
-
By 2025, three-fifths of businesses are expected to have a SASE strategy in place, according to Gartner.
Challenges
-
Generative AI models may consist of billions of parameters, and their training methods require quick and effective pipelines of information. A sizable amount of financial investment, technical know-how, and computing infrastructure are required to construct and maintain generative models.
-
Conversations must occur quickly and precisely for collaborative use cases like chatbots, AI voice assistants, or customer service applications. Diffusion models' slow sampling rates have come to light as a result of their growing popularity and the high-quality samples they can provide.
-
To create artificial data for various use cases, generative AI models are frequently utilized. Still, not all data can be used to train AI models, even though enormous amounts of data are produced daily around the globe. To function, generative models need reliable, unbiased information.
-
Getting commercial authorization to use pre-existing datasets or to create new evidence-based datasets to train generative models is a challenge for many organizations. This procedure is crucial for preventing concerns about intellectual property violations.
-
Regarding the use of creative AI tools, legal and ethical issues can arise. One of these abilities is the ability to quickly produce "deepfakes," which are computer-generated images or movies that appear genuine but are fake or misleading. ChatGPT is already causing problems for universities. They are particularly having trouble with generated degree work since it is simpler to duplicate. Midjourney and Dall-E have faced similar criticism from artists who view them as either a form of stealing or just "not art."
-
Machine learning, statistics, and computer science are just a few of the highly specialized fields that must be thoroughly understood to work in the field of generative AI. This may make it difficult for a small number of businesses to design and execute unique generative AI solutions, which may slow down the use of generative AI and hike compliance costs. Additionally, there is a significant demand for skilled individuals in the field of generative AI, but only a few are available.
-
The next difficulty is assuring generative AI's social and human effect, including preserving trust and openness, encouraging inclusiveness and diversity, and promoting ethical and advantageous use cases.
-
Making sure that generative AI is used in a way that respects intellectual property rights, protects security and privacy, and steers clear of dangerous or immoral use cases is another challenge.
Ethical generative AI
The use of generative AI systems, especially those that mimic human artistic ability, has raised ethical questions for certain individuals. Deepfake films and false information produced by generative AI may be difficult to link back to the sources, making it tricky to hold those responsible accountable. This has sparked a larger discussion about ethical AI and the need for regulations to stop data professionals from scraping the internet to create the massive data sets required for training their machine learning models. Currently, the legality of collecting free data from the internet for training purposes through web scraping relies on several criteria, including the regulations and laws of the area, the sort of data being gathered, and the intended use of the data. Machine learning engineers (MLEs) might be obligated to pay site owners for any information they use to train their generative models as the value of reliable data sets continues to rise and data owners become increasingly conscious of the value of the content they provide to data scientists.
How will the future look if generative AI takes the lead?
Generative AI's capabilities have already proven to be useful in various contexts, and as the technology develops, so will its possibilities as well as its usage. Progress in generative model research and development fosters innovation across a range of AI-related domains. The potential for generative AI to fundamentally alter many facets of human existence remains enormous as it develops, setting the path for a future characterized by innovation, customization, and increased effectiveness. While some occupations may be replaced by generative AI, according to the technology's proponents, new ones will be created because there will always be a demand for a human-in-the-loop (HITL). Humans are still needed to choose the best generative AI model for the task, assemble and prepare training data, and assess the output of the AI model. Nevertheless, tackling the dangers that generative AI may pose is essential to its continued development. As AI becomes more advanced, maintaining data governance and reducing biases will be essential for ensuring that it is utilized ethically. To maximize the advantages of generative AI while minimizing any potential negative effects on the workforce, a balance between artificial intelligence and interactions with humans will be essential. Over time, more generative AI application cases are anticipated to surface. We must proceed cautiously, even though generative AI's future will enhance numerous processes specific to particular industries. The potential of generative AI and other methods is still not fully appreciated, despite the abundance of promising examples. It's crucial to use AI carefully and with reasonable expectations for those who choose to do so in their organizations.
Let's see what the rest of 2023 and the future have in store for us in the field of AI!
References:
- Emmanuel Ramos, (2023). Unlock The Potential Of Generative AI: A Guide For Tech Leaders. Forbes Technology Council.
- S Akash, (2023). What is the State of Machine Learning in 2023? Analytics Insight.
- Stuart Bingë, (2023). The State of Machine Learning 2023. sitepen.
- Yuri Musienko, (2023). Machine Learning Trends in 2023. MEREHEAD.
- Stephen Weigand, (2022). 2023 tech predictions: AI and machine learning will come into their own for security. SCMEDIA.
- Geri Mileva, (2023). Top 10 AI Trends That Will Transform Businesses in 2023. Influencer Marketing Hub.
- Yulia Gavrilova, (2022). Machine Learning Trends for 2023. serokell.io
- James Maguire, (2023). Generative AI Examples. eWEEK.
- Yuri Musienko, (2023). BIGGEST ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) TRENDS IN 2023. MEREHEAD.
- Owen Hughes, (2023). Generative AI defined: How it works, benefits and dangers. TechRepublic.
- Eray Eliaçik, (2023). Generative AI: The origin of the popular AI tools. DATACONOMY.
- Margaret Rouse, (2023), Generative AI. techopedia.
- Generative AI -- What is it and How Does it Work? NVIDIA.
- Jason Nelson, (2023). What's the Environmental Impact of Generative AI Tools? Decrypt.
- Richard Waters, (2023). Microsoft launches generative AI tools for developers. San Francisco. FINANCIAL TIMES.
- Shelby Hiter, (2023). Top 9 Generative AI Applications and Tools. eWEEK.
- Kate Saenko, (2023). Is generative AI bad for the environment? A computer scientist explains the carbon footprint of ChatGPT and its cousins. The Conversation.
- Supantha Mukherjee, Foo Yun Chee, Martin Coulter, (2023). EU proposes new copyright rules for generative AI. REUTERS.
- What Is Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)? CISCO.
- Aminu Abdullahi, (2022). What is a data governance program? TechRepublic.
- Margaret Rouse, (2022). What is Synthetic Data? techopedia.
- Cem Dilmegani, (2023). Top 70+ Generative AI Applications / Use Cases in 2023. AIMultiple.
- Akash Takyar, GENERATIVE AI USE CASES AND APPLICATIONS. LeewayHetrz.
- Generative AI: What is it, Tools, Models, Applications, and Use cases. Gartner.
- Prathamesh Ingle, (2023). Best AI 3D Generators in 2023. MARKTECHPOST.
- Harry Guinness, (2023). The top AI text generators in 2023. zapier.
- Alex McFarland, (2023). 10 Best AI Voice Generators. UNITE.AI.
- Alex McFarland, (2023). 10 Best AI Video Generators. UNITE.AI.
- Melanie Easton, (2023). 13 Best AI Image Generators You Can Try in 2023. fotor.
- 14 Best AI Code Generators of 2023. Renaissance Rachel.
- Generative AI Models. GreatLearning.
- Generative AI Terms and Their Definitions. C3.ai
- Natasha Nel, (2023). The ultimate A-Z guide to generative AI terminology. producthunt.
- Ashley Eusanio, (2023). AI From A to Z: The Generative AI Glossary for Business Leaders. Salesforce.
- Avijeet Biswal, (2023). Top 10 Deep Learning Algorithms You Should Know in 2023. simplilearn.
- The AI Index Report - Measuring trends in Artificial Intelligence. Stanford University.
- Cornellius Yudha Wijaya, (2023). 2023 AI Index Report: AI Trends We Can Expect in the Future. KDnuggets.
- Michael Chui, Eric Hazan, Roger Roberts, Alex Singla, Kate Smaje, Alex Sukharevsky, Lareina Yee, and Rodney Zemmel, (2023). The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier. McKinsey Digital.
- Amy Sarah John, (2023). How generative AI can boost productivity in enterprises and industries. WIRE19.
- The Rise of Generative AI. J.P.Morgan.
- Neeru Gupta, (2023). What is Generative AI and Its Impact On Various Industries? LABELLERR.
- Jackie Wiles, (2023). Beyond ChatGPT: The Future of Generative AI for Enterprises. Gartner.
- Deborah Nas, (2023). 5 Sectors that will be most affected by Generative AI. Medium.
- Tekla S. Perry, (2023). 10 Graphs That Sum Up the State of AI in 2023. IEEE Spectrum.
- Generative AI could raise global GDP by 7%. GoldmanSachs.
- Matt Carmichael, (2023). AI is making the world more nervous. Ipsos.
- Chris Vallance, (2023). AI could replace equivalent of 300 million jobs - report. BBC NEWS.
- Aaron Mok, Jacob Zinkula, (2023). ChatGPT may be coming for our jobs. Here are the 10 roles that AI is most likely to replace. BUSINESS INSIDER.
- Artificial Intelligence: Key insights, data and tables. Ipsos.
- Shana Lynch, (2023). 2023 State of AI in 14 Charts. HAI.
Coding:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from textblob import TextBlob
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import os
for dirname, _, filenames in os.walk('/kaggle/input'):
for filename in filenames:
print(os.path.join(dirname, filename))/kaggle/input/generative-ai-tweets/GenerativeAI tweets.csv
/kaggle/input/2023-kaggle-ai-report/sample_submission.csv
/kaggle/input/2023-kaggle-ai-report/arxiv_metadata_20230510.json
/kaggle/input/2023-kaggle-ai-report/kaggle_writeups_20230510.csvDataset courtesy: Arinjay Pathak.
df = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/generative-ai-tweets/GenerativeAI tweets.csv', parse_dates=['Datetime'])
df.head()| | Unnamed: 0 | Datetime | Tweet Id | Text | Username |
| 0 | 0 | 2023-04-19 21:27:19+00:00 | 1648800467206672384 | From Studio Gangster to Synthetic Gangster 🎤..... | resembleai |
| 1 | 1 | 2023-04-19 21:27:09+00:00 | 1648800425540476929 | Took me some time to find this. I build this #... | devaanparbhoo |
| 2 | 2 | 2023-04-19 21:26:57+00:00 | 1648800376479715328 | Mind blowing next wave #generativeai platform... | timreha |
| 3 | 3 | 2023-04-19 21:26:49+00:00 | 1648800341193027584 | Open Source Generative AI Image Specialist Sta... | VirtReview |
| 4 | 4 | 2023-04-19 21:25:00+00:00 | 1648799883934203905 | Are you an #HR leader considering which future... | FrozeElle |
|---|
This set of data includes statistics for a single year, from 2022 to 2023.
df.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 56221 entries, 0 to 56220
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Unnamed: 0 56221 non-null int64
1 Datetime 56221 non-null datetime64[ns, UTC]
2 Tweet Id 56221 non-null int64
3 Text 56221 non-null object
4 Username 56221 non-null object
dtypes: datetime64[ns, UTC](1), int64(2), object(2)
memory usage: 2.1+ MBThe dataset consists of 56221 number of tweets about Generative AI and has no null values.
We will plot a graph of the frequency of the term "Generative AI" in order to identify the trend. This can be accomplished by counting the daily occurrences of tweets and then creating a graph.
daily_counts = df.set_index('Datetime').resample('D')['Tweet Id'].count()
print(daily_counts)Datetime
2022-04-21 00:00:00+00:00 2
2022-04-22 00:00:00+00:00 1
2022-04-23 00:00:00+00:00 1
2022-04-24 00:00:00+00:00 1
2022-04-25 00:00:00+00:00 7
...
2023-04-15 00:00:00+00:00 522
2023-04-16 00:00:00+00:00 531
2023-04-17 00:00:00+00:00 800
2023-04-18 00:00:00+00:00 885
2023-04-19 00:00:00+00:00 886
Freq: D, Name: Tweet Id, Length: 364, dtype: int64max(daily_counts)1011From above, we can observe that a certain day had an average of 1011 tweets.
df['Datetime'].groupby(df.Datetime.dt.to_period("M")).agg('count')/tmp/ipykernel_32/325763368.py:1: UserWarning: Converting to PeriodArray/Index representation will drop timezone information.
df['Datetime'].groupby(df.Datetime.dt.to_period("M")).agg('count')Datetime
2022-04 24
2022-05 105
2022-06 61
2022-07 55
2022-08 135
2022-09 219
2022-10 630
2022-11 1670
2022-12 3977
2023-01 6881
2023-02 11108
2023-03 19003
2023-04 12353
Freq: M, Name: Datetime, dtype: int64Out of all the months, March 2023 has the most tweets due to the introduction of Generative AI tools and announcements like GPT-4, Microsoft Bing, Github Copilot, ChatGPT plugins, UNESCO calling for AI ethics implementation, AI to predict cancer patient survival, Concerns about deepfakes, Canva and Zoom introducing AI features and tools, PyTorch 2.0 release, Ford choosing autonomous driving with Latitude AI, Launching of Snapchats chatbot-My AI, and many more.
plt.plot(daily_counts.index, daily_counts.values)
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Number of tweets')
plt.title('Usage of Generative AI from 2022-2023')
plt.show()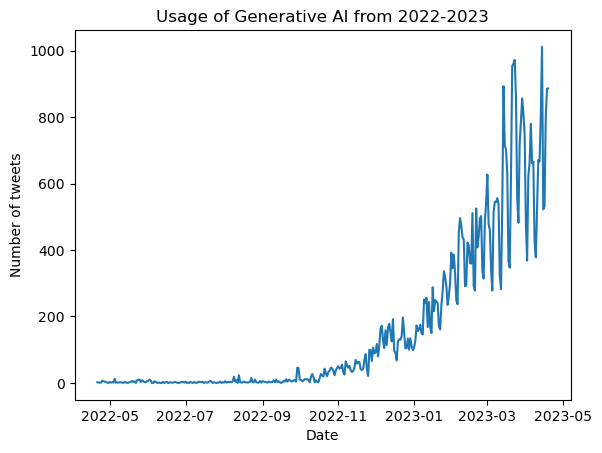
We can infer from the rising volume of tweets about "generative AI" that as more people become aware of it, the average usage of the technology will rise as well. And ChatGPT's influence is primarily accountable for the rise in popularity of Generative AI in 2023.
Let's perform sentiment analysis and visualize the results.
# Defining a function to classify sentiment
def get_sentiment(text):
blob = TextBlob(text)
sentiment = blob.sentiment.polarity
if sentiment > 0:
return "Positive"
elif sentiment < 0:
return "Negative"
else:
return "Neutral"
# To add a new column with the sentiment classification
df["sentiment"] = df["Text"].apply(get_sentiment)
# To print the number of tweets in each category
print("Sentiment Distribution:\n", df["sentiment"].value_counts())
# To print 10 tweets from each category
print("\nPositive Tweets:")
print(df[df["sentiment"] == "Positive"]["Text"].head(10))
print("\nNegative Tweets:")
print(df[df["sentiment"] == "Negative"]["Text"].head(10))
print("\nNeutral Tweets:")
print(df[df["sentiment"] == "Neutral"]["Text"].head(10))
# To visualize the distribution of sentiment
sns.countplot(x="sentiment", data=df)
plt.savefig('blob.png')Sentiment Distribution:
Positive 29199
Neutral 21709
Negative 5313
Name: sentiment, dtype: int64
Positive Tweets:
5 #GenerativeAI is a new technology that can cre...
6 Salesforce announces plans to integrate Einste...
7 Discover the limitless possibilities of #Gener...
9 Salesforce announces plans to integrate Einste...
10 Check out my latest article: Four Ways #Genera...
12 @MoldyWarp Here are the images you requested, ...
15 Acquire a premium AI startup domain!\nStill av...
18 One more. Starting to get to grips with this w...
19 A person's surprised face as they spot a celeb...
20 🎯 Achieve “Product Market Fit” with Ai — https...
Name: Text, dtype: object
Negative Tweets:
22 What GenAI use cases are you exploring in the ...
37 Now some post-processing experiments to make t...
41 @Atlassian is adding an AI capability to the e...
42 The traffic at Stack Overflow has been declini...
44 well yes flawed, dangerous, and nothing about ...
46 The traffic at Stack Overflow has been declini...
47 Follow the #XenobiologyMuseum !\nFacebook: @ X...
55 Shocking Revelation: AI Chatbots Perpetuate Bi...
89 https://t.co/TL0vd84Jgl #technews »#StabilityA...
103 https://t.co/r9KP1kKwUx #technews »#StabilityA...
Name: Text, dtype: object
Neutral Tweets:
0 From Studio Gangster to Synthetic Gangster 🎤.....
1 Took me some time to find this. I build this #...
2 Mind blowing next wave #generativeai platform...
3 Open Source Generative AI Image Specialist Sta...
4 Are you an #HR leader considering which future...
8 Local art fam: Come join us at Adobe SF to lea...
11 This week on Big Martech, the second installat...
13 Three Ways Media Leaders Can Leverage Generati...
14 #CreatorEconomy - 💭 Is creativity at risk? As ...
16 Midjourney and Adobe Firefly Prompts\n\n#adobe...
Name: Text, dtype: object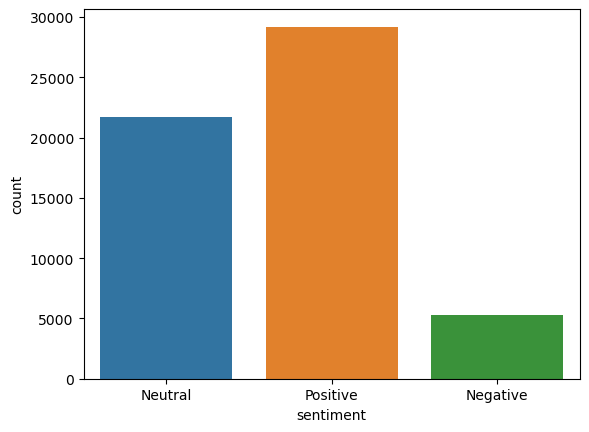
Positive sentiment about generative AI can be found in 52% of tweets. Neutral and negative tweets made up 39% and 9% of the total, respectively.
Word Cloud
def show_wordcloud(data, title = None):
wordcloud = WordCloud(
background_color = 'white',
max_words = 200,
max_font_size = 40,
scale = 3,
random_state = 42
).generate(str(data))
fig = plt.figure(1, figsize = (20, 20))
plt.axis('off')
if title:
fig.suptitle(title, fontsize = 20)
fig.subplots_adjust(top = 2.3)
plt.imshow(wordcloud)
plt.show()
# print wordcloud
show_wordcloud(df["Text"])
Above are the most commonly used words
Submission Process
submission=pd.read_csv("/kaggle/input/2023-kaggle-ai-report/sample_submission.csv")
submission.head()| | type | value |
| 0 | essay_category | 'copy/paste the exact category that you are su... |
| 1 | essay_url | 'http://www.kaggle.com/your_username/your_note... |
| 2 | feedback1_url | 'http://www.kaggle.com/.../your_1st_peer_feedb... |
| 3 | feedback2_url | 'http://www.kaggle.com/.../your_2nd_peer_feedb... |
| 4 | feedback3_url | 'http://www.kaggle.com/.../your_3rd_peer_feedb... |
|---|
submission.loc[0]['value']='Generative AI'
submission.loc[1]['value']='https://www.kaggle.com/code/sanjushasuresh/2023-kaggle-ai-report-generative-ai'
submission.loc[2]['value']='https://www.kaggle.com/code/satyaprakashshukl/2023-kaggle-ai-generative-ai-summary/comments#2309341'
submission.loc[3]['value']='https://www.kaggle.com/code/ahmedfzl/generative-ai-advancements-from-2021-to-2023/comments#2309270'
submission.loc[4]['value']='https://www.kaggle.com/code/manansoam/evolution-of-generative-ai/comments#2327705'
submission.head()| | type | value |
| 0 | essay_category | Generative AI |
| 1 | essay_url | https://www.kaggle.com/code/sanjushasuresh/202... |
| 2 | feedback1_url | https://www.kaggle.com/code/satyaprakashshukl/... |
| 3 | feedback2_url | https://www.kaggle.com/code/ahmedfzl/generativ... |
| 4 | feedback3_url | https://www.kaggle.com/code/manansoam/evolutio... |
|---|
submission.to_csv('submission.csv',index=False)