FastAPI基础 -- pd的FastAPI笔记
文章目录
-
- [FastAPI基础 -- pd的FastAPI笔记](#FastAPI基础 -- pd的FastAPI笔记)
- 第一个FastAPI应用
- FastAPI异步处理
- FastAPI响应数据
环境配置
python
conda create -n fastapipy312 python=3.12
pip install "fastapi[standard]"
pip install fastapi==0.115.12
pip install uvicorn==0.34.2第一个FastAPI应用
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get("/")
def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 注意 01FastAPI启动表示文件名 app为上面定义的app
uvicorn.run("01FastAPI启动:app", host="127.0.0.1", port=8003,
reload=True,)其他访问方式
cmd
uvicorn 01FastAPI启动:app --host 127.0.0.1 --port 8003 --reload
调试模式
fastapi dev 01FastAPI启动.py --host 127.0.0.1 --port 8003FastAPI的文档地址: http://127.0.0.1:8003/docs
路径参数
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get("/args1/1")
def path_args_1():
return {"message": "id1"}
@app.get("/args2/{id}")
def path_args_2():
return {"message": "id2"}
@app.get("/args3/{id}")
def path_args_3(id: int):
return {"message": f"id3: {id}"}
@app.get("/args4/{id}/{name}")
def path_args_4(id: int, name: str):
return {"message": f"id4: {id}, name: {name}"}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("02FastAPI路径参数:app", host="127.0.0.1", port=8003, reload=True)依次访问:
- http://127.0.0.1:8003/args1/1 --> 显示{"message": "id1"}
- http://127.0.0.1:8003/args2/2 --> 显示{"message": "id2"}
- http://127.0.0.1:8003/args3/3 --> 显示{"message": "id3: 3"}
- http://127.0.0.1:8003/args4/4/pdnbplus --> 显示{"message": "id4: 4, name: pdnbplus"}
查询参数
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get("/query/")
def page_limit(page: int, limit: int):
return {"page": page, "limit": limit}
@app.get("/query2/")
def page_limit2(page: int, limit=None):
if limit:
return {"page": page, "limit": limit}
else:
return {"page": page}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("03FastAPI查询参数:app", host="127.0.0.1", port=8003, reload=True)在浏览器中访问:127.0.0.1:8003/docs,可以看到查询参数的定义,可以进行参数测试
请求体
FastAPI 使用请求体从客户端(例如浏览器)向 API 发送数据。
发送数据使用 POST(最常用)、PUT 、DELETE 、PATCH 等操作。
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
import uvicorn
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
# str | None = None 表示 description 表示这个字段可以是字符串类型,也可以是 None类型, 默认值是 None
description: str | None = None
price: float
@app.post("/items/")
async def create_item(item: Item):
return item
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("04FastAPI请求体:app", host="127.0.0.1", port=8003, reload=True)浏览器中访问:127.0.0.1:8003/docs,可以看到请求体的定义,可以进行请求体测试,
FastAPI请求参数验证
原生类型验证
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from typing import Union, Optional, List
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get("/items1/{item_id}")
def read_item1(item_id: int):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items2/{item_id}")
def read_item2(item_id: str):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items3/{item_id}")
# Union[str, int] 类型注解,表示参数可以是字符串或整数
def read_item3(item_id: Union[str, int]):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items4/{item_id}")
# 由于是路径参数 默认值不可用
def read_item4(item_id: Union[str, int] = 123):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items5/")
def read_item5(item_id: Union[str, int] = 123):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items6/")
def read_item6(item_id: Optional[int] = None):
# 其中 Optional[int] 可以理解为 Union[int, None] 的缩写 表示参数可以是整数或 None
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.post("/items7/")
def read_item7(item_ids: List[int]):
return {"item_id": item_ids}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("05FastAPI类型验证:app", host="127.0.0.1", port=8003, reload=True)其中以items7的response为例
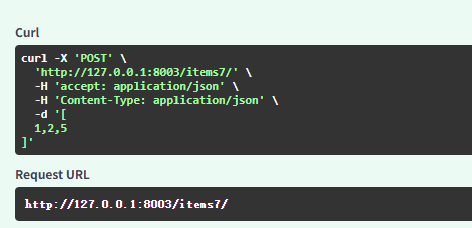
- -X 'POST': 指定 HTTP 方法为 POST(通常用于提交数据)。
- 'http://127.0.0.1:8003/items7/':请求的目标 URL(本地 FastAPI 或其他 Web 服务)。
- -H 'accept: application/json': 设置 Accept请求头,表示客户端希望接收 JSON 格式的响应。
- -H 'Content-Type: application/json': 设置 Content-Type请求头,表示请求体是 JSON 格式。
- -d '[1,2,5]': 发送 JSON 格式的请求体 [1, 2, 5](POST 请求通常带请求体)。
Query参数验证
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get("/items1")
# item_id参数默认值为123
def read_item1(item_id=Query(123)):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items2")
# item_id参数必填
def read_item2(item_id=Query(...)):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items3")
# item_id参数长度限制为3-10个字符
def read_item3(item_id: str = Query(..., min_length=3, max_length=10)):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items4")
# item_id参数必须为整数,且在0-5之间
def read_item4(item_id: int = Query(..., gt=0, lt=5)):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items5")
# 给前端参数起别名 id 并给出描述
def read_item5(item_id: int = Query(..., alias='id', description='商品ID')):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items6")
# 给参数设置deprecated=True,表示参数已废弃
def read_item6(item_id: int = Query(..., deprecated=True)):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items7")
# 给参数设置regex(pattern),表示参数必须符合正则表达式 如: a08
def read_item7(item_id: str = Query(..., regex='^a\d{2}$')):
return {"item_id": item_id}
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='06FastAPIQuery参数认证:app',
host='127.0.0.1', port=8003, reload=True)Path参数验证
python
from enum import Enum
from typing import Annotated
from pydantic import BeforeValidator
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get("/items1/{item_id}")
def read_item1(item_id: int):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items2/{item_id}")
# Path(...)表示路径参数必填
def read_item2(item_id: int = Path(...)):
return {"item_id": item_id}
@app.get("/items3/{item_id}")
# Path(...)表示路径参数必填, gt=0表示接受的最小值是0, lt=100表示接受的最大值是100
def read_item3(item_id: int = Path(..., gt=0, lt=100)):
return {"item_id": item_id}
# 也可以使用正则 Path(..., regex="^a\d{2}$") 表示路径参数必须以a开头,后面跟着2位数字
# 枚举类型
class ItemName(str, Enum):
apple = "apple"
banana = "banana"
orange = "orange"
@app.get("/items4/{item_name}")
# 传递参数的时候就只能传入枚举类型的值
def read_item4(item_name: ItemName):
return {"item_name": item_name}
# 自定义类型
def validate(value):
if not value.startswith("P-"):
raise ValueError("必须以P-开头")
return value
Item = Annotated[str, BeforeValidator(validate)]
@app.get("/item5/{item_name}")
# 传递参数的时候就只能传入枚举类型的值
def read_item4(item_name: Item):
return {"item_name": item_name}
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='07FastAPIPath参数验证:app',
host='127.0.0.1', port=8003, reload=True)Field参数验证
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field, field_validator
from enum import Enum
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
class User(BaseModel):
name: str = Field(default='pdnbplus')
age: int = Field(...) # 必填项
@app.post("/users")
def create_user(user: User):
return user
class Product(BaseModel):
price: float = Field(..., gt=0, lt=1000, description='商品价格')
name: str = Field(..., min_length=1, max_length=100,
description='商品名称', example='锤子')
@app.post("/products")
def create_product(product: Product):
return product
class Order(BaseModel):
items: list[Product] = Field(..., min_items=1)
address: dict = Field(..., description='收货地址')
@app.post("/orders")
def create_order(order: Order):
return order
class UserEmail(BaseModel):
email: str
# 自定义验证器 优先级高于pydantic内置验证器
# validate_email方法必须是类方法, 可以起别名
# v 表示验证的字段值
@field_validator("email")
def validate_email(cls, v):
if "@" not in v:
raise ValueError("Invalid email")
return v
@app.post("/user_email")
def create_user_email(user: UserEmail):
return user
class Task(str, Enum):
ACTIVE = 'active'
INACTIVE = 'inactive'
@app.post("/tasks")
def create_task(task: Task):
return task
# 动态默认值
from uuid import uuid4
class Document(BaseModel):
id: str = Field(default_factory=uuid4)
title: str = Field(..., min_length=1, max_length=100)
content: str = Field(..., min_length=1, max_length=1000)
@app.post("/documents")
def create_document(document: Document):
return document
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run('08FastAPIField参数验证:app', host='127.0.0.1', port=8003,
reload=True)FastAPI表单数据
使用表单需要安装python-multipart模块
cmd
pip install python-multipart==0.0.20
python
# 查询参数形式
@app.post('/login1/')
def login1(username: str, password: str):
return {'username': username, 'password': password}
python
# 表单形式
@app.post('/login2/')
def login2(username: str = Form(...), password: str = Form(...)):
return {'username': username, 'password': password}
python
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Annotated
# 使用自定义模型
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
password: str
@app.post('/login3/')
# 通过表单提交的用户对象,使用Annotated进行类型注解,
# 指定该参数应从表单数据中解析
def login3(user: Annotated[User, Form()]):
return userFastAPI异步处理
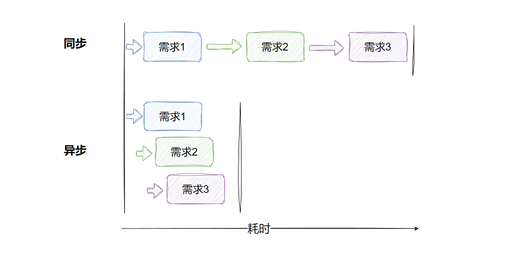
异步 (async def)
- 事件循环:异步代码运行在 Python 的异步事件循环(如 asyncio)中。事件循环负责协调多个协程(coroutines),在某个协程等待 I/O 操作(如数据库查询或 HTTP 请求)时,事件循环可以切换到其他协程执行。
- 非阻塞:当一个异步函数调用 await,它会暂停执行,将控制权交回事件循环,允许其他任务运行,直到等待的操作完成。
- 并发性:异步模式允许单个线程处理大量并发请求,特别适合高并发场景(如 Web 服务器处理大量客户端请求)。
非异步(def)
- 阻塞式执行:同步函数在调用时会完全占用线程,直到函数执行完成才会释放线程。
- 线程池:在 FastAPI 中,同步函数由工作线程(worker threads)处理,Uvicorn(FastAPI 常用的 ASGI 服务器)会将同步函数放入线程池运行。
- 并发限制:线程池的大小限制了同步函数的并发能力。如果线程池耗尽(例如,处理大量阻塞请求),新请求将排队等待。
为什么flask、django没有用异步处理,却也能满足多用户场景?
- 因为在启动服务时,会开启多个线程,使用线程池,主线程接收请求 → 分配给线程池中的工作线程 → 并发处理多个请求
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
import asyncio
import time
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
# 异步 endpoint: 模拟并发 I/O 操作
@app.get('/async')
async def async_endpoint():
start_time = time.time()
tasks = [asyncio.sleep(1) for _ in range(5)]
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
end_time = time.time()
return {"异步时长:", f'{end_time - start_time: .2f}s'}
# 同步 endpoint: 模拟并发 I/O 操作
@app.get('/sync')
def sync_endpoint():
start_time = time.time()
for _ in range(5):
time.sleep(1)
end_time = time.time()
return {"同步时长:", f'{end_time - start_time: .2f}s'}
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run('10测试异步:app', host='127.0.0.1', port=8003,
reload=True)FastAPI文件上传
安装异步文件处理模块
cmd
pip install aiofiles==24.1.0
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, File, UploadFile
import aiofiles
import os
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
# 小文件 btyes 类型 btyes 内容直接加载到内存
@app.post('/upload_bytes/')
def upload_bytes(file: bytes = File(...)):
# 判断是否存在文件夹
if not os.path.exists('files'):
os.mkdir('files')
with open('files/file.txt', 'wb') as f:
f.write(file)
return {'msg': '文件上传成功!'}
# 大文件 UploadFile 类型 (推荐)
@app.post('/upload_file/')
async def upload_file(file: UploadFile = File(...)):
if not os.path.exists('files'):
os.mkdir('files')
async with aiofiles.open(f'files/{file.filename}', 'wb') as f:
# 分块读取
chunk = await file.read(1024 * 1024)
while chunk:
# 循环写入
await f.write(chunk)
chunk = await file.read(1024 * 1024)
# 可以用海象符 简化上面四行代码
# while chunk := await file.read(1024 * 1024):
# await f.write(chunk)
return {'msg': '文件上传成功!'}
@app.post('/batch_upload/')
async def batch_upload(files: list[UploadFile] = File(...)):
"""
并发批量上传多个文件(更快)
"""
if not os.path.exists('files'):
os.mkdir('files')
async def save_single_file(file: UploadFile):
try:
file_path = f'files/{file.filename}'
async with aiofiles.open(file_path, 'wb') as f:
while chunk := await file.read(1024 * 1024):
await f.write(chunk)
result = {
"filename": file.filename,
"status": "success",
"size": file.size
}
except Exception as e:
result = {
"filename": file.filename,
"status": "error",
"error": str(e)
}
finally:
await file.close()
return result
# 并发处理所有文件上传
import asyncio
tasks = [save_single_file(file) for file in files]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
successful_uploads = len([r for r in results if r["status"] == "success"])
return {
"msg": f"并发批量上传完成!成功: {successful_uploads}/{len(files)}",
"results": results
}
# 表单和文件一起上传
@app.post('/submit-form/')
async def submit_form(uname: str = Form(...),
file: UploadFile = File(...)):
if not os.path.exists('files'):
os.mkdir('files')
old_file_path = f'files/{file.filename}'
new_file_path = f'files/{uname}-{file.filename}'
if os.path.exists(old_file_path): # 判断文件是否存在
os.remove(old_file_path)
async with aiofiles.open(new_file_path, 'wb') as f: # 创建文件
while chunk := await file.read(1024*1024): # 读取文件
await f.write(chunk)
return {"username": uname, "upload_msg": '文件上传成功!'}
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run("11FastAPI文件上传:app", host='127.0.0.1',
port=8003, reload=True)FastAPI请求对象Request
通过注入 Request 对象可获取完整的请求信息景:
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, File
import os
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get('/client-info/')
async def client_info(request: Request):
return {
"请求URL": request.url,
"请求方法": request.method,
"请求参数": request.query_params,
"请求IP": request.client.host,
"请求头": request.headers,
# 如果request的body中有内容 例如post请求上传了json数据
# 下面这些就能获取相关内容
# "请求体": await request.body(),
# "请求path_params": request.path_params,
# "请求JSON": await request.json(),
# "请求form": await request.form(),
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run("12FastAPI请求对象Request:app", host='127.0.0.1',
port=8003, reload=True)FastAPI响应数据
在企业级应用中,以下响应类型最为常见:
- JSON 响应:用于 RESTful API 的数据交互,占主导地位(如用户信息、订单、配置)。
- 列表响应:用于分页查询或批量数据返回(如商品列表、日志记录)
- 文件响应:用于报表导出、文件下载(如 CSV、PDF)。
- 字符串响应:用于健康检查或简单状态反馈。
- HTML 响应:用于管理后台或简单的 Web 页面。
- 重定向响应:用于认证流程或 URL 迁移。
- 流式响应:用于实时数据传输或大文件处理。
常见响应数据模型
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Query
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Union, Generic, TypeVar, Optional
import os
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get('/items/dict')
async def get_items_dict():
return {'name': 'iphone', 'price': 8000}
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float
description: str | None = None
@app.post('/items/model')
async def create_item():
return Item(name='iphone', price=8000, description='手机')
# 在路由处理函数中,使用response_model参数指定响应数据模型类
@app.post('/items/model2', response_model=Item)
async def create_item():
return Item(name='iphone', price=8000, description='手机')
# 定义泛型T
T = TypeVar('T')
class SuccessResponse(BaseModel, Generic[T]):
status: str = 'success'
data: T
class ErrorResponse(BaseModel):
status: str = 'error'
message: str
code: int
# response_model 表示返回的数据类型为SuccessResponse[Item]或者ErrorResponse
@app.post('/items/{item_id}', response_model=Union[SuccessResponse[Item], ErrorResponse])
async def create_item(item_id: int):
if item_id == 1:
item = Item(name='iphone', price=8000, description='手机')
# 这里的data对应着SuccessResponse[Item]的 data: T 中的data
return SuccessResponse[Item](data=item)
else:
return ErrorResponse(message='Item not found', code=404)
# 分页查询
@app.get('/items/pagination')
async def get_items_pagination(
page: int = Query(1, ge=1, description='当前页码'),
page_size: int = Query(10, ge=1, description='每页数量'),
category: Optional[str] = Query(None, description='商品类别'),
):
# 模拟数据库
DB = [
{'name': 'iphone', 'price': 8000, 'category': '手机'},
{'name': 'ipad', 'price': 6000, 'category': '手机'},
{'name': 'macbook', 'price': 12000, 'category': '电脑'},
{'name': 'macbook pro', 'price': 15000, 'category': '电脑'},
{'name': 'macbook air', 'price': 9000, 'category': '电脑'},
]
item_DB = DB
if category:
item_DB = [item for item in item_DB if item['category'] == category]
# 对数据进行分页
total = len(item_DB)
total_pages = (total + page_size - 1) // page_size
start = (page - 1) * page_size
end = min(start + page_size, total)
return {
'items': item_DB[start:end],
'category': category,
'total_pages': total_pages,
'page': page,
'page_size': page_size,
}
# 更好的封装
class Pagination(BaseModel):
category: Optional[str] = None
total_pages: int
page: int
page_size: int
class ListResponse(BaseModel):
status: str = 'success'
data: list[Item]
pagination: Pagination
@app.get('/items/pagination2')
async def get_items_pagination(
page: int = Query(1, ge=1, description='当前页码'),
page_size: int = Query(10, ge=1, description='每页数量'),
category: Optional[str] = Query(None, description='商品类别'),
):
# 模拟数据库
DB = [
{'name': 'iphone', 'price': 8000, 'category': '手机'},
{'name': 'ipad', 'price': 6000, 'category': '手机'},
{'name': 'macbook', 'price': 12000, 'category': '电脑'},
{'name': 'macbook pro', 'price': 15000, 'category': '电脑'},
{'name': 'macbook air', 'price': 9000, 'category': '电脑'},
]
item_DB = DB
if category:
item_DB = [item for item in item_DB if item['category'] == category]
# 对数据进行分页
total = len(item_DB)
total_pages = (total + page_size - 1) // page_size
start = (page - 1) * page_size
end = min(start + page_size, total)
return ListResponse(
data=item_DB[start:end],
pagination=Pagination(
category=category,
total_pages=total_pages,
page=page,
page_size=page_size,
)
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run("13FastAPI响应类型:app", host='127.0.0.1',
port=8003, reload=True)FastAPI响应文件
文件响应是指 API 在响应客户端请求时,返回一个文件内容的 HTTP 响应,通常包含文件的二进制数据或文本数据。
文件响应的关键特点:
- 内容类型:通过 Content-Type 头指定文件的 MIME 类型,如 application/pdf(PDF 文件)、text/csv(CSV 文件)、application/vnd.ms-excel(Excel 文件)。
- 文件内容:响应的 body 包含文件的实际数据,可能是二进制(如 PDF、图片)或文本(如 CSV、JSON 文件)
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Query
from fastapi.responses import Response, FileResponse, StreamingResponse
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Union, Generic, TypeVar, Optional
import os
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get('/download_file')
async def get_custom_file():
info = b'File Content'
return Response(content=info,
# 'text/plain' 表示返回的是纯文本
media_type='text/plain',
# attachment 表示立即下载
headers={'Content-Disposition': 'attachment; filename="file.txt"'})
@app.get('/download_pdf')
async def get_custom_pdf():
path = './files/file.pdf'
return FileResponse(
path,
# application/pdf 表示返回的是pdf文件
media_type='application/pdf',
headers={'Content-Disposition': 'attachment; filename="file.pdf"'}
)
# 流式响应
@app.get('/download_mp4')
async def get_custom_mp4():
path = './files/file.mp4'
def generate_chunks(file_path: str, chunk_size: int = 1024 * 1024):
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
while chunk := f.read(chunk_size):
yield chunk
# streaming 响应 本身就处理了异步 generate_chunks不需要写成异步函数
return StreamingResponse(
generate_chunks(path),
media_type='video/mp4',
headers={'Content-Disposition': 'attachment; filename="file.mp4"'}
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run("14FastAPI文件响应:app", host='127.0.0.1',
port=8003, reload=True)FastAPI其他响应对象
- 字符串响应
- 重定向
- HTML 响应
- 静态文件
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse, RedirectResponse
from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
app = FastAPI(debug=True)
@app.get('/get_string')
def get_string():
# 这样访问会返回字符串
return '<html><h1>hello world</h1></html>'
@app.get('/get_html', response_class=HTMLResponse)
def get_html():
# 这样访问会返回HTML 因为response_class定义了响应类型
return '<html><h1>hello world</h1></html>'
@app.get('/get_json')
def get_json(message: str):
return {'message': message}
@app.get('/redirect1')
def get_redirect1(message: str):
# 301 永久重定向
return RedirectResponse(url=f'/get_json?message={message}', status_code=301)
# 挂载静态资源 内容放在files目录下 直接访问 /static/pic.png 就可以访问图片
app.mount('/static', StaticFiles(directory='files'), name='static')
# 访问静态网页 内容放在templates目录下 直接访问 /html/index.html 访问html文件
app.mount('/html', StaticFiles(directory='templates', html=True), name='html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run("15FastAPI其他响应对象:app", host='127.0.0.1',
port=8003, reload=True)