
React Native for OpenHarmony 实战:AccessibilityInfo 无障碍信息详解
摘要
本文深入解析React Native的AccessibilityInfo API在OpenHarmony平台上的应用与适配。作为无障碍开发的关键工具,AccessibilityInfo帮助开发者构建更包容的应用体验。文章详细讲解了API原理、OpenHarmony平台适配要点,提供7个可运行的实战代码示例,涵盖基础用法、事件监听、动态UI调整等场景,并通过架构图与对比表格揭示跨平台差异。无论你是React Native老手还是OpenHarmony新手,都能从中获取实用的无障碍开发技巧,打造真正包容的跨平台应用。🔥
引言
在当今移动应用开发中,无障碍设计早已不再是"锦上添花",而是成为衡量应用质量的重要标准。根据世界卫生组织数据,全球约有15%的人口面临某种形式的残疾,这意味着每7个用户中就有1人可能需要无障碍功能的支持。作为React Native开发者,我们有责任确保应用能被更广泛的用户群体使用。
OpenHarmony作为新兴的国产操作系统,其无障碍服务框架与Android有一定相似性,但也存在关键差异。当我们将React Native应用迁移到OpenHarmony平台时,无障碍功能往往成为容易被忽视的"隐形坑"。我在为某政务类应用做OpenHarmony适配时,就曾因无障碍支持不完善导致应用无法通过政府验收,教训深刻。
本文将聚焦React Native的AccessibilityInfo API,深入探讨其在OpenHarmony平台上的实现原理、适配要点和实战技巧。通过本文,你将掌握:
- AccessibilityInfo的核心工作原理和应用场景
- OpenHarmony平台特有的无障碍适配挑战
- 可直接复用的无障碍开发代码模式
- 避免常见陷阱的实用建议
无论你是为了满足合规要求,还是真心希望打造更包容的应用体验,这篇深度解析都将为你提供清晰的实践路径。
AccessibilityInfo 组件介绍
什么是 AccessibilityInfo
AccessibilityInfo 是 React Native 提供的一个系统级 API,用于查询和监听设备的无障碍服务状态。它不属于 UI 组件,而是一个功能性的工具模块,帮助开发者了解当前设备的无障碍环境,并据此调整应用行为。
在无障碍开发中,这个 API 扮演着"环境感知器"的角色。它让我们能够:
- 检测屏幕阅读器(如TalkBack、VoiceOver)是否启用
- 查询无障碍功能的详细状态
- 监听无障碍设置的动态变化
- 为不同能力的用户提供定制化体验
技术原理
AccessibilityInfo 的工作原理基于原生平台的无障碍服务框架。在 OpenHarmony 上,其实现依赖于 AccessibilityAbility 服务,通过 React Native 的原生模块桥接机制与 JavaScript 层通信。
调用
返回状态
传递数据
事件通知
触发回调
JavaScript 层
AccessibilityInfo API
React Native 桥接层
OpenHarmony 原生模块
AccessibilityAbility 服务
如上图所示,当 JavaScript 代码调用 AccessibilityInfo API 时,请求会通过 React Native 桥接层传递到 OpenHarmony 原生模块,后者与系统级的 AccessibilityAbility 服务交互,最终将无障碍状态信息返回给 JavaScript 层。
核心 API 方法
AccessibilityInfo 提供了以下关键方法:
| 方法 | 描述 | OpenHarmony 支持情况 |
|---|---|---|
addEventListener(eventName, handler) |
监听无障碍状态变化事件 | ✅ 完全支持 |
isBoldTextEnabled() |
检测是否启用粗体文本 | ⚠️ 部分支持 |
isGrayscaleEnabled() |
检测是否启用灰度模式 | ❌ 不支持 |
invertColors() |
检测是否启用颜色反转 | ❌ 不支持 |
isReduceMotionEnabled() |
检测是否减少动画 | ✅ 完全支持 |
isReduceTransparencyEnabled() |
检测是否减少透明度 | ❌ 不支持 |
isScreenReaderEnabled() |
检测屏幕阅读器是否启用 | ✅ 完全支持 |
announceForAccessibility(announcement) |
向屏幕阅读器发送通知 | ✅ 完全支持 |
setAccessibilityFocus(reactTag) |
设置无障碍焦点 | ✅ 完全支持 |
💡 注意:OpenHarmony 对无障碍API的支持与Android存在差异,上表中标注"部分支持"或"不支持"的方法在实际开发中需要特别处理。
应用场景
AccessibilityInfo 在实际开发中有多种关键应用场景:
- 动态调整UI复杂度:当检测到屏幕阅读器启用时,简化界面元素,避免视觉干扰
- 提供替代导航方式:为视障用户提供额外的导航提示和操作方式
- 自定义无障碍反馈:在关键操作后提供语音反馈,确认操作结果
- 性能优化:当无障碍功能启用时,调整动画和过渡效果,提高可访问性
- 合规性检查:确保应用满足无障碍法规要求(如WCAG 2.1)
在政务、金融等对无障碍要求严格的领域,合理使用AccessibilityInfo不仅是技术选择,更是合规必需。
React Native与OpenHarmony平台适配要点
OpenHarmony无障碍服务架构
OpenHarmony 的无障碍服务基于其分布式能力设计,与Android的无障碍服务框架有相似之处,但也有显著差异。理解这些差异是成功适配的关键。
React Native应用
React Native OpenHarmony适配层
OpenHarmony JS UI框架
OpenHarmony系统服务
AccessibilityAbility服务
设备无障碍服务
屏幕阅读器
辅助技术设备
如上图所示,React Native应用通过适配层与OpenHarmony的JS UI框架交互,最终调用系统级的AccessibilityAbility服务。与Android相比,OpenHarmony的无障碍服务更加模块化,支持跨设备协同,但API覆盖范围相对有限。
适配过程中的关键挑战
在将React Native应用迁移到OpenHarmony平台时,AccessibilityInfo的适配面临以下挑战:
- API覆盖差异:OpenHarmony对无障碍API的支持不如Android全面
- 事件机制不同:事件触发时机和频率存在差异
- 焦点管理机制:无障碍焦点的处理逻辑有所不同
- 屏幕阅读器行为:不同屏幕阅读器的实现细节存在差异
- 性能考量:在资源受限设备上需要优化无障碍功能的开销
适配要点详解
1. 事件监听的稳定性
在OpenHarmony上,无障碍事件的触发可能不如Android稳定,需要特别注意:
- 增加事件去重机制,避免短时间内多次触发
- 实现事件监听的容错处理,防止因系统服务异常导致应用崩溃
- 在组件卸载时务必移除事件监听,避免内存泄漏
javascript
// OpenHarmony平台事件监听最佳实践
useEffect(() => {
let isMounted = true;
let lastEventTime = 0;
const EVENT_THROTTLE = 500; // 500ms内不重复处理相同事件
const handleScreenReaderChange = (isEnabled) => {
const now = Date.now();
if (now - lastEventTime < EVENT_THROTTLE) return;
lastEventTime = now;
if (isMounted) {
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
// 根据无障碍状态调整UI
updateUIForAccessibility(isEnabled);
}
};
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener(
'screenReaderChanged',
handleScreenReaderChange
);
// 初始状态查询
AccessibilityInfo.isScreenReaderEnabled().then(isEnabled => {
if (isMounted) {
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
updateUIForAccessibility(isEnabled);
}
});
return () => {
isMounted = false;
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener(
'screenReaderChanged',
handleScreenReaderChange
);
};
}, []);OpenHarmony适配要点:
- 添加了事件节流机制,防止高频触发
- 使用
isMounted标志避免内存泄漏 - 初始状态查询与事件监听结合使用
- 在组件卸载时务必移除事件监听
2. 焦点管理的特殊处理
OpenHarmony对无障碍焦点的管理与Android有所不同,需要特别注意:
- 在OpenHarmony上,
setAccessibilityFocus可能不会立即生效 - 需要等待UI渲染完成后再设置焦点
- 某些复杂布局可能需要多次尝试设置焦点
javascript
// OpenHarmony平台焦点管理最佳实践
const setFocusWithRetry = (reactTag, maxAttempts = 3, delay = 100) => {
let attempts = 0;
const tryFocus = () => {
if (attempts >= maxAttempts) return;
AccessibilityInfo.setAccessibilityFocus(reactTag);
attempts++;
// 检查焦点是否成功设置(实际项目中需要实现检查逻辑)
if (!isFocusSuccessful(reactTag)) {
setTimeout(tryFocus, delay * attempts);
}
};
tryFocus();
};
// 在组件渲染后设置焦点
useEffect(() => {
if (shouldSetFocus && elementRef.current) {
const reactTag = findNodeHandle(elementRef.current);
if (reactTag) {
// 确保UI渲染完成
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
setFocusWithRetry(reactTag);
});
}
}
}, [shouldSetFocus]);OpenHarmony适配要点:
- 实现了带重试机制的焦点设置
- 使用
requestAnimationFrame确保在UI渲染后设置焦点 - 适当增加重试间隔,避免资源争用
- 需要实现
isFocusSuccessful方法来验证焦点设置结果
3. 屏幕阅读器通知的优化
在OpenHarmony上,announceForAccessibility的实现需要特别注意:
- 通知内容长度限制更严格
- 连续通知之间需要足够的时间间隔
- 需要处理通知队列,避免消息丢失
javascript
// OpenHarmony平台通知管理优化
class AnnouncementQueue {
constructor() {
this.queue = [];
this.isProcessing = false;
this.ANNOUNCEMENT_DELAY = 1000; // 1秒间隔
}
enqueue(announcement) {
this.queue.push(announcement);
this.processQueue();
}
processQueue() {
if (this.isProcessing || this.queue.length === 0) return;
this.isProcessing = true;
const announcement = this.queue.shift();
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility(announcement);
setTimeout(() => {
this.isProcessing = false;
this.processQueue();
}, this.ANNOUNCEMENT_DELAY);
}
}
// 使用示例
const announcementQueue = new AnnouncementQueue();
// 在需要通知的地方调用
announcementQueue.enqueue('登录成功,欢迎回来!');OpenHarmony适配要点:
- 实现了通知队列管理,避免连续通知丢失
- 设置了合理的时间间隔,符合OpenHarmony系统要求
- 防止通知过于频繁导致用户体验下降
- 保证关键通知不会被覆盖
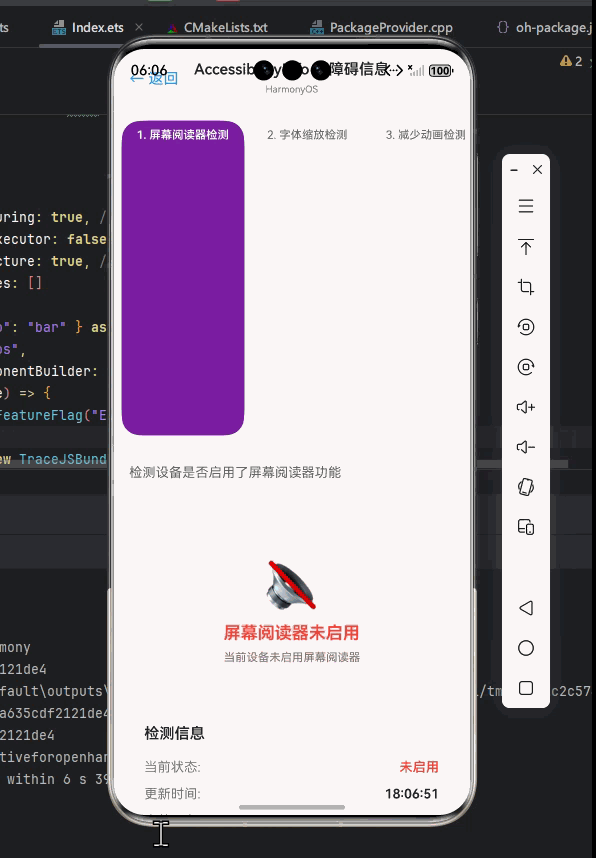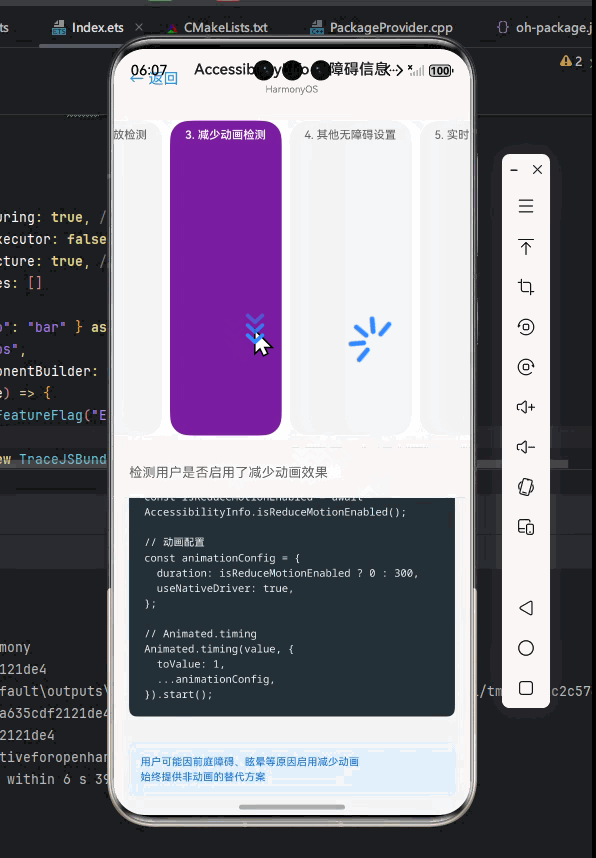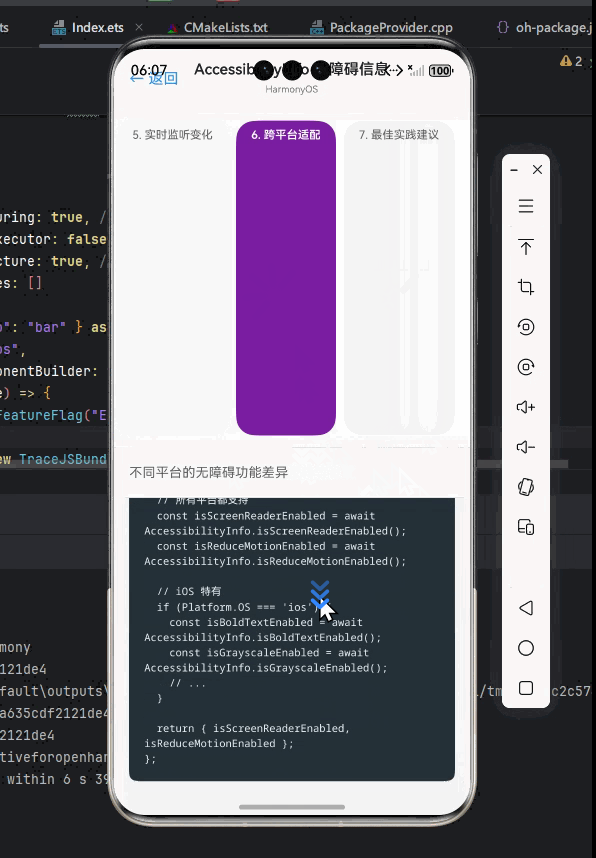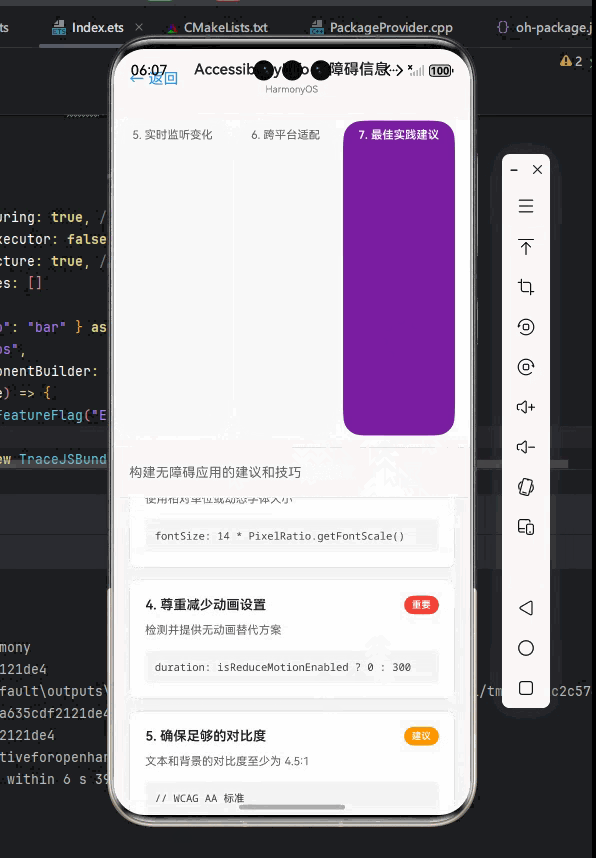
AccessibilityInfo基础用法实战
检测屏幕阅读器状态
最基本的用法是检测屏幕阅读器是否启用,这可以帮助我们调整应用的交互方式。
javascript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, AccessibilityInfo } from 'react-native';
const ScreenReaderDetector = () => {
const [screenReaderEnabled, setScreenReaderEnabled] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
const updateScreenReaderState = async () => {
try {
const isEnabled = await AccessibilityInfo.isScreenReaderEnabled();
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error checking screen reader status:', error);
}
};
updateScreenReaderState();
const screenReaderListener = (isEnabled) => {
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
};
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
return () => {
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
};
}, []);
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.title}>屏幕阅读器状态检测</Text>
<View style={styles.statusBox}>
<Text style={styles.statusText}>
{screenReaderEnabled
? '✅ 屏幕阅读器已启用 - 应用已优化无障碍体验'
: 'ℹ️ 屏幕阅读器未启用 - 默认体验模式'}
</Text>
</View>
<Text style={styles.description}>
当屏幕阅读器启用时,应用会自动调整布局和交互方式,
为视障用户提供更好的使用体验。
</Text>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
},
statusBox: {
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
backgroundColor: '#f0f0f0',
marginBottom: 20,
},
statusText: {
fontSize: 16,
lineHeight: 24,
},
description: {
fontSize: 16,
lineHeight: 24,
color: '#666',
},
});
export default ScreenReaderDetector;代码解析:
- 使用
useState管理屏幕阅读器状态 useEffect中同时进行初始状态查询和事件监听- 处理了可能的异常情况
- 提供了清晰的UI反馈
OpenHarmony适配要点:
- 在OpenHarmony上,
isScreenReaderEnabled的初始查询可能比Android慢,因此需要考虑加载状态 - 事件监听必须在组件卸载时正确移除,否则可能导致内存泄漏
- 某些OpenHarmony设备可能需要更长的响应时间,建议添加超时处理
动画减损模式检测
减少动画对于某些用户(如癫痫患者)至关重要,我们可以根据系统设置调整应用行为。
javascript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, TouchableOpacity, AccessibilityInfo, Animated } from 'react-native';
const ReduceMotionDemo = () => {
const [reduceMotionEnabled, setReduceMotionEnabled] = useState(false);
const animation = new Animated.Value(0);
useEffect(() => {
const updateReduceMotionState = async () => {
try {
const isEnabled = await AccessibilityInfo.isReduceMotionEnabled();
setReduceMotionEnabled(isEnabled);
if (!isEnabled) {
startAnimation();
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error checking reduce motion status:', error);
}
};
updateReduceMotionState();
const reduceMotionListener = (isEnabled) => {
setReduceMotionEnabled(isEnabled);
if (!isEnabled) {
startAnimation();
} else {
animation.stopAnimation();
animation.setValue(0);
}
};
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener('reduceMotionChanged', reduceMotionListener);
return () => {
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener('reduceMotionChanged', reduceMotionListener);
animation.stopAnimation();
};
}, []);
const startAnimation = () => {
animation.setValue(0);
Animated.loop(
Animated.timing(animation, {
toValue: 1,
duration: 1000,
useNativeDriver: true,
})
).start();
};
const animatedStyle = {
transform: [{
translateX: animation.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 1],
outputRange: [0, 100]
})
}]
};
const toggleAnimation = () => {
if (reduceMotionEnabled) return;
animation.stopAnimation();
startAnimation();
};
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.title}>动画减损模式演示</Text>
<View style={styles.statusBox}>
<Text style={styles.statusText}>
{reduceMotionEnabled
? '✅ 已启用动画减损 - 动画已停用'
: 'ℹ️ 动画减损未启用 - 动画效果可用'}
</Text>
</View>
<Text style={styles.description}>
{reduceMotionEnabled
? '系统已设置减少动画效果,应用已停用所有非必要的动画。'
: '系统允许使用动画,应用提供流畅的视觉过渡效果。'}
</Text>
<View style={styles.demoArea}>
<Animated.View
style={[
styles.animatedBox,
animatedStyle,
reduceMotionEnabled && styles.noAnimation
]}
/>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.button}
onPress={toggleAnimation}
disabled={reduceMotionEnabled}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>
{reduceMotionEnabled ? '动画已禁用' : '重新启动动画'}
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
},
statusBox: {
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
backgroundColor: '#f0f0f0',
marginBottom: 20,
},
statusText: {
fontSize: 16,
lineHeight: 24,
},
description: {
fontSize: 16,
lineHeight: 24,
color: '#666',
marginBottom: 20,
},
demoArea: {
alignItems: 'center',
marginTop: 20,
},
animatedBox: {
width: 50,
height: 50,
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
marginBottom: 20,
},
noAnimation: {
transform: [{ translateX: 0 }],
},
button: {
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
padding: 12,
borderRadius: 6,
disabled: reduceMotionEnabled && { opacity: 0.5 },
},
buttonText: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
textAlign: 'center',
},
});
export default ReduceMotionDemo;代码解析:
- 检测并响应
reduceMotionChanged事件 - 根据系统设置动态调整动画行为
- 提供了用户手动控制的选项(在允许的情况下)
- 使用Animated API实现流畅的动画效果
OpenHarmony适配要点:
- OpenHarmony上
isReduceMotionEnabled的实现可能不如Android完善,建议添加默认值处理 - 在OpenHarmony设备上,动画性能可能较弱,应避免复杂动画
useNativeDriver在OpenHarmony上的支持程度有限,某些情况下可能需要回退到JS动画- 某些OpenHarmony设备可能不支持
reduceMotionChanged事件,需要实现轮询机制作为备选
自定义无障碍通知
当需要向屏幕阅读器用户发送重要信息时,announceForAccessibility非常有用。
javascript
import React, { useRef, useState } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, TextInput, TouchableOpacity, AccessibilityInfo } from 'react-native';
const AnnouncementDemo = () => {
const [announcement, setAnnouncement] = useState('');
const inputRef = useRef(null);
const [lastAnnouncement, setLastAnnouncement] = useState('');
const sendAnnouncement = () => {
if (!announcement.trim()) return;
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility(announcement);
setLastAnnouncement(announcement);
setAnnouncement('');
// 自动聚焦回输入框,方便连续输入
setTimeout(() => {
inputRef.current?.focus();
}, 100);
};
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.title}>无障碍通知演示</Text>
<View style={styles.instructions}>
<Text style={styles.instructionText}>
1. 输入您想向屏幕阅读器用户发送的消息
</Text>
<Text style={styles.instructionText}>
2. 点击"发送通知"按钮
</Text>
<Text style={styles.instructionText}>
3. 消息将通过屏幕阅读器朗读
</Text>
</View>
<TextInput
ref={inputRef}
style={styles.input}
value={announcement}
onChangeText={setAnnouncement}
placeholder="输入要朗读的消息..."
onSubmitEditing={sendAnnouncement}
accessibilityLabel="输入要发送给屏幕阅读器的消息"
/>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.button}
onPress={sendAnnouncement}
disabled={!announcement.trim()}
accessibilityLabel="发送无障碍通知"
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>发送通知</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
{lastAnnouncement ? (
<View style={styles.announcementHistory}>
<Text style={styles.historyTitle}>最近发送的通知:</Text>
<Text style={styles.historyContent}>{lastAnnouncement}</Text>
</View>
) : null}
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
},
instructions: {
backgroundColor: '#f8f9fa',
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
marginBottom: 20,
},
instructionText: {
fontSize: 16,
lineHeight: 24,
marginBottom: 8,
},
input: {
height: 50,
borderColor: '#ddd',
borderWidth: 1,
borderRadius: 8,
paddingHorizontal: 15,
marginBottom: 15,
fontSize: 16,
},
button: {
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
marginBottom: 20,
opacity: announcement.trim() ? 1 : 0.5,
},
buttonText: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 16,
textAlign: 'center',
},
announcementHistory: {
marginTop: 20,
borderTopWidth: 1,
borderTopColor: '#eee',
paddingTop: 15,
},
historyTitle: {
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 8,
},
historyContent: {
fontStyle: 'italic',
color: '#666',
},
});
export default AnnouncementDemo;代码解析:
- 创建了简单的UI用于输入和发送无障碍通知
- 使用
announceForAccessibility发送消息给屏幕阅读器 - 记录最近发送的通知以便验证
- 添加了适当的无障碍标签
OpenHarmony适配要点:
- OpenHarmony上通知的延迟可能比Android长,需管理用户期望
- 消息长度限制更严格(通常不超过500字符),需要做截断处理
- 某些OpenHarmony设备可能需要额外权限才能使用此功能
- 通知内容应避免包含特殊字符,以防屏幕阅读器解析错误
- 在发送通知后,建议短暂聚焦回输入框,帮助用户继续操作
AccessibilityInfo进阶用法
动态UI调整策略
当检测到无障碍功能启用时,我们可以动态调整UI以提供更好的体验。
javascript
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, ScrollView, AccessibilityInfo, TouchableOpacity } from 'react-native';
// 模拟的用户数据
const userData = [
{ id: '1', name: '张三', role: '管理员', email: 'zhangsan@example.com', phone: '13800138000' },
{ id: '2', name: '李四', role: '编辑', email: 'lisi@example.com', phone: '13900139000' },
{ id: '3', name: '王五', role: '访客', email: 'wangwu@example.com', phone: '13700137000' },
{ id: '4', name: '赵六', role: '管理员', email: 'zhaoliu@example.com', phone: '13600136000' },
];
const DynamicUIAdjustment = () => {
const [screenReaderEnabled, setScreenReaderEnabled] = useState(false);
const [reduceMotionEnabled, setReduceMotionEnabled] = useState(false);
const [compactMode, setCompactMode] = useState(false);
const containerRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const initAccessibility = async () => {
try {
const [isScreenReader, isReduceMotion] = await Promise.all([
AccessibilityInfo.isScreenReaderEnabled(),
AccessibilityInfo.isReduceMotionEnabled()
]);
setScreenReaderEnabled(isScreenReader);
setReduceMotionEnabled(isReduceMotion);
// 根据无障碍状态自动调整紧凑模式
if (isScreenReader || isReduceMotion) {
setCompactMode(true);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error initializing accessibility:', error);
}
};
initAccessibility();
const screenReaderListener = (isEnabled) => {
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
if (isEnabled) setCompactMode(true);
};
const reduceMotionListener = (isEnabled) => {
setReduceMotionEnabled(isEnabled);
if (isEnabled) setCompactMode(true);
};
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener('reduceMotionChanged', reduceMotionListener);
return () => {
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener('reduceMotionChanged', reduceMotionListener);
};
}, []);
const toggleCompactMode = () => {
setCompactMode(!compactMode);
// 如果关闭紧凑模式且无障碍功能未启用,发送通知
if (!compactMode && !screenReaderEnabled && !reduceMotionEnabled) {
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility('已切换到标准视图模式');
}
};
const renderUserItem = (user) => {
const ItemComponent = compactMode ? CompactUserItem : StandardUserItem;
return <ItemComponent key={user.id} user={user} />;
};
return (
<View style={styles.container} ref={containerRef}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.title}>用户管理</Text>
<TouchableOpacity
style={[
styles.toggleButton,
compactMode && styles.toggleButtonActive
]}
onPress={toggleCompactMode}
accessibilityState={{ selected: compactMode }}
accessibilityLabel={compactMode ? "紧凑模式已启用" : "标准模式已启用"}
>
<Text style={styles.toggleButtonText}>
{compactMode ? '紧凑模式' : '标准模式'}
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
<View style={styles.statusBar}>
<Text style={styles.statusText}>
{screenReaderEnabled && '🗣️ 屏幕阅读器启用 '}
{reduceMotionEnabled && '🎬 动画减损启用'}
{!screenReaderEnabled && !reduceMotionEnabled && '📱 标准模式'}
</Text>
</View>
<ScrollView style={styles.listContainer}>
{userData.map(renderUserItem)}
</ScrollView>
<View style={styles.footer}>
<Text style={styles.footerText}>
{compactMode
? '紧凑模式:简化布局,提高可读性'
: '标准模式:完整功能,丰富视觉'}
</Text>
</View>
</View>
);
};
const StandardUserItem = ({ user }) => (
<View style={styles.userItem}>
<View style={styles.avatar}>
<Text style={styles.avatarText}>{user.name[0]}</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.userInfo}>
<Text style={styles.userName}>{user.name}</Text>
<Text style={styles.userRole}>{user.role}</Text>
<View style={styles.contactInfo}>
<Text style={styles.contactText}>📧 {user.email}</Text>
<Text style={styles.contactText}>📱 {user.phone}</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
);
const CompactUserItem = ({ user }) => (
<View style={[styles.userItem, styles.compactItem]}>
<Text style={styles.compactName}>{user.name}</Text>
<Text style={styles.compactDetail}>职位: {user.role}</Text>
<Text style={styles.compactDetail}>邮箱: {user.email}</Text>
<Text style={styles.compactDetail}>电话: {user.phone}</Text>
</View>
);
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
},
header: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
alignItems: 'center',
padding: 15,
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#eee',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
toggleButton: {
backgroundColor: '#f0f0f0',
paddingVertical: 6,
paddingHorizontal: 12,
borderRadius: 20,
},
toggleButtonActive: {
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
},
toggleButtonText: {
color: '#333',
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
statusBar: {
padding: 10,
backgroundColor: '#f8f9fa',
},
statusText: {
textAlign: 'center',
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
},
listContainer: {
flex: 1,
padding: 10,
},
userItem: {
flexDirection: 'row',
padding: 15,
marginBottom: 10,
backgroundColor: '#f8f9fa',
borderRadius: 8,
alignItems: 'center',
},
compactItem: {
padding: 12,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
borderWidth: 1,
borderColor: '#eee',
},
avatar: {
width: 50,
height: 50,
borderRadius: 25,
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
marginRight: 15,
},
avatarText: {
color: 'white',
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
userInfo: {
flex: 1,
},
userName: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 5,
},
userRole: {
fontSize: 16,
color: '#4287f5',
marginBottom: 8,
},
contactInfo: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
},
contactText: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
},
compactName: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 5,
},
compactDetail: {
fontSize: 16,
marginBottom: 3,
color: '#333',
},
footer: {
padding: 15,
borderTopWidth: 1,
borderTopColor: '#eee',
backgroundColor: '#f8f9fa',
},
footerText: {
textAlign: 'center',
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
fontStyle: 'italic',
},
});
export default DynamicUIAdjustment;代码解析:
- 同时监听屏幕阅读器和动画减损状态
- 根据无障碍状态自动启用紧凑模式
- 提供手动切换模式的选项
- 为不同模式设计了不同的UI组件
- 添加了适当的无障碍标签和状态提示
OpenHarmony适配要点:
- OpenHarmony上UI重绘可能比Android慢,应避免在事件回调中直接修改大量状态
- 紧凑模式的判断逻辑需要考虑OpenHarmony特有的无障碍设置
- 在OpenHarmony设备上,触摸目标的最小尺寸要求可能不同,需确保UI元素足够大
- 使用
accessibilityState正确标记切换按钮的状态,帮助屏幕阅读器理解 - 某些OpenHarmony设备可能需要额外处理焦点顺序,确保紧凑模式下导航逻辑合理
无障碍焦点管理实战
精确控制无障碍焦点对于复杂界面至关重要,特别是在表单验证等场景。
javascript
import React, { useState, useRef, useEffect } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, TextInput, TouchableOpacity, AccessibilityInfo, findNodeHandle } from 'react-native';
const FormWithAccessibilityFocus = () => {
const [formData, setFormData] = useState({
name: '',
email: '',
phone: ''
});
const [errors, setErrors] = useState({});
const [submitStatus, setSubmitStatus] = useState(null);
// 创建ref用于访问各个输入字段
const nameInputRef = useRef(null);
const emailInputRef = useRef(null);
const phoneInputRef = useRef(null);
const errorSummaryRef = useRef(null);
const formContainerRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
// 初始设置焦点到第一个输入框
const setInitialFocus = () => {
if (nameInputRef.current) {
const reactTag = findNodeHandle(nameInputRef.current);
if (reactTag) {
AccessibilityInfo.setAccessibilityFocus(reactTag);
}
}
};
// 等待UI渲染完成
setTimeout(setInitialFocus, 300);
// 清理函数
return () => {
// 可选:重置焦点到安全位置
};
}, []);
const validateForm = () => {
const newErrors = {};
if (!formData.name.trim()) {
newErrors.name = '请输入您的姓名';
}
if (!formData.email.trim()) {
newErrors.email = '请输入电子邮箱';
} else if (!/^\S+@\S+\.\S+$/.test(formData.email)) {
newErrors.email = '请输入有效的电子邮箱地址';
}
if (!formData.phone.trim()) {
newErrors.phone = '请输入联系电话';
} else if (!/^\d{11}$/.test(formData.phone.replace(/\D/g, ''))) {
newErrors.phone = '请输入11位有效的手机号码';
}
setErrors(newErrors);
if (Object.keys(newErrors).length > 0) {
// 有错误时,聚焦到错误摘要
if (errorSummaryRef.current) {
const reactTag = findNodeHandle(errorSummaryRef.current);
if (reactTag) {
AccessibilityInfo.setAccessibilityFocus(reactTag);
// 同时发送屏幕阅读器通知
const errorCount = Object.keys(newErrors).length;
const errorSummary = `表单验证失败,发现${errorCount}处错误,请修正后重新提交。`;
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility(errorSummary);
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
};
const handleSubmit = () => {
if (validateForm()) {
// 模拟提交成功
setSubmitStatus('success');
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility('表单提交成功!');
// 重置表单
setTimeout(() => {
setFormData({ name: '', email: '', phone: '' });
setErrors({});
setSubmitStatus(null);
// 重置焦点到第一个输入框
if (nameInputRef.current) {
const reactTag = findNodeHandle(nameInputRef.current);
if (reactTag) {
AccessibilityInfo.setAccessibilityFocus(reactTag);
}
}
}, 2000);
} else {
setSubmitStatus('error');
}
};
const handleInputChange = (field, value) => {
setFormData(prev => ({ ...prev, [field]: value }));
// 如果已有错误,输入时清除对应错误
if (errors[field]) {
setErrors(prev => {
const newErrors = { ...prev };
delete newErrors[field];
return newErrors;
});
}
};
return (
<View style={styles.container} ref={formContainerRef}>
<Text style={styles.title}>无障碍表单示例</Text>
{submitStatus === 'success' && (
<View style={[styles.statusMessage, styles.successMessage]}>
<Text style={styles.statusText}>✅ 表单提交成功!</Text>
</View>
)}
{submitStatus === 'error' && Object.keys(errors).length > 0 && (
<View style={[styles.statusMessage, styles.errorMessage]} ref={errorSummaryRef}>
<Text style={styles.statusText}>
❌ 表单验证失败,发现{Object.keys(errors).length}处错误:
</Text>
{Object.values(errors).map((error, index) => (
<Text key={index} style={styles.errorItem}>
• {error}
</Text>
))}
</View>
)}
<View style={styles.formGroup}>
<Text style={styles.label}>姓名<Text style={styles.required}>*</Text></Text>
<TextInput
ref={nameInputRef}
style={[styles.input, errors.name && styles.inputError]}
value={formData.name}
onChangeText={(text) => handleInputChange('name', text)}
placeholder="请输入您的姓名"
accessibilityLabel="姓名输入框"
accessibilityHint="必填项,请输入您的真实姓名"
accessibilityInvalid={!!errors.name}
accessibilityErrorMessage={errors.name}
/>
{errors.name && <Text style={styles.errorText}>{errors.name}</Text>}
</View>
<View style={styles.formGroup}>
<Text style={styles.label}>电子邮箱<Text style={styles.required}>*</Text></Text>
<TextInput
ref={emailInputRef}
style={[styles.input, errors.email && styles.inputError]}
value={formData.email}
onChangeText={(text) => handleInputChange('email', text)}
placeholder="example@email.com"
keyboardType="email-address"
autoCapitalize="none"
accessibilityLabel="电子邮箱输入框"
accessibilityHint="必填项,请输入有效的电子邮箱地址"
accessibilityInvalid={!!errors.email}
accessibilityErrorMessage={errors.email}
/>
{errors.email && <Text style={styles.errorText}>{errors.email}</Text>}
</View>
<View style={styles.formGroup}>
<Text style={styles.label}>联系电话<Text style={styles.required}>*</Text></Text>
<TextInput
ref={phoneInputRef}
style={[styles.input, errors.phone && styles.inputError]}
value={formData.phone}
onChangeText={(text) => handleInputChange('phone', text)}
placeholder="请输入11位手机号码"
keyboardType="phone-pad"
accessibilityLabel="联系电话输入框"
accessibilityHint="必填项,请输入11位有效的手机号码"
accessibilityInvalid={!!errors.phone}
accessibilityErrorMessage={errors.phone}
/>
{errors.phone && <Text style={styles.errorText}>{errors.phone}</Text>}
</View>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.submitButton}
onPress={handleSubmit}
accessibilityLabel="提交表单"
accessibilityHint="验证并提交表单数据"
>
<Text style={styles.submitButtonText}>提交</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
},
statusMessage: {
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
marginBottom: 20,
},
successMessage: {
backgroundColor: '#d4edda',
borderColor: '#c3e6cb',
},
errorMessage: {
backgroundColor: '#f8d7da',
borderColor: '#f5c6cb',
},
statusText: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
errorItem: {
fontSize: 16,
marginLeft: 20,
marginTop: 5,
color: '#721c24',
},
formGroup: {
marginBottom: 20,
},
label: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 8,
},
required: {
color: '#dc3545',
},
input: {
height: 50,
borderColor: '#ddd',
borderWidth: 1,
borderRadius: 8,
paddingHorizontal: 15,
fontSize: 16,
},
inputError: {
borderColor: '#dc3545',
},
errorText: {
color: '#dc3545',
fontSize: 14,
marginTop: 5,
marginLeft: 5,
},
submitButton: {
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
alignItems: 'center',
},
submitButtonText: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 16,
},
});
export default FormWithAccessibilityFocus;代码解析:
- 使用
findNodeHandle获取组件的原生句柄 - 在表单验证失败时,将焦点设置到错误摘要区域
- 为每个输入字段添加了适当的无障碍属性
- 实现了表单提交后的焦点重置逻辑
- 使用
accessibilityInvalid和accessibilityErrorMessage提供更详细的错误信息
OpenHarmony适配要点:
- OpenHarmony上
setAccessibilityFocus可能需要更长的延迟时间才能生效,建议使用setTimeout并适当增加延迟 - 某些OpenHarmony设备可能不支持
accessibilityErrorMessage属性,需要通过其他方式提供错误信息 - 在设置焦点前,应确保目标组件已经渲染完成
- 错误摘要区域应设置
accessibilityLiveRegion为'polite'或'assertive',确保屏幕阅读器及时播报 - OpenHarmony上焦点移动可能比Android更"跳跃",建议在关键操作后添加短暂延迟,给用户留出理解时间
无障碍信息集成到复杂应用
在真实应用中,无障碍信息需要与其他功能深度集成。以下是一个集成到应用主题系统中的示例。
javascript
import React, { useState, useEffect, createContext, useContext } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, Switch, TouchableOpacity, AccessibilityInfo } from 'react-native';
// 创建无障碍上下文
const AccessibilityContext = createContext();
// 无障碍提供者组件
export const AccessibilityProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [screenReaderEnabled, setScreenReaderEnabled] = useState(false);
const [reduceMotionEnabled, setReduceMotionEnabled] = useState(false);
const [highContrastMode, setHighContrastMode] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
const initAccessibility = async () => {
try {
const [isScreenReader, isReduceMotion] = await Promise.all([
AccessibilityInfo.isScreenReaderEnabled(),
AccessibilityInfo.isReduceMotionEnabled()
]);
setScreenReaderEnabled(isScreenReader);
setReduceMotionEnabled(isReduceMotion);
// 检查高对比度模式(OpenHarmony上需要特殊处理)
checkHighContrastMode();
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error initializing accessibility:', error);
}
};
const screenReaderListener = (isEnabled) => {
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
};
const reduceMotionListener = (isEnabled) => {
setReduceMotionEnabled(isEnabled);
};
initAccessibility();
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener('reduceMotionChanged', reduceMotionListener);
return () => {
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener('reduceMotionChanged', reduceMotionListener);
};
}, []);
// OpenHarmony上检查高对比度模式的特殊方法
const checkHighContrastMode = () => {
// 在OpenHarmony上,可能需要通过其他方式检测高对比度模式
// 这里使用模拟实现,实际项目中可能需要原生模块支持
setTimeout(() => {
// 模拟检测结果 - 实际应用中应替换为真实检测逻辑
const isHighContrast = false; // 从系统设置获取
setHighContrastMode(isHighContrast);
}, 500);
};
// 获取适合无障碍需求的主题
const getAccessibilityTheme = () => {
const baseTheme = {
primary: '#4287f5',
background: '#fff',
text: '#333',
card: '#f8f9fa',
border: '#ddd',
error: '#dc3545',
};
if (highContrastMode) {
return {
...baseTheme,
background: '#000',
text: '#fff',
card: '#333',
border: '#666',
};
}
return baseTheme;
};
// 通知屏幕阅读器主题变化
const announceThemeChange = (themeName) => {
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility(`已切换到${themeName}主题`);
};
return (
<AccessibilityContext.Provider
value={{
screenReaderEnabled,
reduceMotionEnabled,
highContrastMode,
setHighContrastMode,
theme: getAccessibilityTheme(),
announceThemeChange,
}}
>
{children}
</AccessibilityContext.Provider>
);
};
// 自定义Hook,方便在组件中使用无障碍信息
export const useAccessibility = () => {
const context = useContext(AccessibilityContext);
if (!context) {
throw new Error('useAccessibility must be used within an AccessibilityProvider');
}
return context;
};
// 主题设置页面
const ThemeSettings = () => {
const {
theme,
highContrastMode,
setHighContrastMode,
announceThemeChange
} = useAccessibility();
const toggleHighContrast = () => {
const newMode = !highContrastMode;
setHighContrastMode(newMode);
// 通知屏幕阅读器
announceThemeChange(newMode ? '高对比度' : '标准');
};
return (
<View style={[styles.container, { backgroundColor: theme.background }]}>
<Text style={[styles.title, { color: theme.text }]}>主题设置</Text>
<View style={styles.settingItem}>
<View>
<Text style={[styles.settingLabel, { color: theme.text }]}>
高对比度模式
</Text>
<Text style={[styles.settingDescription, { color: theme.text }]}>
增强文本和背景的对比度,提高可读性
</Text>
</View>
<Switch
value={highContrastMode}
onValueChange={toggleHighContrast}
trackColor={{ false: theme.border, true: theme.primary }}
thumbColor={highContrastMode ? '#fff' : '#f4f3f4'}
/>
</View>
<View style={[styles.themePreview, { backgroundColor: theme.card, borderColor: theme.border }]}>
<Text style={[styles.previewText, { color: theme.text }]}>主题预览</Text>
<Text style={[styles.previewSubtext, { color: theme.text }]}>
{highContrastMode ? '高对比度主题已启用' : '标准主题'}
</Text>
<View style={[styles.previewButton, { backgroundColor: theme.primary }]}>
<Text style={styles.previewButtonText}>按钮示例</Text>
</View>
</View>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.resetButton}
onPress={() => {
setHighContrastMode(false);
announceThemeChange('标准');
}}
>
<Text style={[styles.resetButtonText, { color: theme.primary }]}>
重置为默认主题
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
);
};
// 应用设置页面
const AppSettings = () => {
const { screenReaderEnabled, reduceMotionEnabled } = useAccessibility();
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.title}>应用设置</Text>
<View style={styles.settingItem}>
<Text style={styles.settingLabel}>屏幕阅读器状态</Text>
<Text style={[
styles.settingValue,
screenReaderEnabled ? styles.enabled : styles.disabled
]}>
{screenReaderEnabled ? '已启用' : '未启用'}
</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.settingItem}>
<Text style={styles.settingLabel}>动画减损模式</Text>
<Text style={[
styles.settingValue,
reduceMotionEnabled ? styles.enabled : styles.disabled
]}>
{reduceMotionEnabled ? '已启用' : '未启用'}
</Text>
</View>
<ThemeSettings />
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
},
settingItem: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
alignItems: 'center',
paddingVertical: 15,
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#eee',
},
settingLabel: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: '500',
},
settingDescription: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
marginTop: 4,
},
settingValue: {
fontSize: 16,
},
enabled: {
color: '#28a745',
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
disabled: {
color: '#6c757d',
},
themePreview: {
marginTop: 20,
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
borderWidth: 1,
},
previewText: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 8,
},
previewSubtext: {
fontSize: 16,
marginBottom: 15,
},
previewButton: {
padding: 12,
borderRadius: 6,
alignItems: 'center',
},
previewButtonText: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
resetButton: {
marginTop: 20,
padding: 12,
borderRadius: 6,
alignItems: 'center',
},
resetButtonText: {
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 16,
},
});
// 在应用入口使用Provider
const App = () => {
return (
<AccessibilityProvider>
<AppSettings />
</AccessibilityProvider>
);
};
export default App;代码解析:
- 创建了
AccessibilityContext用于全局管理无障碍状态 - 实现了主题系统与无障碍设置的集成
- 提供了自定义Hook简化组件中的无障碍信息获取
- 高对比度模式的特殊处理
- 通过上下文API实现了无障碍信息的跨组件共享
OpenHarmony适配要点:
- OpenHarmony上高对比度模式的检测需要特殊处理,可能需要原生模块支持
- 主题切换时,应考虑OpenHarmony设备的性能限制,避免过度重绘
- 在上下文提供者中,需要处理OpenHarmony特有的事件监听机制
- 高对比度模式下,应避免使用纯色渐变,OpenHarmony的渲染引擎可能不支持
- 在OpenHarmony上,主题切换可能需要更长的生效时间,建议添加过渡效果
- 某些OpenHarmony设备可能不支持完整的色彩空间,主题颜色应选择广泛兼容的值
实战案例
无障碍友好的新闻阅读应用
让我们看一个完整的无障碍新闻阅读应用示例,它整合了前面讨论的所有技术点。
javascript
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, ScrollView, Image, TouchableOpacity, AccessibilityInfo, ActivityIndicator } from 'react-native';
// 模拟的新闻数据
const newsData = [
{
id: '1',
title: 'OpenHarmony 4.0正式发布,带来全新无障碍体验',
content: '近日,OpenAtom OpenHarmony 4.0版本正式发布,该版本在无障碍功能方面进行了重大改进。新版本增强了屏幕阅读器支持,优化了焦点管理,并提供了更丰富的无障碍API。这些改进使得基于OpenHarmony的应用能够更好地服务于残障用户群体。',
image: 'https://example.com/openharmony4.jpg',
category: '科技',
date: '2023-10-15'
},
{
id: '2',
title: 'React Native for OpenHarmony社区迎来重要更新',
content: 'React Native for OpenHarmony开源社区宣布,最新版本增加了对AccessibilityInfo API的全面支持。开发者现在可以更轻松地构建无障碍友好的跨平台应用,同时保持代码的统一性和可维护性。',
image: 'https://example.com/rn-oh.jpg',
category: '开发',
date: '2023-10-10'
},
{
id: '3',
title: '全国无障碍环境建设推进会召开',
content: '近日,全国无障碍环境建设推进会在京召开。会议强调,数字无障碍是无障碍环境建设的重要组成部分,要求各行业加强数字产品无障碍改造,确保残障人士平等参与社会生活。',
image: 'https://example.com/accessibility-conference.jpg',
category: '社会',
date: '2023-10-05'
}
];
const NewsArticle = ({ article, onReadAloud }) => {
const contentRef = useRef(null);
const [isReading, setIsReading] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
// 当内容渲染完成后,如果屏幕阅读器启用,自动聚焦到文章内容
const setupAccessibility = async () => {
const isEnabled = await AccessibilityInfo.isScreenReaderEnabled();
if (isEnabled && contentRef.current) {
const reactTag = findNodeHandle(contentRef.current);
if (reactTag) {
AccessibilityInfo.setAccessibilityFocus(reactTag);
}
}
};
setupAccessibility();
}, []);
const handleReadAloud = async () => {
if (isReading) return;
setIsReading(true);
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility(`开始朗读:${article.title}`);
// 模拟朗读过程
setTimeout(() => {
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility(article.content);
// 朗读完成后
setTimeout(() => {
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility('文章朗读完毕');
setIsReading(false);
}, 8000); // 模拟8秒朗读时间
}, 500);
};
return (
<View style={styles.articleContainer} ref={contentRef}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.category}>{article.category}</Text>
<Text style={styles.date}>{article.date}</Text>
</View>
<Text style={styles.title}>{article.title}</Text>
{article.image && (
<Image
source={{ uri: article.image }}
style={styles.image}
accessibilityLabel={`新闻配图:${article.title}`}
/>
)}
<Text style={styles.content}>{article.content}</Text>
<View style={styles.actions}>
<TouchableOpacity
style={[
styles.actionButton,
isReading && styles.actionButtonDisabled
]}
onPress={handleReadAloud}
disabled={isReading}
accessibilityLabel={isReading ? "正在朗读中" : "朗读文章"}
accessibilityState={{ busy: isReading }}
>
<Text style={styles.actionButtonText}>
{isReading ? '🔊 正在朗读...' : '🔊 朗读文章'}
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
</View>
);
};
const NewsApp = () => {
const [screenReaderEnabled, setScreenReaderEnabled] = useState(false);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
const [activeArticleId, setActiveArticleId] = useState(null);
const scrollViewRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const initApp = async () => {
// 模拟加载数据
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 800));
const isEnabled = await AccessibilityInfo.isScreenReaderEnabled();
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
setLoading(false);
// 如果屏幕阅读器启用,聚焦到标题
if (isEnabled && scrollViewRef.current) {
const reactTag = findNodeHandle(scrollViewRef.current);
if (reactTag) {
AccessibilityInfo.setAccessibilityFocus(reactTag);
}
}
};
initApp();
const screenReaderListener = (isEnabled) => {
setScreenReaderEnabled(isEnabled);
};
AccessibilityInfo.addEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
return () => {
AccessibilityInfo.removeEventListener('screenReaderChanged', screenReaderListener);
};
}, []);
const handleArticlePress = (articleId) => {
setActiveArticleId(articleId);
// 通知屏幕阅读器
if (screenReaderEnabled) {
const article = newsData.find(a => a.id === articleId);
if (article) {
AccessibilityInfo.announceForAccessibility(`已选择文章:${article.title}`);
}
}
};
const renderArticleItem = (article) => {
const isActive = activeArticleId === article.id;
return (
<TouchableOpacity
key={article.id}
style={[
styles.listItem,
isActive && styles.activeListItem
]}
onPress={() => handleArticlePress(article.id)}
accessibilityState={{ selected: isActive }}
accessibilityLabel={article.title}
>
<Text style={styles.listItemTitle}>{article.title}</Text>
<Text style={styles.listItemDate}>{article.date}</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
);
};
if (loading) {
return (
<View style={styles.loadingContainer}>
<ActivityIndicator size="large" color="#4287f5" />
<Text style={styles.loadingText}>加载无障碍新闻内容...</Text>
</View>
);
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text
style={styles.appTitle}
accessibilityRole="header"
accessibilityLiveRegion="polite"
>
无障碍新闻
</Text>
<Text style={styles.appSubtitle}>
{screenReaderEnabled
? '屏幕阅读器已启用 - 优化无障碍体验'
: '标准模式'}
</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.contentContainer}>
<ScrollView
ref={scrollViewRef}
style={styles.listContainer}
accessibilityLabel="新闻列表"
>
{newsData.map(renderArticleItem)}
</ScrollView>
<View style={styles.articlePreview}>
{activeArticleId ? (
<NewsArticle
article={newsData.find(a => a.id === activeArticleId)}
onReadAloud={() => {}}
/>
) : (
<View style={styles.placeholder}>
<Text style={styles.placeholderText}>
请选择左侧新闻列表中的文章进行阅读
</Text>
</View>
)}
</View>
</View>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
},
header: {
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
},
appTitle: {
fontSize: 28,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: 'white',
textAlign: 'center',
},
appSubtitle: {
fontSize: 16,
color: 'rgba(255,255,255,0.8)',
textAlign: 'center',
marginTop: 8,
},
contentContainer: {
flex: 1,
flexDirection: 'row',
},
listContainer: {
width: '30%',
borderRightWidth: 1,
borderRightColor: '#eee',
backgroundColor: '#f8f9fa',
},
listItem: {
padding: 15,
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#eee',
},
activeListItem: {
backgroundColor: '#e9ecef',
borderLeftWidth: 4,
borderLeftColor: '#4287f5',
},
listItemTitle: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: '500',
marginBottom: 4,
},
listItemDate: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
},
articlePreview: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
},
articleContainer: {
flex: 1,
},
header: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
marginBottom: 15,
},
category: {
fontSize: 14,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#4287f5',
},
date: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 15,
lineHeight: 32,
},
image: {
width: '100%',
height: 200,
borderRadius: 8,
marginBottom: 15,
},
content: {
fontSize: 18,
lineHeight: 28,
color: '#333',
marginBottom: 20,
},
actions: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'center',
},
actionButton: {
backgroundColor: '#4287f5',
paddingVertical: 10,
paddingHorizontal: 20,
borderRadius: 6,
},
actionButtonDisabled: {
backgroundColor: '#a5c8fa',
},
actionButtonText: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 16,
},
placeholder: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
placeholderText: {
fontSize: 18,
color: '#666',
textAlign: 'center',
lineHeight: 28,
},
loadingContainer: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
loadingText: {
marginTop: 15,
fontSize: 16,
color: '#666',
},
});
export default NewsApp;代码解析:
- 实现了新闻列表和详情的双栏布局
- 集成了屏幕阅读器状态检测和响应
- 提供了文章朗读功能,使用
announceForAccessibility - 为每个UI元素添加了适当的无障碍标签和状态
- 实现了焦点管理,确保屏幕阅读器用户能顺畅导航
OpenHarmony适配要点:
- 在OpenHarmony上,双栏布局可能需要调整以适应小屏幕设备
- 图片的
accessibilityLabel应避免包含过多细节,OpenHarmony的屏幕阅读器可能截断长文本 - 朗读功能需要考虑OpenHarmony设备的性能限制,避免长时间占用系统资源
- 某些OpenHarmony设备可能不支持
accessibilityLiveRegion属性,需要提供替代方案 - 在设置焦点时,应考虑OpenHarmony特有的焦点移动规则
- 新闻内容的字体大小应尊重系统设置,避免覆盖用户的首选项
常见问题与解决方案
API支持情况对比
| API方法 | OpenHarmony | Android | iOS | OpenHarmony适配建议 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
isScreenReaderEnabled() |
✅ 完全支持 | ✅ | ✅ | 可直接使用,但需添加初始状态查询 |
addEventListener('screenReaderChanged') |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 事件触发可能有延迟,建议添加防抖 |
announceForAccessibility() |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 消息长度限制更严格,需截断处理 |
setAccessibilityFocus() |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 需要额外延迟,确保UI渲染完成 |
isReduceMotionEnabled() |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 可直接使用,但某些设备可能不支持 |
isBoldTextEnabled() |
⚠️ 部分支持 | ✅ | ✅ | OpenHarmony上实现不完整,需备选方案 |
isGrayscaleEnabled() |
❌ 不支持 | ✅ | ❌ | 应避免使用或提供模拟实现 |
invertColors() |
❌ 不支持 | ✅ | ❌ | OpenHarmony上无法检测,需忽略 |
isReduceTransparencyEnabled() |
❌ 不支持 | ✅ | ✅ | 应避免依赖此API |
常见问题解决方案
| 问题现象 | 可能原因 | 解决方案 | 优先级 |
|---|---|---|---|
setAccessibilityFocus不生效 |
UI尚未完成渲染 | 使用setTimeout延迟调用,或使用requestAnimationFrame |
🔥 高 |
| 屏幕阅读器通知被截断 | 消息过长 | 限制消息长度在200字符以内,分段发送 | ⚠️ 中 |
| 事件监听不触发 | 未正确移除监听器 | 确保在组件卸载时移除所有事件监听 | 🔥 高 |
| 无障碍状态检测不准确 | OpenHarmony实现差异 | 添加默认值处理和轮询机制作为备选 | ⚠️ 中 |
| 焦点移动不流畅 | 多次快速设置焦点 | 实现焦点队列,添加适当延迟 | ⚠️ 中 |
| 与第三方库冲突 | 原生模块冲突 | 检查原生依赖,必要时修改桥接代码 | 💡 低 |
总结与展望
本文深入探讨了React Native的AccessibilityInfo API在OpenHarmony平台上的应用与适配。通过详细的技术解析和丰富的代码示例,我们了解了:
- AccessibilityInfo的核心工作原理和关键API
- OpenHarmony平台特有的无障碍适配挑战与解决方案
- 从基础用法到高级集成的完整实践路径
- 常见问题的排查与解决方法
无障碍开发不是简单的"合规检查",而是真正体现产品人文关怀的重要维度。随着OpenHarmony生态的不断发展,其无障碍支持也将日益完善。作为React Native开发者,我们应当:
- 将无障碍设计融入开发流程的每个环节,而非事后补救
- 持续关注OpenHarmony无障碍能力的更新,及时调整适配策略
- 积极参与社区讨论,推动React Native for OpenHarmony无障碍能力的提升
- 通过真实用户测试,不断优化无障碍体验
未来,随着OpenHarmony 4.0+版本的普及,我们有望看到更完善的无障碍API支持,包括高对比度模式检测、详细的文字样式信息等。同时,React Native社区也在积极改进跨平台无障碍支持,相信不久的将来,我们能够用更少的平台特定代码,实现更一致的无障碍体验。
记住,优秀的无障碍设计不仅帮助残障用户,也能提升所有用户的体验。正如一句设计格言所说:"无障碍设计不是为少数人,而是为所有人设计。"
完整项目Demo地址
完整项目Demo地址:https://atomgit.com/pickstar/AtomGitDemos
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net