文章目录
这一节的内容在前几节中都有写过,就当是复习了~
1、27 移除元素
题目
这道题在数组那里写过了,就不再重复了。
代码
c
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {
int left = 0;
for(int right = 0;right < numsSize;right++){
if(nums[right] != val){
nums[left++] = nums[right];
}
}
return left;
}时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
相关题目:
代码:
c
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize) {
int i = 0;
if(numsSize == 1){
return 1;
}
for(int j = 1;j < numsSize;j++){
if(nums[i] != nums[j]){
nums[++i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i+1;
}
代码:
c
void moveZeroes(int* nums, int numsSize) {
int i = 0;
for(int j = 0;j < numsSize;j++){
if(nums[j] != 0){
int tmp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = tmp;
i++;
}
}
}
代码:
c
bool backspaceCompare(char* s, char* t) {
int a = strlen(s);
int b = strlen(t);
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < a;i++){
if(j > 0 && s[i] == '#'){
j--;
}else if(s[i] != '#'){
s[j++] = s[i];
}
}
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < b;i++){
if(k > 0 && t[i] == '#'){
k--;
}else if(t[i] != '#'){
t[k++] = t[i];
}
}
if(j != k){
return false;
}
for(int i = 0;i < j;i++){
if(s[i] != t[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
代码:
c
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int cmp(const void* a,const void* b){
return *(int*)a - *(int*)b;
}
int* sortedSquares(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize) {
for(int i = 0;i < numsSize;i++){
nums[i] = nums[i]*nums[i];
}
qsort(nums,numsSize,sizeof(int),cmp);
*returnSize = numsSize;
return nums;
}其实刚开始见这些题时我一个都不会写,不过现在基本上都能写出来,夸夸自己xixi
2、344 反转字符串
题目
这道题上一篇也写过
代码
c
void reverseString(char* s, int sSize) {
int i = 0;
int j = sSize-1;
while(i < j){
int tmp = s[i];
s[i] = s[j];
s[j] = tmp;
i++;
j--;
}
}时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
3、替换数字
题目
这道题上一篇也写过
代码
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main(){
char s[10000];
scanf("%s",s);
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0;s[i];i++){
if(isdigit(s[i])){
k+=6;
}
else{
k+=1;
}
}
int j = 0;
char* res = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(k+1));
for(int i = 0;s[i];i++){
if(isdigit(s[i])){
res[j++] = 'n';
res[j++] = 'u';
res[j++] = 'm';
res[j++] = 'b';
res[j++] = 'e';
res[j++] = 'r';
}
else{
res[j++] = s[i];
}
}
printf("%s",res);
free(res);
return 0;
}时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
4、151 反转字符串里的单词
题目
代码
先删除多余的空格,再翻转字符串,再翻转单词
c
void reverse(char* s,int start,int end){
int i = start;
int j = end;
while(i < j){
int tmp = s[i];
s[i] = s[j];
s[j] = tmp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
void del_space(char* s){
int start = 0;
int end = strlen(s) - 1;
while(s[start] == ' '){
start++;
}
while(s[end] == ' '){
end--;
}
int k = 0;
for(int i = start;i <= end;i++){
if(s[i] == ' ' && s[i+1] == ' '){
continue;
}else{
s[k++] = s[i];
}
}
s[k] = '\0';
}
char* reverseWords(char* s) {
del_space(s);
reverse(s,0,strlen(s)-1);
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0;i <= strlen(s);i++){
if(s[i] == ' ' || s[i] == '\0'){
reverse(s,j,i-1);
j = i+1;
}
}
return s;
}mid题大概思路记得,但是具体的代码忘记咋写了悲
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
5、206 反转链表
题目
代码
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){
return head;
}
struct ListNode* tmp;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur != NULL){
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
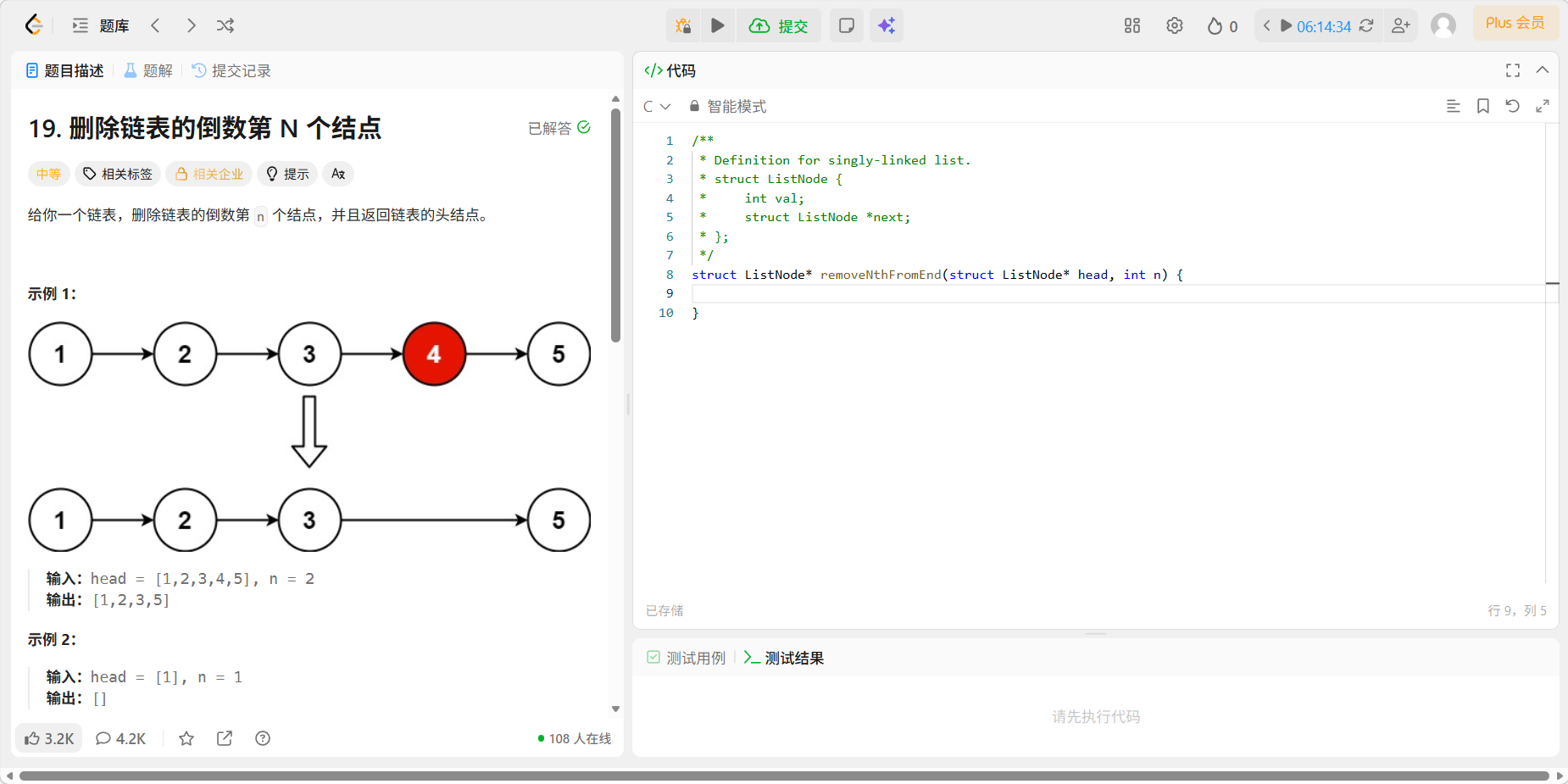
6、19 删除链表的倒数第N个结点
题目
代码
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {
struct ListNode dummy;
dummy.next = head;
struct ListNode* p = &dummy;
struct ListNode* q = &dummy;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
p = p->next;
}
while(p->next != NULL){
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
struct ListNode* tmp = q->next;
q->next = tmp->next;
free(tmp);
return dummy.next;
}时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
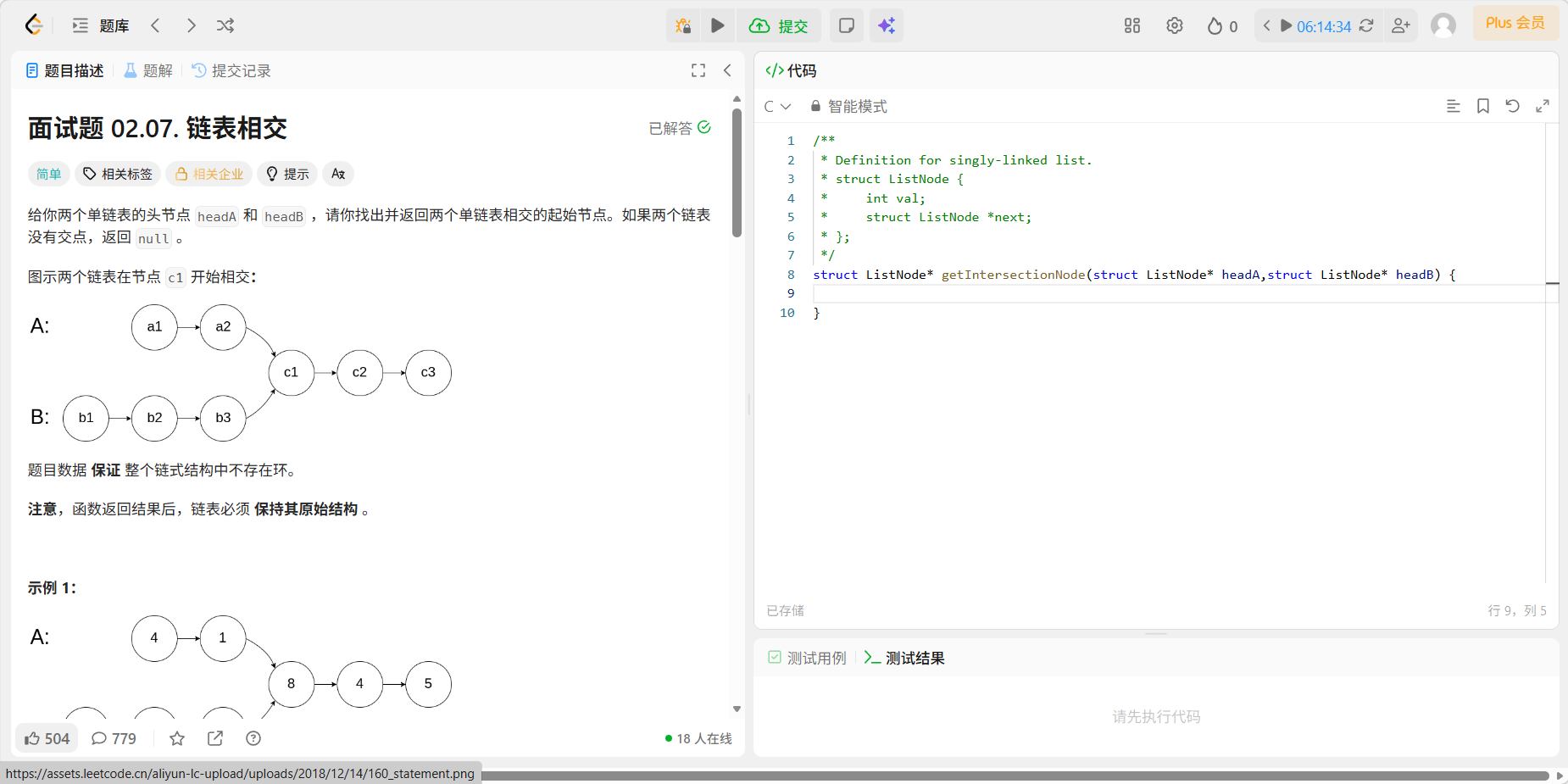
7、02.07 链表相交
题目
代码
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA,struct ListNode* headB) {
struct ListNode dummy1;
dummy1.next = headA;
struct ListNode* p = &dummy1;
struct ListNode dummy2;
dummy2.next = headB;
struct ListNode* q = &dummy2;
int n = 0;
while(p->next != NULL){
p = p->next;
n++;
}
int m = 0;
while(q->next != NULL){
q = q->next;
m++;
}
p = &dummy1;
q = &dummy2;
if(n > m){
for(int i = 0;i < (n-m);i++){
p = p->next;
}
}
else if(m > n){
for(int i = 0;i < (m-n);i++){
q = q->next;
}
}
while(p != NULL){
if(p == q){
return p;
}else{
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
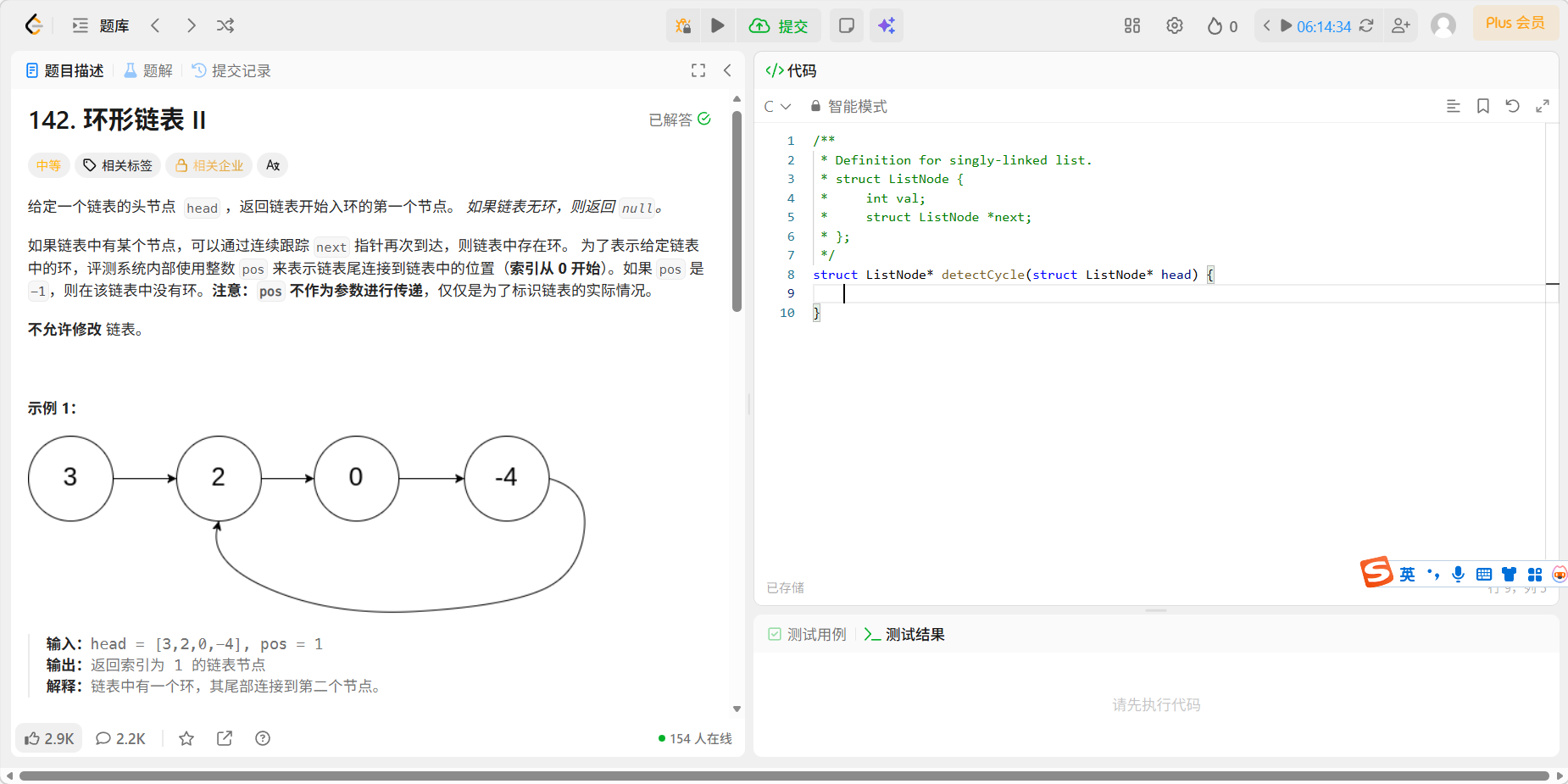
8、142 环形链表②
题目
代码
先p走两步,q走一步,若有环,p,q一定会在环内相遇,然后此时令h从head开始与q同时向后走一步,二者必在入环口相遇。
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* p = head;
struct ListNode* q = head;
while(p != NULL && p->next != NULL){
p = p->next;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
if(p == q){
struct ListNode* h = head;
// struct ListNode* k = q;
while(h != q){
h = h->next;
q = q->next;
}
return h;
}
}
return NULL;
}时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
9、15 三数之和
题目
代码
c
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume
* caller calls free().
*/
int cmp(const void* a,const void* b){
return *(int*)a - *(int*)b;
}
int** threeSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize,int** returnColumnSizes) {
int count = 0;
int n = numsSize;
int** res = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*)*n*n);
qsort(nums,numsSize,sizeof(int),cmp);
for(int i = 0;i < n-2;i++){
if(nums[i] > 0){
continue;
}
if(nums[i] + nums[n-1]+nums[n-2] < 0){
continue;
}
if(nums[i] + nums[i+1] + nums[i+2] > 0){
continue;
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){
continue;
}
int left = i+1;
int right = n-1;
while(right > left){
if(nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0){
right--;
}
else if(nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0){
left++;
}
else{
int* triple = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*3);
triple[0] = nums[i];
triple[1] = nums[left];
triple[2] = nums[right];
res[count++] = triple;
right--;
left++;
while(right > left && nums[right] == nums[right+1]){
right--;
}
while(right > left && nums[left] == nums[left-1]){
left++;
}
}
}
}
*returnSize = count;
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*count);
for(int i = 0;i < count;i++){
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = 3;
}
return res;
}时间复杂度:O( n 2 n^2 n2)
空间复杂度:O( n 2 n^2 n2)
10、四数之和
题目
代码
c
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int cmp(const void* a,const void* b){
return *(int*)a - *(int*)b;
}
int** fourSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
int n = numsSize;
int** res = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*)*n*n);
int count = 0;
long long sum = 0;
qsort(nums,n,sizeof(int),cmp);
for(int i = 0;i < n-3;i++){
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){
continue;
}
if(nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] > target){
continue;
}
for(int j = i+1;j < n-2;j++){
if(nums[j] >=0 && nums[j]+nums[i] > target){
continue;
}
if(j > i+1 && nums[j] == nums[j-1]){
continue;
}
int left = j+1;
int right = n-1;
sum = (long long)nums[i]+nums[j];
while(right > left){
long long val = (long long)sum+nums[left]+nums[right];
if(val > target){
right--;
}
else if(val < target){
left++;
}
else{
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*4);
tmp[0] = nums[i];
tmp[1] = nums[j];
tmp[2] = nums[left];
tmp[3] = nums[right];
res[count++] = tmp;
left++;
right--;
while(right > left && nums[right] == nums[right+1]){
right--;
}
while(right > left && nums[left] == nums[left-1]){
left++;
}
}
}
}
}
*returnSize = count;
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*count);
for(int i =0;i < count;i++){
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = 4;
}
return res;
}时间复杂度:O( n 3 n^3 n3)
空间复杂度:O( n 3 n^3 n3)
ending~~