文章目录
前言
JDK 1.8 引入的 Stream API 是 Java 函数式编程的核心特性之一,它提供了一种高效、声明式的方式来处理集合数据(如 List、Set 等),支持链式操作、并行处理和惰性求值。
什么是 Stream?
- Stream 不是数据结构,不存储元素,而是对数据源(如集合、数组)进行计算的一系列操作(操作数据的管道)。
- 不可变:不会修改原始数据源。
- 惰性求值(Lazy Evaluation):中间操作(如 filter、map)不会立即执行,只有遇到终端操作(如 collect、forEach)才会触发整个流水线。
- 可并行处理(ParallelStream):提高大数据处理效率
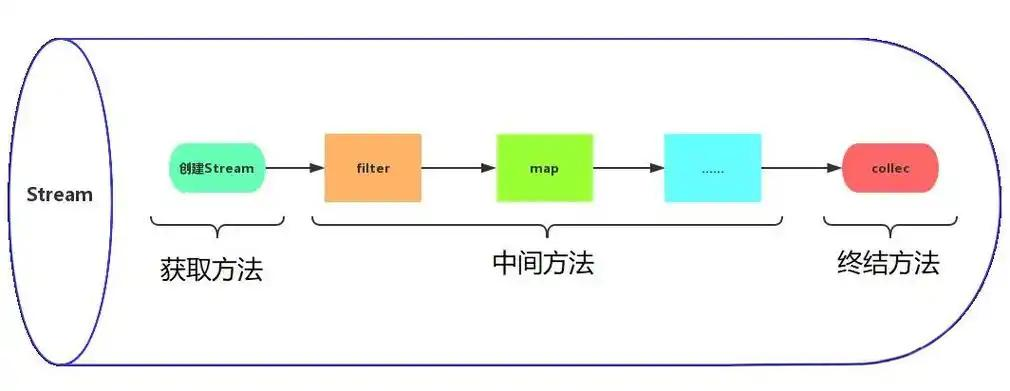
Stream API 的基本概念
数据源:可以是任何实现了 Collection 接口的数据结构,或者是数组、迭代器等。
中间操作:一系列按需惰性处理数据的管道操作,如过滤、映射、排序等。
终止操作:执行计算并返回结果的操作,如收集、聚合等。一旦执行了终止操作,流就会被消费掉,不能再被重复使用。
中间操作
中间操作可以链接起来形成流水线,常见的中间操作有:
filter(Predicate):过滤元素
map(Function):映射转换
flatMap(Function):扁平化映射(将流中的每个元素转为流,再合并)
distinct():去重
sorted() / sorted(Comparator):排序
peek(Consumer):调试用,对每个元素执行操作但不改变流
limit(long):截取前 N 个
skip(long):跳过前 N 个
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange", "avocado","apple");
// 过滤
List<String> list1 = list.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("a"))
.filter(s -> s.length() > 5).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list1);//[avocado]
// 映射
// 将字符串映射为对应的长度
List<Integer> list2 = list.stream().map(String::length).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list2);//[5, 6, 6, 7, 5]
// 将字符串映射为大写
List<String> list3 = list.stream().map(String::toUpperCase).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list3);//[APPLE, BANANA, ORANGE, AVOCADO, APPLE]
// 映射为指定字符串
List<String> list4 = list.stream().map(item->item+"z").collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list4);//[applez, bananaz, orangez, avocadoz, applez]
// 去重
List<String> list5 = list.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list5);//[apple, banana, orange, avocado]
// 排序
List<String> list6 = list.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list6);//[apple, apple, avocado, banana, orange]
List<String> list7 = list.stream()
.sorted((s1, s2) -> s2.compareTo(s1)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list7);//[orange, banana, avocado, apple, apple]
// 限制和跳过
// 取前3个
List<String> list8 = list.stream()
.limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list8);//[apple, banana, orange]
// 跳过第1个
List<String> list9 = list.stream()
.skip(1).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list9);//[banana, orange, avocado, apple]
}终止操作
终止操作会触发流的执行,并且返回结果。常见的终止操作包括:
forEach(Consumer):遍历
collect(Collector):聚合成集合、字符串等(最常用)
reduce(BinaryOperator):归约(如求和、拼接)
count():元素个数
min() / max(Comparator):最值
anyMatch(Predicate) / allMatch / noneMatch:匹配检查
findFirst() / findAny():查找元素(Optional)
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "a");
// 遍历
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
// 转换为数组
String[] array = list.stream().toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println(array);//["a", "b", "c", "a"]
// 聚合操作
Optional<String> first = list.stream().findFirst();
System.out.println(first.get());//a
// 检查列表中是否存在以字母"a"开头的字符串
boolean anyMatch = list.stream().anyMatch(s -> s.startsWith("a"));
System.out.println(anyMatch);//true
// 检查列表中所有字符串的长度是否都等于1
boolean allMatch = list.stream().allMatch(s -> s.length() == 1);
System.out.println(allMatch);//true
// 检查列表中是否没有任何空字符串
boolean noneMatch = list.stream().noneMatch(s -> s.isEmpty());
System.out.println(noneMatch);//true
// 计数
long count = list.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);//4
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(4,5,6,7);
// 最值
// 获取最大值
Integer max = list2.stream().max(Integer::compareTo).orElse(0);
System.out.println("最大值: " + max);//最大值: 7
int max2 = list2.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).max().orElse(0);
System.out.println("最大值: " + max2);//最大值: 7
// 获取最小值
Integer min = list2.stream().min(Integer::compareTo).orElse(0);
System.out.println("最小值: " + min);//最小值: 4
int min2 = list2.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).min().orElse(0);
System.out.println("最小值: " + min2);//最小值: 4
// 平均值
double avg = list2.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).average().orElse(0.0);
System.out.println("平均数: " + avg);//平均数: 5.5
//求和
int sum = list2.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
System.out.println("累计总和: " + sum);//累计总和: 22
// 或者使用reduce方法计算总和
Integer sum2 = list2.stream().reduce(Integer::sum).orElse(0);
System.out.println("使用reduce计算总和: " + sum2);//使用reduce计算总和: 22
//orElse()方法,主要作用是提供默认值。
List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
Integer max3 = list3.stream().max(Integer::compareTo).orElse(999);
System.out.println("最大值: " + max3);//最大值: 999
IntSummaryStatistics stats = list2.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Integer::intValue));
System.out.println("计数: " + stats.getCount()); // 计数: 4
System.out.println("总和: " + stats.getSum()); // 总和: 22
System.out.println("平均值: " + stats.getAverage()); // 平均值: 5.5
System.out.println("最大值: " + stats.getMax()); // 最大值: 7
System.out.println("最小值: " + stats.getMin()); // 最小值: 4
}集合元素为类的处理
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> person = Arrays.asList(
new Person("John", 25, "北京"),
new Person("Jane", 30, "深圳"),
new Person("Bob", 30, "上海"),
new Person("Mike", 20, "深圳"),
new Person("Lucy", 20, "深圳")
);
//toMap
Map<String, Person> personMap = person.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, item -> item));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(personMap));//{"Mike":{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Mike"},"Bob":{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"Bob"},"John":{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"John"},"Lucy":{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Lucy"},"Jane":{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"Jane"}}
//处理key值冲突,当有冲突时保留上一个
Map<Integer, Person> personMap2 = person.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, item -> item, (k1, k2) -> k1));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(personMap2));//{20:{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Mike"},25:{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"John"},30:{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"Jane"}}
//分组
Map<String, List<Person>> groupingMap = person.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getCity));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(groupingMap));//{"上海":[{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"Bob"}],"深圳":[{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"Jane"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Mike"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Lucy"}],"北京":[{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"John"}]}
// 多级分组
Map<String, Map<Integer, List<Person>>> multiGroupingMap = person.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
Person::getCity,
Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge)
));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(multiGroupingMap));//{"上海":{30:[{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"Bob"}]},"深圳":{20:[{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Mike"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Lucy"}],30:[{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"Jane"}]},"北京":{25:[{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"John"}]}}
// 分区(分成true/false两组)
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> partition = person.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(p -> p.getAge() > 25));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(partition));//{false:[{"age":25,"city":"北京","name":"John"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Mike"},{"age":20,"city":"深圳","name":"Lucy"}],true:[{"age":30,"city":"深圳","name":"Jane"},{"age":30,"city":"上海","name":"Bob"}]}
}
// 静态内部类
static class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String city;
public Person(String name, Integer age, String city) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.city = city;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public Integer getAge() { return age; }
public String getCity() { return city; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", city='" + city + '\'' +
'}';
}
}并行流
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
int j = i % 30;
Person person = new Person("用户"+i, j, "test"+i);
list.add(person);
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<Person> test1 = list.stream().filter(item -> item.getAge() > 20).map(item -> {
item.setAge(item.getAge() * 2);
return item;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行时间: " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");//执行时间: 63 毫秒
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<Person> test2 = list.parallelStream().filter(item -> item.getAge() > 20).map(item -> {
item.setAge(item.getAge() * 2);
return item;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行时间: " + (endTime2 - startTime2) + " 毫秒");//执行时间: 19 毫秒
}
// 静态内部类
static class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String city;
public Person(String name, Integer age, String city) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.city = city;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public Integer getAge() { return age; }
public String getCity() { return city; }
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", city='" + city + '\'' +
'}';
}
}