目录
[一、为什么选择 QLExpress 处理复杂数据结构](#一、为什么选择 QLExpress 处理复杂数据结构)
[(一)传统手动 Java 逻辑存在问题](#(一)传统手动 Java 逻辑存在问题)
[(二)QLExpress 的优势](#(二)QLExpress 的优势)
干货分享,感谢您的阅读!
在现代企业级应用中,规则引擎的应用场景非常广泛,从价格计算、优惠策略、到风控审批、智能推荐等,都需要对复杂数据结构进行高效处理和灵活计算。QLExpress 作为国内常用的 Java 轻量级表达式引擎,具有快速解析、灵活扩展和良好的嵌套对象支持能力,非常适合用于业务逻辑复杂、对象结构多层嵌套的场景。

我们将围绕 QLExpress 在复杂对象和集合处理上的实践,结合企业真实案例,讲解如何构建可维护、高性能的规则引擎,并提供完整 Java 示例代码。
我直接写了ComplexDataStructureDemo来进行QLExpress复杂数据结构处理演示:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.advancedfeatures.core;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
import lombok.Data;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress复杂数据结构处理演示 - 展示如何处理复杂对象和集合
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-27 08:34
**/
public class ComplexDataStructureDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public ComplexDataStructureDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
initCustomFunctions();
}
/**
* 初始化自定义函数
*/
private void initCustomFunctions() {
try {
// 集合处理函数
runner.addFunction("sum", new SumFunction());
runner.addFunction("count", new CountFunction());
runner.addFunction("filter", new FilterFunction());
runner.addFunction("exists", new ExistsFunction());
// 对象属性访问函数
runner.addFunction("getProperty", new GetPropertyFunction());
runner.addFunction("hasProperty", new HasPropertyFunction());
System.out.println("✅ 复杂数据结构处理引擎初始化完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("初始化复杂数据结构引擎失败", e);
}
}
/**
* 演示复杂数据结构处理
*/
public void demonstrateComplexDataStructures() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress复杂数据结构处理演示 ===\n");
// 创建复杂测试数据
List<Product> products = createSampleProducts();
Customer customer = createSampleCustomer();
Order order = createSampleOrder(customer, products);
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
context.put("products", products);
context.put("customer", customer);
context.put("order", order);
// 演示1:集合操作和聚合计算
demonstrateCollectionOperations(context);
// 演示2:嵌套对象属性访问
demonstrateNestedObjectAccess(context);
// 演示3:复杂业务逻辑计算
demonstrateComplexBusinessLogic(context);
// 演示4:动态条件过滤
demonstrateDynamicFiltering(context);
// 演示5:多层级数据处理
demonstrateMultiLevelDataProcessing(context);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("演示过程中发生错误: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void demonstrateCollectionOperations(DefaultContext<String, Object> context) throws Exception {
System.out.println("1. 集合操作和聚合计算:");
// 计算商品总价
Object result = runner.execute("sum(products, \"price\")", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 商品总价: ¥" + result);
// 计算商品数量
result = runner.execute("count(products)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 商品数量: " + result + "个");
// 检查是否存在特定类型商品
context.put("targetCategory", "电子产品");
result = runner.execute("exists(products, 'category', targetCategory)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 是否存在电子产品: " + result);
System.out.println();
}
private void demonstrateNestedObjectAccess(DefaultContext<String, Object> context) throws Exception {
System.out.println("2. 嵌套对象属性访问:");
// 访问客户信息
Object result = runner.execute("customer.name", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 客户姓名: " + result);
result = runner.execute("customer.address.city", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 客户城市: " + result);
// 检查客户是否为VIP
result = runner.execute("customer.vipLevel > 0", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 是否为VIP: " + result);
// 获取订单状态
result = runner.execute("order.status", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 订单状态: " + result);
System.out.println();
}
private void demonstrateComplexBusinessLogic(DefaultContext<String, Object> context) throws Exception {
System.out.println("3. 复杂业务逻辑计算:");
// 计算VIP折扣 (使用Java计算避免QLExpress语法问题)
Customer customer = (Customer) context.get("customer");
int vipLevel = customer.getVipLevel();
// 直接使用Java计算商品总价
BigDecimal totalPrice = BigDecimal.ZERO;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Product> productList = (List<Product>) context.get("products");
for (Product product : productList) {
totalPrice = totalPrice.add(product.getPrice());
}
BigDecimal vipDiscount;
if (vipLevel >= 3) {
vipDiscount = totalPrice.multiply(new BigDecimal("0.2"));
} else if (vipLevel >= 1) {
vipDiscount = totalPrice.multiply(new BigDecimal("0.1"));
} else {
vipDiscount = BigDecimal.ZERO;
}
System.out.println(" VIP折扣金额: ¥" + vipDiscount);
// 计算运费(满200免运费,否则按重量计算)
Object shipping;
if (totalPrice.compareTo(new BigDecimal("200")) >= 0) {
shipping = BigDecimal.ZERO;
} else {
// 计算总重量
double totalWeight = 0;
for (Product product : productList) {
totalWeight += product.getWeight();
}
shipping = new BigDecimal(totalWeight * 2 + 10);
}
System.out.println(" 运费: ¥" + shipping);
// 计算最终价格
BigDecimal finalPrice = totalPrice.subtract((BigDecimal) vipDiscount).add((BigDecimal) shipping);
System.out.println(" 最终价格: ¥" + finalPrice);
System.out.println();
}
private void demonstrateDynamicFiltering(DefaultContext<String, Object> context) throws Exception {
System.out.println("4. 动态条件过滤:");
// 过滤高价商品
context.put("minPrice", 1000);
Object result = runner.execute("filter(products, 'price', '>=', minPrice)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 高价商品(>=1000): " + ((List<?>) result).size() + "个");
// 过滤特定类别商品
context.put("category", "电子产品");
result = runner.execute("filter(products, 'category', '==', category)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 电子产品数量: " + ((List<?>) result).size() + "个");
System.out.println();
}
private void demonstrateMultiLevelDataProcessing(DefaultContext<String, Object> context) throws Exception {
System.out.println("5. 多层级数据处理:");
// 复杂的嵌套计算
Object vipCheck = runner.execute("customer.vipLevel >= 2", context, null, true, false);
Object cityCheck = runner.execute("customer.address.city == '北京'", context, null, true, false);
// 计算商品总价(Java方式)
BigDecimal totalPriceForCheck = BigDecimal.ZERO;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Product> productList = (List<Product>) context.get("products");
for (Product product : productList) {
totalPriceForCheck = totalPriceForCheck.add(product.getPrice());
}
boolean priceCheck2 = totalPriceForCheck.compareTo(new BigDecimal("1500")) > 0;
String orderType;
if ((Boolean) vipCheck && priceCheck2 && (Boolean) cityCheck) {
orderType = "享受特殊优惠";
} else {
orderType = "普通订单";
}
System.out.println(" 订单类型: " + orderType);
// 基于多个条件的积分计算
Object vipLevel = runner.execute("customer.vipLevel", context, null, true, false);
BigDecimal basePoints = totalPriceForCheck.divide(new BigDecimal("100")).multiply(new BigDecimal((Integer) vipLevel + 1));
int cityBonus = (Boolean) cityCheck ? 50 : 0;
BigDecimal totalPoints = basePoints.add(new BigDecimal(cityBonus));
System.out.println(" 获得积分: " + totalPoints);
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 创建示例商品数据
*/
private List<Product> createSampleProducts() {
List<Product> products = new ArrayList<>();
products.add(new Product("iPhone 15 Pro", "电子产品", new BigDecimal("7999"), 0.2));
products.add(new Product("MacBook Pro", "电子产品", new BigDecimal("12999"), 2.0));
products.add(new Product("AirPods Pro", "电子产品", new BigDecimal("1999"), 0.1));
products.add(new Product("保温杯", "生活用品", new BigDecimal("299"), 0.5));
products.add(new Product("运动鞋", "服装", new BigDecimal("899"), 0.8));
return products;
}
/**
* 创建示例客户数据
*/
private Customer createSampleCustomer() {
Address address = new Address("北京", "朝阳区", "100000");
return new Customer("张彦峰", "zhangyanfeng@example.com", 3, address);
}
/**
* 创建示例订单数据
*/
private Order createSampleOrder(Customer customer, List<Product> products) {
return new Order("ORD2025001", customer, products, "已支付", new Date());
}
// 数据模型类
@Data
public static class Product {
private String name;
private String category;
private BigDecimal price;
private double weight; // kg
public Product(String name, String category, BigDecimal price, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.category = category;
this.price = price;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
@Data
public static class Customer {
private String name;
private String email;
private int vipLevel;
private Address address;
public Customer(String name, String email, int vipLevel, Address address) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.vipLevel = vipLevel;
this.address = address;
}
}
@Data
public static class Address {
private String city;
private String district;
private String zipCode;
public Address(String city, String district, String zipCode) {
this.city = city;
this.district = district;
this.zipCode = zipCode;
}
}
@Data
public static class Order {
private String orderId;
private Customer customer;
private List<Product> products;
private String status;
private Date orderDate;
public Order(String orderId, Customer customer, List<Product> products, String status, Date orderDate) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.customer = customer;
this.products = products;
this.status = status;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
}
// 自定义函数实现
public static class SumFunction extends com.ql.util.express.Operator {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
List<Object> objects = (List<Object>) list[0];
String property = (String) list[1];
BigDecimal sum = BigDecimal.ZERO;
for (Object obj : objects) {
Object value = getProperty(obj, property);
if (value instanceof BigDecimal) {
sum = sum.add((BigDecimal) value);
} else if (value instanceof Number) {
sum = sum.add(BigDecimal.valueOf(((Number) value).doubleValue()));
}
}
return sum;
}
}
public static class CountFunction extends com.ql.util.express.Operator {
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
if (list[0] instanceof Collection) {
return ((Collection<?>) list[0]).size();
}
return 0;
}
}
public static class FilterFunction extends com.ql.util.express.Operator {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
List<Object> objects = (List<Object>) list[0];
String property = (String) list[1];
String operator = (String) list[2];
Object value = list[3];
List<Object> filtered = new ArrayList<>();
for (Object obj : objects) {
Object propertyValue = getProperty(obj, property);
if (compareValues(propertyValue, operator, value)) {
filtered.add(obj);
}
}
return filtered;
}
}
public static class ExistsFunction extends com.ql.util.express.Operator {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
List<Object> objects = (List<Object>) list[0];
String property = (String) list[1];
Object value = list[2];
for (Object obj : objects) {
Object propertyValue = getProperty(obj, property);
if (Objects.equals(propertyValue, value)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
public static class GetPropertyFunction extends com.ql.util.express.Operator {
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
Object obj = list[0];
String property = (String) list[1];
return getProperty(obj, property);
}
}
public static class HasPropertyFunction extends com.ql.util.express.Operator {
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
Object obj = list[0];
String property = (String) list[1];
try {
getProperty(obj, property);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
}
// 工具方法
private static Object getProperty(Object obj, String property) throws Exception {
return obj.getClass().getMethod("get" + capitalize(property)).invoke(obj);
}
private static String capitalize(String str) {
return str.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + str.substring(1);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static boolean compareValues(Object value1, String operator, Object value2) {
if (value1 == null || value2 == null) {
return "==".equals(operator) ? Objects.equals(value1, value2) : false;
}
// 处理数值比较,统一转换为BigDecimal
if (isNumericComparison(operator) && isNumeric(value1) && isNumeric(value2)) {
try {
BigDecimal bd1 = convertToBigDecimal(value1);
BigDecimal bd2 = convertToBigDecimal(value2);
switch (operator) {
case ">":
return bd1.compareTo(bd2) > 0;
case ">=":
return bd1.compareTo(bd2) >= 0;
case "<":
return bd1.compareTo(bd2) < 0;
case "<=":
return bd1.compareTo(bd2) <= 0;
default:
return false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
// 非数值比较
switch (operator) {
case "==":
return Objects.equals(value1, value2);
case "!=":
return !Objects.equals(value1, value2);
default:
return false;
}
}
private static boolean isNumericComparison(String operator) {
return ">".equals(operator) || ">=".equals(operator) ||
"<".equals(operator) || "<=".equals(operator);
}
private static boolean isNumeric(Object value) {
return value instanceof Number || value instanceof BigDecimal;
}
private static BigDecimal convertToBigDecimal(Object value) {
if (value instanceof BigDecimal) {
return (BigDecimal) value;
} else if (value instanceof Number) {
return BigDecimal.valueOf(((Number) value).doubleValue());
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Value is not numeric: " + value);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ComplexDataStructureDemo demo = new ComplexDataStructureDemo();
demo.demonstrateComplexDataStructures();
}
}一、为什么选择 QLExpress 处理复杂数据结构
(一)传统手动 Java 逻辑存在问题
在业务系统中,常常遇到如下情况:
-
对象层级多,如客户(Customer)包含地址(Address)、订单(Order)包含商品列表(Product);
-
集合嵌套计算复杂,如计算 VIP 客户折扣、积分、运费;
-
条件逻辑多样化,如动态过滤商品、判断特殊优惠订单类型;
-
希望业务逻辑可配置,减少频繁改动 Java 代码。
传统方式是手动写 Java 逻辑,但存在以下问题:
-
业务逻辑难以维护:随着规则复杂化,代码膨胀,容易出现 bug;
-
灵活性低:每次规则变更都需要改动代码、重启服务;
-
表达能力有限:嵌套集合、条件判断、多层对象计算在普通 Java 代码中可读性差。
(二)QLExpress 的优势
QLExpress 的优势在于:
-
嵌套对象访问 :支持
customer.address.city这样的链式访问; -
集合计算与自定义函数 :如
sum(products, "price")、filter(...)、exists(...); -
可扩展性强:可自定义函数扩展业务逻辑;
-
执行性能高 :通过
InstructionSet缓存和ExpressRunner执行,可支持高并发计算。
二、QLExpress复杂数据结构处理核心示例
我们基于一个实际业务场景进行演示:电商系统中的订单计算,涉及客户信息、商品列表、VIP 优惠、运费规则和积分计算。
下面是核心示例代码(完整 Java 类):
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.advancedfeatures.core;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
import lombok.Data;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress复杂数据结构处理演示 - 展示如何处理复杂对象和集合
*/
public class ComplexDataStructureDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public ComplexDataStructureDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
initCustomFunctions();
}
private void initCustomFunctions() {
try {
runner.addFunction("sum", new SumFunction());
runner.addFunction("count", new CountFunction());
runner.addFunction("filter", new FilterFunction());
runner.addFunction("exists", new ExistsFunction());
runner.addFunction("getProperty", new GetPropertyFunction());
runner.addFunction("hasProperty", new HasPropertyFunction());
System.out.println("✅ 复杂数据结构处理引擎初始化完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("初始化复杂数据结构引擎失败", e);
}
}
public void demonstrateComplexDataStructures() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress复杂数据结构处理演示 ===\n");
List<Product> products = createSampleProducts();
Customer customer = createSampleCustomer();
Order order = createSampleOrder(customer, products);
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
context.put("products", products);
context.put("customer", customer);
context.put("order", order);
demonstrateCollectionOperations(context);
demonstrateNestedObjectAccess(context);
demonstrateComplexBusinessLogic(context);
demonstrateDynamicFiltering(context);
demonstrateMultiLevelDataProcessing(context);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("演示过程中发生错误: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 以下方法省略,可参考原始代码
}此类通过 ExpressRunner 执行多种业务场景,包括集合聚合、嵌套对象访问、条件过滤、复杂计算逻辑等。
自定义函数如 SumFunction、FilterFunction 和 ExistsFunction 可以直接在规则中使用,极大提升了可读性和可维护性。
三、复杂集合操作与聚合计算
在电商订单处理中,集合计算是最常见的需求:
-
计算商品总价
-
统计商品数量
-
判断集合中是否存在某类型商品
通过自定义函数,QLExpress 可以实现如下表达式:
java
Object result = runner.execute("sum(products, \"price\")", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("商品总价: ¥" + result);
result = runner.execute("count(products)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("商品数量: " + result);
context.put("targetCategory", "电子产品");
result = runner.execute("exists(products, 'category', targetCategory)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("是否存在电子产品: " + result);扩展说明:
在传统 Java 中,通常需要手动循环计算,而使用 QLExpress 和自定义函数后,表达式更加直观,维护成本显著降低。同时,也方便规则在配置文件或数据库中动态加载,无需修改 Java 代码。
四、嵌套对象属性访问
业务系统中,常常需要访问对象的深层次属性,例如:
-
客户姓名
customer.name -
客户所在城市
customer.address.city -
VIP 等级判断
customer.vipLevel > 0
QLExpress 支持链式访问,结合上下文传入对象即可:
java
Object result = runner.execute("customer.name", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("客户姓名: " + result);
result = runner.execute("customer.address.city", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("客户城市: " + result);
result = runner.execute("customer.vipLevel > 0", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("是否为VIP: " + result);这在复杂对象结构的场景下尤其有价值,可以减少层层调用 getter 方法,保证表达式可读性和维护性。
五、复杂业务逻辑计算
除了基础计算,企业系统常常需要执行复杂的业务逻辑,例如:
-
VIP 折扣计算
-
运费计算(满减或按重量)
-
最终价格计算
在示例中,我们结合 Java 与 QLExpress 混合使用:
java
Customer customer = (Customer) context.get("customer");
int vipLevel = customer.getVipLevel();
BigDecimal totalPrice = BigDecimal.ZERO;
List<Product> productList = (List<Product>) context.get("products");
for (Product product : productList) {
totalPrice = totalPrice.add(product.getPrice());
}
BigDecimal vipDiscount;
if (vipLevel >= 3) {
vipDiscount = totalPrice.multiply(new BigDecimal("0.2"));
} else if (vipLevel >= 1) {
vipDiscount = totalPrice.multiply(new BigDecimal("0.1"));
} else {
vipDiscount = BigDecimal.ZERO;
}
System.out.println("VIP折扣金额: ¥" + vipDiscount);业务扩展点:
-
VIP 规则可以通过配置文件动态加载,结合 QLExpress 表达式进行计算;
-
运费计算也可通过表达式实现动态策略,如不同城市、重量不同费率。
六、动态条件过滤
业务中常见需求:
-
过滤高价商品
-
过滤特定类别商品
-
判断集合是否满足特定条件
示例实现:
java
context.put("minPrice", 1000);
Object result = runner.execute("filter(products, 'price', '>=', minPrice)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("高价商品(>=1000): " + ((List<?>) result).size() + "个");
context.put("category", "电子产品");
result = runner.execute("filter(products, 'category', '==', category)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.println("电子产品数量: " + ((List<?>) result).size() + "个");通过自定义函数 FilterFunction,可以实现灵活的动态过滤逻辑,支持任意属性和操作符。
七、多层级数据处理与积分计算
在电商系统中,积分、优惠类型通常需要基于多个条件计算:
-
VIP 等级
-
客户城市
-
订单总价
示例:
java
Object vipCheck = runner.execute("customer.vipLevel >= 2", context, null, true, false);
Object cityCheck = runner.execute("customer.address.city == '北京'", context, null, true, false);
BigDecimal totalPriceForCheck = BigDecimal.ZERO;
for (Product product : productList) {
totalPriceForCheck = totalPriceForCheck.add(product.getPrice());
}
boolean priceCheck2 = totalPriceForCheck.compareTo(new BigDecimal("1500")) > 0;
String orderType;
if ((Boolean) vipCheck && priceCheck2 && (Boolean) cityCheck) {
orderType = "享受特殊优惠";
} else {
orderType = "普通订单";
}
System.out.println("订单类型: " + orderType);
BigDecimal basePoints = totalPriceForCheck.divide(new BigDecimal("100"))
.multiply(new BigDecimal((Integer) runner.execute("customer.vipLevel", context, null, true, false) + 1));
int cityBonus = (Boolean) cityCheck ? 50 : 0;
BigDecimal totalPoints = basePoints.add(new BigDecimal(cityBonus));
System.out.println("获得积分: " + totalPoints);这种基于多条件、多层级对象的计算方式,极大简化了业务逻辑复杂度,同时保证可读性。
八、自定义函数扩展机制
QLExpress 支持通过继承 Operator 自定义函数:
java
public static class SumFunction extends com.ql.util.express.Operator {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
List<Object> objects = (List<Object>) list[0];
String property = (String) list[1];
BigDecimal sum = BigDecimal.ZERO;
for (Object obj : objects) {
Object value = getProperty(obj, property);
if (value instanceof BigDecimal) {
sum = sum.add((BigDecimal) value);
} else if (value instanceof Number) {
sum = sum.add(BigDecimal.valueOf(((Number) value).doubleValue()));
}
}
return sum;
}
}通过自定义函数,可以将企业业务规则封装成独立模块,表达式逻辑简洁,便于运维和二次开发。
九、性能优化与缓存策略
在实际企业应用中,复杂数据结构和规则数量庞大时,需要关注性能问题:
-
InstructionSet 缓存: QLExpress 支持将表达式编译成
InstructionSet,避免每次解析,提高执行效率。 -
**上下文复用:**对象和集合可以在上下文中复用,避免重复创建。
-
**函数粒度控制:**对高频计算的逻辑,如 sum、count,可通过 Java 实现而不是表达式中每次遍历。
-
批量执行: 在批量订单处理时,可将表达式批量执行,避免重复构建
ExpressRunner实例。
十、企业级应用场景
结合上述技术,QLExpress 在以下场景中有突出优势:
-
**电商订单计算:**VIP折扣、运费规则、积分计算、优惠活动。
-
**风控与审批:**多条件风险评分、黑名单匹配、异常订单识别。
-
**智能推荐系统:**根据用户行为动态计算推荐权重、过滤不符合条件的商品。
-
**报表与统计分析:**动态计算汇总、过滤和聚合指标。
通过自定义函数与表达式结合,业务规则可配置化,运维和迭代成本大幅降低。
十一、总结
本文通过 QLExpress 复杂数据结构处理示例,展示了如何在企业应用中实现:
-
集合操作与聚合计算
-
嵌套对象属性访问
-
复杂业务逻辑计算
-
动态条件过滤
-
多层级数据处理
结合自定义函数和 Java 混合计算方式,QLExpress 不仅满足业务灵活性需求,还保证了可维护性和高性能执行。
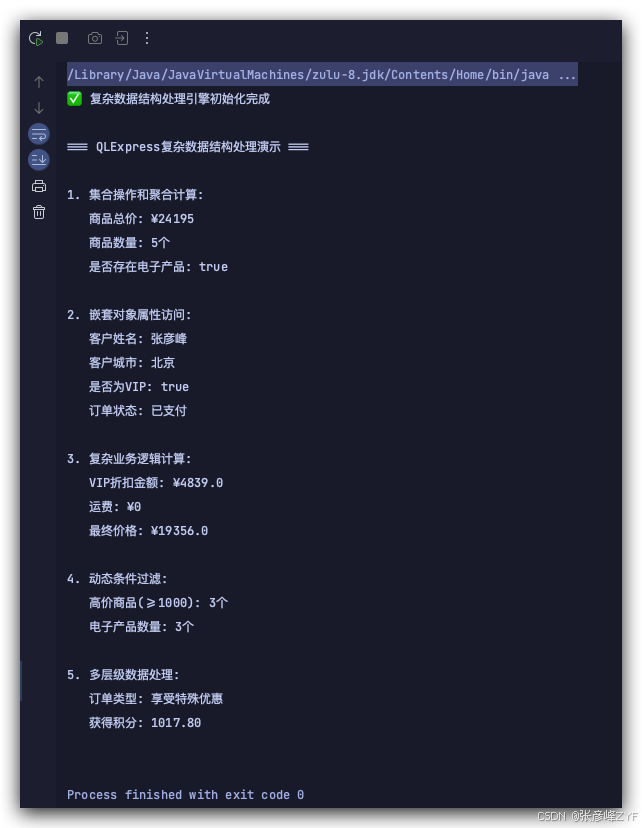
最后我们针对该开始提供的代码运行结果进行展示如下:
参考资料
-
QLExpress 官方文档
-
Rule Engines in Java
-
Enterprise Business Rules Management
-
BigDecimal 使用最佳实践
-
高性能规则引擎设计