目录
[一、QLExpress 总体架构与执行模型概览](#一、QLExpress 总体架构与执行模型概览)
七、数组与集合能力:承载"批量数据"和"规则作用对象"的核心结构
[九、工程实践总结:QLExpress 的适用边界](#九、工程实践总结:QLExpress 的适用边界)
干货分享,感谢您的阅读!
在企业级 Java 系统中,"规则"几乎无处不在:
-
风控规则
-
计费与促销策略
-
审批流转条件
-
配置化业务判断
传统做法往往将规则硬编码在 Java 代码中,导致以下问题:
-
规则变更成本高:一次规则调整就需要重新发版
-
业务与技术耦合严重:业务人员无法参与规则维护
-
系统复杂度持续上升:if-else / switch 失控
在这一背景下,规则引擎(Rule Engine)与表达式引擎(Expression Engine)成为企业系统的基础设施组件之一。
QLExpress 是阿里巴巴开源的一款 高性能、轻量级 Java 表达式语言引擎,其核心目标非常明确:
在保证性能与安全性的前提下,让业务规则"像脚本一样可配置,但又像 Java 一样可靠"。
本文将基于你提供的 QLExpress 基本语法学习模块 ,从语法、机制、工程实践三个层面,对 QLExpress 的基础能力进行一次系统性梳理与扩展,帮助读者真正达到"会用、敢用、能落地"的程度。
一、QLExpress 总体架构与执行模型概览
在进入语法细节之前,有必要先建立一个宏观认知。
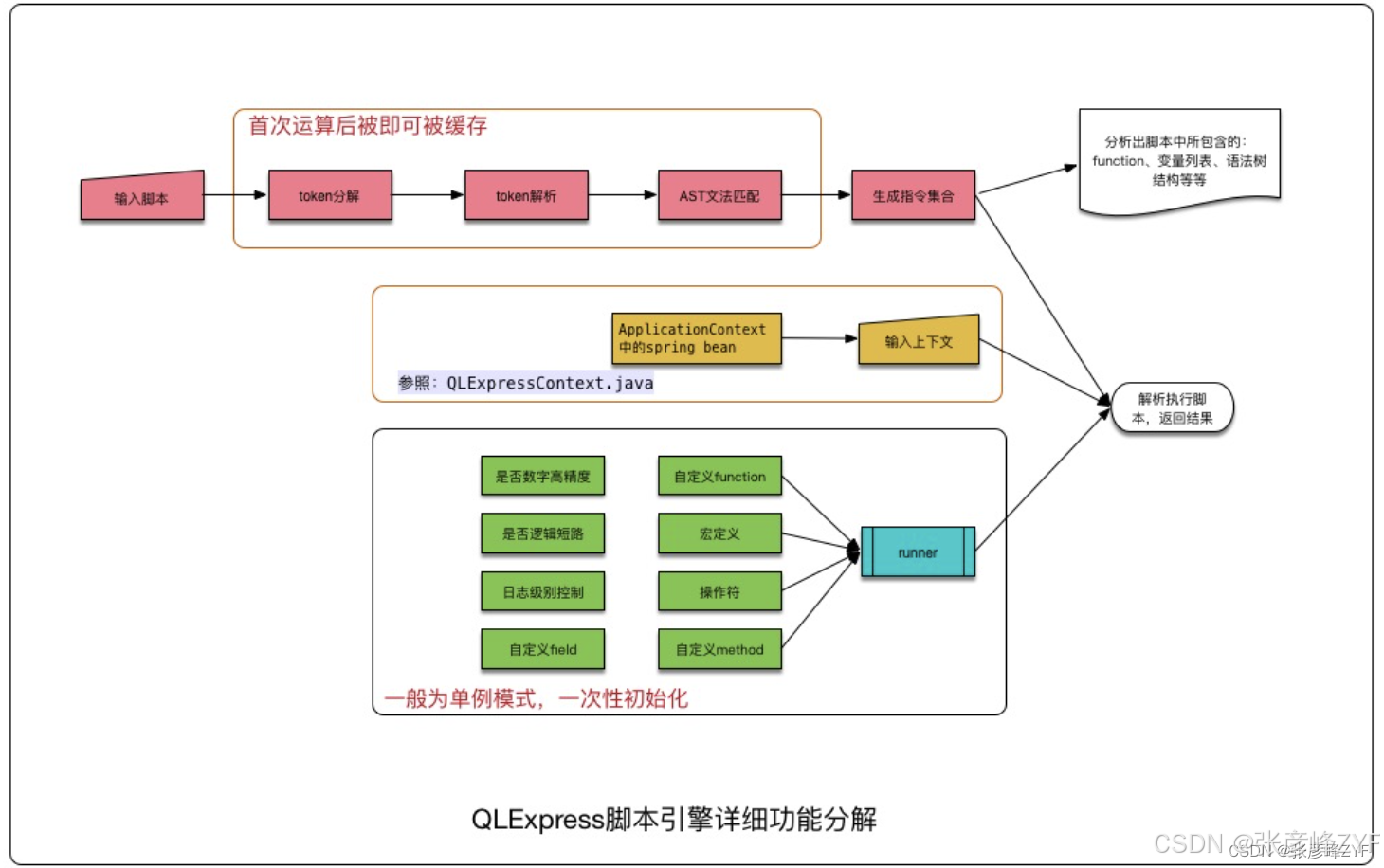
(一)核心组件
QLExpress 的执行过程,主要围绕三个核心对象展开:
-
ExpressRunner
表达式解析与执行的核心入口,负责语法解析、指令编译与运行。
-
Context(上下文)
表达式运行时的数据环境,常见实现是
DefaultContext<String, Object>。 -
Expression(表达式字符串)
即业务规则本身,例如:
Delphiage >= 18 && score >= 60
(二)执行流程简述
从工程角度看,QLExpress 的执行模型可以简化为四个阶段:
-
表达式解析(Parse)
-
语法树构建(AST)
-
指令编译(Instruction Set)
-
上下文驱动执行(Execute)
这一模式与许多脚本语言(如 Groovy、SpEL)类似,但 QLExpress 更偏向受限脚本 + 高性能执行的设计哲学。
此部分快速开启可见:掌握 QLExpress:阿里巴巴开源的业务规则动态解析神器
二、变量与数据类型:表达式世界的基础单元
在任何表达式引擎或规则引擎中,变量与数据类型都是最底层、也是最容易被低估的一环。
在 QLExpress 中,这一层设计得非常克制,但恰恰因此,它具备了极强的工程稳定性。
可以用一句话概括:QLExpress 不创造类型体系,而是最大限度复用 Java 类型系统。
我这里给出的 VariablesAndDataTypesDemo,基本可以完整覆盖了这一设计,具体代码演示如下:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.basic.variables;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress变量和数据类型基础语法演示 - 全面展示基本数据类型和变量操作
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-25 23:49
**/
public class VariablesAndDataTypesDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public VariablesAndDataTypesDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress变量和数据类型演示引擎初始化完成");
}
/**
* 演示基本数据类型
*/
public void demonstrateBasicDataTypes() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress基本数据类型演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 整数类型 (int, long)
System.out.println("🔢 1. 整数类型演示:");
context.put("intValue", 42);
context.put("longValue", 1000000L);
Object result1 = runner.execute("intValue", context, null, true, false);
Object result2 = runner.execute("longValue", context, null, true, false);
Object result3 = runner.execute("intValue + longValue", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" intValue = %s (类型: %s)%n", result1, result1.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" longValue = %s (类型: %s)%n", result2, result2.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" intValue + longValue = %s%n%n", result3);
// 2. 浮点数类型 (float, double)
System.out.println("💰 2. 浮点数类型演示:");
context.put("floatValue", 3.14f);
context.put("doubleValue", 2.718281828);
Object result4 = runner.execute("floatValue", context, null, true, false);
Object result5 = runner.execute("doubleValue", context, null, true, false);
Object result6 = runner.execute("floatValue * doubleValue", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" floatValue = %s (类型: %s)%n", result4, result4.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" doubleValue = %s (类型: %s)%n", result5, result5.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" floatValue * doubleValue = %s%n%n", result6);
// 3. BigDecimal类型 (精确小数计算)
System.out.println("🎯 3. BigDecimal精确计算演示:");
context.put("price", new BigDecimal("99.99"));
context.put("quantity", new BigDecimal("3"));
Object result7 = runner.execute("price", context, null, true, false);
Object result8 = runner.execute("price * quantity", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" price = %s (类型: %s)%n", result7, result7.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" price * quantity = %s%n%n", result8);
// 4. 布尔类型
System.out.println("✅ 4. 布尔类型演示:");
context.put("isActive", true);
context.put("isExpired", false);
Object result9 = runner.execute("isActive", context, null, true, false);
Object result10 = runner.execute("isExpired", context, null, true, false);
Object result11 = runner.execute("isActive && !isExpired", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" isActive = %s (类型: %s)%n", result9, result9.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" isExpired = %s (类型: %s)%n", result10, result10.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" isActive && !isExpired = %s%n%n", result11);
// 5. 字符串类型
System.out.println("📝 5. 字符串类型演示:");
context.put("name", "张彦峰");
context.put("title", "资深工程师");
Object result12 = runner.execute("name", context, null, true, false);
Object result13 = runner.execute("name + ' - ' + title", context, null, true, false);
Object result14 = runner.execute("name.length()", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" name = %s (类型: %s)%n", result12, result12.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" name + ' - ' + title = %s%n", result13);
System.out.printf(" name.length() = %s%n%n", result14);
// 6. 日期类型
System.out.println("📅 6. 日期类型演示:");
context.put("currentDate", new Date());
Object result15 = runner.execute("currentDate", context, null, true, false);
Object result16 = runner.execute("currentDate.getTime()", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" currentDate = %s (类型: %s)%n", result15, result15.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" currentDate.getTime() = %s%n%n", result16);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 基本数据类型演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示变量赋值和操作
*/
public void demonstrateVariableOperations() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress变量操作演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 变量赋值
System.out.println("✏️ 1. 变量赋值演示:");
runner.execute("a = 10", context, null, true, false);
runner.execute("b = 20", context, null, true, false);
runner.execute("result = a + b", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 执行: a = 10, a = %s%n", context.get("a"));
System.out.printf(" 执行: b = 20, b = %s%n", context.get("b"));
System.out.printf(" 执行: result = a + b, result = %s%n%n", context.get("result"));
// 2. 变量类型转换
System.out.println("🔄 2. 变量类型转换演示:");
context.put("strNumber", "123");
context.put("intValue", 456);
Object result1 = runner.execute("strNumber + intValue", context, null, true, false);
Object result2 = runner.execute("Integer.parseInt(strNumber) + intValue", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" strNumber + intValue = %s (字符串拼接)%n", result1);
System.out.printf(" Integer.parseInt(strNumber) + intValue = %s (数值相加)%n%n", result2);
// 3. 变量作用域和覆盖
System.out.println("🔍 3. 变量作用域演示:");
context.put("globalVar", "全局变量");
Object result3 = runner.execute("globalVar", context, null, true, false);
runner.execute("globalVar = '修改后的全局变量'", context, null, true, false);
Object result4 = runner.execute("globalVar", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 原始值: %s%n", result3);
System.out.printf(" 修改后: %s%n%n", result4);
// 4. null值处理
System.out.println("❓ 4. null值处理演示:");
context.put("nullValue", null);
context.put("normalValue", "正常值");
Object result5 = runner.execute("nullValue == null", context, null, true, false);
Object result6 = runner.execute("normalValue != null", context, null, true, false);
Object result7 = runner.execute("nullValue == null ? '空值' : nullValue", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" nullValue == null: %s%n", result5);
System.out.printf(" normalValue != null: %s%n", result6);
System.out.printf(" 三元表达式处理null: %s%n%n", result7);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 变量操作演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示复杂变量类型
*/
public void demonstrateComplexVariableTypes() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress复杂变量类型演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 数组
System.out.println("📋 1. 数组类型演示:");
int[] intArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
String[] strArray = {"apple", "banana", "orange"};
context.put("numbers", intArray);
context.put("fruits", strArray);
Object result1 = runner.execute("numbers[0]", context, null, true, false);
Object result2 = runner.execute("fruits[1]", context, null, true, false);
Object result3 = runner.execute("numbers.length", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" numbers[0] = %s%n", result1);
System.out.printf(" fruits[1] = %s%n", result2);
System.out.printf(" numbers.length = %s%n%n", result3);
// 2. 自定义对象
System.out.println("🏗️ 2. 自定义对象演示:");
Person person = new Person("张彦峰", 30, "北京");
context.put("person", person);
Object result4 = runner.execute("person.name", context, null, true, false);
Object result5 = runner.execute("person.age", context, null, true, false);
Object result6 = runner.execute("person.age >= 18", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" person.name = %s%n", result4);
System.out.printf(" person.age = %s%n", result5);
System.out.printf(" person.age >= 18 = %s%n%n", result6);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 复杂变量类型演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 运行所有演示
*/
public void runAllDemonstrations() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始QLExpress变量和数据类型完整演示...\n");
demonstrateBasicDataTypes();
demonstrateVariableOperations();
demonstrateComplexVariableTypes();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress变量和数据类型演示完成!");
System.out.println("\n📚 学习要点:");
System.out.println(" 1. QLExpress支持Java的所有基本数据类型");
System.out.println(" 2. 支持BigDecimal进行精确的小数计算");
System.out.println(" 3. 变量可以在表达式中动态赋值和修改");
System.out.println(" 4. 支持复杂的对象属性访问");
System.out.println(" 5. null值需要特殊处理,建议使用三元表达式");
}
/**
* 用于演示的Person类
*/
public static class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private String city;
public Person(String name, int age, String city) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.city = city;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
public String getCity() { return city; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("Person{name='%s', age=%d, city='%s'}", name, age, city);
}
}
/**
* 主方法 - 运行演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
VariablesAndDataTypesDemo demo = new VariablesAndDataTypesDemo();
demo.runAllDemonstrations();
}
}基本运行验证如下:
php
✅ QLExpress变量和数据类型演示引擎初始化完成
🚀 开始QLExpress变量和数据类型完整演示...
=== QLExpress基本数据类型演示 ===
🔢 1. 整数类型演示:
intValue = 42 (类型: Integer)
longValue = 1000000 (类型: Long)
intValue + longValue = 1000042
💰 2. 浮点数类型演示:
floatValue = 3.14 (类型: Float)
doubleValue = 2.718281828 (类型: Double)
floatValue * doubleValue = 8.535405225079112
🎯 3. BigDecimal精确计算演示:
price = 99.99 (类型: BigDecimal)
price * quantity = 299.97
✅ 4. 布尔类型演示:
isActive = true (类型: Boolean)
isExpired = false (类型: Boolean)
isActive && !isExpired = true
📝 5. 字符串类型演示:
name = 张彦峰 (类型: String)
name + ' - ' + title = 张彦峰 - 资深工程师
name.length() = 3
📅 6. 日期类型演示:
currentDate = Fri Jan 02 11:45:16 CST 2026 (类型: Date)
currentDate.getTime() = 1767325516349
=== QLExpress变量操作演示 ===
✏️ 1. 变量赋值演示:
执行: a = 10, a = 10
执行: b = 20, b = 20
执行: result = a + b, result = 30
🔄 2. 变量类型转换演示:
strNumber + intValue = 123456 (字符串拼接)
Integer.parseInt(strNumber) + intValue = 579 (数值相加)
🔍 3. 变量作用域演示:
原始值: 全局变量
修改后: 修改后的全局变量
❓ 4. null值处理演示:
nullValue == null: true
normalValue != null: true
三元表达式处理null: 空值
=== QLExpress复杂变量类型演示 ===
📋 1. 数组类型演示:
numbers[0] = 1
fruits[1] = banana
numbers.length = 5
🏗️ 2. 自定义对象演示:
person.name = 张彦峰
person.age = 30
person.age >= 18 = true
✅ QLExpress变量和数据类型演示完成!
📚 学习要点:
1. QLExpress支持Java的所有基本数据类型
2. 支持BigDecimal进行精确的小数计算
3. 变量可以在表达式中动态赋值和修改
4. 支持复杂的对象属性访问
5. null值需要特殊处理,建议使用三元表达式
Process finished with exit code 0通过你这份 VariablesAndDataTypesDemo,实际上已经覆盖了 QLExpress 80% 的基础认知成本。
真正的收获不在于:
- 会写
price * quantity
而在于理解了:
-
QLExpress 是 Java 类型驱动的表达式引擎
-
Context 是唯一的变量来源
-
类型安全优先于灵活性
-
BigDecimal 是业务规则中的第一选择
-
null 必须显式处理
其详细的说明可见:QLExpress变量与数据类型:表达式世界的基础单元
三、基本操作符:表达式能力的核心引擎
如果说变量与数据类型解决的是"表达式能看见什么数据",那么操作符决定的就是:
这些数据在表达式中"能做什么"以及"以什么规则做"。
在 QLExpress 中,操作符体系并没有追求"花样繁多",而是围绕业务规则最常见的计算与判断场景,提供了一套高度贴近 Java 语义、同时又适合规则编排的操作能力。
我将提供 BasicOperatorsDemo,可以清晰看出,QLExpress 的操作符体系主要分为四大类:
-
算术操作符
-
比较操作符
-
逻辑操作符
-
三元操作符
这四类,基本覆盖了 90% 以上的规则表达需求。
展示详细代码如下:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.basic.operators;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress基本操作符演示 - 全面展示算术、逻辑、比较等操作符
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-25 23:51
**/
public class BasicOperatorsDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public BasicOperatorsDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress基本操作符演示引擎初始化完成");
}
/**
* 演示算术操作符
*/
public void demonstrateArithmeticOperators() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress算术操作符演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("a", 10);
context.put("b", 3);
context.put("c", 2.5);
context.put("price", new BigDecimal("99.99"));
context.put("quantity", new BigDecimal("3"));
// 1. 基本算术操作
System.out.println("🔢 1. 基本算术操作演示:");
Object add = runner.execute("a + b", context, null, true, false);
Object subtract = runner.execute("a - b", context, null, true, false);
Object multiply = runner.execute("a * b", context, null, true, false);
Object divide = runner.execute("a / b", context, null, true, false);
Object modulo = runner.execute("a % b", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" a + b = %s + %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), add);
System.out.printf(" a - b = %s - %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), subtract);
System.out.printf(" a * b = %s * %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), multiply);
System.out.printf(" a / b = %s / %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), divide);
System.out.printf(" a %% b = %s %% %s = %s%n%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), modulo);
// 2. 浮点数运算
System.out.println("💰 2. 浮点数运算演示:");
Object floatAdd = runner.execute("a + c", context, null, true, false);
Object floatMultiply = runner.execute("a * c", context, null, true, false);
Object floatDivide = runner.execute("a / c", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" a + c = %s + %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("c"), floatAdd);
System.out.printf(" a * c = %s * %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("c"), floatMultiply);
System.out.printf(" a / c = %s / %s = %s%n%n", context.get("a"), context.get("c"), floatDivide);
// 3. BigDecimal精确运算
System.out.println("🎯 3. BigDecimal精确运算演示:");
Object bigAdd = runner.execute("price + 10.01", context, null, true, false);
Object bigMultiply = runner.execute("price * quantity", context, null, true, false);
Object bigDivide = runner.execute("price / 2", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" price + 10.01 = %s + 10.01 = %s%n", context.get("price"), bigAdd);
System.out.printf(" price * quantity = %s * %s = %s%n", context.get("price"), context.get("quantity"), bigMultiply);
System.out.printf(" price / 2 = %s / 2 = %s%n%n", context.get("price"), bigDivide);
// 4. 复合运算
System.out.println("🧮 4. 复合运算演示:");
Object complex1 = runner.execute("(a + b) * c", context, null, true, false);
Object complex2 = runner.execute("a * b + c", context, null, true, false);
Object complex3 = runner.execute("a / b + a % b", context, null, true, false);
Object complex4 = runner.execute("(a + b) / (a - b + 1)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" (a + b) * c = (%s + %s) * %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), context.get("c"), complex1);
System.out.printf(" a * b + c = %s * %s + %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), context.get("c"), complex2);
System.out.printf(" a / b + a %% b = %s / %s + %s %% %s = %s%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), context.get("a"), context.get("b"), complex3);
System.out.printf(" (a + b) / (a - b + 1) = (%s + %s) / (%s - %s + 1) = %s%n%n", context.get("a"), context.get("b"), context.get("a"), context.get("b"), complex4);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 算术操作符演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示比较操作符
*/
public void demonstrateComparisonOperators() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress比较操作符演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("x", 10);
context.put("y", 5);
context.put("z", 10);
context.put("str1", "hello");
context.put("str2", "world");
context.put("str3", "hello");
// 1. 数值比较
System.out.println("🔍 1. 数值比较操作演示:");
Object eq = runner.execute("x == z", context, null, true, false);
Object ne = runner.execute("x != y", context, null, true, false);
Object gt = runner.execute("x > y", context, null, true, false);
Object ge = runner.execute("x >= z", context, null, true, false);
Object lt = runner.execute("y < x", context, null, true, false);
Object le = runner.execute("y <= x", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" x == z: %s == %s = %s%n", context.get("x"), context.get("z"), eq);
System.out.printf(" x != y: %s != %s = %s%n", context.get("x"), context.get("y"), ne);
System.out.printf(" x > y: %s > %s = %s%n", context.get("x"), context.get("y"), gt);
System.out.printf(" x >= z: %s >= %s = %s%n", context.get("x"), context.get("z"), ge);
System.out.printf(" y < x: %s < %s = %s%n", context.get("y"), context.get("x"), lt);
System.out.printf(" y <= x: %s <= %s = %s%n%n", context.get("y"), context.get("x"), le);
// 2. 字符串比较
System.out.println("📝 2. 字符串比较操作演示:");
Object strEq = runner.execute("str1 == str3", context, null, true, false);
Object strNe = runner.execute("str1 != str2", context, null, true, false);
Object strEqMethod = runner.execute("str1.equals(str3)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" str1 == str3: '%s' == '%s' = %s%n", context.get("str1"), context.get("str3"), strEq);
System.out.printf(" str1 != str2: '%s' != '%s' = %s%n", context.get("str1"), context.get("str2"), strNe);
System.out.printf(" str1.equals(str3): '%s'.equals('%s') = %s%n%n", context.get("str1"), context.get("str3"), strEqMethod);
// 3. null值比较
System.out.println("❓ 3. null值比较操作演示:");
context.put("nullValue", null);
context.put("nonNullValue", "not null");
Object nullEq = runner.execute("nullValue == null", context, null, true, false);
Object nullNe = runner.execute("nonNullValue != null", context, null, true, false);
Object nullCompare = runner.execute("nullValue == nonNullValue", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" nullValue == null: %s == null = %s%n", context.get("nullValue"), nullEq);
System.out.printf(" nonNullValue != null: '%s' != null = %s%n", context.get("nonNullValue"), nullNe);
System.out.printf(" nullValue == nonNullValue: %s == '%s' = %s%n%n", context.get("nullValue"), context.get("nonNullValue"), nullCompare);
// 4. 复合比较
System.out.println("🔗 4. 复合比较操作演示:");
Object range1 = runner.execute("x >= 5 && x <= 15", context, null, true, false);
Object range2 = runner.execute("y < 0 || y > 20", context, null, true, false);
Object complex = runner.execute("(x > y) && (str1 != str2)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" x >= 5 && x <= 15: %s >= 5 && %s <= 15 = %s%n", context.get("x"), context.get("x"), range1);
System.out.printf(" y < 0 || y > 20: %s < 0 || %s > 20 = %s%n", context.get("y"), context.get("y"), range2);
System.out.printf(" (x > y) && (str1 != str2): (%s > %s) && ('%s' != '%s') = %s%n%n",
context.get("x"), context.get("y"), context.get("str1"), context.get("str2"), complex);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 比较操作符演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示逻辑操作符
*/
public void demonstrateLogicalOperators() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress逻辑操作符演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("isActive", true);
context.put("isExpired", false);
context.put("hasPermission", true);
context.put("isLocked", false);
context.put("age", 25);
context.put("score", 85);
// 1. 基本逻辑操作
System.out.println("🔐 1. 基本逻辑操作演示:");
Object and = runner.execute("isActive && hasPermission", context, null, true, false);
Object or = runner.execute("isExpired || isLocked", context, null, true, false);
Object not = runner.execute("!isExpired", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" isActive && hasPermission: %s && %s = %s%n", context.get("isActive"), context.get("hasPermission"), and);
System.out.printf(" isExpired || isLocked: %s || %s = %s%n", context.get("isExpired"), context.get("isLocked"), or);
System.out.printf(" !isExpired: !%s = %s%n%n", context.get("isExpired"), not);
// 2. 复合逻辑操作
System.out.println("🧩 2. 复合逻辑操作演示:");
Object complex1 = runner.execute("isActive && !isExpired && hasPermission", context, null, true, false);
Object complex2 = runner.execute("(isActive || hasPermission) && !isLocked", context, null, true, false);
Object complex3 = runner.execute("!(isExpired || isLocked)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" isActive && !isExpired && hasPermission: %s && !%s && %s = %s%n",
context.get("isActive"), context.get("isExpired"), context.get("hasPermission"), complex1);
System.out.printf(" (isActive || hasPermission) && !isLocked: (%s || %s) && !%s = %s%n",
context.get("isActive"), context.get("hasPermission"), context.get("isLocked"), complex2);
System.out.printf(" !(isExpired || isLocked): !(%s || %s) = %s%n%n",
context.get("isExpired"), context.get("isLocked"), complex3);
// 3. 逻辑与数值比较结合
System.out.println("🎯 3. 逻辑与数值比较结合演示:");
Object ageCheck = runner.execute("age >= 18 && age <= 65", context, null, true, false);
Object scoreCheck = runner.execute("score >= 60 && isActive", context, null, true, false);
Object eligibility = runner.execute("(age >= 18) && (score >= 80) && isActive && !isExpired", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" age >= 18 && age <= 65: %s >= 18 && %s <= 65 = %s%n", context.get("age"), context.get("age"), ageCheck);
System.out.printf(" score >= 60 && isActive: %s >= 60 && %s = %s%n", context.get("score"), context.get("isActive"), scoreCheck);
System.out.printf(" 综合资格检查: (%s >= 18) && (%s >= 80) && %s && !%s = %s%n%n",
context.get("age"), context.get("score"), context.get("isActive"), context.get("isExpired"), eligibility);
// 4. 短路求值演示
System.out.println("⚡ 4. 短路求值演示:");
context.put("nullObj", null);
Object shortCircuit1 = runner.execute("nullObj != null && nullObj.toString().length() > 0", context, null, true, false);
Object shortCircuit2 = runner.execute("nullObj == null || nullObj.toString().length() > 0", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 短路AND: nullObj != null && nullObj.toString().length() > 0 = %s%n", shortCircuit1);
System.out.printf(" 短路OR: nullObj == null || nullObj.toString().length() > 0 = %s%n%n", shortCircuit2);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 逻辑操作符演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示三元操作符
*/
public void demonstrateTernaryOperator() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress三元操作符演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("score", 85);
context.put("age", 17);
context.put("balance", 1000);
context.put("name", null);
// 1. 基本三元操作
System.out.println("❓ 1. 基本三元操作演示:");
Object grade = runner.execute("score >= 60 ? '及格' : '不及格'", context, null, true, false);
Object ageGroup = runner.execute("age >= 18 ? '成年人' : '未成年人'", context, null, true, false);
Object balanceStatus = runner.execute("balance > 0 ? '有余额' : '无余额'", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" score >= 60 ? '及格' : '不及格': %s >= 60 ? '及格' : '不及格' = %s%n", context.get("score"), grade);
System.out.printf(" age >= 18 ? '成年人' : '未成年人': %s >= 18 ? '成年人' : '未成年人' = %s%n", context.get("age"), ageGroup);
System.out.printf(" balance > 0 ? '有余额' : '无余额': %s > 0 ? '有余额' : '无余额' = %s%n%n", context.get("balance"), balanceStatus);
// 2. 处理null值
System.out.println("🔍 2. null值处理演示:");
Object nameCheck = runner.execute("name != null ? name : '匿名用户'", context, null, true, false);
Object nameLength = runner.execute("name != null ? name.length() : 0", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" name != null ? name : '匿名用户': %s != null ? %s : '匿名用户' = %s%n", context.get("name"), context.get("name"), nameCheck);
System.out.printf(" name != null ? name.length() : 0: %s != null ? name.length() : 0 = %s%n%n", context.get("name"), nameLength);
// 3. 嵌套三元操作
System.out.println("🎯 3. 嵌套三元操作演示:");
// 使用分步方式处理复杂的嵌套三元操作,避免QLExpress解析器限制
String levelScript =
"if (score >= 90) return '优秀';" +
"else if (score >= 80) return '良好';" +
"else if (score >= 70) return '中等';" +
"else if (score >= 60) return '及格';" +
"else return '不及格';";
Object level = runner.execute(levelScript, context, null, true, false);
// 简化嵌套三元操作
Object discount = runner.execute("age < 12 ? 0.5 : (age < 18 ? 0.7 : (age > 65 ? 0.8 : 1.0))", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 成绩等级: %s = %s%n", context.get("score"), level);
System.out.printf(" 年龄折扣: %s岁 = %s折%n%n", context.get("age"), discount);
// 4. 与其他操作符结合
System.out.println("🔗 4. 与其他操作符结合演示:");
Object finalScore = runner.execute("(score >= 60 ? score : 0) + (age >= 18 ? 5 : 0)", context, null, true, false);
Object status = runner.execute("balance > 0 && age >= 18 ? '可用' : '不可用'", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 最终得分: (score >= 60 ? score : 0) + (age >= 18 ? 5 : 0) = %s%n", finalScore);
System.out.printf(" 账户状态: balance > 0 && age >= 18 ? '可用' : '不可用' = %s%n%n", status);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 三元操作符演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 运行所有演示
*/
public void runAllDemonstrations() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始QLExpress基本操作符完整演示...\n");
demonstrateArithmeticOperators();
demonstrateComparisonOperators();
demonstrateLogicalOperators();
demonstrateTernaryOperator();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress基本操作符演示完成!");
System.out.println("\n📚 学习要点:");
System.out.println(" 1. 算术操作符: +, -, *, /, % 支持各种数值类型");
System.out.println(" 2. 比较操作符: ==, !=, >, >=, <, <= 返回布尔值");
System.out.println(" 3. 逻辑操作符: &&, ||, ! 支持短路求值");
System.out.println(" 4. 三元操作符: condition ? value1 : value2 简化条件判断");
System.out.println(" 5. 操作符优先级: 算术 > 比较 > 逻辑,使用括号改变优先级");
System.out.println(" 6. BigDecimal运算保证精度,适合金融计算");
}
/**
* 主方法 - 运行演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BasicOperatorsDemo demo = new BasicOperatorsDemo();
demo.runAllDemonstrations();
}
}基本验证打印结果如下:
python
✅ QLExpress基本操作符演示引擎初始化完成
🚀 开始QLExpress基本操作符完整演示...
=== QLExpress算术操作符演示 ===
🔢 1. 基本算术操作演示:
a + b = 10 + 3 = 13
a - b = 10 - 3 = 7
a * b = 10 * 3 = 30
a / b = 10 / 3 = 3
a % b = 10 % 3 = 1
💰 2. 浮点数运算演示:
a + c = 10 + 2.5 = 12.5
a * c = 10 * 2.5 = 25.0
a / c = 10 / 2.5 = 4.0
🎯 3. BigDecimal精确运算演示:
price + 10.01 = 99.99 + 10.01 = 110.00
price * quantity = 99.99 * 3 = 299.97
price / 2 = 99.99 / 2 = 50.00
🧮 4. 复合运算演示:
(a + b) * c = (10 + 3) * 2.5 = 32.5
a * b + c = 10 * 3 + 2.5 = 32.5
a / b + a % b = 10 / 3 + 10 % 3 = 4
(a + b) / (a - b + 1) = (10 + 3) / (10 - 3 + 1) = 1
=== QLExpress比较操作符演示 ===
🔍 1. 数值比较操作演示:
x == z: 10 == 10 = true
x != y: 10 != 5 = true
x > y: 10 > 5 = true
x >= z: 10 >= 10 = true
y < x: 5 < 10 = true
y <= x: 5 <= 10 = true
📝 2. 字符串比较操作演示:
str1 == str3: 'hello' == 'hello' = true
str1 != str2: 'hello' != 'world' = true
str1.equals(str3): 'hello'.equals('hello') = true
❓ 3. null值比较操作演示:
nullValue == null: null == null = true
nonNullValue != null: 'not null' != null = true
nullValue == nonNullValue: null == 'not null' = false
🔗 4. 复合比较操作演示:
x >= 5 && x <= 15: 10 >= 5 && 10 <= 15 = true
y < 0 || y > 20: 5 < 0 || 5 > 20 = false
(x > y) && (str1 != str2): (10 > 5) && ('hello' != 'world') = true
=== QLExpress逻辑操作符演示 ===
🔐 1. 基本逻辑操作演示:
isActive && hasPermission: true && true = true
isExpired || isLocked: false || false = false
!isExpired: !false = true
🧩 2. 复合逻辑操作演示:
isActive && !isExpired && hasPermission: true && !false && true = true
(isActive || hasPermission) && !isLocked: (true || true) && !false = true
!(isExpired || isLocked): !(false || false) = true
🎯 3. 逻辑与数值比较结合演示:
age >= 18 && age <= 65: 25 >= 18 && 25 <= 65 = true
score >= 60 && isActive: 85 >= 60 && true = true
综合资格检查: (25 >= 18) && (85 >= 80) && true && !false = true
⚡ 4. 短路求值演示:
短路AND: nullObj != null && nullObj.toString().length() > 0 = false
短路OR: nullObj == null || nullObj.toString().length() > 0 = true
=== QLExpress三元操作符演示 ===
❓ 1. 基本三元操作演示:
score >= 60 ? '及格' : '不及格': 85 >= 60 ? '及格' : '不及格' = 及格
age >= 18 ? '成年人' : '未成年人': 17 >= 18 ? '成年人' : '未成年人' = 未成年人
balance > 0 ? '有余额' : '无余额': 1000 > 0 ? '有余额' : '无余额' = 有余额
🔍 2. null值处理演示:
name != null ? name : '匿名用户': null != null ? null : '匿名用户' = 匿名用户
name != null ? name.length() : 0: null != null ? name.length() : 0 = 0
🎯 3. 嵌套三元操作演示:
成绩等级: 85 = 良好
年龄折扣: 17岁 = 0.7折
🔗 4. 与其他操作符结合演示:
最终得分: (score >= 60 ? score : 0) + (age >= 18 ? 5 : 0) = 85
账户状态: balance > 0 && age >= 18 ? '可用' : '不可用' = 不可用
✅ QLExpress基本操作符演示完成!
📚 学习要点:
1. 算术操作符: +, -, *, /, % 支持各种数值类型
2. 比较操作符: ==, !=, >, >=, <, <= 返回布尔值
3. 逻辑操作符: &&, ||, ! 支持短路求值
4. 三元操作符: condition ? value1 : value2 简化条件判断
5. 操作符优先级: 算术 > 比较 > 逻辑,使用括号改变优先级
6. BigDecimal运算保证精度,适合金融计算
Process finished with exit code 0通过演示可以得出几个非常明确的结论:
-
QLExpress 的操作符体系高度贴近 Java
-
算术、比较、逻辑、三元构成了规则表达的最小完备集
-
BigDecimal 是规则计算中的首选数值类型
-
逻辑短路是规则安全的基础保障
-
三元操作符应以"清晰"为第一原则,而非"炫技"
具体详细说明可见:QLExpress基本操作符:表达式能力的核心引擎
四、控制流程:让规则具备"过程性思维"
在 QLExpress 中,控制流程(Control Flow)是规则从"表达式"迈向"逻辑程序"的关键能力。
如果说操作符解决的是"怎么算",那么控制流程解决的就是"按什么顺序算、在什么条件下算、算到什么时候停"。
通过 if / else、for、while、break、continue 等控制结构,QLExpress 规则脚本已经具备了接近 Java 的过程化执行能力,这也是它区别于纯声明式规则语言的重要特征。
我这里给出的 VariablesAndDataTypesDemo,基本可以完整覆盖了这一设计,具体代码演示如下:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.basic.controlflow;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress控制流程演示 - 全面展示条件判断和循环控制
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-25 23:53
**/
public class ControlFlowDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public ControlFlowDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress控制流程演示引擎初始化完成");
}
/**
* 演示if-else条件判断
*/
public void demonstrateIfElseStatements() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress条件判断演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 简单if判断
System.out.println("🔀 1. 简单if条件判断演示:");
context.put("score", 85);
context.put("age", 20);
context.put("isActive", true);
String ifScript1 =
"if (score >= 60) {" +
" result = '及格';" +
"} else {" +
" result = '不及格';" +
"}" +
"return result;";
Object result1 = runner.execute(ifScript1, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" if (score >= 60) 判断: score=%s, 结果=%s%n%n", context.get("score"), result1);
// 2. 多重if-else判断
System.out.println("🎯 2. 多重if-else判断演示:");
String ifScript2 =
"if (score >= 90) {" +
" grade = '优秀';" +
"} else if (score >= 80) {" +
" grade = '良好';" +
"} else if (score >= 70) {" +
" grade = '中等';" +
"} else if (score >= 60) {" +
" grade = '及格';" +
"} else {" +
" grade = '不及格';" +
"}" +
"return grade;";
Object result2 = runner.execute(ifScript2, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 多重if-else判断: score=%s, 等级=%s%n%n", context.get("score"), result2);
// 3. 嵌套if判断
System.out.println("🏗️ 3. 嵌套if判断演示:");
String ifScript3 =
"if (age >= 18) {" +
" if (isActive) {" +
" if (score >= 80) {" +
" status = '优秀成年用户';" +
" } else {" +
" status = '普通成年用户';" +
" }" +
" } else {" +
" status = '非活跃成年用户';" +
" }" +
"} else {" +
" if (score >= 80) {" +
" status = '优秀未成年用户';" +
" } else {" +
" status = '普通未成年用户';" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return status;";
Object result3 = runner.execute(ifScript3, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 嵌套if判断: age=%s, isActive=%s, score=%s%n",
context.get("age"), context.get("isActive"), context.get("score"));
System.out.printf(" 用户状态: %s%n%n", result3);
// 4. 复合条件判断
System.out.println("🔗 4. 复合条件判断演示:");
context.put("hasPermission", true);
context.put("balance", 1000);
String ifScript4 =
"if (age >= 18 && isActive && hasPermission) {" +
" if (balance > 500) {" +
" permission = '高级权限';" +
" } else if (balance > 100) {" +
" permission = '中级权限';" +
" } else {" +
" permission = '基础权限';" +
" }" +
"} else {" +
" permission = '无权限';" +
"}" +
"return permission;";
Object result4 = runner.execute(ifScript4, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 复合条件: age=%s, isActive=%s, hasPermission=%s, balance=%s%n",
context.get("age"), context.get("isActive"), context.get("hasPermission"), context.get("balance"));
System.out.printf(" 权限级别: %s%n%n", result4);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ if-else条件判断演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示for循环
*/
public void demonstrateForLoops() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress for循环演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 基本for循环
System.out.println("🔄 1. 基本for循环演示:");
String forScript1 =
"sum = 0;" +
"for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {" +
" sum = sum + i;" +
"}" +
"return sum;";
Object result1 = runner.execute(forScript1, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 计算1到10的和: sum = %s%n%n", result1);
// 2. for循环处理数组
System.out.println("📋 2. for循环处理数组演示:");
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
context.put("numbers", numbers);
String forScript2 =
"sum = 0;" +
"count = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {" +
" if (numbers[i] % 2 == 0) {" +
" sum = sum + numbers[i];" +
" count = count + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '偶数和: ' + sum + ', 偶数个数: ' + count;";
Object result2 = runner.execute(forScript2, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 数组偶数处理: %s%n%n", result2);
// 3. 嵌套for循环
System.out.println("🏗️ 3. 嵌套for循环演示:");
String forScript3 =
"result = '';" +
"for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {" +
" for (j = 1; j <= i; j++) {" +
" result = result + '*';" +
" }" +
" result = result + '\\n';" +
"}" +
"return result;";
Object result3 = runner.execute(forScript3, context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(" 星号三角形:");
System.out.print(result3);
System.out.println();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ for循环演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示while循环
*/
public void demonstrateWhileLoops() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress while循环演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 基本while循环
System.out.println("🔄 1. 基本while循环演示:");
String whileScript1 =
"sum = 0;" +
"for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {" +
" sum = sum + i;" +
"}" +
"return sum;";
Object result1 = runner.execute(whileScript1, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" while循环计算1到10的和: %s%n%n", result1);
// 2. while循环查找
System.out.println("🔍 2. while循环查找演示:");
String whileScript2 =
"n = 100;" +
"count = 0;" +
"for (step = 0; step < 200 && n > 1; step++) {" +
" if (n % 2 == 0) {" +
" n = n / 2;" +
" } else {" +
" n = 3 * n + 1;" +
" }" +
" count = count + 1;" +
" if (count > 100) {" +
" break;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '考拉兹猜想: 从100到1需要 ' + count + ' 步';";
Object result2 = runner.execute(whileScript2, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", result2);
// 3. while循环与复杂条件
System.out.println("🔗 3. while循环复杂条件演示:");
context.put("data", new int[]{3, 7, 2, 9, 1, 8, 4, 6, 5});
String whileScript3 =
"maxValue = 0;" +
"maxIndex = -1;" +
"searchCount = 0;" +
"for (index = 0; index < data.length; index++) {" +
" currentValue = data[index];" +
" searchCount = searchCount + 1;" +
" if (currentValue > maxValue) {" +
" maxValue = currentValue;" +
" maxIndex = index;" +
" }" +
" if (maxValue >= 8) {" +
" break;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '找到最大值: ' + maxValue + ', 位置: ' + maxIndex + ', 搜索了 ' + searchCount + ' 个元素';";
Object result3 = runner.execute(whileScript3, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 复杂条件搜索: %s%n%n", result3);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ while循环演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示循环与条件的结合使用
*/
public void demonstrateComplexControlFlow() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress复杂控制流演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 循环中的条件判断
System.out.println("🎲 1. 循环中的条件判断演示:");
String complexScript1 =
"results = '';" +
"primeCount = 0;" +
"for (num = 2; num <= 30; num++) {" +
" isPrime = true;" +
" for (i = 2; i * i <= num; i++) {" +
" if (num % i == 0) {" +
" isPrime = false;" +
" break;" +
" }" +
" }" +
" if (isPrime) {" +
" if (primeCount > 0) {" +
" results = results + ', ';" +
" }" +
" results = results + num;" +
" primeCount = primeCount + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '30以内的质数: ' + results + ' (共' + primeCount + '个)';";
Object result1 = runner.execute(complexScript1, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", result1);
// 2. 多层嵌套控制流
System.out.println("🏗️ 2. 多层嵌套控制流演示:");
context.put("matrix", new int[][]{{1,2,3}, {4,5,6}, {7,8,9}});
String complexScript2 =
"diagonal1 = 0;" +
"diagonal2 = 0;" +
"evenCount = 0;" +
"oddCount = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {" +
" for (j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {" +
" value = matrix[i][j];" +
" if (value % 2 == 0) {" +
" evenCount = evenCount + 1;" +
" } else {" +
" oddCount = oddCount + 1;" +
" }" +
" if (i == j) {" +
" diagonal1 = diagonal1 + value;" +
" }" +
" if (i + j == matrix.length - 1) {" +
" diagonal2 = diagonal2 + value;" +
" }" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '主对角线和: ' + diagonal1 + ', 副对角线和: ' + diagonal2 + " +
" ', 偶数个数: ' + evenCount + ', 奇数个数: ' + oddCount;";
Object result2 = runner.execute(complexScript2, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 矩阵分析: %s%n%n", result2);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 复杂控制流演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 运行所有演示
*/
public void runAllDemonstrations() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始QLExpress控制流程完整演示...\n");
demonstrateIfElseStatements();
demonstrateForLoops();
demonstrateWhileLoops();
demonstrateComplexControlFlow();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress控制流程演示完成!");
System.out.println("\n📚 学习要点:");
System.out.println(" 1. if-else条件判断支持多重嵌套和复合条件");
System.out.println(" 2. for循环适合已知次数的迭代,支持break和continue");
System.out.println(" 3. while循环适合条件控制的迭代");
System.out.println(" 4. 控制流可以任意嵌套组合,实现复杂逻辑");
System.out.println(" 5. 使用break和continue控制循环执行流程");
System.out.println(" 6. 注意防止无限循环,设置合理的退出条件");
}
/**
* 主方法 - 运行演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ControlFlowDemo demo = new ControlFlowDemo();
demo.runAllDemonstrations();
}
}基本运行验证如下:
cs
✅ QLExpress控制流程演示引擎初始化完成
🚀 开始QLExpress控制流程完整演示...
=== QLExpress条件判断演示 ===
🔀 1. 简单if条件判断演示:
if (score >= 60) 判断: score=85, 结果=及格
🎯 2. 多重if-else判断演示:
多重if-else判断: score=85, 等级=良好
🏗️ 3. 嵌套if判断演示:
嵌套if判断: age=20, isActive=true, score=85
用户状态: 优秀成年用户
🔗 4. 复合条件判断演示:
复合条件: age=20, isActive=true, hasPermission=true, balance=1000
权限级别: 高级权限
=== QLExpress for循环演示 ===
🔄 1. 基本for循环演示:
计算1到10的和: sum = 55
📋 2. for循环处理数组演示:
数组偶数处理: 偶数和: 30, 偶数个数: 5
🏗️ 3. 嵌套for循环演示:
星号三角形:
*n**n***n****n*****n
=== QLExpress while循环演示 ===
🔄 1. 基本while循环演示:
while循环计算1到10的和: 55
🔍 2. while循环查找演示:
考拉兹猜想: 从100到1需要 25 步
🔗 3. while循环复杂条件演示:
复杂条件搜索: 找到最大值: 9, 位置: 3, 搜索了 4 个元素
=== QLExpress复杂控制流演示 ===
🎲 1. 循环中的条件判断演示:
30以内的质数: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29 (共10个)
🏗️ 2. 多层嵌套控制流演示:
矩阵分析: 主对角线和: 15, 副对角线和: 15, 偶数个数: 4, 奇数个数: 5
✅ QLExpress控制流程演示完成!
📚 学习要点:
1. if-else条件判断支持多重嵌套和复合条件
2. for循环适合已知次数的迭代,支持break和continue
3. while循环适合条件控制的迭代
4. 控制流可以任意嵌套组合,实现复杂逻辑
5. 使用break和continue控制循环执行流程
6. 注意防止无限循环,设置合理的退出条件
Process finished with exit code 0整体控制流程在 QLExpress 中的定位如下:
| 能力 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| if / else | 决策与分支 |
| for / while | 批量与迭代 |
| break / continue | 流程控制 |
| 嵌套结构 | 复杂业务建模 |
一句话总结:控制流程让 QLExpress 从"会算"升级为"会思考、会决策、会推导"的规则执行引擎。
具体详细内容可见:QLExpress控制流程:让规则具备"过程性思维"
五、内置函数体系:避免重复造轮子
在规则引擎的设计中,一个经常被忽视但极其关键的问题是:
规则到底要"写到什么程度"?
如果规则脚本需要频繁实现:
-
数学计算
-
字符串处理
-
时间换算
-
类型转换
-
集合操作
那么规则系统将迅速演变为"脚本化业务代码",维护成本和出错概率都会急剧上升。
QLExpress 在这一点上的核心设计理念非常明确:
规则不重复造轮子,优先复用 Java 生态中成熟、稳定的函数能力。
这正是其内置函数体系(Built-in Functions)存在的意义。
我这里给出的 BuiltinFunctionsDemo,基本可以完整覆盖了这一设计,具体代码演示如下:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.basic.functions;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress内置函数演示 - 全面展示数学、字符串、日期等内置函数
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-25 23:52
**/
public class BuiltinFunctionsDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public BuiltinFunctionsDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress内置函数演示引擎初始化完成");
}
/**
* 演示数学函数
*/
public void demonstrateMathFunctions() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress数学函数演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("x", 16.0);
context.put("y", -3.7);
context.put("angle", 45.0);
// 1. 基本数学函数
System.out.println("🔢 1. 基本数学函数演示:");
Object abs = runner.execute("Math.abs(y)", context, null, true, false);
Object sqrt = runner.execute("Math.sqrt(x)", context, null, true, false);
Object pow = runner.execute("Math.pow(2, 3)", context, null, true, false);
Object max = runner.execute("Math.max(x, Math.abs(y))", context, null, true, false);
Object min = runner.execute("Math.min(x, Math.abs(y))", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" Math.abs(%s) = %s (绝对值)%n", context.get("y"), abs);
System.out.printf(" Math.sqrt(%s) = %s (平方根)%n", context.get("x"), sqrt);
System.out.printf(" Math.pow(2, 3) = %s (幂运算)%n", pow);
System.out.printf(" Math.max(%s, %s) = %s (最大值)%n", context.get("x"), abs, max);
System.out.printf(" Math.min(%s, %s) = %s (最小值)%n%n", context.get("x"), abs, min);
// 2. 舍入函数
System.out.println("🎯 2. 舍入函数演示:");
context.put("decimal", 3.7856);
Object ceil = runner.execute("Math.ceil(decimal)", context, null, true, false);
Object floor = runner.execute("Math.floor(decimal)", context, null, true, false);
Object round = runner.execute("Math.round(decimal)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" Math.ceil(%s) = %s (向上取整)%n", context.get("decimal"), ceil);
System.out.printf(" Math.floor(%s) = %s (向下取整)%n", context.get("decimal"), floor);
System.out.printf(" Math.round(%s) = %s (四舍五入)%n%n", context.get("decimal"), round);
// 3. 三角函数
System.out.println("📐 3. 三角函数演示:");
Object sin = runner.execute("Math.sin(Math.toRadians(angle))", context, null, true, false);
Object cos = runner.execute("Math.cos(Math.toRadians(angle))", context, null, true, false);
Object tan = runner.execute("Math.tan(Math.toRadians(angle))", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" Math.sin(%s°) = %.4f%n", context.get("angle"), sin);
System.out.printf(" Math.cos(%s°) = %.4f%n", context.get("angle"), cos);
System.out.printf(" Math.tan(%s°) = %.4f%n%n", context.get("angle"), tan);
// 4. 对数和指数函数
System.out.println("📊 4. 对数和指数函数演示:");
Object log = runner.execute("Math.log(x)", context, null, true, false);
Object log10 = runner.execute("Math.log10(x)", context, null, true, false);
Object exp = runner.execute("Math.exp(1)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" Math.log(%s) = %s (自然对数)%n", context.get("x"), log);
System.out.printf(" Math.log10(%s) = %s (常用对数)%n", context.get("x"), log10);
System.out.printf(" Math.exp(1) = %s (e的1次方)%n%n", exp);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 数学函数演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示字符串函数
*/
public void demonstrateStringFunctions() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress字符串函数演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("text", "Hello QLExpress World");
context.put("name", " 张彦峰 ");
context.put("email", "zhangyanfeng@example.com");
// 1. 基本字符串函数
System.out.println("📝 1. 基本字符串函数演示:");
Object length = runner.execute("text.length()", context, null, true, false);
Object upper = runner.execute("text.toUpperCase()", context, null, true, false);
Object lower = runner.execute("text.toLowerCase()", context, null, true, false);
Object trim = runner.execute("name.trim()", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.length() = %s%n", context.get("text"), length);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.toUpperCase() = %s%n", context.get("text"), upper);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.toLowerCase() = %s%n", context.get("text"), lower);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.trim() = '%s'%n%n", context.get("name"), trim);
// 2. 字符串查找函数
System.out.println("🔍 2. 字符串查找函数演示:");
Object indexOf = runner.execute("text.indexOf('QL')", context, null, true, false);
Object lastIndexOf = runner.execute("text.lastIndexOf(\"o\")", context, null, true, false);
Object contains = runner.execute("text.contains('Express')", context, null, true, false);
Object startsWith = runner.execute("text.startsWith('Hello')", context, null, true, false);
Object endsWith = runner.execute("text.endsWith('World')", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.indexOf('QL') = %s%n", context.get("text"), indexOf);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.lastIndexOf('o') = %s%n", context.get("text"), lastIndexOf);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.contains('Express') = %s%n", context.get("text"), contains);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.startsWith('Hello') = %s%n", context.get("text"), startsWith);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.endsWith('World') = %s%n%n", context.get("text"), endsWith);
// 3. 字符串截取函数
System.out.println("✂️ 3. 字符串截取函数演示:");
Object substring1 = runner.execute("text.substring(6)", context, null, true, false);
Object substring2 = runner.execute("text.substring(6, 15)", context, null, true, false);
Object charAt = runner.execute("text.charAt(0)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.substring(6) = '%s'%n", context.get("text"), substring1);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.substring(6, 15) = '%s'%n", context.get("text"), substring2);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.charAt(0) = '%s'%n%n", context.get("text"), charAt);
// 4. 字符串替换和分割函数
System.out.println("🔄 4. 字符串替换和分割函数演示:");
Object replace = runner.execute("text.replace('World', '世界')", context, null, true, false);
Object replaceAll = runner.execute("text.replaceAll(\"[aeiou]\", \"*\")", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.replace('World', '世界') = '%s'%n", context.get("text"), replace);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.replaceAll('[aeiou]', '*') = '%s'%n%n", context.get("text"), replaceAll);
// 5. 字符串分割演示
System.out.println("📋 5. 字符串分割演示:");
context.put("csv", "apple,banana,orange,grape");
String[] parts = (String[]) runner.execute("csv.split(\",\")", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" '%s'.split(',') = [", context.get("csv"));
for (int i = 0; i < parts.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("'%s'", parts[i]);
if (i < parts.length - 1) System.out.print(", ");
}
System.out.println("]");
Object join = runner.execute("String.join(' | ', csv.split(\",\"))", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 重新连接: %s%n%n", join);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 字符串函数演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示日期时间函数
*/
public void demonstrateDateTimeFunctions() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress日期时间函数演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
Date currentDate = new Date();
context.put("now", currentDate);
context.put("birthYear", 1990);
// 1. 基本日期函数
System.out.println("📅 1. 基本日期函数演示:");
Object getTime = runner.execute("now.getTime()", context, null, true, false);
Object year = runner.execute("now.getYear() + 1900", context, null, true, false);
Object month = runner.execute("now.getMonth() + 1", context, null, true, false);
Object day = runner.execute("now.getDate()", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 当前时间: %s%n", currentDate);
System.out.printf(" 时间戳: %s%n", getTime);
System.out.printf(" 年份: %s%n", year);
System.out.printf(" 月份: %s%n", month);
System.out.printf(" 日期: %s%n%n", day);
// 2. 时间计算
System.out.println("⏰ 2. 时间计算演示:");
Object age = runner.execute("(now.getYear() + 1900) - birthYear", context, null, true, false);
Object millisecondsPerDay = runner.execute("24 * 60 * 60 * 1000", context, null, true, false);
Object daysSinceEpoch = runner.execute("now.getTime() / (24 * 60 * 60 * 1000)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 根据出生年份计算年龄: %s岁%n", age);
System.out.printf(" 一天的毫秒数: %s%n", millisecondsPerDay);
System.out.printf(" 距离1970年的天数: %s天%n%n", daysSinceEpoch);
// 3. 日期格式化(通过字符串操作)
System.out.println("🎨 3. 日期格式化演示:");
String formatScript =
"year = now.getYear() + 1900;" +
"month = now.getMonth() + 1;" +
"day = now.getDate();" +
"hour = now.getHours();" +
"minute = now.getMinutes();" +
"second = now.getSeconds();" +
"return year + \"-\" + " +
"(month < 10 ? \"0\" + month : month + \"\") + \"-\" + " +
"(day < 10 ? \"0\" + day : day + \"\") + \" \" + " +
"(hour < 10 ? \"0\" + hour : hour + \"\") + \":\" + " +
"(minute < 10 ? \"0\" + minute : minute + \"\") + \":\" + " +
"(second < 10 ? \"0\" + second : second + \"\");";
Object formattedDate = runner.execute(formatScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 格式化日期时间: %s%n%n", formattedDate);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 日期时间函数演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示类型转换函数
*/
public void demonstrateTypeConversionFunctions() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress类型转换函数演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("strNumber", "123");
context.put("strFloat", "45.67");
context.put("intValue", 789);
context.put("doubleValue", 3.14159);
context.put("boolStr", "true");
// 1. 字符串转数值
System.out.println("🔄 1. 字符串转数值演示:");
Object parseInt = runner.execute("Integer.parseInt(strNumber)", context, null, true, false);
Object parseDouble = runner.execute("Double.parseDouble(strFloat)", context, null, true, false);
Object parseBoolean = runner.execute("Boolean.parseBoolean(boolStr)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" Integer.parseInt('%s') = %s (类型: %s)%n",
context.get("strNumber"), parseInt, parseInt.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" Double.parseDouble('%s') = %s (类型: %s)%n",
context.get("strFloat"), parseDouble, parseDouble.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.printf(" Boolean.parseBoolean('%s') = %s (类型: %s)%n%n",
context.get("boolStr"), parseBoolean, parseBoolean.getClass().getSimpleName());
// 2. 数值转字符串
System.out.println("📝 2. 数值转字符串演示:");
Object intToString = runner.execute("Integer.toString(intValue)", context, null, true, false);
Object doubleToString = runner.execute("Double.toString(doubleValue)", context, null, true, false);
Object stringValueOf = runner.execute("String.valueOf(intValue)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" Integer.toString(%s) = '%s'%n", context.get("intValue"), intToString);
System.out.printf(" Double.toString(%s) = '%s'%n", context.get("doubleValue"), doubleToString);
System.out.printf(" String.valueOf(%s) = '%s'%n%n", context.get("intValue"), stringValueOf);
// 3. BigDecimal转换
System.out.println("💰 3. BigDecimal转换演示:");
// 使用Java代码创建BigDecimal对象,因为QLExpress可能不支持静态方法调用
BigDecimal bigFromString = new BigDecimal(context.get("strFloat").toString());
BigDecimal bigFromDouble = new BigDecimal(context.get("doubleValue").toString());
System.out.printf(" new BigDecimal('%s') = %s%n", context.get("strFloat"), bigFromString);
System.out.printf(" new BigDecimal(%s) = %s%n%n", context.get("doubleValue"), bigFromDouble);
// 4. 类型检查函数
System.out.println("🔍 4. 类型检查演示:");
context.put("obj1", "Hello");
context.put("obj2", 123);
context.put("obj3", null);
Object instanceof1 = runner.execute("obj1 instanceof String", context, null, true, false);
Object instanceof2 = runner.execute("obj2 instanceof Integer", context, null, true, false);
Object isNull = runner.execute("obj3 == null", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" '%s' instanceof String = %s%n", context.get("obj1"), instanceof1);
System.out.printf(" %s instanceof Integer = %s%n", context.get("obj2"), instanceof2);
System.out.printf(" obj3 == null = %s%n%n", isNull);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 类型转换函数演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示集合操作函数
*/
public void demonstrateCollectionFunctions() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress集合操作函数演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
List<String> fruits = new ArrayList<>();
fruits.add("apple");
fruits.add("banana");
fruits.add("orange");
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
context.put("fruits", fruits);
context.put("numbers", numbers);
// 1. 集合基本操作
System.out.println("📋 1. 集合基本操作演示:");
Object size = runner.execute("fruits.size()", context, null, true, false);
Object get = runner.execute("fruits.get(0)", context, null, true, false);
Object contains = runner.execute("fruits.contains('apple')", context, null, true, false);
Object indexOf = runner.execute("fruits.indexOf('banana')", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" fruits.size() = %s%n", size);
System.out.printf(" fruits.get(0) = %s%n", get);
System.out.printf(" fruits.contains('apple') = %s%n", contains);
System.out.printf(" fruits.indexOf('banana') = %s%n%n", indexOf);
// 2. 数组操作
System.out.println("🔢 2. 数组操作演示:");
Object arrayLength = runner.execute("numbers.length", context, null, true, false);
Object arrayElement = runner.execute("numbers[2]", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" numbers.length = %s%n", arrayLength);
System.out.printf(" numbers[2] = %s%n%n", arrayElement);
// 3. 集合遍历和处理
System.out.println("🔄 3. 集合遍历演示:");
String sumScript =
"sum = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {" +
" sum = sum + numbers[i];" +
"}" +
"return sum;";
Object sum = runner.execute(sumScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 数组元素求和: %s%n", sum);
String joinScript =
"result = '';" +
"for (i = 0; i < fruits.size(); i++) {" +
" if (i > 0) result = result + ', ';" +
" result = result + fruits.get(i);" +
"}" +
"return result;";
Object joined = runner.execute(joinScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 集合元素连接: %s%n%n", joined);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 集合操作函数演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 运行所有演示
*/
public void runAllDemonstrations() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始QLExpress内置函数完整演示...\n");
demonstrateMathFunctions();
demonstrateStringFunctions();
demonstrateDateTimeFunctions();
demonstrateTypeConversionFunctions();
demonstrateCollectionFunctions();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress内置函数演示完成!");
System.out.println("\n📚 学习要点:");
System.out.println(" 1. 数学函数: Math.abs, Math.sqrt, Math.pow, Math.max, Math.min等");
System.out.println(" 2. 字符串函数: length, substring, indexOf, replace, split等");
System.out.println(" 3. 日期函数: getTime, getYear, getMonth, getDate等");
System.out.println(" 4. 类型转换: parseInt, parseDouble, toString, valueOf等");
System.out.println(" 5. 集合操作: size, get, contains, indexOf等");
System.out.println(" 6. QLExpress支持Java标准库的大部分函数和方法");
}
/**
* 主方法 - 运行演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuiltinFunctionsDemo demo = new BuiltinFunctionsDemo();
demo.runAllDemonstrations();
}
}基本运行验证如下:
Go
✅ QLExpress内置函数演示引擎初始化完成
🚀 开始QLExpress内置函数完整演示...
=== QLExpress数学函数演示 ===
🔢 1. 基本数学函数演示:
Math.abs(-3.7) = 3.7 (绝对值)
Math.sqrt(16.0) = 4.0 (平方根)
Math.pow(2, 3) = 8.0 (幂运算)
Math.max(16.0, 3.7) = 16.0 (最大值)
Math.min(16.0, 3.7) = 3.7 (最小值)
🎯 2. 舍入函数演示:
Math.ceil(3.7856) = 4.0 (向上取整)
Math.floor(3.7856) = 3.0 (向下取整)
Math.round(3.7856) = 4 (四舍五入)
📐 3. 三角函数演示:
Math.sin(45.0°) = 0.7071
Math.cos(45.0°) = 0.7071
Math.tan(45.0°) = 1.0000
📊 4. 对数和指数函数演示:
Math.log(16.0) = 2.772588722239781 (自然对数)
Math.log10(16.0) = 1.2041199826559248 (常用对数)
Math.exp(1) = 2.7182818284590455 (e的1次方)
=== QLExpress字符串函数演示 ===
📝 1. 基本字符串函数演示:
'Hello QLExpress World'.length() = 21
'Hello QLExpress World'.toUpperCase() = HELLO QLEXPRESS WORLD
'Hello QLExpress World'.toLowerCase() = hello qlexpress world
' 张彦峰 '.trim() = '张彦峰'
🔍 2. 字符串查找函数演示:
'Hello QLExpress World'.indexOf('QL') = 6
'Hello QLExpress World'.lastIndexOf('o') = 17
'Hello QLExpress World'.contains('Express') = true
'Hello QLExpress World'.startsWith('Hello') = true
'Hello QLExpress World'.endsWith('World') = true
✂️ 3. 字符串截取函数演示:
'Hello QLExpress World'.substring(6) = 'QLExpress World'
'Hello QLExpress World'.substring(6, 15) = 'QLExpress'
'Hello QLExpress World'.charAt(0) = 'H'
🔄 4. 字符串替换和分割函数演示:
'Hello QLExpress World'.replace('World', '世界') = 'Hello QLExpress 世界'
'Hello QLExpress World'.replaceAll('[aeiou]', '*') = 'H*ll* QLExpr*ss W*rld'
📋 5. 字符串分割演示:
'apple,banana,orange,grape'.split(',') = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape']
重新连接: apple | banana | orange | grape
=== QLExpress日期时间函数演示 ===
📅 1. 基本日期函数演示:
当前时间: Fri Jan 02 14:17:16 CST 2026
时间戳: 1767334636483
年份: 2026
月份: 1
日期: 2
⏰ 2. 时间计算演示:
根据出生年份计算年龄: 36岁
一天的毫秒数: 86400000
距离1970年的天数: 20455天
🎨 3. 日期格式化演示:
格式化日期时间: 2026-01-02 14:17:16
=== QLExpress类型转换函数演示 ===
🔄 1. 字符串转数值演示:
Integer.parseInt('123') = 123 (类型: Integer)
Double.parseDouble('45.67') = 45.67 (类型: Double)
Boolean.parseBoolean('true') = true (类型: Boolean)
📝 2. 数值转字符串演示:
Integer.toString(789) = '789'
Double.toString(3.14159) = '3.14159'
String.valueOf(789) = '789'
💰 3. BigDecimal转换演示:
new BigDecimal('45.67') = 45.67
new BigDecimal(3.14159) = 3.14159
🔍 4. 类型检查演示:
'Hello' instanceof String = true
123 instanceof Integer = true
obj3 == null = true
=== QLExpress集合操作函数演示 ===
📋 1. 集合基本操作演示:
fruits.size() = 3
fruits.get(0) = apple
fruits.contains('apple') = true
fruits.indexOf('banana') = 1
🔢 2. 数组操作演示:
numbers.length = 5
numbers[2] = 3
🔄 3. 集合遍历演示:
数组元素求和: 15
集合元素连接: apple, banana, orange
✅ QLExpress内置函数演示完成!
📚 学习要点:
1. 数学函数: Math.abs, Math.sqrt, Math.pow, Math.max, Math.min等
2. 字符串函数: length, substring, indexOf, replace, split等
3. 日期函数: getTime, getYear, getMonth, getDate等
4. 类型转换: parseInt, parseDouble, toString, valueOf等
5. 集合操作: size, get, contains, indexOf等
6. QLExpress支持Java标准库的大部分函数和方法
Process finished with exit code 0从示例可以清晰看出,QLExpress 的函数体系并不是"自造一套 DSL 函数",而是遵循三条原则:
-
最大限度复用 Java 标准库
-
方法调用语义与 Java 保持一致
-
规则脚本只关心"使用",不关心"实现"
因此,在 QLExpress 中:
-
Math.abs -
String.substring -
Date.getTime -
List.size -
Integer.parseInt
这些都是 Java 原生能力的直接暴露。这使得 QLExpress 的学习成本、可预测性和稳定性极高。
具体详细用法可见:QLExpress内置函数体系:避免重复造轮子
六、字符串操作:规则工程中的"高频战场"
在规则引擎、动态表达式、业务配置化等场景中,字符串处理能力几乎贯穿所有逻辑。QLExpress 作为一款面向 Java 生态的高性能表达式引擎,其字符串模型并非"附属能力",而是深度融入语言语义层的一等公民。
我们将围绕 QLExpress 中的字符串能力,从表达式语义、执行模型、常用操作模式、复杂处理技巧以及工程实践建议五个层面进行系统讲解,我这里给出的 StringOperationsDemo 具体代码演示如下:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.basic.strings;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress字符串操作演示 - 全面展示字符串处理和操作技巧
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-25 23:50
**/
public class StringOperationsDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public StringOperationsDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress字符串操作演示引擎初始化完成");
}
/**
* 演示字符串拼接操作
*/
public void demonstrateStringConcatenation() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress字符串拼接演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("firstName", "张");
context.put("lastName", "彦峰");
context.put("age", 30);
context.put("city", "北京");
context.put("salary", 15000.50);
// 1. 基本字符串拼接
System.out.println("🔗 1. 基本字符串拼接演示:");
Object concat1 = runner.execute("firstName + lastName", context, null, true, false);
Object concat2 = runner.execute("'姓名:' + firstName + lastName", context, null, true, false);
Object concat3 = runner.execute("firstName + lastName + ',年龄:' + age", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" firstName + lastName = %s%n", concat1);
System.out.printf(" '姓名:' + firstName + lastName = %s%n", concat2);
System.out.printf(" firstName + lastName + ',年龄:' + age = %s%n%n", concat3);
// 2. 复杂字符串拼接
System.out.println("🎯 2. 复杂字符串拼接演示:");
Object complex1 = runner.execute("'员工信息:' + firstName + lastName + '(' + age + '岁),居住在' + city", context, null, true, false);
Object complex2 = runner.execute("'薪资:¥' + salary + '元/月,年薪:¥' + (salary * 12) + '元'", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 员工基本信息: %s%n", complex1);
System.out.printf(" 薪资信息: %s%n%n", complex2);
// 3. 条件拼接
System.out.println("❓ 3. 条件拼接演示:");
Object conditional1 = runner.execute("firstName + lastName + (age >= 18 ? '(成年)' : '(未成年)')", context, null, true, false);
Object conditional2 = runner.execute("'居住地:' + (city != null ? city : '未知')", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 条件年龄拼接: %s%n", conditional1);
System.out.printf(" 条件城市拼接: %s%n%n", conditional2);
// 4. 循环拼接
System.out.println("🔄 4. 循环拼接演示:");
String loopScript =
"result = '';" +
"for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {" +
" if (i > 1) result = result + ', ';" +
" result = result + '第' + i + '项';" +
"}" +
"return result;";
Object loopResult = runner.execute(loopScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 循环拼接结果: %s%n%n", loopResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 字符串拼接演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示字符串格式化操作
*/
public void demonstrateStringFormatting() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress字符串格式化演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("name", "张彦峰");
context.put("score", 85.678);
context.put("count", 1234);
context.put("ratio", 0.75);
// 1. 数字格式化
System.out.println("🔢 1. 数字格式化演示:");
Object formatScore = runner.execute("'分数:' + Math.round(score * 100) / 100.0", context, null, true, false);
Object formatPercent = runner.execute("'比例:' + Math.round(ratio * 10000) / 100.0 + '%'", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 保留两位小数: %s%n", formatScore);
System.out.printf(" 百分比格式: %s%n%n", formatPercent);
// 2. 数字补零格式化
System.out.println("0️⃣ 2. 数字补零格式化演示:");
String padZeroScript =
"num = 5;" +
"padded = num < 10 ? \"0\" + num : String.valueOf(num);" +
"return '编号:' + padded;";
Object padded = runner.execute(padZeroScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 补零格式化: %s%n%n", padded);
// 3. 千分位格式化(简单实现)
System.out.println("💰 3. 千分位格式化演示:");
String thousandScript =
"numStr = String.valueOf(count);" +
"len = numStr.length();" +
"result = '';" +
"for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {" +
" if (i > 0 && (len - i) % 3 == 0) {" +
" result = result + ',';" +
" }" +
" result = result + numStr.charAt(i);" +
"}" +
"return '金额:¥' + result;";
Object thousand = runner.execute(thousandScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 千分位格式: %s%n%n", thousand);
// 4. 字符串模板格式化
System.out.println("📝 4. 字符串模板演示:");
System.out.println(" 模板演示已跳过");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 字符串格式化演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示字符串验证操作
*/
public void demonstrateStringValidation() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress字符串验证演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("email", "zhangyanfeng@example.com");
context.put("phone", "13812345678");
context.put("idCard", "110101199001011234");
context.put("password", "Abc123456!");
context.put("emptyStr", "");
context.put("nullStr", null);
context.put("spaceStr", " ");
// 1. 基本验证
System.out.println("✅ 1. 基本字符串验证演示:");
Object isEmpty1 = runner.execute("emptyStr == null || emptyStr.length() == 0", context, null, true, false);
Object isEmpty2 = runner.execute("nullStr == null", context, null, true, false);
Object isBlank = runner.execute("spaceStr.trim().length() == 0", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 空字符串检查: %s%n", isEmpty1);
System.out.printf(" null字符串检查: %s%n", isEmpty2);
System.out.printf(" 空白字符串检查: %s%n%n", isBlank);
// 2. 长度验证
System.out.println("📏 2. 字符串长度验证演示:");
Object phoneLength = runner.execute("phone.length() == 11", context, null, true, false);
Object passwordLength = runner.execute("password.length() >= 8 && password.length() <= 20", context, null, true, false);
Object idCardLength = runner.execute("idCard.length() == 18", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 手机号长度验证: phone=%s, 长度正确=%s%n", context.get("phone"), phoneLength);
System.out.printf(" 密码长度验证: 长度合规=%s%n", passwordLength);
System.out.printf(" 身份证长度验证: 长度正确=%s%n%n", idCardLength);
// 3. 格式验证
System.out.println("🎯 3. 字符串格式验证演示:");
Object emailFormat = runner.execute("email.contains(\"@\") && email.contains(\".\")", context, null, true, false);
Object phoneFormat = runner.execute("phone.startsWith(\"1\") && phone.length() == 11", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 邮箱格式验证: email=%s, 格式正确=%s%n", context.get("email"), emailFormat);
System.out.printf(" 手机号格式验证: 格式正确=%s%n%n", phoneFormat);
// 4. 内容验证
System.out.println("🔍 4. 字符串内容验证演示:");
Object hasUpperCase = runner.execute("!password.equals(password.toLowerCase())", context, null, true, false);
Object hasLowerCase = runner.execute("!password.equals(password.toUpperCase())", context, null, true, false);
Object hasDigit = runner.execute("password.replaceAll(\"[^0-9]\", \"\").length() > 0", context, null, true, false);
Object hasSpecial = runner.execute("password.replaceAll(\"[a-zA-Z0-9]\", \"\").length() > 0", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 密码包含大写字母: %s%n", hasUpperCase);
System.out.printf(" 密码包含小写字母: %s%n", hasLowerCase);
System.out.printf(" 密码包含数字: %s%n", hasDigit);
System.out.printf(" 密码包含特殊字符: %s%n%n", hasSpecial);
// 5. 综合验证
System.out.println("🏆 5. 综合验证演示:");
String validateScript =
"emailValid = email != null && email.contains(\"@\") && email.contains(\".\") && email.length() > 5;" +
"phoneValid = phone != null && phone.length() == 11 && phone.startsWith(\"1\");" +
"passwordValid = password != null && password.length() >= 8 && " +
" !password.equals(password.toLowerCase()) && " +
" !password.equals(password.toUpperCase()) && " +
" password.replaceAll(\"[^0-9]\", \"\").length() > 0;" +
"return \"邮箱:\" + (emailValid ? \"✓\" : \"✗\") + \" 手机:\" + (phoneValid ? \"✓\" : \"✗\") + \" 密码:\" + (passwordValid ? \"✓\" : \"✗\");";
Object validation = runner.execute(validateScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 综合验证结果: %s%n%n", validation);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 字符串验证演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示字符串处理操作
*/
public void demonstrateStringProcessing() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress字符串处理演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
context.put("text", "Hello QLExpress World! 你好,QLExpress世界!");
context.put("messyText", " Hello World \n\t ");
context.put("mixedCase", "hElLo WoRlD");
context.put("csvData", "apple,banana,orange;grape|watermelon");
// 1. 字符串清理
System.out.println("🧹 1. 字符串清理演示:");
Object trimmed = runner.execute("messyText.trim()", context, null, true, false);
Object normalized = runner.execute("messyText.trim().replaceAll(\"\\\\s+\", \" \")", context, null, true, false);
Object cleaned = runner.execute("text.replaceAll(\"[!,]\", \"\")", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 原始文本: '%s'%n", context.get("messyText"));
System.out.printf(" 去除首尾空格: '%s'%n", trimmed);
System.out.printf(" 规范化空格: '%s'%n", normalized);
System.out.printf(" 清理标点符号: '%s'%n%n", cleaned);
// 2. 大小写转换
System.out.println("🔄 2. 大小写转换演示:");
Object upperCase = runner.execute("mixedCase.toUpperCase()", context, null, true, false);
Object lowerCase = runner.execute("mixedCase.toLowerCase()", context, null, true, false);
// 首字母大写
String capitalizeScript =
"str = mixedCase.toLowerCase();" +
"return str.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + str.substring(1);";
Object capitalized = runner.execute(capitalizeScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 原始文本: %s%n", context.get("mixedCase"));
System.out.printf(" 全部大写: %s%n", upperCase);
System.out.printf(" 全部小写: %s%n", lowerCase);
System.out.printf(" 首字母大写: %s%n%n", capitalized);
// 3. 字符串分割和重组
System.out.println("✂️ 3. 字符串分割和重组演示:");
String splitScript =
"parts1 = csvData.split(\",\");" +
"parts2 = csvData.split(\"[,;|]\");" +
"return \"按逗号分割: \" + parts1.length + \"个, 按多字符分割: \" + parts2.length + \"个\";";
Object splitResult = runner.execute(splitScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 分割结果: %s%n", splitResult);
String joinScript =
"words = text.split(\" \");" +
"result = \"\";" +
"for (i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {" +
" if (i > 0) result = result + \" | \";" +
" result = result + words[i];" +
"}" +
"return result;";
Object joinResult = runner.execute(joinScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 重新连接: %s%n%n", joinResult);
// 4. 字符串提取
System.out.println("🔍 4. 字符串提取演示:");
Object firstWord = runner.execute("text.substring(0, text.indexOf(\" \"))", context, null, true, false);
Object lastWord = runner.execute("text.substring(text.lastIndexOf(\" \") + 1)", context, null, true, false);
Object middlePart = runner.execute("text.substring(6, 15)", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 提取第一个单词: %s%n", firstWord);
System.out.printf(" 提取最后一个词: %s%n", lastWord);
System.out.printf(" 提取中间部分: %s%n%n", middlePart);
// 5. 字符统计
System.out.println("📊 5. 字符统计演示:");
String countScript =
"totalLength = text.length();" +
"englishCount = text.replaceAll(\"[^a-zA-Z]\", \"\").length();" +
"chineseCount = text.replaceAll(\"[^\\\\u4e00-\\\\u9fa5]\", \"\").length();" +
"spaceCount = text.replaceAll(\"[^ ]\", \"\").length();" +
"return \"总字符:\" + totalLength + \", 英文:\" + englishCount + \", 中文:\" + chineseCount + \", 空格:\" + spaceCount;";
Object countResult = runner.execute(countScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 字符统计: %s%n%n", countResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 字符串处理演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 运行所有演示
*/
public void runAllDemonstrations() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始QLExpress字符串操作完整演示...\n");
demonstrateStringConcatenation();
demonstrateStringFormatting();
demonstrateStringValidation();
demonstrateStringProcessing();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress字符串操作演示完成!");
System.out.println("\n📚 学习要点:");
System.out.println(" 1. 字符串拼接: 使用 + 操作符,支持与各种类型混合");
System.out.println(" 2. 字符串格式化: 数字格式化、模板替换、条件拼接");
System.out.println(" 3. 字符串验证: 长度检查、格式验证、内容验证");
System.out.println(" 4. 字符串处理: 清理、转换、分割、提取、统计");
System.out.println(" 5. 正则表达式: replaceAll方法支持正则表达式替换");
System.out.println(" 6. 中文处理: 支持中文字符的各种操作");
}
/**
* 主方法 - 运行演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringOperationsDemo demo = new StringOperationsDemo();
demo.runAllDemonstrations();
}
}基本运行验证如下:
python
✅ QLExpress字符串操作演示引擎初始化完成
🚀 开始QLExpress字符串操作完整演示...
=== QLExpress字符串拼接演示 ===
🔗 1. 基本字符串拼接演示:
firstName + lastName = 张彦峰
'姓名:' + firstName + lastName = 姓名:张彦峰
firstName + lastName + ',年龄:' + age = 张彦峰,年龄:30
🎯 2. 复杂字符串拼接演示:
员工基本信息: 员工信息:张彦峰(30岁),居住在北京
薪资信息: 薪资:¥15000.5元/月,年薪:¥180006.0元
❓ 3. 条件拼接演示:
条件年龄拼接: 张彦峰(成年)
条件城市拼接: 居住地:北京
🔄 4. 循环拼接演示:
循环拼接结果: 第1项, 第2项, 第3项, 第4项, 第5项
=== QLExpress字符串格式化演示 ===
🔢 1. 数字格式化演示:
保留两位小数: 分数:85.68
百分比格式: 比例:75.0%
0️⃣ 2. 数字补零格式化演示:
补零格式化: 编号:05
💰 3. 千分位格式化演示:
千分位格式: 金额:¥1,234
📝 4. 字符串模板演示:
模板演示已跳过
=== QLExpress字符串验证演示 ===
✅ 1. 基本字符串验证演示:
空字符串检查: true
null字符串检查: true
空白字符串检查: true
📏 2. 字符串长度验证演示:
手机号长度验证: phone=13812345678, 长度正确=true
密码长度验证: 长度合规=true
身份证长度验证: 长度正确=true
🎯 3. 字符串格式验证演示:
邮箱格式验证: email=zhangyanfeng@example.com, 格式正确=true
手机号格式验证: 格式正确=true
🔍 4. 字符串内容验证演示:
密码包含大写字母: true
密码包含小写字母: true
密码包含数字: true
密码包含特殊字符: true
🏆 5. 综合验证演示:
综合验证结果: 邮箱:✓ 手机:✓ 密码:✓
=== QLExpress字符串处理演示 ===
🧹 1. 字符串清理演示:
原始文本: ' Hello World
'
去除首尾空格: 'Hello World'
规范化空格: 'Hello World'
清理标点符号: 'Hello QLExpress World! 你好QLExpress世界'
🔄 2. 大小写转换演示:
原始文本: hElLo WoRlD
全部大写: HELLO WORLD
全部小写: hello world
首字母大写: Hello world
✂️ 3. 字符串分割和重组演示:
分割结果: 按逗号分割: 3个, 按多字符分割: 5个
重新连接: Hello | QLExpress | World! | 你好,QLExpress世界!
🔍 4. 字符串提取演示:
提取第一个单词: Hello
提取最后一个词: 你好,QLExpress世界!
提取中间部分: QLExpress
📊 5. 字符统计演示:
字符统计: 总字符:38, 英文:28, 中文:4, 空格:3
✅ QLExpress字符串操作演示完成!
📚 学习要点:
1. 字符串拼接: 使用 + 操作符,支持与各种类型混合
2. 字符串格式化: 数字格式化、模板替换、条件拼接
3. 字符串验证: 长度检查、格式验证、内容验证
4. 字符串处理: 清理、转换、分割、提取、统计
5. 正则表达式: replaceAll方法支持正则表达式替换
6. 中文处理: 支持中文字符的各种操作
Process finished with exit code 0在代码中覆盖的场景包括:
-
拼接(Concatenation)
-
格式化(Formatting)
-
校验(Validation)
-
清洗 / 规范化(Processing)
-
分割与重组(Split & Join)
这正是规则工程中最典型的字符串生命周期。
具体详细的内容可见:QLExpress 字符串能力全解析:机制、用法与工程实践
七、数组与集合能力:承载"批量数据"和"规则作用对象"的核心结构
在规则引擎、动态计算、可配置逻辑等系统中,数组与集合是承载"批量数据"和"规则作用对象"的核心结构。QLExpress 作为一款嵌入式表达式引擎,并未重新发明集合模型,而是以 Java 原生数组与集合为基础,提供了一套高度一致、低心智负担的表达式访问与控制能力。
QLExpress 对数组和集合的核心原则是:
最大限度复用 Java 原生语义,而非引入 DSL 私有集合模型
我这里给出的 ArrayOperationsDemo 具体代码演示如下:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.basic.arrays;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress数组操作演示 - 全面展示数组和集合的操作技巧
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-25 23:55
**/
public class ArrayOperationsDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public ArrayOperationsDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress数组操作演示引擎初始化完成");
}
/**
* 演示基本数组操作
*/
public void demonstrateBasicArrayOperations() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress基本数组操作演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
int[] numbers = {10, 25, 3, 47, 15, 8, 92, 33, 61, 7};
String[] names = {"张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "钱七"};
double[] scores = {85.5, 92.0, 78.5, 88.0, 95.5};
context.put("numbers", numbers);
context.put("names", names);
context.put("scores", scores);
// 1. 数组基本属性
System.out.println("📊 1. 数组基本属性演示:");
Object numbersLength = runner.execute("numbers.length", context, null, true, false);
Object firstNumber = runner.execute("numbers[0]", context, null, true, false);
Object lastNumber = runner.execute("numbers[numbers.length - 1]", context, null, true, false);
Object middleNumber = runner.execute("numbers[numbers.length / 2]", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 数组长度: numbers.length = %s%n", numbersLength);
System.out.printf(" 第一个元素: numbers[0] = %s%n", firstNumber);
System.out.printf(" 最后一个元素: numbers[%s] = %s%n", (Integer.parseInt(numbersLength.toString()) - 1), lastNumber);
System.out.printf(" 中间元素: numbers[%s] = %s%n%n", (Integer.parseInt(numbersLength.toString()) / 2), middleNumber);
// 2. 数组元素访问
System.out.println("🔍 2. 数组元素访问演示:");
Object name1 = runner.execute("names[1]", context, null, true, false);
Object score2 = runner.execute("scores[2]", context, null, true, false);
Object dynamicAccess = runner.execute("numbers[3 + 2]", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" names[1] = %s%n", name1);
System.out.printf(" scores[2] = %s%n", score2);
System.out.printf(" numbers[3 + 2] = %s%n%n", dynamicAccess);
// 3. 数组边界检查
System.out.println("⚠️ 3. 数组边界检查演示:");
Object safeAccess1 = runner.execute("numbers.length > 5 ? numbers[5] : -1", context, null, true, false);
Object safeAccess2 = runner.execute("names.length > 10 ? names[10] : '不存在'", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 安全访问 numbers[5]: %s%n", safeAccess1);
System.out.printf(" 安全访问 names[10]: %s%n%n", safeAccess2);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 基本数组操作演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示数组遍历操作
*/
public void demonstrateArrayIteration() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress数组遍历演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
String[] fruits = {"苹果", "香蕉", "橙子", "葡萄", "西瓜"};
context.put("numbers", numbers);
context.put("fruits", fruits);
// 1. 基本for循环遍历
System.out.println("🔄 1. 基本for循环遍历演示:");
String traverseScript1 =
"result = '';" +
"for (i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {" +
" if (i > 0) result = result + ', ';" +
" result = result + numbers[i];" +
"}" +
"return '数组元素: [' + result + ']';";
Object traverse1 = runner.execute(traverseScript1, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", traverse1);
// 2. 条件遍历
System.out.println("❓ 2. 条件遍历演示:");
String conditionalScript =
"evenNumbers = '';" +
"oddNumbers = '';" +
"evenCount = 0;" +
"oddCount = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {" +
" if (numbers[i] % 2 == 0) {" +
" if (evenCount > 0) evenNumbers = evenNumbers + ', ';" +
" evenNumbers = evenNumbers + numbers[i];" +
" evenCount = evenCount + 1;" +
" } else {" +
" if (oddCount > 0) oddNumbers = oddNumbers + ', ';" +
" oddNumbers = oddNumbers + numbers[i];" +
" oddCount = oddCount + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '偶数[' + evenCount + '个]: ' + evenNumbers + '; 奇数[' + oddCount + '个]: ' + oddNumbers;";
Object conditional = runner.execute(conditionalScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", conditional);
// 3. 带索引的遍历
System.out.println("🔢 3. 带索引的遍历演示:");
String indexedScript =
"result = '';" +
"for (i = 0; i < fruits.length; i++) {" +
" if (i > 0) result = result + ', ';" +
" result = result + (i + 1) + '.' + fruits[i];" +
"}" +
"return result;";
Object indexed = runner.execute(indexedScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 带序号的水果列表: %s%n%n", indexed);
// 4. 反向遍历
System.out.println("🔄 4. 反向遍历演示:");
String reverseScript =
"result = '';" +
"for (i = fruits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {" +
" if (i < fruits.length - 1) result = result + ' <- ';" +
" result = result + fruits[i];" +
"}" +
"return '反向遍历: ' + result;";
Object reverse = runner.execute(reverseScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", reverse);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 数组遍历演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示数组统计操作
*/
public void demonstrateArrayStatistics() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress数组统计演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
int[] scores = {85, 92, 78, 95, 88, 76, 90, 82, 94, 87};
double[] prices = {19.99, 25.50, 12.30, 45.00, 8.75, 33.20, 15.80, 28.90};
context.put("scores", scores);
context.put("prices", prices);
// 1. 基本统计
System.out.println("📈 1. 基本统计演示:");
String basicStatsScript =
"sum = 0;" +
"count = scores.length;" +
"for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {" +
" sum = sum + scores[i];" +
"}" +
"avg = sum / count;" +
"return '总分: ' + sum + ', 平均分: ' + Math.round(avg * 100) / 100.0;";
Object basicStats = runner.execute(basicStatsScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", basicStats);
// 2. 最值统计
System.out.println("🏆 2. 最值统计演示:");
String minMaxScript =
"minVal = scores[0];" +
"maxVal = scores[0];" +
"for (i = 1; i < scores.length; i++) {" +
" if (scores[i] < minVal) {" +
" minVal = scores[i];" +
" }" +
" if (scores[i] > maxVal) {" +
" maxVal = scores[i];" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return minVal + \",\" + maxVal;";
Object minMax = runner.execute(minMaxScript, context, null, true, false);
String[] parts = minMax.toString().split(",");
System.out.printf(" 最低分: %s, 最高分: %s%n%n", parts[0], parts[1]);
// 3. 条件统计
System.out.println("📊 3. 条件统计演示:");
String conditionalStatsScript =
"excellent = 0;" + // >= 90
"good = 0;" + // 80-89
"fair = 0;" + // 70-79
"poor = 0;" + // < 70
"for (i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {" +
" if (scores[i] >= 90) {" +
" excellent = excellent + 1;" +
" } else if (scores[i] >= 80) {" +
" good = good + 1;" +
" } else if (scores[i] >= 70) {" +
" fair = fair + 1;" +
" } else {" +
" poor = poor + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '优秀:' + excellent + '个, 良好:' + good + '个, 一般:' + fair + '个, 较差:' + poor + '个';";
Object conditionalStats = runner.execute(conditionalStatsScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 成绩分布: %s%n%n", conditionalStats);
// 4. 范围统计
System.out.println("📏 4. 范围统计演示:");
String rangeStatsScript =
"totalPrice = 0;" +
"expensiveCount = 0;" + // > 30
"moderateCount = 0;" + // 15-30
"cheapCount = 0;" + // < 15
"for (i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {" +
" totalPrice = totalPrice + prices[i];" +
" if (prices[i] > 30) {" +
" expensiveCount = expensiveCount + 1;" +
" } else if (prices[i] >= 15) {" +
" moderateCount = moderateCount + 1;" +
" } else {" +
" cheapCount = cheapCount + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"avgPrice = Math.round(totalPrice / prices.length * 100) / 100.0;" +
"return '总价:¥' + totalPrice + ', 平均:¥' + avgPrice + ', 贵:' + expensiveCount + ', 中:' + moderateCount + ', 便宜:' + cheapCount;";
Object rangeStats = runner.execute(rangeStatsScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 价格分析: %s%n%n", rangeStats);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 数组统计演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示数组搜索和过滤操作
*/
public void demonstrateArraySearchAndFilter() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress数组搜索和过滤演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
int[] numbers = {15, 28, 33, 42, 17, 55, 23, 61, 9, 38};
String[] products = {"手机", "电脑", "平板", "手机壳", "充电器", "电脑包", "鼠标", "键盘"};
context.put("numbers", numbers);
context.put("products", products);
// 1. 线性搜索
System.out.println("🔍 1. 线性搜索演示:");
String searchScript1 =
"target = 42;" +
"found = false;" +
"index = -1;" +
"for (i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {" +
" if (numbers[i] == target) {" +
" found = true;" +
" index = i;" +
" break;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '搜索' + target + ': ' + (found ? '找到,位置' + index : '未找到');";
Object search1 = runner.execute(searchScript1, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", search1);
// 2. 字符串搜索
System.out.println("📱 2. 字符串搜索演示:");
String searchScript2 =
"keyword = \"手机\";" +
"results = '';" +
"count = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < products.length; i++) {" +
" if (products[i].indexOf(keyword) >= 0) {" +
" if (count > 0) results = results + ', ';" +
" results = results + products[i] + '(位置' + i + ')';" +
" count = count + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '搜索 "手机" : ' + (count > 0 ? '找到' + count + '个: ' + results : '未找到');";
Object search2 = runner.execute(searchScript2, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", search2);
// 3. 数值过滤
System.out.println("🎯 3. 数值过滤演示:");
String filterScript1 =
"threshold = 30;" +
"filtered = '';" +
"count = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {" +
" if (numbers[i] > threshold) {" +
" if (count > 0) filtered = filtered + ', ';" +
" filtered = filtered + numbers[i];" +
" count = count + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '大于' + threshold + '的数: [' + filtered + '] (' + count + '个)';";
Object filter1 = runner.execute(filterScript1, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", filter1);
// 4. 复杂条件过滤
System.out.println("🎪 4. 复杂条件过滤演示:");
String filterScript2 =
"evenLarge = '';" + // 偶数且>20
"oddSmall = '';" + // 奇数且<=20
"evenLargeCount = 0;" +
"oddSmallCount = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {" +
" if (numbers[i] % 2 == 0 && numbers[i] > 20) {" +
" if (evenLargeCount > 0) evenLarge = evenLarge + ', ';" +
" evenLarge = evenLarge + numbers[i];" +
" evenLargeCount = evenLargeCount + 1;" +
" } else if (numbers[i] % 2 == 1 && numbers[i] <= 20) {" +
" if (oddSmallCount > 0) oddSmall = oddSmall + ', ';" +
" oddSmall = oddSmall + numbers[i];" +
" oddSmallCount = oddSmallCount + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '偶数且>20: [' + evenLarge + '](' + evenLargeCount + '个); 奇数且<=20: [' + oddSmall + '](' + oddSmallCount + '个)';";
Object filter2 = runner.execute(filterScript2, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", filter2);
// 5. 多条件搜索
System.out.println("🔎 5. 多条件搜索演示:");
String multiSearchScript =
"keyword1 = \"电\";" +
"keyword2 = \"手机\";" +
"electronics = '';" +
"count = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < products.length; i++) {" +
" if (products[i].indexOf(keyword1) >= 0 || products[i].indexOf(keyword2) >= 0) {" +
" if (count > 0) electronics = electronics + ', ';" +
" electronics = electronics + products[i];" +
" count = count + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '电子产品搜索结果: [' + electronics + '] (' + count + '个)';";
Object multiSearch = runner.execute(multiSearchScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", multiSearch);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 数组搜索和过滤演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示集合操作
*/
public void demonstrateListOperations() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress集合操作演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 准备测试数据
List<String> cities = new ArrayList<>();
cities.add("北京");
cities.add("上海");
cities.add("深圳");
cities.add("广州");
cities.add("杭州");
List<Integer> grades = new ArrayList<>();
grades.add(85);
grades.add(92);
grades.add(78);
grades.add(95);
grades.add(88);
context.put("cities", cities);
context.put("grades", grades);
// 1. 集合基本操作
System.out.println("📋 1. 集合基本操作演示:");
Object size = runner.execute("cities.size()", context, null, true, false);
Object firstCity = runner.execute("cities.get(0)", context, null, true, false);
Object contains = runner.execute("cities.contains('北京')", context, null, true, false);
Object indexOf = runner.execute("cities.indexOf('深圳')", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" cities.size() = %s%n", size);
System.out.printf(" cities.get(0) = %s%n", firstCity);
System.out.printf(" cities.contains('北京') = %s%n", contains);
System.out.printf(" cities.indexOf('深圳') = %s%n%n", indexOf);
// 2. 集合遍历
System.out.println("🔄 2. 集合遍历演示:");
String listTraverseScript =
"result = '';" +
"for (i = 0; i < cities.size(); i++) {" +
" if (i > 0) result = result + ' -> ';" +
" result = result + cities.get(i);" +
"}" +
"return '城市列表: ' + result;";
Object traverse = runner.execute(listTraverseScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", traverse);
// 3. 集合统计
System.out.println("📊 3. 集合统计演示:");
String listStatsScript =
"sum = 0;" +
"highCount = 0;" + // >= 90
"for (i = 0; i < grades.size(); i++) {" +
" grade = grades.get(i);" +
" sum = sum + grade;" +
" if (grade >= 90) {" +
" highCount = highCount + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"avg = Math.round(sum / grades.size() * 100) / 100.0;" +
"return '总分:' + sum + ', 平均分:' + avg + ', 优秀(' + highCount + '/' + grades.size() + ')';";
Object listStats = runner.execute(listStatsScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 成绩统计: %s%n%n", listStats);
// 4. 集合搜索
System.out.println("🔍 4. 集合搜索演示:");
String listSearchScript =
"target = \"上\";" +
"results = '';" +
"count = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < cities.size(); i++) {" +
" city = cities.get(i);" +
" if (city.indexOf(target) >= 0) {" +
" if (count > 0) results = results + ', ';" +
" results = results + city;" +
" count = count + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '包含\"上\"的城市: ' + (count > 0 ? results + '(' + count + '个)' : '未找到');";
Object listSearch = runner.execute(listSearchScript, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", listSearch);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 集合操作演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 运行所有演示
*/
public void runAllDemonstrations() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始QLExpress数组操作完整演示...\n");
demonstrateBasicArrayOperations();
demonstrateArrayIteration();
demonstrateArrayStatistics();
demonstrateArraySearchAndFilter();
demonstrateListOperations();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress数组操作演示完成!");
System.out.println("\n📚 学习要点:");
System.out.println(" 1. 数组访问: array[index], array.length");
System.out.println(" 2. 数组遍历: for循环配合索引访问");
System.out.println(" 3. 数组统计: 求和、平均值、最值、条件统计");
System.out.println(" 4. 数组搜索: 线性搜索、条件过滤");
System.out.println(" 5. 集合操作: List的size(), get(), contains(), indexOf()等");
System.out.println(" 6. 安全访问: 边界检查,防止数组越界");
}
/**
* 主方法 - 运行演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayOperationsDemo demo = new ArrayOperationsDemo();
demo.runAllDemonstrations();
}
}基本运行验证如下:
python
✅ QLExpress数组操作演示引擎初始化完成
🚀 开始QLExpress数组操作完整演示...
=== QLExpress基本数组操作演示 ===
📊 1. 数组基本属性演示:
数组长度: numbers.length = 10
第一个元素: numbers[0] = 10
最后一个元素: numbers[9] = 7
中间元素: numbers[5] = 8
🔍 2. 数组元素访问演示:
names[1] = 李四
scores[2] = 78.5
numbers[3 + 2] = 8
⚠️ 3. 数组边界检查演示:
安全访问 numbers[5]: 8
安全访问 names[10]: 不存在
=== QLExpress数组遍历演示 ===
🔄 1. 基本for循环遍历演示:
数组元素: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
❓ 2. 条件遍历演示:
偶数[5个]: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10; 奇数[5个]: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
🔢 3. 带索引的遍历演示:
带序号的水果列表: 1.苹果, 2.香蕉, 3.橙子, 4.葡萄, 5.西瓜
🔄 4. 反向遍历演示:
反向遍历: 西瓜 <- 葡萄 <- 橙子 <- 香蕉 <- 苹果
=== QLExpress数组统计演示 ===
📈 1. 基本统计演示:
总分: 867, 平均分: 86.0
🏆 2. 最值统计演示:
最低分: 76, 最高分: 95
📊 3. 条件统计演示:
成绩分布: 优秀:4个, 良好:4个, 一般:2个, 较差:0个
📏 4. 范围统计演示:
价格分析: 总价:¥189.44000000000003, 平均:¥23.68, 贵:2, 中:4, 便宜:2
=== QLExpress数组搜索和过滤演示 ===
🔍 1. 线性搜索演示:
搜索42: 找到,位置3
📱 2. 字符串搜索演示:
搜索 "手机" : 找到2个: 手机(位置0), 手机壳(位置3)
🎯 3. 数值过滤演示:
大于30的数: [33, 42, 55, 61, 38] (5个)
🎪 4. 复杂条件过滤演示:
偶数且>20: [28, 42, 38](3个); 奇数且<=20: [15, 17, 9](3个)
🔎 5. 多条件搜索演示:
电子产品搜索结果: [手机, 电脑, 手机壳, 充电器, 电脑包] (5个)
=== QLExpress集合操作演示 ===
📋 1. 集合基本操作演示:
cities.size() = 5
cities.get(0) = 北京
cities.contains('北京') = true
cities.indexOf('深圳') = 2
🔄 2. 集合遍历演示:
城市列表: 北京 -> 上海 -> 深圳 -> 广州 -> 杭州
📊 3. 集合统计演示:
成绩统计: 总分:438, 平均分:87.0, 优秀(2/5)
🔍 4. 集合搜索演示:
包含"上"的城市: 上海(1个)
✅ QLExpress数组操作演示完成!
📚 学习要点:
1. 数组访问: array[index], array.length
2. 数组遍历: for循环配合索引访问
3. 数组统计: 求和、平均值、最值、条件统计
4. 数组搜索: 线性搜索、条件过滤
5. 集合操作: List的size(), get(), contains(), indexOf()等
6. 安全访问: 边界检查,防止数组越界
Process finished with exit code 0不追求花哨的 API,而是让你:
-
用最直观的方式表达业务
-
用最可控的方式执行规则
-
用最易理解的方式解释结果
从给出的示例可以看出,这套能力在教学、规则系统、配置化业务逻辑 中都非常成熟、稳定且值得推广。详细可见:QLExpress 数组与集合能力全解析:语义模型、使用范式与工程实践
八、上下文变量:规则引擎的"运行时世界"
如果说 QLExpress 的表达式语言定义了"规则能写什么",那么 上下文变量(Context)则决定了"规则运行在怎样的世界里"。
在 QLExpress 中,上下文不是一个简单的 Map,而是:
规则执行期间所有"数据、状态、变量、副作用"的统一载体
我这里给出的 ContextVariablesDemo,实际上尽量完整演示了上下文从"参数容器"到"运行时世界模型"的演进过程。
展示详细代码如下:
java
package org.zyf.javabasic.qlexpress.basic.context;
import com.ql.util.express.DefaultContext;
import com.ql.util.express.ExpressRunner;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @program: zyfboot-javabasic
* @description: QLExpress上下文变量演示 - 全面展示上下文管理和变量作用域
* @author: zhangyanfeng
* @create: 2025-12-25 23:54
**/
public class ContextVariablesDemo {
private ExpressRunner runner;
public ContextVariablesDemo() {
this.runner = new ExpressRunner();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress上下文变量演示引擎初始化完成");
}
/**
* 演示基本上下文操作
*/
public void demonstrateBasicContextOperations() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress基本上下文操作演示 ===\n");
try {
// 1. 创建和使用基本上下文
System.out.println("🏗️ 1. 基本上下文创建和使用演示:");
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
context.put("name", "张彦峰");
context.put("age", 30);
context.put("salary", 15000);
context.put("isManager", true);
Object result1 = runner.execute("name + '今年' + age + '岁'", context, null, true, false);
Object result2 = runner.execute("isManager ? '管理员' : '普通员工'", context, null, true, false);
Object result3 = runner.execute("salary > 10000 ? '高薪' : '一般'", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 基本信息: %s%n", result1);
System.out.printf(" 职位类型: %s%n", result2);
System.out.printf(" 薪资等级: %s%n%n", result3);
// 2. 上下文变量修改
System.out.println("🔄 2. 上下文变量修改演示:");
System.out.printf(" 修改前 - age: %s, salary: %s%n", context.get("age"), context.get("salary"));
runner.execute("age = age + 1", context, null, true, false);
runner.execute("salary = salary * 1.1", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 修改后 - age: %s, salary: %s%n%n", context.get("age"), context.get("salary"));
// 3. 上下文变量检查
System.out.println("🔍 3. 上下文变量检查演示:");
Object hasName = runner.execute("name != null", context, null, true, false);
Object hasEmail = runner.execute("email != null", context, null, true, false); // 不存在的变量
System.out.printf(" name变量存在: %s%n", hasName);
System.out.printf(" email变量存在: %s%n%n", hasEmail);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 基本上下文操作演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示复杂上下文数据
*/
public void demonstrateComplexContextData() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress复杂上下文数据演示 ===\n");
try {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
// 1. 对象类型上下文变量
System.out.println("🏗️ 1. 对象类型上下文变量演示:");
Employee emp = new Employee("张彦峰", 30, "技术部", 15000.0);
context.put("employee", emp);
Object result1 = runner.execute("employee.name + ' - ' + employee.department", context, null, true, false);
Object result2 = runner.execute("employee.salary > 12000", context, null, true, false);
Object result3 = runner.execute("employee.age >= 25 && employee.salary > 10000", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 员工信息: %s%n", result1);
System.out.printf(" 薪资检查: %s%n", result2);
System.out.printf(" 综合条件: %s%n%n", result3);
// 2. Map类型上下文变量
System.out.println("📋 2. Map类型上下文变量演示:");
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put("maxUsers", 1000);
config.put("timeout", 30);
config.put("enableCache", true);
config.put("version", "1.2.3");
context.put("config", config);
Object result4 = runner.execute("config.get('maxUsers') > 500", context, null, true, false);
Object result5 = runner.execute("config.get('enableCache') ? '缓存开启' : '缓存关闭'", context, null, true, false);
Object result6 = runner.execute("'系统版本: ' + config.get('version')", context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 用户数量检查: %s%n", result4);
System.out.printf(" 缓存状态: %s%n", result5);
System.out.printf(" 版本信息: %s%n%n", result6);
// 3. 数组类型上下文变量
System.out.println("📊 3. 数组类型上下文变量演示:");
String[] departments = {"技术部", "市场部", "财务部", "人事部"};
int[] budgets = {500000, 300000, 200000, 150000};
context.put("departments", departments);
context.put("budgets", budgets);
String script =
"totalBudget = 0;" +
"highBudgetDepts = '';" +
"count = 0;" +
"for (i = 0; i < budgets.length; i++) {" +
" totalBudget = totalBudget + budgets[i];" +
" if (budgets[i] > 250000) {" +
" if (count > 0) highBudgetDepts = highBudgetDepts + ', ';" +
" highBudgetDepts = highBudgetDepts + departments[i];" +
" count = count + 1;" +
" }" +
"}" +
"return '总预算: ¥' + totalBudget + ', 高预算部门: ' + highBudgetDepts;";
Object result7 = runner.execute(script, context, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 预算分析: %s%n%n", result7);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 复杂上下文数据演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示上下文作用域
*/
public void demonstrateContextScope() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress上下文作用域演示 ===\n");
try {
// 1. 全局上下文
System.out.println("🌍 1. 全局上下文演示:");
DefaultContext<String, Object> globalContext = new DefaultContext<>();
globalContext.put("globalVar", "我是全局变量");
globalContext.put("counter", 0);
Object result1 = runner.execute("globalVar + ', 初始计数: ' + counter", globalContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n%n", result1);
// 2. 局部变量创建
System.out.println("📍 2. 局部变量创建演示:");
String localScript =
"localVar = '我是局部变量';" +
"counter = counter + 1;" +
"return globalVar + ', ' + localVar + ', 计数: ' + counter;";
Object result2 = runner.execute(localScript, globalContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 执行结果: %s%n", result2);
System.out.printf(" 执行后全局counter: %s%n%n", globalContext.get("counter"));
// 3. 变量覆盖
System.out.println("🔄 3. 变量覆盖演示:");
globalContext.put("message", "原始消息");
String overrideScript =
"originalMessage = message;" +
"message = '被覆盖的消息';" +
"return '原始: ' + originalMessage + ', 现在: ' + message;";
Object result3 = runner.execute(overrideScript, globalContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 覆盖演示: %s%n", result3);
System.out.printf(" 执行后全局message: %s%n%n", globalContext.get("message"));
// 4. 条件作用域
System.out.println("❓ 4. 条件作用域演示:");
globalContext.put("userLevel", 5);
String conditionalScript =
"if (userLevel >= 5) {" +
" privilegeMessage = '您有高级权限';" +
" canAccess = true;" +
"} else {" +
" privilegeMessage = '权限不足';" +
" canAccess = false;" +
"}" +
"return privilegeMessage + ', 可访问: ' + canAccess;";
Object result4 = runner.execute(conditionalScript, globalContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 权限检查: %s%n%n", result4);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 上下文作用域演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示上下文传递和共享
*/
public void demonstrateContextSharing() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress上下文传递和共享演示 ===\n");
try {
// 1. 多个表达式共享上下文
System.out.println("🔗 1. 多个表达式共享上下文演示:");
DefaultContext<String, Object> sharedContext = new DefaultContext<>();
sharedContext.put("balance", 1000);
// 第一个表达式:消费
runner.execute("balance = balance - 300", sharedContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 消费后余额: %s%n", sharedContext.get("balance"));
// 第二个表达式:充值
runner.execute("balance = balance + 500", sharedContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 充值后余额: %s%n", sharedContext.get("balance"));
// 第三个表达式:检查状态
String statusScript =
"if (balance > 1000) {" +
" return '富裕';" +
"} else if (balance > 500) {" +
" return '一般';" +
"} else {" +
" return '紧张';" +
"}";
Object status = runner.execute(statusScript, sharedContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 财务状态: %s%n%n", status);
// 2. 上下文数据累积
System.out.println("📈 2. 上下文数据累积演示:");
DefaultContext<String, Object> accContext = new DefaultContext<>();
accContext.put("totalSales", 0);
accContext.put("transactionCount", 0);
// 模拟多次交易
int[] salesAmounts = {150, 200, 300, 80, 250};
for (int i = 0; i < salesAmounts.length; i++) {
accContext.put("currentSale", salesAmounts[i]);
String script =
"totalSales = totalSales + currentSale;" +
"transactionCount = transactionCount + 1;" +
"return '交易' + transactionCount + ': ¥' + currentSale + ', 累计: ¥' + totalSales;";
Object result = runner.execute(script, accContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n", result);
}
// 计算平均值
Object avgSale = runner.execute("Math.round(totalSales / transactionCount * 100) / 100.0", accContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 平均交易额: ¥%s%n%n", avgSale);
// 3. 上下文状态管理
System.out.println("📊 3. 上下文状态管理演示:");
DefaultContext<String, Object> stateContext = new DefaultContext<>();
// 初始化状态
String initScript =
"currentUser = 'admin';" +
"loginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();" +
"sessionActive = true;" +
"operationCount = 0;" +
"return '用户 ' + currentUser + ' 已登录';";
Object initResult = runner.execute(initScript, stateContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 初始化: %s%n", initResult);
// 执行操作
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
String opScript =
"if (sessionActive) {" +
" operationCount = operationCount + 1;" +
" result = '执行操作' + operationCount;" +
"} else {" +
" result = '会话已失效';" +
"}" +
"return result;";
Object opResult = runner.execute(opScript, stateContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" %s%n", opResult);
}
// 注销
String logoutScript =
"sessionActive = false;" +
"logoutTime = System.currentTimeMillis();" +
"duration = (logoutTime - loginTime) / 1000;" +
"return currentUser + ' 注销,会话时长: ' + duration + '秒,共执行' + operationCount + '次操作';";
Object logoutResult = runner.execute(logoutScript, stateContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 注销: %s%n%n", logoutResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 上下文传递和共享演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 演示自定义上下文
*/
public void demonstrateCustomContext() {
System.out.println("\n=== QLExpress自定义上下文演示 ===\n");
try {
// 1. 自定义上下文实现
System.out.println("🛠️ 1. 自定义上下文实现演示:");
CustomContext customContext = new CustomContext();
customContext.put("user", "张彦峰");
customContext.put("role", "admin");
Object result1 = runner.execute("user + ' 的角色是 ' + role", customContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 自定义上下文结果: %s%n", result1);
// 展示自定义上下文的特殊功能
System.out.printf(" 访问统计: %s%n", customContext.getAccessCount());
System.out.printf(" 访问历史: %s%n%n", customContext.getAccessHistory());
// 2. 上下文继承
System.out.println("🔄 2. 上下文继承演示:");
DefaultContext<String, Object> parentContext = new DefaultContext<>();
parentContext.put("company", "ZYF科技");
parentContext.put("version", "1.0");
DefaultContext<String, Object> childContext = new DefaultContext<>();
// 将父上下文的数据复制到子上下文
for (String key : parentContext.keySet()) {
childContext.put(key, parentContext.get(key));
}
// 子上下文添加自己的数据
childContext.put("module", "用户管理");
childContext.put("user", "张彦峰");
Object result2 = runner.execute("company + ' - ' + module + ' v' + version + ' (用户: ' + user + ')'", childContext, null, true, false);
System.out.printf(" 继承上下文结果: %s%n%n", result2);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("❌ 自定义上下文演示失败: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 运行所有演示
*/
public void runAllDemonstrations() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始QLExpress上下文变量完整演示...\n");
demonstrateBasicContextOperations();
demonstrateComplexContextData();
demonstrateContextScope();
demonstrateContextSharing();
demonstrateCustomContext();
System.out.println("✅ QLExpress上下文变量演示完成!");
System.out.println("\n📚 学习要点:");
System.out.println(" 1. 上下文创建: DefaultContext是最常用的上下文实现");
System.out.println(" 2. 变量存取: context.put()设置, 表达式中直接使用变量名");
System.out.println(" 3. 复杂数据: 支持对象、Map、数组等复杂数据类型");
System.out.println(" 4. 作用域: 表达式中可创建局部变量,会影响上下文状态");
System.out.println(" 5. 数据共享: 多个表达式可共享同一个上下文实例");
System.out.println(" 6. 自定义扩展: 可继承实现IExpressContext接口定制上下文行为");
}
/**
* 员工类 - 用于演示对象类型上下文变量
*/
public static class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
private String department;
private double salary;
public Employee(String name, int age, String department, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.department = department;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
public String getDepartment() { return department; }
public double getSalary() { return salary; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("Employee{name='%s', age=%d, department='%s', salary=%.2f}",
name, age, department, salary);
}
}
/**
* 自定义上下文 - 演示上下文扩展
*/
public static class CustomContext extends DefaultContext<String, Object> {
private int accessCount = 0;
private StringBuilder accessHistory = new StringBuilder();
@Override
public Object get(Object name) {
accessCount++;
accessHistory.append(name).append(", ");
return super.get(name);
}
public int getAccessCount() {
return accessCount;
}
public String getAccessHistory() {
return accessHistory.toString();
}
}
/**
* 主方法 - 运行演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ContextVariablesDemo demo = new ContextVariablesDemo();
demo.runAllDemonstrations();
}
}基本验证打印结果如下:
Go
✅ QLExpress上下文变量演示引擎初始化完成
🚀 开始QLExpress上下文变量完整演示...
=== QLExpress基本上下文操作演示 ===
🏗️ 1. 基本上下文创建和使用演示:
基本信息: 张彦峰今年30岁
职位类型: 管理员
薪资等级: 高薪
🔄 2. 上下文变量修改演示:
修改前 - age: 30, salary: 15000
修改后 - age: 31, salary: 16500.0
🔍 3. 上下文变量检查演示:
name变量存在: true
email变量存在: false
=== QLExpress复杂上下文数据演示 ===
🏗️ 1. 对象类型上下文变量演示:
员工信息: 张彦峰 - 技术部
薪资检查: true
综合条件: true
📋 2. Map类型上下文变量演示:
用户数量检查: true
缓存状态: 缓存开启
版本信息: 系统版本: 1.2.3
📊 3. 数组类型上下文变量演示:
预算分析: 总预算: ¥1150000, 高预算部门: 技术部, 市场部
=== QLExpress上下文作用域演示 ===
🌍 1. 全局上下文演示:
我是全局变量, 初始计数: 0
📍 2. 局部变量创建演示:
执行结果: 我是全局变量, 我是局部变量, 计数: 1
执行后全局counter: 1
🔄 3. 变量覆盖演示:
覆盖演示: 原始: 原始消息, 现在: 被覆盖的消息
执行后全局message: 被覆盖的消息
❓ 4. 条件作用域演示:
权限检查: 您有高级权限, 可访问: true
=== QLExpress上下文传递和共享演示 ===
🔗 1. 多个表达式共享上下文演示:
消费后余额: 700
充值后余额: 1200
财务状态: 富裕
📈 2. 上下文数据累积演示:
交易1: ¥150, 累计: ¥150
交易2: ¥200, 累计: ¥350
交易3: ¥300, 累计: ¥650
交易4: ¥80, 累计: ¥730
交易5: ¥250, 累计: ¥980
平均交易额: ¥196.0
📊 3. 上下文状态管理演示:
初始化: 用户 admin 已登录
执行操作1
执行操作2
执行操作3
注销: admin 注销,会话时长: 0秒,共执行3次操作
=== QLExpress自定义上下文演示 ===
🛠️ 1. 自定义上下文实现演示:
自定义上下文结果: 张彦峰 的角色是 admin
访问统计: 2
访问历史: user, role,
🔄 2. 上下文继承演示:
继承上下文结果: ZYF科技 - 用户管理 v1.0 (用户: 张彦峰)
✅ QLExpress上下文变量演示完成!
📚 学习要点:
1. 上下文创建: DefaultContext是最常用的上下文实现
2. 变量存取: context.put()设置, 表达式中直接使用变量名
3. 复杂数据: 支持对象、Map、数组等复杂数据类型
4. 作用域: 表达式中可创建局部变量,会影响上下文状态
5. 数据共享: 多个表达式可共享同一个上下文实例
6. 自定义扩展: 可继承实现IExpressContext接口定制上下文行为
Process finished with exit code 0基本的核心结论:
-
Context 是 QLExpress 的运行时世界
-
变量不是"参数",而是"状态"
-
规则可以、也应该修改上下文
-
上下文天然支持对象、Map、数组等复杂结构
-
所谓"局部变量",本质仍是上下文变量
-
多规则共享 Context = 状态机 + 决策流
-
自定义 Context 是规则引擎高级玩法的入口
详细的可见:QLExpress上下文变量:规则引擎的「运行时世界」
九、工程实践总结:QLExpress 的适用边界
通过以上模块可以得出一个清晰结论:
QLExpress 非常适合:
-
业务规则频繁变化
-
规则逻辑可配置
-
对性能有要求
-
规则执行受限、安全可控
但它并不适合:
-
复杂算法
-
大规模数据处理
-
强 IO 依赖逻辑
十、结语:从"会写表达式"到"能设计规则系统"
QLExpress 的真正价值,并不在于语法本身,而在于:
它为系统提供了一种"规则可配置、逻辑可治理"的能力边界。
当你掌握了本文所述的语法体系与设计原则,就已经具备了:
-
设计规则 DSL 的基础能力
-
将业务逻辑从代码中解耦的工程思维
-
构建可演进规则系统的技术视角