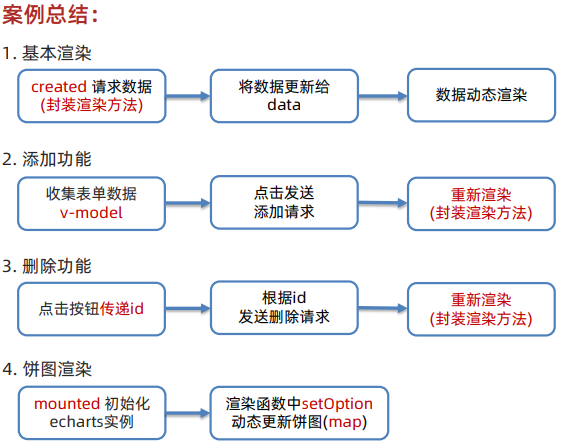
一、指令补充
**1.**指令修饰符

(1)按键修饰符
@keyup.enter → 键盘回车监听
javascript
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>@keyup.enter => 监听键盘回车事件</h3>
<input @keyup.enter="fn" v-model="username" type="text">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: ''
},
methods: {
fn (e) {
if(e.key === 'enter') {
console.log('键盘回车的时候触发', this.username)
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>(2)v-model 修饰符

(3)事件修饰符
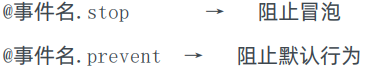
javascript
<div id="app">
<h3>v-model修饰符 .trim .number</h3>
姓名:<input v-model.trim="username" type="text"><br>
年纪:<input v-model.number="age" type="text"><br>
<h3>@事件名.stop → 阻止冒泡</h3>
<div @click="fatherFn" class="father">
<div @click.stop="sonFn" class="son">儿子</div>
</div>
<h3>@事件名.prevent → 阻止默认行为</h3>
<a @click.prevent href="http://www.baidu.com">阻止默认行为</a>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: '',
age: '',
},
methods: {
fatherFn () {
alert('老父亲被点击了')
},
sonFn () {
alert('儿子被点击了')
}
}
})
</script>2. v-bind 对于样式操作的增强
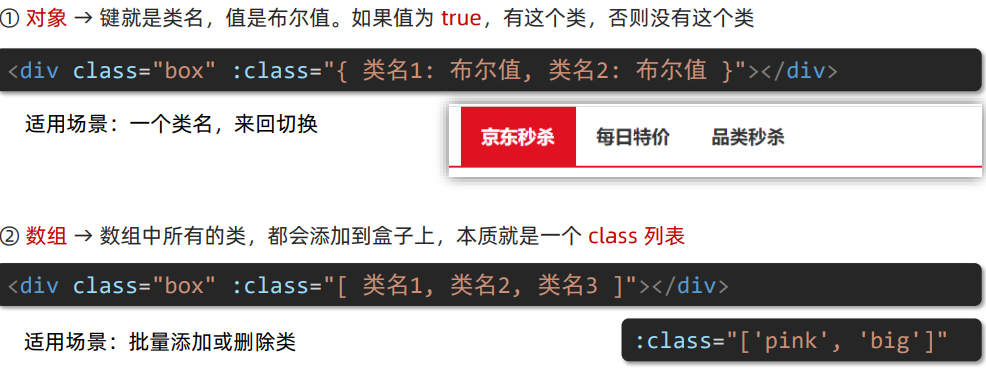
(1)操作 class
语法 :class = "对象/数组"
javascript
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid #000;
font-size: 30px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.pink {
background-color: pink;
}
.big {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box" :class="{ pink: false, big: true}">黑马程序员</div>
<div class="box" :class="['pink', 'big']">黑马程序员</div>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
}
})
</script>
</body>(2)操作 style
语法 :style = "样式对象"
适用场景:某个具体属性的动态设置
javascript
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(187, 150, 156);
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box" :style="{ width: '400px', height: '400px', backgroundColor: 'skyblue'}"></div>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
}
})
</script>
</body>3. v-model 应用于其他表单元素

javascript
<style>
textarea {
display: block;
width: 240px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑学习网</h3>
姓名:
<input type="text" v-model="username">
<br><br>
是否单身:
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isSingle">
<br><br>
<!--
前置理解:
1. name: 给单选框加上 name 属性 可以分组 → 同一组互相会互斥
2. value: 给单选框加上 value 属性,用于提交给后台的数据
结合 Vue 使用 → v-model
-->
性别:
<input v-model="gender" type="radio" name="gender" value="1">男
<input v-model="gender" type="radio" name="gender" value="2">女
<br><br>
<!--
前置理解:
1. option 需要设置 value 值,提交给后台
2. select 的 value 值,关联了选中的 option 的 value 值
结合 Vue 使用 → v-model
-->
所在城市:
<select v-model="cityId">
<option value="101" >厦门</option>
<option value="102" >漳州</option>
<option value="103" >扬州</option>
<option value="104" >南京</option>
</select>
<br><br>
自我描述:
<textarea v-model="desc"></textarea>
<button>立即注册</button>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: '',
isSingle: true,
gender: "2",
cityId: '102',
desc: ""
}
})
</script>
</body>二、computed 计算属性
**1.**计算属性
(1)定义:基于现有的数据,计算出来的新属性。依赖的数据变化,自动重新计算。
(2)语法:

javascript
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid #000;
text-align: center;
width: 240px;
}
th,td {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
h3 {
position: relative;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑的礼物清单</h3>
<table>
<tr>
<th>名字</th>
<th>数量</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.num }}个</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- 目标:统计求和,求得礼物总数 -->
<p>礼物总数:{{ totalCount}} 个</p>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 现有的数据
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '篮球', num: 1 },
{ id: 2, name: '玩具', num: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '铅笔', num: 5 },
]
},
computed: {
totalCount () {
// 基于现有的数据,编写求值逻辑
// 计算属性函数内部,可以直接通过 this 访问到 app 实例
// console.log(this.list)
// 需求:对 this.list 数组里面的 num 进行求和 => reduce
let total = this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.num, 0)
return total
}
}
})
</script>
</body>2. computed 计算属性 与 methods 方法
(1)计算属性

(2)方法

javascript
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid #000;
text-align: center;
width: 300px;
}
th,td {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
h3 {
position: relative;
}
span {
position: absolute;
left: 145px;
top: -4px;
width: 16px;
height: 16px;
color: white;
font-size: 12px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: #e63f32;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑的礼物清单🛒<span>{{ totalCount }}</span></h3>
<table>
<tr>
<th>名字</th>
<th>数量</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.num }}个</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>礼物总数:{{ totalCount }} 个</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 现有的数据
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '篮球', num: 3 },
{ id: 2, name: '玩具', num: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '铅笔', num: 5 },
]
},
computed: {
// 计算属性:有缓存的,一旦计算出来啊结果,就会立刻缓存
// 下次读取 => 直接读缓存执行 => 性能特别高
totalCount () {
console.log('计算属性执行了')
let total = this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.num, 0)
return total
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
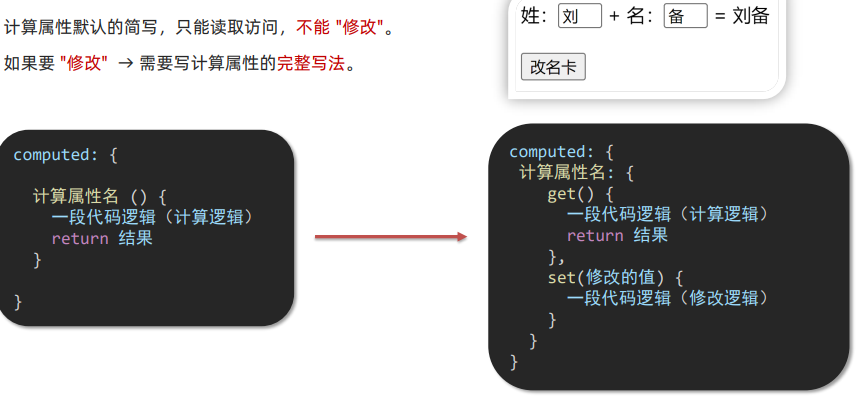
**3.**计算属性完整写法
语法:
javascript
<div id="app">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br>
<p>{{ fullName}}</p>
<button @click="changeName">修改姓名</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: '灰',
lastName: '太狼',
},
computed: {
// 简写 => 获取
// fullName () {
// return this.firstName + this.lastName
// }
// 完整写法 => 获取 + 设置
fullName: {
// (1)当fullName计算属性,被获取求值时,执行get (有缓存,优先读缓存)
// 会将返回值作为最终的求值结果
get () {
return this.firstName + this.lastName
},
// (2)当fullName计算属性,被修改赋值时,执行set
// 修改的值,传递给set 方法的形参
set (value) {
this.firstName = value.slice(0, 1)
this.lastName = value.slice(1)
}
}
},
methods: {
changeName () {
this.fullName = '红太狼'
}
}
})
</script>4.综合案例

三、watch 侦听器
1.作用:监视数据变化,执行一些 业务逻辑或异步操作。
2.语法:

(1)简单写法
javascript
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 18px;
}
#app {
padding: 10px 20px;
}
.query {
margin: 10px 0;
}
.box {
display: flex;
}
textarea {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
font-size: 18px;
border: 1px solid #dedede;
outline: none;
resize: none;
padding: 10px;
}
textarea:hover {
border: 1px solid #1589f5;
}
.transbox {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
padding: 10px;
border: none;
}
.tip-box {
width: 300px;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
display: flex;
}
.tip-box span {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
}
.query span {
font-size: 18px;
}
.input-wrap {
position: relative;
}
.input-wrap span {
position: absolute;
right: 15px;
bottom: 15px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.input-wrap i {
font-size: 20px;
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 条件选择框 -->
<div class="query">
<span>翻译成的语言:</span>
<select>
<option value="italy">意大利</option>
<option value="english">英语</option>
<option value="german">德语</option>
</select>
</div>
<!-- 翻译框 -->
<div class="box">
<div class="input-wrap">
<textarea v-model="obj.words"></textarea>
<span><i>⌨️</i>文档翻译</span>
</div>
<div class="output-wrap">
<div class="transbox">{{ result }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="./axios.js"></script>
<script>
// 接口地址:https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate
// 请求方式:get
// 请求参数:
// (1)words:需要被翻译的文本(必传)
// (2)lang:需要翻译成的语言(可选)默认值-意大利
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// words: '',
obj: {
words: ''
},
result: '', // 翻译结果
// timer: null // 延时器id
},
// 具体讲解:(1) watch语法 (2) 具体业务实现
watch: {
// 该方法会在我数据变化时调用执行
// newValue新值,oldValue老值(一般不用)
// words (newValue) {
// console.log('变化了', newValue)
// }
'obj.words' (newValue) {
// console.log('变化了', newValue)
// 防抖:延迟执行 => 干啥事先等一等,延迟一会,一段时间内没有再次触发,才执行
clearTimeout(this.timer)
this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
const res = await axios({
url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
params: {
words: newValue
}
}, 300)
this.result = res.data.data
})
}
}
})
</script>
</body>(2)完整写法 → 添加额外配置项

javascript
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 18px;
}
#app {
padding: 10px 20px;
}
.query {
margin: 10px 0;
}
.box {
display: flex;
}
textarea {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
font-size: 18px;
border: 1px solid #dedede;
outline: none;
resize: none;
padding: 10px;
}
textarea:hover {
border: 1px solid #1589f5;
}
.transbox {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
padding: 10px;
border: none;
}
.tip-box {
width: 300px;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
display: flex;
}
.tip-box span {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
}
.query span {
font-size: 18px;
}
.input-wrap {
position: relative;
}
.input-wrap span {
position: absolute;
right: 15px;
bottom: 15px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.input-wrap i {
font-size: 20px;
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 条件选择框 -->
<div class="query">
<span>翻译成的语言:</span>
<select v-model="obj.lang">
<option value="italy">意大利</option>
<option value="english">英语</option>
<option value="german">德语</option>
</select>
</div>
<!-- 翻译框 -->
<div class="box">
<div class="input-wrap">
<textarea v-model="obj.words"></textarea>
<span><i>⌨️</i>文档翻译</span>
</div>
<div class="output-wrap">
<div class="transbox">{{ result }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="./axios.js"></script>
<script>
// 需求:输入内容,修改语言,都实时翻译
// 接口地址:https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate
// 请求方式:get
// 请求参数:
// (1)words:需要被翻译的文本(必传)
// (2)lang:需要翻译成的语言(可选)默认值-意大利
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// words: '',
obj: {
words: '小黑',
lang: 'italy'
},
result: '', // 翻译结果
},
// 具体讲解:(1) watch语法 (2) 具体业务实现
watch: {
obj: {
deep: true, // 深度监视
immediate: true, // 立刻执行,一进页面handler就立刻执行
handler (newValue) {
clearTimeout(this.timer)
this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
const res = await axios({
url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
params: newValue
}, 300)
this.result = res.data.data
})
}
}
// 'obj.words' (newValue) {
// clearTimeout(this.timer)
// this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
// const res = await axios({
// url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
// params: {
// words: newValue
// }
// }, 300)
// this.result = res.data.data
// })
// }
}
})
</script>
</body>四、综合案例

五、生命周期
**1.**生命周期 & 生命周期四个阶段

**2.**生命周期钩子
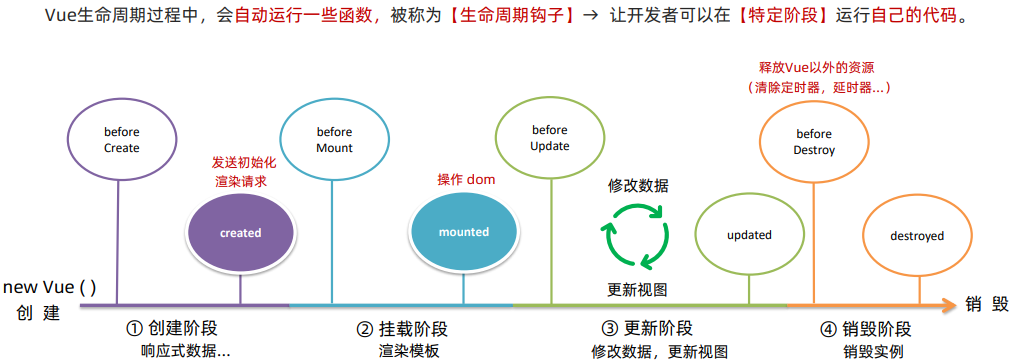
**3.**综合案例
javascript
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>{{ title }}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="count--">-</button>
<span>{{ count }}</span>
<button @click="count++">+</button>
</div>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
count: 100,
title: '计数器'
},
// 1. 创建阶段(准备数据)
beforeCreate () {
console.log('beforecreate 响应式数据准备好之前', this.count)
},
created () {
console.log('created 响应式数据准备好之后', this.count)
// this.数据名 = 请求回来的数据
// 可以开始发送初始化渲染的请求了
},
// 2. 挂载阶段(渲染模板)
beforeMount () {
console.log('beforemount 模板渲染之前', document.querySelector('h3').innerHTML)
},
mounted () {
console.log('mounted 模板渲染之后', document.querySelector('h3').innerHTML)
// 可以开始操作dom了
},
// 3.更新阶段(修改数据 => 更新视图)
beforeUpdate () {
console.log('beforeUpdate 数据修改了,视图还没更新', document.querySelector('span').innerHTML)
},
updated () {
console.log('updated 数据修改了,视图已经更新', document.querySelector('span').innerHTML)
},
// 4.卸载阶段
beforeDestroy () {
console.log('beforeDestroy 卸载前')
console.log('清除掉一些Vue以外的资源占用,定时器,延时器···')
},
destroyed () {
console.log('destroyed 卸载后')
}
})
</script>
</body>六、综合案例