一、get()
requests.get() 是 Python 中 requests 库 用于发送 HTTP GET 请求 的核心函数。它常用于从服务器获取数据,如网页内容、API 返回的 JSON 数据等。使用形式如下:
python
import requests
response = requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs)- 参数url:表示需要获取的HTML网址(也称url)
- 参数params:表示可选参数,以字典的形式发送信息,当需要向网页中提交查询信息时使用。
- 参数**kwargs:可选关键字参数,用于自定义请求行为(如添加参数、请求头、超时等。
常用参数详解
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
params |
dict / list of tuples | URL 查询参数(自动拼接到 URL 后,用于搜索、分页等) | params={'q': 'python', 'page': 1} → ?q=python&page=1 |
headers |
dict | 自定义请求头(如 User-Agent、Referer,绕过反爬) | headers={'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0...'} |
cookies |
dict / RequestsCookieJar | 发送指定 Cookie | cookies={'sessionid': 'abc123'} |
timeout |
float / tuple | 超时时间(秒),防止请求卡死(强烈建议设置!) | timeout=5 或 timeout=(3, 7)(连接3秒,读取7秒) |
allow_redirects |
bool | 是否允许重定向(默认 True) |
allow_redirects=False |
proxies |
dict | 使用代理服务器 | proxies={'http': 'http://10.10.1.10:3128'} |
verify |
bool / str | 是否验证 SSL 证书(默认 True);设为 False 可跳过 HTTPS 验证(不安全) |
verify=False |
stream |
bool | 是否启用流式下载(处理大文件时用) | stream=True |
⚠️ 注意:
requests.get()不能通过 body 发送数据 (GET 请求规范不允许),所有附加信息必须通过params(URL 参数)或headers/cookies传递。
典型使用场景示例
1. 基础请求(无参数)
r = requests.get('https://httpbin.org/get')2. 搜索/带查询参数(最常见)
r = requests.get(
'https://www.baidu.com/s',
params={'wd': 'Python requests'}
)
# 实际请求 URL: https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=Python+requests3. 添加请求头(模拟浏览器)
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64)',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9'
}
r = requests.get('https://example.com', headers=headers)4. 设置超时(避免程序卡死)
try:
r = requests.get('https://slow-site.com', timeout=10)
except requests.Timeout:
print("请求超时!")二、返回Response对象
在使用 Python 的 requests 库发起 HTTP 请求(如 requests.get())后,会返回一个 Response 对象。这个对象包含了服务器返回的所有信息,是我们获取网页内容、状态码、响应头等数据的关键。
1、返回 Response 对象
当你执行:
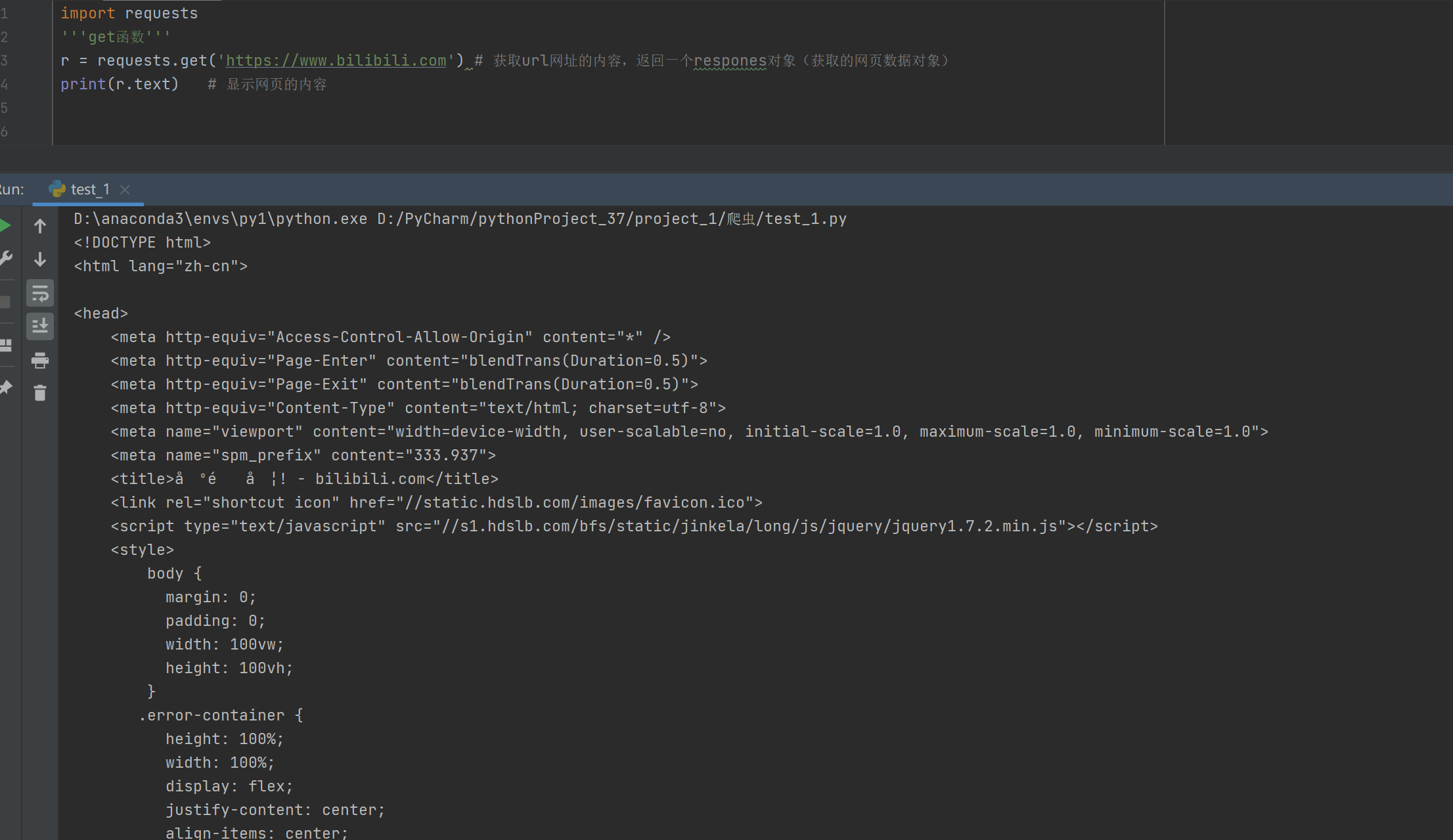
import requests
response = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com")变量 response 就是一个 requests.models.Response 类的实例 ,即 Response 对象。
✅ 所有与服务器响应相关的信息都封装在这个对象中。
2、Response 的常用属性与方法
| 属性/方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
.status_code |
HTTP 状态码(如 200 成功,404 未找到) | print(response.status_code) → 200 |
.headers |
响应头(字典类型) | response.headers['Content-Type'] |
.url |
实际请求的完整 URL(可能因重定向而改变) | response.url |
.encoding |
当前用于解码 .text 的编码方式(可读写) |
response.encoding = 'utf-8' |
.apparent_encoding |
根据内容自动检测的编码(基于 chardet 库) |
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding |
.text |
响应内容的字符串形式 (已按 .encoding 解码) |
print(response.text[:100]) |
.content |
响应内容的原始字节(bytes),适合下载图片、文件等 | with open('image.jpg', 'wb') as f: f.write(response.content) |
.json() |
将响应内容解析为 Python 字典/列表(仅当返回 JSON 时可用) | data = response.json() |
⚠️ 注意:
.text和.content是最常用的两个属性,前者是字符串,后者是字节流。
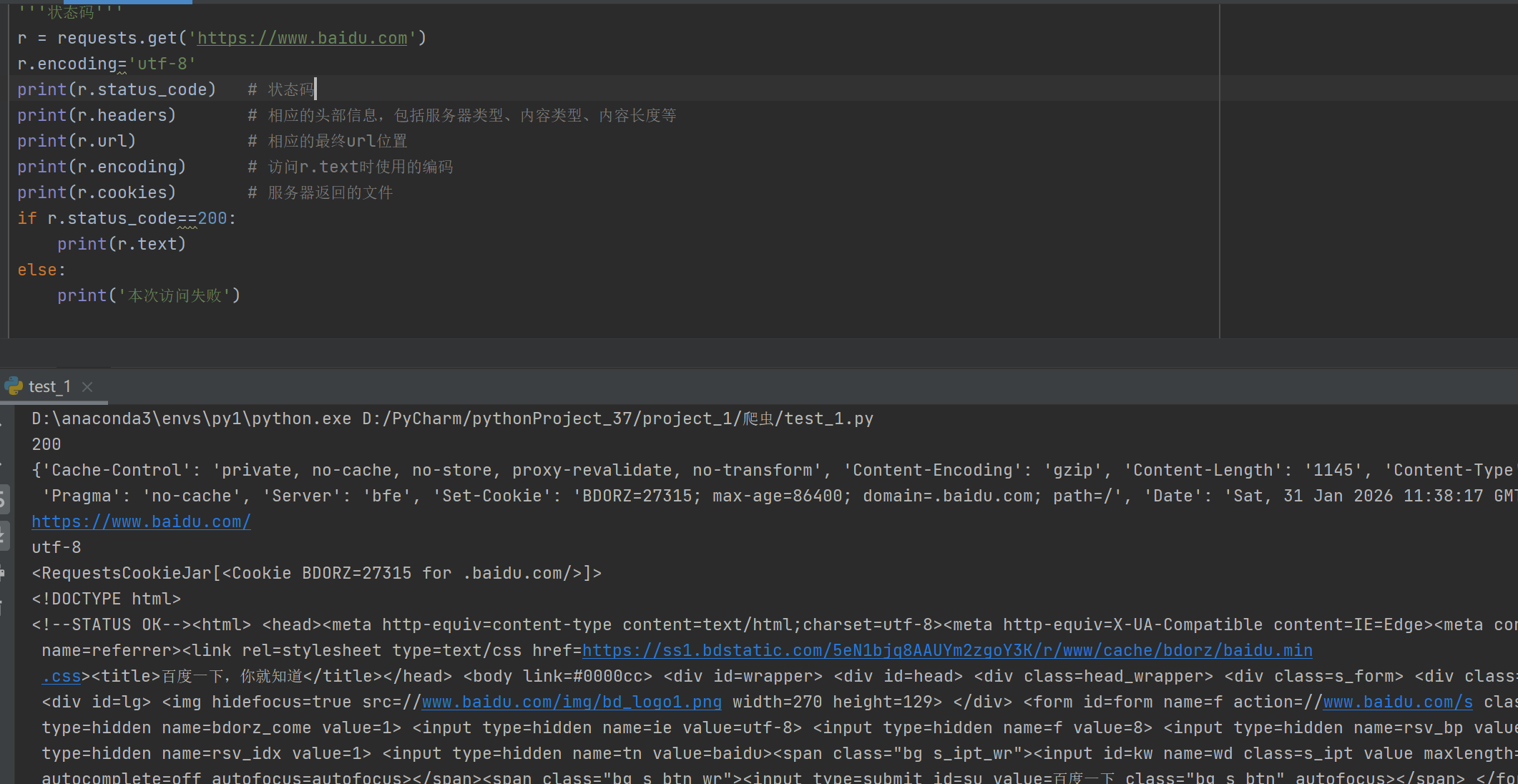
3、设置编码(解决中文乱码)
很多中文网站使用 UTF-8 编码,但 requests 有时会错误地将编码识别为 ISO-8859-1,导致 .text 出现乱码。
正确做法:
python
response = requests.get("https://some-chinese-site.com")
# 方法1:手动指定编码(推荐)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
print(response.text)
# 方法2:使用自动检测的编码(更智能)
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding
print(response.text)💡
response.apparent_encoding通过分析内容字节自动判断真实编码,比默认更可靠。
4、返回网页内容
要获取网页的 HTML 源代码(即"网页内容"),使用 .text 属性:
python
import requests
url = "https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-tutorial.html"
response = requests.get(url)
# 设置正确编码(避免中文乱码)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
# 获取网页内容
html_content = response.text
print(html_content[:500]) # 打印前500个字符运行结果:
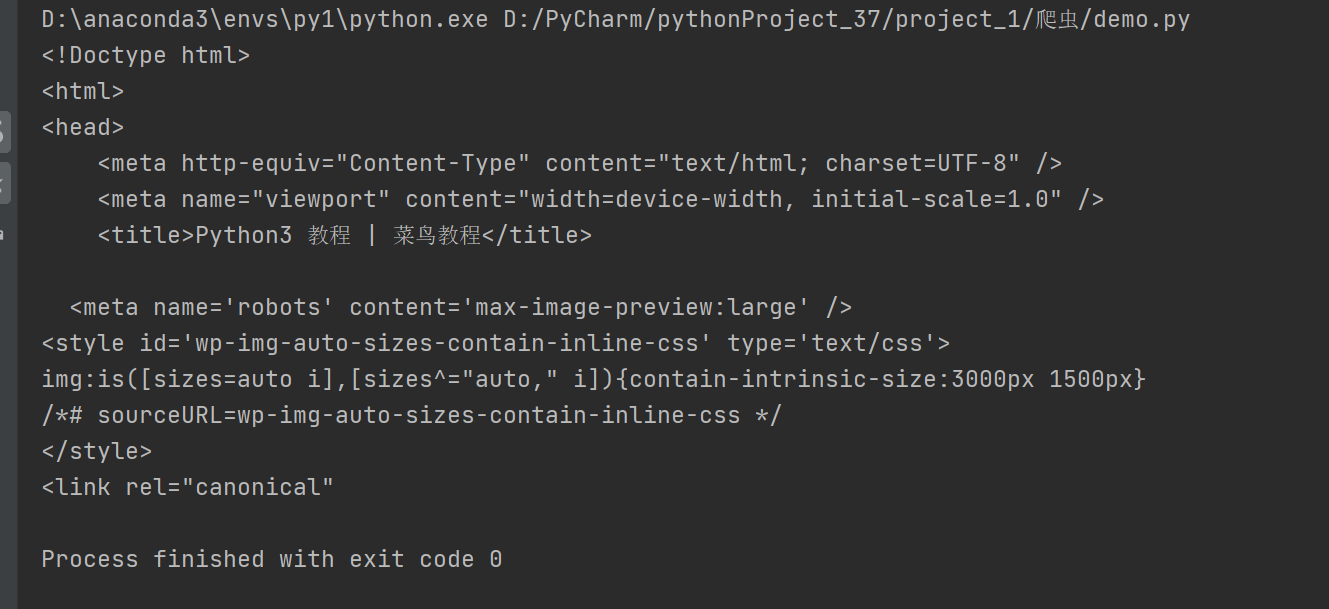
如果是要下载非文本资源(如图片、PDF):
python
import requests
response = requests.get("https://c-ssl.dtstatic.com/uploads/blog/202407/13/5zSdg6P8sOM1eE5.thumb.1000_0.png")
with open("photo.jpg", "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content) # 使用 .content 写入二进制数据
f.close()运行结果:
