一、队列
遵循"先进先出,后进后出"的原则
1.队头:出队的一端;
队尾:入队的一端;
2.循环队列
- 队空 :Head
== Tail(队头和队尾指针指向同一位置); - 队满 :
(Tail + 1) % maxlen== Head(队尾指针的下一个位置是队头,利用预留空位区分队满 / 队空)。 - 队列容量maxlen :数组的总长度(为了区分 "队满" 和 "队空",通常会预留 1 个空位,实际可存储元素数 = maxlen-1)
3.指针移动规则
无论是入队(Tail 后移)还是出队(Head 后移),都通过取模 % maxlen实现循环:
- 入队后:Tail
= (Tail + 1) % maxlen; - 出队后:Head
= (Head + 1) % maxlen
示例:
- 头文件:
cpp
#ifndef _SEQQUEUE_H
#define _SEQQUEUE_H
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct seqque
{
DataType *pData;
int Head;
int Tail;
int Maxlen;
}seqqueue_t;
extern seqqueue_t *CreateSeqQueue(int len);
extern int IsEmptySeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue);
extern int IsFullSeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue);
extern int EnterSeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue, DataType TmpData);
extern DataType QuitSeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue);
extern int DestorySeqQueue(seqqueue_t **ppTmpQueue);
#endif- 函数:
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"seqqueue.h"
seqqueue_t *CreateSeqQueue(int len)
{
seqqueue_t *pNewNode = NULL;
// DataType *pTmpNode = NULL;
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(seqqueue_t));
if(pNewNode == NULL)
{
perror("fail to malloc");
return NULL;
}
#if 0
pTmpNode = malloc(len * (sizeof(DataType)));
if(pTmpNode == NULL)
{
perror("fail to malloc");
return NULL;
}
#endif
// pNewNode->pData = pTmpNode;
pNewNode->Head = 0;
pNewNode->Tail = 0;
pNewNode->Maxlen = len;
pNewNode->pData = malloc(sizeof(DataType) * len);
if(pNewNode->pData == NULL)
{
perror("fail to malloc");
return NULL;
}
return pNewNode;
}
int IsEmptySeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue)
{
return pTmpQueue->Head == pTmpQueue->Tail ? 1 : 0;
}
int IsFullSeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue)
{
return ((pTmpQueue->Tail + 1) % pTmpQueue->Maxlen == pTmpQueue->Head) ? 1 : 0;
}
int EnterSeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue, DataType TmpData)
{
if(IsFullSeqQueue(pTmpQueue))
{
return -1;
}
pTmpQueue->pData[pTmpQueue->Tail] = TmpData;//从队尾开始入列
pTmpQueue->Tail = (pTmpQueue->Tail+1) % pTmpQueue->Maxlen;//尾向后走,走到最后一个回到开头
return 0;
}
DataType QuitSeqQueue(seqqueue_t *pTmpQueue)
{
DataType TmpData;
if(IsEmptySeqQueue(pTmpQueue))
{
return -1;
}
TmpData = pTmpQueue->pData[pTmpQueue->Head];
pTmpQueue->Head = (pTmpQueue->Head + 1) % pTmpQueue->Maxlen;
return TmpData;
}
int DestorySeqQueue(seqqueue_t **ppTmpQueue)
{
free((*ppTmpQueue)->pData);
free(*ppTmpQueue);
*ppTmpQueue = NULL;
return 0;
}- 主函数:
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"seqqueue.h"
int main(void)
{
seqqueue_t *pseqqueue = NULL;
int i = 0;
pseqqueue = CreateSeqQueue(10);
while(!IsFullSeqQueue(pseqqueue))
{
EnterSeqQueue(pseqqueue, i);
i++;
}
while(!IsEmptySeqQueue(pseqqueue))
{
printf("%d ", QuitSeqQueue(pseqqueue));
}
printf("\n");
DestorySeqQueue(&pseqqueue);
return 0;
}2.链式队列
核心是利用单向链表尾插法入队
- 入队 :新建节点,让尾指针的
next指向新节点,再将尾指针移到新节点(空队列时头、尾指针同时指向新节点); - 出队:保存头节点的数,将头指针移到下一个节点(出队后为空时,尾指针也要置空),再返回保存的数;
- 仅需判空,无需判满(链表可动态新增节点,理论上仅受内存限制)
示例:
- 头文件:
cpp
#ifndef _LINKQUEUE_H
#define _LINKQUEUE_H
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct node
{
DataType Data;
struct node *pNext;
}Node_t;
extern Node_t *CreatEmptyLinkQueue(void);
extern int IsEmptyLinkQueue(Node_t *pHead);
extern int EnterLinkQueue(Node_t *pHead, DataType TmpData);
extern DataType QuitLinkQueue(Node_t *pHead);
extern int DestoryLinkQueue(Node_t **ppHead);
#endif- 函数:
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"linkqueue.h"
Node_t *CreatEmptyLinkQueue(void)
{
Node_t *pNewNode = NULL;
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(Node_t));
if(pNewNode == NULL)
{
perror("fail to malloc");
return NULL;
}
pNewNode->pNext = NULL;
return pNewNode;
}
int IsEmptyLinkQueue(Node_t *pHead)
{
return pHead->pNext == NULL ? 1 : 0;
}
int EnterLinkQueue(Node_t *pHead, DataType TmpData)
{
Node_t *pNewNode = NULL;
Node_t *pLastQueue = NULL;
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(Node_t));
if(pNewNode == NULL)
{
perror("fail to malloc");
return -1;
}
pNewNode->Data = TmpData;
pNewNode->pNext = NULL;
pLastQueue = pHead;
while(pLastQueue->pNext != NULL)
{
pLastQueue = pLastQueue->pNext;
}
pLastQueue->pNext = pNewNode;
return 0;
}
DataType QuitLinkQueue(Node_t *pHead)
{
Node_t *pTmpQueue = NULL;
DataType TmpData;
if(IsEmptyLinkQueue(pHead))
{
return 0;
}
pTmpQueue = pHead->pNext;
TmpData = pTmpQueue->Data;
pHead->pNext = pTmpQueue->pNext;
free(pTmpQueue);
pTmpQueue = NULL;
return TmpData;
}
int DestoryLinkQueue(Node_t **ppHead)
{
Node_t *pTmpQueue = NULL;
Node_t *pFreeQueue = NULL;
pTmpQueue = pFreeQueue = *ppHead;
while(pTmpQueue != NULL)
{
pTmpQueue = pTmpQueue->pNext;
free(pFreeQueue);
pFreeQueue = pTmpQueue;
}
*p- 主函数:
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include"linkqueue.h"
int main(void)
{
Node_t *plinkqueue = NULL;
plinkqueue = CreatEmptyLinkQueue();
EnterLinkQueue(plinkqueue, 1);
EnterLinkQueue(plinkqueue, 2);
EnterLinkQueue(plinkqueue, 3);
EnterLinkQueue(plinkqueue, 4);
EnterLinkQueue(plinkqueue, 5);
while(!IsEmptyLinkQueue(plinkqueue))
{
printf("%d ", QuitLinkQueue(plinkqueue));
}
printf("\n");
DestoryLinkQueue(&plinkqueue);
return 0;
}二、二叉树
1.概念
- 树:描述数据一对多关系的数据结构;
- 前驱:数据从哪来;
- 后继:数据对应后续的节点;
- 节点 :二叉树的基本单元,包含数据域 (存值)、左孩子指针 (指向左子节点)、右孩子指针(指向右子节点);
- 根节点:最顶层节点,没有前驱只有后继;
- 叶子节点:只有前驱没有后继;
- 分支节点:既有前驱又有后继;
- **层:**根节点所在的位置称为第一层,每过一个节点层数+1;
- 树的高度:距离该节点最远的叶子节点的距离;
- 树的深度:距离根节点的节点个数;
- 度 :前驱或者后继的个数
- 入度:均为1;
- 出度:后继节点的个数;
2.二叉树
- 树形结构中每个节点最多有两个后继节点;
- 满二叉树 :除叶子节点外,每个节点都有两个子节点,且所有叶子节点在同一层;
- 完全二叉树 :按层序(从上到下、从左到右)编号,所有节点的编号和同深度的满二叉树完全一致(叶子节点只出现在最后两层,且最后一层的叶子都靠左)。
- 右孩子:二叉树中节点左侧的子节点;
- 左孩子:二叉树中节点右侧的子节点;
- 二叉树特性:
- 第k层最多有:2^(k-1) 个节点
- 前k层最多有:2^k -1 个节点
- 二叉树的遍历:
- 深度优先遍历:DFS
- 前序遍历:根左右,先访问根节点 → 递归遍历左子树 → 递归遍历右子树
- 中序遍历:左根右,先递归遍历左子树 → 访问根节点 → 递归遍历右子树
- 后续遍历:左右根,先递归遍历左子树 → 递归遍历右子树 → 访问根节点
- 深度优先遍历:DFS
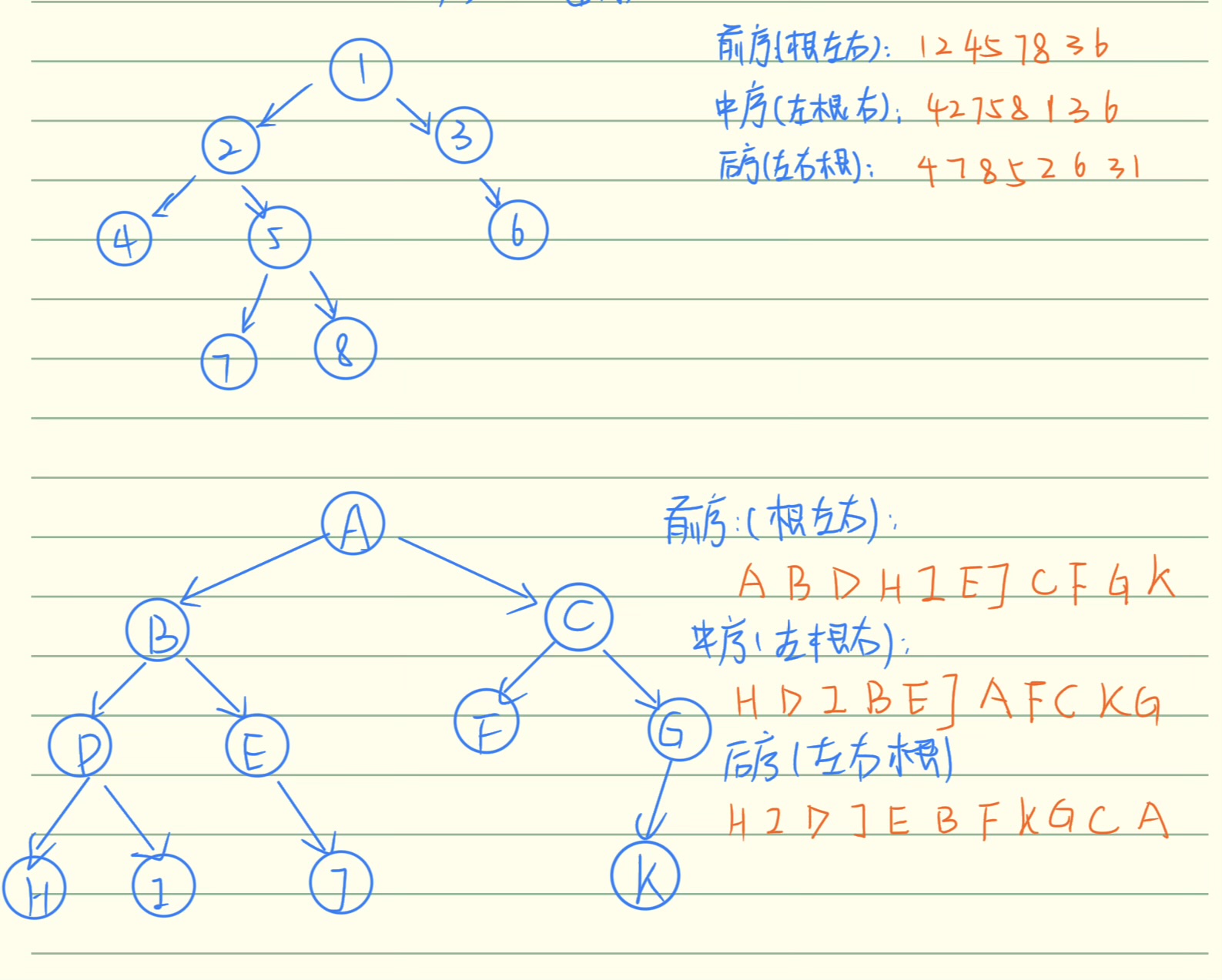
- 广度优先遍历:BFS
- 层序遍历:每层从左到右遍历