文章目录
-
- 资源创建
- 资源加载
-
-
- [Drawable 资源加载流程](#Drawable 资源加载流程)
- [Color 资源加载流程](#Color 资源加载流程)
- 应用图标资源加载流程
-
- AssetManager
基于 Android U
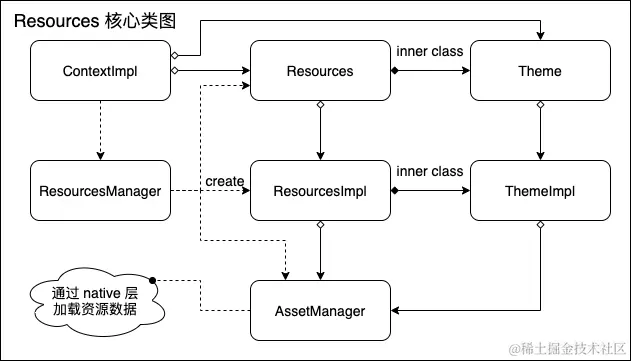
在使用一般资源时,我们通过 Context 上下文类获取 Resources 类,然后通过资源管理类(Resources)加载资源文件,在 Resources 类内部的 impl(ResourcesImpl) 进行加载资源,而 ResourcesImpl 内部则通过 AssetManager 进行资源真正的加载操作;AssetManager 内部主要是 native 方法,所以资源的加载操作主要在 native 层进行的。
而与 style 相关的资源则是通过 Theme 进行加载,Theme 同样由 Context 上下文类获取,Theme 同时也是 Resources 的内部类,Theme 内部通过 ThemeImpl 进行 style 资源的操作,而 ThemeImpl 是 ResourcesImpl 的内部类,在 ThemeImpl 内引用着 ResourcesImpl 的 mAssets(AssetManager)对象,所以通过 Theme 加载 style 资源时,同样是通过 AssetManager 进行加载,并将加载的数据通过 TypedArray 数组进行返回;
资源创建
创建 System 的 Resources
Zygote 初始化时会对资源进行预加载。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
private static void preloadResources() {
try {
mResources = Resources.getSystem();
mResources.startPreloading();
... // 系统资源加载,代码省略
mResources.finishPreloading();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failure preloading resources", e);
}
}在 Zygote 初始化时 mSystem 就被赋值了。所有的应用程序都是从 Zygote 进程 fork 而来的,这意味着所有进程中的 mSystem 引用的 Resources 实例在整个 Android 系统中是共享的,这部分其实也就是 framework 的资源。
通过 Resources.getSystem().getX() 调用资源时,就是在调用 framework 的资源。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/Resources.java
public static Resources getSystem() {
synchronized (sSync) {
Resources ret = mSystem;
if (ret == null) {
ret = new Resources();
mSystem = ret;
}
return ret;
}
}
private Resources() {
this(null);
final DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
metrics.setToDefaults();
final Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.setToDefaults();
mResourcesImpl = new ResourcesImpl(AssetManager.getSystem(), metrics, config,
new DisplayAdjustments());
}Resources.getSystem() 方法会对 mSystem 初始化,创建 ResourcesImpl 实例时传入的 AssetManager 是通过 AssetManager.getSystem() 获取的,会加载 framework-res.apk。
创建 Application Context 的 Resources
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
static ContextImpl createAppContext(ActivityThread mainThread, LoadedApk packageInfo,
String opPackageName) {
if (packageInfo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("packageInfo");
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo,
ContextParams.EMPTY, null, null, null, null, null, 0, null, opPackageName);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources()); // 1
context.mContextType = isSystemOrSystemUI(context) ? CONTEXT_TYPE_SYSTEM_OR_SYSTEM_UI
: CONTEXT_TYPE_NON_UI;
return context;
}注释1处创建 Resources 对象,并赋值给 ContextImpl。
- 创建 Resources 对象
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
public Resources getResources() {
if (mResources == null) {
...
mResources = ResourcesManager.getInstance().getResources(...); // 1
}
return mResources;
}注释1处调用 ResourcesManager#getResources。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java
public Resources getResources(
@Nullable IBinder activityToken,
@Nullable String resDir,
@Nullable String[] splitResDirs,
@Nullable String[] legacyOverlayDirs,
@Nullable String[] overlayPaths,
@Nullable String[] libDirs,
@Nullable Integer overrideDisplayId,
@Nullable Configuration overrideConfig,
@NonNull CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader,
@Nullable List<ResourcesLoader> loaders) {
try {
...
final ResourcesKey key = new ResourcesKey(
resDir,
splitResDirs,
combinedOverlayPaths(legacyOverlayDirs, overlayPaths),
libDirs,
overrideDisplayId != null ? overrideDisplayId : INVALID_DISPLAY,
overrideConfig,
compatInfo,
loaders == null ? null : loaders.toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0])); // 1
classLoader = classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
// Preload the ApkAssets required by the key to prevent performing heavy I/O while the
// ResourcesManager lock is held.
final ApkAssetsSupplier assetsSupplier = createApkAssetsSupplierNotLocked(key); // 2
...
Resources resources;
if (activityToken != null) {
Configuration initialOverrideConfig = new Configuration(key.mOverrideConfiguration);
rebaseKeyForActivity(activityToken, key, overrideDisplayId != null);
resources = createResourcesForActivity(activityToken, key, initialOverrideConfig,
overrideDisplayId, classLoader, assetsSupplier);
} else {
resources = createResources(key, classLoader, assetsSupplier); // 3
}
return resources;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES);
}
}注释1处创建 key,用于缓存 resources 对象。
注释2处创建 APK 加载资源的内存表示,同时防止 GC 回收,用于 C++ 交互。
注释3处创建 Resources。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java
private Resources createResources(@NonNull ResourcesKey key, @NonNull ClassLoader classLoader,
@Nullable ApkAssetsSupplier apkSupplier) {
synchronized (mLock) {
...
ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key, apkSupplier); // 1
if (resourcesImpl == null) {
return null;
}
return createResourcesLocked(classLoader, resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo); // 2
}
}注释1处创建 / 获取 ResourcesImpl 对象。
注释2处创建 Resources 对象。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java
// 第一部分,创建ResourcesImpl
private @Nullable ResourcesImpl findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(
@NonNull ResourcesKey key, @Nullable ApkAssetsSupplier apkSupplier) {
// 1.1 从缓存加载ResourcesImpl
ResourcesImpl impl = findResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key);
if (impl == null) {
// 1.2 创建ResourcesImpl
impl = createResourcesImpl(key, apkSupplier);
if (impl != null) {
// 1.3 将创建的ResourcesImpl对象放入缓存
mResourceImpls.put(key, new WeakReference<>(impl));
}
}
return impl;
}
private @Nullable ResourcesImpl createResourcesImpl(@NonNull ResourcesKey key,
@Nullable ApkAssetsSupplier apkSupplier) {
// 1.2.1 创建AssetManager
final AssetManager assets = createAssetManager(key, apkSupplier);
if (assets == null) {
return null;
}
final DisplayAdjustments daj = new DisplayAdjustments(key.mOverrideConfiguration);
daj.setCompatibilityInfo(key.mCompatInfo);
final Configuration config = generateConfig(key);
final DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = getDisplayMetrics(generateDisplayId(key), daj);
// 1.2.2 创建ResourcesImpl
final ResourcesImpl impl = new ResourcesImpl(assets, displayMetrics, config, daj);
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "- creating impl=" + impl + " with key: " + key);
}
return impl;
}
// 第二部分,创建Resources
private @NonNull Resources createResourcesLocked(@NonNull ClassLoader classLoader,
@NonNull ResourcesImpl impl, @NonNull CompatibilityInfo compatInfo) {
cleanupReferences(mResourceReferences, mResourcesReferencesQueue);
// 2.1 创建Resources对象
Resources resources = compatInfo.needsCompatResources() ? new CompatResources(classLoader)
: new Resources(classLoader);
// 2.2 将impl设置到Resources内
resources.setImpl(impl);
resources.setCallbacks(mUpdateCallbacks);
// 2.3 将resources放入缓存内
mResourceReferences.add(new WeakReference<>(resources, mResourcesReferencesQueue));
...
return resources;
}- 将 Resources 赋值给 ContextImpl 的 mResources 对象
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
void setResources(Resources r) {
if (r instanceof CompatResources) {
((CompatResources) r).setContext(this);
}
mResources = r; // 1
}注释1处将 resources 赋值给 ContextImpl 的 mResources 对象。
-
总结
Resources 资源管理对象的创建,主要分为7个步骤:
-
创建 ContextImpl 时,同步会创建相关的 Resources 对象,并将 Resources 赋值给 mResources 对象;
-
通过 ResourcesManager 的 getResources 方法创建 Resources 对象;
-
创建 ResourcesKey 对象,作为缓存 key 和记录 Resource 相关的信息;
-
创建 ApkAssetsSupplier 对象,内部维护了一个 Map 集合,用于缓存不同目录下的资源数据,Key 为 Appkey(目录path生成),Value 为 ApkAssets 的 Map;
-
创建 AssetManager,用于和 native 层进行交互;
-
创建 ResourceImpl,作为 Resources 的实现类;
-
创建 Resources,并将 resources 设置到 ContextImpl;
非 Activity 类型的 Resources 最终会通过 ResourcesManager#createResourcesLocked 创建。
-
创建 Activity Context 的 Resources
前置信息
-
ActivityResources
javaprivate static class ActivityResources { public final Configuration overrideConfig = new Configuration(); public final ArrayList<ActivityResource> activityResources = new ArrayList<>(); ... }包含了与一个 Activity 或者 WindowContext 相关联的基础 Configuration 和 Resources 集合。
这也就是说,每一个 Activity 或者 WindowContext,都可能对应多个 Resources。在创建一个 Activity 或者 WindowContext 的时候,系统都会为其创建一个 ActivityResources 对象,这个 ActivityResources 的作用之一就是通过 activityResources 变量为 Activity 或者 WindowContext 保存与之联系的所有 Resources 对象。overrideConfig 成员变量会被应用到 ActivityResources.activityResources 队列中的所有 Resources 的 Configuration。
-
ActivityResource
javaprivate static class ActivityResource { public final Configuration overrideConfig = new Configuration(); @Nullable public WeakReference<Resources> resources; ... }ActivityResource 就是对 Resources 的一层封装。resources,即当前 ActivityResource 对象保存的那个 Resources 对象的弱引用。overrideConfig 保存了一个 Activity 或者 WindowContext 对象创建的时候的初始 Configuration,这个变量在 Configuration 更新的时候不会被新传入的 Configuration 覆盖掉。
-
ResourceManager
用于管理 App 所有的 resources,内部有一个
mActivityResourceReferencesmap 保存着所有 Activity或者 WindowToken 对应的 Resources 对象。javaprivate final WeakHashMap<IBinder, ActivityResources> mActivityResourceReferences = new WeakHashMap<>();
创建流程
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
static ContextImpl createActivityContext(ActivityThread mainThread,
LoadedApk packageInfo, ActivityInfo activityInfo, IBinder activityToken, int displayId,
Configuration overrideConfiguration) {
...
String[] splitDirs = packageInfo.getSplitResDirs(); // 1
ClassLoader classLoader = packageInfo.getClassLoader(); // 2
...
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, ContextParams.EMPTY,
attributionTag, null, activityInfo.splitName, activityToken, null, 0, classLoader,
null); // 3
...
final ResourcesManager resourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance(); // 4
// Create the base resources for which all configuration contexts for this Activity
// will be rebased upon.
context.setResources(resourcesManager.createBaseTokenResources(activityToken,
packageInfo.getResDir(),
splitDirs,
packageInfo.getOverlayDirs(),
packageInfo.getOverlayPaths(),
packageInfo.getApplicationInfo().sharedLibraryFiles,
displayId,
overrideConfiguration,
compatInfo,
classLoader,
packageInfo.getApplication() == null ? null
: packageInfo.getApplication().getResources().getLoaders())); // 5
context.setDisplay(resourcesManager.getAdjustedDisplay(
displayId, context.getResources()));
return context;
}注释1、2处获取当前的分辨率文件、ClassLoader。
注释3处初始化 ContextImpl。
注释4、5处获取 ResourcesManager 单例对象,然后使用其 createBaseTokenResources() 去创建最终的 Resources。接着将 Resources 对象保存到 Context 中,即赋值给 ContextImpl.mResources。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java
public @Nullable Resources createBaseTokenResources(@NonNull IBinder token,
@Nullable String resDir,
@Nullable String[] splitResDirs,
@Nullable String[] legacyOverlayDirs,
@Nullable String[] overlayPaths,
@Nullable String[] libDirs,
int displayId,
@Nullable Configuration overrideConfig,
@NonNull CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader,
@Nullable List<ResourcesLoader> loaders) {
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES,
"ResourcesManager#createBaseActivityResources");
final ResourcesKey key = new ResourcesKey(
resDir,
splitResDirs,
combinedOverlayPaths(legacyOverlayDirs, overlayPaths),
libDirs,
displayId,
overrideConfig,
compatInfo,
loaders == null ? null : loaders.toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]));
classLoader = classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
...
synchronized (mLock) {
// Force the creation of an ActivityResourcesStruct.
getOrCreateActivityResourcesStructLocked(token); // 1
}
// Update any existing Activity Resources references.
updateResourcesForActivity(token, overrideConfig, displayId); // 2
synchronized (mLock) {
Resources resources = findResourcesForActivityLocked(token, key,
classLoader); // 3
if (resources != null) {
return resources;
}
}
// Now request an actual Resources object.
return createResourcesForActivity(token, key,
/* initialOverrideConfig */ Configuration.EMPTY, /* overrideDisplayId */ null,
classLoader, /* apkSupplier */ null); // 4
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES);
}
}注释1处创建对应的 ActivityResources 对象。
注释2处更新该 token 对应的 resources。
注释3处查找当前 Activity 对应的 resources 对象,存在则复用。如果不存在,注释4处创建。
该方法内部会经历如下步骤:
-
先查找或创建当前 token(activity) 对应的 resources。
找到了,什么都不做;
没找到,创建一个 ActivityResources 对象,并将其添加到
mActivityResourceReferencesmap 中。 -
更新该 activity 对应的 resources(内部会再执行第一步)。
-
再次查找当前 activity 对应的 resources,如果找到,则直接返回。
-
如果没找到,则重新创建一个 resources(内部会再执行第一步)。
-
getOrCreateActivityResourcesStructLocked
javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java private ActivityResources getOrCreateActivityResourcesStructLocked( @NonNull IBinder activityToken) { ActivityResources activityResources = mActivityResourceReferences.get(activityToken); if (activityResources == null) { activityResources = new ActivityResources(); mActivityResourceReferences.put(activityToken, activityResources); } return activityResources; } -
updateResourcesForActivity
javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java public void updateResourcesForActivity(@NonNull IBinder activityToken, @Nullable Configuration overrideConfig, int displayId) { try { ... synchronized (mLock) { final ActivityResources activityResources = getOrCreateActivityResourcesStructLocked(activityToken); boolean movedToDifferentDisplay = activityResources.overrideDisplayId != displayId; if (Objects.equals(activityResources.overrideConfig, overrideConfig) && !movedToDifferentDisplay) { // 1 // They are the same and no change of display id, no work to do. return; } // Grab a copy of the old configuration so we can create the delta's of each // Resources object associated with this Activity. final Configuration oldConfig = new Configuration(activityResources.overrideConfig); // 2 // Update the Activity's base override. if (overrideConfig != null) { activityResources.overrideConfig.setTo(overrideConfig); } else { activityResources.overrideConfig.unset(); } // Update the Activity's override display id. activityResources.overrideDisplayId = displayId; // If a application info update was scheduled to occur in this process but has not // occurred yet, apply it now so the resources objects will have updated paths if // the assets sequence changed. applyAllPendingAppInfoUpdates(); ... // Rebase each Resources associated with this Activity. // 3 final int refCount = activityResources.activityResources.size(); for (int i = 0; i < refCount; i++) { final ActivityResource activityResource = activityResources.activityResources.get(i); final Resources resources = activityResource.resources.get(); if (resources == null) { continue; } final ResourcesKey newKey = rebaseActivityOverrideConfig(activityResource, overrideConfig, displayId); // 4 if (newKey == null) { continue; } // TODO(b/173090263): Improve the performance of AssetManager & ResourcesImpl // constructions. final ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(newKey); // 5 if (resourcesImpl != null && resourcesImpl != resources.getImpl()) { // Set the ResourcesImpl, updating it for all users of this Resources // object. resources.setImpl(resourcesImpl); // 6 } } } } finally { Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES); } }内部会先获取当前 activity 对应的 resources(如果不存在,则创建),如果当前传入的配置与之前一致,则直接返回(注释1);否则先使用当前 activity 对应的配置创建一个旧的 Configuration 对象(注释2),接着去更新该 activity 所有的 resourcesImpl(注释3)。每次更新时会先与当前的配置进行差异更新并返回并返回新的 ResourcesKey(注释4),并使用这个 key 获取其对应的 impl,如果没有则创建(注释5)。获取到的 impl 如果与当前的不一致,则更新当前 resources 的 impl。
-
findResourcesForActivityLocked
javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java private Resources findResourcesForActivityLocked(@NonNull IBinder targetActivityToken, @NonNull ResourcesKey targetKey, @NonNull ClassLoader targetClassLoader) { ActivityResources activityResources = getOrCreateActivityResourcesStructLocked( targetActivityToken); // 1 final int size = activityResources.activityResources.size(); for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) { ActivityResource activityResource = activityResources.activityResources.get(index); Resources resources = activityResource.resources.get(); ResourcesKey key = resources == null ? null : findKeyForResourceImplLocked( resources.getImpl()); if (key != null && Objects.equals(resources.getClassLoader(), targetClassLoader) && Objects.equals(key, targetKey)) { // 2 return resources; } } return null; // 3 }通过 findResourcesForActivityLocked 获取指定的 resources 时,内部会先获取当前 token 对应的 activityResources(注释1),从而拿到其所有的 resources;然后遍历所有 resources,如果某个 resources 对应的 key(ResourcesKey)与当前查找的一致并且符合其他规则(注释2),则直接返回;否则返回 null(注释3)。
-
createResourcesForActivity
javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/app/ResourcesManager.java private Resources createResourcesForActivity(@NonNull IBinder activityToken, @NonNull ResourcesKey key, @NonNull Configuration initialOverrideConfig, @Nullable Integer overrideDisplayId, @NonNull ClassLoader classLoader, @Nullable ApkAssetsSupplier apkSupplier) { synchronized (mLock) { ... ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key, apkSupplier); // 1 if (resourcesImpl == null) { return null; } return createResourcesForActivityLocked(activityToken, initialOverrideConfig, overrideDisplayId, classLoader, resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo); // 2 } } private Resources createResourcesForActivityLocked(@NonNull IBinder activityToken, @NonNull Configuration initialOverrideConfig, @Nullable Integer overrideDisplayId, @NonNull ClassLoader classLoader, @NonNull ResourcesImpl impl, @NonNull CompatibilityInfo compatInfo) { final ActivityResources activityResources = getOrCreateActivityResourcesStructLocked( activityToken); cleanupReferences(activityResources.activityResources, activityResources.activityResourcesQueue, (r) -> r.resources); Resources resources = compatInfo.needsCompatResources() ? new CompatResources(classLoader) : new Resources(classLoader); resources.setImpl(impl); resources.setCallbacks(mUpdateCallbacks); ActivityResource activityResource = new ActivityResource(); activityResource.resources = new WeakReference<>(resources, activityResources.activityResourcesQueue); activityResource.overrideConfig.setTo(initialOverrideConfig); activityResource.overrideDisplayId = overrideDisplayId; activityResources.activityResources.add(activityResource); ... return resources; }创建 Resources 时,内部会先使用 key 查找或创建相应的 ResourcesImpl(注释1),然后创建新的 Resources。
-
总结
Activity 类型的 Resources 最终会通过 ResourcesManager#createResourcesForActivityLocked 创建。
资源加载
Drawable 资源加载流程
Context#getDrawable -> Resources#getDrawable -> Resources#getDrawableForDensity -> Resources#loadDrawable -> ResourcesImpl#loadDrawable
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/ResourcesImpl.java
Drawable loadDrawable(@NonNull Resources wrapper, @NonNull TypedValue value, int id,
int density, @Nullable Resources.Theme theme)
throws NotFoundException {
...
try {
...
final boolean isColorDrawable;
final DrawableCache caches;
final long key;
if (value.type >= TypedValue.TYPE_FIRST_COLOR_INT
&& value.type <= TypedValue.TYPE_LAST_COLOR_INT) {
isColorDrawable = true;
caches = mColorDrawableCache;
key = value.data;
} else {
isColorDrawable = false;
caches = mDrawableCache;
key = (((long) value.assetCookie) << 32) | value.data;
}
int cacheGeneration = caches.getGeneration();
// First, check whether we have a cached version of this drawable
// that was inflated against the specified theme. Skip the cache if
// we're currently preloading or we're not using the cache.
if (!mPreloading && useCache) {
Drawable cachedDrawable = caches.getInstance(key, wrapper, theme); // 1
if (cachedDrawable != null) {
cachedDrawable.setChangingConfigurations(value.changingConfigurations);
return cachedDrawable;
}
}
// Next, check preloaded drawables. Preloaded drawables may contain
// unresolved theme attributes.
final Drawable.ConstantState cs; // 2
if (isColorDrawable) {
cs = sPreloadedColorDrawables.get(key);
} else {
cs = sPreloadedDrawables[mConfiguration.getLayoutDirection()].get(key);
}
Drawable dr;
boolean needsNewDrawableAfterCache = false;
if (cs != null) {
dr = cs.newDrawable(wrapper);
} else if (isColorDrawable) {
dr = new ColorDrawable(value.data); // 3.1
} else {
dr = loadDrawableForCookie(wrapper, value, id, density); // 3.2
}
...
if (dr != null) {
dr.setChangingConfigurations(value.changingConfigurations);
if (useCache) {
cacheDrawable(value, isColorDrawable, caches, theme, canApplyTheme, key, dr,
cacheGeneration); // 4
if (needsNewDrawableAfterCache) {
Drawable.ConstantState state = dr.getConstantState();
if (state != null) {
dr = state.newDrawable(wrapper);
}
}
}
}
return dr;
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}注释1处尝试从缓存中获取资源。
注释2处检查预加载资源中是否存在当前需要的 drawable,并将其状态与参数保存。
注释3.1处,如果是颜色 drawable,直接创建;注释3.2处,如果不是颜色 drawable,调用 loadDrawableForCookie() 创建。
注释4处,将资源写入缓存中。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/ResourcesImpl.java
private Drawable loadDrawableForCookie(@NonNull Resources wrapper, @NonNull TypedValue value,
int id, int density) {
...
final Drawable dr;
...
try {
...
try {
if (file.endsWith(".xml")) {
final String typeName = getResourceTypeName(id);
if (typeName != null && typeName.equals("color")) {
dr = loadColorOrXmlDrawable(wrapper, value, id, density, file); // 1
} else {
dr = loadXmlDrawable(wrapper, value, id, density, file); // 2
}
} else if (file.startsWith("frro://")) {
...
dr = decodeImageDrawable(is, wrapper);
} else {
final InputStream is = mAssets.openNonAsset(
value.assetCookie, file, AssetManager.ACCESS_STREAMING); // 3
final AssetInputStream ais = (AssetInputStream) is;
dr = decodeImageDrawable(ais, wrapper, value);
}
} finally {
stack.pop();
}
} catch (Exception | StackOverflowError e) {
...
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES);
return dr;
}根据资源文件类型分别处理。
如果是 xml 类型,颜色资源解析为 ColorStateListDrawable,其他资源调用 loadXmlDrawable 解析为 Drawable。
如果不是xml类型,调用 AssetManager.openNonAsset() 打开文件。调用 decodeImageDrawable(),这里一般对应 png 等二进制图片资源,一般解析成 BitmapDrawable、NinePatchDrawable 或 AnimatedImageDrawable。
-
是 color 类型的 xml 文件
javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/ResourcesImpl.java private Drawable loadColorOrXmlDrawable(@NonNull Resources wrapper, @NonNull TypedValue value, int id, int density, String file) { try { ColorStateList csl = loadColorStateList(wrapper, value, id, null); return new ColorStateListDrawable(csl); } catch (NotFoundException originalException) { // If we fail to load as color, try as normal XML drawable try { return loadXmlDrawable(wrapper, value, id, density, file); } catch (Exception ignored) { // If fallback also fails, throw the original exception throw originalException; } } } ColorStateList loadColorStateList(Resources wrapper, TypedValue value, int id, Resources.Theme theme) throws NotFoundException { if (TRACE_FOR_PRELOAD) { // Log only framework resources if ((id >>> 24) == 0x1) { final String name = getResourceName(id); if (name != null) android.util.Log.d("PreloadColorStateList", name); } } final long key = (((long) value.assetCookie) << 32) | value.data; // Handle inline color definitions. if (value.type >= TypedValue.TYPE_FIRST_COLOR_INT && value.type <= TypedValue.TYPE_LAST_COLOR_INT) { return getColorStateListFromInt(value, key); // 1 } ComplexColor complexColor = loadComplexColorFromName(wrapper, theme, value, id); if (complexColor != null && complexColor instanceof ColorStateList) { return (ColorStateList) complexColor; } throw new NotFoundException( "Can't find ColorStateList from drawable resource ID #0x" + Integer.toHexString(id)); } -
不是 color 类型的 xml 文件
javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/ResourcesImpl.java private Drawable loadXmlDrawable(@NonNull Resources wrapper, @NonNull TypedValue value, int id, int density, String file) throws IOException, XmlPullParserException { try ( XmlResourceParser rp = loadXmlResourceParser(file, id, value.assetCookie, "drawable") ) { return Drawable.createFromXmlForDensity(wrapper, rp, density, null); } } XmlResourceParser loadXmlResourceParser(@NonNull String file, @AnyRes int id, int assetCookie, @NonNull String type) throws NotFoundException { if (id != 0) { try { synchronized (mCachedXmlBlocks) { ... final XmlBlock block = mAssets.openXmlBlockAsset(assetCookie, file); ... return block.newParser(id); } } catch (Exception e) { ... } } throw new NotFoundException("File " + file + " from xml type " + type + " resource ID #0x" + Integer.toHexString(id)); }最终调用了 AssetManager.openXmlBlockAsset()。
-
不是 xml 文件
调用 Assets.openNonAsset()。
Color 资源加载流程
ContextCompat#getColor -> ContextCompatApi23#getColor -> Context#getColor -> Resources#getColor
java
ContextCompat.java
public static final int getColor(Context context, int id) {
final int version = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
if (version >= 23) {
return ContextCompatApi23.getColor(context, id);
} else {
return context.getResources().getColor(id);
}
}
ContextCompatApi23.java
public static int getColor(Context context, int id) {
return context.getColor(id);
}
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/Context.java
public final int getColor(@ColorRes int id) {
return getResources().getColor(id, getTheme());
}调用到了 Resources#getColor
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/Resources.java
public int getColor(@ColorRes int id, @Nullable Theme theme) throws NotFoundException {
final TypedValue value = obtainTempTypedValue();
try {
final ResourcesImpl impl = mResourcesImpl;
impl.getValue(id, value, true); // 1
if (value.type >= TypedValue.TYPE_FIRST_INT
&& value.type <= TypedValue.TYPE_LAST_INT) {
return value.data;
} else if (value.type != TypedValue.TYPE_STRING) {
throw new NotFoundException("Resource ID #0x" + Integer.toHexString(id)
+ " type #0x" + Integer.toHexString(value.type) + " is not valid");
}
final ColorStateList csl = impl.loadColorStateList(this, value, id, theme); // 2
return csl.getDefaultColor();
} finally {
releaseTempTypedValue(value);
}
}通过 getValue() 获取相应的 color 资源,并将其保存到 TypedValue 中(注释1)。然后通过 ResourcesImpl.loadColorStateList() 加载,返回颜色状态列表的默认显示颜色(注释2)。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/ResourcesImpl.java
ColorStateList loadColorStateList(Resources wrapper, TypedValue value, int id,
Resources.Theme theme)
throws NotFoundException {
...
final long key = (((long) value.assetCookie) << 32) | value.data;
// Handle inline color definitions.
if (value.type >= TypedValue.TYPE_FIRST_COLOR_INT
&& value.type <= TypedValue.TYPE_LAST_COLOR_INT) {
return getColorStateListFromInt(value, key); // 1
}
ComplexColor complexColor = loadComplexColorFromName(wrapper, theme, value, id); // 2
if (complexColor != null && complexColor instanceof ColorStateList) {
return (ColorStateList) complexColor;
}
...
}
private ColorStateList getColorStateListFromInt(@NonNull TypedValue value, long key) {
ColorStateList csl;
final android.content.res.ConstantState<ComplexColor> factory =
sPreloadedComplexColors.get(key);
if (factory != null) {
return (ColorStateList) factory.newInstance(); // 1.1
}
csl = ColorStateList.valueOf(value.data); // 1.2
if (mPreloading) {
if (verifyPreloadConfig(value.changingConfigurations, 0, value.resourceId,
"color")) {
sPreloadedComplexColors.put(key, csl.getConstantState()); // 1.3
}
}
return csl;
}
private ComplexColor loadComplexColorFromName(Resources wrapper, Resources.Theme theme,
TypedValue value, int id) {
final long key = (((long) value.assetCookie) << 32) | value.data;
final ConfigurationBoundResourceCache<ComplexColor> cache = mComplexColorCache;
ComplexColor complexColor = cache.getInstance(key, wrapper, theme); // 2.1
if (complexColor != null) {
return complexColor;
}
int cacheGeneration = cache.getGeneration();
final android.content.res.ConstantState<ComplexColor> factory =
sPreloadedComplexColors.get(key);
if (factory != null) {
complexColor = factory.newInstance(wrapper, theme); // 2.2
}
if (complexColor == null) {
complexColor = loadComplexColorForCookie(wrapper, value, id, theme); // 2.3
}
if (complexColor != null) {
complexColor.setBaseChangingConfigurations(value.changingConfigurations);
if (mPreloading) {
if (verifyPreloadConfig(complexColor.getChangingConfigurations(),
0, value.resourceId, "color")) {
sPreloadedComplexColors.put(key, complexColor.getConstantState()); // 2.4
}
} else {
cache.put(key, theme, complexColor.getConstantState(), cacheGeneration); // 2.5
}
}
return complexColor;
}如果当前要获取的颜色类型是 RGB 颜色值(#XXX),则先从预加载数组中取(注释1);如果此时没有加载,则创建新的 ColorStateList(注释1.1),并将其存到预加载数组中(注释1.3)。
如果当前要获取的颜色类型是引用类型,则要从 xml 中取。内部先从缓存数组中取(注释2.1)。如果不存在,从预加载数组中取(注释2.2)。如果仍不存在,则调用 loadComplexColorForCookie() 重新初始化(注释2.3)。加载完成后,如果此时正在预加载(注释2.4),将其添加到预加载数组中,否则添加到缓存中(注释2.5)。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/ResourcesImpl.java
private ComplexColor loadComplexColorForCookie(Resources wrapper, TypedValue value, int id,
Resources.Theme theme) {
...
ComplexColor complexColor = null;
...
if (file.endsWith(".xml")) {
try {
final XmlResourceParser parser = loadXmlResourceParser(
file, id, value.assetCookie, "ComplexColor"); // 1
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG
&& type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Seek parser to start tag.
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new XmlPullParserException("No start tag found");
}
final String name = parser.getName(); // 2
if (name.equals("gradient")) {
complexColor = GradientColor.createFromXmlInner(wrapper, parser, attrs, theme); // 渐变颜色
} else if (name.equals("selector")) {
complexColor = ColorStateList.createFromXmlInner(wrapper, parser, attrs, theme); // 带状态颜色
}
parser.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
} else {
...
}
...
return complexColor;
}如果资源文件不是 xml 类型,抛出异常;否则调用 loadXmlResourceParser() 拿到该资源文件的 xml 解析器(注释1)。再由解析器的 name 判断具体的资源类型,从而初始化具体的颜色类(注释2)。
-
总结
当我们调用 getColor() 获取某个颜色资源时,内部会先通过 AssetManager 加载该资源,并将其保存到 TypedValue 中,如果没有读到,则抛出异常;否则调用 ResoucesImpl.loadColorStateList() 获取颜色资源。如果该资源在缓存中存在,则直接取出并返回新的实例,否则根据当前要加载的类型,如果是 "#xxx" ,则直接初始化并添加到缓存,否则判断 TypedValue 中保存的资源信息后缀是否为 xml ,如果不是则直接抛出异常,证明此时非 .xml 文件,文件无法读取,否则通过 AssetManager 获取该资源对应的xml解析器 ,并判断解析器的名字,从而决定创建 GradientColor 还是 ColorStateList,然后将结果缓存到 ResourcesImpl 中并返回。
应用图标资源加载流程
应用图标加载方式:
- 方式1
java
PackageManager pm = getPackageManager();
PackageInfo packageInfo = pm.getPackageInfo(packageName, 0);
ApplicationInfo appInfo = packageInfo.applicationInfo;
Drawable icon = pm.getDrawable(appInfo.packageName, appInfo.icon, null);- 方式2
java
PackageManager pm = getPackageManager();
ApplicationInfo appInfo = pm.getApplicationInfo(packageName, PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
Drawable icon = pm.getApplicationIcon(appInfo);PackageManager#getApplicationIcon(实现在 ApplicationPackageManager#getApplicationIcon)
-> ApplicationInfo#loadIcon (实现在 PackageItemInfo.loadIcon)
-> PackageManager#loadItemIcon(实现在 ApplicationPackageManager#loadItemIcon)
-> ApplicationPackageManager#loadUnbadgedItemIcon(先获取图标)
-> ApplicationPackageManager#getDrawable
-> ApplicationPackageManager#getUserBadgedIcon(再根据 UserHandle 设置分身图标)
- 方式3
Android13 + 时:
java
PackageManager pm = getPackageManager();
Drawable icon = pm.getApplicationIcon(packageName);和方式2类似:
java
@Override public Drawable getApplicationIcon(ApplicationInfo info) {
return info.loadIcon(this);
}
@Override public Drawable getApplicationIcon(String packageName)
throws NameNotFoundException {
return getApplicationIcon(getApplicationInfo(packageName, sDefaultFlags));
}- 方式4
获取 Activity 图标:
java
ComponentName component = new ComponentName(packageName, className);
ActivityInfo activityInfo = context.getPackageManager()
.getActivityInfo(component, PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
Drawable icon = activityInfo.loadIcon(context.getPackageManager());ActivityInfo#loadIcon (实现在 ComponentInfo.loadIcon)
-> ApplicationInfo#loadIcon (实现在 PackageItemInfo.loadIcon)
-> PackageManager#loadItemIcon(实现在 ApplicationPackageManager#loadItemIcon)
-> ApplicationPackageManager#loadUnbadgedItemIcon(先获取图标)
-> ApplicationPackageManager#getDrawable
-> ApplicationPackageManager#getUserBadgedIcon(再根据 UserHandle 设置分身图标)
- 共同逻辑
四种方式都会调用到 ApplicationPackageManager#getDrawable。先尝试获取缓存,没有缓存再通过 Resources 加载资源。
java
public Drawable getDrawable(String packageName, @DrawableRes int resId,
@Nullable ApplicationInfo appInfo) {
final ResourceName name = new ResourceName(packageName, resId);
final Drawable cachedIcon = getCachedIcon(name);
if (cachedIcon != null) {
return cachedIcon;
}
...
if (resId != 0) {
try {
final Resources r = getResourcesForApplication(appInfo);
final Drawable dr = r.getDrawable(resId, null);
if (dr != null) {
putCachedIcon(name, dr);
}
...
return dr;
}...
}
return null;
}ApplicationPackageManager#getDrawable -> Resources#getDrawable,后续流程同"Drawable 资源加载流程"。
AssetManager
AssetManager 类是 Android 中实际管理资源的模块,在 Java 层和 Native 层都有代码。
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/AssetManager.java
public final class AssetManager implements AutoCloseable {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
@GuardedBy("sSync") static AssetManager sSystem = null;
@GuardedBy("sSync") private static ApkAssets[] sSystemApkAssets = new ApkAssets[0];
@GuardedBy("sSync") private static ArraySet<ApkAssets> sSystemApkAssetsSet;
@UnsupportedAppUsage
@GuardedBy("this") private long mObject;
// The loaded asset paths.
@GuardedBy("this") private ApkAssets[] mApkAssets;
...
}-
sSystem 是和 Resources 类中 mSystem 对应的 AssetManager 对象,用来管理系统 framework 的资源。
-
sSystemApkAssets、sSystemApkAssetsSet 都是和系统资源相关的 ApkAssets 的集合,在 Zygote 初始化时就已经创建完成。
javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/ApkAssets.java public final class ApkAssets { @GuardedBy("this") private long mNativePtr; @Nullable @GuardedBy("this") private final StringBlock mStringBlock; ... private ApkAssets(@FormatType int format, @NonNull String path, @PropertyFlags int flags, @Nullable AssetsProvider assets) throws IOException { Objects.requireNonNull(path, "path"); mFlags = flags; mNativePtr = nativeLoad(format, path, flags, assets); mStringBlock = new StringBlock(nativeGetStringBlock(mNativePtr), true /*useSparse*/); mAssets = assets; } }通常一个 ApkAssets 管理的是一个资源包中的资源。ApkAssets 主要是与 native 层进行联系,通过各种 native 调用加载相关资源。另一个功能是把 native 层加载字符串资源保存到 mStringBlock 中。
-
mObject 用来存储在 native 层创建的 AssetManager 对象指针。
-
mApkAssets 记录所有已经加载的 assets 资源,也包括 sSystemApkAssets。
创建 Application Context 的 Resources 部分提到:创建 ResourcesImpl 实例时传入的 AssetManager 是通过 AssetManager.getSystem() 获取的,会加载 framework-res.apk。具体逻辑如下:
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/AssetManager.java
public static AssetManager getSystem() {
synchronized (sSync) {
createSystemAssetsInZygoteLocked(false, FRAMEWORK_APK_PATH);
return sSystem;
}
}
public static void createSystemAssetsInZygoteLocked(boolean reinitialize,
String frameworkPath) {
if (sSystem != null && !reinitialize) {
return;
}
try {
final ArrayList<ApkAssets> apkAssets = new ArrayList<>();
apkAssets.add(ApkAssets.loadFromPath(frameworkPath, ApkAssets.PROPERTY_SYSTEM)); // 1
final String[] systemIdmapPaths =
OverlayConfig.getZygoteInstance().createImmutableFrameworkIdmapsInZygote();
for (String idmapPath : systemIdmapPaths) {
apkAssets.add(ApkAssets.loadOverlayFromPath(idmapPath, ApkAssets.PROPERTY_SYSTEM));
}
sSystemApkAssetsSet = new ArraySet<>(apkAssets); // 2
sSystemApkAssets = apkAssets.toArray(new ApkAssets[apkAssets.size()]); // 3
if (sSystem == null) {
sSystem = new AssetManager(true /*sentinel*/); // 4
}
sSystem.setApkAssets(sSystemApkAssets, false /*invalidateCaches*/); // 5
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to create system AssetManager", e);
}
}注释1处通过 loadFromPath() 来加载 framework 资源,最终是通过 nativeLoad() native 函数来完成。
注释2、3处分别对 sSystemApkAssetsSet 和 sSystemApkAssets 赋值。
注释4处创建系统专用的 AssetManager 实例,最终调用的是 nativeCreate 函数。
注释5处设置资源到已加载集合,并赋值给 mApkAssets 变量。
-
加载 framework-res.apk 的入口是 ApkAssets.loadFromPath();
-
设置资源的是 AssetManager.setApkAssets()。
ApkAssets.loadFromPath()
ApkAssets.loadFromPath() -> new ApkAssets() -> nativeLoad()
cpp
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_content_res_ApkAssets.cpp
static jlong NativeLoad(JNIEnv* env, jclass /*clazz*/, const format_type_t format,
jstring java_path, const jint property_flags, jobject assets_provider) {
...
auto loader_assets = LoaderAssetsProvider::Create(env, assets_provider); // 1
AssetManager2::ApkAssetsPtr apk_assets; // 2
switch (format) {
case FORMAT_APK: {
auto assets = MultiAssetsProvider::Create(std::move(loader_assets),
ZipAssetsProvider::Create(path.c_str(),
property_flags));
apk_assets = ApkAssets::Load(std::move(assets), property_flags);
break;
}
case FORMAT_IDMAP:
apk_assets = ApkAssets::LoadOverlay(path.c_str(), property_flags);
break;
case FORMAT_ARSC:
apk_assets = ApkAssets::LoadTable(AssetsProvider::CreateAssetFromFile(path.c_str()),
std::move(loader_assets),
property_flags);
break;
case FORMAT_DIRECTORY: {
auto assets = MultiAssetsProvider::Create(std::move(loader_assets),
DirectoryAssetsProvider::Create(path.c_str()));
apk_assets = ApkAssets::Load(std::move(assets), property_flags);
break;
}
default:
const std::string error_msg = base::StringPrintf("Unsupported format type %d", format);
jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", error_msg.c_str());
return 0;
}
...
return CreateGuardedApkAssets(std::move(apk_assets)); // 3
}注释1处使用提供的 assets_provider 创建资源加载器,这个加载器处理资源的加载过程。
注释2处声明一个指针,用于存储加载的 Apk 资源。
接下来根据不同的格式来选择相应的资源加载方式的分支结构。
- FORMAT_APK:创建一个多资源提供者,它将 loader_assets 与一个 zip 提供者结合,zip 提供者负责从 apk 文件中提取资源,然后使用提供的属性标志加载 apk 资源。
- FORMAT_IDMAP:将 apk 资源作为覆盖资源加载。
- FORMAT_ARSC:将 apk 资源作为表格加载。
- FORMAT_DIRECTORY:创建一个多资源提供者,将 loader_assets 与目录资源提供者结合,然后使用提供的属性标志加载 apk 资源。
- 默认:如果传入的格式不支持,抛出一个异常,并返回错误信息。
注释3处成功加载资源,返回结果。CreateGuardedApkAssets() 将加载的 apk 资源包装成一个受保护的对象。
以 FORMAT_APK 为例:
cpp
frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/ApkAssets.cpp
ApkAssetsPtr ApkAssets::Load(std::unique_ptr<AssetsProvider> assets, package_property_t flags) {
return LoadImpl(std::move(assets), flags, nullptr /* idmap_asset */, nullptr /* loaded_idmap */);
}调用 LoadImpl() 进行实际的资源加载。
cpp
frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/ApkAssets.cpp
ApkAssetsPtr ApkAssets::LoadImpl(std::unique_ptr<AssetsProvider> assets,
package_property_t property_flags,
std::unique_ptr<Asset> idmap_asset,
std::unique_ptr<LoadedIdmap> loaded_idmap) {
...
auto resources_asset = assets->Open(kResourcesArsc, Asset::AccessMode::ACCESS_BUFFER,
&resources_asset_exists); // 1
...
return LoadImpl(std::move(resources_asset), std::move(assets), property_flags,
std::move(idmap_asset), std::move(loaded_idmap)); // 2
}注释1处尝试打开资源文件(kResourcesArsc)并读取资源,如果文件不存在,resources_asset 为 nullptr。
注释2处如果打开资源文件成功,继续调用 LoadImpl 处理后续逻辑,传递资源文件、资源提供者和其他参数。
cpp
frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/ApkAssets.cpp
ApkAssetsPtr ApkAssets::LoadImpl(std::unique_ptr<Asset> resources_asset,
std::unique_ptr<AssetsProvider> assets,
package_property_t property_flags,
std::unique_ptr<Asset> idmap_asset,
std::unique_ptr<LoadedIdmap> loaded_idmap) {
// 如果assets为nullptr,表示资源加载失败,返回空指针
if (assets == nullptr ) {
return {};
}
std::unique_ptr<LoadedArsc> loaded_arsc; // 用于存储加载后的ARSC资源表
// 如果资源文件(resources_asset)不为空,表示需要加载ARSC资源表
if (resources_asset != nullptr) {
// 获取资源文件的数据缓冲区,并确保数据对齐
const auto data = resources_asset->getIncFsBuffer(true /* aligned */);
const size_t length = resources_asset->getLength();
// 如果资源文件读取失败或者数据长度为零,输出错误日志并返回空指针
if (!data || length == 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read resources table in APK '" << assets->GetDebugName() << "'.";
return {};
}
// 调用LoadedArsc::Load()加载资源表
loaded_arsc = LoadedArsc::Load(data, length, loaded_idmap.get(), property_flags);
} else if (loaded_idmap != nullptr &&
IsFabricatedOverlay(std::string(loaded_idmap->OverlayApkPath()))) {
// 如果没有资源文件但有已加载的IDMAP,并且该IDMAP是一个FabricatedOverlay(即时生成的运行时资源覆盖),则加载ARSC数据
loaded_arsc = LoadedArsc::Load(loaded_idmap.get());
} else {
// 如果没有资源文件且没有有效的IDMAP,创建一个空的ARSC数据
loaded_arsc = LoadedArsc::CreateEmpty();
}
// 如果加载ARSC资源表失败,输出错误日志并返回空指针
if (loaded_arsc == nullptr) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to load resources table in APK '" << assets->GetDebugName() << "'.";
return {};
}
// 最终构造并返回一个ApkAssets对象
return ApkAssetsPtr::make(PrivateConstructorUtil{}, std::move(resources_asset),
std::move(loaded_arsc), std::move(assets), property_flags,
std::move(idmap_asset), std::move(loaded_idmap));
}-
总结
ApkAssets 类是 Android 系统中用于表示 Apk 文件资源的底层实现类。它提供了 Apk 文件的不可变内存表示,并与 AssetManager 配合使用,允许高效地访问和共享 Apk 内的资源。其实现主要是本地 C++ 代码,目的是为了提高性能和减少资源消耗。
AssetManager.setApkAssets()
java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/AssetManager.java
public void setApkAssets(@NonNull ApkAssets[] apkAssets, boolean invalidateCaches) {
Objects.requireNonNull(apkAssets, "apkAssets");
ApkAssets[] newApkAssets = new ApkAssets[sSystemApkAssets.length + apkAssets.length];
// Copy the system assets first.
System.arraycopy(sSystemApkAssets, 0, newApkAssets, 0, sSystemApkAssets.length); // 1
// Copy the given ApkAssets if they are not already in the system list.
int newLength = sSystemApkAssets.length;
for (ApkAssets apkAsset : apkAssets) { // 2
if (!sSystemApkAssetsSet.contains(apkAsset)) {
newApkAssets[newLength++] = apkAsset;
}
}
// Truncate if necessary.
if (newLength != newApkAssets.length) {
newApkAssets = Arrays.copyOf(newApkAssets, newLength);
}
synchronized (this) {
ensureOpenLocked();
mApkAssets = newApkAssets; // 3
nativeSetApkAssets(mObject, mApkAssets, invalidateCaches); // 4
if (invalidateCaches) {
// Invalidate all caches.
invalidateCachesLocked(-1);
}
}
}注释1处把 sSystemApkAssets 中的资源拷贝到一个全新数组 newApkAssets 中。
注释2处检查 sSystemApkAssetsSet 没有的资源,并添加到数组 newApkAssets。
注释3处更新已加载资源集合 mApkAssets。
注释4处调用 nativeSetApkAssets() 处理 native 层的资源。
cpp
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_AssetManager.cpp
static void NativeSetApkAssets(JNIEnv* env, jclass /*clazz*/, jlong ptr,
jobjectArray apk_assets_array, jboolean invalidate_caches) {
...
auto assetmanager = LockAndStartAssetManager(ptr);
assetmanager->SetApkAssets(apk_assets, invalidate_caches);
}NativeSetApkAssets() 函数对 Java 层的数据进行简单处理后,调用了 AssetManager2 的 SetApkAssets() 函数。
cpp
frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/AssetManager2.cpp
bool AssetManager2::SetApkAssets(ApkAssetsList apk_assets, bool invalidate_caches) {
BuildDynamicRefTable(apk_assets); // 1
RebuildFilterList(); // 2
if (invalidate_caches) {
InvalidateCaches(static_cast<uint32_t>(-1));
}
return true;
}注释1处构建动态资源引用表。这个函数会把 LoadedArsc 中的 package 提取出来,填充到 package_group 中。
注释2处重新构建符合当前设备的资源,即 filtered_configs_。