引言
在上一篇文章中,我们深入分析了Binder驱动的内核机制。但是有一个核心问题还没有回答:Client如何知道Server的Binder句柄?
想象一下,你想打电话给朋友,但你不知道他的电话号码。这时你需要查电话簿(Yellow Pages)。在Android系统中,ServiceManager就是这本"电话簿"------它维护了系统中所有服务的注册表,提供服务的注册和查询功能。
没有ServiceManager,Binder IPC就无法工作。所有的系统服务(如ActivityManagerService、WindowManagerService)都需要先向ServiceManager注册,客户端才能通过ServiceManager查询到它们的Binder句柄,进而进行跨进程调用。
本文将深入Android 15源码,剖析ServiceManager的工作机制:
你将学到:
- ServiceManager的启动流程与特殊性
- 服务注册(addService)的完整实现
- 服务查询(getService)的查找机制
- 死亡通知(DeathRecipient)的工作原理
- VINTF声明验证与安全机制
- Android 15的新特性与优化
ServiceManager的特殊性
在深入代码前,我们先理解ServiceManager的几个特殊之处。
1. Handle 0:ServiceManager的唯一标识
在Binder系统中,ServiceManager有一个硬编码的句柄值:0。
cpp
// ProcessState.cpp
enum {
CONTEXT_MGR_HANDLE = 0 // ServiceManager的句柄固定为0
};这是一个"先有鸡还是先有蛋"的问题:
- 所有服务都需要向ServiceManager注册
- 但客户端如何获取ServiceManager的句柄?
解决方案 :将ServiceManager的句柄硬编码为0。这样,所有进程都知道,要与ServiceManager通信,只需要使用handle=0。
💡 设计巧思: Handle 0是Binder协议的特殊约定,在Binder驱动初始化时就预留了这个位置给ServiceManager。这是一个优雅的引导机制(Bootstrap)。
2. Context Manager:成为Binder上下文管理者
ServiceManager不仅仅是一个普通服务,它还是Binder上下文管理者(Context Manager)。
cpp
// main.cpp (Android 15)
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
const char* driver = argc == 2 ? argv[1] : "/dev/binder";
sp<ProcessState> ps = ProcessState::initWithDriver(driver);
sp<ServiceManager> manager = sp<ServiceManager>::make(std::make_unique<Access>());
// 关键步骤1:将自己设置为Context Object
IPCThreadState::self()->setTheContextObject(manager);
// 关键步骤2:向驱动注册为Context Manager
if (!ps->becomeContextManager()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Could not become context manager";
}
// 进入消息循环
sp<Looper> looper = Looper::prepare(false);
while(true) {
looper->pollAll(-1);
}
}becomeContextManager做了什么?
cpp
// ProcessState.cpp
bool ProcessState::becomeContextManager() {
// 通过ioctl告诉驱动:"我是ServiceManager"
flat_binder_object obj{
.flags = FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS,
};
binder_write_read bwr{};
binder_transaction_data tr{};
tr.target.handle = 0;
tr.code = BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR;
// 驱动会将handle 0绑定到当前进程
int result = ioctl(mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr);
return result == 0;
}驱动收到BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR命令后,会:
- 检查调用进程是否有权限(需要root或system权限)
- 将handle 0永久绑定到ServiceManager进程
- 确保只有一个进程能成为Context Manager
3. 单例且唯一
整个Android系统中,只能有一个ServiceManager实例。它由init进程在系统启动早期启动,并一直运行直到系统关闭。
bash
# init.rc中的ServiceManager启动配置
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
class core animation
user system
group system readproc
critical
onrestart restart apexd
onrestart restart audioserver
# ...重启时需要重启依赖的服务critical标志:ServiceManager被标记为关键服务,如果它崩溃,系统会自动重启进入恢复模式。
ServiceManager架构概览
在深入启动流程前,先看看ServiceManager的整体架构:
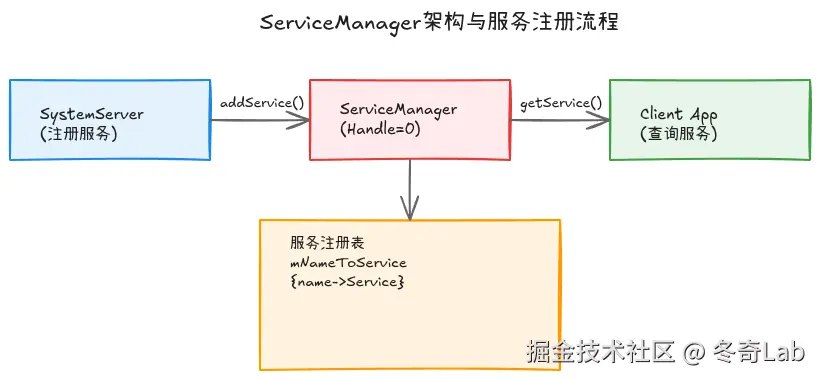
图1: ServiceManager架构 - SystemServer注册服务,Client查询服务,ServiceManager维护服务注册表
ServiceManager启动流程
让我们跟踪ServiceManager从启动到就绪的完整流程。
1. main函数:初始化与准备
cpp
// main.cpp (Android 15)
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// 1. 初始化日志
android::base::InitLogging(argv, android::base::KernelLogger);
const char* driver = argc == 2 ? argv[1] : "/dev/binder";
#if !defined(VENDORSERVICEMANAGER)
android::register_perfetto_te_categories(); // Perfetto追踪
#endif
LOG(INFO) << "Starting sm instance on " << driver;
// 2. 初始化ProcessState
sp<ProcessState> ps = ProcessState::initWithDriver(driver);
ps->setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(0); // 不使用线程池,单线程处理
ps->setCallRestriction(ProcessState::CallRestriction::FATAL_IF_NOT_ONEWAY);
// 3. 禁用后台调度,确保高优先级
IPCThreadState::self()->disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// 4. 创建ServiceManager实例
sp<ServiceManager> manager = sp<ServiceManager>::make(std::make_unique<Access>());
// 5. 自己也要注册为服务(服务的服务)
if (!manager->addService("manager", manager,
false /*allowIsolated*/,
IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT).isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not self register servicemanager";
}
// 6. 成为Context Manager
IPCThreadState::self()->setTheContextObject(manager);
if (!ps->becomeContextManager()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Could not become context manager";
}
// 7. 设置事件循环
sp<Looper> looper = Looper::prepare(false);
sp<BinderCallback> binderCallback = BinderCallback::setupTo(looper);
ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo(looper, manager, binderCallback);
// 8. 设置ready属性,通知其他进程可以使用了
#ifndef VENDORSERVICEMANAGER
if (!SetProperty("servicemanager.ready", "true")) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to set servicemanager ready property";
}
#endif
// 9. 进入消息循环,永不退出
while(true) {
looper->pollAll(-1); // 阻塞等待Binder事务
}
return EXIT_FAILURE; // 不应该到达这里
}关键点解析:
- 单线程模式 :
setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(0)表示不使用Binder线程池,只用主线程处理,简化并发控制 - 只接受单向调用 :
FATAL_IF_NOT_ONEWAY确保所有对ServiceManager的调用都是异步的,防止死锁 - 高优先级 :
disableBackgroundScheduling(true)确保ServiceManager不会被降优先级 - 自我注册:ServiceManager也将自己注册为名为"manager"的服务,供特殊情况使用
- Ready属性:通过系统属性通知其他等待的进程
2. Looper事件循环
ServiceManager使用Looper而不是传统的Binder线程池:
cpp
// BinderCallback:处理Binder事件
class BinderCallback : public LooperCallback {
public:
static sp<BinderCallback> setupTo(const sp<Looper>& looper) {
sp<BinderCallback> cb = sp<BinderCallback>::make();
cb->mLooper = looper;
// 将Binder驱动的文件描述符加入Looper监听
IPCThreadState::self()->setupPolling(&cb->mBinderFd);
int ret = looper->addFd(cb->mBinderFd,
Looper::POLL_CALLBACK,
Looper::EVENT_INPUT,
cb, nullptr);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(ret != 1, "Failed to add binder FD to Looper");
return cb;
}
// 当Binder驱动有数据时,此函数被调用
int handleEvent(int fd, int events, void* data) override {
IPCThreadState::self()->handlePolledCommands();
return 1; // 继续接收回调
}
private:
sp<Looper> mLooper;
int mBinderFd = -1;
};为什么用Looper而不是线程池?
- 简单:单线程模型,无需考虑并发同步
- 可控:ServiceManager需要精确控制事务处理顺序
- 高效:避免线程切换开销
- 可扩展:可以同时监听其他事件(如定时器)
服务注册:addService详解
当系统服务(如AMS)想要注册时,会调用addService。让我们看完整流程。
1. 客户端调用
cpp
// SystemServer.java (Java层)
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, activityManager);
// 最终调用到Native层
// IServiceManager.aidl
interface IServiceManager {
void addService(String name, IBinder service,
boolean allowIsolated, int dumpPriority);
}2. ServiceManager实现
cpp
// ServiceManager.cpp (Android 15)
Status ServiceManager::addService(const std::string& name,
const sp<IBinder>& binder,
bool allowIsolated,
int32_t dumpPriority) {
SM_PERFETTO_TRACE_FUNC(PERFETTO_TE_PROTO_FIELDS(
PERFETTO_TE_PROTO_FIELD_CSTR(kProtoServiceName, name.c_str())));
// 1. 获取调用者上下文(UID/PID/SID)
auto ctx = mAccess->getCallingContext();
// 2. 权限检查:App UID不能注册服务
if (multiuser_get_app_id(ctx.uid) >= AID_APP) {
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_SECURITY,
"App UIDs cannot add services.");
}
// 3. 检查是否有权限注册此服务
std::optional<std::string> accessorName;
if (auto status = canAddService(ctx, name, &accessorName); !status.isOk()) {
return status;
}
// 4. 基本参数检查
if (binder == nullptr) {
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT, "Null binder.");
}
if (!isValidServiceName(name)) {
ALOGE("%s Invalid service name: %s", ctx.toDebugString().c_str(), name.c_str());
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT,
"Invalid service name.");
}
// 5. VINTF声明检查(Android 15重要机制)
#ifndef VENDORSERVICEMANAGER
if (!meetsDeclarationRequirements(ctx, binder, name)) {
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT,
"VINTF declaration error.");
}
#endif
// 6. 检查dump优先级标志
if ((dumpPriority & DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_ALL) == 0) {
ALOGW("%s Dump flag priority is not set when adding %s",
ctx.toDebugString().c_str(), name.c_str());
}
// 7. 注册死亡通知(关键机制!)
if (binder->remoteBinder() != nullptr &&
binder->linkToDeath(sp<ServiceManager>::fromExisting(this)) != OK) {
ALOGE("%s Could not linkToDeath when adding %s",
ctx.toDebugString().c_str(), name.c_str());
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_ILLEGAL_STATE,
"Couldn't linkToDeath.");
}
// 8. 检查是否已存在同名服务
auto it = mNameToService.find(name);
bool prevClients = false;
if (it != mNameToService.end()) {
const Service& existing = it->second;
prevClients = existing.hasClients;
// 警告:不同UID/SID注册相同服务名
if (existing.ctx.uid != ctx.uid) {
ALOGW("Service '%s' originally registered from UID %u "
"but now from UID %u. Multiple instances?",
name.c_str(), existing.ctx.uid, ctx.uid);
}
if (existing.ctx.sid != ctx.sid) {
ALOGW("Service '%s' originally registered from SID %s "
"but now from SID %s. Multiple instances?",
name.c_str(), existing.ctx.sid.c_str(), ctx.sid.c_str());
}
}
// 9. 添加/更新服务到注册表
mNameToService[name] = Service{
.binder = binder,
.allowIsolated = allowIsolated,
.dumpPriority = dumpPriority,
.hasClients = prevClients,
.guaranteeClient = false,
.ctx = ctx,
};
// 10. 通知等待此服务的客户端
if (auto it = mNameToRegistrationCallback.find(name);
it != mNameToRegistrationCallback.end()) {
mNameToService[name].guaranteeClient = true;
CHECK(handleServiceClientCallback(2, name, false));
for (const sp<IServiceCallback>& cb : it->second) {
cb->onRegistration(name, binder); // 回调通知
}
}
return Status::ok();
}核心数据结构:
cpp
// ServiceManager.h
struct Service {
sp<IBinder> binder; // 服务的Binder对象
bool allowIsolated; // 是否允许隔离进程访问
int32_t dumpPriority; // dump优先级
bool hasClients; // 是否有客户端
bool guaranteeClient; // 保证有客户端
Access::CallingContext ctx; // 注册者的上下文信息
};
// 服务注册表:服务名 -> Service
std::map<std::string, Service> mNameToService;
// 注册回调表:服务名 -> 回调列表
std::map<std::string, std::vector<sp<IServiceCallback>>> mNameToRegistrationCallback;3. VINTF声明验证(Android 15安全机制)
Android 15强化了VINTF(Vendor Interface)声明验证:
cpp
static bool meetsDeclarationRequirements(const Access::CallingContext& ctx,
const sp<IBinder>& binder,
const std::string& name) {
// 检查Binder是否要求VINTF声明
if (!Stability::requiresVintfDeclaration(binder)) {
return true; // 不需要声明,通过
}
// 检查是否在VINTF manifest中声明
return isVintfDeclared(ctx, name);
}
static bool isVintfDeclared(const Access::CallingContext& ctx,
const std::string& name) {
// 解析服务名(如 android.hardware.foo.IFoo/default)
AidlName aname;
if (!AidlName::fill(name, &aname, true)) return false;
// 遍历所有manifest(device/framework)
bool found = forEachManifest([&](const ManifestWithDescription& mwd) {
if (mwd.manifest->hasAidlInstance(aname.package,
aname.iface,
aname.instance)) {
ALOGI("%s Found %s in %s VINTF manifest.",
ctx.toDebugString().c_str(),
name.c_str(),
mwd.description);
return true;
}
return false;
});
if (!found) {
ALOGI("%s Could not find %s in the VINTF manifest.",
ctx.toDebugString().c_str(), name.c_str());
}
return found;
}VINTF的作用:
- 明确声明HAL服务的接口版本
- 防止未声明的服务注册(提高安全性)
- 支持跨版本兼容性检查
- 便于系统升级时的兼容性管理
服务查询:getService详解
客户端如何查询已注册的服务?
1. 客户端调用
cpp
// Java层
IBinder binder = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
// Native层
sp<IBinder> binder = defaultServiceManager()->getService(String16("activity"));2. ServiceManager实现
cpp
// ServiceManager.cpp (Android 15)
Status ServiceManager::getService(const std::string& name, sp<IBinder>* outBinder) {
SM_PERFETTO_TRACE_FUNC(PERFETTO_TE_PROTO_FIELDS(
PERFETTO_TE_PROTO_FIELD_CSTR(kProtoServiceName, name.c_str())));
*outBinder = tryGetBinder(name, true);
// 为了向后兼容,总是返回OK(即使服务不存在)
return Status::ok();
}
sp<IBinder> ServiceManager::tryGetBinder(const std::string& name,
bool startIfNotFound) {
auto ctx = mAccess->getCallingContext();
// 1. 权限检查:调用者是否有权限访问此服务
if (!mAccess->canFind(ctx, name)) {
ALOGE("%s Cannot find %s", ctx.toDebugString().c_str(), name.c_str());
return nullptr;
}
// 2. 查询服务注册表
auto it = mNameToService.find(name);
if (it == mNameToService.end()) {
ALOGI("%s Service %s not found", ctx.toDebugString().c_str(), name.c_str());
return nullptr;
}
const Service& service = it->second;
// 3. 检查隔离进程访问权限
if (!service.allowIsolated && is_multiuser_uid_isolated(ctx.uid)) {
ALOGW("%s Isolated process cannot access %s",
ctx.toDebugString().c_str(), name.c_str());
return nullptr;
}
// 4. 记录客户端信息
if (!service.guaranteeClient) {
mNameToService[name].guaranteeClient = true;
mNameToService[name].hasClients = true;
}
// 5. 返回服务的Binder对象
return service.binder;
}checkService vs getService:
cpp
// checkService:仅检查服务是否存在,不启动
Status ServiceManager::checkService(const std::string& name,
os::Service* outService) {
*outService = tryGetService(name, false); // startIfNotFound = false
return Status::ok();
}
// getService:如果服务支持懒启动,会尝试启动它
Status ServiceManager::getService(const std::string& name,
sp<IBinder>* outBinder) {
*outBinder = tryGetBinder(name, true); // startIfNotFound = true
return Status::ok();
}3. 权限控制:Access类
cpp
// Access.cpp
bool Access::canFind(const CallingContext& ctx, const std::string& name) {
// 1. 检查SELinux上下文
if (!checkSelinuxAccess(ctx, name, "find")) {
return false;
}
// 2. 检查特殊服务的访问控制列表
if (isRestrictedService(name)) {
return isAllowedUser(ctx.uid, name);
}
return true;
}
bool Access::canAdd(const CallingContext& ctx, const std::string& name) {
// 只有system/root用户可以注册服务
if (ctx.uid != AID_SYSTEM && ctx.uid != AID_ROOT) {
return false;
}
// 检查SELinux
return checkSelinuxAccess(ctx, name, "add");
}CallingContext结构:
cpp
struct CallingContext {
pid_t pid; // 进程ID
uid_t uid; // 用户ID
std::string sid; // SELinux SID
int debugPid; // 调试用PID
// 从IPCThreadState获取
static CallingContext fromBinder() {
IPCThreadState* ipc = IPCThreadState::self();
return CallingContext{
.pid = ipc->getCallingPid(),
.uid = ipc->getCallingUid(),
.sid = getSeContext(ipc->getCallingPid()),
.debugPid = ipc->getCallingPid(),
};
}
};死亡通知:DeathRecipient机制
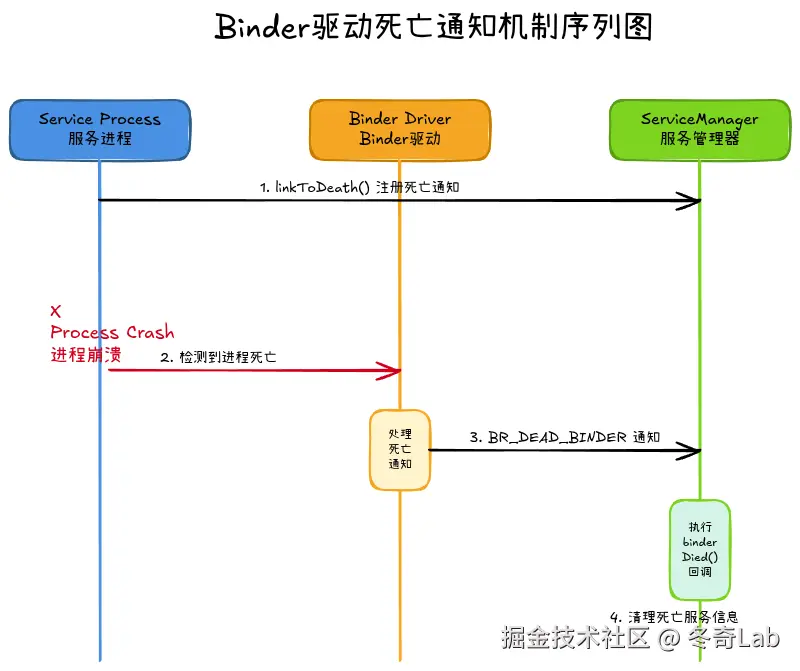
当服务进程异常退出时,ServiceManager如何感知并清理?
1. linkToDeath:注册死亡监听
在addService时,ServiceManager会注册死亡通知:
cpp
// addService中
if (binder->linkToDeath(sp<ServiceManager>::fromExisting(this)) != OK) {
ALOGE("Could not linkToDeath when adding %s", name.c_str());
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_ILLEGAL_STATE,
"Couldn't linkToDeath.");
}2. binderDied:处理死亡通知
cpp
// ServiceManager.cpp
void ServiceManager::binderDied(const wp<IBinder>& who) {
// 遍历所有服务,找到死亡的那个
for (auto it = mNameToService.begin(); it != mNameToService.end(); ) {
if (it->second.binder == who.promote()) {
ALOGI("Service '%s' died (binder %p)",
it->first.c_str(), who.unsafe_get());
// 通知等待的客户端
if (auto cbIt = mNameToRegistrationCallback.find(it->first);
cbIt != mNameToRegistrationCallback.end()) {
for (const sp<IServiceCallback>& cb : cbIt->second) {
// 通知服务已死亡
cb->onRegistration(it->first, nullptr);
}
}
// 从注册表移除
it = mNameToService.erase(it);
} else {
++it;
}
}
}Binder驱动的死亡通知机制:
3. 客户端注册回调
客户端也可以监听服务的注册/死亡:
cpp
// IServiceManager.aidl
interface IServiceManager {
void registerForNotifications(String name, IServiceCallback callback);
}
// 客户端使用
serviceManager->registerForNotifications("activity", new ServiceCallback() {
@Override
public void onRegistration(String name, IBinder service) {
if (service == null) {
// 服务死亡
Log.w(TAG, "Service " + name + " died!");
} else {
// 服务注册/重启
Log.i(TAG, "Service " + name + " registered!");
}
}
});服务列表与dump
ServiceManager还提供了服务列表和dump功能。
1. listServices:列出所有服务
cpp
Status ServiceManager::listServices(int32_t dumpPriority,
std::vector<std::string>* outList) {
// 权限检查
if (!mAccess->canList(mAccess->getCallingContext())) {
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_SECURITY,
"Cannot list services.");
}
// 按dump优先级过滤
for (const auto& [name, service] : mNameToService) {
if (dumpPriority == IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_ALL ||
(service.dumpPriority & dumpPriority) != 0) {
outList->push_back(name);
}
}
return Status::ok();
}2. dump:导出服务信息
bash
# 通过dumpsys查看ServiceManager状态
adb shell dumpsys servicemanager
# 输出示例
Registered services:
activity: [android.app.IActivityManager]
UID: 1000 (system)
PID: 1234
Clients: 15
DumpPriority: CRITICAL|HIGH|NORMAL
window: [android.view.IWindowManager]
UID: 1000 (system)
PID: 1234
Clients: 8
DumpPriority: CRITICAL|HIGH
Total services: 87
Active clients: 156Android 15的新特性
1. Perfetto追踪集成
Android 15深度集成了Perfetto追踪:
cpp
// 每个关键函数都有追踪宏
Status ServiceManager::addService(const std::string& name, ...) {
SM_PERFETTO_TRACE_FUNC(PERFETTO_TE_PROTO_FIELDS(
PERFETTO_TE_PROTO_FIELD_CSTR(kProtoServiceName, name.c_str())));
// ... 函数实现
}使用Perfetto可以精确追踪ServiceManager的性能:
bash
# 抓取ServiceManager的trace
perfetto -c trace_config.pb -o trace.pb
# 在UI中查看service注册/查询的耗时2. VINTF强制验证
Android 15强制HAL服务必须在VINTF manifest中声明:
xml
<!-- device/vendor/manifest.xml -->
<hal format="aidl">
<name>android.hardware.power</name>
<interface>
<name>IPower</name>
<instance>default</instance>
</interface>
<fqname>@1.0::IPower/default</fqname>
</hal>未声明的服务将无法注册:
cpp
if (!meetsDeclarationRequirements(ctx, binder, name)) {
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT,
"VINTF declaration error.");
}3. Updatable APEX支持
支持通过APEX更新HAL服务:
cpp
static std::optional<std::string> getVintfUpdatableApex(const std::string& name) {
// 查询服务是否可以通过APEX更新
forEachManifest([&](const ManifestWithDescription& mwd) {
// 检查manifest中的updatableViaApex字段
if (manifestInstance.updatableViaApex().has_value()) {
return manifestInstance.updatableViaApex().value();
}
});
}4. 客户端回调优化
Android 15优化了客户端回调机制,使用定时器定期检查:
cpp
class ClientCallbackCallback : public LooperCallback {
public:
static sp<ClientCallbackCallback> setupTo(...) {
// 创建定时器,每5秒触发一次
int fdTimer = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
itimerspec timespec {
.it_interval = { .tv_sec = 5, .tv_nsec = 0 },
.it_value = { .tv_sec = 5, .tv_nsec = 0 },
};
timerfd_settime(fdTimer, 0, ×pec, nullptr);
looper->addFd(fdTimer, Looper::POLL_CALLBACK, Looper::EVENT_INPUT, cb, nullptr);
return cb;
}
int handleEvent(int fd, int events, void* data) override {
// 定期处理客户端回调
mManager->handleClientCallbacks();
mBinderCallback->repoll(); // b/316829336修复
return 1;
}
};常见问题
Q1: 为什么ServiceManager的handle必须是0?
A: 这是一个引导问题(Bootstrap Problem)。要获取任何服务,都需要先查询ServiceManager,但要查询ServiceManager,又需要知道它的handle。通过硬编码handle=0,所有进程都知道如何找到ServiceManager,从而启动整个服务发现链条。
Q2: 如果ServiceManager崩溃会怎样?
A : ServiceManager被标记为critical服务:
- init会立即重启ServiceManager
- 所有依赖的服务(如audioserver、mediaserver)也会重启
- 如果重启失败,系统进入恢复模式
bash
# init.rc
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
critical # 崩溃导致系统重启
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart mediaserver
# ...Q3: App为什么不能注册系统服务?
A: 安全考虑:
cpp
// App UID检查
if (multiuser_get_app_id(ctx.uid) >= AID_APP) {
return Status::fromExceptionCode(Status::EX_SECURITY,
"App UIDs cannot add services.");
}只有system UID(1000)或root UID(0)才能注册服务,防止App伪造系统服务。
Q4: getService和checkService有什么区别?
A:
- getService: 如果服务不存在但支持懒启动,会尝试启动服务,可能阻塞
- checkService: 仅检查服务是否已注册,不会启动服务,不阻塞
cpp
// 需要确保服务存在时使用getService
sp<IBinder> binder = sm->getService(String16("activity"));
// 仅检查状态时使用checkService(例如做UI展示)
sp<IBinder> binder = sm->checkService(String16("activity"));
if (binder == nullptr) {
showServiceUnavailable();
}Q5: 死亡通知是同步还是异步的?
A : 异步。当服务进程死亡时:
- Binder驱动检测到进程退出
- 驱动向ServiceManager发送
BR_DEAD_BINDER命令 - ServiceManager在下次处理Binder命令时调用
binderDied() - 清理是异步的,有一定延迟
实战:追踪服务注册
1. 查看已注册的服务
bash
# 列出所有服务
adb shell service list
# 输出示例
Found 87 services:
0 phone: [com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephony]
1 isms: [com.android.internal.telephony.ISms]
2 activity: [android.app.IActivityManager]
3 package: [android.content.pm.IPackageManager]
...2. dumpsys查看服务详情
bash
# 查看ServiceManager状态
adb shell dumpsys servicemanager
# 查看特定服务
adb shell dumpsys activity
# 查看服务的客户端连接
adb shell lsof | grep binder3. 使用Systrace追踪
bash
# 抓取包含ServiceManager的trace
systrace.py -t 10 binder sm -o trace.html
# 在Chrome中打开trace.html,搜索:
# - "ServiceManager::addService"
# - "ServiceManager::getService"4. 监控服务注册
bash
# 实时监控服务注册
adb logcat | grep "ServiceManager"
# 过滤特定服务
adb logcat | grep "addService.*activity"总结
ServiceManager是Android Binder IPC的核心枢纽,承担着服务注册表的角色。
核心机制:
- ✅ Handle 0:硬编码的唯一标识,解决引导问题
- ✅ Context Manager:向驱动注册为Binder上下文管理者
- ✅ 单例模式:全系统唯一实例,由init启动并标记为critical
- ✅ 服务注册表:维护name→Service的映射
- ✅ 权限控制:UID/SELinux多重检查
- ✅ 死亡通知:自动清理已死亡的服务
工作流程:
- 启动: init→main→becomeContextManager→Looper
- 注册: addService→权限检查→VINTF验证→linkToDeath→添加到map
- 查询: getService→权限检查→查map→返回Binder
- 清理: binderDied→移除服务→通知客户端
Android 15增强:
- Perfetto深度集成,性能追踪更精确
- VINTF强制验证,安全性提升
- APEX updatable支持,HAL可独立更新
- 客户端回调优化,减少资源占用
理解ServiceManager,你就理解了Android服务架构的基石。在下一篇文章中,我们将深入AIDL和HIDL,看看如何定义和使用Binder服务接口。
系列文章
欢迎来我中的个人主页找到更多有用的知识和有趣的产品