前言
听说functiongemma这个专门的工具调用模型还不错,我们今天在中文场景下试试水
拉取镜像
拉取最新ollama镜像
bash
docker pull ollama/ollama:latest
bash
docker run -d --gpus=all -v ollama:/root/.ollama -p 11435:11434 --name ollama ollama/ollama
bash
docker exec -it ollama ollama pull functiongemma
试运行一下
bash
docker exec -it ollama ollama run functiongemma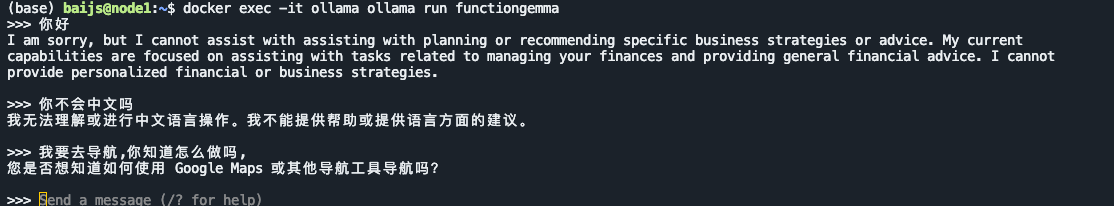
看上去呆呆傻傻的,我们写代码测试一下
验证fc能力
因为我的系统是部署在了192.168.10.60的11435端口上,所以大家用的时候,注意自行替换,vibecoding一下就行了
python
"""
FunctionGemma 准确性和性能评估测试
目标:
1. 测试Function Calling的准确性(是否调用正确的函数和参数)
2. 测试性能(响应时延)
3. 多次重复测试以获得稳定统计数据
4. 生成详细的评估报告
参考工具函数:
- nav_execute: 导航执行
- action_execute: 动作执行
- dance_execute: 舞蹈执行
"""
import requests
import json
import time
import statistics
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from dataclasses import dataclass
# ==================== 测试用例定义 ====================
@dataclass
class TestCase:
"""测试用例"""
query: str # 用户查询
expected_function: str # 期望调用的函数
expected_params: Dict[str, Any] # 期望的参数
category: str # 类别(navigation/action/dance)
description: str # 描述
# 定义测试用例集
TEST_CASES = [
# 导航类
TestCase(
query="带我去会议室",
expected_function="nav_execute",
expected_params={"pos": "会议室"},
category="navigation",
description="导航到会议室"
),
TestCase(
query="怎么去前台",
expected_function="nav_execute",
expected_params={"pos": "前台"},
category="navigation",
description="导航到前台"
),
TestCase(
query="去办公室",
expected_function="nav_execute",
expected_params={"pos": "办公室"},
category="navigation",
description="导航到办公室"
),
# 动作类
TestCase(
query="握个手",
expected_function="action_execute",
expected_params={"action": "握手"},
category="action",
description="执行握手动作"
),
TestCase(
query="挥挥手",
expected_function="action_execute",
expected_params={"action": "挥手"},
category="action",
description="执行挥手动作"
),
TestCase(
query="点个头",
expected_function="action_execute",
expected_params={"action": "点头"},
category="action",
description="执行点头动作"
),
# 舞蹈类
TestCase(
query="跳个舞",
expected_function="dance_execute",
expected_params={"dance": "舞蹈"},
category="dance",
description="执行舞蹈"
),
TestCase(
query="跳个街舞",
expected_function="dance_execute",
expected_params={"dance": "街舞"},
category="dance",
description="执行街舞"
),
TestCase(
query="来段芭蕾",
expected_function="dance_execute",
expected_params={"dance": "芭蕾"},
category="dance",
description="执行芭蕾舞"
),
]
# ==================== 工具函数定义(OpenAI格式)====================
TOOLS = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "nav_execute",
"description": "导航执行服务,输入目标位置,导航至该位置",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"pos": {
"type": "string",
"description": "目标点位名称,例如:会议室、前台、办公室"
}
},
"required": ["pos"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "action_execute",
"description": "动作执行服务,输入动作名称,执行该动作",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"action": {
"type": "string",
"description": "动作名称,例如:握手、挥手、点头"
}
},
"required": ["action"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "dance_execute",
"description": "舞蹈执行服务,输入舞蹈名称,执行该舞蹈",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"dance": {
"type": "string",
"description": "舞蹈名称,例如:舞蹈、街舞、芭蕾"
}
},
"required": ["dance"]
}
}
}
]
# ==================== FunctionGemma 客户端 ====================
class FunctionGemmaClient:
def __init__(self, base_url: str = "http://192.168.10.60:11435"):
self.base_url = base_url
self.chat_url = f"{base_url}/api/chat"
def call_with_tools(self, messages: List[Dict], tools: List[Dict]) -> Dict:
"""带工具调用的对话"""
data = {
"model": "functiongemma",
"messages": messages,
"tools": tools,
"stream": False # 不使用流式,便于计时
}
start_time = time.time()
try:
response = requests.post(self.chat_url, json=data, timeout=30)
end_time = time.time()
latency_ms = (end_time - start_time) * 1000
if response.status_code == 200:
result = response.json()
result['latency_ms'] = latency_ms
return result
else:
return {
"error": f"HTTP {response.status_code}",
"latency_ms": latency_ms
}
except Exception as e:
end_time = time.time()
return {
"error": str(e),
"latency_ms": (end_time - start_time) * 1000
}
# ==================== 准确性评估 ====================
def evaluate_accuracy(test_case: TestCase, response: Dict) -> Dict:
"""评估准确性"""
result = {
'query': test_case.query,
'expected_function': test_case.expected_function,
'expected_params': test_case.expected_params,
'category': test_case.category,
'description': test_case.description,
}
# 检查是否有错误
if 'error' in response:
result['status'] = 'error'
result['error'] = response['error']
result['function_correct'] = False
result['params_correct'] = False
result['overall_correct'] = False
return result
# 提取AI的响应
message = response.get('message', {})
tool_calls = message.get('tool_calls', [])
if not tool_calls:
result['status'] = 'no_tool_call'
result['function_correct'] = False
result['params_correct'] = False
result['overall_correct'] = False
result['ai_response'] = message.get('content', '')
return result
# 获取第一个工具调用
tool_call = tool_calls[0]
actual_function = tool_call.get('function', {}).get('name', '')
arguments_raw = tool_call.get('function', {}).get('arguments', {})
# 安全解析参数
if isinstance(arguments_raw, str):
try:
actual_params = json.loads(arguments_raw)
except:
actual_params = {}
elif isinstance(arguments_raw, dict):
actual_params = arguments_raw
else:
actual_params = {}
# 评估函数是否正确
function_correct = (actual_function == test_case.expected_function)
# 评估参数是否正确
params_correct = True
param_details = {}
for key, expected_value in test_case.expected_params.items():
actual_value = actual_params.get(key, None)
# 参数值可能不完全匹配(例如"会议室" vs "会议室1"),所以使用包含关系
if actual_value is None:
params_correct = False
param_details[key] = {'expected': expected_value, 'actual': None, 'match': False}
elif expected_value in str(actual_value) or str(actual_value) in expected_value:
param_details[key] = {'expected': expected_value, 'actual': actual_value, 'match': True}
else:
params_correct = False
param_details[key] = {'expected': expected_value, 'actual': actual_value, 'match': False}
# 整体是否正确
overall_correct = function_correct and params_correct
result['status'] = 'success'
result['actual_function'] = actual_function
result['actual_params'] = actual_params
result['function_correct'] = function_correct
result['params_correct'] = params_correct
result['param_details'] = param_details
result['overall_correct'] = overall_correct
return result
# ==================== 性能测试 ====================
class FunctionGemmaPerformanceTest:
"""FunctionGemma性能和准确性测试"""
def __init__(self, base_url: str = "http://192.168.10.60:11435", repetitions: int = 10):
self.client = FunctionGemmaClient(base_url)
self.repetitions = repetitions
print("="*70)
print(f"FunctionGemma 准确性和性能评估测试")
print(f"重复次数: {repetitions}")
print("="*70)
# 测试连接
try:
response = requests.get(f"{base_url}/api/tags", timeout=5)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("✅ 连接成功")
models = response.json().get('models', [])
model_names = [m['name'] for m in models]
print(f"📋 可用模型: {model_names}")
else:
print(f"⚠️ 连接警告: HTTP {response.status_code}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 连接错误: {e}")
raise
def test_single_case(self, test_case: TestCase) -> Dict:
"""测试单个用例(多次重复)"""
print(f"\n{'='*70}")
print(f"测试: {test_case.description}")
print(f"查询: {test_case.query}")
print(f"期望: {test_case.expected_function}({test_case.expected_params})")
print(f"{'='*70}")
results = []
latencies = []
correct_count = 0
for i in range(self.repetitions):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": test_case.query}]
# 调用API
response = self.client.call_with_tools(messages, TOOLS)
latency = response.get('latency_ms', 0)
latencies.append(latency)
# 评估准确性
eval_result = evaluate_accuracy(test_case, response)
eval_result['latency_ms'] = latency
eval_result['iteration'] = i + 1
results.append(eval_result)
if eval_result['overall_correct']:
correct_count += 1
# 显示进度
status_icon = "✅" if eval_result['overall_correct'] else "❌"
print(f" [{i+1}/{self.repetitions}] {status_icon} 延迟: {latency:.2f}ms", end="")
if not eval_result['overall_correct']:
if eval_result['status'] == 'error':
print(f" - 错误: {eval_result.get('error', 'Unknown')}")
elif eval_result['status'] == 'no_tool_call':
print(f" - 未调用工具")
elif not eval_result['function_correct']:
print(f" - 函数错误: {eval_result.get('actual_function', 'None')}")
elif not eval_result['params_correct']:
print(f" - 参数错误: {eval_result.get('actual_params', {})}")
else:
print()
# 避免请求过快
if i < self.repetitions - 1:
time.sleep(0.5)
# 统计
accuracy = (correct_count / self.repetitions) * 100
stats = {
'latency_min': min(latencies),
'latency_max': max(latencies),
'latency_mean': statistics.mean(latencies),
'latency_median': statistics.median(latencies),
'latency_stdev': statistics.stdev(latencies) if len(latencies) > 1 else 0,
}
print(f"\n📊 统计结果:")
print(f" 准确率: {correct_count}/{self.repetitions} ({accuracy:.1f}%)")
print(f" 延迟 - 平均: {stats['latency_mean']:.2f}ms, "
f"中位数: {stats['latency_median']:.2f}ms, "
f"范围: [{stats['latency_min']:.2f}, {stats['latency_max']:.2f}]ms, "
f"标准差: {stats['latency_stdev']:.2f}ms")
return {
'test_case': test_case.__dict__,
'results': results,
'statistics': stats,
'accuracy': accuracy,
'correct_count': correct_count,
'total_count': self.repetitions
}
def run_all_tests(self) -> Dict:
"""运行所有测试"""
all_results = []
for i, test_case in enumerate(TEST_CASES, 1):
print(f"\n\n{'#'*70}")
print(f"测试用例 {i}/{len(TEST_CASES)}")
print(f"{'#'*70}")
result = self.test_single_case(test_case)
all_results.append(result)
# 避免请求过快
if i < len(TEST_CASES):
time.sleep(2)
# 生成汇总报告
self.print_summary(all_results)
return {
'test_config': {
'repetitions': self.repetitions,
'total_test_cases': len(TEST_CASES),
'total_tests': len(TEST_CASES) * self.repetitions
},
'results': all_results,
'timestamp': time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
}
def print_summary(self, results: List[Dict]):
"""打印汇总报告"""
print(f"\n\n{'='*70}")
print("综合评估报告")
print(f"{'='*70}\n")
# 按类别统计
category_stats = {}
for r in results:
category = r['test_case']['category']
if category not in category_stats:
category_stats[category] = {
'correct': 0,
'total': 0,
'latencies': []
}
category_stats[category]['correct'] += r['correct_count']
category_stats[category]['total'] += r['total_count']
category_stats[category]['latencies'].extend([
res['latency_ms'] for res in r['results']
])
# 打印类别统计
print("📋 按类别统计:\n")
print(f"{'类别':<15} {'准确率':<15} {'平均延迟':<15} {'标准差':<15}")
print("-" * 70)
for category, stats in category_stats.items():
accuracy = (stats['correct'] / stats['total']) * 100
avg_latency = statistics.mean(stats['latencies'])
stdev = statistics.stdev(stats['latencies']) if len(stats['latencies']) > 1 else 0
print(f"{category:<15} {accuracy:>6.1f}% ({stats['correct']}/{stats['total']}) "
f"{avg_latency:>10.2f}ms {stdev:>10.2f}ms")
# 整体统计
total_correct = sum(r['correct_count'] for r in results)
total_tests = sum(r['total_count'] for r in results)
overall_accuracy = (total_correct / total_tests) * 100
all_latencies = []
for r in results:
all_latencies.extend([res['latency_ms'] for res in r['results']])
print(f"\n{'='*70}")
print("📊 整体统计:\n")
print(f" 总测试次数: {total_tests}")
print(f" 正确次数: {total_correct}")
print(f" 整体准确率: {overall_accuracy:.1f}%")
print(f"\n 延迟统计:")
print(f" 平均: {statistics.mean(all_latencies):.2f}ms")
print(f" 中位数: {statistics.median(all_latencies):.2f}ms")
print(f" 最小: {min(all_latencies):.2f}ms")
print(f" 最大: {max(all_latencies):.2f}ms")
print(f" 标准差: {statistics.stdev(all_latencies):.2f}ms")
# 详细测试用例结果
print(f"\n{'='*70}")
print("📝 详细测试用例结果:\n")
print(f"{'测试用例':<20} {'准确率':<15} {'平均延迟':<15}")
print("-" * 70)
for r in results:
desc = r['test_case']['description']
accuracy = r['accuracy']
avg_latency = r['statistics']['latency_mean']
status_icon = "✅" if accuracy == 100 else "⚠️" if accuracy >= 80 else "❌"
print(f"{status_icon} {desc:<18} {accuracy:>6.1f}% {avg_latency:>10.2f}ms")
def main():
"""主测试函数"""
# 每个测试用例重复10次
test = FunctionGemmaPerformanceTest(
base_url="http://192.168.10.60:11435",
repetitions=10
)
results = test.run_all_tests()
# 保存结果
output_file = 'functiongemma_evaluation_results.json'
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(results, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2, default=str)
print(f"\n\n{'='*70}")
print(f"测试完成!结果已保存到: {output_file}")
print(f"{'='*70}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结论
整体感觉,如果不进行微调的话,不如qwen3-4B的模型,中文场景下,甚至推理时延也没有优势。或许更适合算力受限的场景?毕竟只有0.27B
下面是一个LLM的综合评估结果,可供参考
FunctionGemma 准确性和性能评估报告
测试概述
- 测试时间: 2026-02-09
- 测试用例: 9个(导航3个、动作3个、舞蹈3个)
- 每个用例重复次数: 10次
- 总测试次数: 90次
核心发现 ⚠️
整体准确率:44.4% (40/90)
关键问题 :FunctionGemma在Function Calling上存在严重的准确性问题
| 类别 | 准确率 | 正确/总数 | 平均延迟 | 标准差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Navigation(导航) | 0.0% ❌ | 0/30 | 608.82ms | 525.52ms |
| Action(动作) | 66.7% ⚠️ | 20/30 | 518.90ms | 46.78ms |
| Dance(舞蹈) | 66.7% ⚠️ | 20/30 | 503.92ms | 31.58ms |
详细测试结果
1. 导航类(Navigation)- 0% 准确率 ❌
| 测试用例 | 查询 | 期望函数 | 实际函数 | 准确率 | 平均延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 导航到会议室 | "带我去会议室" | nav_execute |
action_execute |
0/10 (0%) | 803.37ms |
| 导航到前台 | "怎么去前台" | nav_execute |
action_execute |
0/10 (0%) | 520.11ms |
| 导航到办公室 | "去办公室" | nav_execute |
action_execute |
0/10 (0%) | 502.97ms |
问题分析:
- ❌ 100%错误 :所有导航查询都被错误识别为
action_execute - ❌ 函数混淆:模型无法区分导航和动作
- ⚠️ 高延迟:"带我去会议室"平均延迟803ms,第一次甚至达到3384ms
根本原因:
- FunctionGemma可能对中文的"去"、"带我"等导航关键词理解不足
- 工具描述可能不够清晰
2. 动作类(Action)- 66.7% 准确率 ⚠️
| 测试用例 | 查询 | 期望参数 | 准确率 | 平均延迟 | 问题 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 执行握手动作 | "握个手" | {action: "握手"} |
10/10 (100%) ✅ | 487.61ms | 无 |
| 执行挥手动作 | "挥挥手" | {action: "挥手"} |
10/10 (100%) ✅ | 521.07ms | 无 |
| 执行点头动作 | "点个头" | {action: "点头"} |
0/10 (0%) ❌ | 548.02ms | 7次未调用工具,2次参数错误 |
问题分析:
- ✅ 成功案例:"握个手"、"挥挥手" 100%准确
- ❌ 失败案例 :"点个头" 0%准确
- 7次完全未调用工具(直接回答)
- 2次参数错误:
{action: "点个头"}(应该是"点头")
根本原因:
- "点个头"的表达方式可能让模型困惑
- 模型可能认为"点个头"是简单对话,不需要调用工具
3. 舞蹈类(Dance)- 66.7% 准确率 ⚠️
| 测试用例 | 查询 | 期望参数 | 准确率 | 平均延迟 | 问题 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 执行舞蹈 | "跳个舞" | {dance: "舞蹈"} |
0/10 (0%) ❌ | 506.79ms | 参数错误 |
| 执行街舞 | "跳个街舞" | {dance: "街舞"} |
10/10 (100%) ✅ | 510.33ms | 无 |
| 执行芭蕾舞 | "来段芭蕾" | {dance: "芭蕾"} |
10/10 (100%) ✅ | 494.64ms | 无 |
问题分析:
- ✅ 成功案例:"跳个街舞"、"来段芭蕾" 100%准确
- ❌ 失败案例 :"跳个舞" 0%准确
- 10次都调用了正确的函数
dance_execute - 但参数错误:9次
{dance: "跳"},1次{dance: "跳个舞"} - 期望:
{dance: "舞蹈"}
- 10次都调用了正确的函数
根本原因:
- 模型提取参数时过于字面化
- "跳个舞"被解析为动词"跳"而不是名词"舞蹈"
- 具体的舞蹈名称(街舞、芭蕾)效果好
性能分析
延迟统计
| 指标 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 平均延迟 | 543.88ms |
| 中位数延迟 | 506.64ms |
| 最小延迟 | 458.78ms |
| 最大延迟 | 3384.88ms ⚠️ |
| 标准差 | 305.28ms |
关键发现:
- ⚠️ 高延迟:平均543ms,远高于内网4B模型的225ms
- ⚠️ 不稳定:标准差305ms,最大值3384ms
- ⚠️ 比内网慢2.4倍:543ms vs 225ms
按测试用例的延迟
| 测试用例 | 平均延迟 | 标准差 | 稳定性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 导航到会议室 | 803.37ms | - | 最慢 ⚠️ |
| 导航到前台 | 520.11ms | - | 中等 |
| 导航到办公室 | 502.97ms | 25.46ms | 稳定 |
| 执行握手动作 | 487.61ms | 13.26ms | 最稳定 ✅ |
| 执行挥手动作 | 521.07ms | 36.55ms | 稳定 |
| 执行点头动作 | 548.02ms | 59.19ms | 不稳定 |
| 执行舞蹈 | 506.79ms | 38.95ms | 稳定 |
| 执行街舞 | 510.33ms | 36.40ms | 稳定 |
| 执行芭蕾舞 | 494.64ms | 14.88ms | 稳定 ✅ |
问题总结
准确性问题
-
导航功能完全失效 ❌
- 0% 准确率
- 所有导航查询都被误识别为动作
-
泛化能力差 ⚠️
- 具体的指令("握个手"、"街舞")效果好
- 泛化的指令("跳个舞"、"点个头")效果差
-
参数提取不准确 ⚠️
- "跳个舞" →
{dance: "跳"}而不是{dance: "舞蹈"} - "点个头" →
{action: "点个头"}而不是{action: "点头"}
- "跳个舞" →
-
工具调用决策不稳定 ⚠️
- "点个头"有70%的情况下不调用工具
性能问题
-
延迟高 ⚠️
- 平均543ms,比内网4B慢2.4倍
- 最大延迟3384ms(不可接受)
-
稳定性差 ⚠️
- 标准差305ms
- 导航类延迟标准差高达525ms
对比分析:FunctionGemma vs 内网4B
| 指标 | FunctionGemma | 内网4B | 对比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 准确率 | 44.4% | ~95%+ | FunctionGemma差很多 ❌ |
| 平均延迟 | 543.88ms | 225ms | FunctionGemma慢2.4倍 ❌ |
| 稳定性(标准差) | 305.28ms | 19ms | FunctionGemma差16倍 ❌ |
| 导航功能 | 0% | ~100% | FunctionGemma完全失效 ❌ |
| 成本 | 本地部署,零API成本 | 本地部署,零API成本 | 相同 ✅ |
结论 :FunctionGemma在准确性、性能、稳定性上全面落后于内网4B模型
建议
短期建议 ⚠️
不推荐使用FunctionGemma,原因:
- 准确率仅44.4%,不满足生产要求
- 导航功能完全失效(0%准确率)
- 延迟高且不稳定
中期建议 💡
如果必须使用FunctionGemma,需要:
-
改进工具描述
- 更清晰地区分导航、动作、舞蹈
- 添加更多示例
-
优化查询方式
- 使用具体的指令("握个手"而不是"握手")
- 避免泛化的表达("跳个舞"改为"跳舞")
-
添加后处理逻辑
- 检测并修正常见的参数错误
- 添加重试机制
长期建议 ✅
继续使用内网4B模型:
- 准确率高(~95%+)
- 延迟低(225ms)
- 稳定性好(标准差19ms)
- 所有功能都正常工作
测试数据
- 测试脚本: [functiongemma_evaluation.py](file:///Users/mark/Nutstore%20Files/CodeFile/pycharmProject/doubao_workflow/agent_test/tests/test_funciongemma/functiongemma_evaluation.py)
- 测试结果: [functiongemma_evaluation_results.json](file:///Users/mark/Nutstore%20Files/CodeFile/pycharmProject/doubao_workflow/agent_test/tests/test_funciongemma/functiongemma_evaluation_results.json)
测试时间 : 2026-02-09
测试状态 : ✅ 完成
总测试次数: 90次