Map
在go 1.24中,对于map的存储更换了新的存储方法,使用Swiss table的方式存储数据,优化了map的操作,下面我们展开讨论map的实现,以下表述默认 64 位架构
首先是简介对hash冲突的解决方法,因为某个 key 应该落在哪个槽位,主要由哈希函数 hash(key) 决定。哈希函数把每个 key 映射为一个整数:同一个 key 总是映射到同一个整数;所以会存在hash冲突问题,下面我们简单介绍开放寻址哈希表方法。
开放寻址哈希表
在开放寻址哈希表中,所有条目都存放在同一个底层数组中。数组中的每个位置称为一个 slot(槽位)。不同 key 理想情况下应当遵循均匀随机的整数分布。开放寻址哈希表的定义性特征在于:它通过把 key 存到数组中的其他位置来解决碰撞。因此,如果目标 slot 已经满了(发生碰撞),就使用探测序列(probe sequence)去尝试其他 slot,直到找到一个空 slot。
swiss table
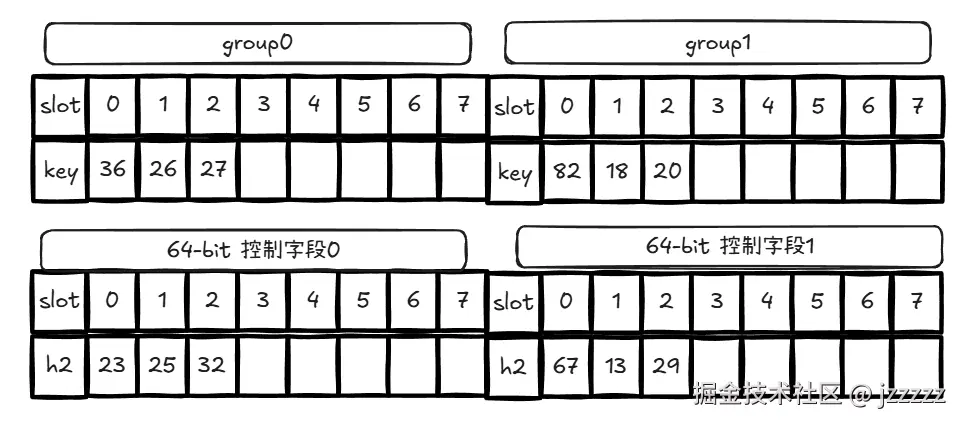
Swiss Table 同样是开放寻址哈希表的一种形式。仍然使用单一底层数组进行存储,但会把数组按逻辑划分为每组 8 个 slot 的 group(组)。此外,每个 group 还有一个 64 位控制字(control word)作为元数据。控制字的 8 个字节分别对应该 group 的 8 个 slot。每个字节的值表示对应 slot 是空、已删除,还是正在使用。如果正在使用,该字节还包含该 slot 的 key 的哈希值低 7 位(称为 h2)。例如:
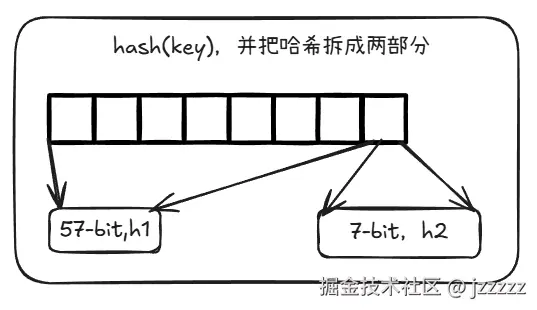
在Swiss Tables中会对hash(key)得到的值,并把哈希拆成两部分,分别为h1(高 57 位)和h2(低 7 位)
在插入操作中:
- hash(key)计算拆分得到h1和h2
- 根据h1计算首先需要查询的group, h1 % group的数量
- 在group内,判断slot是否可以插入or包含key(此时为更新操作)
- 如果没有slot包含key,则寻找empty 插入key
- 如果没empty,则沿探测序列继续搜索下一个 group
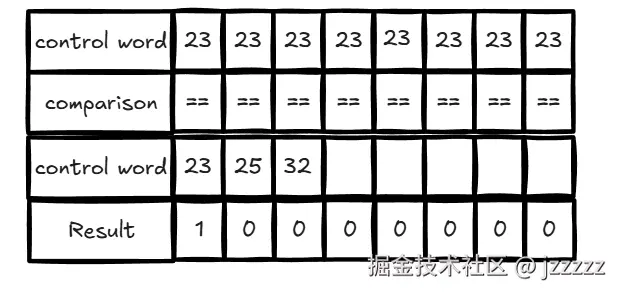
在第三步就是swiss table做的优化,一个 group有8个slot,正常是线性扫描并比较 8 个 key,但存在控制字可以进行快速比较,通过比较控制字中的每个字节为我们的h2,得到候选(一次比较同一 group 的 8 个 slot 控制字节,从而优化)
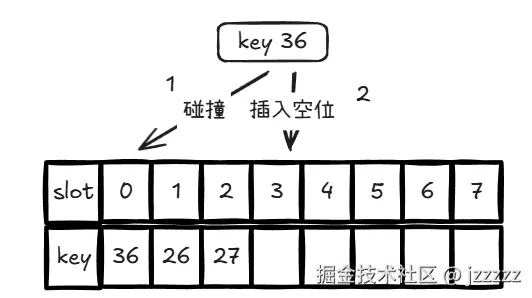
例如查找 key 36,并且 h2 = 23:
map的基本使用
创建map
有两种创建方式分别是带容量和不带容量的创建:
go
m := make(map[int]int, cap)
m2 := make(map[int]int)map写入数据
go
m[key] = valmap读取数据
- 第一种方式如果key不存在返回0值,存在返回对应val
- 第二种方式可以根据返回的bool值判断是否真的取到值
go
v1 := m[key]
v2, ok := m[key]map删除数据
go
delete(m, key)map数据结构
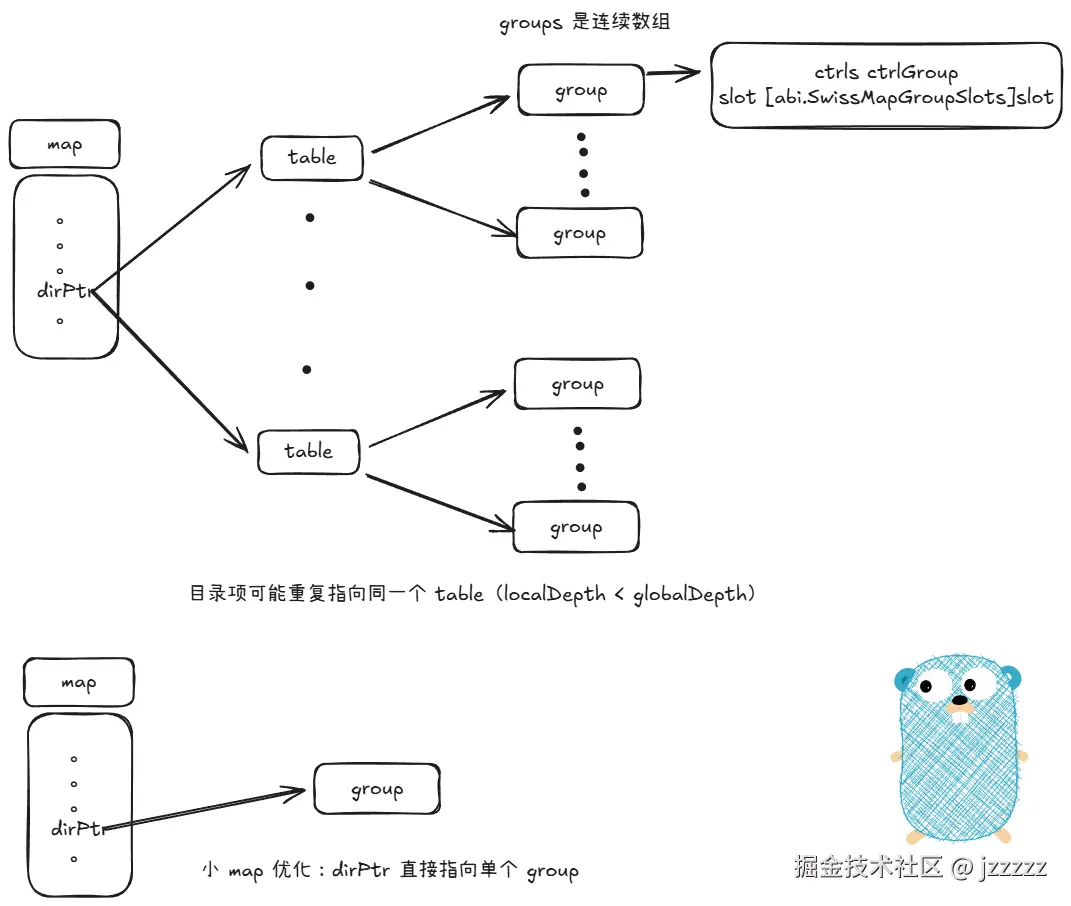
internal/runtime/maps/map.go
go
type Map struct {
used uint64
seed uintptr
dirPtr unsafe.Pointer
dirLen int //*[dirLen]*table
globalDepth uint8
globalShift uint8
writing uint8
clearSeq uint64
}- used 已经填充的slot的数量(所有table中的元素的总数)
- seed 用于hash计算使用
- dirPtr 通常情况下,dirPtr 指向一个由 table 指针组成的数组,如果map中元素数量不超过 8 此时 dirPtr 直接指向一个单独的 group
- globalDepth 在table目录查找时要使用的比特数
- globalShift 在进行目录查找时,需要从哈希值中右移掉的比特数
- writing 是一个标志位:当 map 正在被写入时,会通过异或 1(XOR 1)的方式翻转。
- clearSeq 是对 Clear 调用次数的序列计数器,用于在迭代期间检测 map 是否被清空。
internal/runtime/maps/table.go
go
type table struct {
used uint16
capacity uint16
growthLeft uint16
localDepth uint8
index int
groups groupsReference
}- used 该table已填充的的元素(slot)数量
- capacity 该table的容量,slot的上限
- growthLeft 在无需rehash的情况下,还能继续填充的 slot 数量。(used + tombstones > loadFactor*capacity 时会触发 rehash)
- localDepth 在该 table 之上,用于目录查找(directory lookups)的比特数。(如果目录扩容但该table未拆分可能会小于m.globalDepth)
- index 该 table 在 Map 目录中的索引。这是目录中该 table 出现的"第一个"位置的索引。同一个 table 可能会在目录中连续出现多个索引位置。如果index为-1则已过期不再使用
- groups table 自己持有的一个 group 数组
internal/runtime/maps/group.go
go
type groupsReference struct {
data unsafe.Pointer // data *[length]typ.Group
lengthMask uint64
}- data 指向一个 group 数组
- lengthMask 等于 data 中 group 的数量减一,方便按位
internal/rutime/maps/group.go
go
type groupReference struct {
// data points to the group, which is described by typ.Group and has
// layout:
// group由 abi.SwissMapGroupSlots(8)个 slot 加上一个控制字组成的一组。
// type group struct {
// ctrls ctrlGroup // 控制字节组,每个 slot 1 个控制字节,控制字节最高位区分空/删除/占用;占用时其余 7 位存 H2(hash(key)的低7位)。
// slots [abi.SwissMapGroupSlots]slot
// }
//
// type slot struct {
// key typ.Key
// elem typ.Elem
// }
data unsafe.Pointer // data *typ.Group
}用来表示存放在 data 中的单个 slot group, 一个group包含 abi.SwissMapGroupSlots (8)个 slot(key/elem 对),以及它们的控制字。
创建map
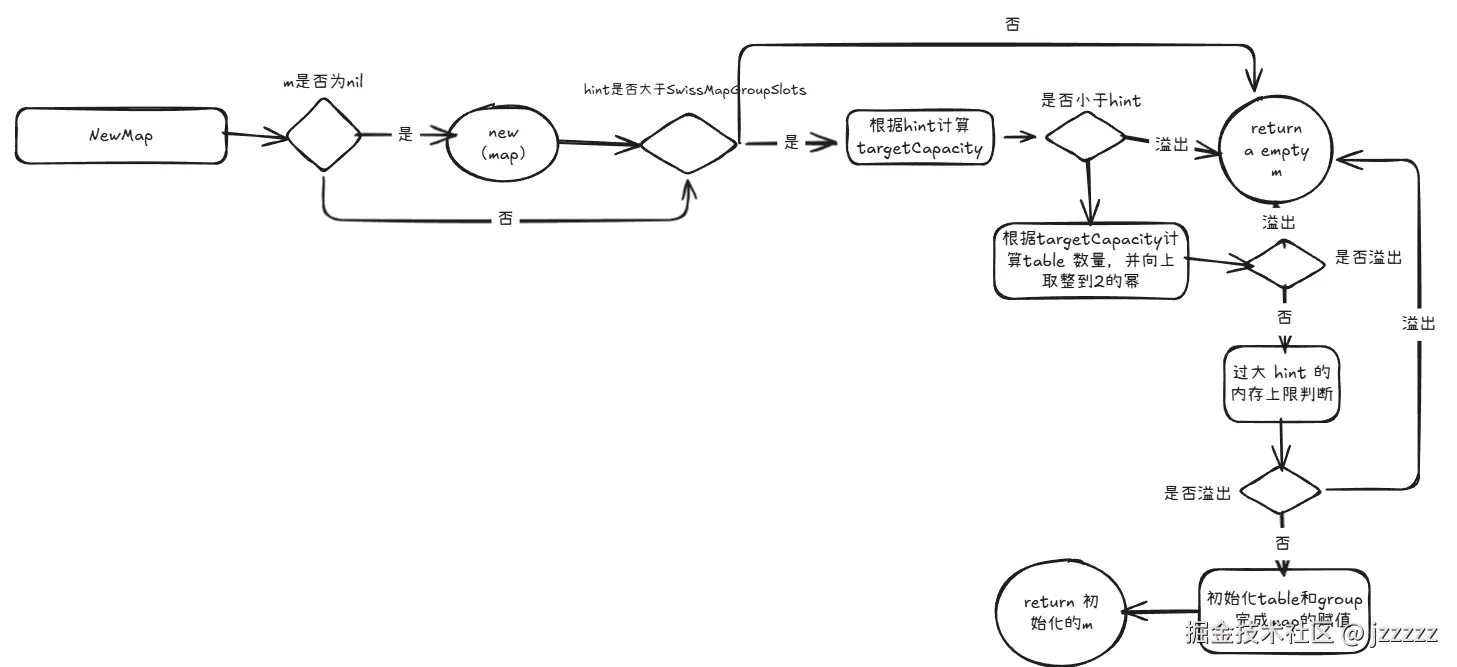
go
func NewMap(mt *abi.SwissMapType, hint uintptr, m *Map, maxAlloc uintptr) *Map {
if m == nil {
m = new(Map)
}
m.seed = uintptr(rand())
if hint <= abi.SwissMapGroupSlots {
return m
}
targetCapacity := (hint * abi.SwissMapGroupSlots) / maxAvgGroupLoad
if targetCapacity < hint {
return m // return an empty map.
}
dirSize := (uint64(targetCapacity) + maxTableCapacity - 1) / maxTableCapacity
dirSize, overflow := alignUpPow2(dirSize)
if overflow || dirSize > uint64(math.MaxUintptr) {
return m // return an empty map.
}
groups, overflow := math.MulUintptr(uintptr(dirSize), maxTableCapacity)
if overflow {
return m // return an empty map.
} else {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(groups, mt.GroupSize)
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc {
return m // return an empty map.
}
}
m.globalDepth = uint8(sys.TrailingZeros64(dirSize))
m.globalShift = depthToShift(m.globalDepth)
directory := make([]*table, dirSize)
for i := range directory {
directory[i] = newTable(mt, uint64(targetCapacity)/dirSize, i, m.globalDepth)
}
m.dirPtr = unsafe.Pointer(&directory[0])
m.dirLen = len(directory)
return m
}该方法有四个参数,mt *abi.SwissMapType:map 的类型元数据,hint uintptr:来自 make(map[K]V, hint) 的期望容量,m *Map:可复用/预分配的 Map 头部指针;maxAlloc uintptr:本次分配允许的最大内存上限;
由于代码过长且判断条件较多所以就划分讲解:
step1:
- 编译器判断 map 逃逸,就不在栈上预分配,直接传 nil,NewMap 会 new(Map),且因为指针要返回给调用方,这个 Map 会逃逸,实际分配在堆上。
- 编译器判断 map 不逃逸,就在调用方栈上放一个临时 Map 头部,并把它的地址传给 NewMap 复用。
go
func NewMap(mt *abi.SwissMapType, hint uintptr, m *Map, maxAlloc uintptr) *Map {
if m == nil {
m = new(Map)
}
//..
return m
}step2: 对m的seed赋值,并根据hint大小:判断当hint <= abi.SwissMapGroupSlots(=8) ,此时一个group即可满足,函数直接返回不分配;在对map首次写入时会分配一个 8-slot group
go
func NewMap(mt *abi.SwissMapType, hint uintptr, m *Map, maxAlloc uintptr) *Map {
//..
m.seed = uintptr(rand())
if hint <= abi.SwissMapGroupSlots {
return m
}
//..
}step3: 计算 targetCapacity = hint * slotsPerGroup / maxAvgGroupLoad,等价于 hint / 负载因子(7/8),防止刚创建后就触发扩容,如果计算分配的预期容量溢出转为则直接返回空map。
go
func NewMap(mt *abi.SwissMapType, hint uintptr, m *Map, maxAlloc uintptr) *Map {
//..
targetCapacity := (hint * abi.SwissMapGroupSlots) / maxAvgGroupLoad
if targetCapacity < hint { // overflow
return m // return an empty map.
}
//..
}step4: 计算 table 个数dirSize = ceil(targetCapacity / maxTableCapacity) ,随后向上取整到 2 的幂;溢出则返回空 map
go
func NewMap(mt *abi.SwissMapType, hint uintptr, m *Map, maxAlloc uintptr) *Map {
//..
dirSize := (uint64(targetCapacity) + maxTableCapacity - 1) / maxTableCapacity
dirSize, overflow := alignUpPow2(dirSize)
if overflow || dirSize > uint64(math.MaxUintptr) {
return m // return an empty map.
}
//..
}step5: 进行过大 hint 的内存上限检查:用 dirSize*maxTableCapacity 得到总 groups 上界,再乘 mt.GroupSize 得到内存上界;任一处溢出或超 maxAlloc 则返回
go
func NewMap(mt *abi.SwissMapType, hint uintptr, m *Map, maxAlloc uintptr) *Map {
//..
groups, overflow := math.MulUintptr(uintptr(dirSize), maxTableCapacity)
if overflow {
return m // return an empty map.
} else {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(groups, mt.GroupSize)
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc {
return m // return an empty map.
}
}
//..
}
go
计算目录需要用的位数,以及取出这 globalDepth 位,哈希值需要右移多少位。然后创建table(容量为预期容量 / table个数)并分配目录数组,记录目录长度,初始化完成返回
func NewMap(mt *abi.SwissMapType, hint uintptr, m *Map, maxAlloc uintptr) *Map {
//..
m.globalDepth = uint8(sys.TrailingZeros64(dirSize))
m.globalShift = depthToShift(m.globalDepth)
directory := make([]*table, dirSize)
for i := range directory {
directory[i] = newTable(mt, uint64(targetCapacity)/dirSize, i, m.globalDepth)
}
m.dirPtr = unsafe.Pointer(&directory[0])
m.dirLen = len(directory)
return m
}接下来看上面调用到的创建table的方法newTable()
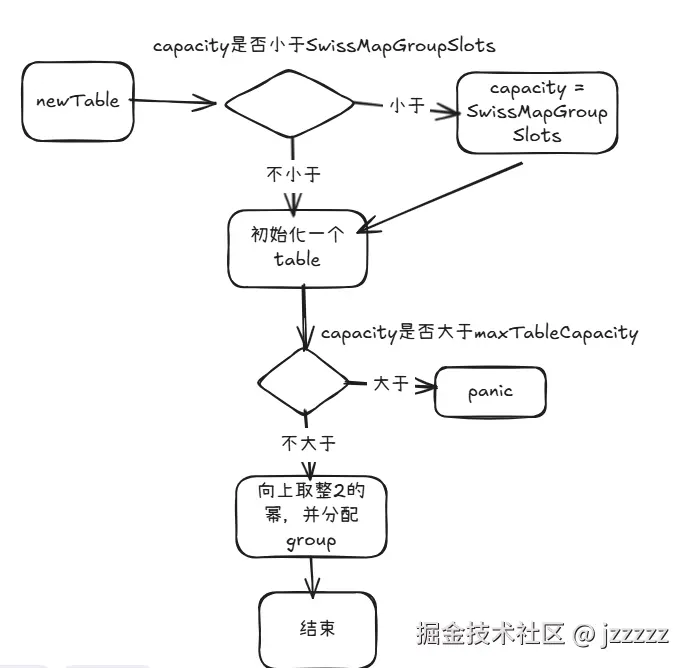
internal/rutime/maps/table.go newTable()
- 首先根据capacity大小进行兜底,避免不够一个group的slot容量,然后对table赋值
- 如果capacity > maxTableCapacity(1024)则panic
- 然后将capacity对齐到 2 的幂,如果对齐后溢出panic
- 调用reset 方法会按容量分配 groups 数组、设置 capacity/ growthLeft,并把 control 字节初始化为 empty。
- 返回创建好的table
go
func newTable(typ *abi.SwissMapType, capacity uint64, index int, localDepth uint8) *table {
if capacity < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots {
capacity = abi.SwissMapGroupSlots
}
t := &table{
index: index,
localDepth: localDepth,
}
if capacity > maxTableCapacity {
panic("initial table capacity too large")
}
capacity, overflow := alignUpPow2(capacity)
if overflow {
panic("rounded-up capacity overflows uint64")
}
t.reset(typ, uint16(capacity))
return t
}对table分配group数组
table.reset()
- 根据capacity计算出groupCount
- newGroups(typ, groupCount)创建了一个groupsReference分配一段连续的 group 数组并返回,对table赋值
- 然后调用resetGrowthLeft计算growthLeft
- 最后清空整张groups表的 control 字节
go
func (t *table) reset(typ *abi.SwissMapType, capacity uint16) {
groupCount := uint64(capacity) / abi.SwissMapGroupSlots
t.groups = newGroups(typ, groupCount)
t.capacity = capacity
t.resetGrowthLeft()
for i := uint64(0); i <= t.groups.lengthMask; i++ {
g := t.groups.group(typ, i) //根据index返回对应的group
g.ctrls().setEmpty()
}
}该方法根据capacity计算当前table不扩容情况下还可以放多少数据
table.resetGrowthLeft()
- 如果 capacity 为0则直接panic,一个table必须有一个有效的容量
- 根据 capacity 计算出growthLeft,对于单 group 表需要至少留 1 个空槽来保证探测终止
- 对于多个 group 负载因子是 maxAvgGroupLoad / SwissMapGroupSlots(7/8),先做溢出检查:t.capacity*maxAvgGroupLoad 如果溢出会panic。最终可用槽数 = capacity * 7 / 8。
- 返回
go
func (t *table) resetGrowthLeft() {
var growthLeft uint16
if t.capacity == 0 {
panic("table must have positive capacity")
} else if t.capacity <= abi.SwissMapGroupSlots {
growthLeft = t.capacity - 1
} else {
if t.capacity*maxAvgGroupLoad < t.capacity {
panic("overflow")
}
growthLeft = (t.capacity * maxAvgGroupLoad) / abi.SwissMapGroupSlots
}
t.growthLeft = growthLeft
}分配一段连续的 group 数组加初始化lengthMask方便快速查找
newGroups()
go
func newGroups(typ *abi.SwissMapType, length uint64) groupsReference {
return groupsReference{
data: newarray(typ.Group, int(length)),
lengthMask: length - 1,
}
}map中读数据
在internal/runtime/maps/runtime_swiss.go中可以查看实现方法
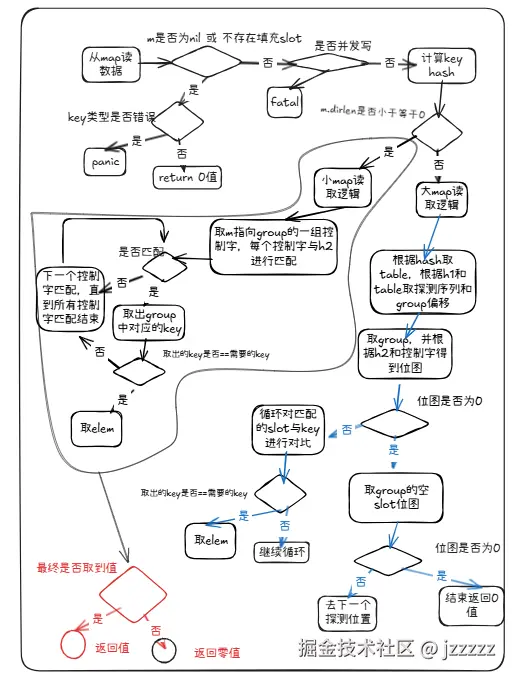
**runtime\_mapaccess1()**
go
func runtime_mapaccess1(typ *abi.SwissMapType, m *Map, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
if m == nil || m.Used() == 0 {
if err := mapKeyError(typ, key); err != nil {
panic(err) // see issue 23734
}
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}
if m.writing != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map read and map write")
}
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
if m.dirLen <= 0 {
_, elem, ok := m.getWithKeySmall(typ, hash, key)
if !ok {
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}
return elem
}
// Select table.
idx := m.directoryIndex(hash)
t := m.directoryAt(idx)
// Probe table.
seq := makeProbeSeq(h1(hash), t.groups.lengthMask)
for ; ; seq = seq.next() {
g := t.groups.group(typ, seq.offset)
match := g.ctrls().matchH2(h2(hash))
for match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
slotKeyOrig := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
slotElem := unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(slotKeyOrig) + typ.ElemOff)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
slotElem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem))
}
return slotElem
}
match = match.removeFirst()
}
match = g.ctrls().matchEmpty()
if match != 0 {
// Finding an empty slot means we've reached the end of
// the probe sequence.
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}
}
}step1:
如果map为nil,或者map中无已填充的数据,首先对key的合法性进行判断,如果key不合法则直接panic,否则返回一个零值;
go
if m == nil || m.Used() == 0 {
if err := mapKeyError(typ, key); err != nil {
panic(err) // see issue 23734
}
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}step2:
此时存在其他goroutine在写该map,则直接fatal
go
if m.writing != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map read and map write")
}step3:
使用typ类型对应的hasher函数得到key对应的hash,如果m.dirLen <= 0说明是一个小map 则调用getWithKeySmall方法取值并返回,若没取到返回零值
go
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
if m.dirLen <= 0 {
_, elem, ok := m.getWithKeySmall(typ, hash, key)
if !ok {
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}
return elem
}step4:
- 根据hash值右移globalShift获取到table的index,然后根据index取出对应的table指针
- 根据h1(hash)和group的lengthMask计算出,起始 offset 和步进序列
- 然后根据取出seq,开启for循环,每次seq.next()会给出下一个要探测的 group 位置。
- 在for循环内部,根据h2(hash)与控制字匹配,得到位图(哪些 slot 的 h2 匹配)例如:mask = 0b00001001
- 当match大于0,开启第二个for遍历,按位图逐个取,mask.first() 取最低位的 1,如果key存的是指向key的指针才解指针
- 如果typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey)成立,则取出对应槽位的elem,并且如果elem存的是指向elem的指针才解指针,最后返回
- 如果没配对则从match中 mask.removeFirst()把最低位的 1 清掉,继续遍历直到取出或,match为空
- 如果第二个for循环没取出值,且当前组有emptyslot,说明探测序列结束,直接返回零值。
- 否则继续执行第一个for循环取出根据步进序列得出要探测的 group 位置继续执行 4 - 8操作
go
idx := m.directoryIndex(hash)
t := m.directoryAt(idx)
seq := makeProbeSeq(h1(hash), t.groups.lengthMask)
for ; ; seq = seq.next() {
g := t.groups.group(typ, seq.offset)
match := g.ctrls().matchH2(h2(hash))
for match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
slotKeyOrig := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
slotElem := unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(slotKeyOrig) + typ.ElemOff)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
slotElem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem))
}
return slotElem
}
match = match.removeFirst()
}
match = g.ctrls().matchEmpty()
if match != 0 {
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}
}接下来看一下里面用到的方法的实现首先是getWithKeySmall,该方法用于小map的key取对应的elem
Map.getWithKeySmall()
首先根据m.dirptr封装了一个group,前面也提到小map无table只有一个group
- 取出h2(hash)和group的控制字
- 开启for循环遍历(结束条件:1.i == SwissMapGroupSlots;2.找到key对应elem返回),先取低8位的第一个字节的控制位,然后将ctrls右移8位
- 如果取出的控制位!=h2则继续循环取下一个控制位
- 如果控制位==h2,首先取出index 偏移量对应的slot key,并且当存放的key为指向key指针时解指针
- 接着判断slot key 是否等于 key,如果等于取出index 偏移量对应的slot Elem,并且当存放的Elem为指向Elem指针时解指针,返回值结束;否则继续for循环直到取出
- 如果到最后还没有找到配对的就直接return false
go
func (m *Map) getWithKeySmall(typ *abi.SwissMapType, hash uintptr, key unsafe.Pointer) (unsafe.Pointer, unsafe.Pointer, bool) {
g := groupReference{
data: m.dirPtr,
}
h2 := uint8(h2(hash))
ctrls := *g.ctrls()
for i := uintptr(0); i < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots; i++ {
c := uint8(ctrls)
ctrls >>= 8
if c != h2 {
continue
}
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
slotElem := g.elem(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
slotElem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem))
}
return slotKey, slotElem, true
}
}
return nil, nil, false
}然后是取table的操作,此时不是小map Map.directoryIndex 和 Map.directoryAt
directoryIndex负责计算table的index,directoryA负责取出对应的table的指针 directoryIndex,如果dirLen == 1说明只有一个table直接返回0,否则将hash右移globalShift位返回 directoryAt根据传进来的index计算出table的指针地址,返回
go
func (m *Map) directoryIndex(hash uintptr) uintptr {
if m.dirLen == 1 {
return 0
}
return hash >> (m.globalShift & 63)
}
func (m *Map) directoryAt(i uintptr) *table {
return *(**table)(unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(m.dirPtr) + goarch.PtrSize*i))
}接着是取探测起始位置和探测序列函数;计算探测起始位置使用到makeProbeSeq函数,利用hash和group的lengthMask按位与得出起始位置,设置index为0并封装为probeSeq返回计算下一个探测位置用到next()函数,采用二次探测的方法,每次 next():index++,然后 offset = (offset + index) & mask
go
func makeProbeSeq(hash uintptr, mask uint64) probeSeq {
return probeSeq{
mask: mask,
offset: uint64(hash) & mask,
index: 0,
}
}
func (s probeSeq) next() probeSeq {
s.index++
s.offset = (s.offset + s.index) & s.mask
return s
}然后看matchH2()用来判断该group中那些slot是候选 ctrlGroup.matchH2()
go
func (g ctrlGroup) matchH2(h uintptr) bitset {
return ctrlGroupMatchH2(g, h)
}
func ctrlGroupMatchH2(g ctrlGroup, h uintptr) bitset {
v := uint64(g) ^ (bitsetLSB * uint64(h)) // bitsetLSB = 0x0101010101010101
return bitset(((v - bitsetLSB) &^ v) & bitsetMSB) //bitsetMSB = 0x8080808080808080
}- bitsetLSB * h 把 8 位的 h 复制到 8 个字节里,例如 : h为00100010,计算后为 0x22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22
- g ^ 用于按位异或, 此时v中每个字节为 0 的位置就表示 g 的对应字节 等于 h;例如前面计算得到0x22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 g为0x21 22 11 33 44 22 22 22,则得到0x03 00 33 11 66 00 00 00
- v - bitsetLSB 将每个字节减一,例如0x03 00 33 11 66 00 00 00得到:0x01 FF 32 10 64 FE FE FF
- ((v - bitsetLSB) &^ v) 按位清除(v为1的为,会把(v - bitsetLSB)的对应位清0),得到0x00 ff 00 00 00 fe fe ff
- 最后于bitsetMSB按位与 得到 0x00 80 00 00 00 80 80 80 返回遍历需要的位图
matchEmpty()用来判断该group中是否有empty slot,有的话说明探测结束,后面无slot ctrlGroup.matchEmpty()
go
func (g ctrlGroup) matchEmpty() bitset {
return ctrlGroupMatchEmpty(g)
}
func ctrlGroupMatchEmpty(g ctrlGroup) bitset {
// An empty slot is 1000 0000
// A deleted slot is 1111 1110
// A full slot is 0??? ????
v := uint64(g)
return bitset((v &^ (v << 6)) & bitsetMSB)
}go官方定义第 7 位被置 1 且第 1 位未置位时则该slot是一个empty slot
- v << 6 会把 每个字节的 bit1(0x02)移动到该字节的 bit7 位置。
- v &^ (v<<6) 会在 v 的 bit7 上 清掉 那些原本 bit1 为 1的字节。
- 然后使用bitsetMSB 按位与确保每个字节只保留最高位,此时0x80的字节就是空empty slot
向map中写数据
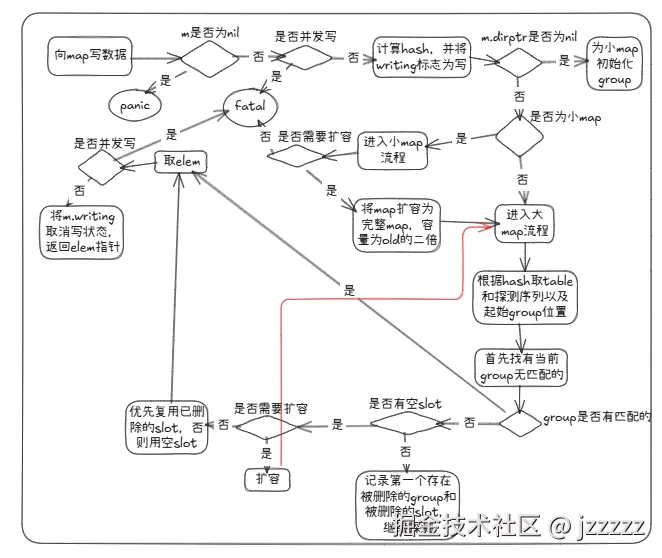
首先总结一下map写数据的大致流程:
- m == nil(nil map)写入会 panic;进入写前若 m.writing != 0 会 fatal。
- 计算 hash 后把 m.writing ^= 1(通常 0 -> 1)。
- 若 m.dirPtr == nil,先 growToSmall 分配首个 group。
- 若 m.dirLen == 0(小 map):未满:直接 small put;已满:growToTable 转成 table 再走大 map 流程。
- 大 map:按 hash 找 table,沿 probe 序列先找"同 key"槽位(找到就是更新并返回)。 没找到时:遇到 empty 表示 probe 结束;若之前记过 deleted 槽位则优先用 deleted,否则用 empty;若 growthLeft == 0 则 rehash 后 continue outer 重试。
- 返回前再做并发校验:若 m.writing == 0 则 fatal,否则再 ^= 1(1 -> 0)恢复。
go
func runtime_mapassign(typ *abi.SwissMapType, m *Map, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
if m == nil {
panic(errNilAssign)
}
if m.writing != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
m.writing ^= 1
if m.dirPtr == nil {
m.growToSmall(typ)
}
if m.dirLen == 0 {
if m.used < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots {
elem := m.putSlotSmall(typ, hash, key)
if m.writing == 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
m.writing ^= 1
return elem
}
m.growToTable(typ)
}
var slotElem unsafe.Pointer
outer:
for {
idx := m.directoryIndex(hash)
t := m.directoryAt(idx)
seq := makeProbeSeq(h1(hash), t.groups.lengthMask)
var firstDeletedGroup groupReference
var firstDeletedSlot uintptr
for ; ; seq = seq.next() {
g := t.groups.group(typ, seq.offset)
match := g.ctrls().matchH2(h2(hash))
for match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
slotKeyOrig := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
if typ.NeedKeyUpdate() {
typedmemmove(typ.Key, slotKey, key)
}
slotElem = unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(slotKeyOrig) + typ.ElemOff)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
slotElem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem))
}
t.checkInvariants(typ, m)
break outer
}
match = match.removeFirst()
}
match = g.ctrls().matchEmpty()
if match != 0 {
var i uintptr
if firstDeletedGroup.data != nil {
g = firstDeletedGroup
i = firstDeletedSlot
t.growthLeft++
} else {
i = match.first()
}
if t.growthLeft > 0 {
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
slotKeyOrig := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
kmem := newobject(typ.Key)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey) = kmem
slotKey = kmem
}
typedmemmove(typ.Key, slotKey, key)
slotElem = unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(slotKeyOrig) + typ.ElemOff)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
emem := newobject(typ.Elem)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem) = emem
slotElem = emem
}
g.ctrls().set(i, ctrl(h2(hash)))
t.growthLeft--
t.used++
m.used++
t.checkInvariants(typ, m)
break outer
}
t.rehash(typ, m)
continue outer
}
if firstDeletedGroup.data == nil {
match = g.ctrls().matchEmptyOrDeleted()
if match != 0 {
firstDeletedGroup = g
firstDeletedSlot = match.first()
}
}
}
}
if m.writing == 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
m.writing ^= 1
return slotElem
}该方法较长分为几步来进行阐述
step1:
向未初始化 map写入会panic;如果该map此时被其他协程写则fatal 如果此时已初始化且没有其他协程写则计算hash并将writing与1做异或(m.writing ^= 1( 0 -> 1))
go
if m == nil {
panic(errNilAssign)
}
if m.writing != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
m.writing ^= 1 step2:
- 若dirptr为nil此时map还未分配group,调用growToSmall初始化一个group供map使用
- 若dirLen为0则以为着该map为小map,此时有两种情况1:当前小map未填满则进入put流程;2:小map填满了此时将小map扩容,创建一个table供当前map使用
- put 成功返回前再检查:如果 m.writing == 0 则 fatal(说明被其他协程并发写修改);否则再 (m.writing ^= 1( 1 -> 0))再返回。
go
if m.dirPtr == nil {
m.growToSmall(typ)
}
if m.dirLen == 0 {
if m.used < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots {
elem := m.putSlotSmall(typ, hash, key)
if m.writing == 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
m.writing ^= 1
return elem
}
m.growToTable(typ)
}step3: 在前面没有返回说明不是小map,或者小map被填满触发扩容了,进入下面的outer 标签的 for循环
- 先用 hash 计算目录索引拿到 table,再得到 probe 序列和起始 group。
go
var slotElem unsafe.Pointer
outer:
for {
idx := m.directoryIndex(hash)
t := m.directoryAt(idx)
seq := makeProbeSeq(h1(hash), t.groups.lengthMask)
var firstDeletedGroup groupReference //第一个存在删除slot的group
var firstDeletedSlot uintptr //第一个被删除的slot
//..
}step4:
- 进入内层for 按 probe 序列继续探测(与前面读路径相似)。
- 内层for循环里,首先获得起始group然后根据h2(hash)与控制字匹配,得到位图(哪些 slot 的 h2 匹配);(与前面读路径相似)。
- 如果该group有与h2匹配的slot则:首先取得第一个匹配的key,倘若是指向key的指针的则解引用;倘若不存在不进入for match != 0 循环
- 判断与传入的key是否equal:equal则判断是否需要更新key需要的话直接基于typedmemmove将key赋给slotkey,不需要进入取elem(倘若是指向elem的指针的则解引用)并复制给slotElem,直接结束outer循环;
- 若不equal则取下一个与h2匹配的key;直到该group没有与h2匹配的slot
go
//..
for ; ; seq = seq.next() {
g := t.groups.group(typ, seq.offset)
match := g.ctrls().matchH2(h2(hash))
// Look for an existing slot containing this key.
for match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
slotKeyOrig := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
if typ.NeedKeyUpdate() {
typedmemmove(typ.Key, slotKey, key)
}
slotElem = unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(slotKeyOrig) + typ.ElemOff)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
slotElem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem))
}
t.checkInvariants(typ, m)
break outer
}
match = match.removeFirst()
}
//..
}step5:
此时该group没有匹配到key对应的slot
- 取出当前group的空slot,若没有则不进入
- 倘若有空slot(说明探测序列要结束了),首先查看firstDeletedGroup是否为空,不为空说明已经找到第一个删除的slot和对应得Group并将t.growthLeft++,否则取出当前group中第一位空的slot
- 接着判断当前t.growthLeft是否大于0.大于0则说明可直接插入无需扩容,否则说明当前table需要扩容才能继续插入
- 倘若可直接插入取出空slot的地址,如果 key 是间接存储(槽里放指针),首先分配给key内存,把指针写进槽位,接着把传入 key 拷贝到最终 key 存储位置。
- 用槽位原始地址 + 偏移,定位到该槽位的 elem 字段。如果 elem 也间接存储,就分配 elem 内存,把指针写进槽位,并让 slotElem 指向新内存。
- 将控制位写入g的控制字并且将g和t的used++,将t.growthLeft--, 调用checkInvariants,结束outer循环
- 倘若当前插入需要rehash则rehash 后重试outer for循环
go
//..
match = g.ctrls().matchEmpty()
if match != 0 {
var i uintptr
if firstDeletedGroup.data != nil {
g = firstDeletedGroup
i = firstDeletedSlot
t.growthLeft++ // will be decremented below tobecome a no-op.
} else {
// Otherwise, use the empty slot.
i = match.first()
}
if t.growthLeft > 0 {
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
slotKeyOrig := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
kmem := newobject(typ.Key)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey) = kmem
slotKey = kmem
}
typedmemmove(typ.Key, slotKey, key)
slotElem = unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(slotKeyOrig) + typElemOff)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
emem := newobject(typ.Elem)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem) = emem
slotElem = emem
}
g.ctrls().set(i, ctrl(h2(hash)))
t.growthLeft--
t.used++
m.used++
t.checkInvariants(typ, m)
break outer
}
t.rehash(typ, m)
continue outer
}
step6: 此时该group没有配对的key也没有结束探寻
- 如果此时没有找到第一个存在删除的group,则检查当前group是否存在被删除得slot,存在的话则进行赋值,不存在则继续探测序列循环
go
if firstDeletedGroup.data == nil {
match = g.ctrls().matchEmptyOrDeleted()
if match != 0 {
firstDeletedGroup = g
firstDeletedSlot = match.first()
}
}step7: 此时找到可以写入的位置
- 先检查:如果 m.writing == 0 则 fatal(说明被其他协程并发写修改);否则再 (m.writing ^= 1( 1 -> 0))再返回slotElem。
go
if m.writing == 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
m.writing ^= 1
return slotElem写入操作结束,接下来阐述其中用到的关键方法:
Map.growToSmall()
该方法用于小 map 路径下首次为 m 分配存储
- 创建一个包含一个group的groupsReference,将m的dirPtr指向该group的地址,并将控制位全部置为 empty。
go
func (m *Map) growToSmall(typ *abi.SwissMapType) {
grp := newGroups(typ, 1)
m.dirPtr = grp.data
g := groupReference{
data: m.dirPtr,
}
g.ctrls().setEmpty()
}Map.putSlotSmall() 该方法用于向小map写入数据,该方法主要有两个流程
第一步:当前group有与h2匹配的slot
- 首先封装一个group指向当前m的group的地址
- 在当前group得到控制位与h2(hash)匹配的位图
- 如果有匹配的,则首先取得第一个匹配的key,倘若是指向key的指针的则解引用;倘若不存在不进入for match != 0 循环
- 判断与传入的key是否equal:equal则判断是否需要更新key需要的话直接基于typedmemmove将key赋给slotkey,不需要进入取elem(如果elem存放的是指向elem的指针则解引用)并复制给slotElem,返回 slotelem;
- 若不equal则取下一个与h2匹配的key;直到该group没有与h2匹配的slot
第二步:当前group没有与h2匹配的slot
- 如果当前group没匹配的slot则获取为空or已删除的slot位图
- 如果位图为空则fatal(因为在进入该函数前确保了存在位置供插入)
- 否则取第一个slot,如果 key 是间接存储(槽里放指针),首先分配给key内存,把指针写进槽位,接着把传入 key 拷贝到最终 key 存储位置。
- 用槽位原始地址 + 偏移,定位到该槽位的 elem 字段。如果 elem 也间接存储,就分配 elem 内存,把指针写进槽位,并让 slotElem 指向新内存
- 最后将控制位写入h2(hash),m.used++并且返回slotElem
go
func (m *Map) putSlotSmall(typ *abi.SwissMapType, hash uintptr, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
g := groupReference{
data: m.dirPtr,
}
match := g.ctrls().matchH2(h2(hash))
for match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
if typ.NeedKeyUpdate() {
typedmemmove(typ.Key, slotKey, key)
}
slotElem := g.elem(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
slotElem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem))
}
return slotElem
}
match = match.removeFirst()
}
match = g.ctrls().matchEmptyOrDeleted()
if match == 0 {
fatal("small map with no empty slot (concurrent map writes?)")
return nil
}
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectKey() {
kmem := newobject(typ.Key)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey) = kmem
slotKey = kmem
}
typedmemmove(typ.Key, slotKey, key)
slotElem := g.elem(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
emem := newobject(typ.Elem)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem) = emem
slotElem = emem
}
g.ctrls().set(i, ctrl(h2(hash)))
m.used++
return slotElem
}table.checkInvariants() table 的调试自检函数(只在 debugLog=true 时运行),用来验证哈希表内部状态没坏。
map扩容
简述扩容的流程: 小map的扩容:直接创建一个2 * SwissMapGroupSlots的table,将非空旧slot插入新table,加入到m的目录里
大map的扩容: 首先新容量设为旧容量的2倍,如果 新容量不大于maxTableCapacity则根据新容量创建一个table,将非空旧slot插入新table,加入到m的目录里,并将旧table的设为弃用;
如果新容量超限制则将table分为两个容量为maxTableCapacity的table,并将非空旧slot根据hash插入分别两个table,并且根据table的localDepth和m的globalDepth决定对目录的操作最后将table加入到m的目录项;
基于extendible hashing 的增量扩容
- 目录(globalDepth)负责把 key 路由到某个 table。
- 每个 table 有自己的 localDepth。
- 写入冲突时,只扩命中的那一个 table:grow 或 split。
- 如果该 table 的 localDepth == globalDepth,先把目录翻倍,再 split 这个 table。
- 其他 table 不搬迁,后续再按需扩。
小容量map扩容
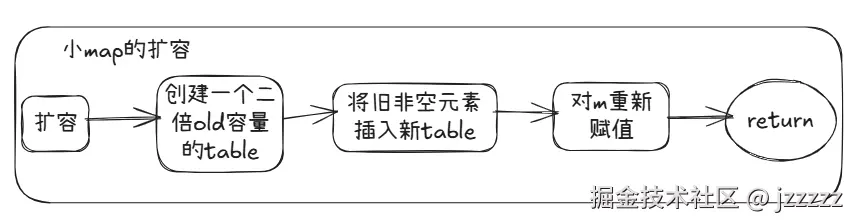
该方法用于小map插入slot时扩容使用,
- 首先创建一个容量为2个group数量槽位的table
- 封装一个group指向当前m的group的地址
- 紧接着开启循环处理group中的slot,如果遇到empty slot则continue,对非空槽位取出 key/elem,重新算 hash 后插入新 table
- 处理完当前m的slot,对m的进行重新赋值,结束,进入大map路径
go
func (m *Map) growToTable(typ *abi.SwissMapType) {
tab := newTable(typ, 2*abi.SwissMapGroupSlots, 0, 0)
g := groupReference{
data: m.dirPtr,
}
for i := uintptr(0); i < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots; i++ {
if (g.ctrls().get(i) & ctrlEmpty) == ctrlEmpty {
continue
}
key := g.key(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
elem := g.elem(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
tab.uncheckedPutSlot(typ, hash, key, elem)
}
directory := make([]*table, 1)
directory[0] = tab
m.dirPtr = unsafe.Pointer(&directory[0])
m.dirLen = len(directory)
m.globalDepth = 0
m.globalShift = depthToShift(m.globalDepth)
}接着看对小map扩容的时候slot是怎么插入到新table的
table.uncheckedPutSlot()
- 如果table的growthLeft为0 违反则直接panic
- 首先也是获取探测序列和起始group,并进入探测迭代
- 在循环里,首先获得group的空或者已经删除的slot的位图(但官方规定该函数要求table中不存在已删除的slot,所以大概率写入empty slot)
- 如果有则取第一个slot,并拿到第 i 槽位的 key 字段地址,typ.IndirectKey() 为真:槽位里存"指针",直接把 key 指针写进去;否则typedmemmove 把 key 内容拷贝进槽位; elem同理
- 写入过后t.growthLeft--,t.used++并将该group的控制位写入当前key的h2(hash)返回
- 如果当前group不存在已删除或者空slot则去下一个探测位置的group
go
func (t *table) uncheckedPutSlot(typ *abi.SwissMapType, hash uintptr, key, elem unsafe.Pointer) {
if t.growthLeft == 0 {
panic("invariant failed: growthLeft is unexpectedly 0")
}
seq := makeProbeSeq(h1(hash), t.groups.lengthMask)
for ; ; seq = seq.next() {
g := t.groups.group(typ, seq.offset)
match := g.ctrls().matchEmptyOrDeleted()
if match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectKey() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey) = key
} else {
typedmemmove(typ.Key, slotKey, key)
}
slotElem := g.elem(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem) = elem
} else {
typedmemmove(typ.Elem, slotElem, elem)
}
t.growthLeft--
t.used++
g.ctrls().set(i, ctrl(h2(hash)))
return
}
}
}大容量map扩容

该方法用于大map插入时扩容
- 将新newCapacity设为老容量的两倍,没超限制的话调用t.grow(typ, m, newCapacity)然后返回
- 超限制则调用t.split(typ, m)
go
func (t *table) rehash(typ *abi.SwissMapType, m *Map) {
newCapacity := 2 * t.capacity
if newCapacity <= maxTableCapacity {
t.grow(typ, m, newCapacity)
return
}
t.split(typ, m)
}首先看新容量没超限制的情况:
- 首先根据新容量创建一个table
- 首先判断t.capacity是否大于0,防止capacity==0(零值/异常状态)时去遍历旧 groups 导致错误。只有当t.capacity大于0才会进入处理旧数据
- 处理旧数据跟小map扩容类似,不过大map时遍历groups,对groups中的每个group的slot进行处理,空slot不管,有数据重新hash的插入新table,具体看小map的解释
- 结束前面操作首先检查table的内部状态,然后将m的table换为新table
- 旧table的index设为-1代表已失效,返回 table.grow()
go
func (t *table) grow(typ *abi.SwissMapType, m *Map, newCapacity uint16) {
newTable := newTable(typ, uint64(newCapacity), t.index, t.localDepth)
if t.capacity > 0 {
for i := uint64(0); i <= t.groups.lengthMask; i++ {
g := t.groups.group(typ, i)
for j := uintptr(0); j < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots; j++ {
if (g.ctrls().get(j) & ctrlEmpty) == ctrlEmpty {
continue
}
key := g.key(typ, j)
if typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
elem := g.elem(typ, j)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
newTable.uncheckedPutSlot(typ, hash, key, elem)
}
}
}
newTable.checkInvariants(typ, m)
m.replaceTable(newTable)
t.index = -1
}table.split() 该方法用于在大map扩容时新容量超出table的限制时将一个table分为两个
- 首先将取出table的localDepth赋值给一个变量,并对该变量++,表示 split 后新表深度 +1
- 然后分别创建left和right两个table,容量时maxTableCapacity,index为-1
- 调用localDepthMask返回一个掩码,用于取哈希值中当前 localDepth 新增出来的那一位(用于 split 时选 left/right)。
- 在处理旧的slot数据时,与直接翻倍容量扩容处理相似,只不过多了一个hash&mask计算落在那一个table,处理结束后调用m.installTableSplit(t, left, right) 把左右表加入目录(必要时先扩目录)。
- 最后将当前table的index设为-1,返回
go
func (t *table) split(typ *abi.SwissMapType, m *Map) {
localDepth := t.localDepth
localDepth++
left := newTable(typ, maxTableCapacity, -1, localDepth)
right := newTable(typ, maxTableCapacity, -1, localDepth)
mask := localDepthMask(localDepth)
for i := uint64(0); i <= t.groups.lengthMask; i++ {
g := t.groups.group(typ, i)
for j := uintptr(0); j < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots; j++ {
if (g.ctrls().get(j) & ctrlEmpty) == ctrlEmpty {
continue
}
key := g.key(typ, j)
if typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
elem := g.elem(typ, j)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
var newTable *table
if hash&mask == 0 {
newTable = left
} else {
newTable = right
}
newTable.uncheckedPutSlot(typ, hash, key, elem)
}
}
m.installTableSplit(t, left, right)
t.index = -1
}Map.installTableSplit() 该方法用于将split后的left和right table加入目录项
- 如果old.localDepth == m.globalDepth,说明当前目录项不够再对table进行细分需要对目录进行翻倍(把所有目录项复制扩展,但不会立刻把其他 table 也一起 split)
- 首先创建一个m.dirLen*2长度的 *table切片,然后将每个table的旧索引 i 扩成新索引 2 * i 和 2 * i+1。t.index 存的是该 table 在目录中的第一个位置。同一个 table 可能在目录里出现多次,所以只在遇到它原来的起始位置(t.index == i)时更新一次为 2 * i,避免重复改错。(确保只更新一次每个 table 的起始索引)
- 并对m的一些参数进行对应的修改
- 调用replaceTable将left和right插入到目录项里,entries表示该 table 需要被多少个目录项共享引用。当 m.globalDepth - left.localDepth == 1 时,entries=2,所以 replaceTable 会把 left(或 right)写入连续 2 个目录项。
- 此时right的目录项紧挨着left的目录项
go
func (m *Map) installTableSplit(old, left, right *table) {
if old.localDepth == m.globalDepth {
newDir := make([]*table, m.dirLen*2)
for i := range m.dirLen {
t := m.directoryAt(uintptr(i))
newDir[2*i] = t
newDir[2*i+1] = t
if t.index == i {
t.index = 2 * i
}
}
m.globalDepth++
m.globalShift--
m.dirPtr = unsafe.Pointer(&newDir[0])
m.dirLen = len(newDir)
}
left.index = old.index
m.replaceTable(left)
entries := 1 << (m.globalDepth - left.localDepth)
right.index = left.index + entries
m.replaceTable(right)
}Map.replaceTable() 用来实现同一个 table 被多个目录项共享引用
go
func (m *Map) replaceTable(nt *table) {
// The number of entries that reference the same table doubles for each
// time the globalDepth grows without the table splitting.
entries := 1 << (m.globalDepth - nt.localDepth)
for i := 0; i < entries; i++ {
//m.directory[nt.index+i] = nt
m.directorySet(uintptr(nt.index+i), nt)
}
}从map中删除数据
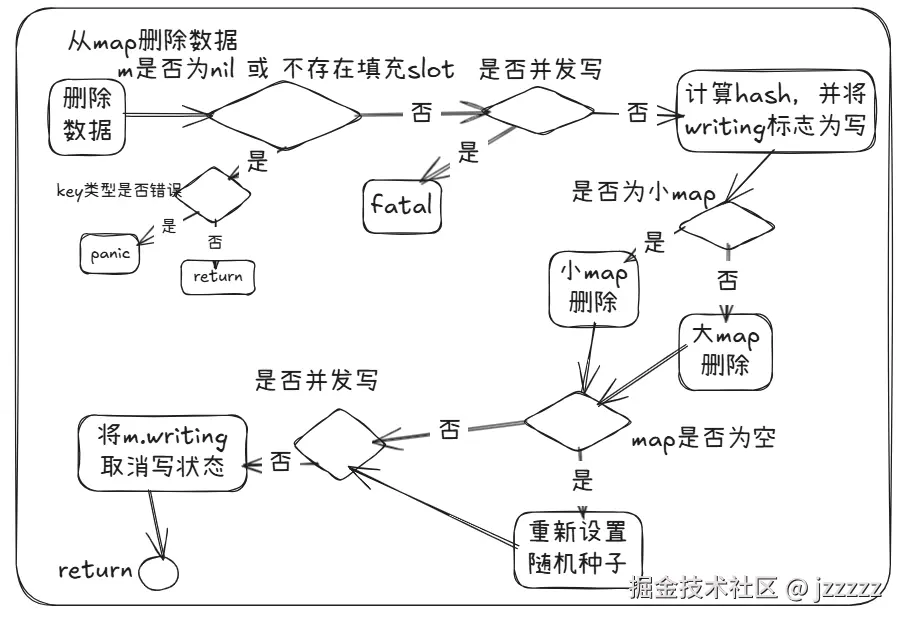
- 如果map为nil,或者map中无已填充的数据,首先对key的合法性进行判断,如果key不合法则直接panic,否则返回;
- 判断是否有其他协程再写map,有的话fatal
- 如没有其他协程写且map不为空则先计算key的hash,并将 m.writing ^= 1
- 接着进入删除操作,小map和大map执行不同操作
- 删除结束,如果 m.used == 0,说明 map 已经空了。重新设置 m.seed = uintptr(rand()),并判断是否有其他协程在过程中进行并发写,有的话fatal,否则m.writing ^= 1返回 Map.Delete()
go
func (m *Map) Delete(typ *abi.SwissMapType, key unsafe.Pointer) {
if m == nil || m.Used() == 0 {
if err := mapKeyError(typ, key); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return
}
if m.writing != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
hash := typ.Hasher(key, m.seed)
m.writing ^= 1
if m.dirLen == 0 {
m.deleteSmall(typ, hash, key)
} else {
idx := m.directoryIndex(hash)
m.directoryAt(idx).Delete(typ, m, hash, key)
}
if m.used == 0 {
m.seed = uintptr(rand())
}
if m.writing == 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
m.writing ^= 1
}接着看小map删除的具体实现 Map.deleteSmall()
- 首先封装一个group指向m.dirPtr(即存放slot的地址)
- 得到group中与h2(hash)匹配的slot的位图,如果没有直接结束deleteSmall()
- 首先取出第一个与h2匹配的slot的slotKey,并赋值变量方便清除elem,如果slotkey存放的是指向 key 的指针则解引用
- 接着判断Equal(key, slotKey),不相等的话则继续取下一个匹配的slot
- 匹配的话进入清除数据,首先将m.used--,然后判断key是否是存放的是指向 key 的指针,是的话清空指针,切断对key的引用;typ.Key.Pointers() 为真说明 key 本身包含指针字段。这时用 typedmemclr 按类型清零,把 key 里的指针字段清掉,防止残留引用。上述两步都是为了方便gc回收
- 对elem判断elem是否是存放的是指向 elem的指针,是的话清空指针,切断对elem的引用,否则直接按类型清空,返回
go
func (m *Map) deleteSmall(typ *abi.SwissMapType, hash uintptr, key unsafe.Pointer) {
g := groupReference{
data: m.dirPtr,
}
match := g.ctrls().matchH2(h2(hash))
for match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
origSlotKey := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
m.used--
if typ.IndirectKey() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(origSlotKey) = nil
} else if typ.Key.Pointers() {
typedmemclr(typ.Key, slotKey)
}
slotElem := g.elem(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem) = nil
} else {
typedmemclr(typ.Elem, slotElem)
}
g.ctrls().set(i, ctrlEmpty)
return
}
match = match.removeFirst()
}
}最后看大map删除的具体实现
- 首先取探测序列和起始group位置,进入探测循环
- 取起始group,首先得到group中与h2(hash)匹配的slot的位图,如果matchH2 为空后,再看 是否存在空 slot;如果有空 slot,探测序列到此结束直接返回;如果没有空 slot,继续下一个 group。
- 下面主要流程与小map一样,主要说在group查找与小map不一样的地方
- 大 map 删除时会 t.used-- 和 m.used--;如果该 group 里已有空 slot,删除位会被设为 ctrlEmpty,并且 t.growthLeft++;否则设为 ctrlDeleted。
- 并且table会有多个group,第一个group没探测到会探测下一个直到结束 table.Delete()
go
func (t *table) Delete(typ *abi.SwissMapType, m *Map, hash uintptr, key unsafe.Pointer) {
seq := makeProbeSeq(h1(hash), t.groups.lengthMask)
for ; ; seq = seq.next() {
g := t.groups.group(typ, seq.offset)
match := g.ctrls().matchH2(h2(hash))
for match != 0 {
i := match.first()
slotKey := g.key(typ, i)
origSlotKey := slotKey
if typ.IndirectKey() {
slotKey = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(slotKey))
}
if typ.Key.Equal(key, slotKey) {
t.used--
m.used--
if typ.IndirectKey() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(origSlotKey) = nil
} else if typ.Key.Pointers() {
typedmemclr(typ.Key, slotKey)
}
slotElem := g.elem(typ, i)
if typ.IndirectElem() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(slotElem) = nil
} else {
typedmemclr(typ.Elem, slotElem)
}
if g.ctrls().matchEmpty() != 0 {
g.ctrls().set(i, ctrlEmpty)
t.growthLeft++
} else {
g.ctrls().set(i, ctrlDeleted)
}
t.checkInvariants(typ, m)
return
}
match = match.removeFirst()
}
match = g.ctrls().matchEmpty()
if match != 0 {
return
}
}
}迭代器
map保证在遍历过程中同一 goroutine 下可改;并发写会触发 fatal对表进行修改,但不保证这些修改会在遍历中可见。 下面首先看迭代器的数据结构;
迭代器数据结构
go
type Iter struct {
key unsafe.Pointer
elem unsafe.Pointer
typ *abi.SwissMapType
m *Map
entryOffset uint64
dirOffset uint64
clearSeq uint64
globalDepth uint8
dirIdx int
tab *table
group groupReference
entryIdx uint64
}- key 槽位对应的key
- elem 槽位对应的elem
- entryOffset 一个随机 slot 偏移开始遍历来打乱遍历顺序
- dirOffset 目录的偏移量使用一个独立的 offset,因为目录增长时需要调整
- clearSeq 用于检测遍历期间是否发生了 Clear
- globalDepth 上一次调用 Next 时 Map.globalDepth 的值,用于检测遍历期间目录是否增长
- dirIdx 当前目录索引,尚未应用 dirOffset 的调整。
- tab 上一次调用 Next 时 dirIdx 对应的 table。
- group 上一次调用 Next 时 entryIdx 对应的 group。
- entryIdx 是当前 entry 的索引,尚未应用 entryOffset 的调整。index 的低 3 位是 slot 索引,高位是 group 索引。
迭代的主流程如下
go
func mapIterStart(t *abi.SwissMapType, m *maps.Map, it *maps.Iter) {
it.Init(t, m)
it.Next()
}在map遍历时首先初始化一个迭代器
- 当map为nil,或者为空时直接结束
- 如果map时小map时,将dirIdx设为-1,并将group设为map的dirPtr存放的数据
- 然后利用rand()分别设置entryOffset和dirOffset偏移和以及初始化其它参数 Iter.Init()
go
func (it *Iter) Init(typ *abi.SwissMapType, m *Map) {
it.typ = typ
if m == nil || m.used == 0 {
return
}
dirIdx := 0
var groupSmall groupReference
if m.dirLen <= 0 {
// Use dirIdx == -1 as sentinel for small maps.
dirIdx = -1
groupSmall.data = m.dirPtr
}
it.m = m
it.entryOffset = rand()
it.dirOffset = rand()
it.globalDepth = m.globalDepth
it.dirIdx = dirIdx
it.group = groupSmall
it.clearSeq = m.clearSeq
}初始化迭代器结束后进入迭代函数 该方法较长拆分解释: 首先看错误情况
- 首先看m是否为nil,如果为nil则将迭代器的key和elem都设为nil,返回
- 如果在迭代过程有其他的协程在写map,则直接fatal返回
go
func (it *Iter) Next() {
if it.m == nil {
it.key = nil
it.elem = nil
return
}
if it.m.writing != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map iteration and map write")
return
}
//小map的迭代对应step1
if it.dirIdx < 0 {
// Map was small at Init.
for ; it.entryIdx < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots; it.entryIdx++ {
k := uintptr(it.entryIdx+it.entryOffset) % abi.SwissMapGroupSlots
if (it.group.ctrls().get(k) & ctrlEmpty) == ctrlEmpty {
continue
}
key := it.group.key(it.typ, k)
if it.typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
grown := it.m.dirLen > 0
var elem unsafe.Pointer
if grown {
var ok bool
newKey, newElem, ok := it.m.getWithKey(it.typ, key)
if !ok {
if it.clearSeq == it.m.clearSeq && !it.typ.Key.Equal(key, key) {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, k)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
} else {
continue
}
} else {
key = newKey
elem = newElem
}
} else {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, k)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
}
it.entryIdx++
it.key = key
it.elem = elem
return
}
it.key = nil
it.elem = nil
return
}
//大map在迭代期间扩容对应step2
if it.globalDepth != it.m.globalDepth {
orders := it.m.globalDepth - it.globalDepth
it.dirIdx <<= orders
it.dirOffset <<= orders
it.globalDepth = it.m.globalDepth
}
//大map的迭代对应step3
for ; it.dirIdx < it.m.dirLen; it.nextDirIdx() {
if it.tab == nil {
dirIdx := int((uint64(it.dirIdx) + it.dirOffset) & uint64(it.m.dirLen-1))
newTab := it.m.directoryAt(uintptr(dirIdx))
if newTab.index != dirIdx {
diff := dirIdx - newTab.index
it.dirOffset -= uint64(diff)
dirIdx = newTab.index
}
it.tab = newTab
}
entryMask := uint64(it.tab.capacity) - 1
if it.entryIdx > entryMask {
continue
}
entryIdx := (it.entryIdx + it.entryOffset) & entryMask
slotIdx := uintptr(entryIdx & (abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - 1))
if slotIdx == 0 || it.group.data == nil {
groupIdx := entryIdx >> abi.SwissMapGroupSlotsBits
it.group = it.tab.groups.group(it.typ, groupIdx)
}
if (it.group.ctrls().get(slotIdx) & ctrlEmpty) == 0 {
key := it.group.key(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
grown := it.tab.index == -1
var elem unsafe.Pointer
if grown {
newKey, newElem, ok := it.grownKeyElem(key, slotIdx)
if !ok {
goto next
} else {
key = newKey
elem = newElem
}
} else {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
}
it.entryIdx++
it.key = key
it.elem = elem
return
}
next:
it.entryIdx++
var groupMatch bitset
for it.entryIdx <= entryMask {
entryIdx := (it.entryIdx + it.entryOffset) & entryMask
slotIdx := uintptr(entryIdx & (abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - 1))
if slotIdx == 0 || it.group.data == nil {
groupIdx := entryIdx >> abi.SwissMapGroupSlotsBits
it.group = it.tab.groups.group(it.typ, groupIdx)
}
if groupMatch == 0 {
groupMatch = it.group.ctrls().matchFull()
if slotIdx != 0 {
groupMatch = groupMatch.removeBelow(slotIdx)
}
if groupMatch == 0 {
it.entryIdx += abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - uint64(slotIdx)
continue
}
i := groupMatch.first()
it.entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
if it.entryIdx > entryMask {
continue
}
entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
slotIdx = i
}
key := it.group.key(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
grown := it.tab.index == -1
var elem unsafe.Pointer
if grown {
newKey, newElem, ok := it.grownKeyElem(key, slotIdx)
if !ok {
groupMatch = groupMatch.removeFirst()
if groupMatch == 0 {
it.entryIdx += abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - uint64(slotIdx)
continue
}
i := groupMatch.first()
it.entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
continue
} else {
key = newKey
elem = newElem
}
} else {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
}
groupMatch = groupMatch.removeFirst()
if groupMatch == 0 {
it.entryIdx += abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - uint64(slotIdx)
} else {
i := groupMatch.first()
it.entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
}
it.key = key
it.elem = elem
return
}
}
it.key = nil
it.elem = nil
return
}step1: 小map的迭代处理逻辑: 这段代码块逻辑也比较复杂拆开来讲 首先可以肯定的是it.dirIdx < 0只有小map才会出现,并且此时entryIdx是为0 首先是获得迭代器取到的slot的key的逻辑
- 使用entryIdx结合entryOffset 随机取到一个index,如果对应slot为空或者被删除则进行下一轮循环
- 否则取出index对应的key,如果slotkey存放的是指向key地址的指针则解引用
go
if it.dirIdx < 0 {
for ; it.entryIdx < abi.SwissMapGroupSlots; it.entryIdx++ {
k := uintptr(it.entryIdx+it.entryOffset) % abi.SwissMapGroupSlots
if (it.group.ctrls().get(k) & ctrlEmpty) == ctrlEmpty {
continue
}
key := it.group.key(it.typ, k)
if it.typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}然后是取slot key对应的slot elem的逻辑
- grown == false 时直接从旧 group 取 elem(必要时解引用);grown == true 时必须 getWithKey 去新表取 newKey/newElem。
- getWithKey 失败时的处理是:若 clearSeq 变了(发生 Clear)直接 continue;若 没 Clear 且 key != key(NaN 情况)才回退用旧 group 的 elem;否则 continue。
- key != key 不仅限于纯 float key,结构体/数组里含 NaN 也会触发。
- 返回时会把 it.elem 和 it.key 设置好,并 entryIdx++。
- 循环结束直接将it.elem 和 it.key 设置 nil,并返回
go
grown := it.m.dirLen > 0
var elem unsafe.Pointer
if grown {
var ok bool
newKey, newElem, ok := it.m.getWithKey(it.typ, key)
if !ok {
if it.clearSeq == it.m.clearSeq && !it.typ.Key.Equal(key, key) {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, k)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
} else {
continue
}
} else {
key = newKey
elem = newElem
}
} else {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, k)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
}
it.entryIdx++
it.key = key
it.elem = elem
return
}
it.key = nil
it.elem = nil
return
}step2: 在迭代大map之前 it.globalDepth != it.m.globalDepth (说明map在迭代时扩容目录)
- 则将目录项和目录偏移按位数差左移,适配目录扩容后的索引空间。
- 将迭代器的globalDepth更新为新的globalDepth
go
if it.globalDepth != it.m.globalDepth {
orders := it.m.globalDepth - it.globalDepth
it.dirIdx <<= orders
it.dirOffset <<= orders
it.globalDepth = it.m.globalDepth
}step3: 大map的迭代
此代码块也较多拆解分析:首先开启一个for循环,迭代的时候使用nextDirIdx()跳过整个重复区间会按该 table 在目录中出现的次数来跳转
- 如果it.tab为空则说明第一次迭代,首先根据dirIdx和dirOffset计算出table的index,然后得到对应table
- 如果table的index(在map的首个记录项)与dirIdx不同说明没有落在该table的起始目录项
- 则把 dirIdx 调回到该 table 的首个索引,并同步回退 dirOffset,保证后续迭代不会重复或错位。并将取出的table赋值给迭代器
go
for ; it.dirIdx < it.m.dirLen; it.nextDirIdx() {
if it.tab == nil {
dirIdx := int((uint64(it.dirIdx) + it.dirOffset) & uint64(it.m.dirLen-1))
newTab := it.m.directoryAt(uintptr(dirIdx))
if newTab.index != dirIdx {
diff := dirIdx - newTab.index
it.dirOffset -= uint64(diff)
dirIdx = newTab.index
}
it.tab = newTab
}如果entryidx已经超过该表的最大 entry 索引,就结束这张表,转到下一张表。
go
entryMask := uint64(it.tab.capacity) - 1
if it.entryIdx > entryMask {
continue
}接着看快速处理路径
- 首先根据it.entryIdx和entryOffset计算entryIdx(低三位用于slot,高位用于group)
- 然后根据entryIdx计算slotidx,在开始遍历这张表的第一次迭代时,需要计算一次group,slotidx从末尾绕到首位时说明开启下一组也需要计算一次group,计算group使用到了entryIdx
- 获得group后,对slotIdx的控制位进行判别是否为存在值的,如果不是则进入慢路径
- 如果存在值则进入if执行,首先根据slotIdx在group取出slotkey(如果是指向key指针解引用)
- 接着判断table是否触发扩容,倘若触发扩容去新表根据slotIdx取出newKey, newElem,如果取到赋值给key和elem,没取到则进入慢路径
- 若没扩容则直接去group取elem(如果是指向elem指针解引用)
- 最后给迭代器更新值,返回
go
entryIdx := (it.entryIdx + it.entryOffset) & entryMask
slotIdx := uintptr(entryIdx & (abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - 1))
if slotIdx == 0 || it.group.data == nil {
groupIdx := entryIdx >> abi.SwissMapGroupSlotsBits
it.group = it.tab.groups.group(it.typ, groupIdx)
}
if (it.group.ctrls().get(slotIdx) & ctrlEmpty) == 0 {
key := it.group.key(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
grown := it.tab.index == -1
var elem unsafe.Pointer
if grown {
newKey, newElem, ok := it.grownKeyElem(key, slotIdx)
if !ok {
goto next
} else {
key = newKey
elem = newElem
}
} else {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
}
it.entryIdx++
it.key = key
it.elem = elem
return
}接着我们来看慢路径是怎么处理
- 将entryIdx++(因为在前面流程中entryIdx游标没有取到值)
- 如果it.entryidx已经超过该表的最大 entry 索引,就结束这张表,转到下一张表。
- 否则进入匹配首先根据it.entryIdx和entryOffset计算entryIdx(低三位用于slot,高位用于group)
- 然后根据entryIdx计算slotidx,在开始遍历这张表的第一次迭代时,需要计算一次group,slotidx从末尾绕到首位时说明开启下一组也需要计算一次group,计算group使用到了entryIdx
go
next:
it.entryIdx++
var groupMatch bitset
for it.entryIdx <= entryMask {
entryIdx := (it.entryIdx + it.entryOffset) & entryMask
slotIdx := uintptr(entryIdx & (abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - 1))
if slotIdx == 0 || it.group.data == nil {
groupIdx := entryIdx >> abi.SwissMapGroupSlotsBits
it.group = it.tab.groups.group(it.typ, groupIdx)
}
//..
- 对group寻找不为空的slot的位图(当第一次进入迭代时)
- 如果slotidx不为0则清除匹配得到位图的低位,只留下 slot i 及之后的位。
- 如果位图为0(无可用的slot),则跳过该group剩余槽位,转到下一轮循环
- 找到第一个可用slot,把线性游标前进到这个位置
- 如果游标超过表尾,下一轮处理回绕。
- 同步更新带 offset 的实际索引。以及更新slotIdx,后续就用去取 key/elem。
go
if groupMatch == 0 {
groupMatch = it.group.ctrls().matchFull()
if slotIdx != 0 {
groupMatch = groupMatch.removeBelow(slotIdx)
}
if groupMatch == 0 {
it.entryIdx += abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - uint64(slotIdx)
continue
}
i := groupMatch.first()
it.entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
if it.entryIdx > entryMask {
continue
}
entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
slotIdx = i
}- 根据slotidx取到slotkey(如果是指向key的指针则解引用)
- 接着判断当前表在迭代时是否发生扩容,即(t.tab.index == -1(发生扩容时会将table的index设为-1)),没扩容的话直接在迭代器的group中取elem(如果是指向elem指针解引用)
- 扩容的话,去新table查询,查到则直接赋值
- 新table没查到的话,将位图第一个匹配的slot移除,接着判断位图是否还有值,没值的话将跳过该group剩余槽位,转到下一轮循;
- 如果位图还有值则接着取和更新游标
- 在前面取完值以后执行和新table没查到情况相同判断,不过此时已经去到值可以给elem和key赋值返回
go
key := it.group.key(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectKey() {
key = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(key))
}
grown := it.tab.index == -1
var elem unsafe.Pointer
if grown {
newKey, newElem, ok := it.grownKeyElem(key, slotIdx)
if !ok {
groupMatch = groupMatch.removeFirst()
if groupMatch == 0 {
it.entryIdx += abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - uint64(slotIdx)
continue
}
i := groupMatch.first()
it.entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
continue
} else {
key = newKey
elem = newElem
}
} else {
elem = it.group.elem(it.typ, slotIdx)
if it.typ.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
}
groupMatch = groupMatch.removeFirst()
if groupMatch == 0 {
it.entryIdx += abi.SwissMapGroupSlots - uint64(slotIdx)
} else {
i := groupMatch.first()
it.entryIdx += uint64(i - slotIdx)
}
it.key = key
it.elem = elem
return
}如果大map没取到值则返回nil,小map没取到值得情况在前面已经提前终止
go
it.key = nil
it.elem = nil
return
}go 新存储方式map的解读到此结束,谢谢阅读!