文档知识来源:抖音 "哲玄前端",《大前端全栈实践课》
重点分享 DSL 的设计 ,以及 DSL 如何分版块映射到整个站点的。
DSL设计的由来/现状
随着业务发展,我们面临以下问题:
- 重复开发严重:多个系统 80% 的代码都是相似的(CRUD、用户管理、权限控制等)
- 维护成本高:相同逻辑在不同系统中重复实现,修改时需要多处同步
- 开发效率低:开发人员花大量时间在重复的 CV 操作上
- 代码质量不一:不同开发者实现相同功能时风格、质量参差不齐
- 新人上手慢:每个系统都有不同的代码结构和约定
为了解决这些问题,我们设计了一套 DSL(Domain Specific Language)模板配置系统,让开发人员通过声明式配置自动生成代码,避免重复的 CV 操作。
DSL 设计
DSL(Domain Specific Language)模板引擎通常指的是一种用于生成动态内容的工具,它允许开发人员通过一种特定于领域的语言来描述模板,而模板引擎会在服务器端根据数据生成最终的HTML或其他输出格式。
在服务端调用的上下文中,DSL模板引擎是指服务器端利用模板引擎渲染动态内容,并返回给客户端。它不是直接在客户端运行的脚本,而是服务端通过传递数据到模板引擎,利用模板文件生成最终结果。
例如:
- 服务器端渲染:在服务端使用DSL模板引擎(如Jinja2、Thymeleaf等)处理数据,将数据填充到模板中,然后生成最终的HTML内容,并将其发送给客户端浏览器。
- 客户端渲染:虽然一些模板引擎(如Handlebars、Mustache等)也可以在客户端运行,但它们本质上是为了在服务端准备好模板和数据后进行渲染,因此DSL模板引擎通常还是在服务端调用为主。
总结来说,DSL模板引擎的典型用法是服务端调用,它帮助处理数据并将渲染结果返回给客户端。
根据DSL模版配置 + 配置解析 + 预留好的各种各样的组件 ----> 生成各种各样的系统
(1) DSL模版配置
js
export default {
mode: 'dashboard', //模版类型,不同模板类型对应不一样的模版数据结构
name: '',// 名称
desc: '', // 描述
icon: '', // 首页(项目配置)
// 头部菜单 header-container
menu: [
{
key: '', //菜单唯一描述
name: '', // 菜单名称
/**
* header-container 里面可能会出现 菜单1 菜单2 菜单组件1 菜单组件2
* meuType设置为两种类型: group 、 module(对应一个板块)
*/
menuType: '', // 枚举值, group / module
// 当 meuType == group 时,可填
subMenu: [{
// 可递归 menuItem 这里递归出来的就是header-container的每一个头部菜单
// ... 表示可以出现多个{}这里面的内容
},
// 更多菜单项...
],
/**
* 点击header-container 中的某一个菜单,可能出现 sider-container/schema-view/iframe-view/custom-view
* schema-view 80%的内容,都已schema沉淀,最终根据配置渲染出页面;
* iframe-view 第三方组件;
* custom-view 自定义页面;
* sider-container 左侧菜单;
* --- 左侧菜单 :里面可能会出现 菜单1 菜单2 菜单组件1 菜单组件2
*/
// 当 meuType == module 时,可填
moduleType: '', // 枚举值: sider/iframe/custom/schema
// 当 moduleType == sider 时,(侧边栏)
siderConfig: {
menu: [{
//可递归 menuItem (除了 moduleType == sider),这里递归出来的就是sider-container的每一个侧边菜单
},
// 更多菜单项...
]
},
// 当 moduleType == iframe 时,
iframeConfig: {
path: '', // iframe的路径
},
// 当 moduleType == custom 时,
customConfig: {
path: '', // 自定义路由路径
},
// 当 moduleType == schema 时,
schemaConfig: {
/**
* DSL(dashboader模版配置)---> schema config ---> 解析器 ---> schema-view
* schema-view 里面有 1.schema-search-bar , select 或者 date-range 或者 其他组件
* 2.其他组件
* 3.schema-table
* 4.schema-table-row , <button>[点击按钮,弹出 schema-form [有 input , select, radio, 其他组件]],其他组件[ 有 其他组件 等]
* 往往重复性的内容,来源于同一份数据,(;可以是同一个api接口返回的数据,也可以是同一份数据库的数据等)
*
*/
api: '/api/user', // 数据源api (遵循 RESTFUL 规范)
schema: { // 板块数据接口
type: 'object',
properties: {
key: {
...schema, // 标准 schema 配置
type: '', // 字段类型
label: '', // 字段的中文名
// 字段在 table 中的相关配置
tableOption: {
...elTableColumnConfig, // 标准 el-tabel-colum 配置
toFixed:0,// 保留小数点后几位
visiable: true, // 是否在表单中展示,默认为true(false,表示不在表单中显示)
},
// 字段在 search-bar 中的相关配置 (搜索框)
searchOption:{
...eleComponentConfjg,// 标准 el-component-colum 配置
comType:'', //配置组件类型 input/select/....
default:'',// 默认值
// comType === 'select'
enumList:[], //下拉框可选项
// comType === 'dynamicSelect'
api:''
},
// 字段在不同动态 component 中的相关配置,前缀对应 componentConfig 中的键值
// 如: componentConfig.creatForm, 这里对应 createFormOption
// 字段在 createFrom 中相关配置
createFormOption:{
...eleComponentConfjg,// 标准 el-component-colum 配置
comType:'',// 控件类型,input/select/input-number
visiable:true,// 是否展示(true/false),默认为 true
disable:false, //是否禁用(true/false),默认为 false
default:'', //默认值
// comType === 'select'
enumList:[], //下拉框可选项
}
// 还可以配置其他的 option
// formOption:{}
},
// 更多菜单项...
}
},
// tabel 配置,表单描述
tableConfig: {
headerButtons:[
{
label:'', // 按钮中文名
eventKey:'', // 按钮事件名
eventOption:{
// 当 eventKey === 'showComponrnt'
comName:'', // 组件名称
}, // 按钮事件具体配置 (点击按钮事件的配置)
...elButtonConfig, //标准 el-button 配置
},
// 更多选项...
], //某一行,某一列会有按钮
rowButtons:[
{
label:'', //按钮中文名
eventKey:'', //按钮事件名
eventOption: {
// 当 eventKey === 'showComponrnt'
comName:'', // 组件名称
// 当 eventKey === ' remove '
params:{
// paramKey = 参数的键值
// rowValue = 参数值 (格式为 schema::tableKey,到 table 中找相应的字段)
paramKey: rowValueKey
}
}, // 按钮事件具体配置
...elButtonConfig, // 标准 el-button 配置
},
// 更多选项...
], //每一行,某一列会有按钮
},
// search-bar 相关配置
searchConfig: {},
// 动态组件
componentConfig: {
// 有多种不同的配置
// comA:{},
// comB:{},
// crate-form 表单相关配置
createForm:{
title:'', // 表单标题
saveBtnText:'', // 保存按钮文案
}
// ...支持用户动态扩展
},
},
}
// 更多菜单项...
]
}(2) 实现 解析引擎
app/pages/dashboard/complex-view/schema-view/hook/schema.js 解析模版信息
js
import { ref, watch, onMounted,nextTick} from 'vue';
import { useRoute } from 'vue-router';
import { useMenuStore } from '$elipsStore/menu.js';
export const useSchema = function(){
const route = useRoute();
const menuStore = useMenuStore();
const api = ref('');
const tableSchema = ref({});
const tableConfig = ref();
const searchSchema = ref({});
const searchConfig = ref();
const components = ref({});
// 构造 schemaConfig 相关配置,输送给 schemaView 解释;
const buildData = function(){
const {key, sider_key: siderKey} = route.query;
const mItem = menuStore.findMenuItem({
key:'key',
value: siderKey ?? key
});
if(mItem && mItem.schemaConfig){
const { schemaConfig:sConfig } = mItem;
// 这里复制出一份拿到的sConfig.schema,目的是为了不污染原来拿到的这个数据源,因为所拿到的,可能会进行改变
const configSchema = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(sConfig.schema));
api.value = sConfig.api ?? '';
tableSchema.value = {};
tableConfig.value = undefined;
searchSchema.value = {};
searchConfig.value = undefined;
components.value = {};
nextTick(() =>{
/**
* tableSchema.value = configSchema;
* 为何 封装一个buildDtoSchema方法:
* 因为拿到的sConfig,可能会有很多种option的配置选项,那么如果都拿出来的话,会有许多没有用处,导致浪费;
* 最终的结果就是,每一个代码 都是单一的
*/
// 处理构造 tableSchema 和 tableConfig
tableSchema.value = buildDtoSchema(configSchema,'table');
tableConfig.value = sConfig.tableConfig;
// 处理构造 searchSchema 和 searchConfig
const dtoSearchSchema = buildDtoSchema(configSchema,'search');
for(const key in dtoSearchSchema.properties){
// 如果是从其他页面跳转过来的,某些搜索项 需要有参数
if(route.query[key] !== undefined){
dtoSearchSchema.properties[key].option.default = route.query[key];
}
}
searchSchema.value = dtoSearchSchema;
searchConfig.value = sConfig.searchConfig;
//构造 components = { conKey: {schema, config} }
const { componentConfig } = sConfig;
if(componentConfig && Object.keys(componentConfig).length>0){
const dtoComponents = {};
for(const comName in componentConfig){
dtoComponents[comName] = {
schema:buildDtoSchema(configSchema,comName),
config:componentConfig[comName]
}
}
components.value = dtoComponents;
}
});
}
}
// 通用构建 schema 方法
const buildDtoSchema = ((_schema, comName) =>{
if(!_schema?.properties){ return };
const dtoShema = {
type: 'object',
properties: {}
}
// 提取有效 schema 字段信息
for(const key in _schema.properties){
const props = _schema.properties[key];
// tableOption schemaBarOption formOption
if(props[`${comName}Option`]){
let dtoPros = {};
// 提取 props 中非 Option 的部分,存放到 dtoProps 中
for(const pKey in props){
if(pKey.indexOf('Option') <0){
dtoPros[pKey] = props[pKey];
}
}
// 处理 comName Option
dtoPros = Object.assign({}, dtoPros, { option: props[`${comName}Option`]});
// 处理 required 字段
const { required } = _schema;
if(required && required.find(pk => pk === key)){
dtoPros.option.required = true;
}
dtoShema.properties[key] = dtoPros;
}
}
return dtoShema;
})
watch([
// 监听 用户点击菜单, key / sider_key 意味着用户点击了不同的菜单; menuList 刷新页面
() => route.query.key,
() => route.query.sider_key,
() => menuStore.menuList
],()=>{
buildData();
},{ deep: true})
onMounted(()=>{
buildData();
})
return {
api,
tableSchema,
tableConfig,
searchSchema,
searchConfig,
components
};
}(3)预留好的各种各样的组件
这一部分指,在不同的系统中,放置不同的定制组件(20%);
每个不同的系统都会出现不一样的需求内容,那么我们需要在有80%重复内容的基础上,也支持20%的定制化内容;
代码实现
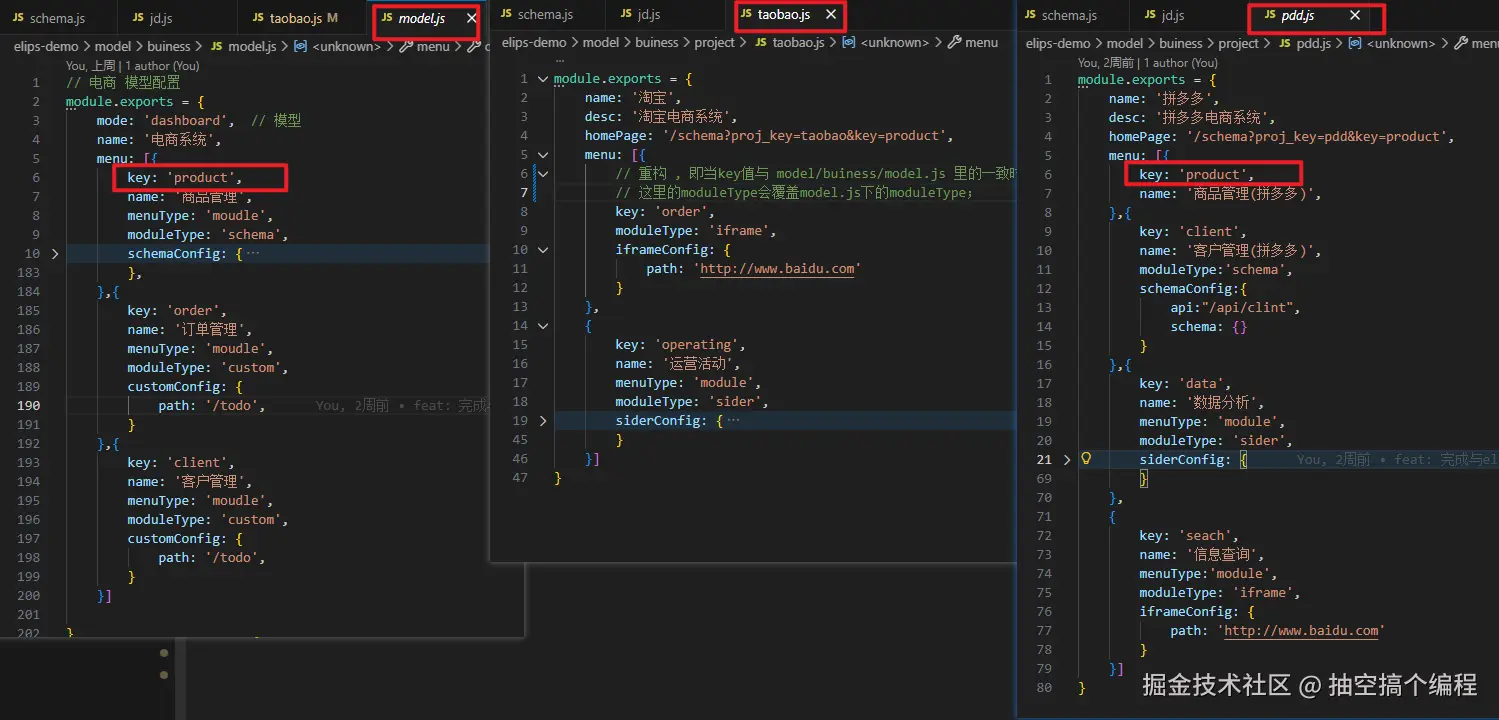
model.js 配置的是公共能力;
pdd.js , tb.js 配置的是自己定制化的能力;
如果在自己的系统和公共能力冲突时,会以本身系统的能力为主;
最终呈现效果
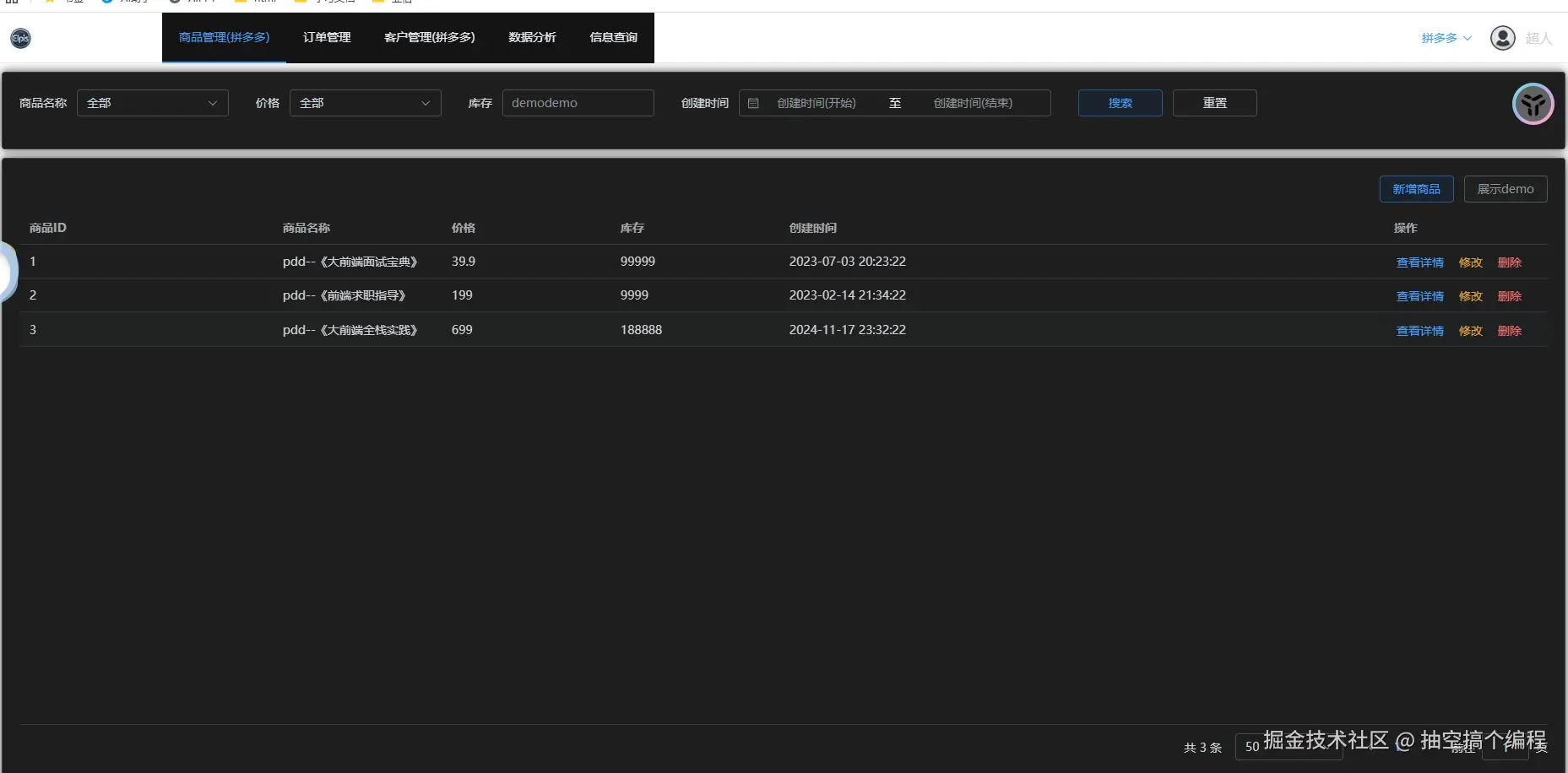
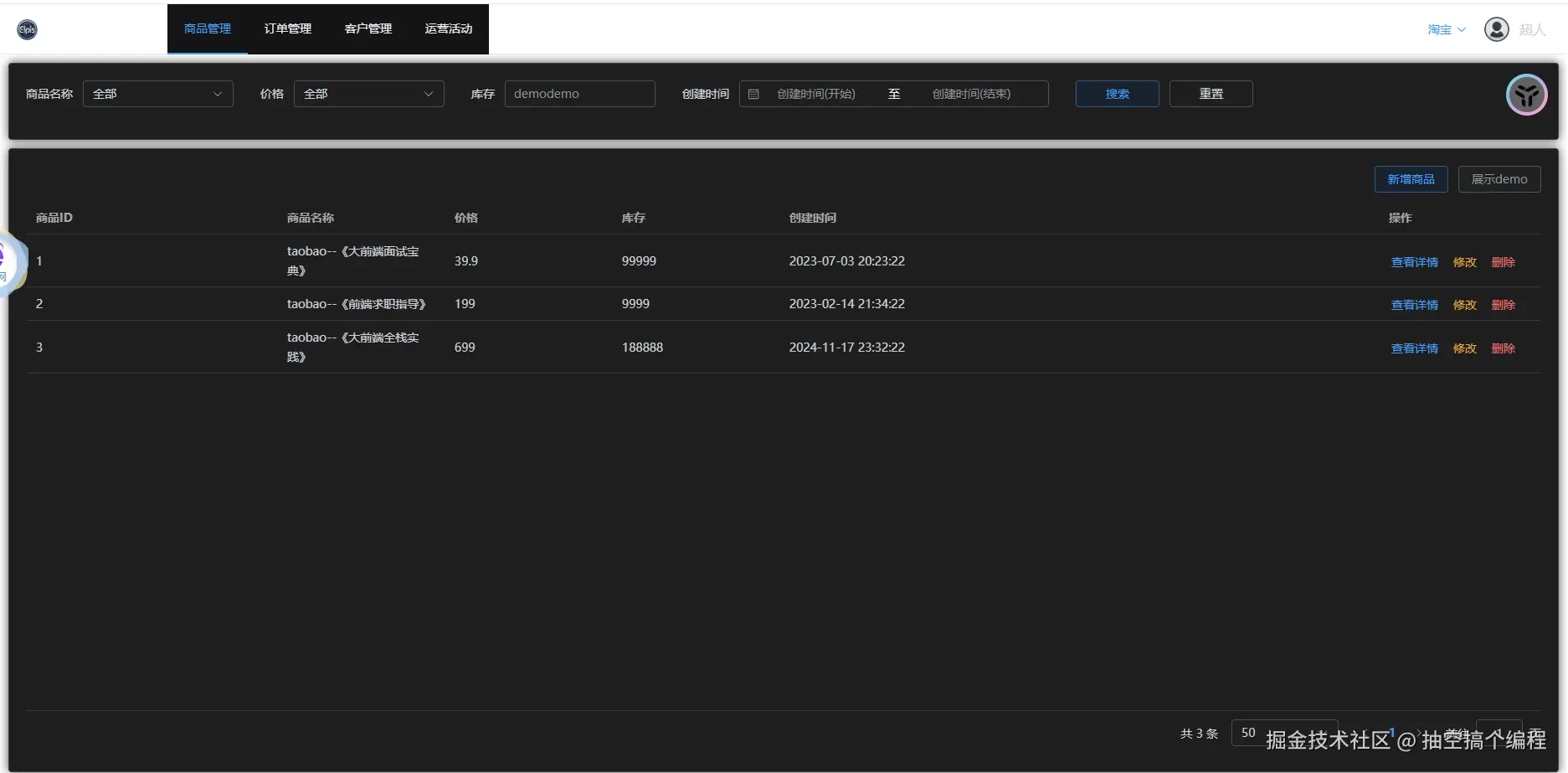
看下面两张图片:
一张登录的系统是pdd,一张登录的系统是tb, 两个不同的系统,展示了一样的订单管理; pdd也展示了定制化的数据分析和信息查询; 还展示了在公共的基础上,可以有对自己系统的不同内容,商品管理(拼多多) tb也展示了定制化的运营活动;
这也就诠释了,DSL设计,既有共同的内容,也可以满足每个系统不一样的内容