🎯欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
🔍 本文将带你深入理解 Flutter 中两种最基础的 Widget 类型------StatelessWidget 和 StatefulWidget,掌握 Flutter 状态管理的核心概念。
一、Widget 体系概述
在 Flutter 中,一切皆 Widget。Widget 是 Flutter 应用的构建块,用于描述 UI 的配置信息。Flutter 提供了两种基础的 Widget 类型:StatelessWidget(无状态组件)和 StatefulWidget(有状态组件)。
🎯 为什么需要区分两种 Widget?
理解 StatelessWidget 和 StatefulWidget 的区别,是掌握 Flutter 开发的关键一步。这两种 Widget 的设计理念不同,适用于不同的场景。
StatelessWidget 的特点:
- 状态不可变,一旦创建就保持不变
- 性能高效,不需要维护状态
- 适用于静态内容、纯展示组件
- 重建时完全重新创建
StatefulWidget 的特点:
- 状态可变,可以响应用户交互和数据变化
- 通过 State 对象管理状态
- 适用于需要动态更新的组件
- 重建时复用 State 对象
💡 核心思想:StatelessWidget 就像一张静态图片,而 StatefulWidget 就像一个可以变化的动画。选择合适的 Widget 类型,可以让代码更简洁、性能更优。
二、StatelessWidget 无状态组件
2.1 基本概念
StatelessWidget 是最简单的 Widget 类型,它的父类是 Widget。StatelessWidget 的配置在创建时确定,之后不会改变。
dart
class MyTextWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final String text;
final Color color;
const MyTextWidget({
super.key,
required this.text,
this.color = Colors.black,
});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(
text,
style: TextStyle(color: color),
);
}
}2.2 工作原理
StatelessWidget 的生命周期非常简单:
- 创建:构造函数被调用,初始化所有 final 字段
- 构建 :
build()方法被调用,返回 Widget 树 - 重建:如果父组件重建,StatelessWidget 会被完全重新创建
dart
// 第一次创建
MyTextWidget(text: 'Hello', color: Colors.blue)
// 父组件重建时,创建新的实例
MyTextWidget(text: 'Hello', color: Colors.blue) // 新实例💡 小贴士:StatelessWidget 的所有字段都应该是 final,确保状态不可变。如果需要修改数据,请使用 StatefulWidget。
2.3 适用场景
StatelessWidget 适用于以下场景:
| 场景 | 示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 纯文本展示 | Text、RichText | 内容固定,不需要交互 |
| 图标显示 | Icon、Image | 静态资源或固定 URL |
| 布局容器 | Container、Padding | 仅用于布局,不保存状态 |
| 样式组件 | Card、Divider | 纯视觉组件 |
| 数据展示 | 列表项、信息卡片 | 数据由父组件传入 |
2.4 最佳实践
dart
// ✅ 好的实践:所有字段都是 final
class UserCard extends StatelessWidget {
final String name;
final String email;
final String avatarUrl;
const UserCard({
super.key,
required this.name,
required this.email,
required this.avatarUrl,
});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Card(
child: ListTile(
leading: CircleAvatar(
backgroundImage: NetworkImage(avatarUrl),
),
title: Text(name),
subtitle: Text(email),
),
);
}
}
// ❌ 不好的实践:字段不是 final
class BadWidget extends StatelessWidget {
String text; // 应该是 final
BadWidget(this.text); // 应该使用 const
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(text);
}
}三、StatefulWidget 有状态组件
3.1 基本概念
StatefulWidget 是可以保存状态并响应变化的 Widget。它由两个类组成:StatefulWidget 本身和对应的 State 类。
dart
class CounterWidget extends StatefulWidget {
final int initialValue;
const CounterWidget({
super.key,
this.initialValue = 0,
});
@override
State<CounterWidget> createState() => _CounterWidgetState();
}
class _CounterWidgetState extends State<CounterWidget> {
late int _counter;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_counter = widget.initialValue;
}
void _increment() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Text('计数: $_counter'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _increment,
child: const Text('增加'),
),
],
);
}
}3.2 工作原理
StatefulWidget 的生命周期比 StatelessWidget 复杂得多:
- 创建 StatefulWidget:调用构造函数,创建 Widget 实例
- 创建 State :调用
createState(),创建对应的 State 对象 - 初始化状态 :调用
initState(),初始化状态数据 - 构建 UI :调用
build(),返回 Widget 树 - 状态更新 :调用
setState(),标记需要重建 - 重建 UI :再次调用
build(),更新 UI - 销毁 :调用
dispose(),清理资源
💡 核心要点:StatefulWidget 本身是不可变的,状态存储在 State 对象中。当 Widget 重建时,State 对象会被复用,而不是重新创建。
3.3 生命周期详解
dart
class LifecycleWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const LifecycleWidget({super.key});
@override
State<LifecycleWidget> createState() => _LifecycleWidgetState();
}
class _LifecycleWidgetState extends State<LifecycleWidget> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
print('initState: 组件初始化');
// 初始化状态、订阅事件流等
}
@override
void didChangeDependencies() {
super.didChangeDependencies();
print('didChangeDependencies: 依赖变化');
// 当依赖的 InheritedWidget 变化时调用
}
@override
void didUpdateWidget(LifecycleWidget oldWidget) {
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
print('didUpdateWidget: Widget 更新');
// 当父组件重建并传入新的配置时调用
}
@override
void setState(VoidCallback fn) {
super.setState(fn);
print('setState: 状态更新,触发重建');
// 调用此方法会触发 build 方法重新执行
}
@override
void deactivate() {
super.deactivate();
print('deactivate: 组件停用');
// 当组件从树中移除时调用,但可能被重新插入
}
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
print('dispose: 组件销毁');
// 清理资源、取消订阅等
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
print('build: 构建 UI');
return const Text('生命周期示例');
}
}3.4 生命周期方法对照表
| 方法 | 调用时机 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
createState() |
创建 StatefulWidget 时 | 创建 State 对象 |
initState() |
State 对象插入树中时 | 初始化状态、订阅事件 |
didChangeDependencies() |
依赖变化时 | 响应 InheritedWidget 变化 |
didUpdateWidget() |
父组件重建时 | 处理配置变化 |
setState() |
状态更新时 | 标记需要重建 |
deactivate() |
从树中移除时 | 临时停用(可能重新插入) |
dispose() |
永久移除时 | 清理资源 |
3.5 setState 的正确使用
setState 是 StatefulWidget 中最重要的方法,用于触发 UI 重建。
dart
class CounterWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const CounterWidget({super.key});
@override
State<CounterWidget> createState() => _CounterWidgetState();
}
class _CounterWidgetState extends State<CounterWidget> {
int _counter = 0;
// ✅ 正确用法:在 setState 中修改状态
void _increment() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
// ❌ 错误用法:不使用 setState
void _badIncrement() {
_counter++; // 不会触发重建
}
// ❌ 错误用法:在 build 中调用 setState
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
setState(() {
// 这会导致无限循环!
});
return Text('$_counter');
}
// ✅ 正确用法:异步操作后更新状态
Future<void> _loadData() async {
final data = await fetchData();
setState(() {
_counter = data;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Text('计数: $_counter'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _increment,
child: const Text('增加'),
),
],
);
}
}⚠️ 重要提示 :
setState会在下一个帧触发build方法,因此不能在build方法中调用setState,否则会导致无限循环。
四、何时使用哪种 Widget
4.1 选择标准
选择 StatelessWidget 还是 StatefulWidget,可以遵循以下标准:
使用 StatelessWidget 的情况:
- Widget 的配置在创建后不会改变
- Widget 不需要响应任何用户交互
- Widget 的数据完全来自父组件
- Widget 纯粹用于展示,不保存任何状态
使用 StatefulWidget 的情况:
- Widget 需要响应用户交互(点击、输入等)
- Widget 需要根据时间或其他条件更新
- Widget 需要保存和修改内部状态
- Widget 需要管理动画效果
4.2 决策流程图
Widget 需要改变吗?
├─ 否 → StatelessWidget
└─ 是 → 需要响应交互吗?
├─ 否 → 考虑数据能否由父组件管理
└─ 是 → StatefulWidget4.3 实际案例分析
案例 1:纯展示卡片 → StatelessWidget
dart
class ProductCard extends StatelessWidget {
final String name;
final double price;
final String imageUrl;
const ProductCard({
super.key,
required this.name,
required this.price,
required this.imageUrl,
});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Card(
child: Column(
children: [
Image.network(imageUrl),
Text(name),
Text('¥$price'),
],
),
);
}
}案例 2:可点击的点赞按钮 → StatefulWidget
dart
class LikeButton extends StatefulWidget {
const LikeButton({super.key});
@override
State<LikeButton> createState() => _LikeButtonState();
}
class _LikeButtonState extends State<LikeButton> {
bool _isLiked = false;
int _likeCount = 0;
void _toggleLike() {
setState(() {
_isLiked = !_isLiked;
_likeCount += _isLiked ? 1 : -1;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return GestureDetector(
onTap: _toggleLike,
child: Row(
children: [
Icon(
_isLiked ? Icons.favorite : Icons.favorite_border,
color: _isLiked ? Colors.red : Colors.grey,
),
const SizedBox(width: 8),
Text('$_likeCount'),
],
),
);
}
}五、StatefulWidget 的高级用法
5.1 使用 widget 访问配置
State 类可以通过 widget 属性访问对应的 StatefulWidget 的配置。
dart
class ConfigurableWidget extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
final Color backgroundColor;
const ConfigurableWidget({
super.key,
required this.title,
required this.backgroundColor,
});
@override
State<ConfigurableWidget> createState() => _ConfigurableWidgetState();
}
class _ConfigurableWidgetState extends State<ConfigurableWidget> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
color: widget.backgroundColor,
child: Text(widget.title),
);
}
}5.2 处理配置变化
当父组件传入新的配置时,可以通过 didUpdateWidget 响应变化。
dart
class UpdatingWidget extends StatefulWidget {
final String message;
const UpdatingWidget({
super.key,
required this.message,
});
@override
State<UpdatingWidget> createState() => _UpdatingWidgetState();
}
class _UpdatingWidgetState extends State<UpdatingWidget> {
late String _displayMessage;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_displayMessage = widget.message;
}
@override
void didUpdateWidget(UpdatingWidget oldWidget) {
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
if (widget.message != oldWidget.message) {
setState(() {
_displayMessage = '更新: ${widget.message}';
});
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(_displayMessage);
}
}5.3 Keys 的使用
Keys 用于标识 Widget,帮助 Flutter 知道哪些 Widget 应该保留,哪些应该重建。
dart
class KeyedListItem extends StatelessWidget {
final String id;
final String title;
const KeyedListItem({
super.key,
required this.id,
required this.title,
});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return ListTile(
key: ValueKey(id), // 使用 ValueKey
title: Text(title),
);
}
}💡 小贴士:在列表中使用唯一且稳定的 Key 可以显著提升性能,避免不必要的重建。
5.4 释放资源
在 dispose 方法中清理资源,避免内存泄漏。
dart
class ResourceWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const ResourceWidget({super.key});
@override
State<ResourceWidget> createState() => _ResourceWidgetState();
}
class _ResourceWidgetState extends State<ResourceWidget> {
late StreamSubscription _subscription;
late AnimationController _controller;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
// 创建资源
_subscription = someStream.listen((data) {
setState(() {});
});
_controller = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(seconds: 1),
vsync: this,
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
// 释放资源
_subscription.cancel();
_controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container();
}
}六、性能优化
6.1 避免不必要的重建
使用 const 构造函数可以避免不必要的 Widget 重建。
dart
// ❌ 不好的实践
class BadWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Text('标题'), // 每次都会创建新的实例
Text('内容'),
],
);
}
}
// ✅ 好的实践
class GoodWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const Column(
children: [
Text('标题'), // 使用 const,只创建一次
Text('内容'),
],
);
}
}6.2 使用 RepaintBoundary
RepaintBoundary 可以创建独立的绘制层,避免整个子树重绘。
dart
class OptimizedWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
const StaticHeader(), // 静态内容
RepaintBoundary(
child: const AnimatedContent(), // 动画内容独立重绘
),
],
);
}
}6.3 分离状态管理
将状态从 UI 中分离,使代码更易于维护和测试。
dart
// 状态管理类
class CounterState {
int value = 0;
void increment() => value++;
}
// UI 组件
class CounterWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const CounterWidget({super.key});
@override
State<CounterWidget> createState() => _CounterWidgetState();
}
class _CounterWidgetState extends State<CounterWidget> {
final CounterState _state = CounterState();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Text('计数: ${_state.value}'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
_state.increment();
});
},
child: const Text('增加'),
),
],
);
}
}七、完整示例代码
下面是一个完整的 Flutter 应用示例,展示 StatelessWidget 和 StatefulWidget 的各种用法。
dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const StateDemo());
}
class StateDemo extends StatelessWidget {
const StateDemo({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'StatelessWidget & StatefulWidget 演示',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
theme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: ColorScheme.dark(
primary: const Color(0xFF6366F1),
secondary: const Color(0xFF8B5CF6),
surface: const Color(0xFF1E293B),
background: const Color(0xFF0F172A),
brightness: Brightness.dark,
),
useMaterial3: true,
),
home: const StatePage(),
);
}
}
class StatePage extends StatelessWidget {
const StatePage({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
backgroundColor: const Color(0xFF0F172A),
body: SafeArea(
child: SingleChildScrollView(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
// 标题区域
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(24),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(
begin: Alignment.topLeft,
end: Alignment.bottomRight,
colors: [
const Color(0xFF6366F1).withOpacity(0.2),
const Color(0xFF8B5CF6).withOpacity(0.2),
],
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(20),
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.1),
),
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text(
'🔍 State Management',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 28,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
letterSpacing: 0.5,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Text(
'深入理解 StatelessWidget 与 StatefulWidget',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.7),
height: 1.5,
),
),
],
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 32),
// Stateless 示例
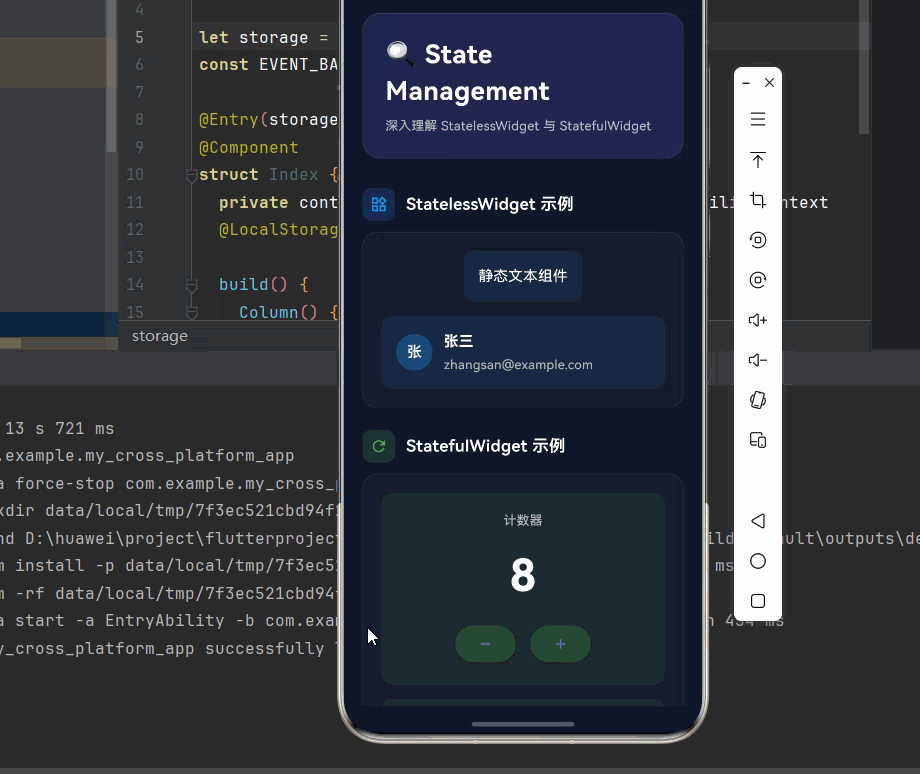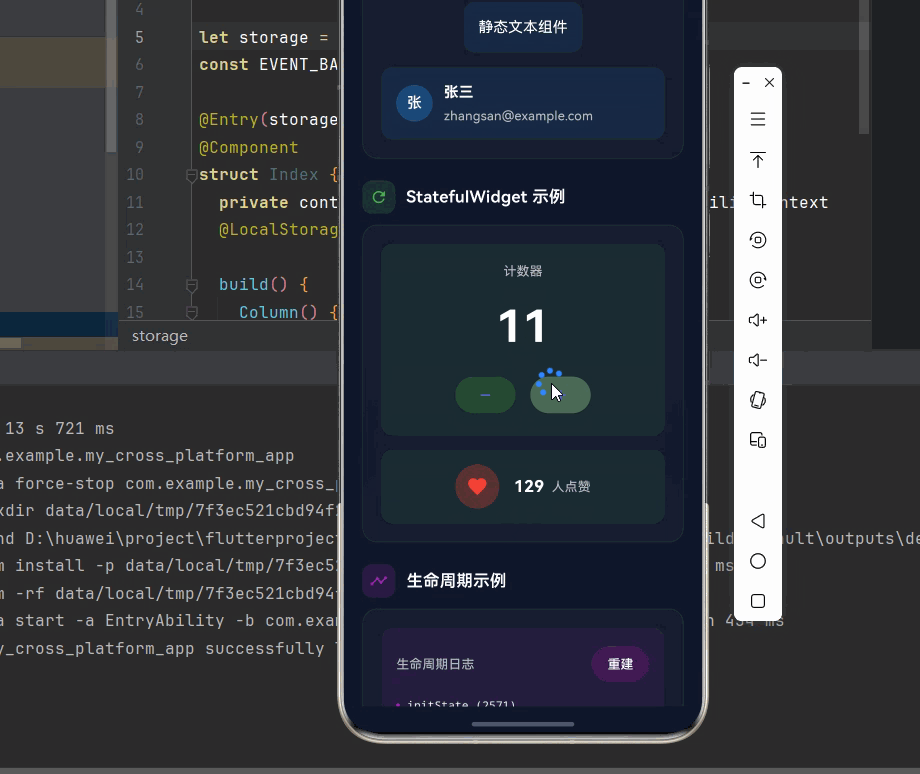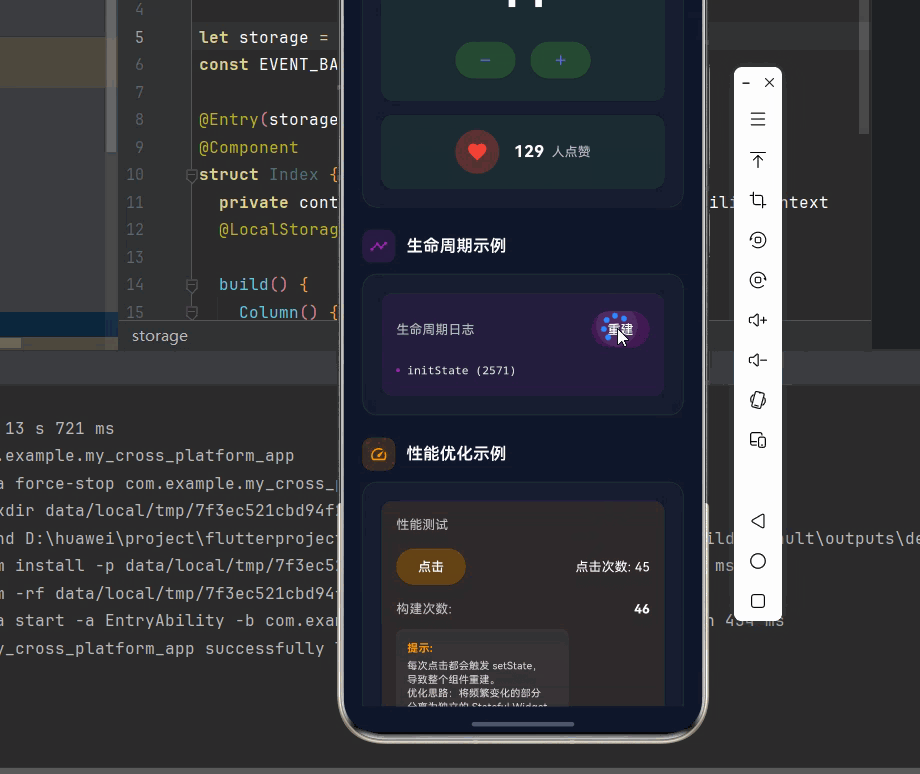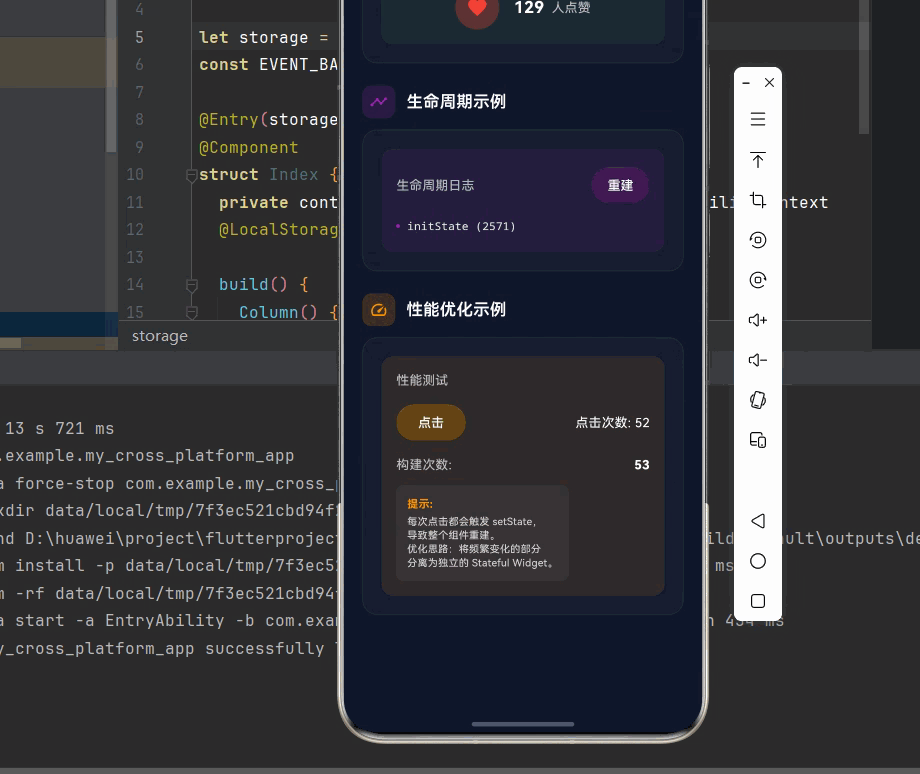
_buildSection(
title: 'StatelessWidget 示例',
icon: Icons.widgets_outlined,
color: Colors.blue,
child: _buildDemoCard([
const StaticTextWidget(text: '静态文本组件'),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
const UserCardWidget(
name: '张三',
email: 'zhangsan@example.com',
),
]),
),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
// Stateful 示例
_buildSection(
title: 'StatefulWidget 示例',
icon: Icons.refresh,
color: Colors.green,
child: _buildDemoCard([
const CounterWidget(),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
const LikeButtonWidget(),
]),
),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
// 生命周期示例
_buildSection(
title: '生命周期示例',
icon: Icons.timeline,
color: Colors.purple,
child: _buildDemoCard([
const LifecycleWidget(),
]),
),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
// 性能优化示例
_buildSection(
title: '性能优化示例',
icon: Icons.speed,
color: Colors.orange,
child: _buildDemoCard([
const PerformanceWidget(),
]),
),
const SizedBox(height: 80),
],
),
),
),
);
}
Widget _buildSection({
required String title,
required IconData icon,
required Color color,
required Widget child,
}) {
return Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Row(
children: [
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: color.withOpacity(0.2),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10),
),
child: Icon(icon, color: color, size: 20),
),
const SizedBox(width: 12),
Text(
title,
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w600,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
child,
],
);
}
Widget _buildDemoCard(List<Widget> children) {
return Container(
width: double.infinity,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.03),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(16),
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.05),
),
),
child: Column(
children: children,
),
);
}
}
// StatelessWidget 示例
class StaticTextWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final String text;
const StaticTextWidget({super.key, required this.text});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.blue.withOpacity(0.1),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
),
child: Text(
text,
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
);
}
}
class UserCardWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final String name;
final String email;
const UserCardWidget({
super.key,
required this.name,
required this.email,
});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.blue.withOpacity(0.1),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
),
child: Row(
children: [
CircleAvatar(
backgroundColor: Colors.blue.withOpacity(0.3),
child: Text(
name[0],
style: const TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
),
const SizedBox(width: 12),
Expanded(
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Text(
name,
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 4),
Text(
email,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.7),
),
),
],
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
// StatefulWidget 示例
class CounterWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const CounterWidget({super.key});
@override
State<CounterWidget> createState() => _CounterWidgetState();
}
class _CounterWidgetState extends State<CounterWidget> {
int _counter = 0;
void _increment() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
void _decrement() {
setState(() {
_counter--;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.green.withOpacity(0.1),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
),
child: Column(
children: [
const Text(
'计数器',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white70,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 48,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _decrement,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.green.withOpacity(0.3),
foregroundColor: Colors.white,
),
child: const Icon(Icons.remove),
),
const SizedBox(width: 16),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _increment,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.green.withOpacity(0.3),
foregroundColor: Colors.white,
),
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
],
),
],
),
);
}
}
class LikeButtonWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const LikeButtonWidget({super.key});
@override
State<LikeButtonWidget> createState() => _LikeButtonWidgetState();
}
class _LikeButtonWidgetState extends State<LikeButtonWidget> {
bool _isLiked = false;
int _likeCount = 128;
void _toggleLike() {
setState(() {
_isLiked = !_isLiked;
_likeCount += _isLiked ? 1 : -1;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.green.withOpacity(0.1),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
GestureDetector(
onTap: _toggleLike,
child: Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(12),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: _isLiked
? Colors.red.withOpacity(0.3)
: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.1),
shape: BoxShape.circle,
),
child: Icon(
_isLiked ? Icons.favorite : Icons.favorite_border,
color: _isLiked ? Colors.red : Colors.white70,
size: 24,
),
),
),
const SizedBox(width: 16),
Text(
'$_likeCount',
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
const SizedBox(width: 8),
Text(
'人点赞',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.7),
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
// 生命周期示例
class LifecycleWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const LifecycleWidget({super.key});
@override
State<LifecycleWidget> createState() => _LifecycleWidgetState();
}
class _LifecycleWidgetState extends State<LifecycleWidget> {
final List<String> _logs = [];
int _counter = 0;
void _addLog(String log) {
setState(() {
_logs.insert(0, '$log (${DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpoch % 10000})');
if (_logs.length > 5) _logs.removeLast();
});
}
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_addLog('initState');
}
@override
void didUpdateWidget(LifecycleWidget oldWidget) {
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
_addLog('didUpdateWidget');
}
void _rebuild() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.purple.withOpacity(0.1),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
const Text(
'生命周期日志',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white70,
),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _rebuild,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.purple.withOpacity(0.3),
foregroundColor: Colors.white,
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 12, vertical: 8),
),
child: const Text('重建'),
),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
..._logs.map((log) => Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 4),
child: Row(
children: [
Container(
width: 4,
height: 4,
margin: const EdgeInsets.only(right: 8),
decoration: const BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.purple,
shape: BoxShape.circle,
),
),
Expanded(
child: Text(
log,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 12,
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.9),
fontFamily: 'monospace',
),
),
),
],
),
)),
],
),
);
}
}
// 性能优化示例
class PerformanceWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const PerformanceWidget({super.key});
@override
State<PerformanceWidget> createState() => _PerformanceWidgetState();
}
class _PerformanceWidgetState extends State<PerformanceWidget> {
int _clickCount = 0;
int _buildCount = 0;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
_buildCount++;
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.orange.withOpacity(0.1),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text(
'性能测试',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white70,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
_clickCount++;
});
},
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.orange.withOpacity(0.3),
foregroundColor: Colors.white,
),
child: const Text('点击'),
),
Text(
'点击次数: $_clickCount',
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
const Text(
'构建次数:',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white70,
),
),
Text(
'$_buildCount',
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(12),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.05),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text(
'提示:',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 12,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.orange,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 4),
Text(
'每次点击都会触发 setState,\n导致整个组件重建。\n优化思路:将频繁变化的部分\n分离为独立的 Stateful Widget。',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 11,
color: Colors.white.withOpacity(0.8),
height: 1.4,
),
),
],
),
),
],
),
);
}
}八、总结
StatelessWidget 和 StatefulWidget 是 Flutter 状态管理的基础,理解它们的区别和使用场景对于开发高效的应用至关重要。
🎯 核心要点
- StatelessWidget:状态不可变,适用于纯展示组件,性能高效
- StatefulWidget:状态可变,通过 State 对象管理状态,需要响应交互
- 生命周期:StatefulWidget 有完整的生命周期,需要正确管理资源
- setState:触发 UI 重建的关键方法,不能在 build 中调用
- 性能优化:使用 const、RepaintBoundary 等技巧提升性能
📚 使用建议
| 场景 | 推荐方案 |
|---|---|
| 纯文本展示 | StatelessWidget |
| 数据展示卡片 | StatelessWidget(数据由父组件传入) |
| 按钮交互 | StatefulWidget 或使用 GestureDetector |
| 表单输入 | StatefulWidget |
| 动画效果 | StatefulWidget + AnimationController |
| 复杂状态管理 | 考虑使用状态管理库(Provider、Riverpod 等) |
💡 最佳实践:优先使用 StatelessWidget,只有在确实需要管理状态时才使用 StatefulWidget。通过合理的状态管理,可以让代码更简洁、性能更优。随着应用复杂度的增加,可以考虑引入专门的状态管理方案。