属性是应用于某些模块、crate 或项的元数据(metadata)。这元数据可以用来:
- 条件编译代码
- 设置 crate 名称、版本和类型(二进制文件或库)
- 禁用 lint (警告)
- 启用编译器的特性(宏、全局导入(glob import)等)
- 链接到一个非 Rust 语言的库
- 标记函数作为单元测试
- 标记函数作为基准测试的某个部分
当属性作用于整个 crate 时,它们的语法为 #![crate_attribute],当它们用于模块或项时,语法为 #[item_attribute](注意少了感叹号 !)。
属性可以接受参数,有不同的语法形式:
#[attribute = "value"]#[attribute(key = "value")]#[attribute(value)]
属性可以多个值,它们可以分开到多行中:
#[attribute(value, value2)]
#[attribute(value, value2, value3,
value4, value5)]13.1 死代码 dead_code
编译器提供了 dead_code(死代码,无效代码)lint,这会对未使用的函数产生警告。可以用一个属性来禁用这个 lint。
// 13.1节 死代码dead_code
fn used_function() {
println!("call used_function()");
}
// `#[allow(dead_code)]` 属性可以禁用 `dead_code` lint
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn unused_functin() {}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn noisy_unused_function() {}
// 改正 ^ 增加一个属性来消除警告
fn main() {
used_function();
println!("Hello Rust");
}
// rustc main.rs
// ./main编译运行:
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_1> rustc main.rs
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_1> ./main
call used_function()
Hello Rust
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_1>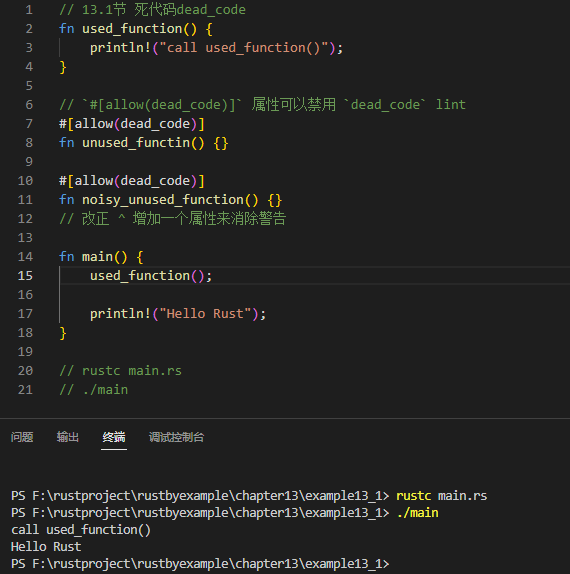
注意在实际程序中,需要将死代码清除掉。由于本书的例子是交互性的,因而其中需要允许一些死代码的出现。
13.2 crate
crate_type 属性可以告知编译器 crate 是一个二进制的可执行文件还是一个库(甚至是哪种类型的库),crate_name 属性可以设定 crate 的名称。
不过,一定要注意在使用 cargo 时,这两种类型时都没有 作用。由于大多数 Rust 工程都使用 cargo,这意味着 crate_type 和 crate_name 的作用事实上很有限。
// 13.2节 crate
// 这个 crate 是一个库文件
#![crate_type = "lib"]
// 库的名称为 "rary"
#![crate_name = "rary"]
pub fn public_function() {
println!("called rary's 'public_function()'");
}
fn private_function() {
println!("called rary's 'private_function()'");
}
pub fn indirect_access() {
print!("called rary's 'indirect_access()', that\n> ");
private_function();
}
// rustc lib.rs
// ls lib*当用到 crate_type 属性时,就不再需要给 rustc 命令加上 --crate-type 标记。
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_2> rustc lib.rs
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_2> ls lib*
library.rlib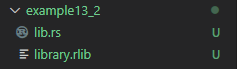
13.3 cfg
条件编译可能通过两种不同的操作符实现:
cfg属性:在属性位置中使用#[cfg(...)]cfg!宏:在布尔表达式中使用cfg!(...)
两种形式使用的参数语法都相同。
// 13.3节 cfg
// 这个函数仅当目标系统是 Linux 的时候才会编译
#[cfg(target_os = "linux")]
fn are_you_on_linux() {
println!("You are running linux!")
}
// 而这个函数仅当目标系统 **不是** Linux 时才会编译
#[cfg(not(target_os = "linux"))]
fn are_you_on_linux() {
println!("You are *not* running linux!")
}
fn main() {
are_you_on_linux();
println!("Are you sure?");
if cfg!(target_os = "linux") {
println!("Yes. It's definitely linux!");
} else {
println!("Yes. It's definitely *not* linux!");
}
if cfg!(target_os = "windows") {
println!("this is windows OS!");
} else {
println!("this not is windows OS!");
}
println!("Hello Rust");
}
// rustc main.rs
// ./main编译运行:
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_3> rustc main.rs
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_3> ./main
You are *not* running linux!
Are you sure?
Yes. It's definitely *not* linux!
this is windows OS!
Hello Rust
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_3>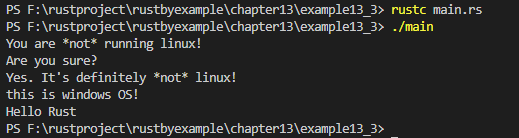
参见:
13.3.1 自定义条件
有部分条件如 target_os 是由 rustc 隐式地提供的,但是自定义条件必须使用 --cfg 标记来传给 rustc。
// 13.3.1节 自定义条件
#[cfg(some_condition)]
fn conditional_function() {
println!("condition met!")
}
fn main() {
conditional_function();
println!("Hello Rust");
}
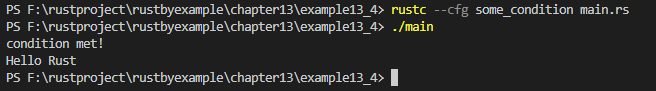
// rustc --cfg some_condition main.rs
// ./main试试不使用自定义的 cfg 标记会发生什么:
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_4> rustc main.rs
error[E0425]: cannot find function `conditional_function` in this scope
--> main.rs:8:5
|
8 | conditional_function();
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ not found in this scope
|
note: found an item that was configured out
--> main.rs:3:4
|
2 | #[cfg(some_condition)]
| -------------- the item is gated here
3 | fn conditional_function() {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
error: aborting due to 1 previous error
For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0425`.
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_4>
使用自定义的 cfg 标记:
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_4> rustc --cfg some_condition main.rs
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_4> ./main
condition met!
Hello Rust
PS F:\rustproject\rustbyexample\chapter13\example13_4>