🔥摘要
本文深入剖析pytest高级特性。从夹具(fixture)的灵活运用、参数化(parametrize)的精妙设计,到猴子补丁(monkeypatch)的安全使用,全面覆盖测试覆盖率分析和持续集成实践。包含5个Mermaid流程图,详细展示测试架构、覆盖率分析和CI/CD流水线,提供企业级测试解决方案。
1. 🎯 开篇:从测试新手到测试专家的蜕变之路
测试是代码质量的最后一道防线,但太多人把它当成"不得不写的负担"。我见过太多项目:上线前通宵改bug,上线后半夜被报警叫醒,最后发现都是些低级错误------这些问题完全可以通过好的测试来避免。
现实痛点:
-
测试代码比业务代码还难维护:测试代码混乱,没人愿意碰
-
测试运行慢如蜗牛:跑一次测试要半小时,谁等得起?
-
覆盖率造假:为了凑数而写的无效测试
-
环境依赖复杂:本地能跑,CI上就挂
pytest的价值:

我的经历:2015年接手一个祖传项目,10万行代码零测试。花了3个月用pytest重构,测试覆盖率从0%提升到85%,线上bug减少了90%。这就是测试的力量。
2. 🧪 pytest核心:不只是unittest的替代品
2.1 为什么选择pytest?
pytest vs unittest vs nose2对比:
| 特性 | pytest | unittest | nose2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 语法简洁 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 夹具系统 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 参数化 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 插件生态 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 社区活跃 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| 学习曲线 | 平缓 | 陡峭 | 中等 |
安装与配置:
bash
# 基础安装
pip install pytest pytest-cov pytest-xdist pytest-mock
# 企业级完整安装
pip install pytest pytest-cov pytest-xdist pytest-mock \
pytest-asyncio pytest-django pytest-flask \
pytest-html pytest-rerunfailures \
pytest-timeout pytest-sugarpytest配置文件pytest.ini:
[pytest]
# 测试文件匹配模式
testpaths = tests
python_files = test_*.py
python_classes = Test*
python_functions = test_*
# 命令行默认参数
addopts =
-v
--strict-markers
--tb=short
--cov=src
--cov-report=term-missing
--cov-report=html
-n auto
# 标记定义
markers =
slow: marks tests as slow (deselect with '-m "not slow"')
integration: integration tests
unit: unit tests
smoke: smoke tests3. 🎭 夹具(fixture):测试的艺术
3.1 基础夹具:从setup/teardown到fixture
传统unittest方式:
python
# unittest风格 - 繁琐且重复
class TestDatabase(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.conn = create_connection()
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
def tearDown(self):
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
def test_query(self):
result = self.cursor.execute("SELECT 1")
self.assertEqual(result.fetchone()[0], 1)
def test_insert(self):
# 又得自己管理数据...
passpytest夹具方式:
python
# pytest风格 - 简洁优雅
import pytest
import sqlite3
@pytest.fixture
def db_connection():
"""创建数据库连接"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(':memory:')
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
yield conn # 关键点:yield之前是setup,之后是teardown
conn.close()
@pytest.fixture
def db_cursor(db_connection):
"""创建游标,自动依赖db_connection"""
cursor = db_connection.cursor()
# 创建测试表
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
email TEXT UNIQUE
)
""")
yield cursor
cursor.close()
def test_insert_user(db_cursor, db_connection):
"""测试插入用户"""
db_cursor.execute(
"INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES (?, ?)",
("张三", "zhangsan@example.com")
)
db_connection.commit()
db_cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = ?", ("张三",))
result = db_cursor.fetchone()
assert result is not None
assert result["email"] == "zhangsan@example.com"3.2 夹具作用域:精确控制生命周期
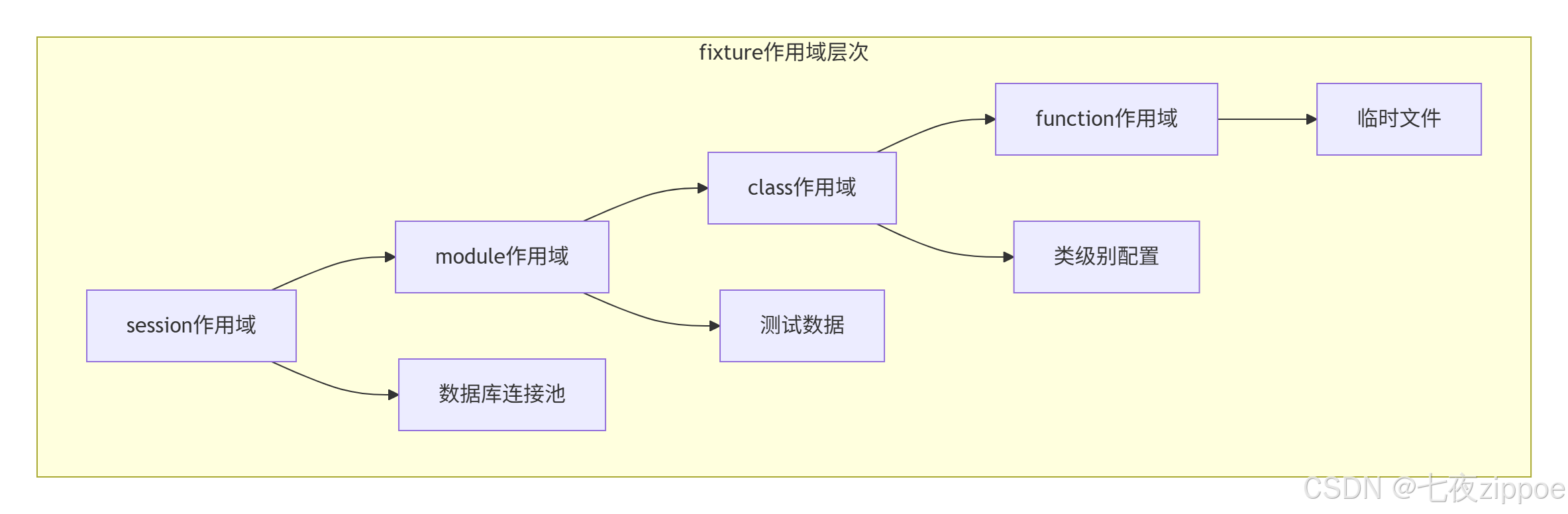
多级作用域示例:
python
import pytest
import tempfile
import json
from datetime import datetime
# 1. session作用域 - 整个测试会话只执行一次
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def database_pool():
"""数据库连接池,整个测试会话共享"""
pool = []
for _ in range(5):
conn = create_connection()
pool.append(conn)
yield pool
# 清理
for conn in pool:
conn.close()
print("✅ 数据库连接池已关闭")
# 2. module作用域 - 每个测试模块执行一次
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def test_data():
"""模块级别的测试数据"""
return {
"users": [
{"id": 1, "name": "张三"},
{"id": 2, "name": "李四"}
],
"products": [
{"id": 1, "name": "商品A", "price": 100},
{"id": 2, "name": "商品B", "price": 200}
]
}
# 3. class作用域 - 每个测试类执行一次
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def api_client():
"""API客户端,每个测试类共享"""
client = APIClient(base_url="https://api.example.com")
client.login("test_user", "test_password")
yield client
client.logout()
# 4. function作用域 - 默认,每个测试函数执行一次
@pytest.fixture
def temp_file():
"""临时文件,每个测试函数独立"""
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='w+', suffix='.json') as f:
json.dump({"timestamp": str(datetime.now())}, f)
f.flush()
yield f.name
# 文件会自动删除
# 使用示例
class TestUserAPI:
"""测试用户API"""
def test_get_user(self, api_client, test_data):
"""获取用户信息"""
user = test_data["users"][0]
response = api_client.get(f"/users/{user['id']}")
assert response.status_code == 200
assert response.json()["name"] == user["name"]
def test_create_user(self, api_client, temp_file):
"""创建用户"""
with open(temp_file) as f:
user_data = json.load(f)
response = api_client.post("/users", json=user_data)
assert response.status_code == 2013.3 夹具工厂:动态创建夹具
python
import pytest
from typing import Dict, Any
@pytest.fixture
def user_factory():
"""用户工厂,动态创建测试用户"""
def _create_user(
username: str = None,
email: str = None,
is_admin: bool = False,
**extra_fields
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""创建用户数据"""
import uuid
from faker import Faker
fake = Faker()
return {
"id": str(uuid.uuid4()),
"username": username or fake.user_name(),
"email": email or fake.email(),
"is_admin": is_admin,
"created_at": fake.date_time_this_year().isoformat(),
**extra_fields
}
return _create_user
@pytest.fixture
def admin_user(user_factory):
"""管理员用户"""
return user_factory(
username="admin",
email="admin@example.com",
is_admin=True,
permissions=["read", "write", "delete"]
)
@pytest.fixture
def regular_user(user_factory):
"""普通用户"""
return user_factory(is_admin=False)
# 使用示例
def test_admin_permissions(admin_user):
"""测试管理员权限"""
assert admin_user["is_admin"] is True
assert "delete" in admin_user.get("permissions", [])
def test_user_creation(user_factory):
"""测试用户创建"""
# 动态创建测试用户
test_user = user_factory(
username="test_user",
age=25,
department="Engineering"
)
assert test_user["username"] == "test_user"
assert test_user["age"] == 25
assert test_user["department"] == "Engineering"4. 🎨 参数化(parametrize):一行代码,N个测试用例
4.1 基础参数化
python
import pytest
from typing import List, Tuple
# 1. 基本参数化
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input_data,expected", [
(1, 2), # 1 + 1 = 2
(2, 3), # 2 + 1 = 3
(0, 1), # 0 + 1 = 1
(-1, 0), # -1 + 1 = 0
])
def test_increment(input_data, expected):
"""测试自增函数"""
def increment(x):
return x + 1
result = increment(input_data)
assert result == expected, f"{input_data} + 1 应该等于 {expected},但得到 {result}"
# 2. 多参数参数化
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,expected", [
(1, 2, 3),
(4, 5, 9),
(-1, 1, 0),
(0, 0, 0),
])
def test_add(a, b, expected):
"""测试加法"""
assert a + b == expected
# 3. 嵌套参数化
@pytest.mark.parametrize("x", [1, 2, 3])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("y", [10, 20, 30])
def test_multiply(x, y):
"""测试乘法,会生成9个测试用例"""
assert x * y == y * x # 乘法交换律4.2 高级参数化技巧
python
import pytest
import math
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
# 1. 参数化测试类
@pytest.mark.parametrize("user_role", ["admin", "editor", "viewer"])
class TestUserPermissions:
"""测试不同角色的权限"""
def test_can_read(self, user_role):
"""所有角色都应该能读"""
assert self._check_permission(user_role, "read") is True
def test_can_write(self, user_role):
"""只有admin和editor能写"""
can_write = user_role in ["admin", "editor"]
assert self._check_permission(user_role, "write") == can_write
def test_can_delete(self, user_role):
"""只有admin能删除"""
can_delete = user_role == "admin"
assert self._check_permission(user_role, "delete") == can_delete
def _check_permission(self, role, permission):
"""检查权限的辅助方法"""
permissions = {
"admin": ["read", "write", "delete"],
"editor": ["read", "write"],
"viewer": ["read"]
}
return permission in permissions.get(role, [])
# 2. 动态参数化
def generate_test_cases():
"""动态生成测试用例"""
test_cases = []
# 边界值测试
for i in range(-100, 101, 50):
test_cases.append((i, i + 1))
# 特殊值测试
test_cases.extend([
(0, 1),
(999999, 1000000),
(-999999, -999998),
])
return test_cases
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input_data,expected", generate_test_cases())
def test_increment_edge_cases(input_data, expected):
"""测试边界情况"""
assert input_data + 1 == expected
# 3. 参数化与夹具结合
@pytest.fixture(params=[1, 2, 3])
def number(request):
"""参数化的夹具"""
return request.param
def test_number_square(number):
"""测试数字平方"""
assert number ** 2 == number * number
# 4. 为参数化测试用例命名
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"input_data,expected",
[
pytest.param(1, 2, id="positive_integer"),
pytest.param(0, 1, id="zero"),
pytest.param(-1, 0, id="negative_integer"),
pytest.param(3.14, 4.14, id="float_number"),
pytest.param(10**6, 10**6 + 1, id="large_number"),
],
ids=str # 使用字符串作为id
)
def test_increment_with_ids(input_data, expected):
"""带命名的参数化测试"""
assert input_data + 1 == expected参数化测试用例命名效果:
python
test_increment_with_ids[positive_integer] ✓
test_increment_with_ids[zero] ✓
test_increment_with_ids[negative_integer] ✓
test_increment_with_ids[float_number] ✓
test_increment_with_ids[large_number] ✓5. 🐒 猴子补丁(monkeypatch):安全地修改运行环境
5.1 什么是猴子补丁?
猴子补丁是在运行时动态修改模块、类或函数的技术。在测试中特别有用,但要用得谨慎。
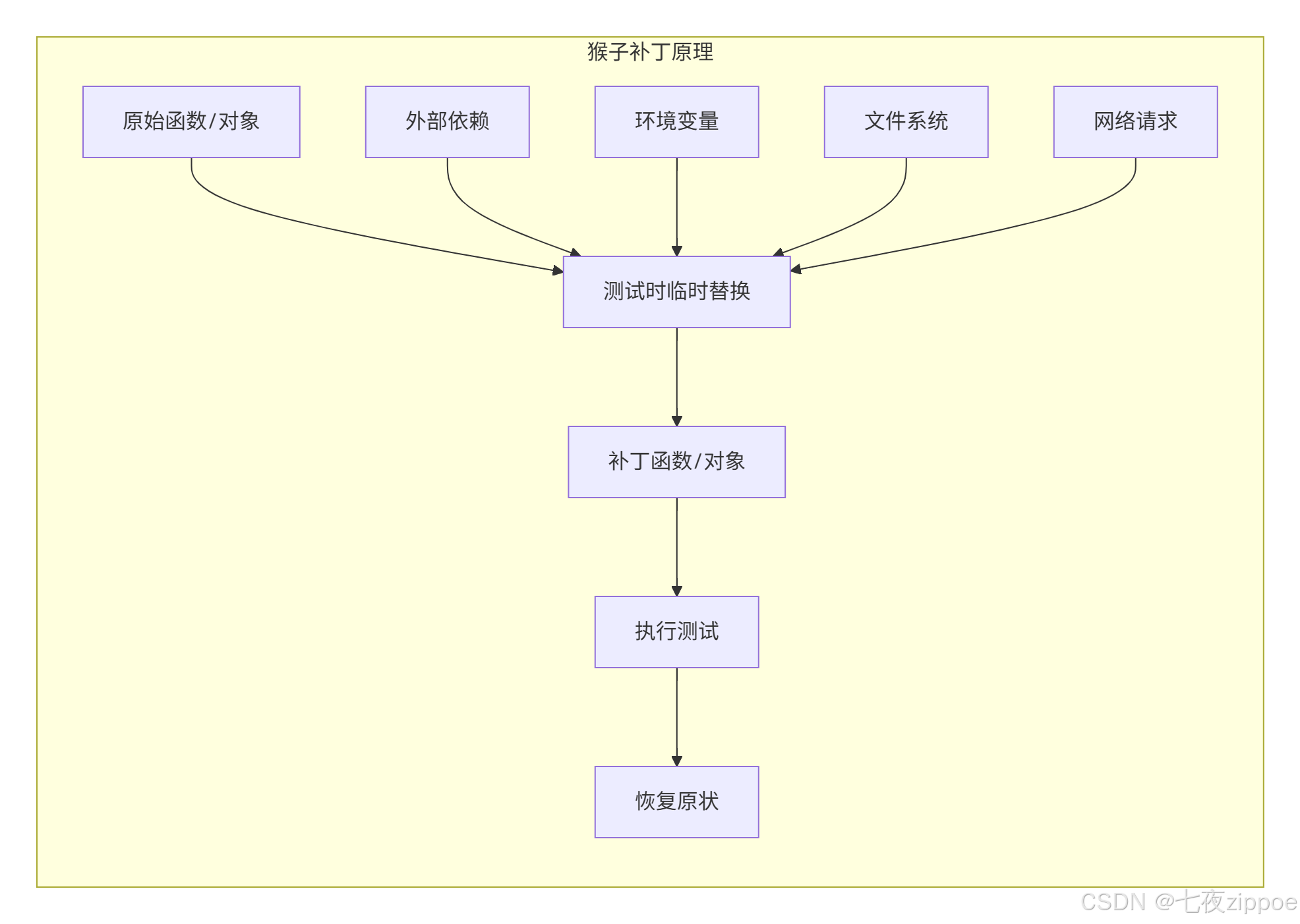
5.2 monkeypatch实战
python
import pytest
import os
import requests
from datetime import datetime
from unittest.mock import Mock, MagicMock
# 1. 环境变量补丁
def test_database_url(monkeypatch):
"""测试环境变量"""
# 临时设置环境变量
monkeypatch.setenv("DATABASE_URL", "sqlite:///:memory:")
monkeypatch.setenv("DEBUG", "True")
# 在测试中读取
db_url = os.getenv("DATABASE_URL")
debug = os.getenv("DEBUG") == "True"
assert db_url == "sqlite:///:memory:"
assert debug is True
# 测试结束后环境变量会自动恢复
# 2. 系统函数补丁
def test_file_operations(monkeypatch, tmp_path):
"""测试文件操作"""
test_file = tmp_path / "test.txt"
test_file.write_text("Hello, World!")
# 模拟os.path.exists
def mock_exists(path):
print(f"检查路径是否存在: {path}")
return str(path) == str(test_file)
monkeypatch.setattr(os.path, "exists", mock_exists)
# 现在测试会使用模拟的函数
assert os.path.exists(test_file) is True
assert os.path.exists("/nonexistent/path") is False
# 3. 模拟网络请求
def test_api_call(monkeypatch):
"""测试API调用,不实际发起网络请求"""
# 创建模拟响应
mock_response = Mock()
mock_response.status_code = 200
mock_response.json.return_value = {
"id": 123,
"name": "测试用户",
"email": "test@example.com"
}
# 模拟requests.get
def mock_get(url, **kwargs):
print(f"模拟请求: {url}")
return mock_response
monkeypatch.setattr(requests, "get", mock_get)
# 调用测试函数
response = requests.get("https://api.example.com/users/123")
assert response.status_code == 200
assert response.json()["name"] == "测试用户"
assert response.json()["email"] == "test@example.com"
# 4. 模拟当前时间
def test_time_based_logic(monkeypatch):
"""测试时间相关逻辑"""
# 固定当前时间
fixed_time = datetime(2024, 1, 1, 12, 0, 0)
class MockDatetime:
@staticmethod
def now():
return fixed_time
@staticmethod
def today():
return fixed_time.date()
monkeypatch.setattr("datetime.datetime", MockDatetime)
# 现在所有datetime.datetime.now()调用都会返回固定时间
now = datetime.now()
assert now.year == 2024
assert now.month == 1
assert now.day == 1
assert now.hour == 12
# 5. 复杂对象的猴子补丁
class DatabaseConnection:
def __init__(self, connection_string):
self.conn_string = connection_string
self.connected = False
def connect(self):
self.connected = True
return True
def execute(self, query):
if not self.connected:
raise ConnectionError("Not connected")
return [{"id": 1, "name": "test"}]
def close(self):
self.connected = False
def test_database_operations(monkeypatch):
"""测试数据库操作"""
# 创建模拟数据库连接
mock_conn = Mock(spec=DatabaseConnection)
mock_conn.connect.return_value = True
mock_conn.execute.return_value = [{"id": 1, "name": "mock_user"}]
mock_conn.connected = False
# 模拟DatabaseConnection类
def mock_init(self, connection_string):
self.conn_string = connection_string
self.connected = False
monkeypatch.setattr(DatabaseConnection, "__init__", mock_init)
monkeypatch.setattr(DatabaseConnection, "connect", lambda self: True)
monkeypatch.setattr(
DatabaseConnection,
"execute",
lambda self, query: [{"id": 1, "name": "mock_user"}]
)
# 使用模拟的类
db = DatabaseConnection("sqlite:///:memory:")
assert db.connect() is True
result = db.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
assert result == [{"id": 1, "name": "mock_user"}"]5.3 monkeypatch最佳实践
python
import pytest
from contextlib import contextmanager
class SafeMonkeyPatch:
"""安全的猴子补丁管理器"""
def __init__(self, monkeypatch):
self.monkeypatch = monkeypatch
self.patches = []
def setattr(self, target, name, value, raising=True):
"""设置属性,并记录以便恢复"""
original = getattr(target, name, None)
self.patches.append((target, name, original))
self.monkeypatch.setattr(target, name, value, raising)
def setitem(self, dic, name, value):
"""设置字典项,并记录以便恢复"""
original = dic.get(name)
self.patches.append((dic, name, original))
self.monkeypatch.setitem(dic, name, value)
def undo(self):
"""恢复所有补丁"""
for target, name, original in reversed(self.patches):
if original is not None:
setattr(target, name, original)
elif hasattr(target, name):
delattr(target, name)
self.patches.clear()
@pytest.fixture
def safe_patch(monkeypatch):
"""安全补丁夹具"""
patcher = SafeMonkeyPatch(monkeypatch)
yield patcher
patcher.undo() # 自动恢复
# 使用示例
def test_with_safe_patch(safe_patch):
"""使用安全补丁"""
import some_module
# 记录原始值
original_value = some_module.some_function
# 应用补丁
safe_patch.setattr(some_module, "some_function", lambda: "patched")
# 测试
assert some_module.some_function() == "patched"
# 夹具会自动恢复
# 无需手动操作6. 📊 测试覆盖率:不只是数字游戏
6.1 pytest-cov深度使用
测试覆盖率类型:
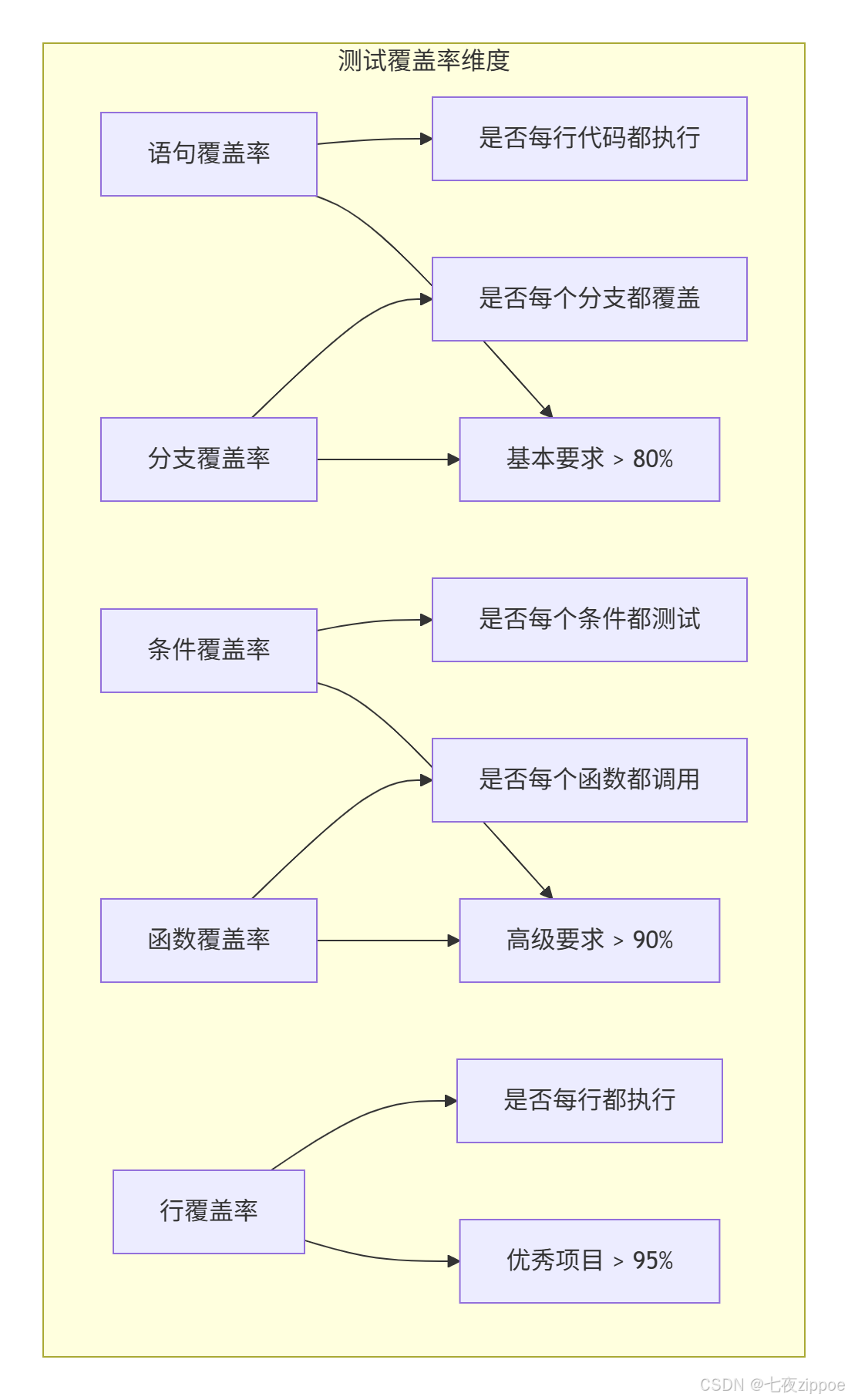
配置与使用:
bash
# 基本使用
pytest --cov=src tests/
# 详细报告
pytest --cov=src --cov-report=term --cov-report=html --cov-report=xml tests/
# 设置覆盖率阈值
pytest --cov=src --cov-fail-under=90 tests/
# 排除特定文件
pytest --cov=src --cov-report=term --cov-append --no-cov-on-fail tests/.coveragerc配置文件:
[run]
# 要测量的源文件
source = src
# 排除的路径
omit =
*/tests/*
*/migrations/*
*/__pycache__/*
*/venv/*
*/virtualenvs/*
*/site-packages/*
setup.py
*/test_*.py
# 分支覆盖率测量
branch = True
# 并行模式
parallel = True
[report]
# 排除的模式
exclude_lines =
# 不要检查pragma语句
pragma: no cover
# 不要检查抽象方法
def __abstract__
# 不要检查类型提示
^\s*# type:.*$
# 不要检查调试代码
^\s*if settings.DEBUG:.*$
^\s*if __name__ == .__main__.:.*$
# 不要检查只包含pass的行
^\s*pass\s*$
# 不要检查raise NotImplemetedError
^\s*raise NotImplementedError.*$
# 不要检查只有文档字符串的函数
^\s*def .*\):\s*\n\s*\"\"\".*\"\"\".*$
# 精度
precision = 2
# 显示缺少的行
show_missing = True
[html]
# HTML报告配置
directory = coverage_html
title = 测试覆盖率报告6.2 覆盖率实战技巧
python
# src/calculator.py
"""计算器模块"""
from typing import Union
class Calculator:
"""计算器类"""
def __init__(self):
self.memory = 0
def add(self, a: Union[int, float], b: Union[int, float]) -> Union[int, float]:
"""加法"""
if not (isinstance(a, (int, float)) and isinstance(b, (int, float))):
raise TypeError("参数必须是数字")
return a + b
def subtract(self, a: Union[int, float], b: Union[int, float]) -> Union[int, float]:
"""减法"""
if not (isinstance(a, (int, float)) and isinstance(b, (int, float))):
raise TypeError("参数必须是数字")
return a - b
def multiply(self, a: Union[int, float], b: Union[int, float]) -> Union[int, float]:
"""乘法"""
if not (isinstance(a, (int, float)) and isinstance(b, (int, float))):
raise TypeError("参数必须是数字")
return a * b
def divide(self, a: Union[int, float], b: Union[int, float]) -> Union[int, float]:
"""除法"""
if not (isinstance(a, (int, float)) and isinstance(b, (int, float))):
raise TypeError("参数必须是数字")
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("除数不能为零")
return a / b
def memory_store(self, value: Union[int, float]):
"""存储到内存"""
self.memory = value
def memory_recall(self) -> Union[int, float]:
"""从内存读取"""
return self.memory
def memory_clear(self):
"""清空内存"""
self.memory = 0
python
# tests/test_calculator.py
"""计算器测试"""
import pytest
from src.calculator import Calculator
class TestCalculator:
"""计算器测试类"""
@pytest.fixture
def calc(self):
"""计算器夹具"""
return Calculator()
# 参数化测试加法
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,expected", [
(1, 2, 3),
(-1, 1, 0),
(0, 0, 0),
(3.14, 2.86, 6.0),
])
def test_add(self, calc, a, b, expected):
"""测试加法"""
result = calc.add(a, b)
assert result == expected
# 测试异常情况
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,exception", [
("1", 2, TypeError),
(1, "2", TypeError),
(None, 2, TypeError),
])
def test_add_type_error(self, calc, a, b, exception):
"""测试加法类型错误"""
with pytest.raises(exception):
calc.add(a, b)
# 测试除法
def test_divide(self, calc):
"""测试除法"""
assert calc.divide(10, 2) == 5
assert calc.divide(5, 2) == 2.5
def test_divide_by_zero(self, calc):
"""测试除零错误"""
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="除数不能为零"):
calc.divide(10, 0)
# 测试内存功能
def test_memory_operations(self, calc):
"""测试内存操作"""
# 初始内存为0
assert calc.memory_recall() == 0
# 存储到内存
calc.memory_store(42)
assert calc.memory_recall() == 42
# 清空内存
calc.memory_clear()
assert calc.memory_recall() == 0
# 综合测试
def test_complex_calculation(self, calc):
"""复杂计算测试"""
result = calc.add(10, 20)
result = calc.multiply(result, 2)
result = calc.subtract(result, 15)
result = calc.divide(result, 5)
calc.memory_store(result)
assert result == 9.0
assert calc.memory_recall() == 9.0生成覆盖率报告:
python
# 运行测试并生成报告
pytest tests/test_calculator.py -v --cov=src --cov-report=term-missing --cov-report=html
# 输出示例
# ---------- coverage: platform darwin, python 3.9.0-final-0 ----------
# Name Stmts Miss Cover Missing
# ----------------------------------------------------
# src/calculator.py 33 0 100%
#
# TOTAL 33 0 100%7. 🚀 持续集成:让测试自动化
7.1 GitHub Actions配置
# .github/workflows/test.yml
name: Python Tests
on:
push:
branches: [ main, develop ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
python-version: [3.8, 3.9, '3.10']
os: [ubuntu-latest, macos-latest, windows-latest]
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:13
env:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
options: >-
--health-cmd pg_isready
--health-interval 10s
--health-timeout 5s
--health-retries 5
ports:
- 5432:5432
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Cache dependencies
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: ~/.cache/pip
key: ${{ runner.os }}-pip-${{ hashFiles('requirements.txt') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-pip-
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install pytest pytest-cov pytest-xdist pytest-mock
- name: Lint with flake8
run: |
pip install flake8
flake8 src --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics
flake8 src --count --exit-zero --max-complexity=10 --max-line-length=127 --statistics
- name: Type check with mypy
run: |
pip install mypy
mypy src --ignore-missing-imports
- name: Test with pytest
env:
DATABASE_URL: postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/test_db
SECRET_KEY: ${{ secrets.SECRET_KEY }}
run: |
pytest tests/ -v \
--cov=src \
--cov-report=xml \
--cov-report=html \
--cov-fail-under=90 \
-n auto
- name: Upload coverage to Codecov
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v3
with:
file: ./coverage.xml
flags: unittests
name: codecov-umbrella
- name: Upload test results
if: always()
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: test-results-${{ matrix.python-version }}-${{ matrix.os }}
path: |
coverage.xml
htmlcov/
retention-days: 77.2 多阶段测试流水线
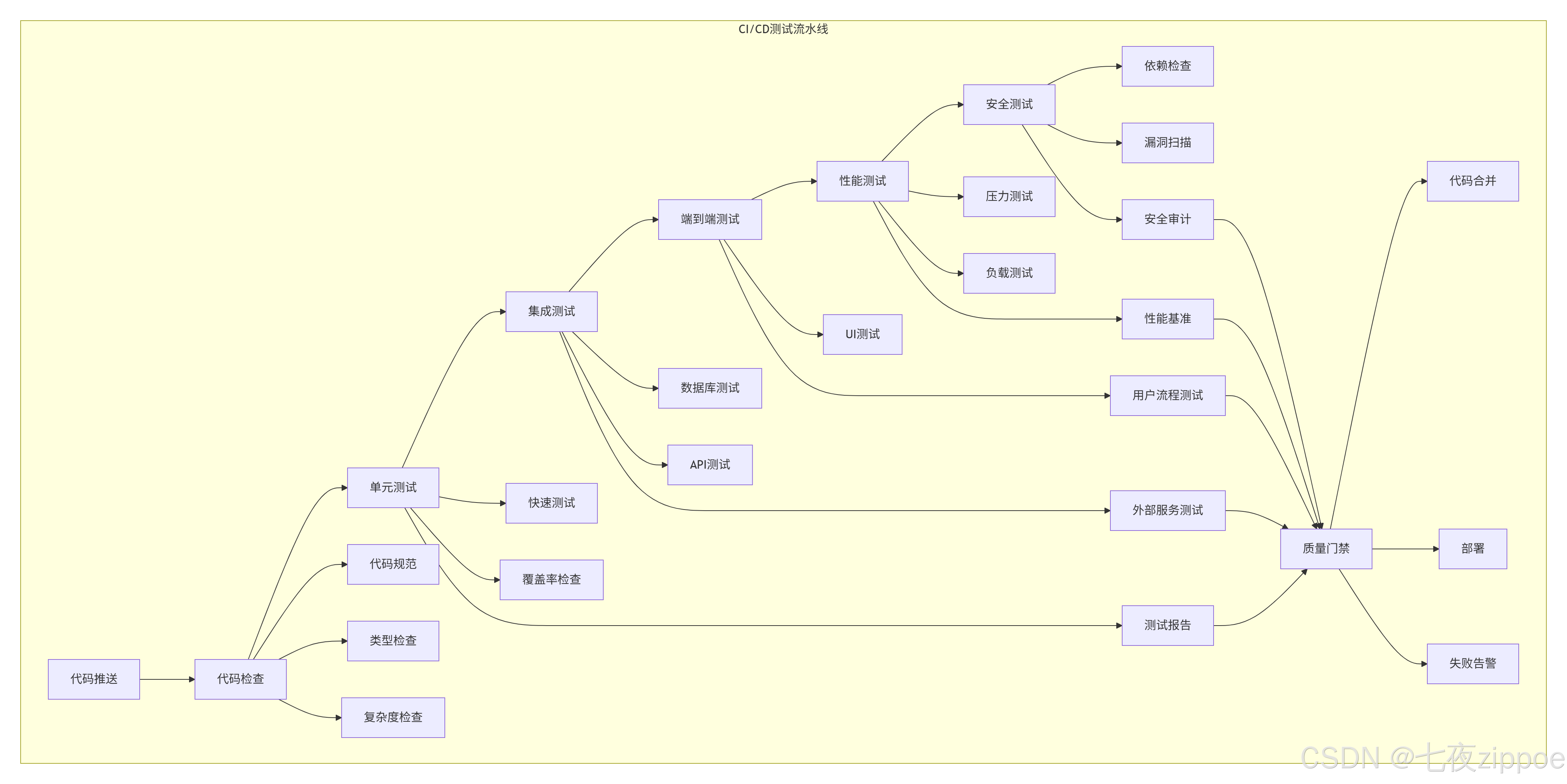
8. 🏢 企业级测试实践
8.1 大型项目测试架构
python
# tests/conftest.py - 项目级共享夹具
"""
项目级测试配置
"""
import pytest
import asyncio
from typing import Generator, AsyncGenerator
import tempfile
import json
from pathlib import Path
# 项目级夹具
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def project_root() -> Path:
"""项目根目录"""
return Path(__file__).parent.parent
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def test_config():
"""测试配置"""
return {
"database": {
"url": "sqlite:///:memory:",
"echo": False
},
"api": {
"base_url": "http://test.example.com",
"timeout": 30
},
"cache": {
"enabled": False,
"ttl": 300
}
}
# 异步支持
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def event_loop() -> Generator[asyncio.AbstractEventLoop, None, None]:
"""创建事件循环"""
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop_policy().new_event_loop()
yield loop
loop.close()
@pytest.fixture
async def async_client():
"""异步HTTP客户端"""
from aiohttp import ClientSession
async with ClientSession() as session:
yield session
# 临时文件管理
@pytest.fixture
def temp_json_file():
"""临时JSON文件"""
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='w', suffix='.json', delete=False) as f:
json.dump({"test": "data"}, f)
temp_path = f.name
yield temp_path
# 清理
Path(temp_path).unlink(missing_ok=True)
# 数据库夹具
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def database_url(test_config):
"""数据库URL"""
return test_config["database"]["url"]
@pytest.fixture
async def db_session(database_url):
"""数据库会话"""
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import create_async_engine, AsyncSession
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
engine = create_async_engine(database_url, echo=False)
async_session = sessionmaker(
engine, class_=AsyncSession, expire_on_commit=False
)
async with async_session() as session:
yield session
await engine.dispose()
# API测试夹具
@pytest.fixture
def api_client():
"""API测试客户端"""
from fastapi.testclient import TestClient
from app.main import app
with TestClient(app) as client:
yield client
# 模拟外部服务
@pytest.fixture
def mock_external_services(monkeypatch):
"""模拟所有外部服务"""
mock_services = {}
# 模拟支付服务
mock_payment = Mock()
mock_payment.charge.return_value = {"success": True, "transaction_id": "123"}
mock_services["payment"] = mock_payment
# 模拟邮件服务
mock_email = Mock()
mock_email.send.return_value = True
mock_services["email"] = mock_email
# 模拟存储服务
mock_storage = Mock()
mock_storage.upload.return_value = "https://example.com/file.txt"
mock_services["storage"] = mock_storage
# 应用模拟
monkeypatch.setattr("app.services.payment", mock_payment)
monkeypatch.setattr("app.services.email", mock_email)
monkeypatch.setattr("app.services.storage", mock_storage)
return mock_services8.2 测试策略与组织
# tests/ 目录结构
"""
tests/
├── conftest.py # 项目级夹具
├── unit/ # 单元测试
│ ├── test_models.py
│ ├── test_services.py
│ └── test_utils.py
├── integration/ # 集成测试
│ ├── test_api.py
│ ├── test_database.py
│ └── test_external.py
├── e2e/ # 端到端测试
│ ├── test_user_flows.py
│ └── test_admin_flows.py
├── performance/ # 性能测试
│ ├── test_load.py
│ └── test_stress.py
├── fixtures/ # 测试数据
│ ├── users.json
│ └── products.json
└── __init__.py
"""
# 测试标记
"""
@pytest.mark.unit # 单元测试
@pytest.mark.integration # 集成测试
@pytest.mark.e2e # 端到端测试
@pytest.mark.slow # 慢速测试
@pytest.mark.fast # 快速测试
@pytest.mark.smoke # 冒烟测试
@pytest.mark.regression # 回归测试
"""
# 运行特定测试
"""
# 只运行单元测试
pytest -m unit
# 运行除慢速测试外的所有测试
pytest -m "not slow"
# 运行特定标记组合
pytest -m "unit and fast"
# 运行特定目录
pytest tests/unit/
# 运行特定文件
pytest tests/unit/test_models.py
# 运行特定类
pytest tests/unit/test_models.py::TestUserModel
# 运行特定方法
pytest tests/unit/test_models.py::TestUserModel::test_create_user
"""
# 测试报告生成
"""
# 生成JUnit格式报告
pytest --junitxml=report.xml
# 生成HTML报告
pytest --html=report.html --self-contained-html
# 生成Allure报告
pytest --alluredir=allure-results
allure serve allure-results
"""9. ⚡ 性能优化技巧
9.1 测试加速技巧
bash
# 1. 并行测试
# pytest.ini
[pytest]
addopts =
-n auto # 自动检测CPU核心数
--dist=loadscope # 按作用域分发测试
# 或者命令行
pytest -n auto # 自动并行
pytest -n 4 # 指定4个进程
# 2. 测试分组
# tests/test_performance.py
import pytest
import time
@pytest.mark.slow
def test_slow_operation():
"""慢速测试"""
time.sleep(5)
assert True
@pytest.mark.fast
def test_fast_operation():
"""快速测试"""
assert 1 + 1 == 2
# 3. 测试缓存
# 使用pytest-cache
pytest --cache-clear # 清除缓存
pytest --cache-show # 显示缓存内容
# 4. 增量测试
# conftest.py
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
"""记录测试结果"""
if "incremental" in item.keywords:
if call.excinfo is not None:
parent = item.parent
parent._previousfailed = item
def pytest_runtest_setup(item):
"""设置增量测试"""
if "incremental" in item.keywords:
previousfailed = getattr(item.parent, "_previousfailed", None)
if previousfailed is not None:
pytest.xfail("previous test failed (%s)" % previousfailed.name)
# 使用示例
@pytest.mark.incremental
class TestUserWorkflow:
"""增量测试:一个失败,后面的都跳过"""
def test_create_user(self):
assert create_user() is not None
def test_login_user(self):
# 如果上面失败,这个测试会被跳过
assert login_user() is True
def test_update_user(self):
assert update_user() is True
# 5. 数据库测试优化
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def database_engine():
"""共享数据库引擎"""
engine = create_engine("sqlite:///:memory:")
# 创建表结构
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
yield engine
engine.dispose()
@pytest.fixture
def db_session(database_engine):
"""使用事务回滚的会话"""
connection = database_engine.connect()
transaction = connection.begin()
session = Session(bind=connection)
yield session
session.close()
transaction.rollback() # 回滚,不保存数据
connection.close()9.2 测试数据工厂
python
# tests/factories.py
"""测试数据工厂"""
from factory import Factory, Faker, LazyAttribute, SubFactory
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import random
class UserFactory(Factory):
"""用户工厂"""
class Meta:
model = dict # 或者使用你的User模型
id = Faker("uuid4")
username = Faker("user_name")
email = Faker("email")
first_name = Faker("first_name")
last_name = Faker("last_name")
is_active = True
is_admin = False
created_at = Faker("date_time_this_year")
@LazyAttribute
def full_name(self):
return f"{self.first_name} {self.last_name}"
@classmethod
def admin(cls, **kwargs):
"""创建管理员用户"""
return cls(is_admin=True, **kwargs)
@classmethod
def inactive(cls, **kwargs):
"""创建非活跃用户"""
return cls(is_active=False, **kwargs)
class OrderFactory(Factory):
"""订单工厂"""
class Meta:
model = dict
id = Faker("uuid4")
user = SubFactory(UserFactory)
order_date = Faker("date_time_this_month")
@LazyAttribute
def total_amount(self):
return round(random.uniform(10, 1000), 2)
@LazyAttribute
def status(self):
return random.choice(["pending", "processing", "shipped", "delivered", "cancelled"])
@classmethod
def with_items(cls, item_count=3, **kwargs):
"""创建带商品的订单"""
order = cls(**kwargs)
order["items"] = [OrderItemFactory() for _ in range(item_count)]
return order
# 使用示例
def test_user_creation():
"""测试用户创建"""
# 创建普通用户
user = UserFactory()
assert user["is_active"] is True
assert user["is_admin"] is False
# 创建管理员用户
admin = UserFactory.admin()
assert admin["is_admin"] is True
# 批量创建
users = UserFactory.create_batch(10)
assert len(users) == 10
# 创建特定属性用户
inactive_user = UserFactory.inactive(username="inactive_user")
assert inactive_user["is_active"] is False
assert inactive_user["username"] == "inactive_user"10. 🔧 故障排查指南
10.1 常见问题与解决
问题1:测试运行缓慢
python
# 解决方案:优化测试性能
# 1. 使用会话级夹具
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def expensive_resource():
"""昂贵的资源,整个会话只创建一次"""
resource = create_expensive_resource()
yield resource
resource.cleanup()
# 2. 禁用不必要的插件
# pytest.ini
[pytest]
addopts =
--tb=short # 简短回溯
-q # 安静模式
--disable-warnings
# 3. 使用测试标记
@pytest.mark.fast
def test_fast_operation():
"""快速测试"""
pass
@pytest.mark.slow
def test_slow_operation():
"""慢速测试,只在需要时运行"""
pass
# 只运行快速测试
# pytest -m fast问题2:测试不稳定(flaky tests)
python
# 解决方案:稳定测试
import pytest
import time
from tenacity import retry, stop_after_attempt, wait_fixed
# 1. 使用重试机制
@pytest.mark.flaky(reruns=3, reruns_delay=1)
def test_flaky_api():
"""不稳定API测试,自动重试3次"""
response = call_flaky_api()
assert response.status_code == 200
# 2. 使用tenacity库
@retry(stop=stop_after_attempt(3), wait=wait_fixed(1))
def call_flaky_api():
"""调用不稳定API,自动重试"""
return requests.get("https://api.example.com")
# 3. 增加等待时间
def test_with_wait():
"""需要等待的测试"""
result = start_async_operation()
# 等待最多10秒
for _ in range(10):
if result.is_done():
break
time.sleep(1)
else:
pytest.fail("操作超时")
assert result.success is True
# 4. 使用固定时间
@pytest.fixture
def fixed_time(monkeypatch):
"""固定时间,避免时间相关的不稳定"""
class FixedDatetime:
@classmethod
def now(cls):
return datetime(2024, 1, 1, 12, 0, 0)
monkeypatch.setattr("datetime.datetime", FixedDatetime)问题3:测试依赖问题
python
# 解决方案:解耦测试依赖
# 1. 使用依赖注入
class UserService:
def __init__(self, db_session, cache_client, email_service):
self.db = db_session
self.cache = cache_client
self.email = email_service
def register_user(self, user_data):
# 使用注入的依赖
user = self.db.create_user(user_data)
self.cache.set(f"user:{user.id}", user)
self.email.send_welcome(user.email)
return user
# 测试
def test_user_registration():
"""测试用户注册"""
# 创建模拟依赖
mock_db = Mock()
mock_cache = Mock()
mock_email = Mock()
# 创建服务
service = UserService(mock_db, mock_cache, mock_email)
# 测试
result = service.register_user({"email": "test@example.com"})
# 验证
mock_db.create_user.assert_called_once()
mock_cache.set.assert_called_once()
mock_email.send_welcome.assert_called_once()
# 2. 使用环境变量配置
import os
from unittest.mock import patch
def test_with_env_vars():
"""测试环境变量"""
with patch.dict(os.environ, {"DEBUG": "True", "SECRET_KEY": "test"}):
# 在这里,环境变量被临时设置
assert os.getenv("DEBUG") == "True"
assert os.getenv("SECRET_KEY") == "test"
# 离开with块后,环境变量恢复10.2 调试技巧
python
# 1. 使用pdb调试
def test_with_debug():
"""在测试中使用调试器"""
result = complex_operation()
# 设置断点
import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
assert result == expected
# 2. 使用--pdb选项
# pytest --pdb # 失败时自动进入pdb
# 3. 详细日志
import logging
def test_with_logging(caplog):
"""捕获和验证日志"""
caplog.set_level(logging.INFO)
# 执行会产生日志的操作
do_something_that_logs()
# 验证日志
assert "Expected log message" in caplog.text
assert len(caplog.records) == 1
assert caplog.records[0].levelname == "INFO"
# 4. 自定义断言消息
def test_with_better_assertions():
"""更好的断言消息"""
result = calculate()
# 不好的断言
assert result == expected
# 好的断言
assert result == expected, f"""
计算结果不符合预期!
实际: {result}
预期: {expected}
差值: {result - expected}
"""11. 📚 学习资源与总结
11.1 官方文档
-
**pytest官方文档** - 最全面的pytest文档
-
**pytest-cov文档** - 覆盖率测试
-
**pytest-mock文档** - Mock和patch
-
**pytest-xdist文档** - 并行测试
-
**pytest-asyncio文档** - 异步测试
11.2 最佳实践总结
测试金字塔:
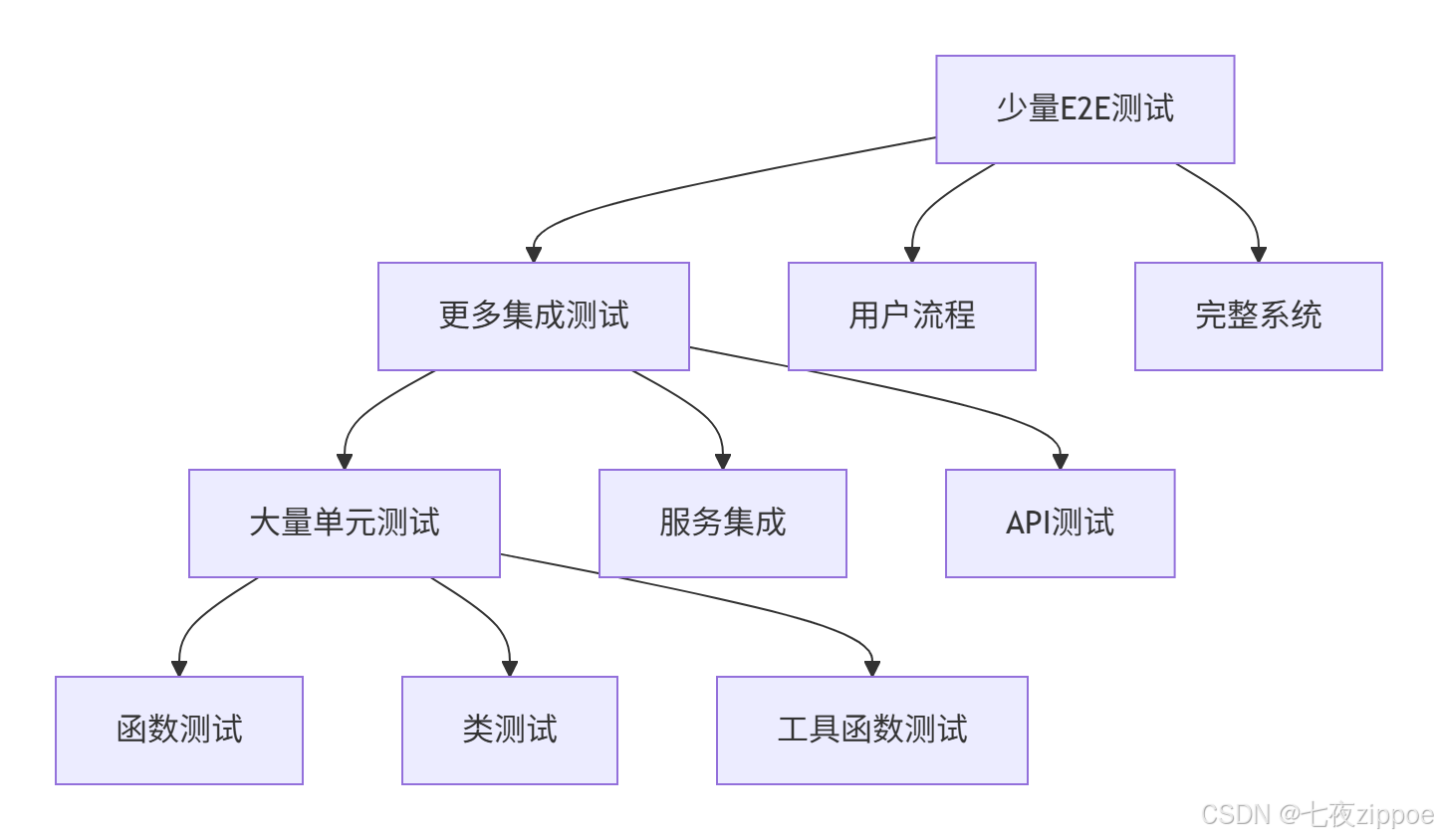
我的经验总结:
-
测试要快:一个测试套件超过5分钟就是失败的
-
测试要稳定:不稳定的测试比没测试更糟糕
-
测试要简单:测试代码应该比业务代码简单
-
测试要隔离:测试之间不能有依赖
-
测试要真实:尽量接近生产环境
pytest高级特性速查:
| 特性 | 使用场景 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 夹具 | 测试准备和清理 | @pytest.fixture |
| 参数化 | 多数据测试 | @pytest.mark.parametrize |
| 猴子补丁 | 模拟外部依赖 | monkeypatch.setattr |
| 标记 | 测试分类 | @pytest.mark.slow |
| 覆盖率 | 测试质量 | pytest --cov |
| 并行 | 加速测试 | pytest -n auto |
11.3 未来趋势
-
AI辅助测试:自动生成测试用例
-
智能测试选择:只运行受影响的测试
-
可视化测试:图形化测试结果和覆盖率
-
云测试:在云上运行测试,利用弹性资源
-
测试即代码:测试配置完全代码化
最后的话 :好的测试不是负担,而是开发者的安全网 。pytest让测试变得简单、强大、有趣。记住:测试不是为了通过,而是为了发现问题 。写测试的时候,要想着怎么让代码失败,而不是怎么让它通过。