目录
[一 stack常见构造](#一 stack常见构造)
[1 空容器构造函数(默认构造函数)](#1 空容器构造函数(默认构造函数))
[2. 使用指定容器构造](#2. 使用指定容器构造)
[3 拷贝构造函数](#3 拷贝构造函数)
[二 其他操作](#二 其他操作)
[1 empty](#1 empty)
[2 size](#2 size)
[3 top](#3 top)
[4 push && pop](#4 push && pop)
[5 emplace](#5 emplace)
[6 swap](#6 swap)
[三 总结](#三 总结)
一 stack常见构造
1 空容器构造函数(默认构造函数)
构造一个没有元素的空容器。
2. 使用指定容器构造
可以使用指定的底层容器来构造栈,默认是 std::deque,但也可以是 std::vector 或 std::list
3 拷贝构造函数
构造一个容器,其中包含 x 中每个元素的副本,顺序相同
cpp
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
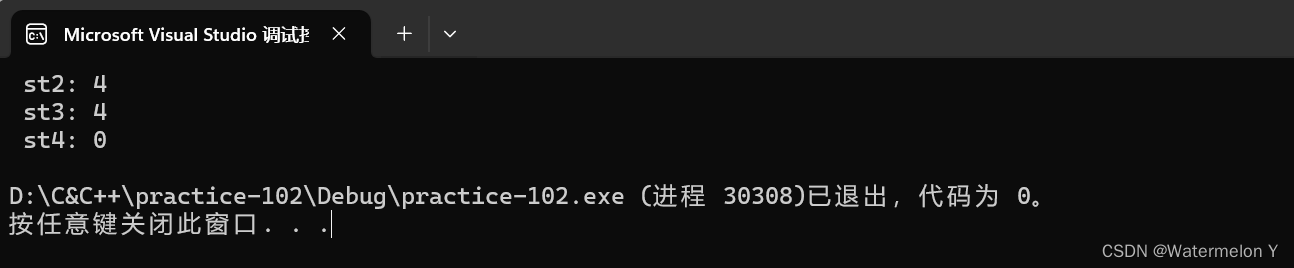
stack<int> st1;
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4 };
stack<int, vector<int>> st2(v);
cout << " st2: " << st2.size() << endl;
stack<int, vector<int>> st3(st2);
cout << " st3: " << st3.size() << endl;
stack<int> st4(st1);
cout << " st4: " << st4.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
二 其他操作
1 empty
返回容器是否为空(即其大小是否为 0)
cpp
void Test1()
{
stack<int> st;
if (st.empty()) cout << " st is empty" << endl;
else cout << "st is not empty" << endl;
}
2 size
上面已经演示过了, 这里不说明了
3 top
返回栈顶元素
cpp
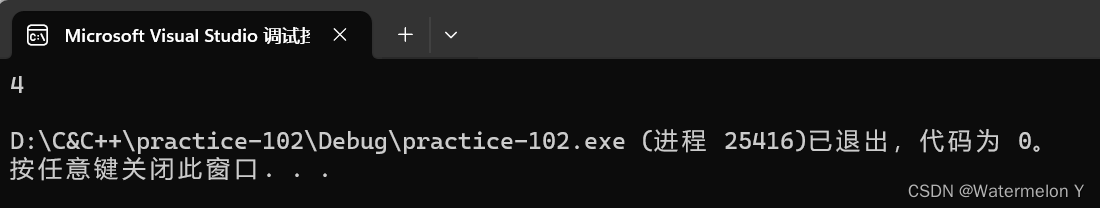
void Test2()
{
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4 };
stack<int, vector<int>> st(v);
cout << st.top() << endl;
}
4 push && pop
cpp
void push (const value_type& val);
void push (value_type&& val);
void pop();
cpp
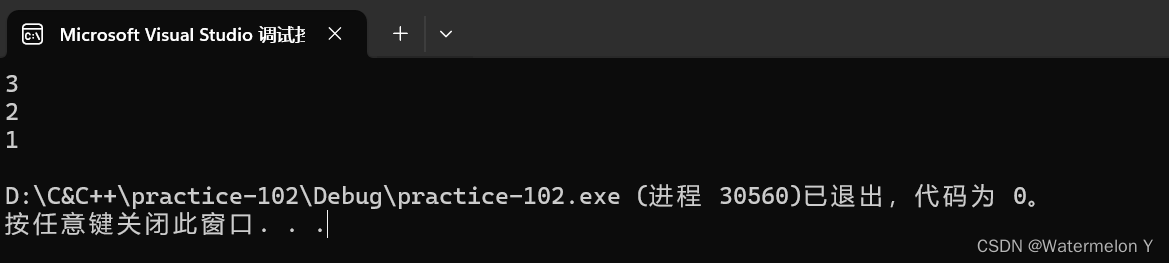
void Test3()
{
stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
while (!st.empty())
{
cout << st.top() << endl;
st.pop();
}
}
5 emplace
emplace 作用和 push 一样的, 只是效率不一样, 涉及到了右值引用问题, 后面再讲
cpp
void Test4()
{
stack<string> st;
st.emplace("first");
st.emplace("second");
while (!st.empty())
{
cout << st.top() << endl;
st.pop();
}
}
6 swap
交换两个容器的内容
cpp
void swap (stack& x)
cpp
void Test5()
{
stack<int> st1, st2;
st1.push(1);
st1.push(2);
cout << st1.size() << endl;
st2.push(10);
st2.push(20);
st2.push(30);
cout << st2.size() << endl;
st1.swap(st2);
cout << st1.size() << endl;
cout << st2.size() << endl;
}
三 总结
这节栈的使用非常简单的, 感觉没有啥要讲的, 重要的是后面 栈的模拟实现还有和 队列联合使用. 对本节概念不清楚的, 可以看看我之前写的栈数据结构. 那里就很清晰了.
这两天成都一直下雨, 冷. 脑壳还有点晕, 最近学习Linux系统, 学到线程了, 早听说线程难, 没想到这么难.继续加油吧!