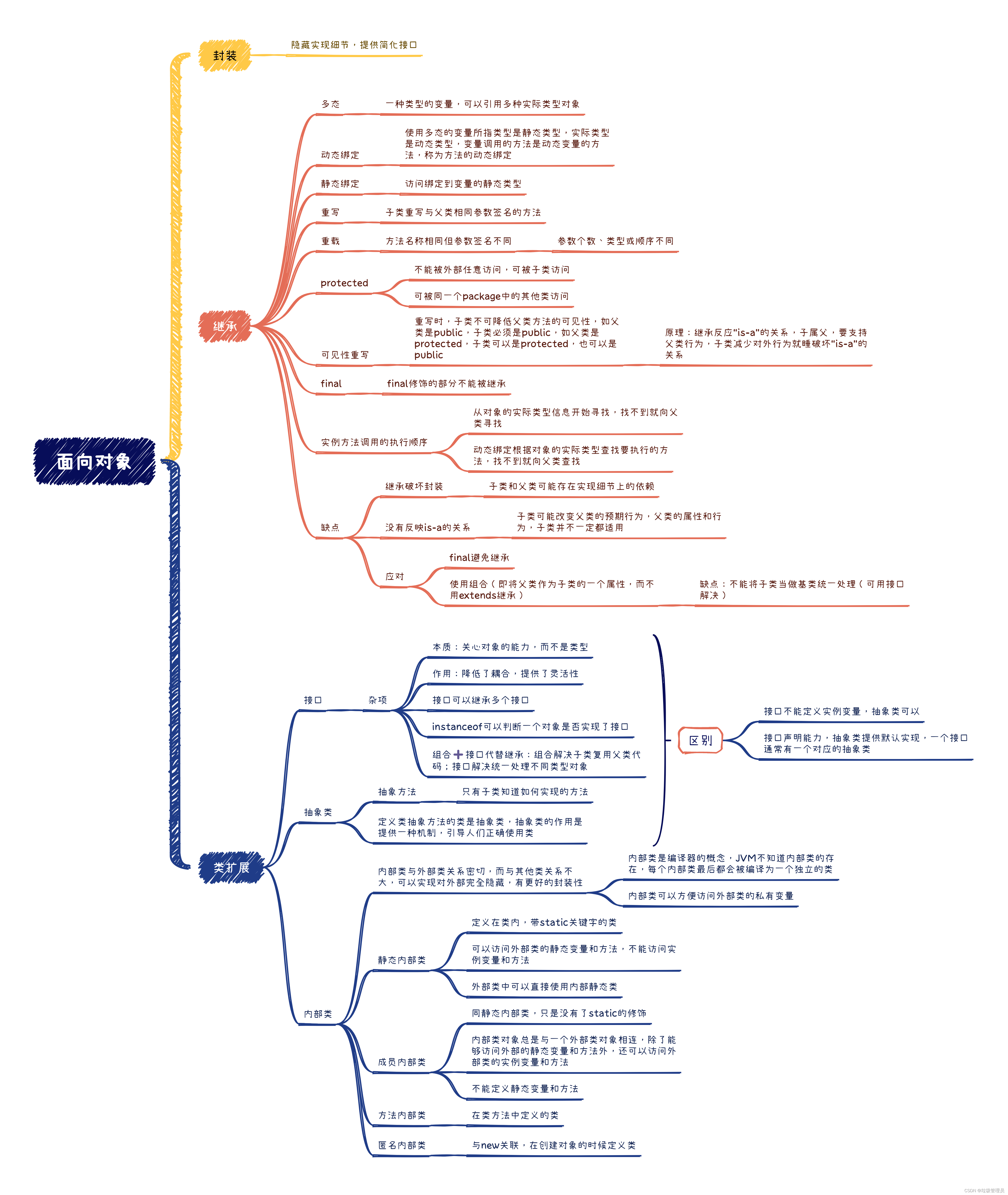
多态
一种类型的变量可以引用多种实际类型的对象
如
java
package ooplearn;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal[] animals = new Animal[2];
animals[0] = new Dog();
animals[1] = new Cat();
for (Animal animal : animals){
animal.eat();
}
}
}
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal eat");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Dog eat");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Cat eat");
}
}Animal类型的变量animal可以引用Dog和Cat类型对象,称为多态 。Animal就是animal变量的静态类型 ,Dog和Cat就是animal变量的动态类型 。animal.eat()调用的是变量动态类型的方法,称为动态绑定。
静态绑定
java
package ooplearn;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d = new Dog();
Animal a = d;
System.out.println(d.title); // return Dog
System.out.println(a.title); // return Animal
}
}
class Animal {
public static String title = "Animal";
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public static String title = "Dog";
}变量d的静态类型是Dog,访问Dog变量和方法,变量a的静态类型是Animal,访问Animal的变量和方法。访问绑定到变量的静态类型,称静态绑定。
实例方法调用顺序
java
package ooplearn;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal[] animals = new Animal[2];
animals[0] = new Dog();
animals[1] = new Cat();
for (Animal animal : animals){
animal.eat();
}
}
}
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal eat");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Dog eat");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
}上述代码返回
Dog eat
Animal eat循环输出的过程animal变量的实际类型分别为Dog和Cat,先从实际类型找方法,找不到就去父类找。
内部类
定义在类里的类称为内部类,一般与外部类(包含内部类的类)关系密切,与其他类关系不大。一般对外隐藏,有更好的封装性。如Swing编程中为组件创建ActionListener:
java
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
public class TwoButtons {
JFrame frame;
JLabel label;
public static void main(String[] args) {
TwoButtons gui = new TwoButtons();
gui.go();
}
public void go() {
frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JButton labelButton = new JButton("Change Label");
labelButton.addActionListener(new LabelListener());
JButton colorButton = new JButton("Change Circle");
colorButton.addActionListener(new ColorListener());
label = new JLabel("I'm a label");
MyDrawPanel drawPanel = new MyDrawPanel();
}
class LabelListener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
label.setText("Ouch!");
}
}
class ColorListener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
frame.repaint();
}
}
}权限修饰符
| 修饰 | 本类 | 本包 | 其他包子类 | 其他包 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| private | Y | N | N | N |
| 不写 | Y | Y | N | N |
| protected | Y | Y | Y | N |
| public | Y | Y | Y | Y |
private修饰部分只能在本类中使用;缺省状态下,可见性上升到当前包内,即在同一个包内的地方可以使用;protected范围还包括本包之外其他包属于自己子类的部分;public没限制。
导图