1.认识线程(Thread)



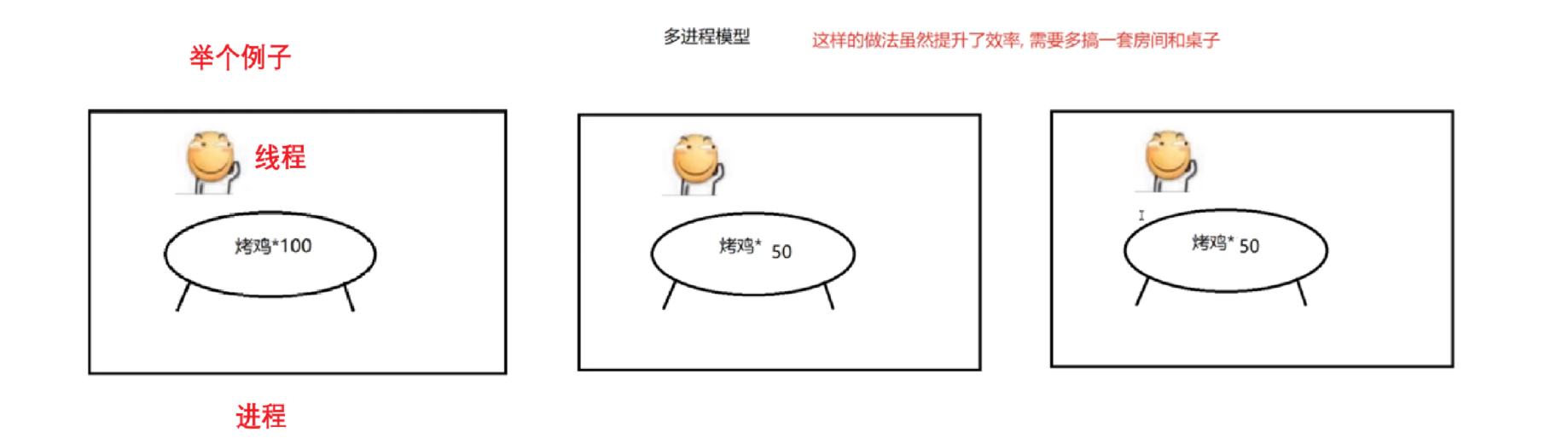


1.1 概念




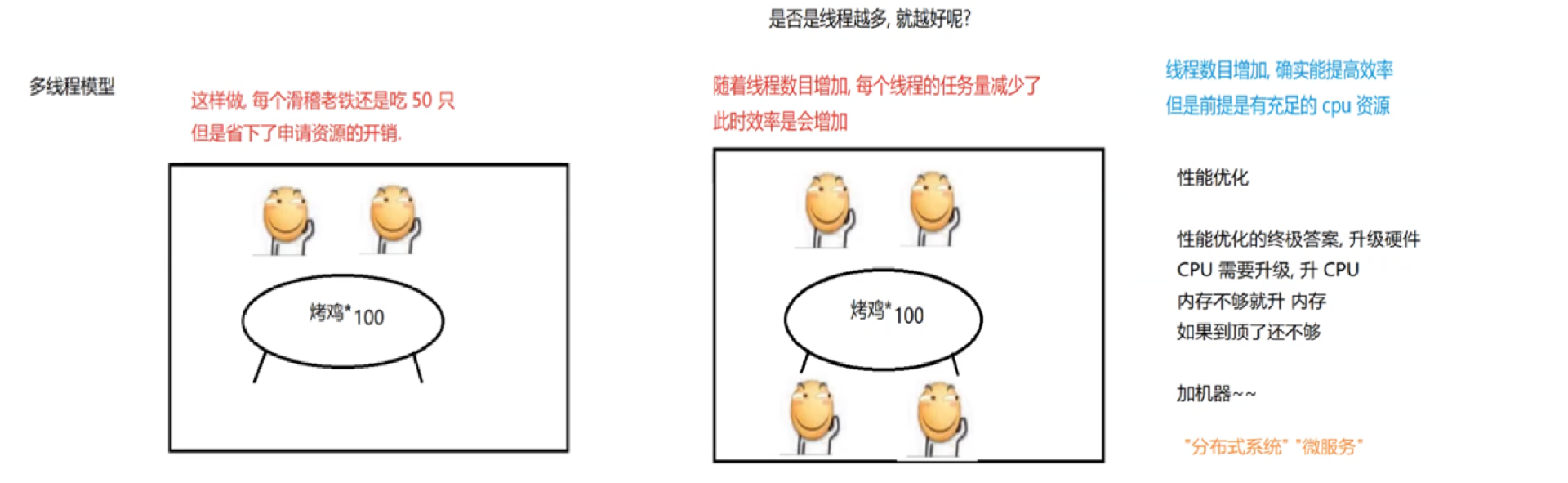
1.2 创建线程(lambda最常用)

1.2.1 方法1 - 继承Thread类
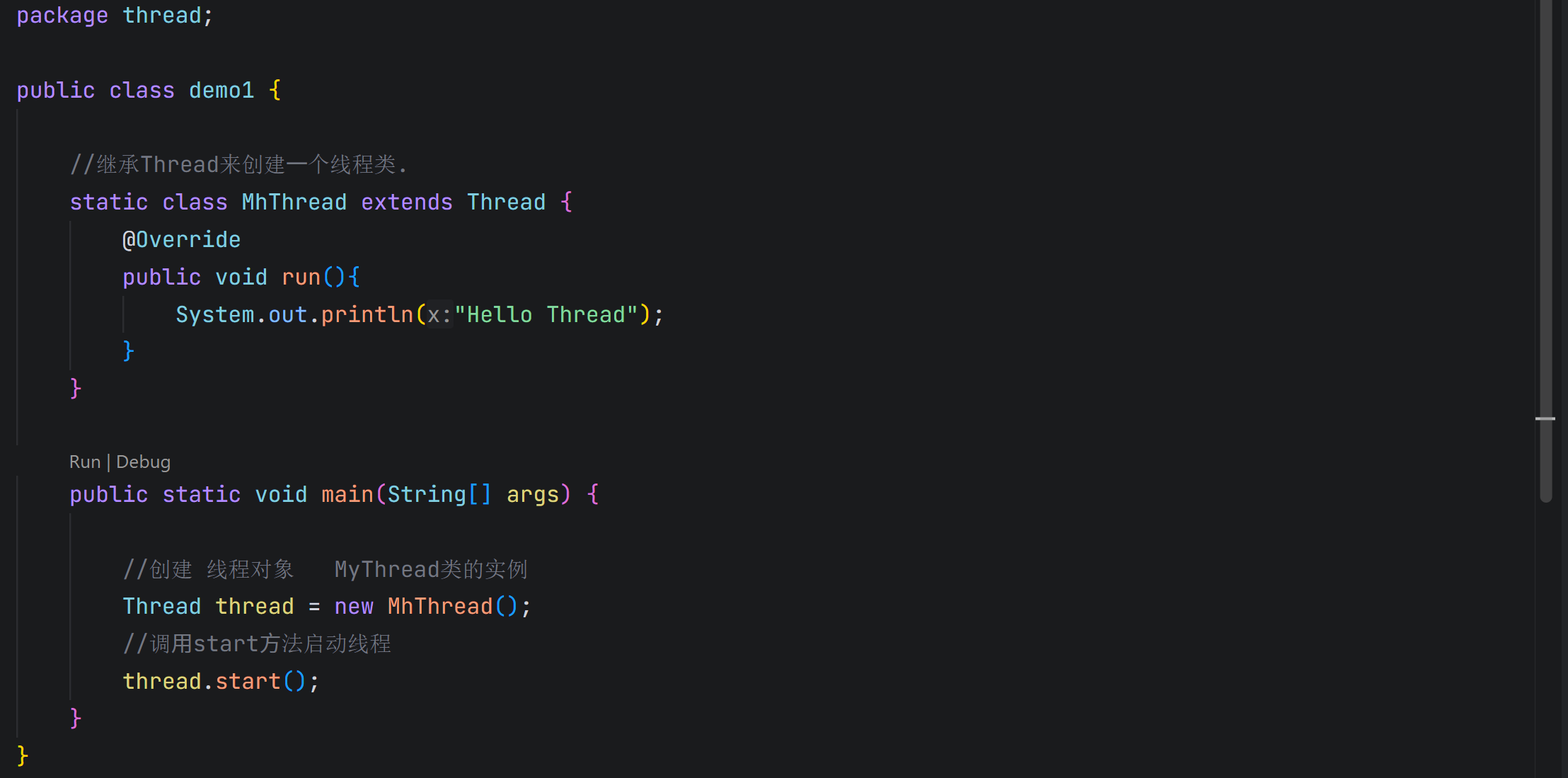


【 Ctrl + C 取消 终止 】



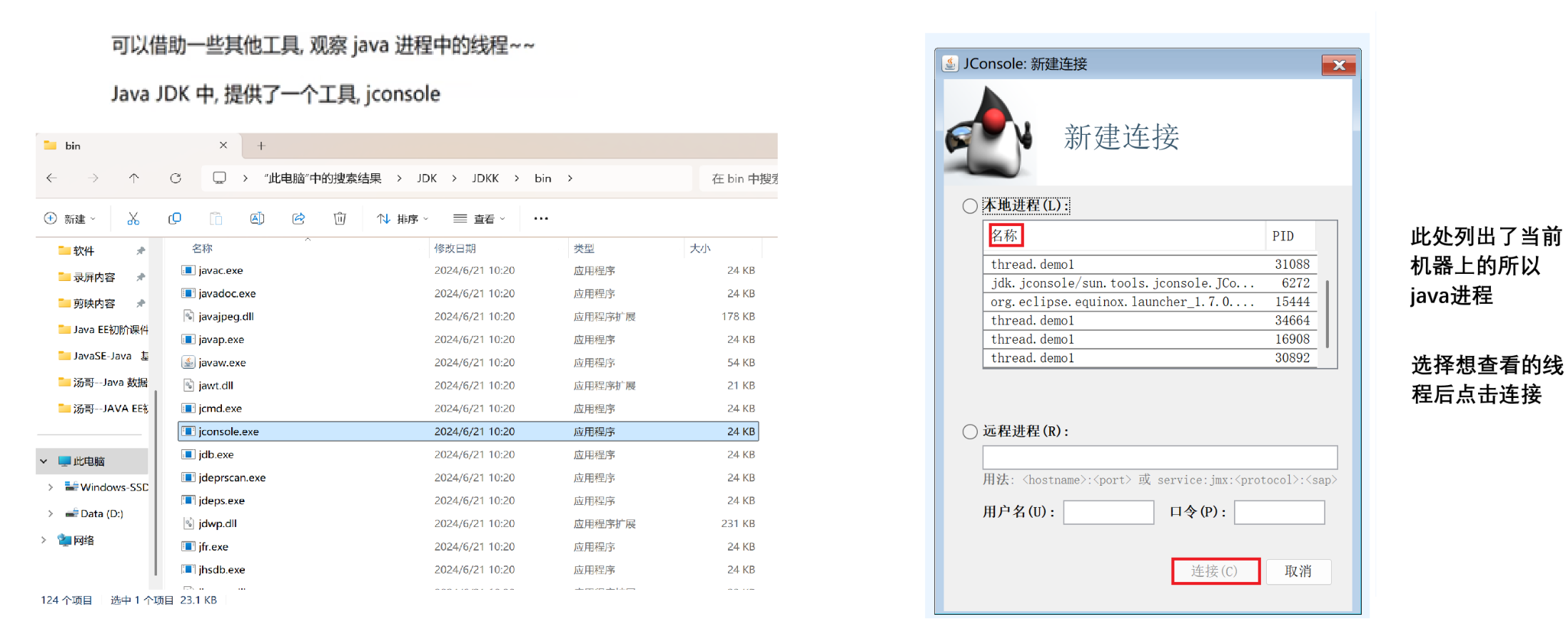
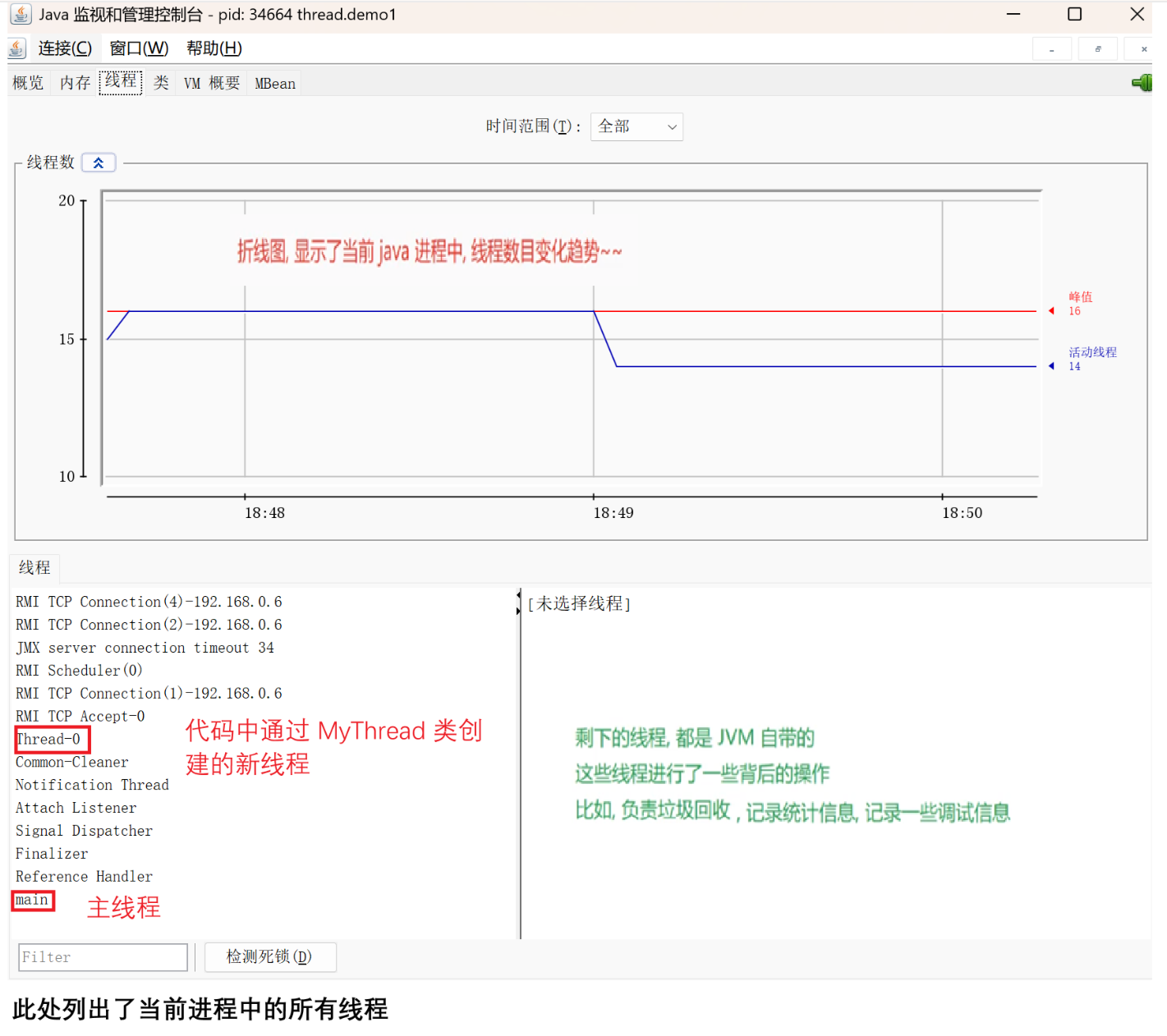
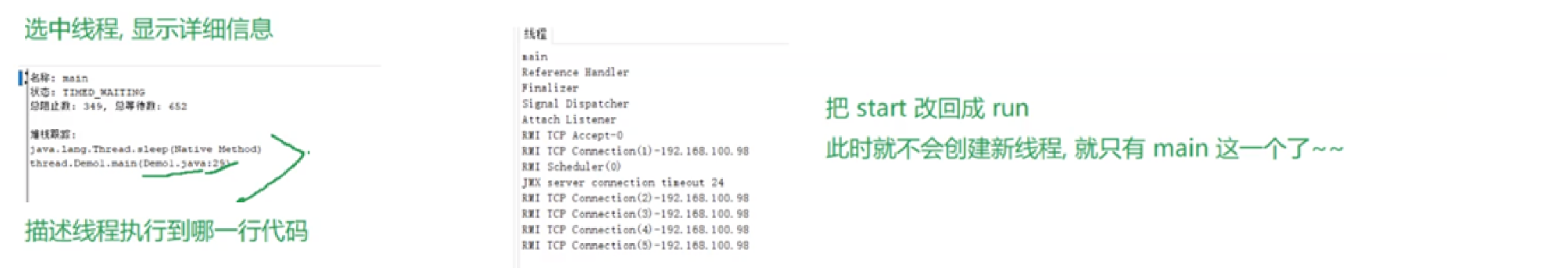
1.2.2 方法2 - 实现Runnable接口
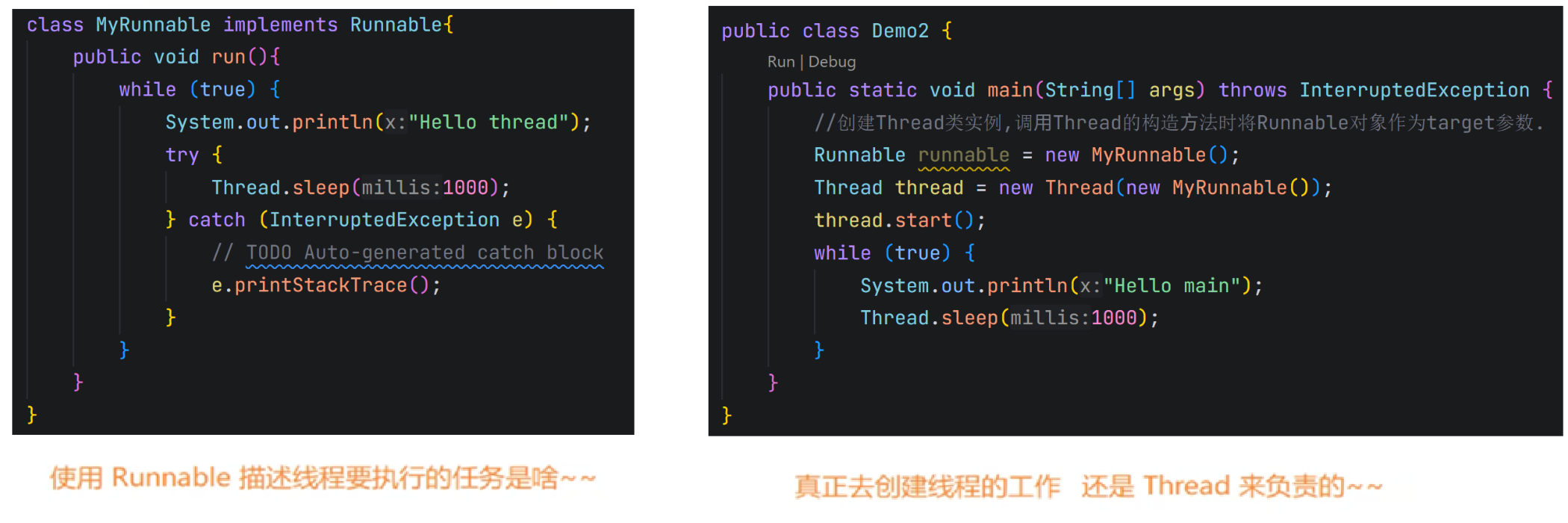
1.2.3 总结


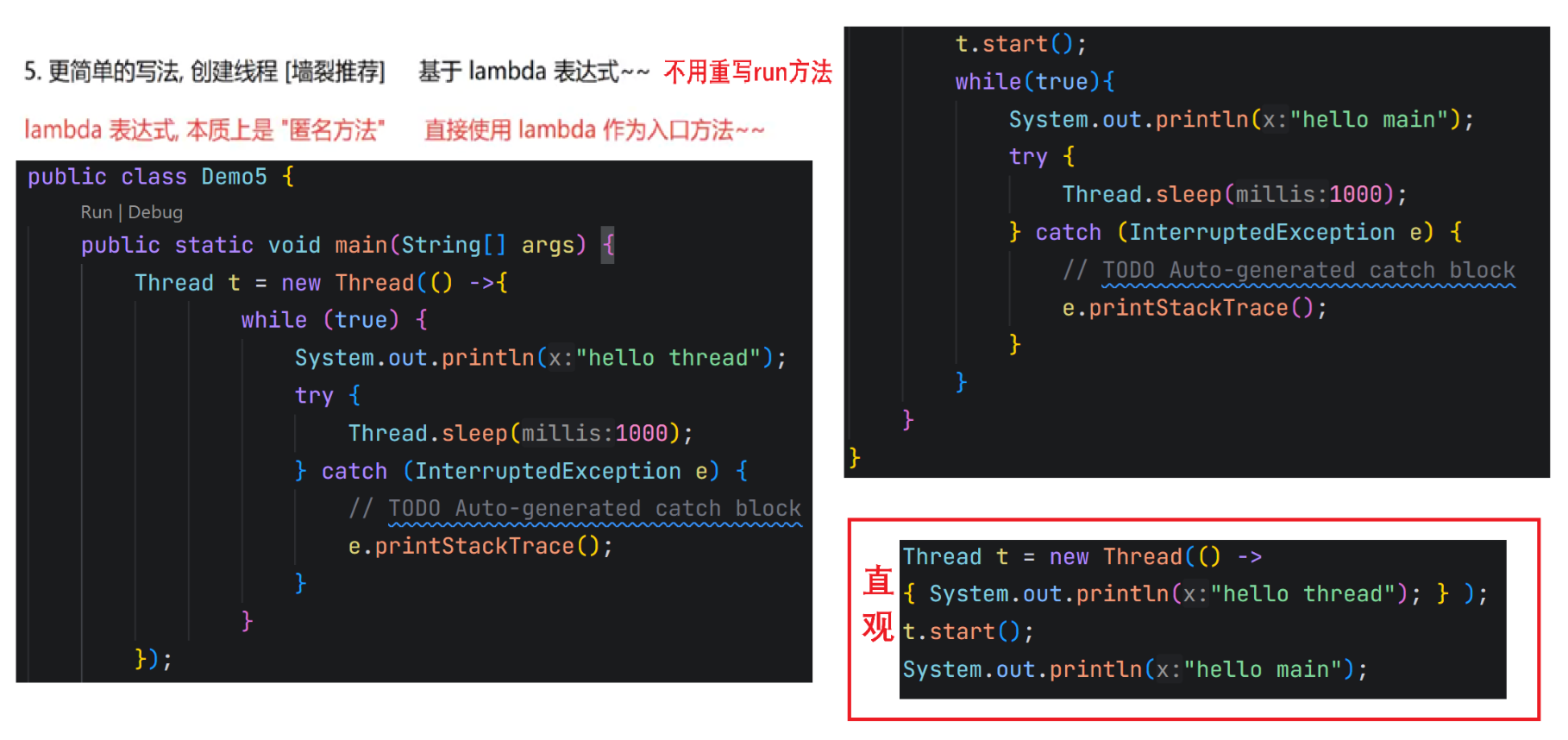
1.2.4 匿名内部类



2.Thread类及常见方法
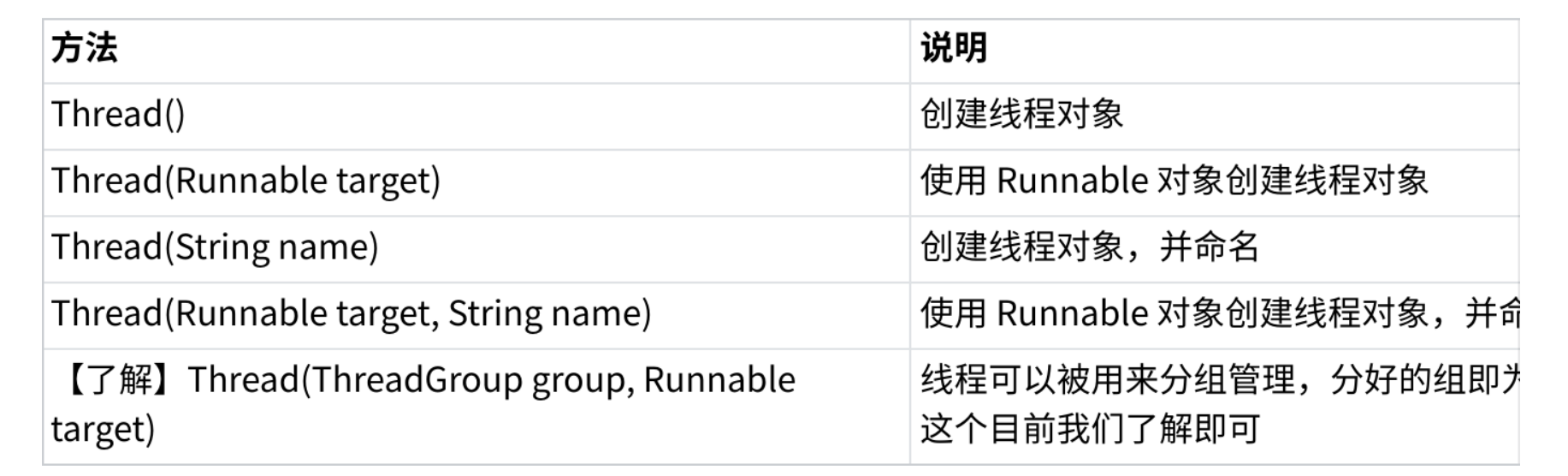
2.1 构造方法
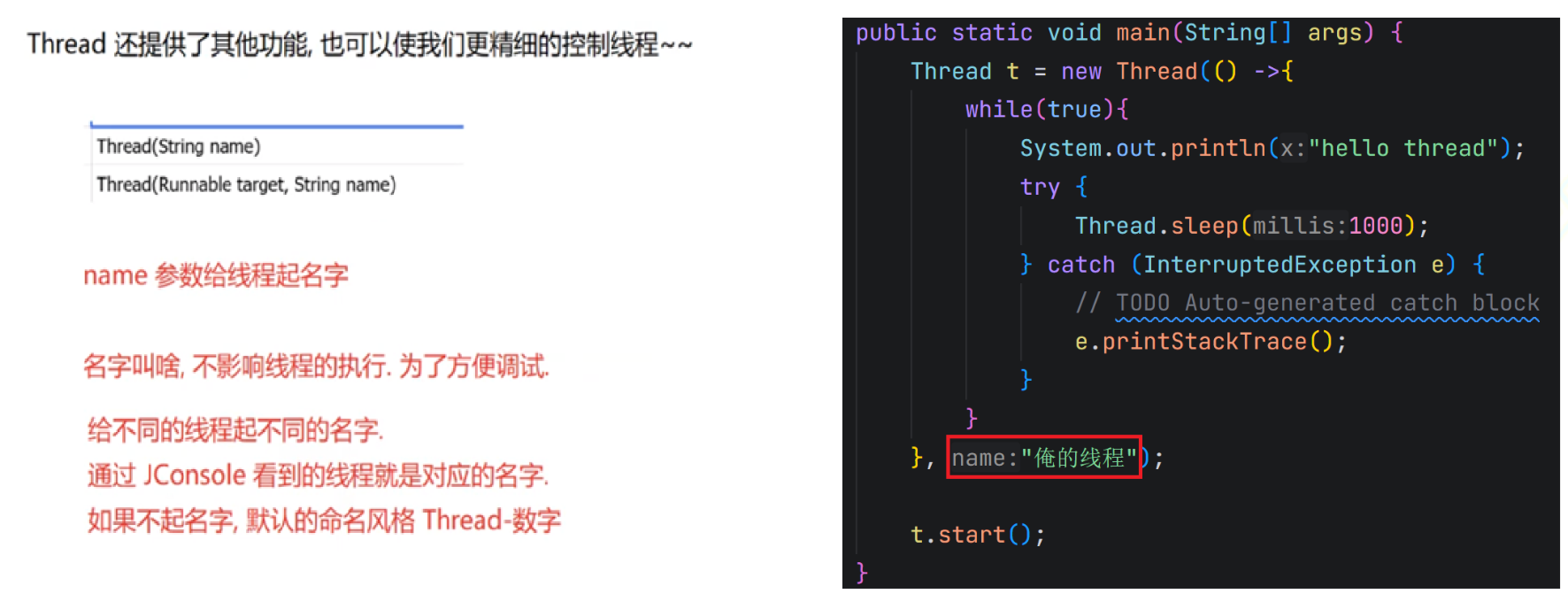

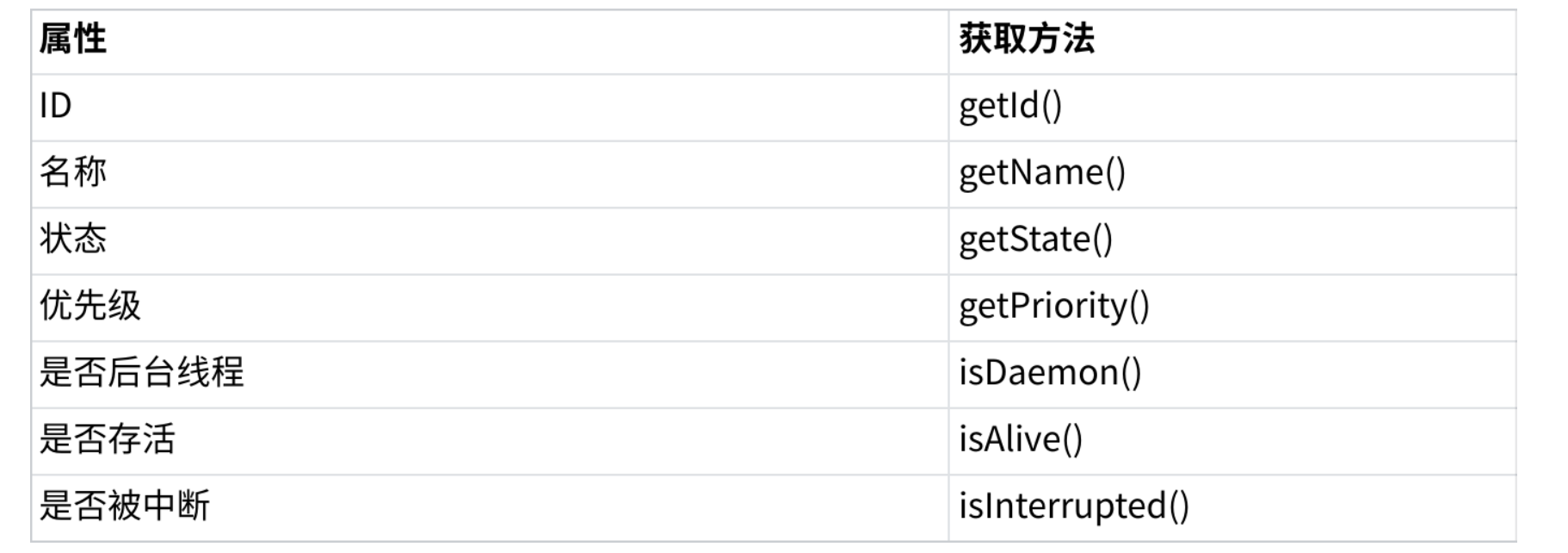
2.2 常见属性
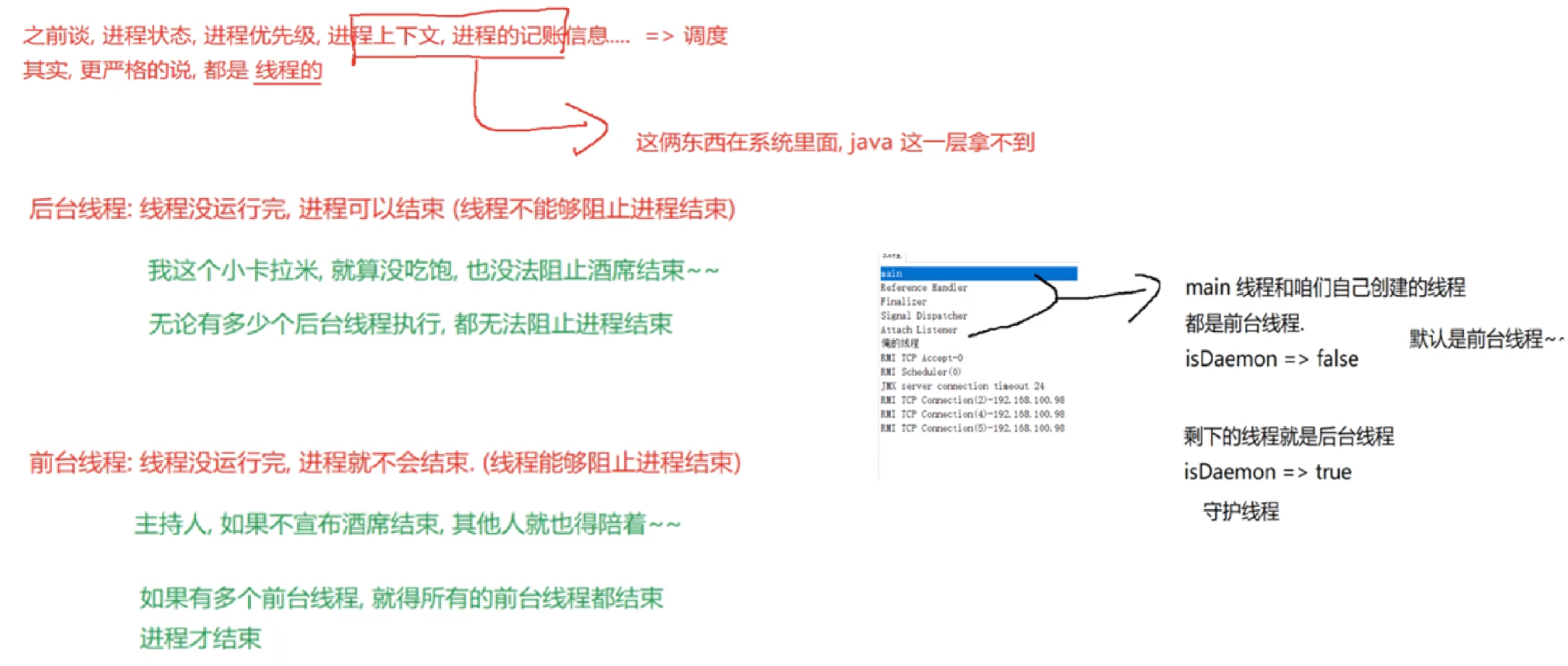
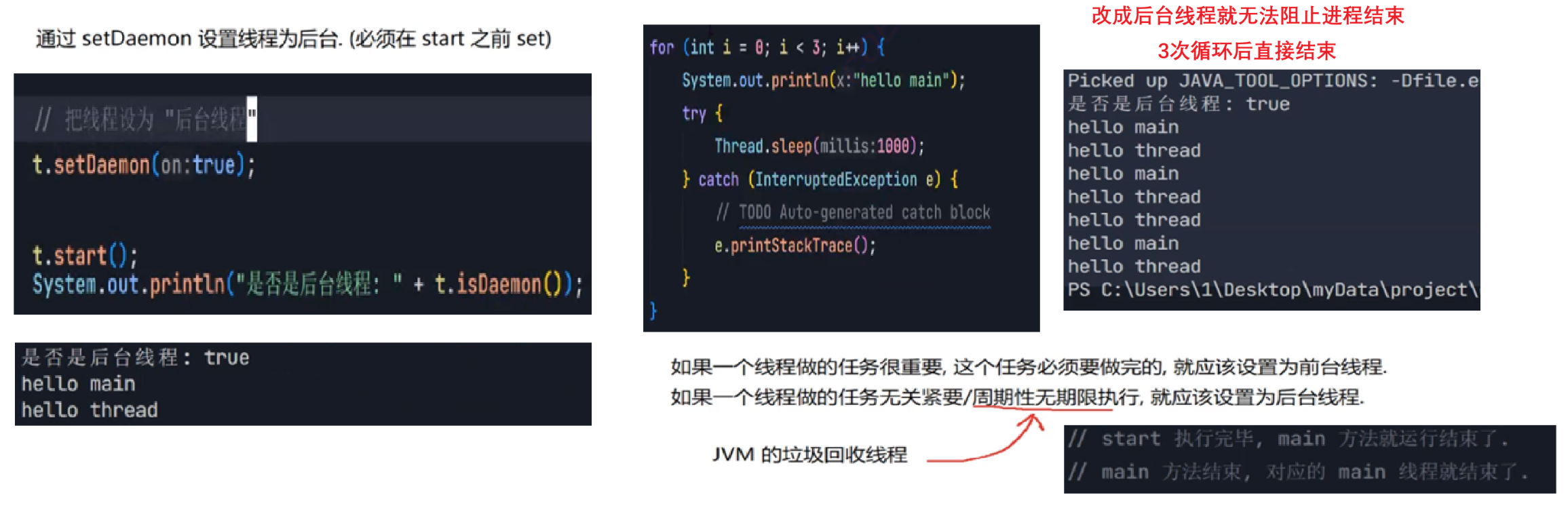

2.3 启动一个线程 start()

调用start方法,才真的在操作系统的底层创建出⼀个线程。


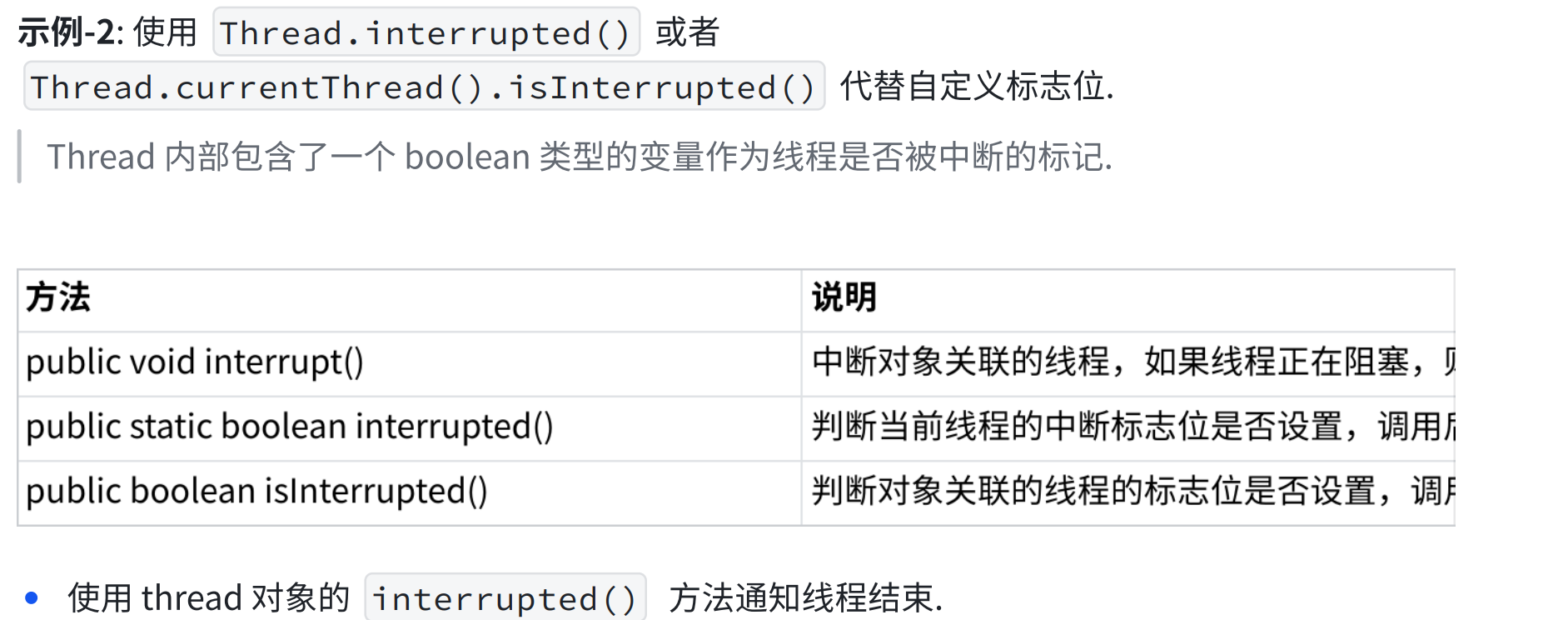
2.4 中断一个线程


java
package thread;
public class Demo7 {
private static boolean flag = true;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while(flag){
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
System.out.println("hello main");
Thread.sleep(3000);
flag = false;
System.out.println("让 t 线程终止");
}
}

java
package thread;
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
System.out.println("hello main");
Thread.sleep(3000);
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("t 线程的中断标志位:" + t.isInterrupted());
}
}



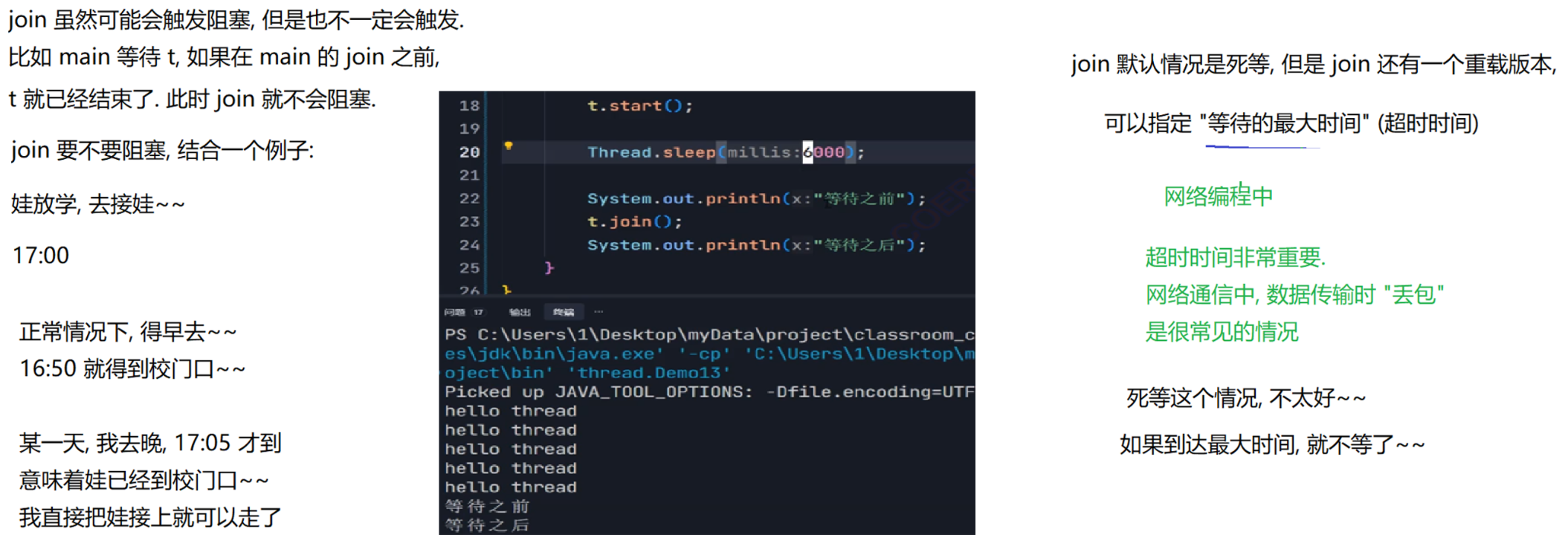
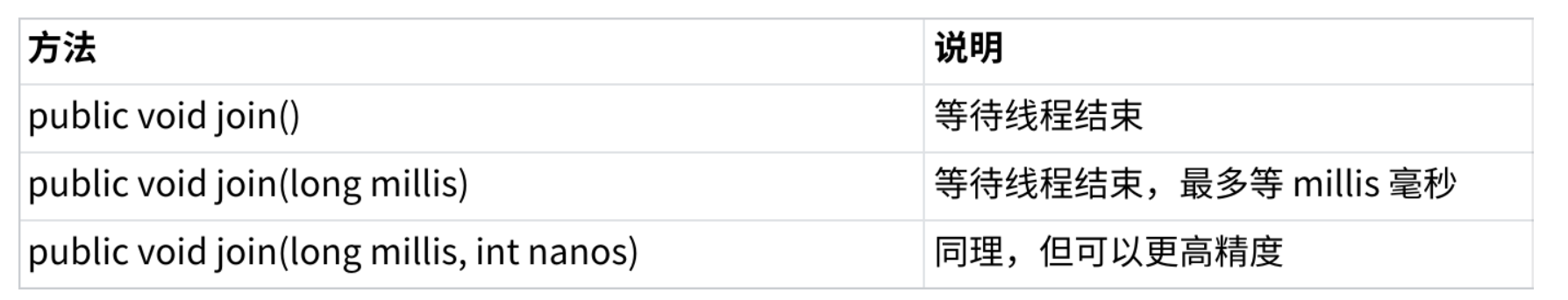
2.5 等待一个线程 join()
有时,我们需要等待一个线程完成它的工作后,才能进的下⼀步工作,这时我们需要⼀个方法明确等待线程的结束。
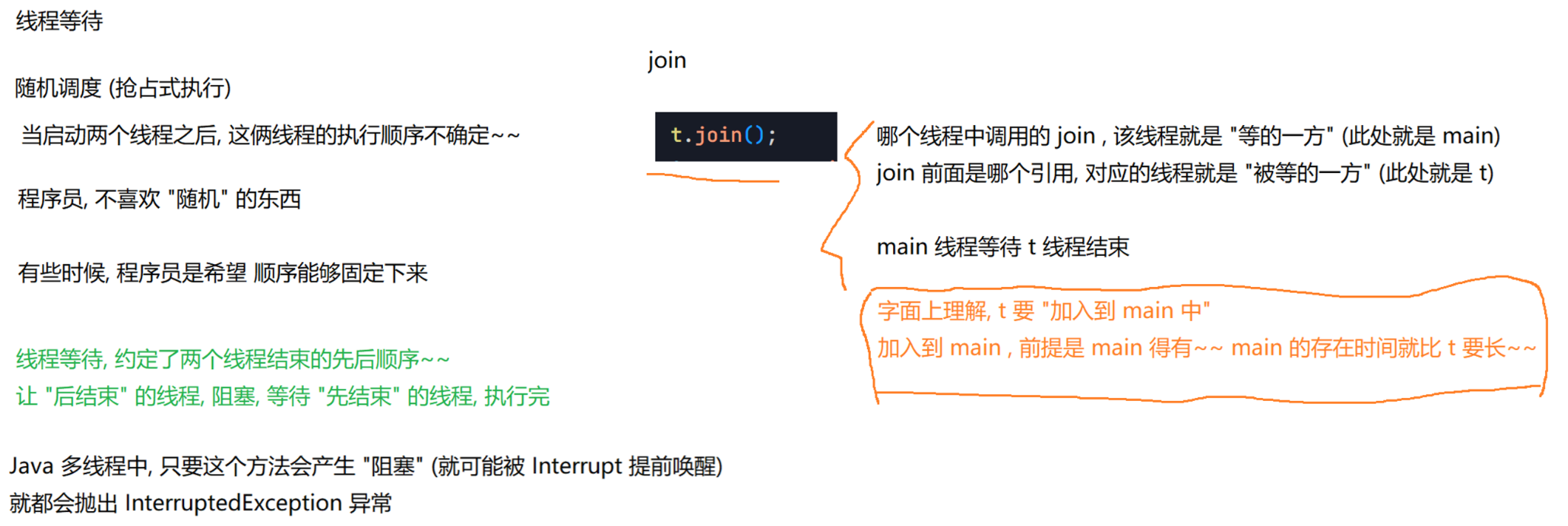
主线程等待代码
java
package thread;
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
//e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
});
System.out.println("主线程开始");
t.start();
System.out.println("主线程等待之前");
t.join();
System.out.println("主线程等待之后");
System.out.println("主线程结束");
}
}t 线程等待代码
java
package thread;
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread();
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("t 线程等待之前");
mainThread.join();
System.out.println("t 线程等待之后");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
t.start();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
System.out.println("hello main");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}

2.6 获取当前线程引用
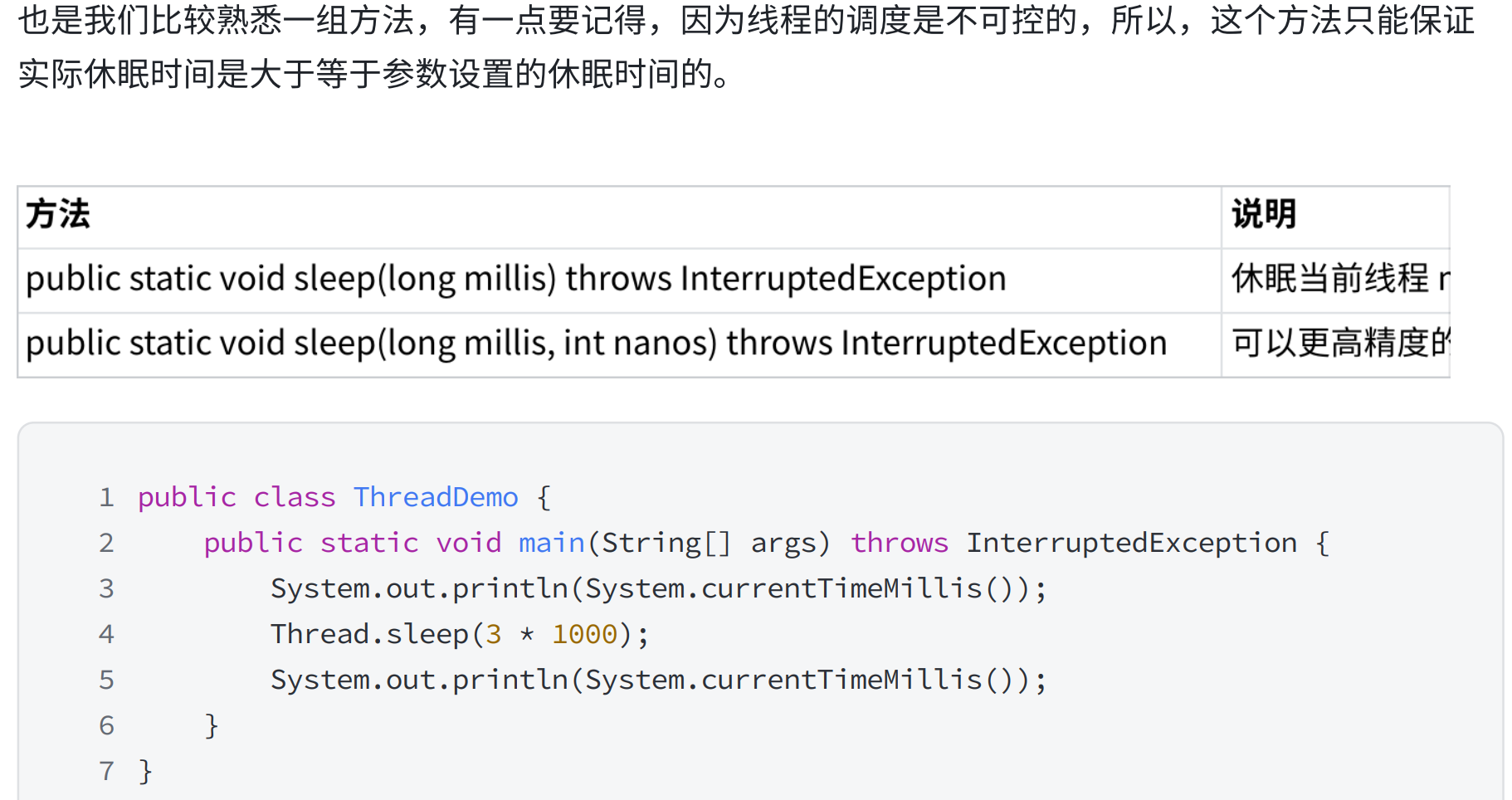
2.7 休眠当前线程

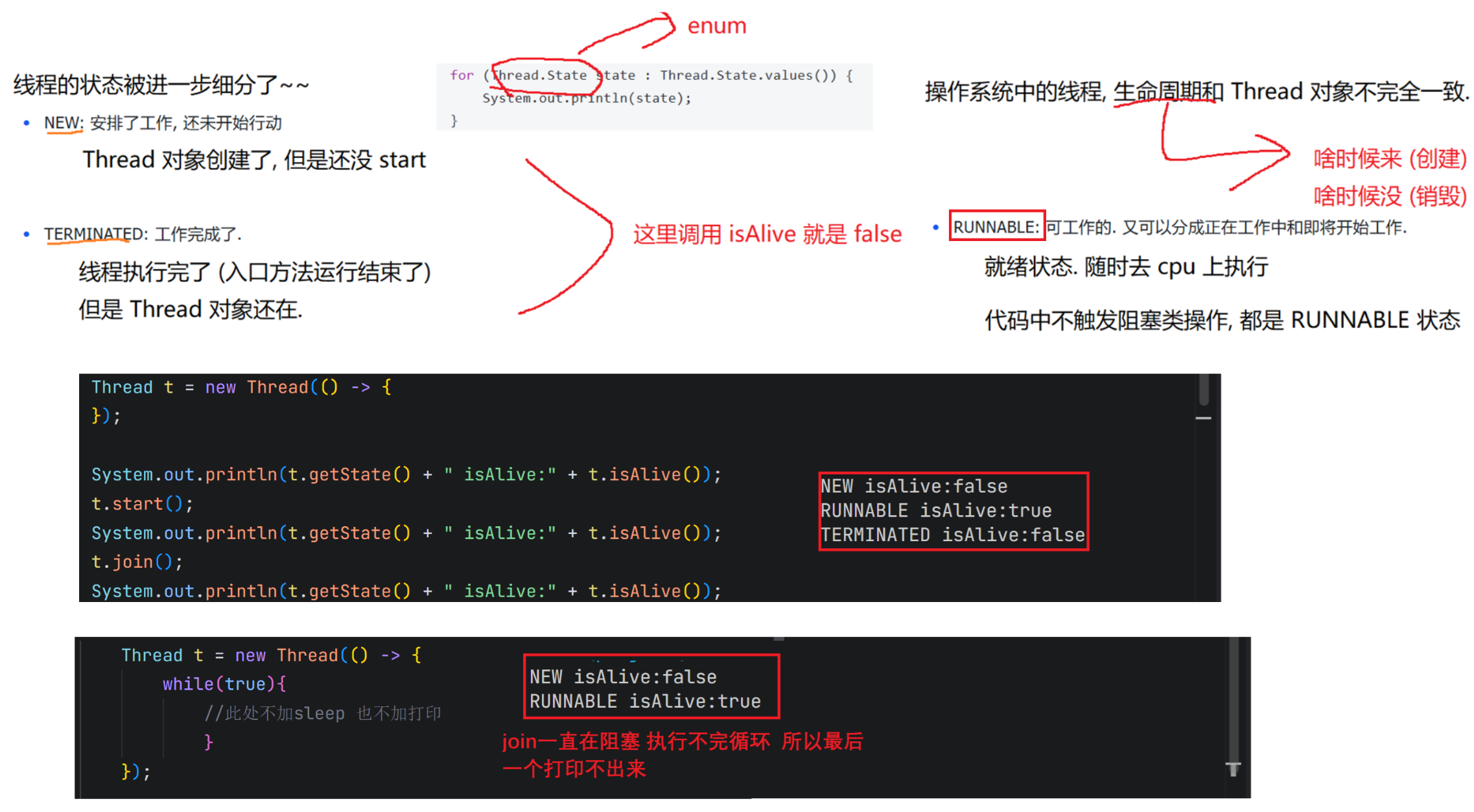
3.线程的状态
线程的状态是⼀个枚举类型 Thread.State

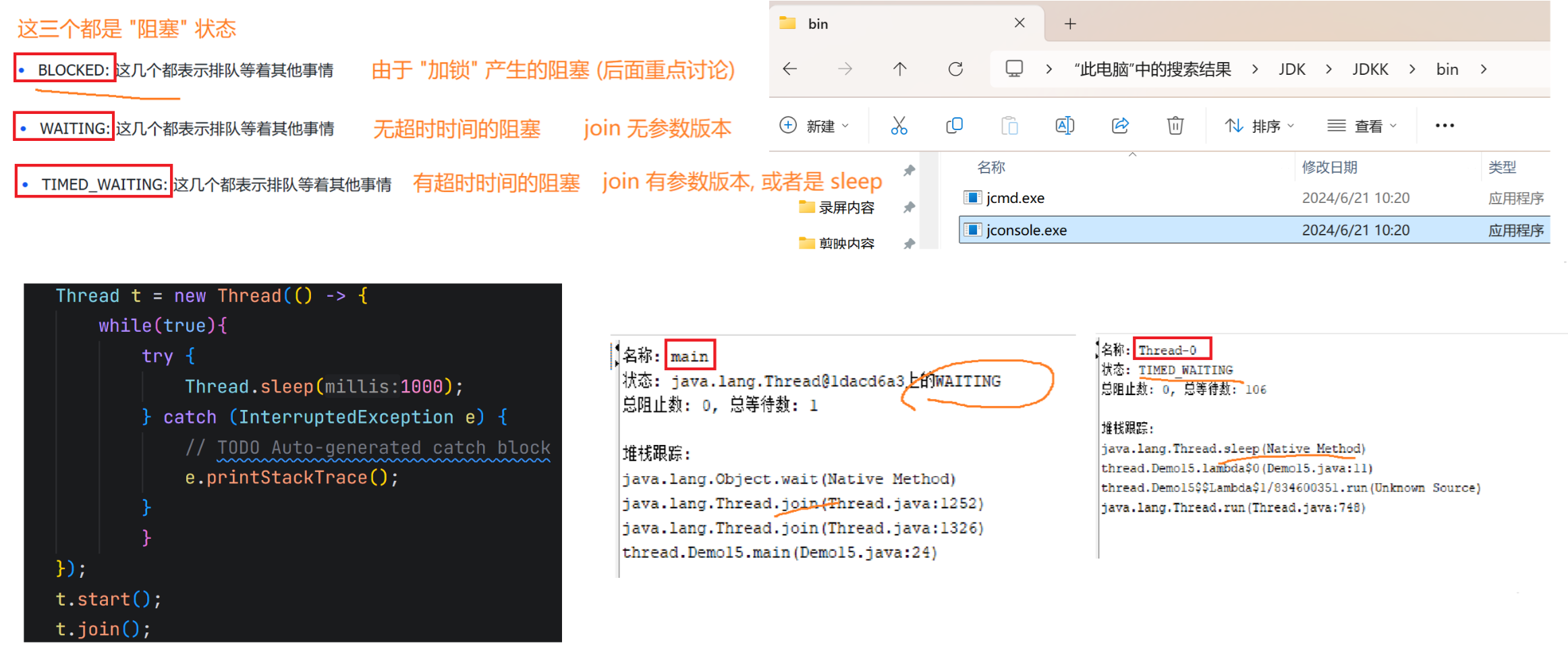
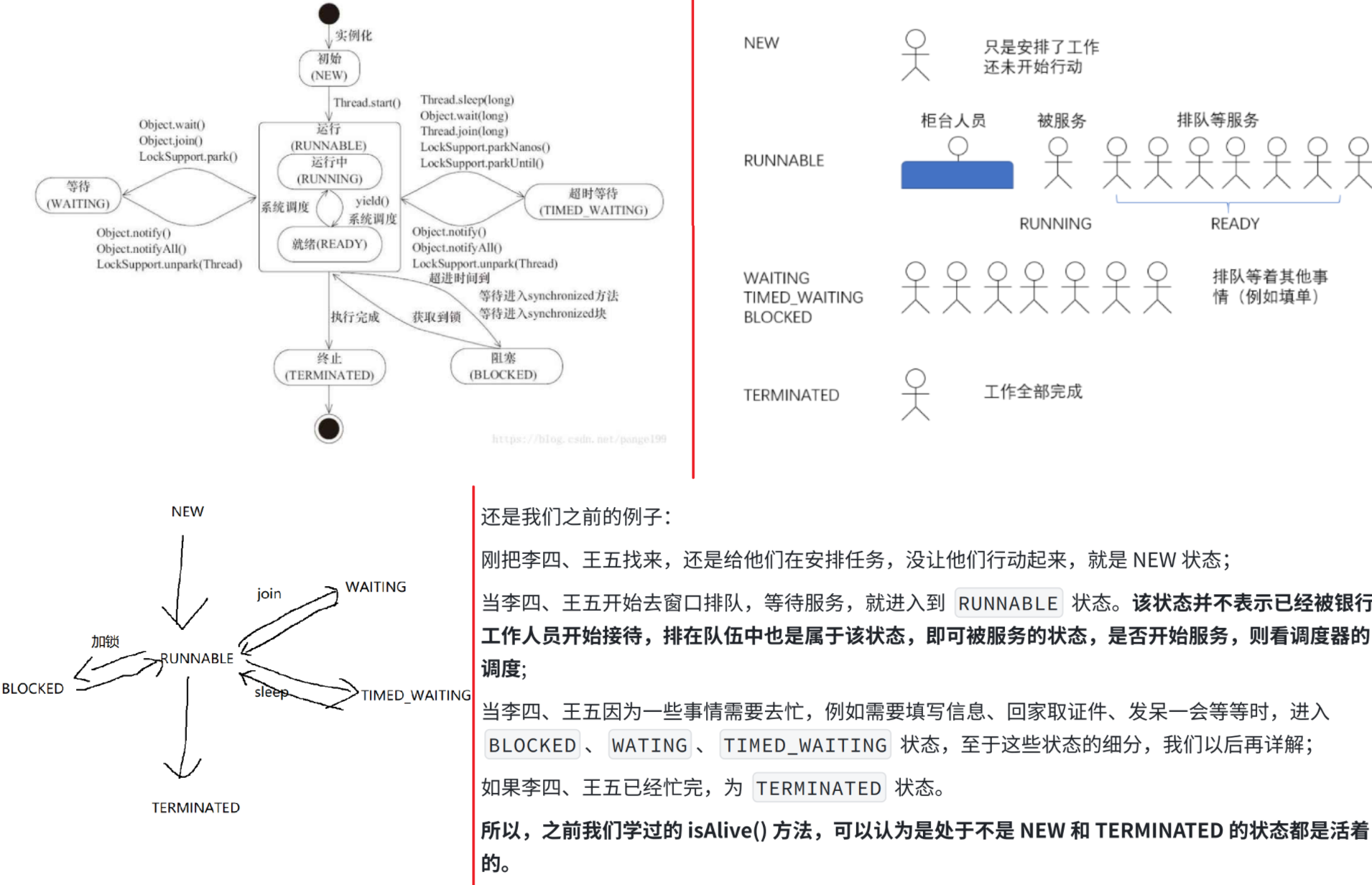
4.多线程带来的的风险-线程安全(重点!)
4.1 概念 例子

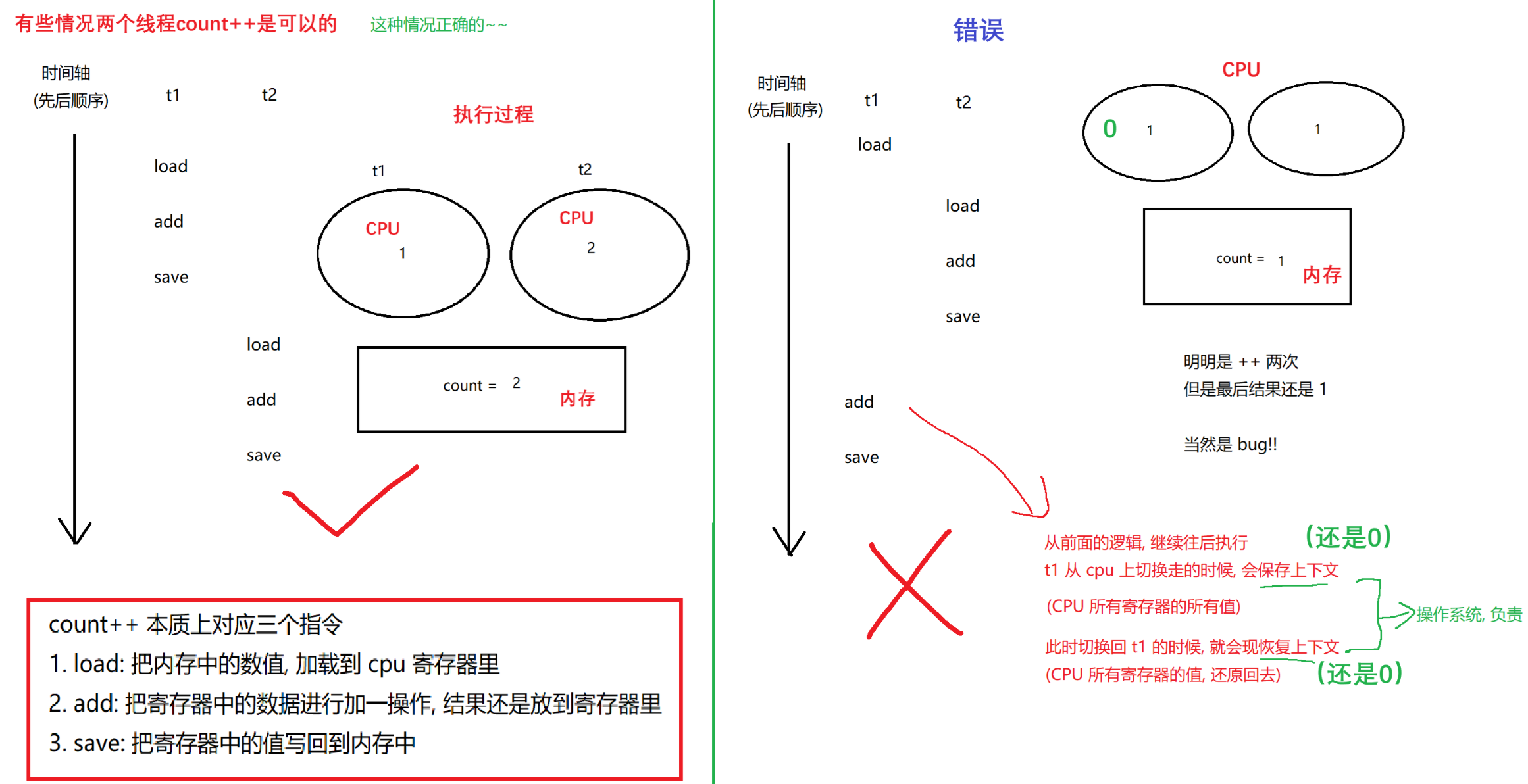

4.2 线程不安全的原因




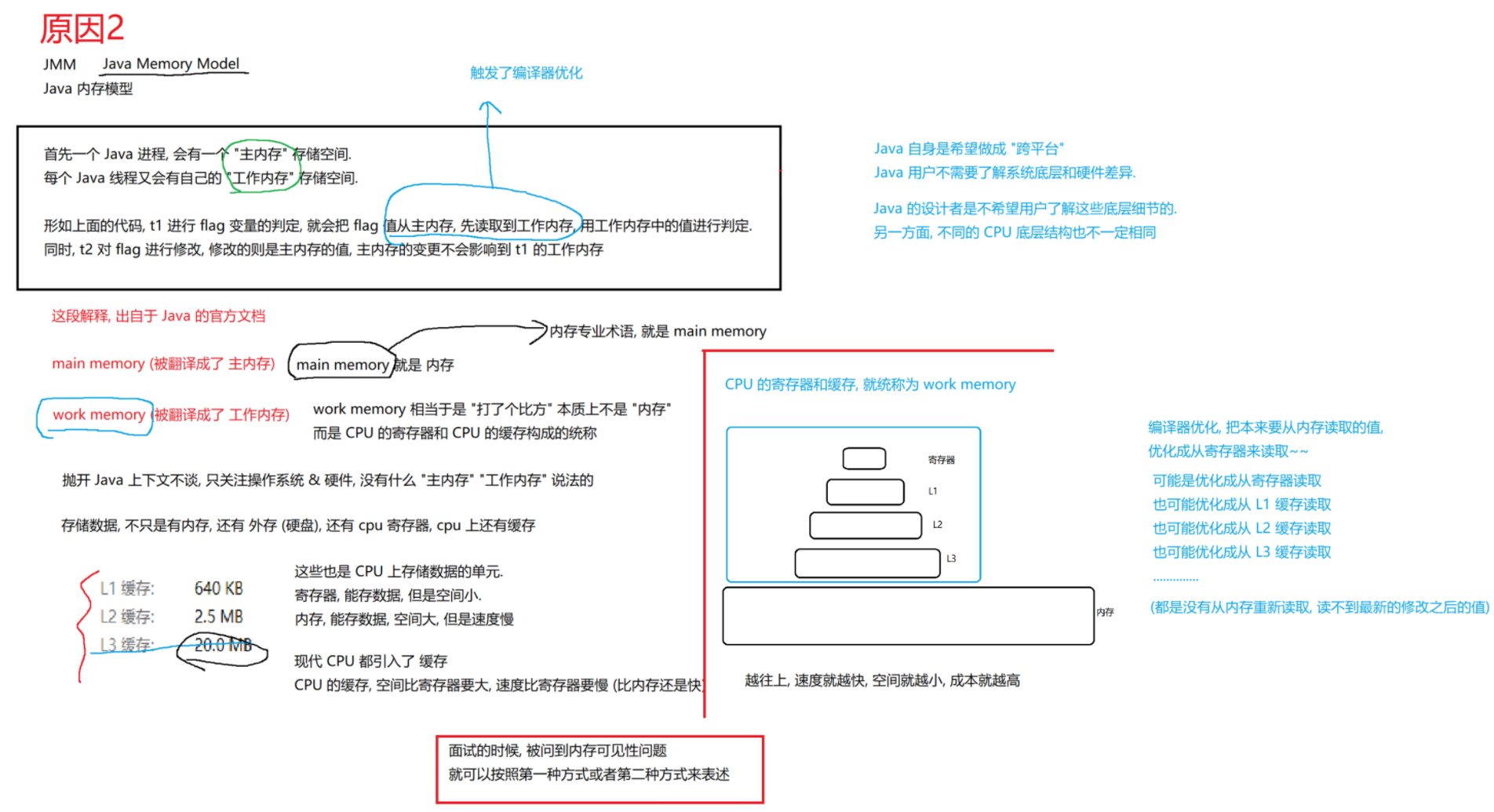

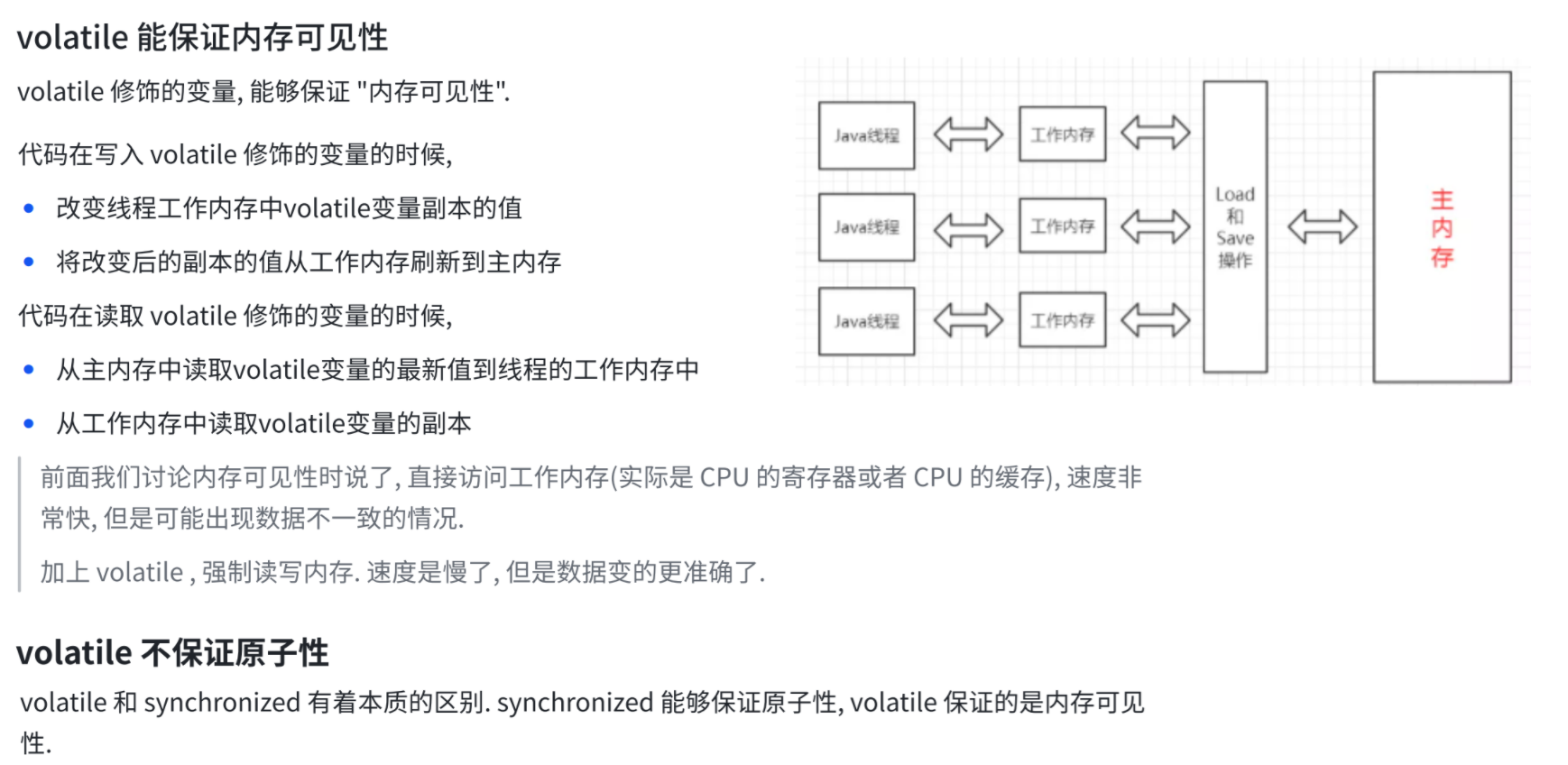


5.死锁(重点)

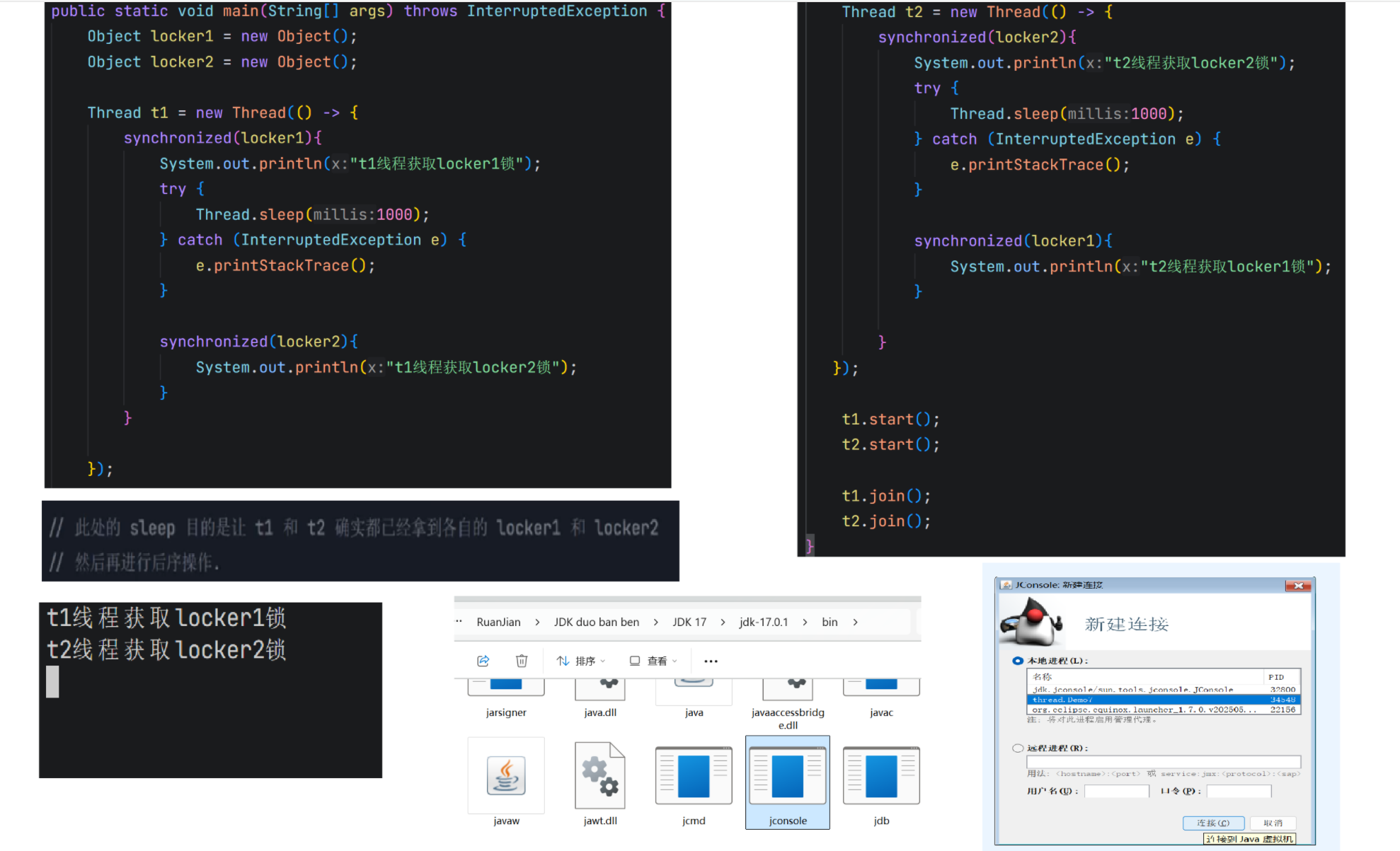
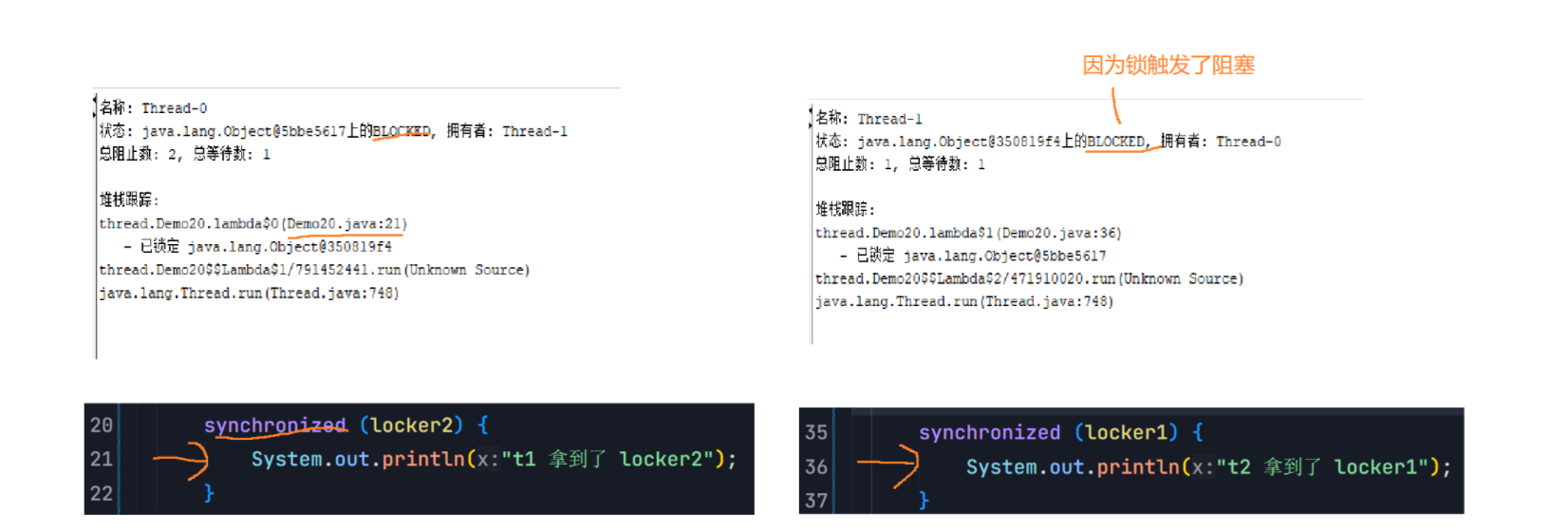



java
Object lock1 = new Object();
Object lock2 = new Object();
Thread t1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
synchronized (lock2) {
// do something...
}
}
}
};
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock2) {
synchronized (lock1) {
// do something...
}
}
}
};
t2.start();不会产生环路等待的代码:约定好先获取lock1,再获取lock2,就不会环路等待。
java
Object lock1 = new Object();
Object lock2 = new Object();
Thread t1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
synchronized (lock2) {
// do something...
}
}
}
};
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
synchronized (lock2) {
// do something...
}
}
}
};
t2.start();6.synchronized关键字 - 监视器锁(monitor lock)
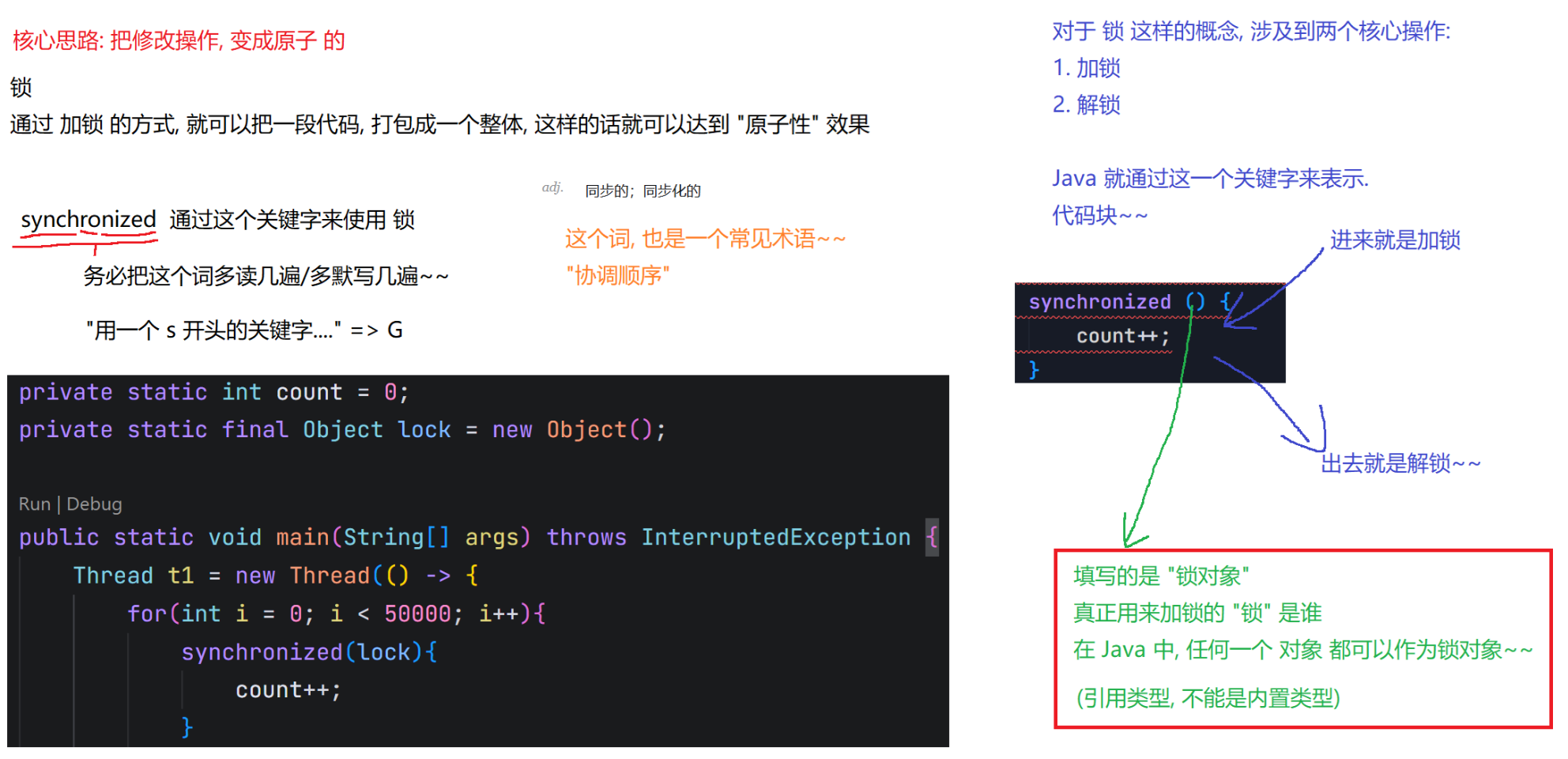

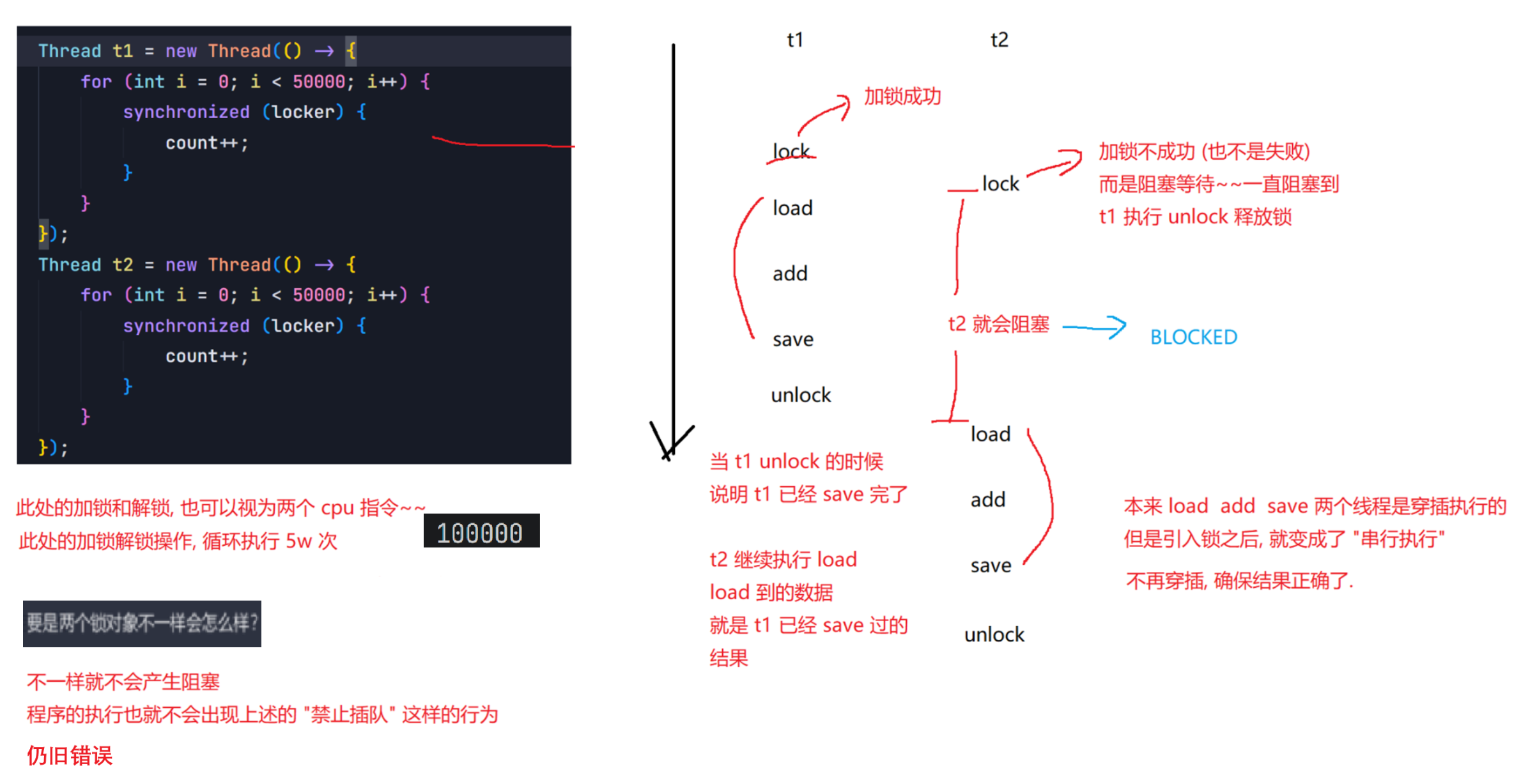
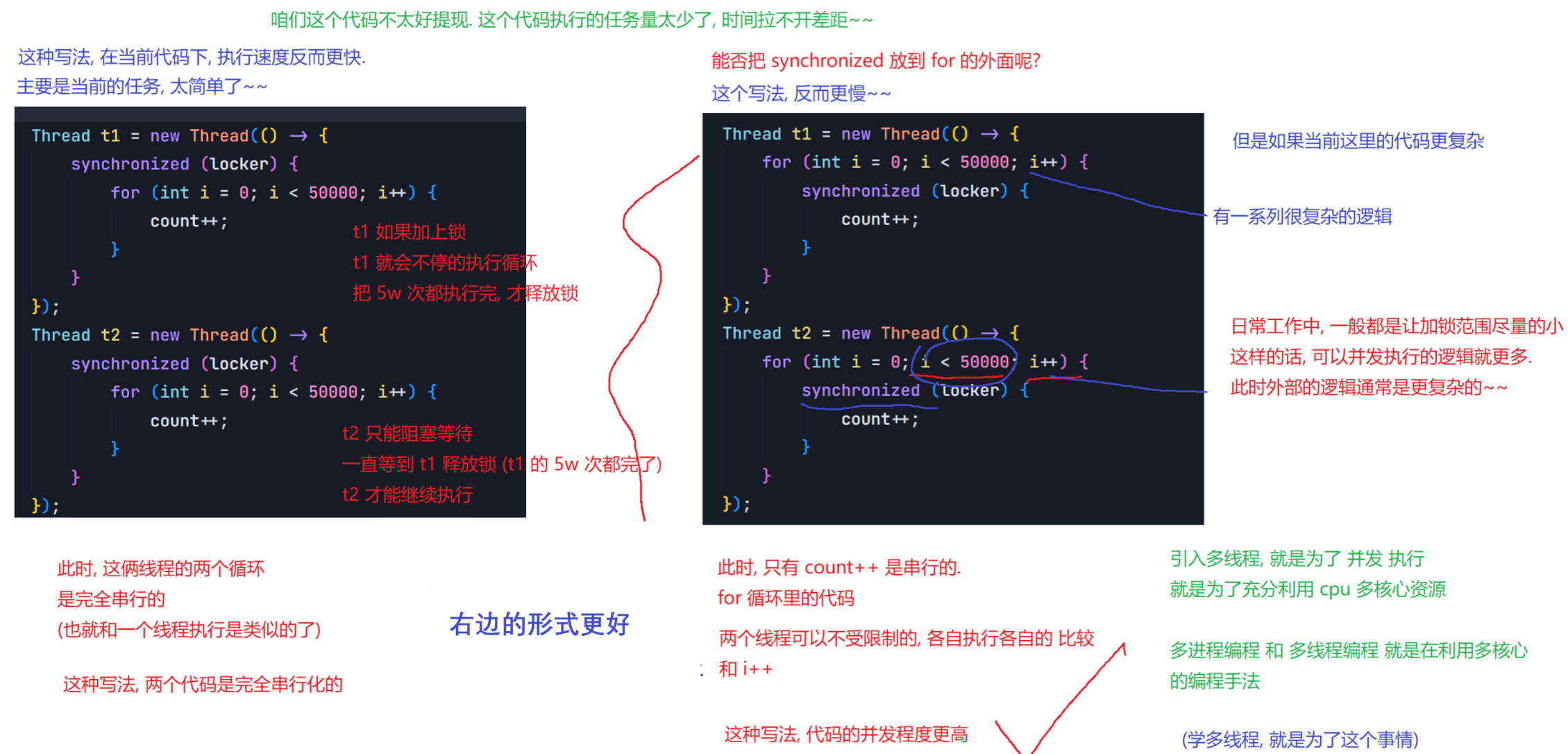
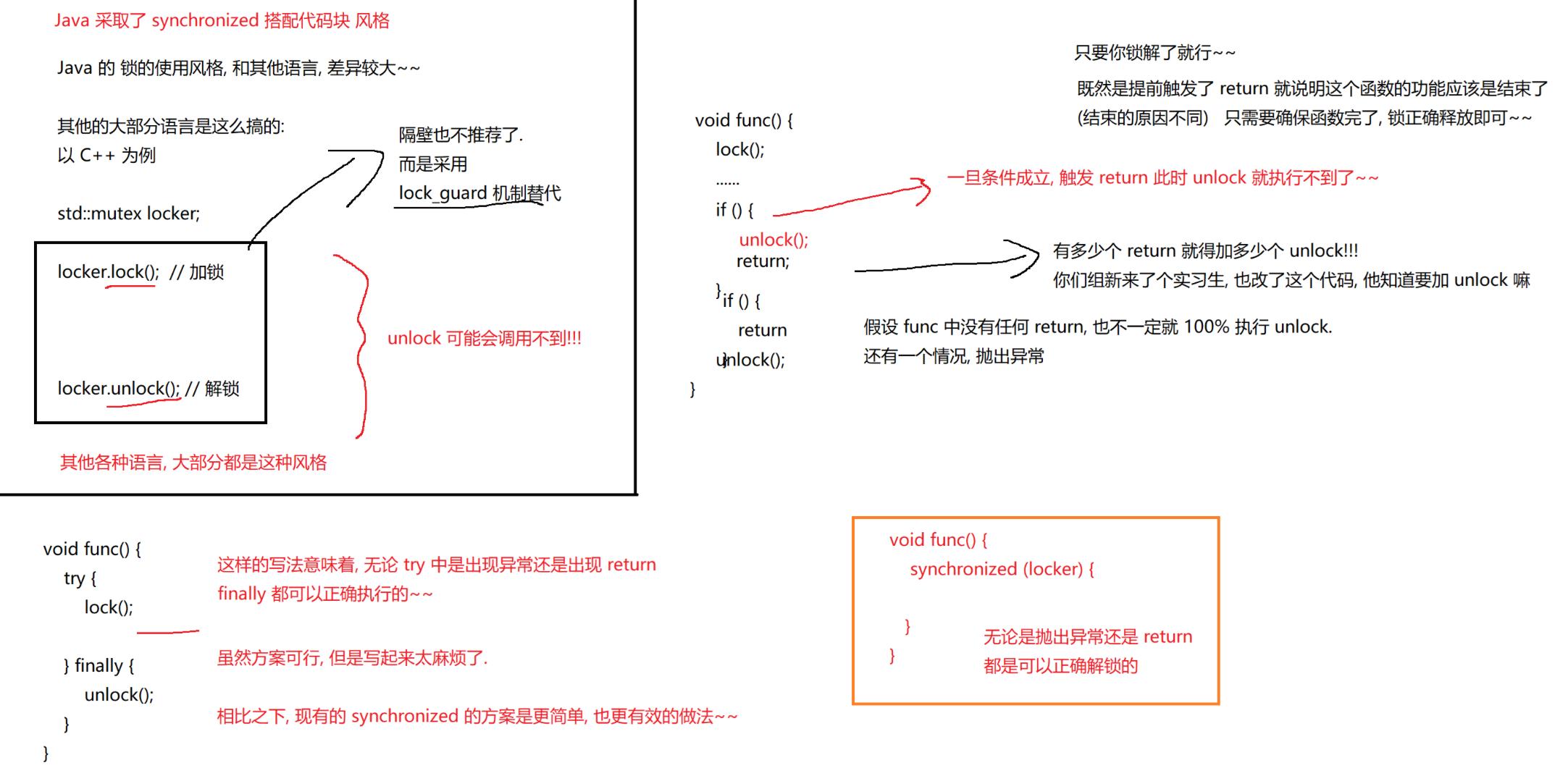
6.1 synchronized的特性




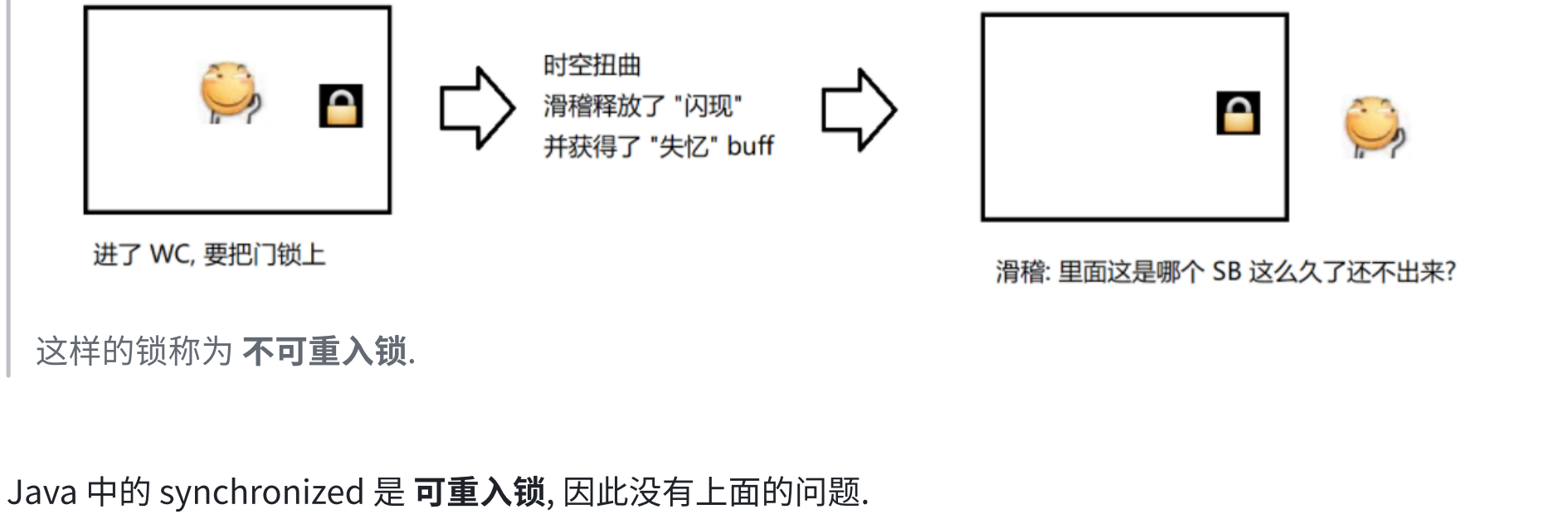




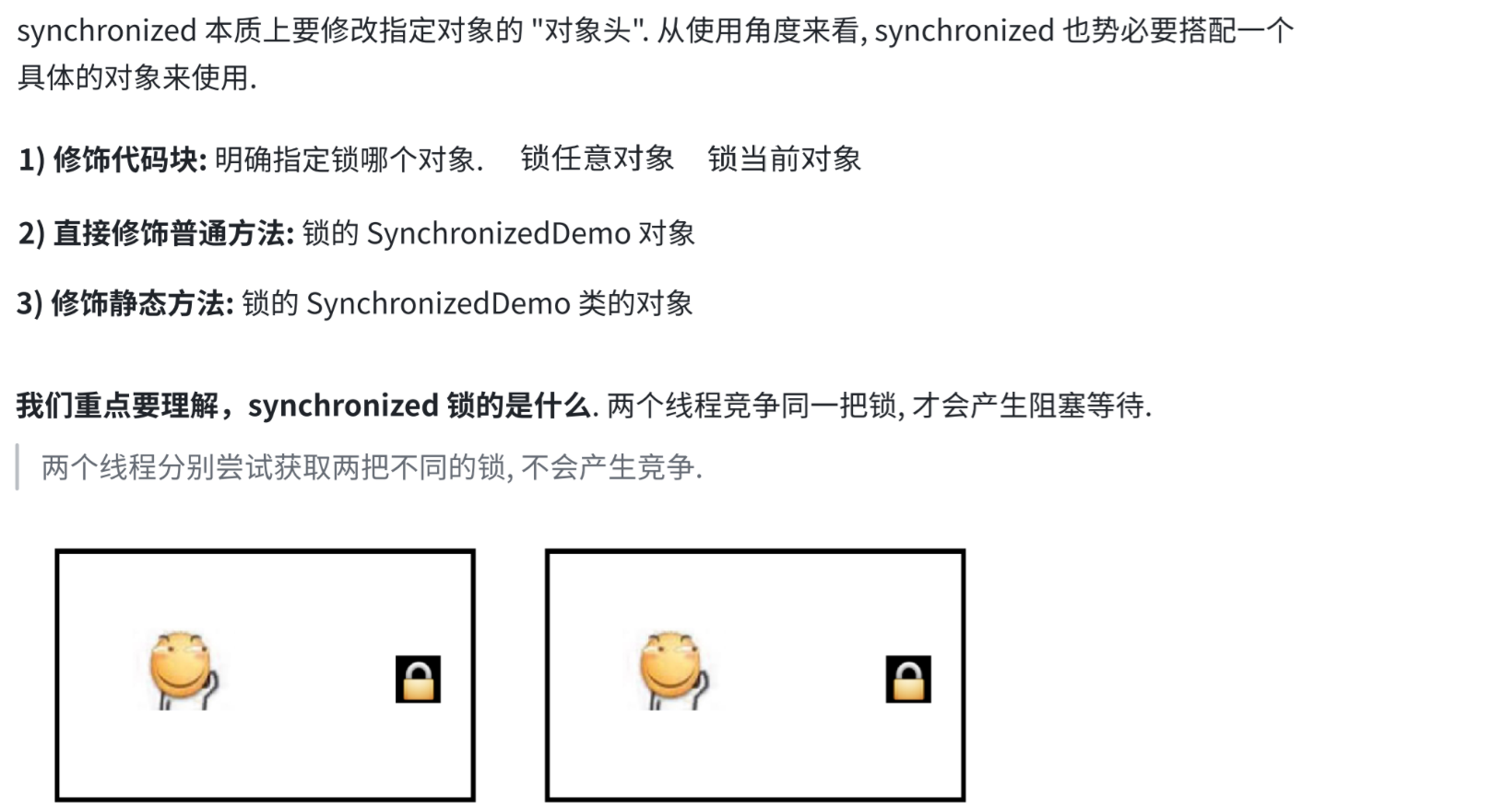
6.2 synchronized使用示例
重点是第一种,也是最常用的。

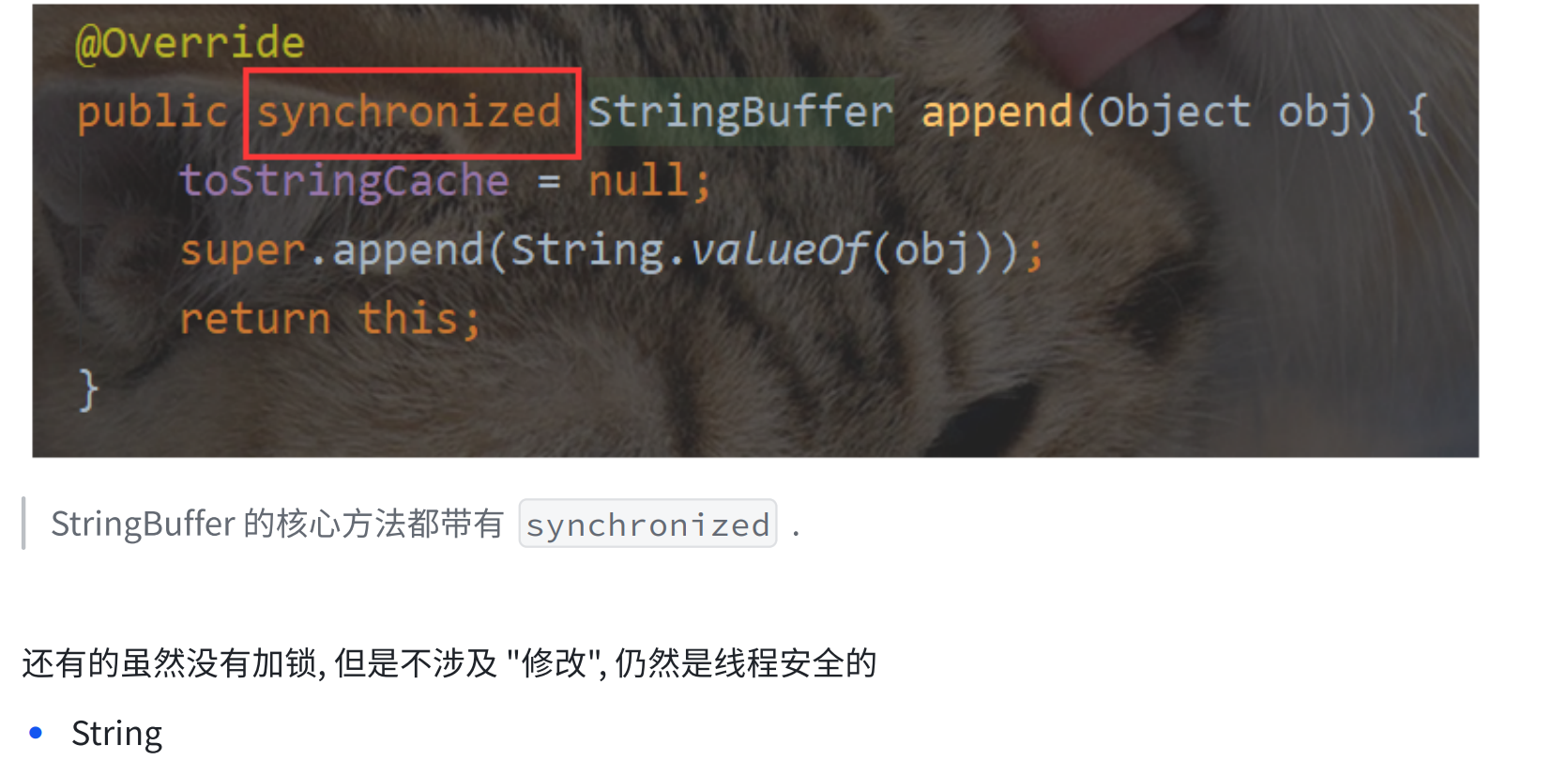
6.3 Java标准库中的线程安全类

7.wait和notify

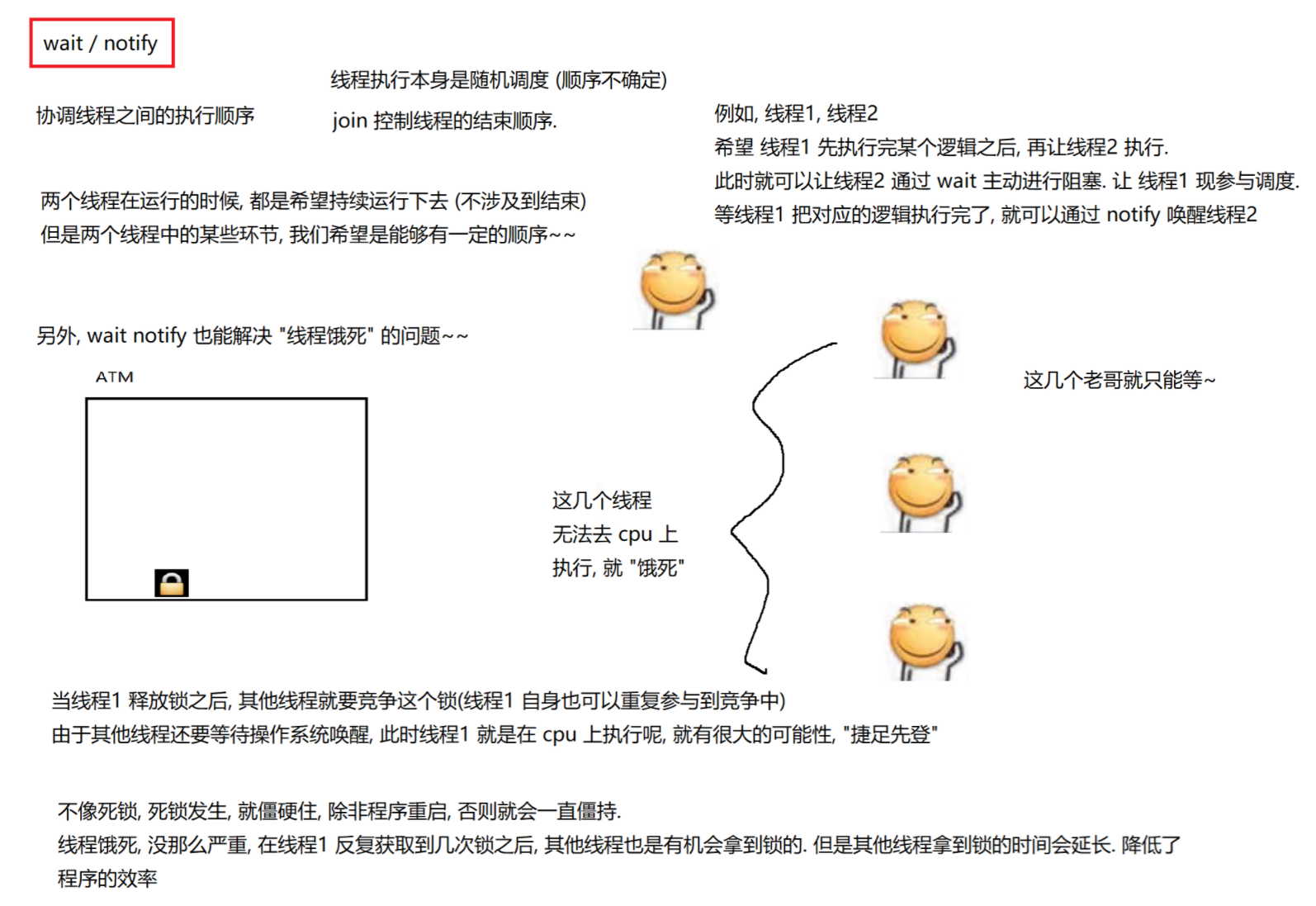

7.1 wait()方法


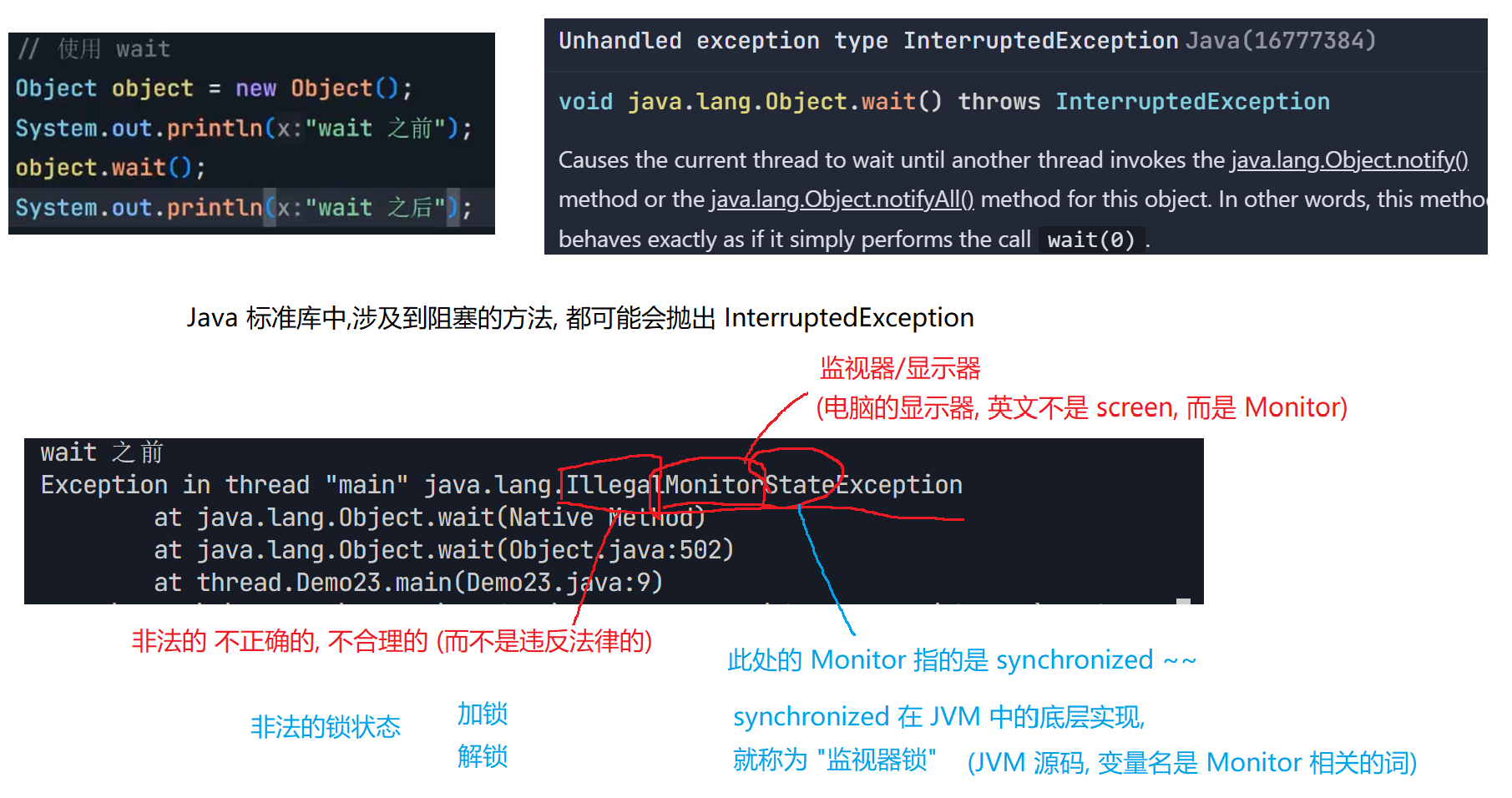
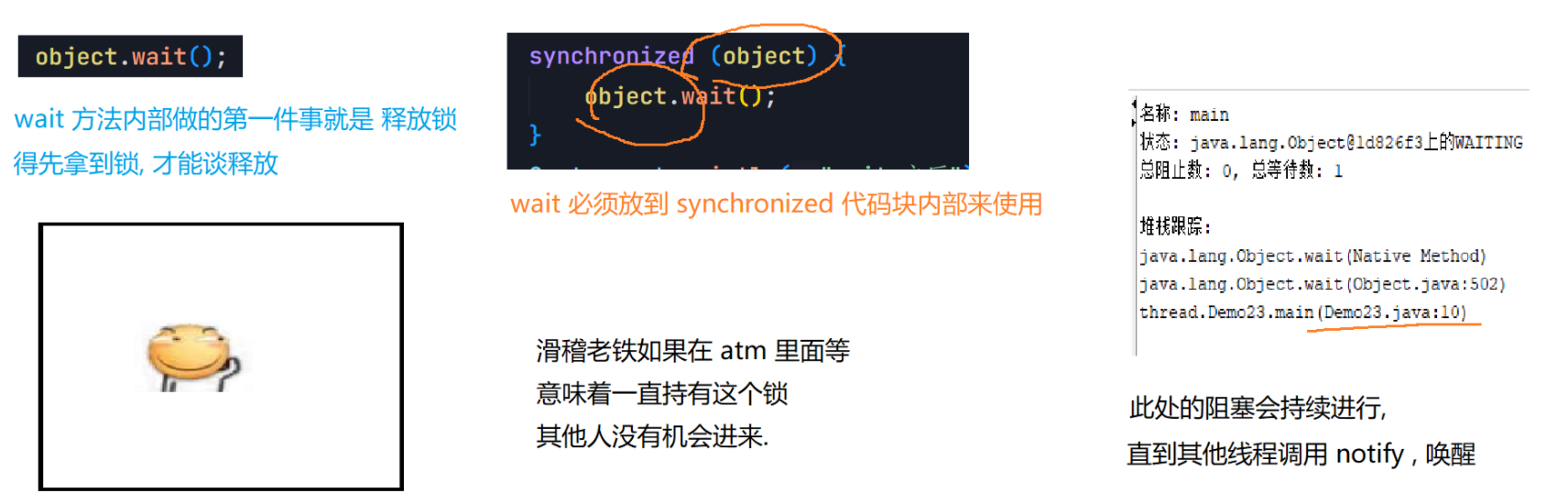
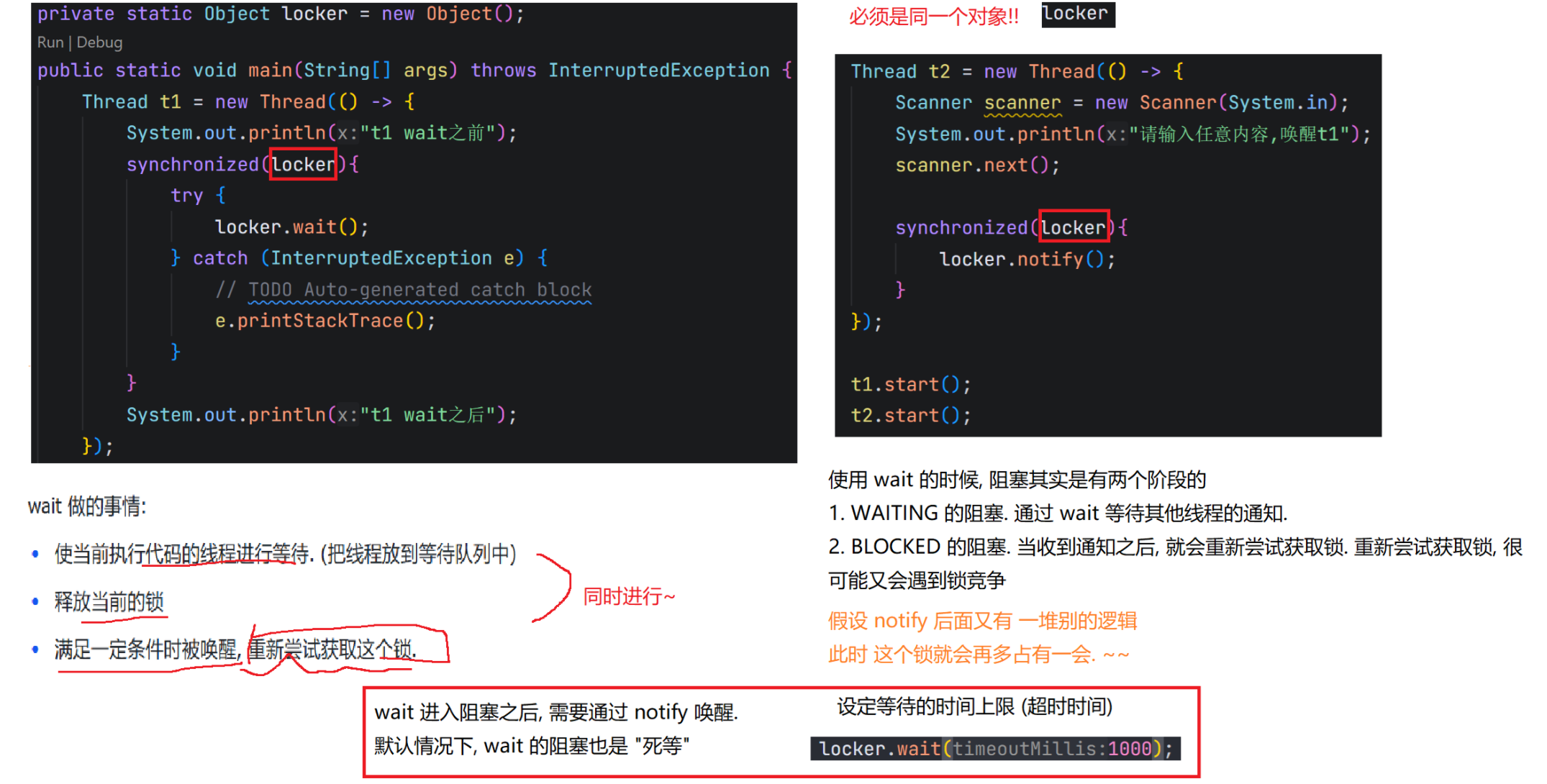
7.2 notify() notifyAll() 方法





7.3 wait和sleep的对比(面试题)


8.多线程案例
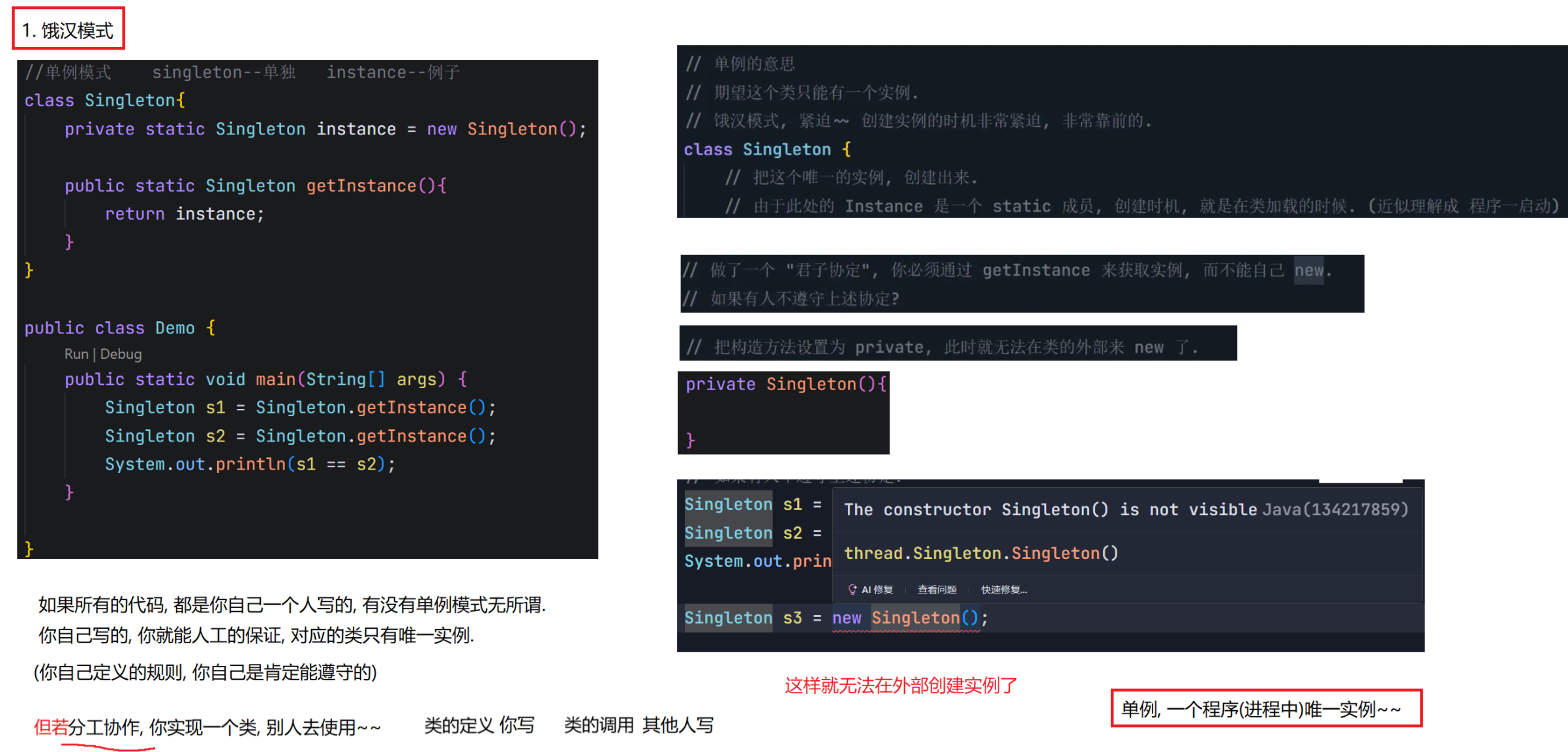
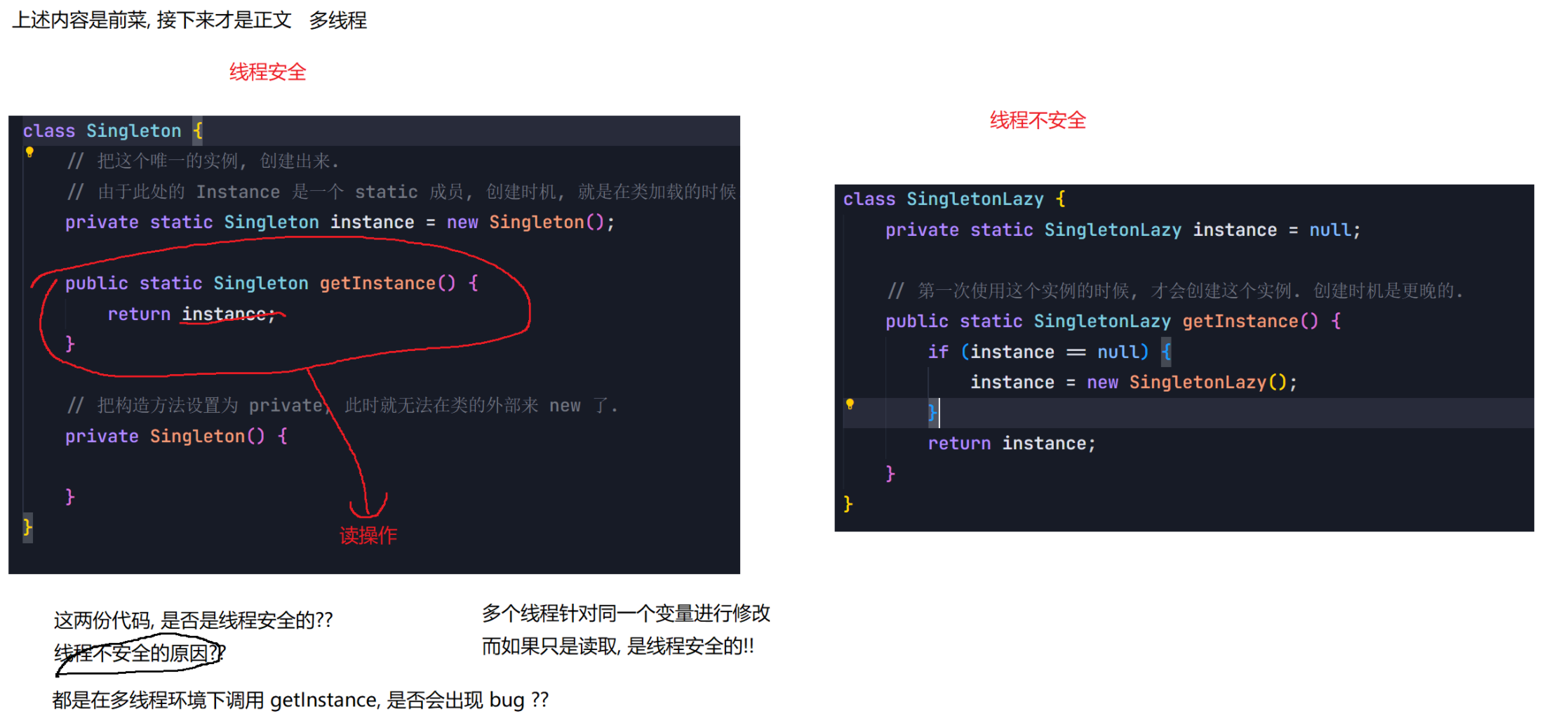
8.1 单例模式(面试常考)
单例模式是校招中最常考的设计模式之一









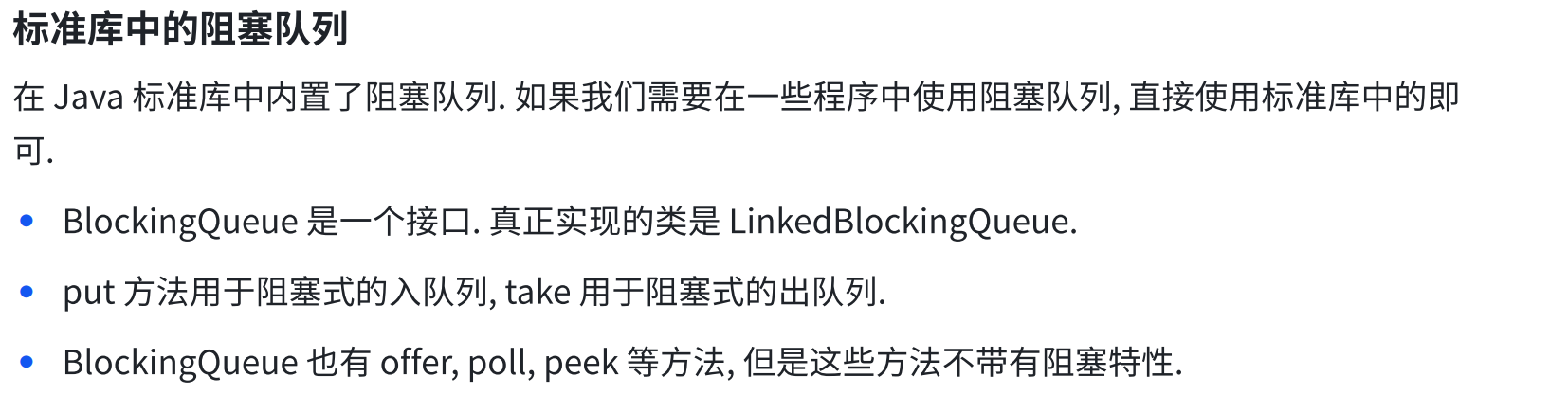
8.2 阻塞队列



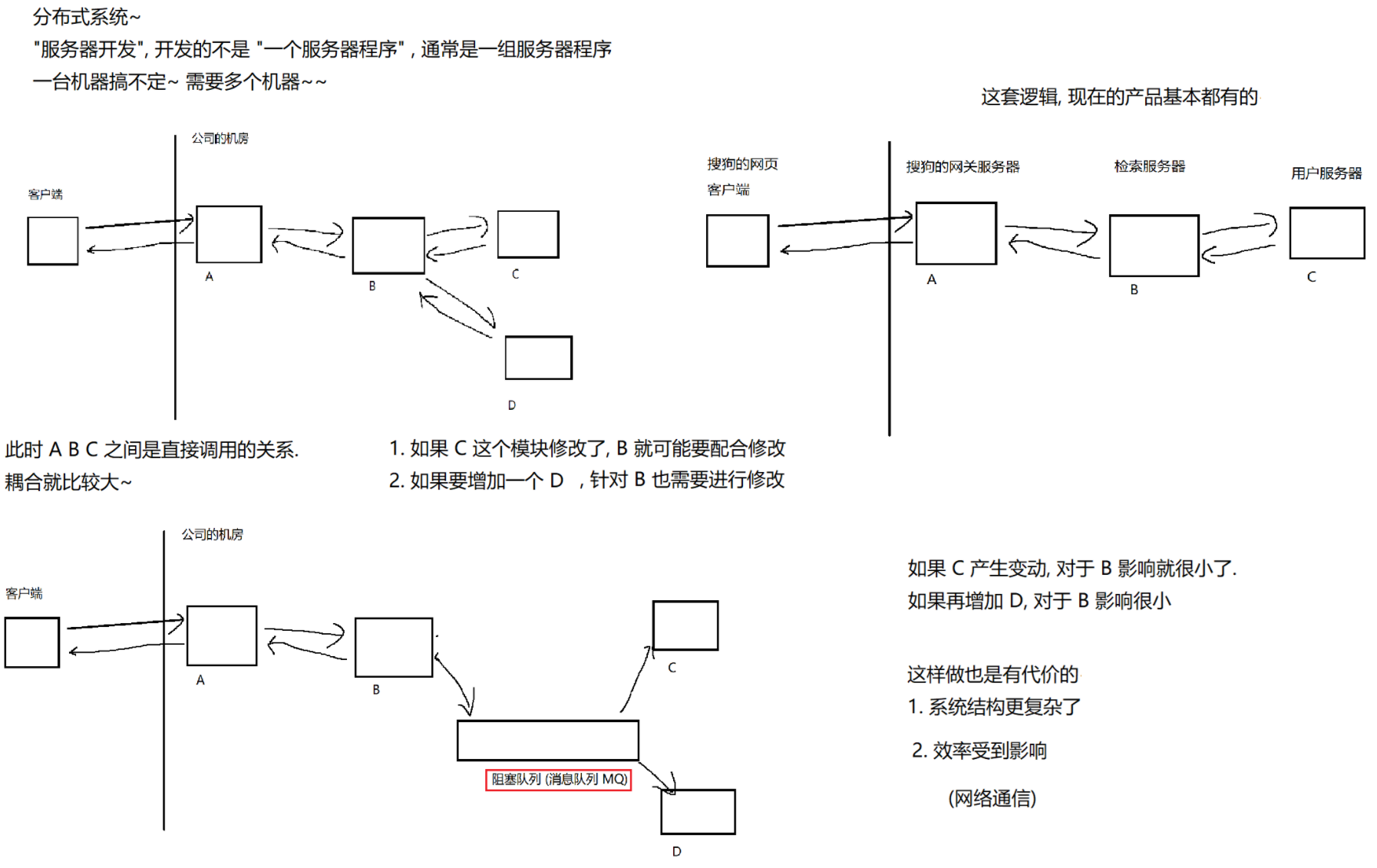
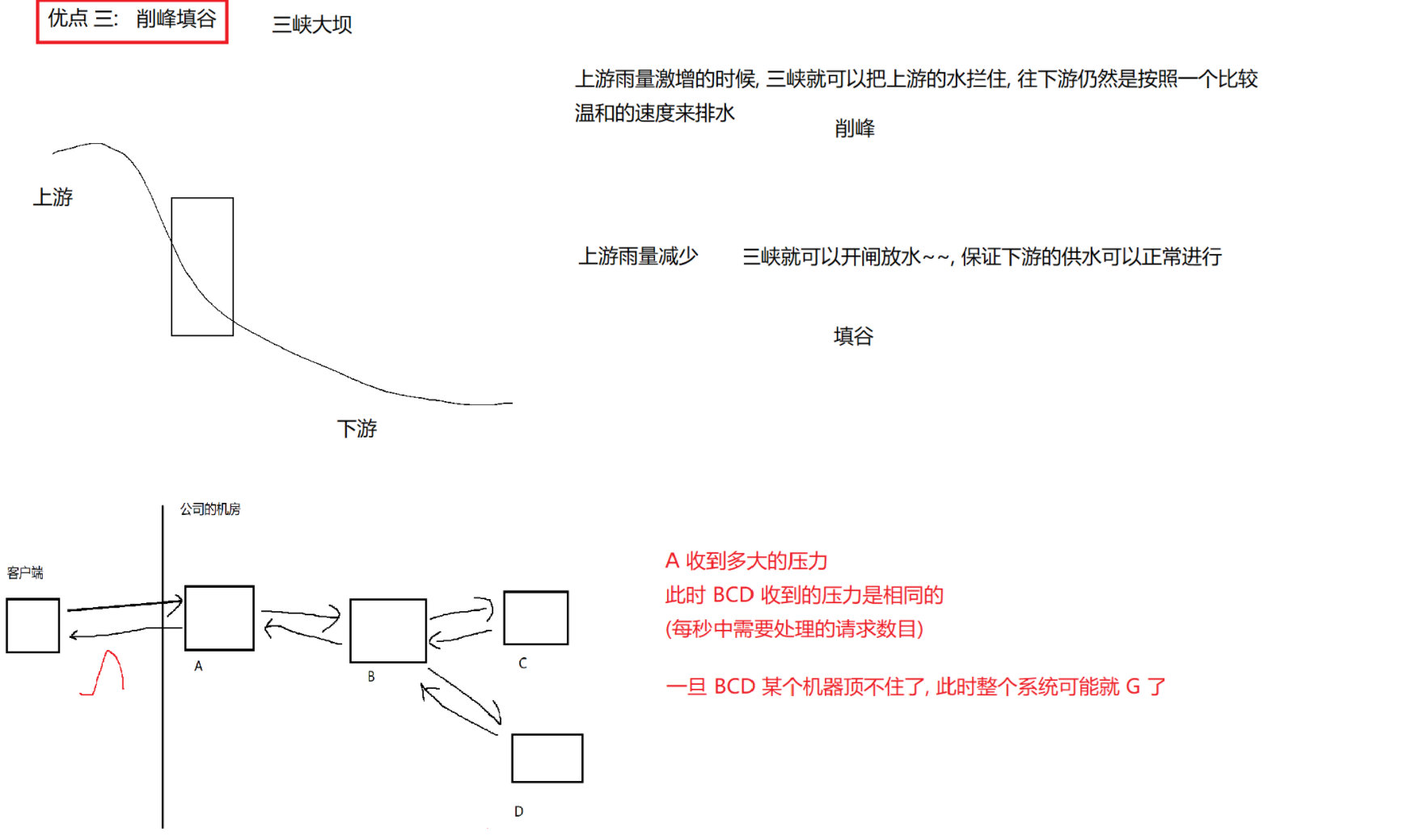
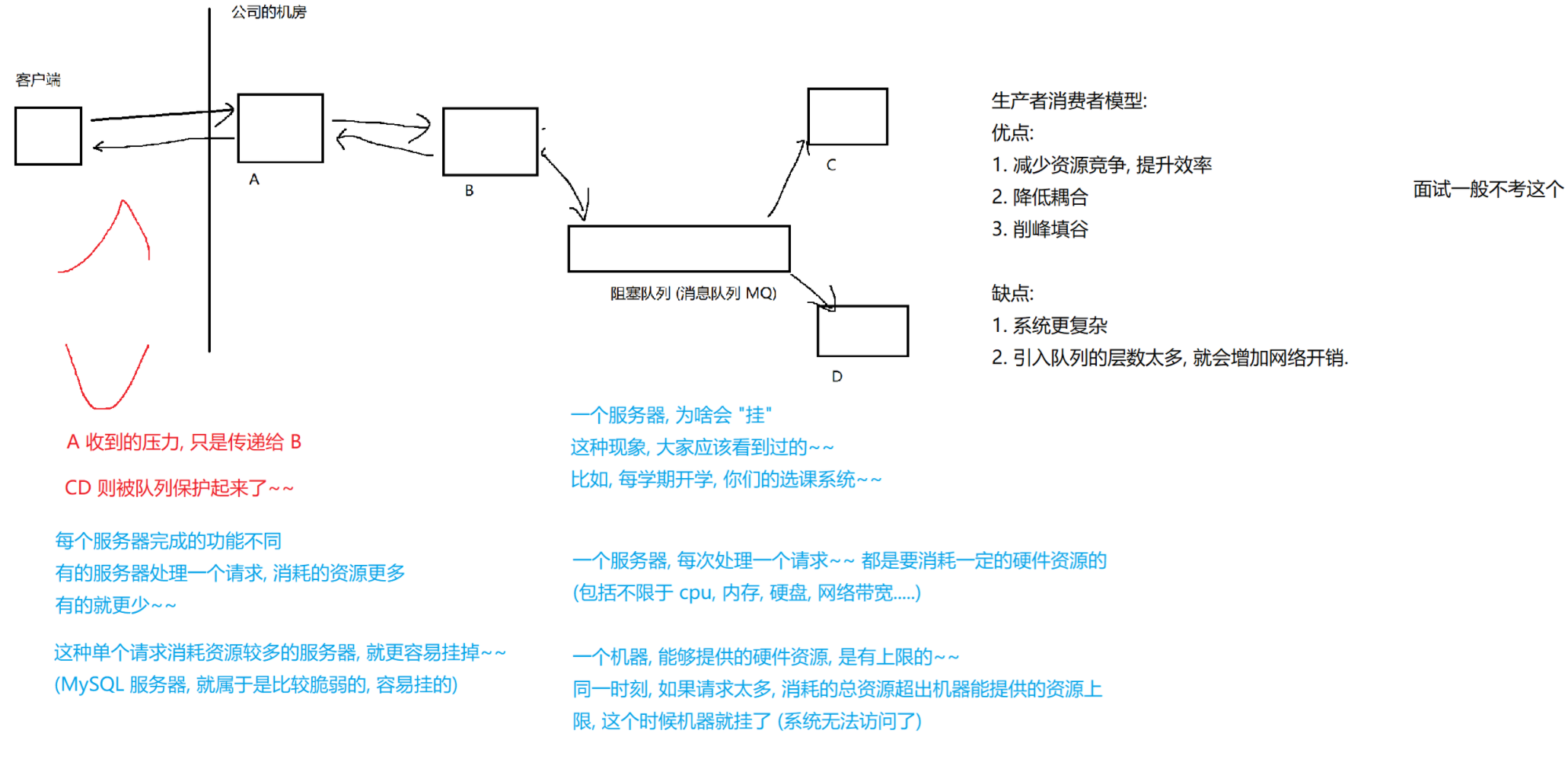
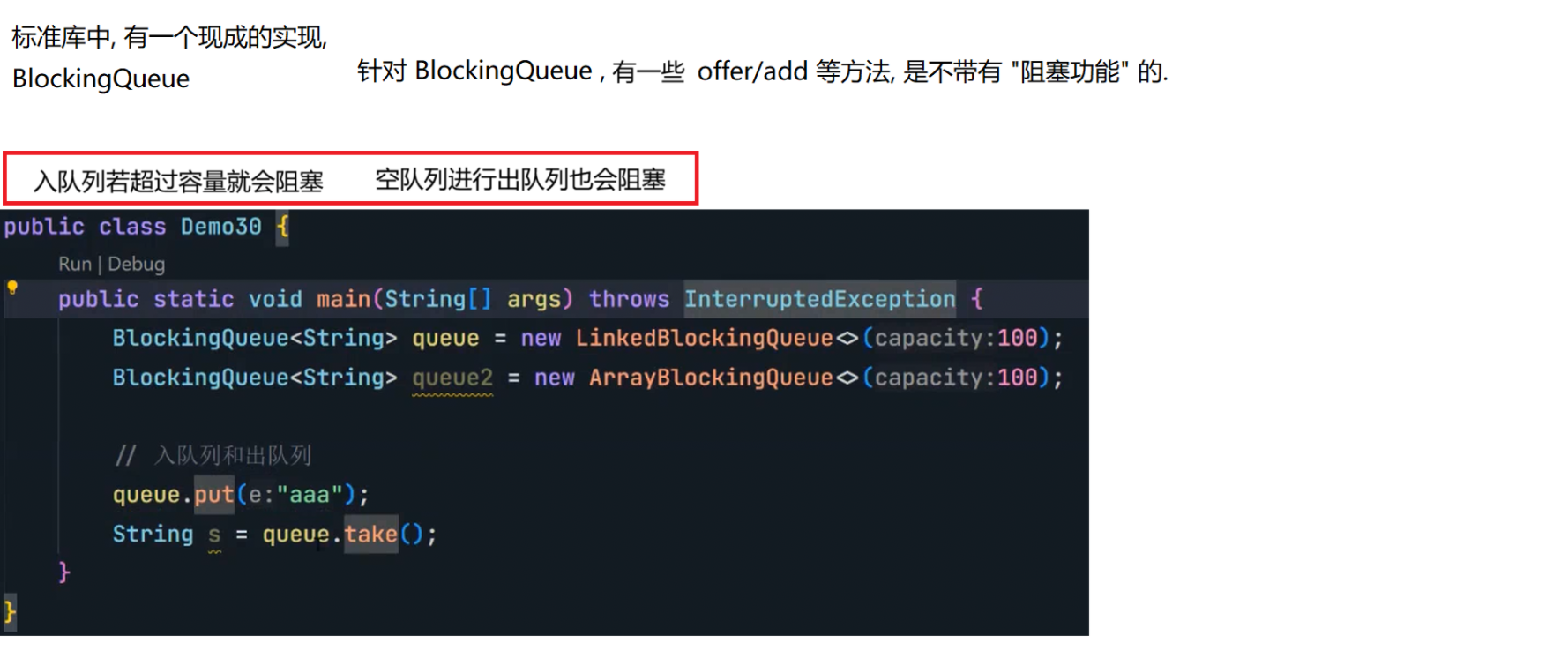
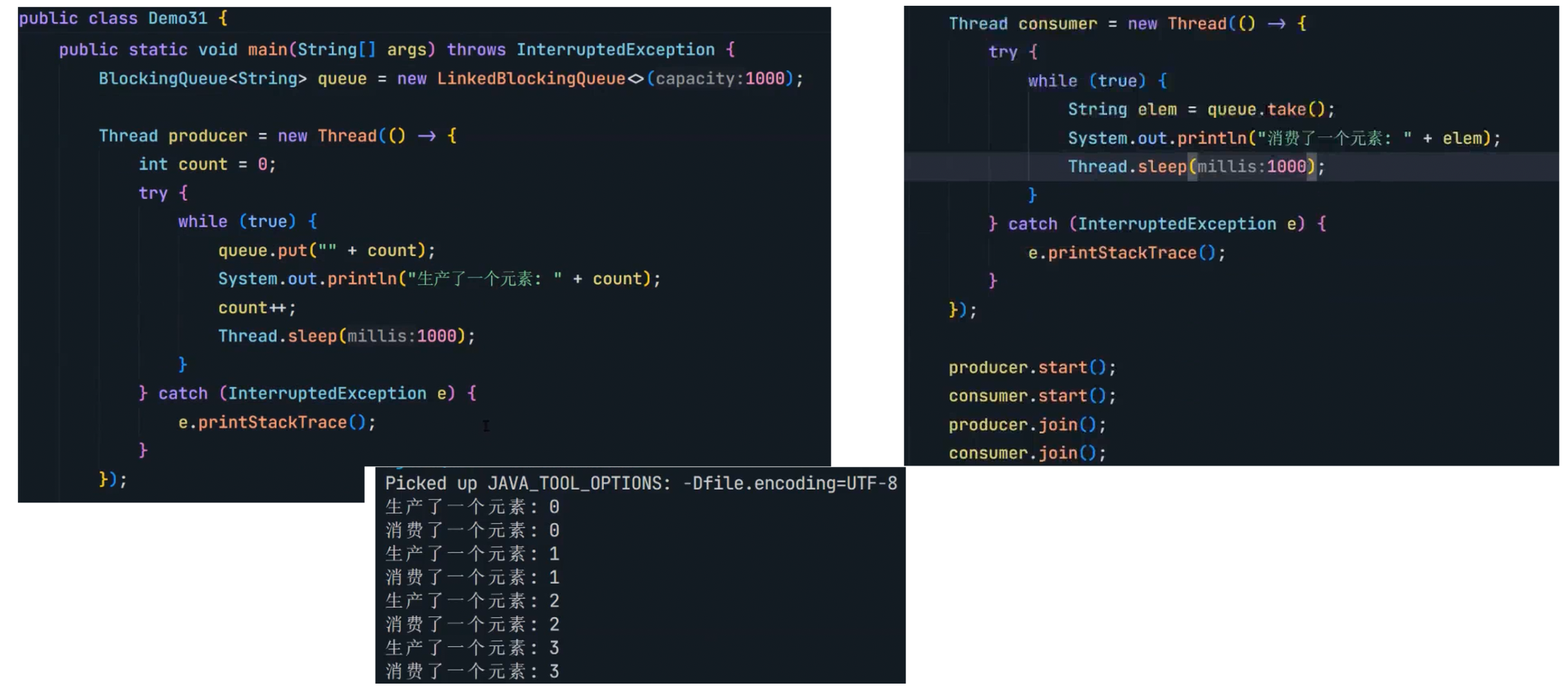

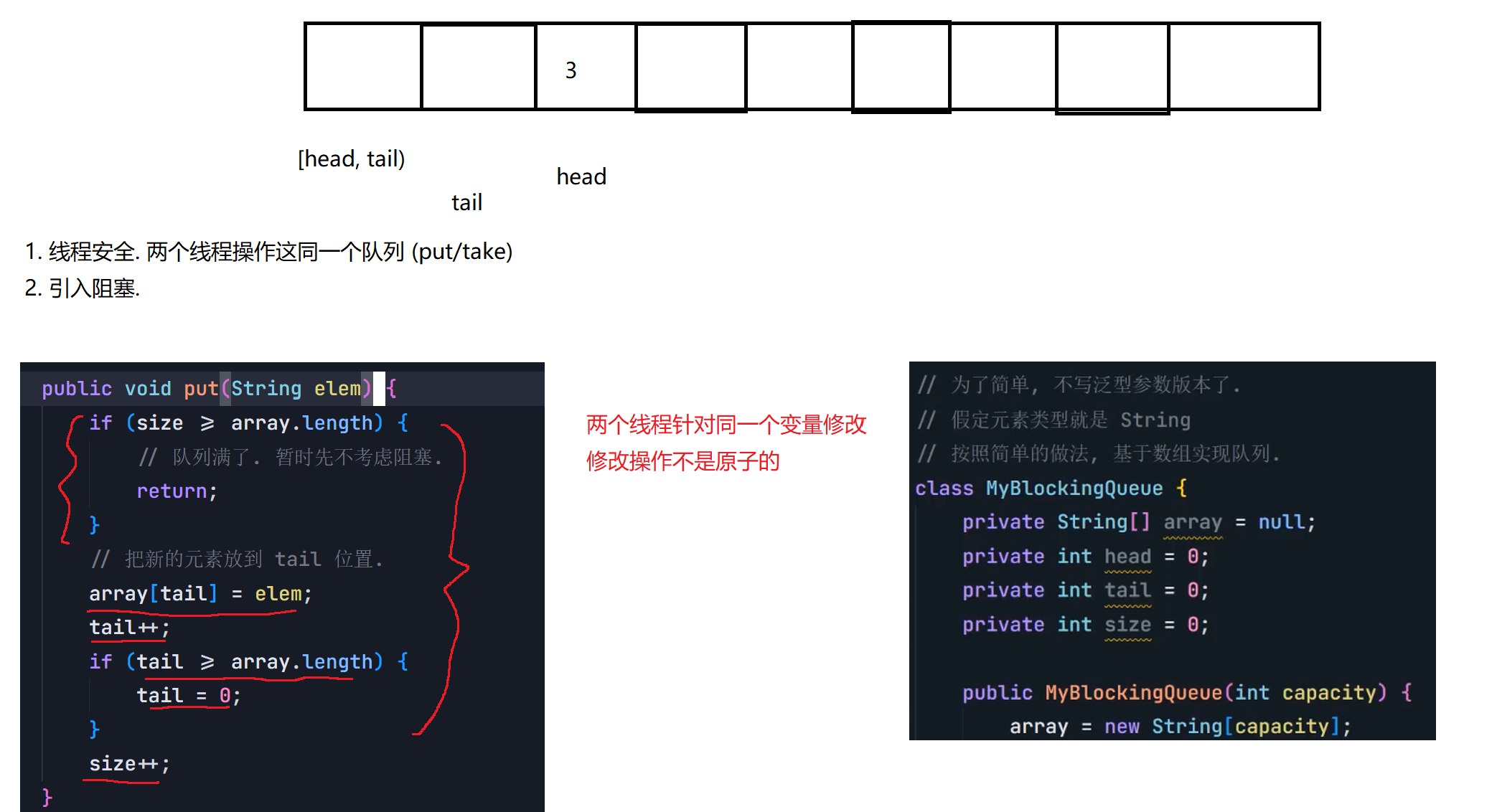
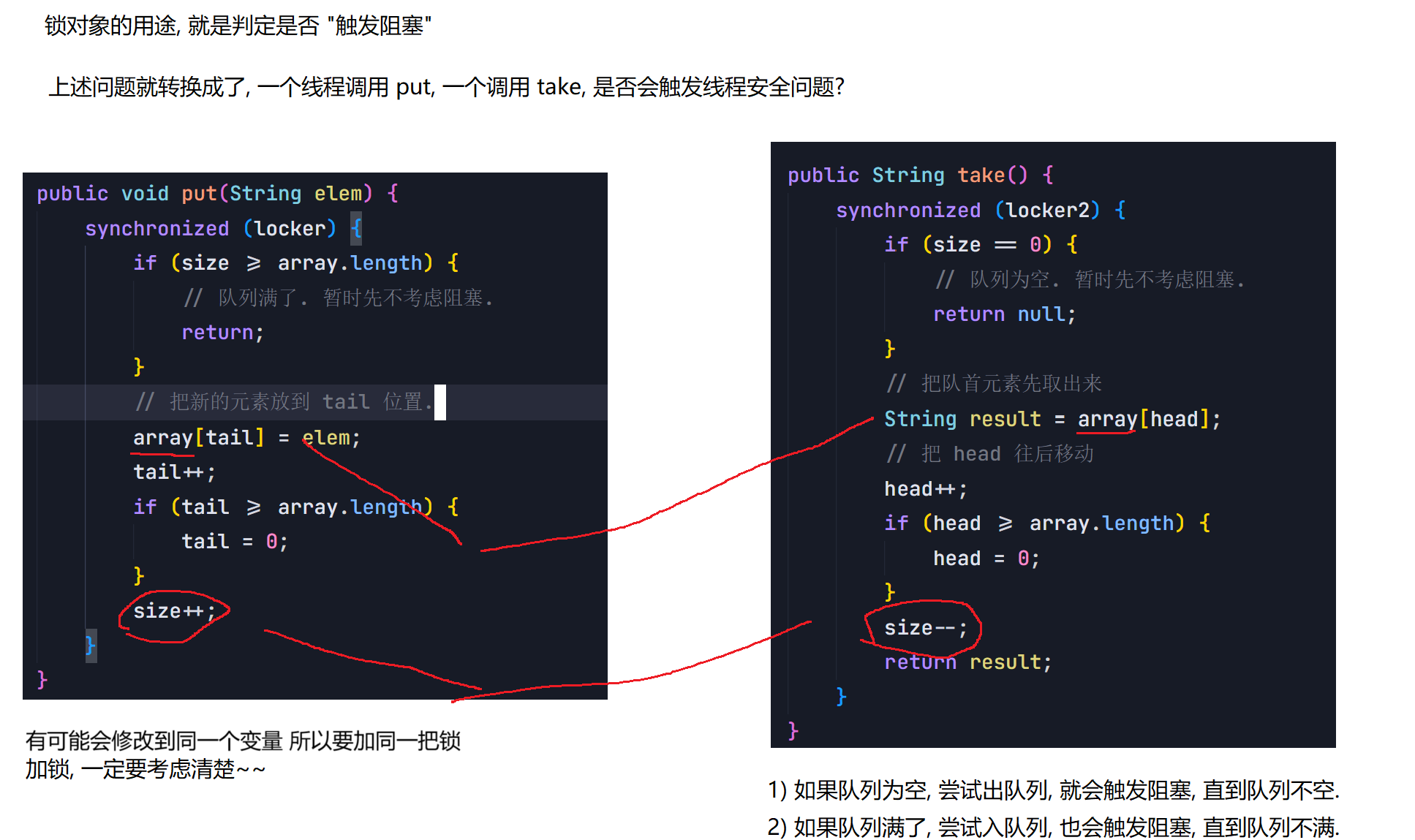
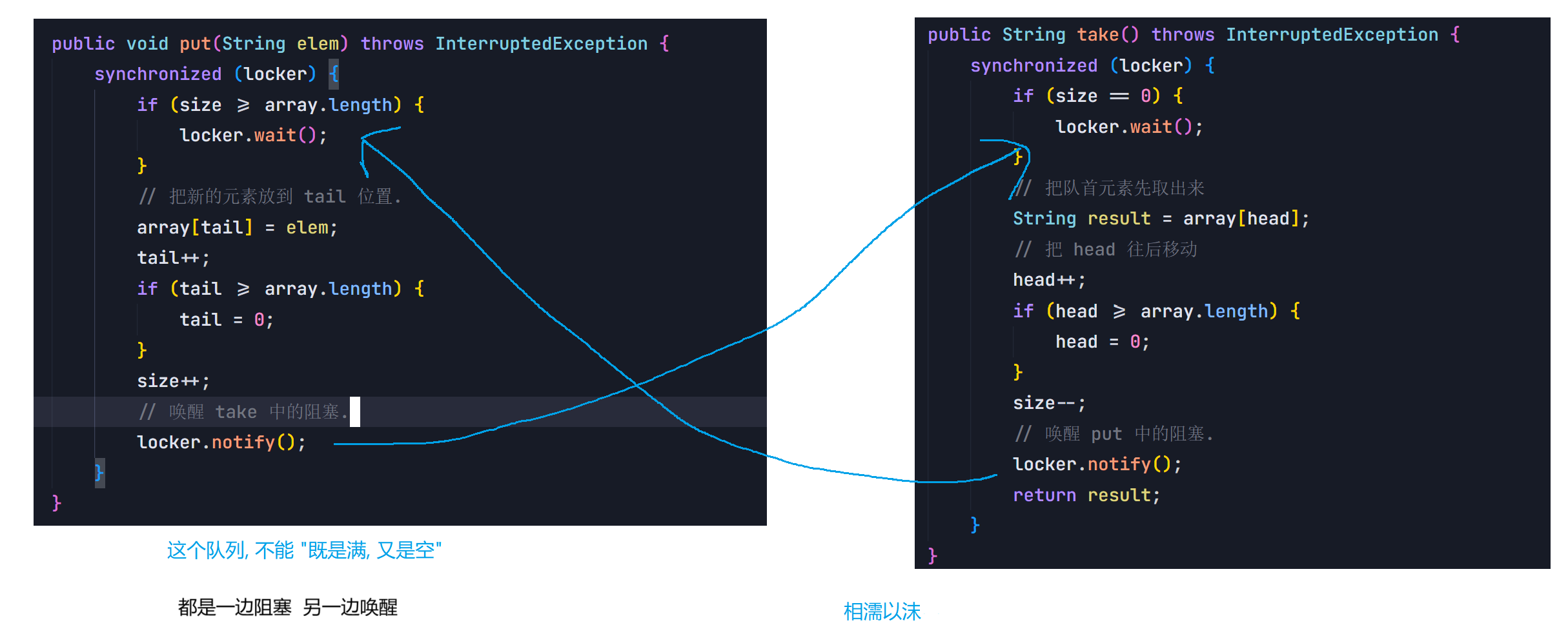
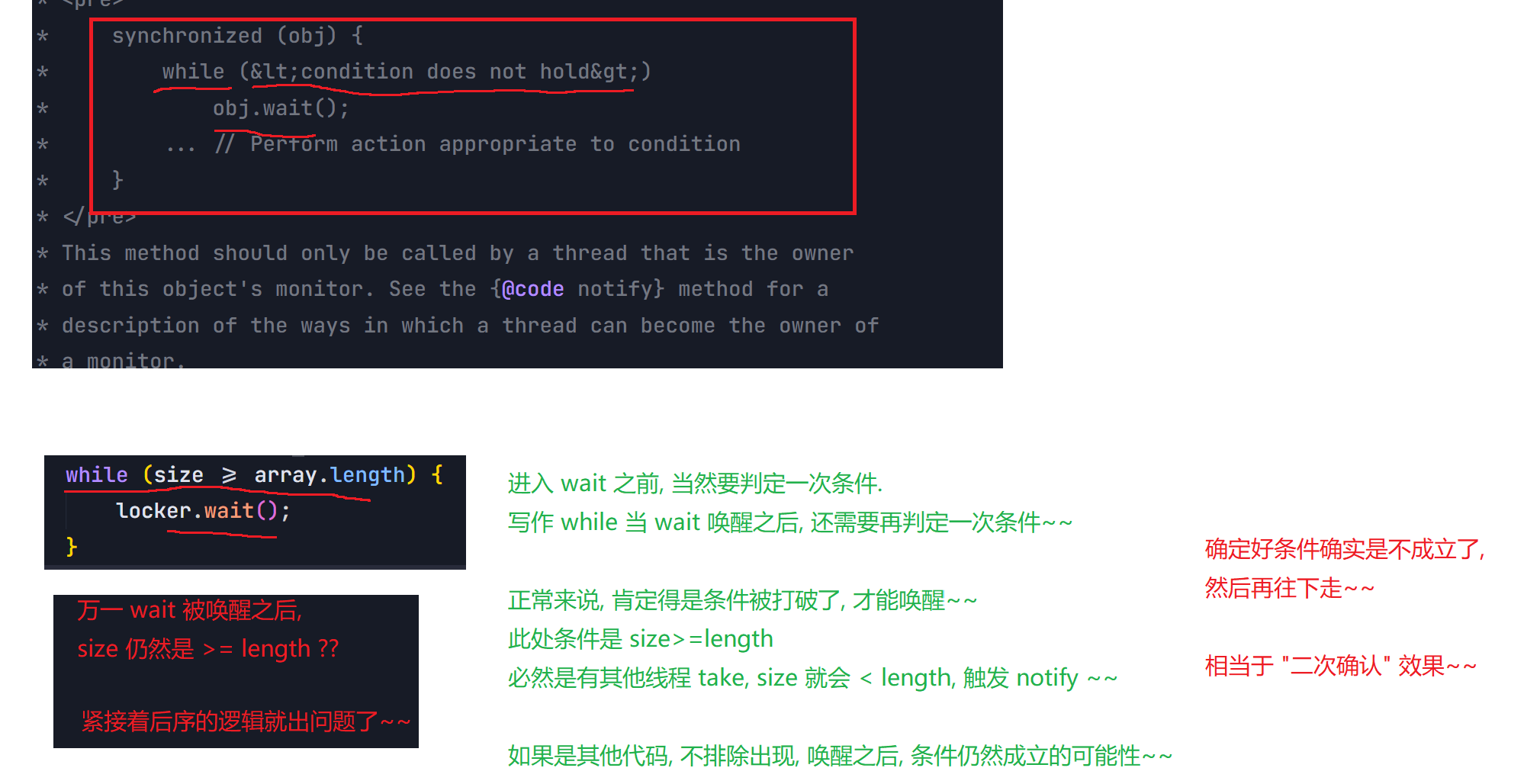
8.3 线程池
(1)概念
 线程池最大的好处就是减少每次启动、销毁线程的损耗。
线程池最大的好处就是减少每次启动、销毁线程的损耗。
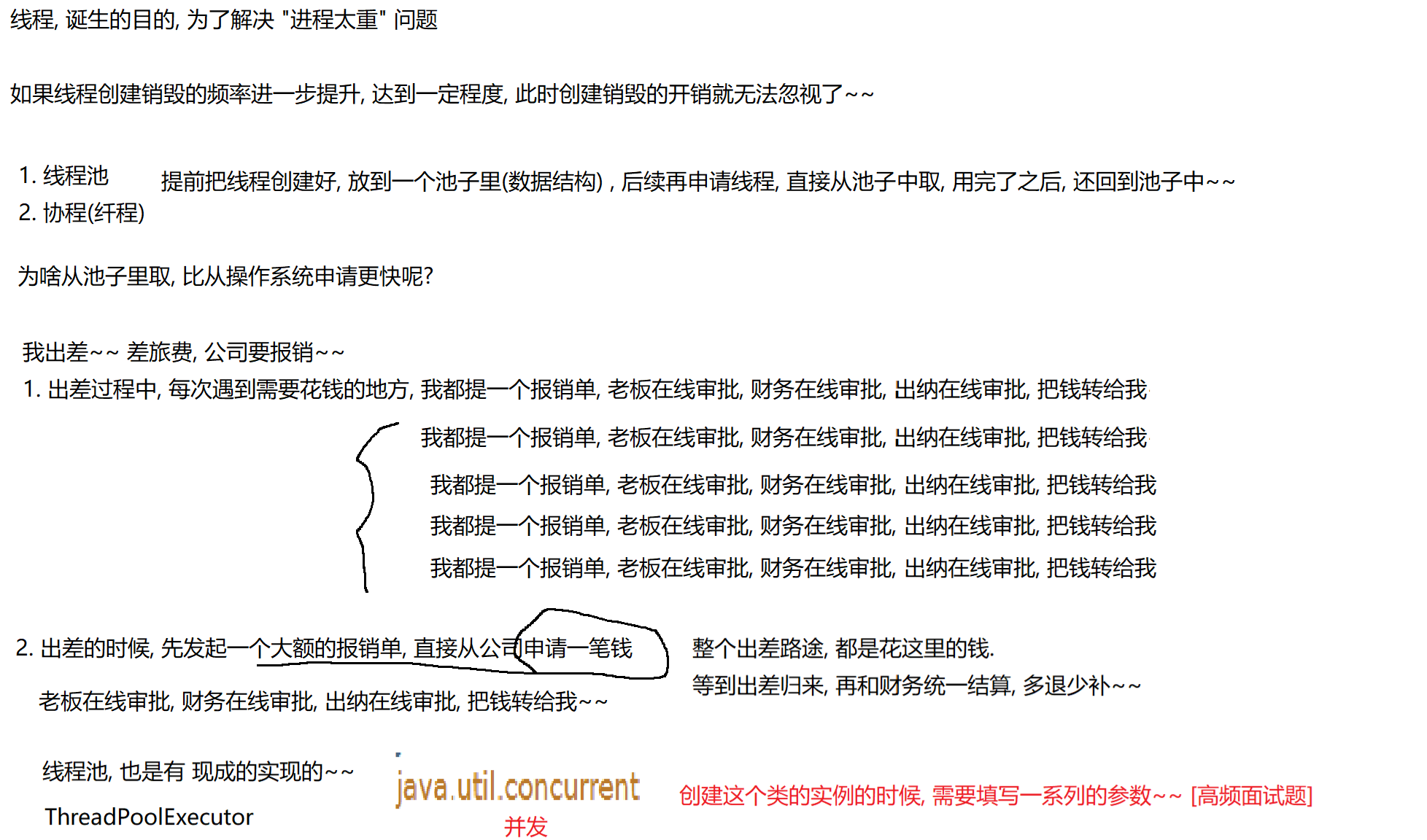


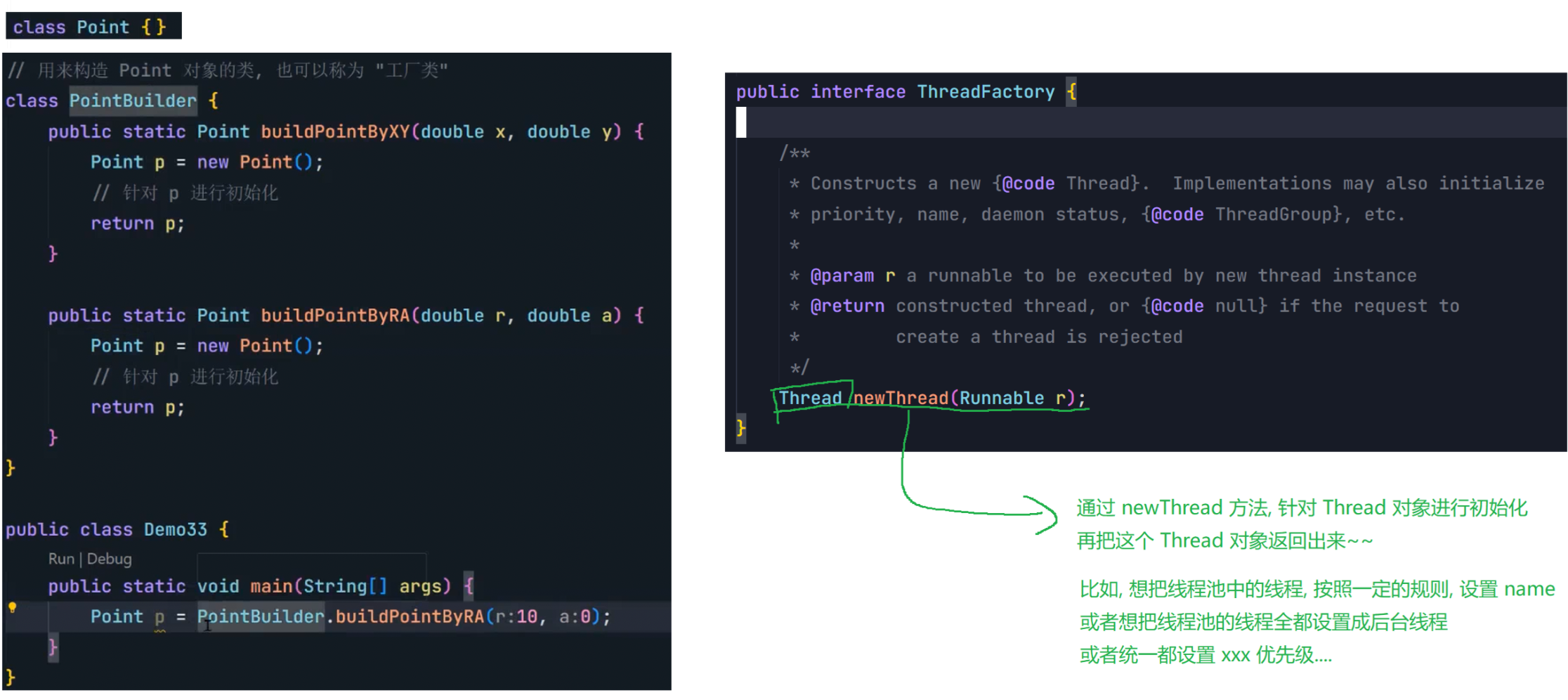
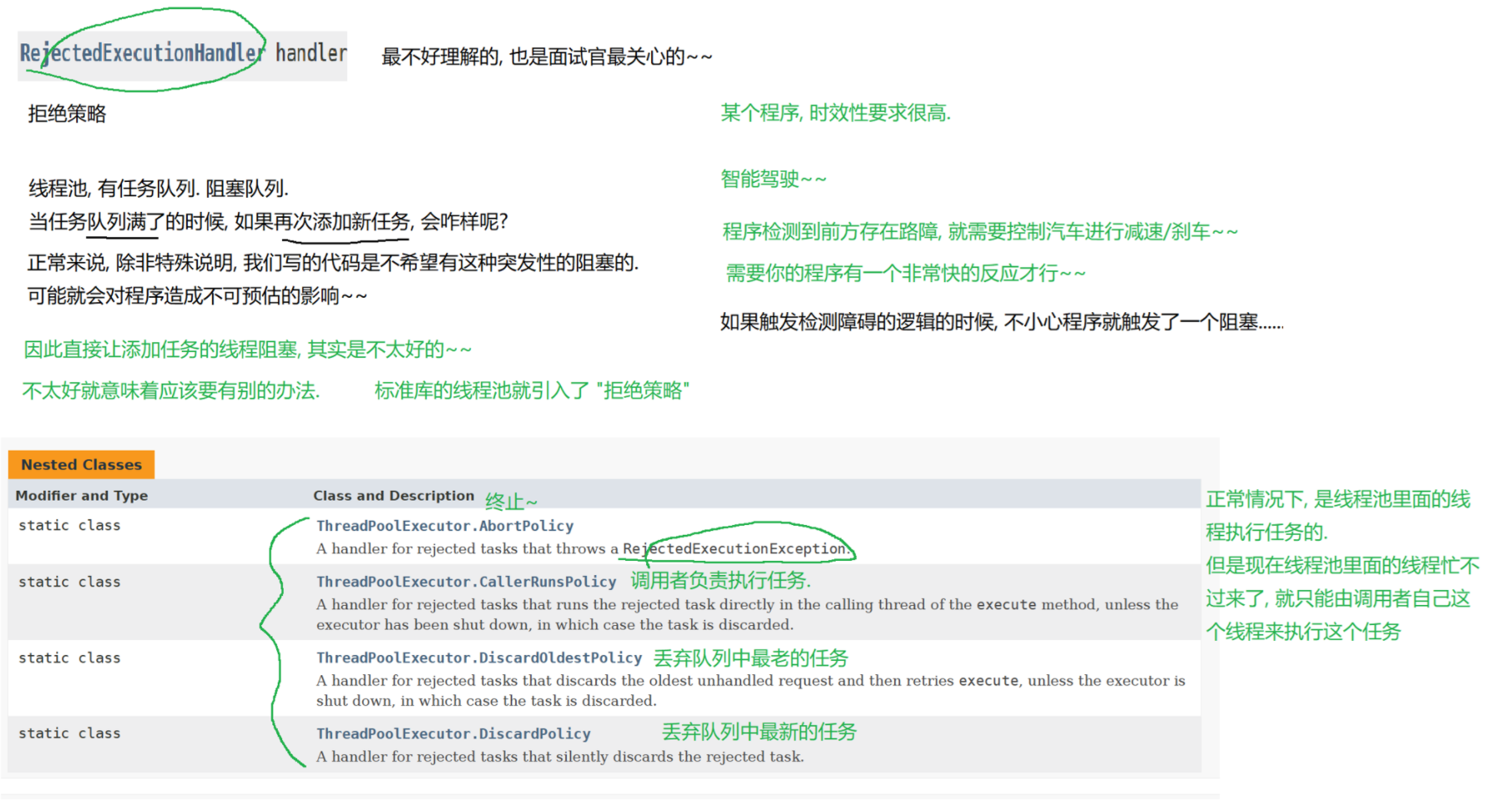
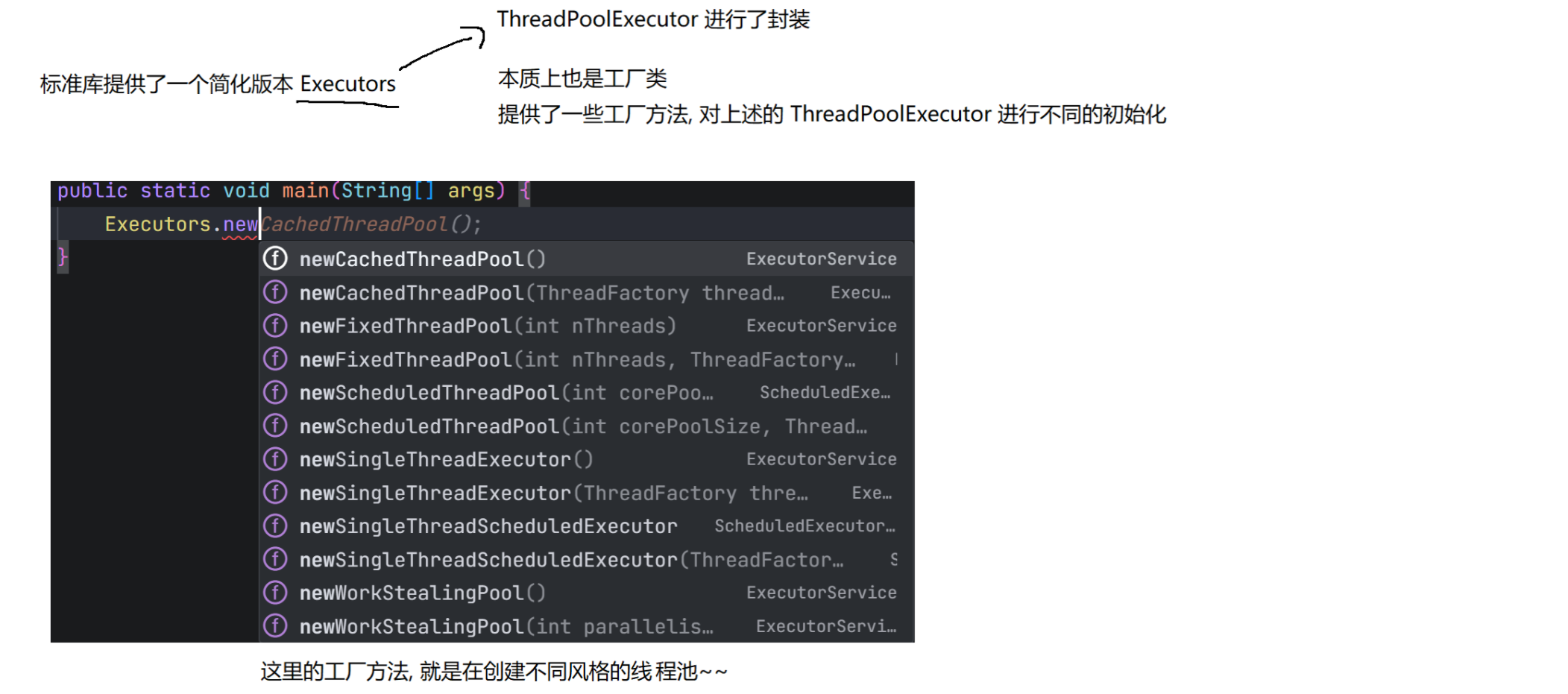
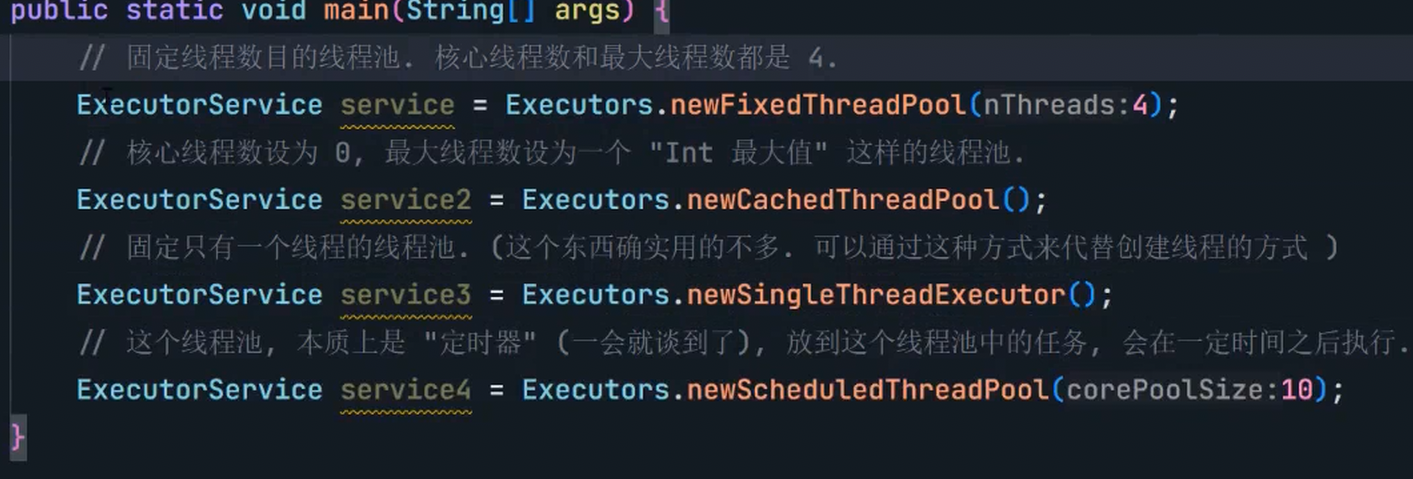

(2)模拟实现
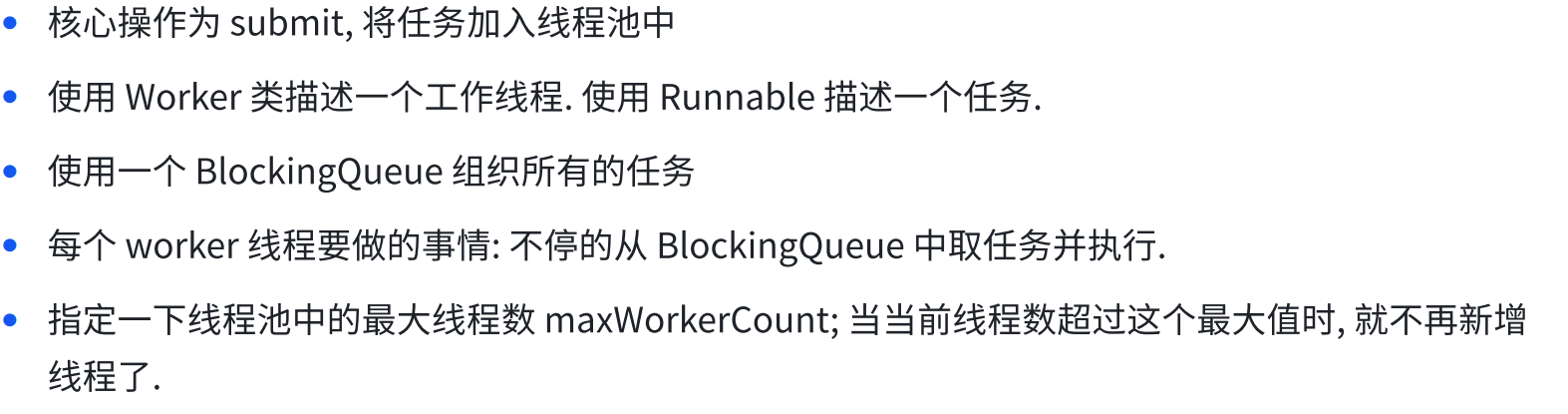

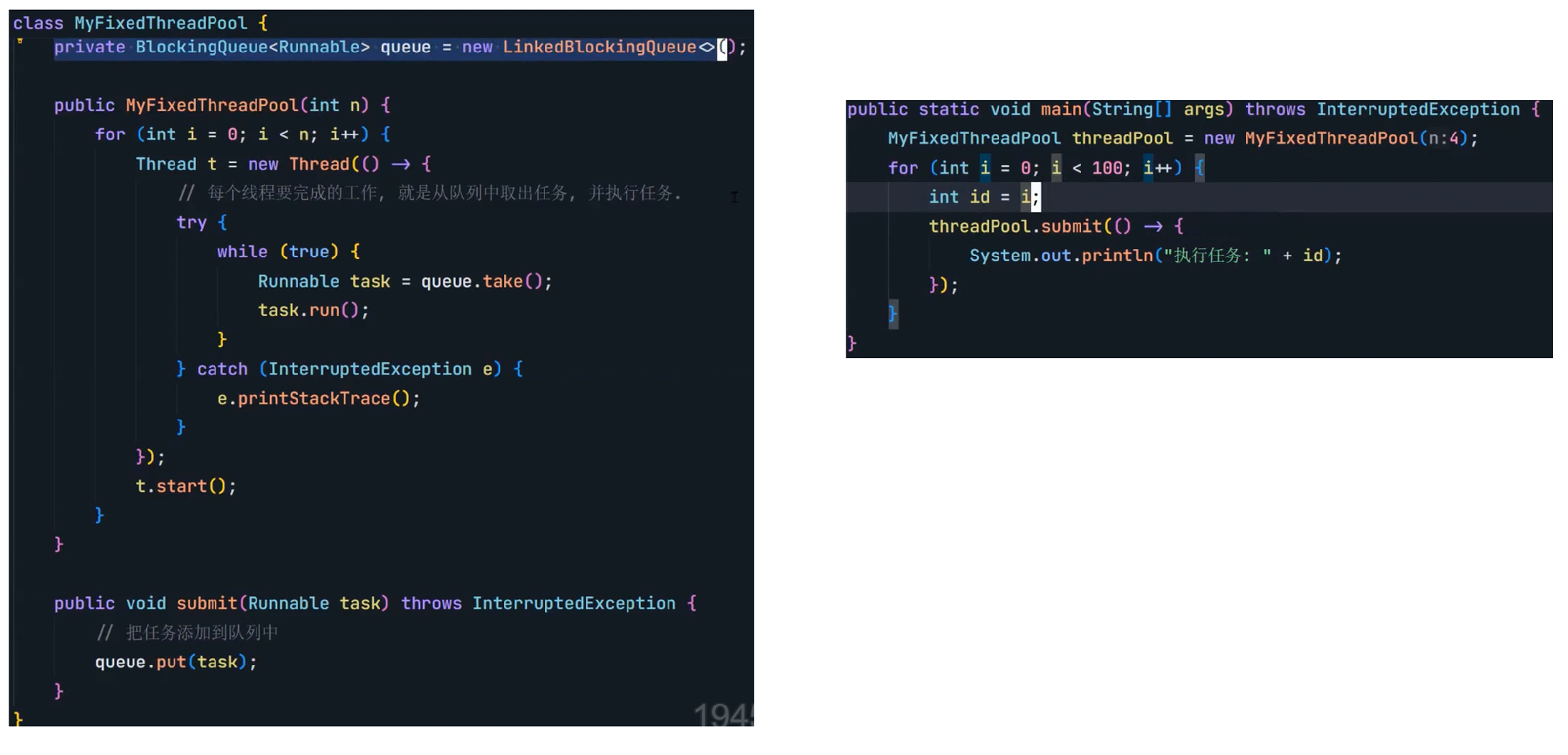
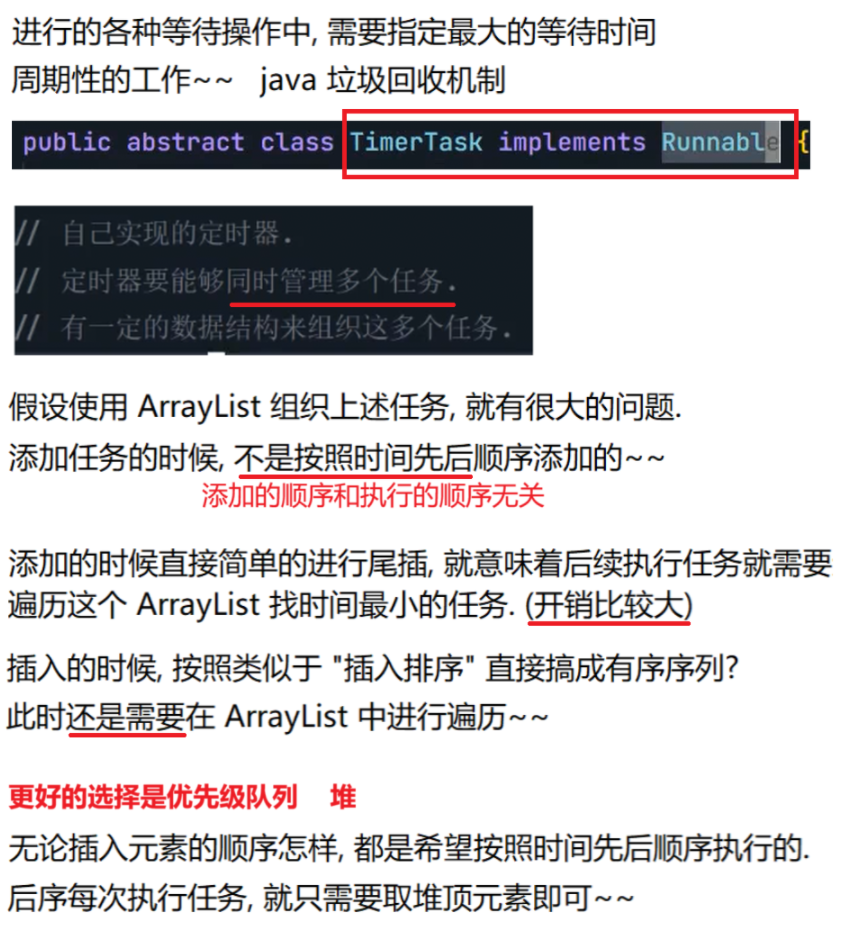
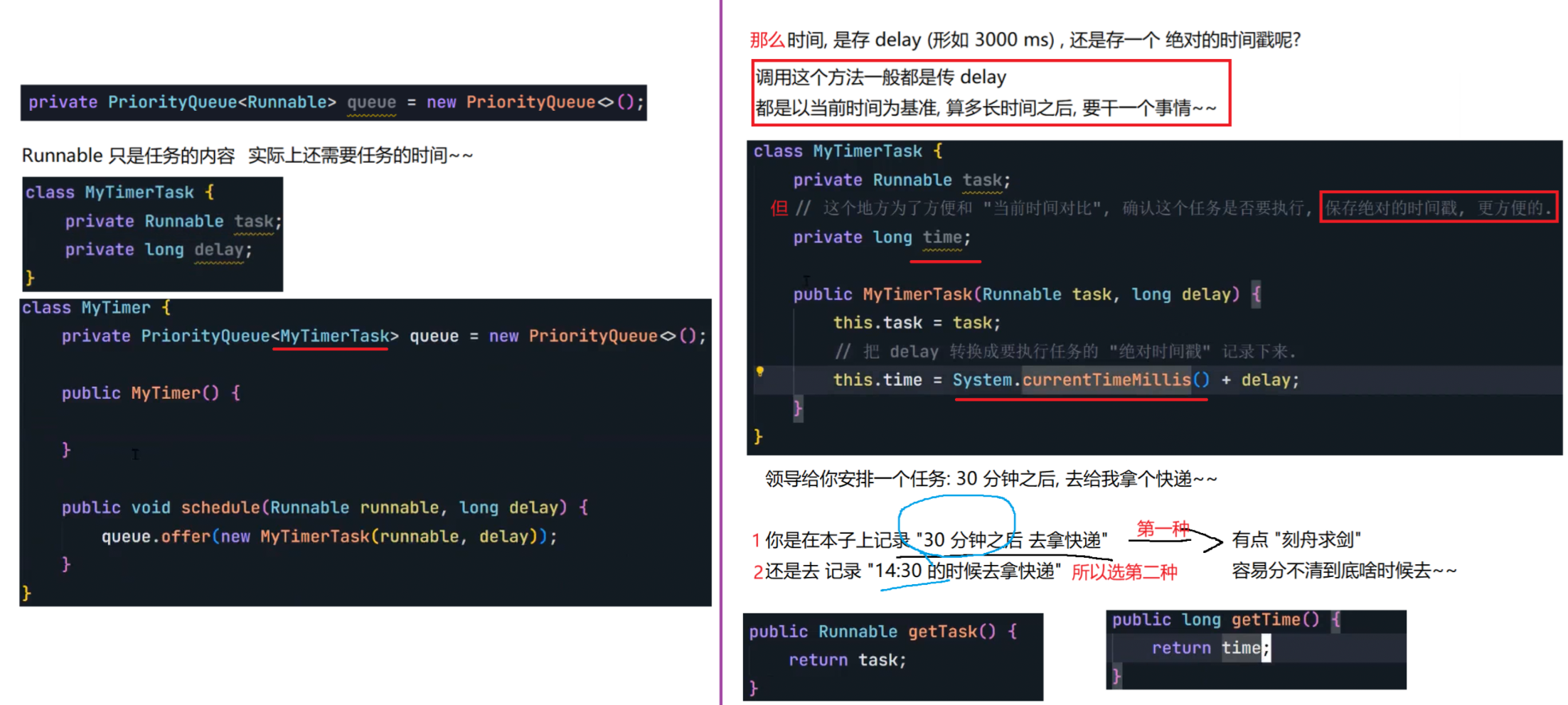
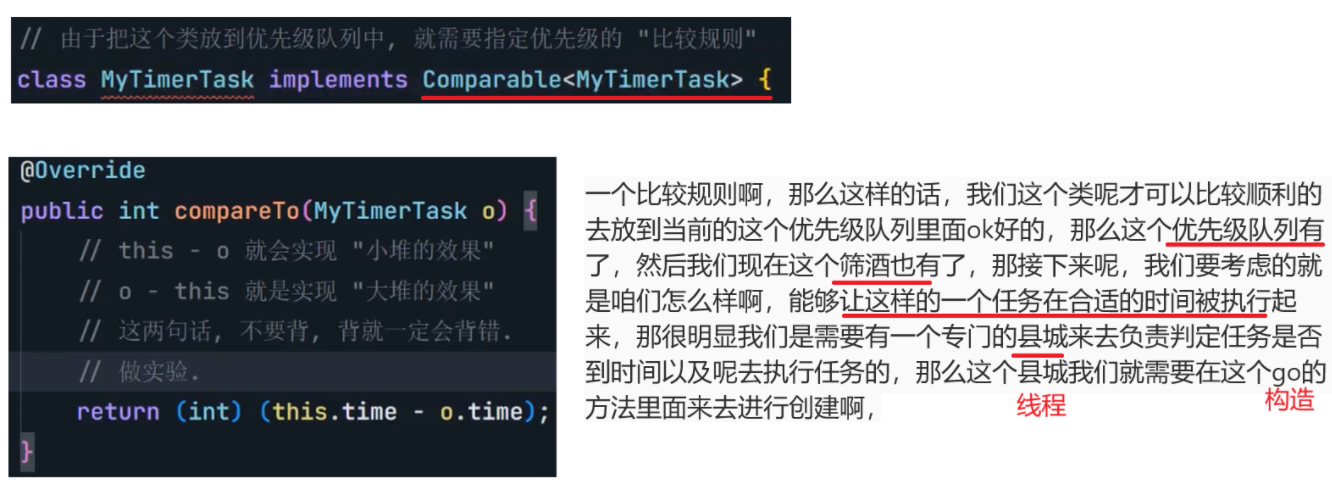
8.4 定时器
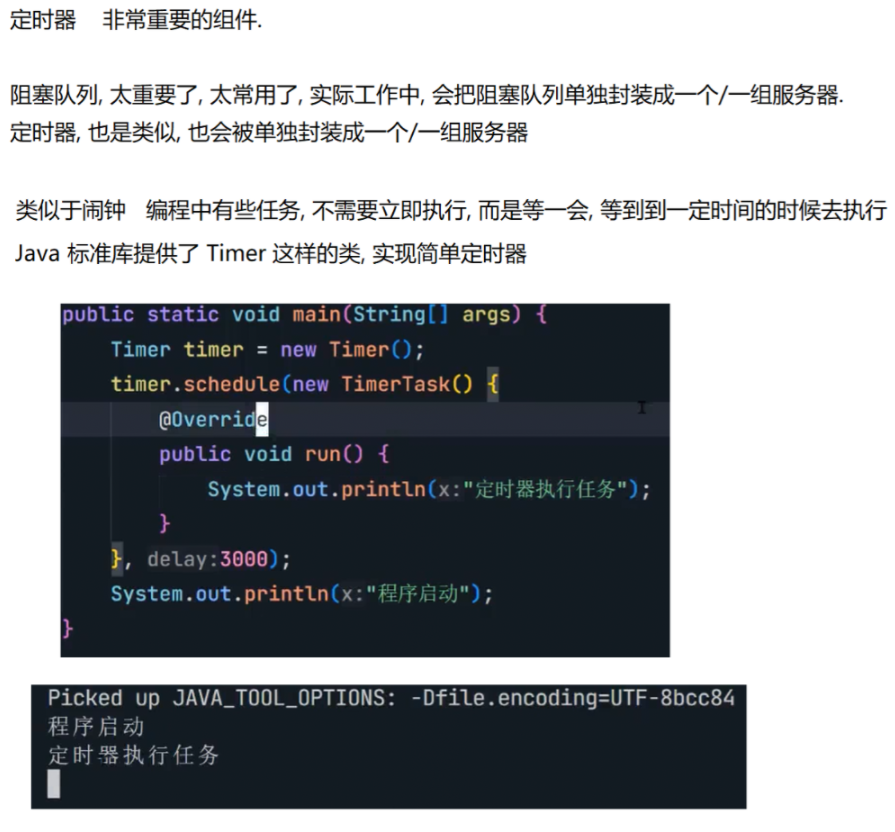

自行实现一个定时器
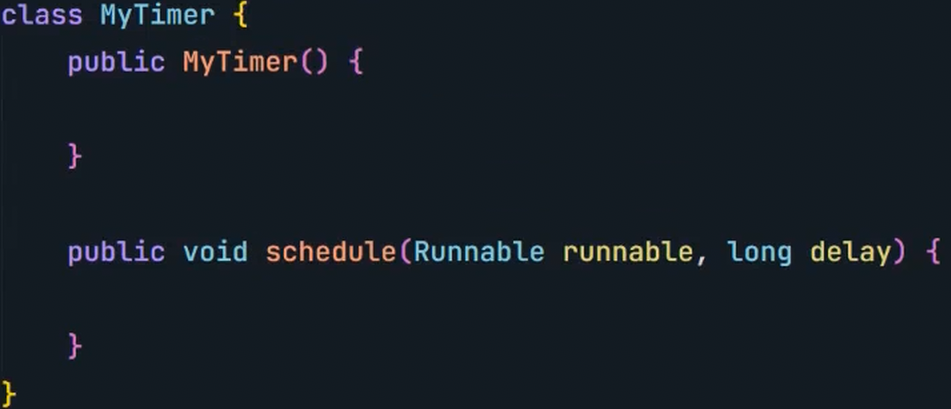
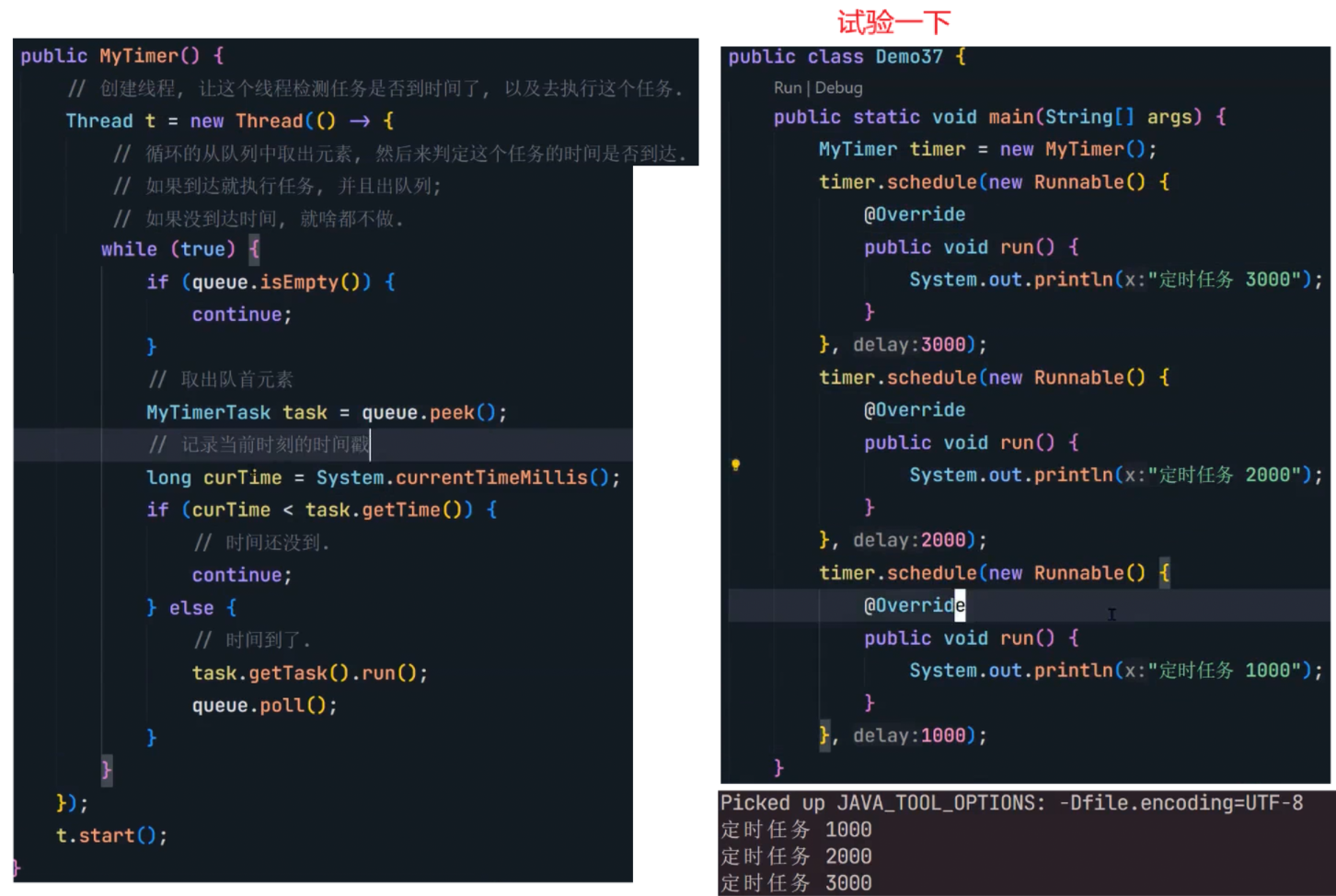
虽然执行结果看起来对了,但其实还是有几个问题的。




9.总结



