倘若代码中有任何问题或疑惑,欢迎提出交流哦~
在上一篇文章我们实现了页面的建设,接下来我们实现JavaScript交互逻辑。
交互功能:
- 密码显示
- 当用户输入的内容不符合规范时报错
- 在提交注册界面是若有报错则提交失败
密码显示
要实现密码显示的逻辑为:
- 获取密码
input对象 - 通过按钮点击事件来进行交互
- 若
input为password类型则转化为text类型,因为text会直接显示文本,而password类型不会,再对应切换图片的地址。
效果如下:
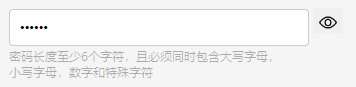
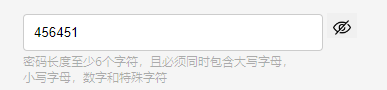
代码如下:
javascript
var password = document.getElementById('password');
var btn = document.getElementById('button');
var img = document.getElementById('img');
btn.onclick = function() {
if(password.type == "password") {
password.type = "text";
img.src = "./image/hide.png";
}else {
password.type = "password";
img.src = "./image/view.png";
}
}需要注意的是,因为button元素的默认类型是submit,当点击按钮时,会触发功能三、表单的提交事件,所以需要再里面加上类型type="button"。
验证内容
实现效果:在输入内容改变时就响应验证是否符合规范,若不符合则将对应提示信息转为红色,且在输入框左边出现红色感叹号。
那么我们在对应的html代码中就需要加入一个感叹号了,如下
html
<li>
<input type="text" id="name" placeholder="请输入用户昵称">
<span id="wrong" class="wrong">!</span>
<p class="prompt">用户名只能包含英文字符、中文字符、数字,长度在2-15。</p>
</li>那么在密码输入框又需要调整一下了,毕竟密码输入框右边有一个显示按钮。
这里给出昵称验证逻辑代码,为了文章篇幅,后面会给出总的代码,大体思路一样,在我之前的文章编写一个问卷界面 并用JavaScript来验证表单内容。里面有更详细地讲述了这里的验证过程。
javascript
// 验证输入部分,提示信息, 报错感叹号
var ipt = document.getElementsByTagName('input');
var p = document.getElementsByTagName('p');
var wrong = document.getElementsByClassName('wrong')
let bool = new Array(5).fill(true);
// 0 昵称验证逻辑
ipt[0].oninput = function() {
var name = ipt[0].value;
var request = /^[\u4e00-\u9fa5_a-zA-Z0-9]{2,15}$/
if(!request.test(name)) {
p[0].style.color = "red";
wrong[0].style.display = "inline"
bool[0] = false;
}else {
p[0].style.color = "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)";
wrong[0].style.display = "none"
bool[0] = true;x
}
}前瞻断言
五个输入验证当中,除了密码验证都与账号验证大差不差,而在密码验证里,因为我们要实现的效果是,同时包含大小写字母、数字和符号,同时包含的效果 ,需要使用正则表达式的"positive lookahead" ,又被称为前瞻断言 ,这里介绍用法:
"positive lookahead" 语法是:(?=...) 其中"..."是你想要寻找的模式。
正则表达式的 "positive lookahead" 是一种前瞻断言,它以特定的方式匹配字符串。具体来说,它会查找字符串中是否存在满足特定模式的部分,但它并不真的包含(消费)这个部分。
前瞻断言有以下两个特性:
它们是不消费(捕获)的,这意味着,正则表达式的进度在完成检查之后不会前进。换言之,它们只是检查可能性,而不消耗字符。
它们可以包含任何正则表达式元素,包括其他的前瞻断言。
请注意,JavaScript 的正则表达式也支持否定前瞻 (?!..),它的功能是与肯定前瞻相反:它会查找后续不匹配特定模式的部分。
密码相应的正则表达式如下所示:
javascript
/^(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*\d)(?=.*[^\da-zA-Z]).{6,20}$/这个表达式的含义如下:
(?=.*[a-z])确保至少有一个小写字母(?=.*[A-Z])确保至少有一个大写字母(?=.*\d)确保至少有一个数字(?=.*[^\da-zA-Z])确保至少有一个特殊字符{6,20}确保字符长度在6-20之间
在正则表达式中,点号 . 表示匹配任何单个字符(除了换行符),星号 * 用于指定前面的元素可以出现零次或多次。
因此, .* 的组合在正则表达式中意味着"匹配任何数量的任何字符"。
在前瞻断言中使用 .* 就会变得非常有用。当你写 (?=.*[a-z]) 时,你的意思是:"向前看,我希望在之后的某个地方看到一个小写字母。这个小写字母前可以有任何数量的任何字符。"
实现如下效果:
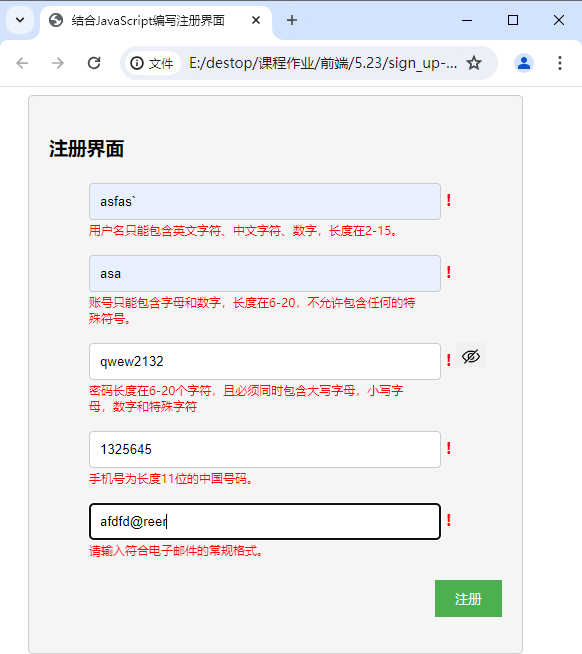
提交验证逻辑
思路为:遍历bool数组,如果有一个未通过,则提出警告框,显示提示信息,并且阻止表单提交。
效果如下:
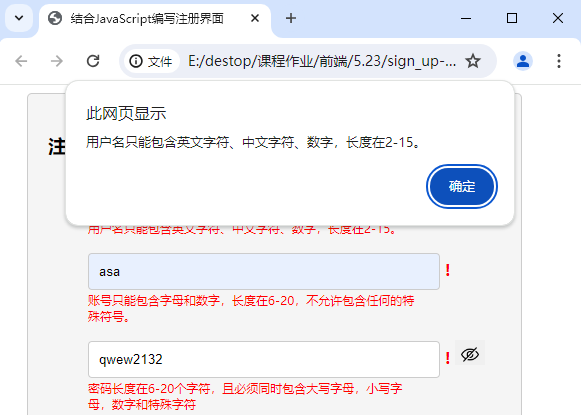
代码如下:
javascript
document.getElementsByTagName('form')[0].onsubmit = function() {
for(let i = 0; i < bool.length; i++) {
if(!bool[i]) {
alert(p[i].innerText);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}总代码
下面给出总代码以及图片:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>结合JavaScript编写注册界面</title>
<style>
.main {
/* 设置内容宽度以及水平居中 */
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-left: 20px;
/* 边框以及边框圆角 */
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
/* 背景颜色 */
background-color: #f5f5f5;
padding: 20px;
}
form ul li {
list-style: none;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
form ul li input[type="text"],
form ul li input[type="password"],
form ul li input[type="email"] {
width: 80%;
margin-top: 5px;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
/* 提示信息部分 */
.prompt {
/* 让文本和输入框更紧凑 */
margin-top: 2px;
width: 80%;
/* 设置提示信息为合适的大小,以及颜色 */
font-size: 12px;
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
}
.wrong {
color: red;
display: none;
font-weight: bold;
}
.pass-right {
display: inline;
}
/* 注册按钮部分 */
form ul li input[type="submit"] {
float: right;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 10px 20px;
border: none;
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
cursor: pointer;
}
form ul li input[type="submit"]:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
/* 显示图标部分 */
form ul li input[type="password"],
button {
display: inline;
}
button {
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
padding-top: 5px;
height: 25px;
width: 30px;
}
img {
/* 让图片占满整个区域 */
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<h3>注册界面</h3>
<form action="#">
<ul>
<li>
<input type="text" id="name" placeholder="请输入用户昵称">
<span id="wrong" class="wrong">!</span>
<p class="prompt">用户名只能包含英文字符、中文字符、数字,长度在2-15。</p>
</li>
<li>
<input type="text" id="account" placeholder="请输入账号">
<span id="wrong" class="wrong">!</span>
<p class="prompt">账号只能包含字母和数字,长度在6-20,不允许包含任何的特殊符号。</p>
</li>
<li>
<input type="password" id="password" placeholder="请输入密码">
<div class="pass-right">
<span id="wrong" class="wrong">!</span>
<button id="button" type="button"><img src="./image/view.png" alt="显示" id="img"></button>
</div>
<p class="prompt">密码长度在6-20个字符,且必须同时包含大写字母,小写字母,数字和特殊字符</p>
</li>
<li><input type="text" id="phone" placeholder="请输入你的手机号码">
<span id="wrong" class="wrong">!</span>
<p class="prompt">手机号为长度11位的中国号码。</p>
</li>
<li>
<input type="email" id="email" placeholder="请输入邮箱地址">
<span id="wrong" class="wrong">!</span>
<p class="prompt">请输入符合电子邮件的常规格式。</p>
</li>
<li>
<input type="submit" id="submit" value="注册">
<!-- 消除浮动类,避免上浮 -->
<div style="clear: both"></div>
</li>
</ul>
</form>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 交互功能:1. 密码显示 2. 当用户输入的内容不符合规范时报错 3. 在提交注册界面是若有报错则提交失败
// 密码显示部分
var password = document.getElementById('password');
var btn = document.getElementById('button');
var img = document.getElementById('img');
btn.onclick = function() {
if(password.type == "password") {
password.type = "text";
img.src = "./image/hide.png";
}else {
password.type = "password";
img.src = "./image/view.png";
}
}
// 验证输入部分,提示信息, 报错感叹号
var ipt = document.getElementsByTagName('input');
var p = document.getElementsByTagName('p');
var wrong = document.getElementsByClassName('wrong')
let bool = new Array(5).fill(false);
// 0 昵称验证逻辑
ipt[0].oninput = function() {
var name = ipt[0].value;
var request = /^[\u4e00-\u9fa5_a-zA-Z0-9]{2,15}$/
if(!request.test(name)) {
p[0].style.color = "red";
wrong[0].style.display = "inline"
bool[0] = false;
}else {
p[0].style.color = "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)";
wrong[0].style.display = "none"
bool[0] = true;
}
}
// 1 账号验证逻辑
ipt[1].oninput = function() {
var account = ipt[1].value;
var request = /^[a-zA-Z0-9]{6,20}$/
if(!request.test(account)){
p[1].style.color = "red";
wrong[1].style.display = "inline"
bool[1] = false;
}else {
p[1].style.color = "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)";
wrong[1].style.display = "none"
bool[1] = true;
}
}
// 2 密码验证逻辑
ipt[2].oninput = function() {
var password = ipt[2].value;
var request = /^(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*\d)(?=.*[^\da-zA-Z]).{6,20}$/
if(!request.test(password)){
p[2].style.color = "red";
wrong[2].style.display = "inline"
bool[2] = false;
}else {
p[2].style.color = "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)";
wrong[2].style.display = "none"
bool[2] = true;
}
}
// 3 手机号验证逻辑
ipt[3].oninput = function() {
var phone = ipt[3].value;
var request = /^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$/;
if(!request.test(phone)){
p[3].style.color = "red";
wrong[3].style.display = "inline"
bool[3] = false;
}else {
p[3].style.color = "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)";
wrong[3].style.display = "none"
bool[3] = true;
}
}
// 4 邮箱验证逻辑
ipt[4].oninput = function() {
var email = ipt[4].value;
// 一个常见的电邮验证正则表达式
var request = /^[\w.-]+@[a-zA-Z\d.-]+\.[a-zA-Z\d.-]+$/;
if(!request.test(email)) {
p[4].style.color = "red";
wrong[4].style.display = "inline";
bool[4] = false;
}else {
p[4].style.color = "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)";
wrong[4].style.display = "none";
bool[4] = true;
}
};
// 提交验证功能
document.getElementsByTagName('form')[0].onsubmit = function() {
for(let i = 0; i < bool.length; i++) {
if(!bool[i]) {
alert(p[i].innerText);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
</script>
</html>