行为型-策略模式
了解策略模式
策略模式是一种行为型设计模式,在策略模式中定义了一系列算法或者策略,并将这些策略封装到独立的类中,使得可以相互替换。在使用时,可以指定响应的策略使用。
角色
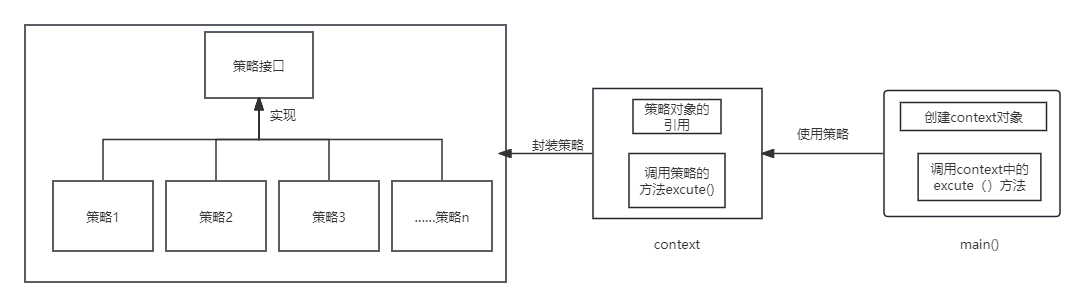
- 策略接口:对于某种行为的抽象,具体的行为由实现类决定;
- 具体策略类:实现策略接口,具体化其中的策略行为;
- 上下文类:次类中包含策略对象的引用,并通过引用调用策略实现类;
图解
实战
比较策略,可以根据不同的策略进行排序;
实体类:
java
/** 动物类*/
public class Animal {
private int height;
private int weight;
......
}
/** 人类*/
public class Person {
private int weight;
private double height;
private BigDecimal money;
......
}策略接口:
java
/** 自定义比较的策略接口*/
public interface Comparator<T> {
int compareTo(T o1,T o2);
}策略的实现类:
java
/** 按动物的重量比较动物*/
public class AnimalComparatorByHeight implements Comparator<Animal> {
@Override
public int compareTo(Animal o1, Animal o2) {
if(o1.getHeight()<o2.getHeight()){
return -1;
}else if (o1.getHeight() > o2.getHeight()){
return 1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
}
/** 按人的钱数量比较人*/
public class PersonComparatorByMoney implements Comparator<Person> {
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o1, Person o2) {
if(o1.getMoney().compareTo(o2.getMoney()) < 0){
return -1;
}else if(o1.getMoney().compareTo(o2.getMoney()) > 0){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
/** ......
* 还可一定义其它的排序策略,只需要实现策略接口
*/context类:
java
/** 排序类,可根据不同的策略排序不同的对象*/
public class Sorter<T> {
private Comparator<T> comparator;
private T [] arr;
public Sorter() {
}
public Sorter(Comparator<T> comparator, T[] arr) {
this.comparator = comparator;
this.arr = arr;
}
/**
* 冒泡排序
*/
public void sort(){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length -1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length -1 -i; j++) {
if(comparator.compareTo(arr[j], arr[j+1]) > 0){
change(j,j+1);
}
}
}
}
public void change(Integer a, Integer b){
T temp = arr[a];
arr[a] = arr[b];
arr[b] = temp;
}
}使用:
java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 根据动物重量排序
*/
Animal[] animals = new Animal[]{
new Animal(3,3),
new Animal(5,5),
new Animal(1,1),
new Animal(4,4)
};
Sorter<Animal> animalSorter = new Sorter<>(new AnimalComparatorByHeight(),animals);
animalSorter.sort();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(animals));
/**
* 根据人钱数量排序
*/
Person[] person = new Person[]{
new Person(3,3,new BigDecimal(900)),
new Person(5,5,new BigDecimal(300)),
new Person(1,1,new BigDecimal(500)),
new Person(4,4,new BigDecimal(600))
};
Sorter<Person> personSorter = new Sorter<>(new PersonComparatorByMoney(),person);
personSorter.sort();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(person));
}
}总结
使用策略模式定义行为的抽象,行为的具体方式由实现类实现;如果再添加其他行为的时候只需要增加策略接口的实现类,而不需要修改现有的代码,提高了代码的拓展性能,同时保证的对拓展开放对修改关闭的开闭原则;