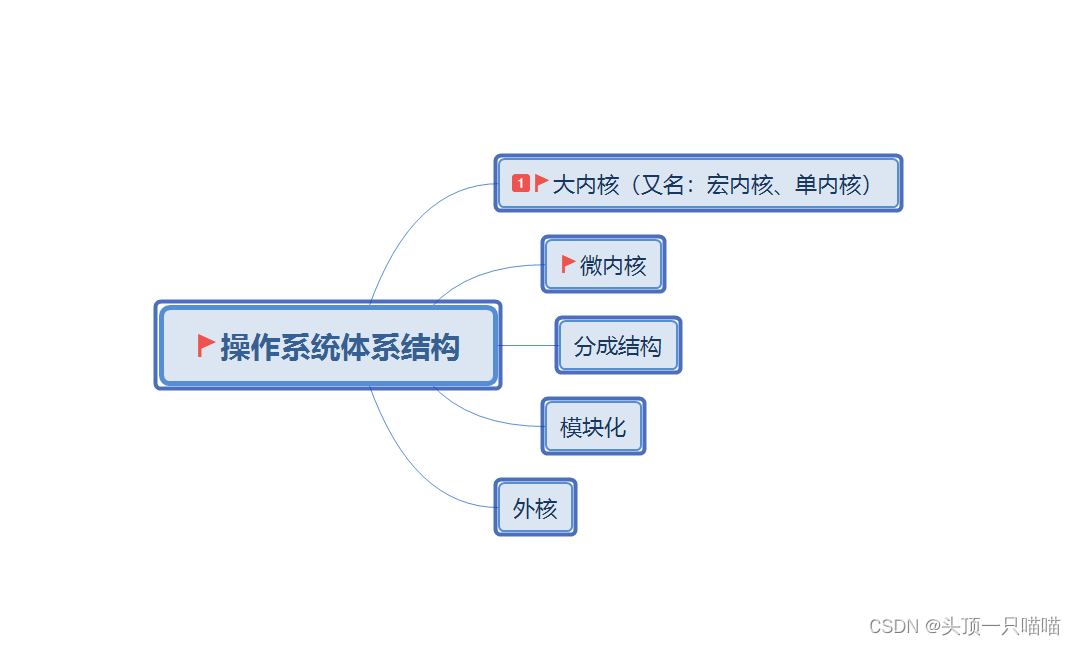
1.操作系统体系结构图:
2.操作系统的内核:
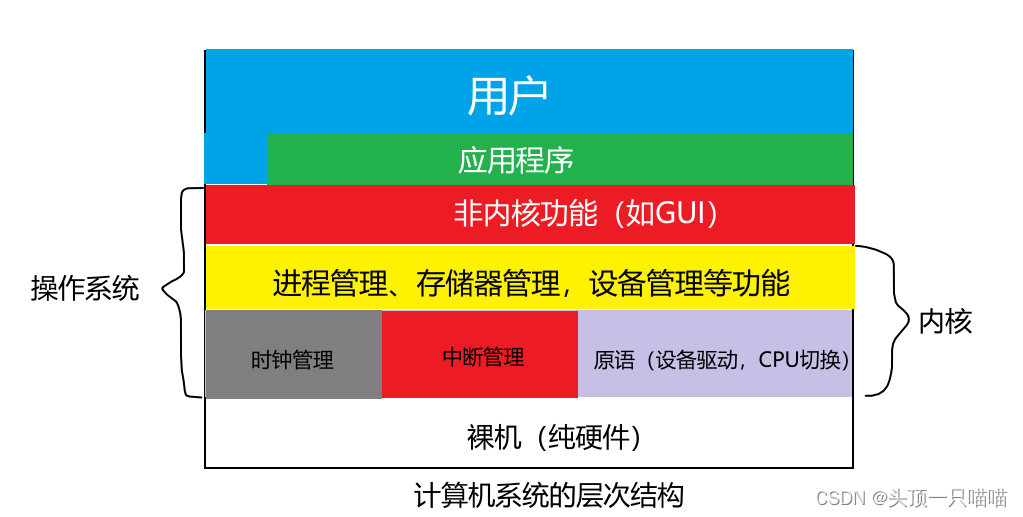
时钟管理:利用时钟中断实现计时功能。
原语:原语是一种特殊的程序,具有原子性。也就是说,这段程序运行必须一气呵成,不能被中断。
ubuntu、centos的开发,其中的主要工作都是为了实现非内核功能,其内核都是用Linux内核。
总的来说:内核是操作系统最基本、最核心的部分。实现操作系统内核功能的那些程序就是内核程序。

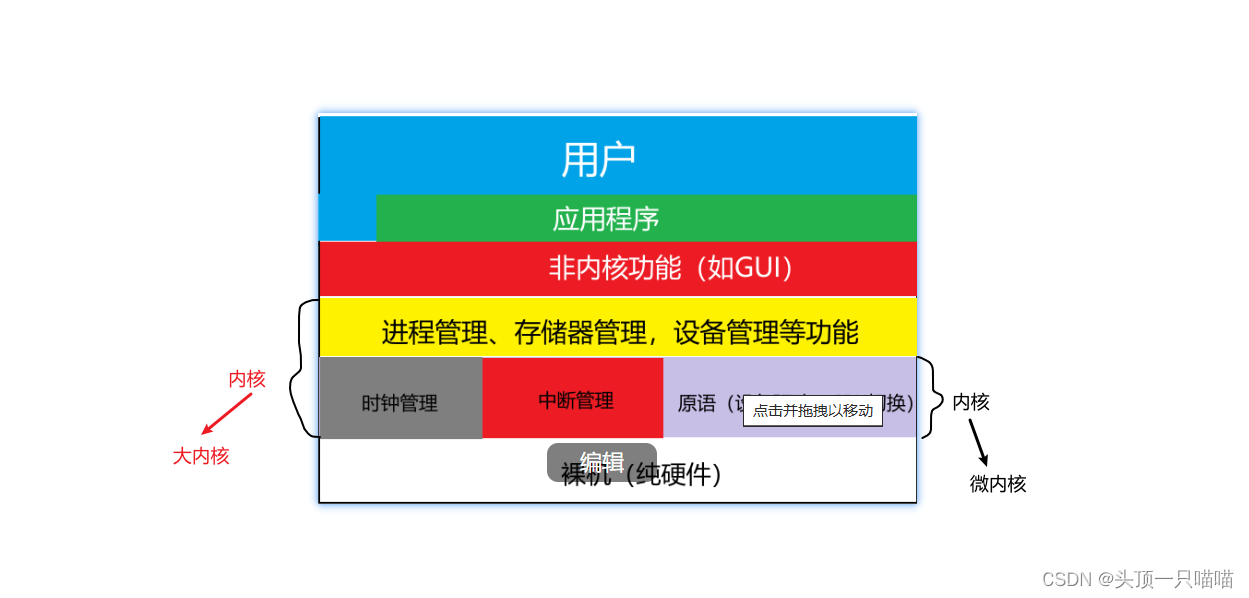
注意:操作系统内核需要运行在内核态。
操作系统的非内核功能运行在用户态。
3.大内核与微内核的区别和优缺点:

典型的大内核/宏内核/单内核操作系统:Linux、UNIX
典型的微内核操作系统:WindowsNT