本文首发在个人博客上,欢迎来踩!
本次分析参考的K8s版本是v1.27.0。
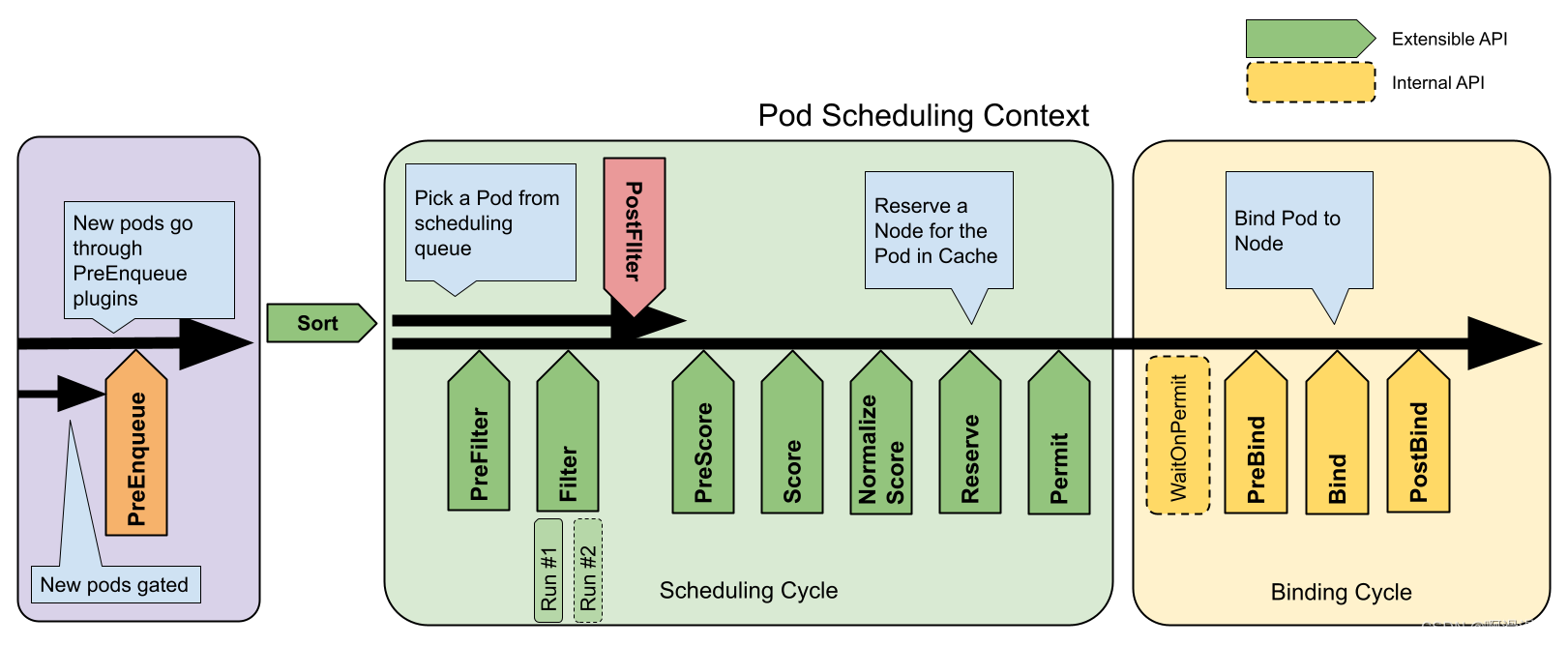
K8s的整体调度框架如下图所示。
调度框架顶层函数
K8s调度器调度的核心函数schedulerone在pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go:62,如下,这里将一些解释写在了注释里
go
// scheduleOne does the entire scheduling workflow for a single pod. It is serialized on the scheduling algorithm's host fitting.
func (sched *Scheduler) scheduleOne(ctx context.Context) {
// 获取调度队列中的下一个 Pod 信息
podInfo := sched.NextPod()
// 如果 podInfo 或者其包含的 Pod 为 nil,说明调度队列关闭或者没有 Pod 需要调度,直接返回
if podInfo == nil || podInfo.Pod == nil {
return
}
// 获取 Pod 对象
pod := podInfo.Pod
// 为当前 Pod 选择一个调度框架(scheduler framework)
fwk, err := sched.frameworkForPod(pod)
if err != nil {
// 这种情况不应该发生,因为我们只接受那些指定了匹配调度器名称的 Pod 进行调度
klog.ErrorS(err, "Error occurred")
return
}
// 如果跳过调度,则直接返回
if sched.skipPodSchedule(fwk, pod) {
return
}
// 记录尝试调度 Pod 的日志
klog.V(3).InfoS("Attempting to schedule pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
// 开始计时,尝试为 Pod 找到合适的宿主机
start := time.Now()
// 初始化调度周期状态
state := framework.NewCycleState()
// 设置是否记录插件指标的随机概率
state.SetRecordPluginMetrics(rand.Intn(100) < pluginMetricsSamplePercent)
// 初始化一个空的 podsToActivate 结构,这个结构将由插件填充或者保持为空
podsToActivate := framework.NewPodsToActivate()
// 将 podsToActivate 写入状态中
state.Write(framework.PodsToActivateKey, podsToActivate)
// 创建一个新的带有取消功能的上下文,用于调度周期
schedulingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
// 执行调度周期,尝试为 Pod 找到合适的宿主机
scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, status := sched.schedulingCycle(schedulingCycleCtx, state, fwk, podInfo, start, podsToActivate)
// 如果调度失败,则调用失败处理器
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.FailureHandler(schedulingCycleCtx, fwk, assumedPodInfo, status, scheduleResult.nominatingInfo, start)
return
}
// 异步绑定 Pod 到其宿主机(可以这样做是因为上面的假设步骤)
go func() {
// 创建一个新的带有取消功能的上下文,用于绑定周期
bindingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
// 增加绑定阶段的 goroutine 指标
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Inc()
defer metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Dec()
metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Inc()
defer metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Dec()
// 执行绑定周期,尝试将 Pod 绑定到宿主机
status := sched.bindingCycle(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, start, podsToActivate)
// 如果绑定失败,则处理绑定周期错误
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.handleBindingCycleError(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, assumedPodInfo, start, scheduleResult, status)
}
}()
}这段代码的主要功能是:
- 从调度队列中获取下一个要调度的 Pod。
- 为 Pod 选择一个调度框架。
- 如果配置允许,跳过调度。
- 记录日志并开始调度周期。
- 如果调度成功,异步地尝试将 Pod 绑定到选定的宿主机。
- 如果调度或绑定失败,执行相应的错误处理逻辑。
此处也指明了两个周期,分别为调度周期schedulingCycle和绑定周期bindingCycle,绑定周期会在后面一节进行介绍,这里主要关注schedulingCycle 。
查看关键的schedulingCycle函数,在pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go:120中,补充了部分注释。
go
// schedulingCycle tries to schedule a single Pod.
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulingCycle(
ctx context.Context, // 调度上下文
state *framework.CycleState, // 调度周期状态
fwk framework.Framework, // 调度框架
podInfo *framework.QueuedPodInfo, // 待调度的 Pod 信息
start time.Time, // 调度开始时间
podsToActivate *framework.PodsToActivate, // 待激活的 Pods
) (ScheduleResult, *framework.QueuedPodInfo, *framework.Status) {
// 获取待调度的 Pod
pod := podInfo.Pod
// 调用调度器的 SchedulePod 方法尝试调度 Pod
scheduleResult, err := sched.SchedulePod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
if err != nil {
// 如果没有可用节点,则返回错误状态
if err == ErrNoNodesAvailable {
status := framework.NewStatus(framework.UnschedulableAndUnresolvable).WithError(err)
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, podInfo, status
}
// 如果错误是 FitError 类型,则说明 Pod 无法适应任何节点
fitError, ok := err.(*framework.FitError)
if !ok {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Error selecting node for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, podInfo, framework.AsStatus(err)
}
// 如果没有 PostFilter 插件,则不执行抢占
if !fwk.HasPostFilterPlugins() {
klog.V(3).InfoS("No PostFilter plugins are registered, so no preemption will be performed")
return ScheduleResult{}, podInfo, framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable).WithError(err)
}
// 运行 PostFilter 插件,尝试使 Pod 在未来的调度周期中可调度
result, status := fwk.RunPostFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod, fitError.Diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
msg := status.Message()
fitError.Diagnosis.PostFilterMsg = msg
if status.Code() == framework.Error {
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Status after running PostFilter plugins for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "status", msg)
} else {
klog.V(5).InfoS("Status after running PostFilter plugins for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "status", msg)
}
// 获取 PostFilter 插件返回的 NominatingInfo
var nominatingInfo *framework.NominatingInfo
if result != nil {
nominatingInfo = result.NominatingInfo
}
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: nominatingInfo}, podInfo, framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable).WithError(err)
}
// 计算并记录调度算法的延迟
metrics.SchedulingAlgorithmLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(start))
// 假设 Pod 已经在给定节点上运行,这样子就不用等它实际绑定就可以执行后续的操作了
assumedPodInfo := podInfo.DeepCopy()
assumedPod := assumedPodInfo.Pod
// 假设操作,设置 Pod 的 NodeName 为调度结果推荐的宿主机
err = sched.assume(assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if err != nil {
// 如果假设操作失败,这可能是重试逻辑中的一个 BUG
// 报告错误以便重新调度 Pod
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode},
assumedPodInfo,
framework.AsStatus(err)
}
// 运行预留插件的 Reserve 方法
if sts := fwk.RunReservePluginsReserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !sts.IsSuccess() {
// 如果预留失败,触发取消预留以清理与预留 Pod 相关的资源
fwk.RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if forgetErr := sched.Cache.ForgetPod(assumedPod); forgetErr != nil {
klog.ErrorS(forgetErr, "Scheduler cache ForgetPod failed")
}
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode},
assumedPodInfo,
sts
}
// 运行 "permit" 插件
runPermitStatus := fwk.RunPermitPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if !runPermitStatus.IsWait() && !runPermitStatus.IsSuccess() {
// 如果许可检查失败,触发取消预留以清理与预留 Pod 相关的资源
fwk.RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if forgetErr := sched.Cache.ForgetPod(assumedPod); forgetErr != nil {
klog.ErrorS(forgetErr, "Scheduler cache ForgetPod failed")
}
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode},
assumedPodInfo,
runPermitStatus
}
// 成功调度周期结束后,查看是否有必要设置一些pod为可调度的状态
if len(podsToActivate.Map) != 0 {
sched.SchedulingQueue.Activate(podsToActivate.Map)
// 激活后清空条目
podsToActivate.Map = make(map[string]*v1.Pod)
}
// 返回调度结果
return scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, nil
}主要流程包括:
- 尝试调度 Pod,并处理可能出现的错误。
- 如果调度失败,根据错误类型执行不同的逻辑,如处理节点不可用或 Pod 不适应任何节点的情况。
- 如果调度成功,记录调度算法的延迟,并提前假设 Pod 已经在推荐的节点上运行。
- 运行预留插件的 Reserve 方法,并处理预留成功或失败的情况。
- 运行抢占插件,并根据结果进行相应的处理。
- 如果有待转为active的 Pods,执行激活操作。
- 返回调度结果。
一般调度
这里最关键的是SchedulePod函数,在pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go:334中
go
// schedulePod tries to schedule the given pod to one of the nodes in the node list.
// If it succeeds, it will return the name of the node.
// If it fails, it will return a FitError with reasons.
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulePod(ctx context.Context, fwk framework.Framework, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) (result ScheduleResult, err error) {
trace := utiltrace.New("Scheduling", utiltrace.Field{Key: "namespace", Value: pod.Namespace}, utiltrace.Field{Key: "name", Value: pod.Name})
defer trace.LogIfLong(100 * time.Millisecond)
if err := sched.Cache.UpdateSnapshot(sched.nodeInfoSnapshot); err != nil {
return result, err
}
trace.Step("Snapshotting scheduler cache and node infos done")
if sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NumNodes() == 0 {
return result, ErrNoNodesAvailable
}
feasibleNodes, diagnosis, err := sched.findNodesThatFitPod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
trace.Step("Computing predicates done")
if len(feasibleNodes) == 0 {
return result, &framework.FitError{
Pod: pod,
NumAllNodes: sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NumNodes(),
Diagnosis: diagnosis,
}
}
// When only one node after predicate, just use it.
if len(feasibleNodes) == 1 {
return ScheduleResult{
SuggestedHost: feasibleNodes[0].Name,
EvaluatedNodes: 1 + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap),
FeasibleNodes: 1,
}, nil
}
priorityList, err := prioritizeNodes(ctx, sched.Extenders, fwk, state, pod, feasibleNodes)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
host, err := selectHost(priorityList)
trace.Step("Prioritizing done")
return ScheduleResult{
SuggestedHost: host,
EvaluatedNodes: len(feasibleNodes) + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap),
FeasibleNodes: len(feasibleNodes),
}, err
}在这里我们就能具体的看到predicates筛选过程和Prioritizing打分过程,整体的逻辑也比较简单,首先是筛选出合适的node,如果只有一个node了,那么就直接返回这个node,如果有多个就进行打分,然后选择评分最高的node返回回去。
筛选过程
然后我们查看predicates筛选过程,其代码在pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go:387中,如下,补充了一些注释
go
// Filters the nodes to find the ones that fit the pod based on the framework
// filter plugins and filter extenders.
func (sched *Scheduler) findNodesThatFitPod(ctx context.Context, fwk framework.Framework, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) ([]*v1.Node, framework.Diagnosis, error) {
// 初始化诊断信息,用于记录调度过程中的详细信息
diagnosis := framework.Diagnosis{
NodeToStatusMap: make(framework.NodeToStatusMap),
UnschedulablePlugins: sets.NewString(),
}
// 获取所有节点的信息
allNodes, err := sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfos().List()
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
// 运行 "prefilter" 插件
preRes, s := fwk.RunPreFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod)
if !s.IsSuccess() {
if !s.IsUnschedulable() {
return nil, diagnosis, s.AsError()
}
// 如果 PreFilter 插件返回的状态是不可调度的,记录相关信息
msg := s.Message()
diagnosis.PreFilterMsg = msg
klog.V(5).InfoS("Status after running PreFilter plugins for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "status", msg)
// 如果有插件失败,记录失败的插件名称
if s.FailedPlugin() != "" {
diagnosis.UnschedulablePlugins.Insert(s.FailedPlugin())
}
return nil, diagnosis, nil
}
// 如果 Pod 已经被提名到一个节点上(可能由于之前的抢占操作),
// 这个节点很可能是唯一一个合适的节点,所以首先评估这个节点
if len(pod.Status.NominatedNodeName) > 0 {
feasibleNodes, err := sched.evaluateNominatedNode(ctx, pod, fwk, state, diagnosis)
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Evaluation failed on nominated node", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "node", pod.Status.NominatedNodeName)
}
// 如果提名的节点通过了所有的过滤,调度器可以决定将这个节点分配给 Pod
if len(feasibleNodes) != 0 {
return feasibleNodes, diagnosis, nil
}
}
// 根据 PreFilter 插件的结果,可能需要过滤掉一些节点
nodes := allNodes
if !preRes.AllNodes() {
nodes = make([]*framework.NodeInfo, 0, len(preRes.NodeNames))
for n := range preRes.NodeNames {
nInfo, err := sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfos().Get(n)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
nodes = append(nodes, nInfo)
}
}
// 寻找通过过滤的节点
feasibleNodes, err := sched.findNodesThatPassFilters(ctx, fwk, state, pod, diagnosis, nodes)
// 无论是否发生错误,都尝试更新下一次开始搜索节点的索引
processedNodes := len(feasibleNodes) + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
sched.nextStartNodeIndex = (sched.nextStartNodeIndex + processedNodes) % len(nodes)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
// 检查过滤扩展器以找到更多通过过滤的节点
feasibleNodes, err = findNodesThatPassExtenders(sched.Extenders, pod, feasibleNodes, diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
// 返回所有通过过滤的节点
return feasibleNodes, diagnosis, nil
}这部分首先运行preFilter插件首先进行一些轻量级的检查,然后再运行filter插件进行正式筛选,然后在运行filter拓展插件。
这里我们主要关注filter插件的运行,查看其对应的findNodesThatPassFilters函数,在pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go:475中,如下,补充了部分注释
go
// findNodesThatPassFilters finds the nodes that fit the filter plugins.
func (sched *Scheduler) findNodesThatPassFilters(
ctx context.Context, // 调度上下文
fwk framework.Framework, // 调度框架
state *framework.CycleState, // 调度周期状态
pod *v1.Pod, // 待调度的 Pod
diagnosis framework.Diagnosis, // 调度诊断信息
nodes []*framework.NodeInfo) ([]*v1.Node, error) { // 所有节点信息
numAllNodes := len(nodes) // 所有节点的数量
// 计算应该找到的可行节点数量
numNodesToFind := sched.numFeasibleNodesToFind(fwk.PercentageOfNodesToScore(), int32(numAllNodes))
// 创建一个足够大的列表来存储通过过滤的节点,以避免在运行时增长该列表
feasibleNodes := make([]*v1.Node, numNodesToFind)
// 如果框架没有过滤插件,直接使用所有节点
if !fwk.HasFilterPlugins() {
for i := range feasibleNodes {
// 从上一个调度周期停止的地方开始检查节点
feasibleNodes[i] = nodes[(sched.nextStartNodeIndex+i)%numAllNodes].Node()
}
return feasibleNodes, nil
}
// 用于并行处理时的错误通道
errCh := parallelize.NewErrorChannel()
var statusesLock sync.Mutex // 用于保护对诊断信息的并发访问
var feasibleNodesLen int32 // 通过过滤的节点数量
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx) // 创建一个可取消的上下文
defer cancel()
// 检查每个节点是否通过过滤
checkNode := func(i int) {
nodeInfo := nodes[(sched.nextStartNodeIndex+i)%numAllNodes] // 获取节点信息
status := fwk.RunFilterPluginsWithNominatedPods(ctx, state, pod, nodeInfo) // 运行过滤插件
if status.Code() == framework.Error {
errCh.SendErrorWithCancel(status.AsError(), cancel) // 发送错误并可能取消整个操作
return
}
if status.IsSuccess() {
// 如果节点通过过滤,将其添加到可行节点列表中
length := atomic.AddInt32(&feasibleNodesLen, 1)
if length > numNodesToFind {
cancel() // 如果找到的节点超过了预定数量,取消剩余的检查
atomic.AddInt32(&feasibleNodesLen, -1)
} else {
feasibleNodes[length-1] = nodeInfo.Node()
}
} else {
// 如果节点没有通过过滤,记录其状态
statusesLock.Lock()
diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap[nodeInfo.Node().Name] = status
diagnosis.UnschedulablePlugins.Insert(status.FailedPlugin())
statusesLock.Unlock()
}
}
// 记录开始检查节点的时间
beginCheckNode := time.Now()
statusCode := framework.Success
defer func() {
// 记录 Filter 扩展点的延迟
metrics.FrameworkExtensionPointDuration.WithLabelValues(metrics.Filter, statusCode.String(), fwk.ProfileName()).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(beginCheckNode))
}()
// 并行检查所有节点,直到找到预定数量的可行节点或检查完所有节点
fwk.Parallelizer().Until(ctx, numAllNodes, checkNode, metrics.Filter)
// 截断可行节点列表到实际找到的节点数量
feasibleNodes = feasibleNodes[:feasibleNodesLen]
if err := errCh.ReceiveError(); err != nil {
statusCode = framework.Error
return feasibleNodes, err
}
return feasibleNodes, nil
}注意到这里首先计算了需要筛选的node的数量,这主要是为了在大规模场景下降低筛选的数量,查看其对应的函数,在pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go:548中,如下,补充了部分注释。
go
// numFeasibleNodesToFind returns the number of feasible nodes that once found, the scheduler stops
// its search for more feasible nodes.
func (sched *Scheduler) numFeasibleNodesToFind(percentageOfNodesToScore *int32, numAllNodes int32) (numNodes int32) {
if numAllNodes < minFeasibleNodesToFind {
// 如果所有节点的数量小于预设的最小可行节点数,则返回所有节点的数量
return numAllNodes
}
// 使用框架(profile)中设置的百分比,如果没有设置,则使用全局的百分比
var percentage int32
if percentageOfNodesToScore != nil {
percentage = *percentageOfNodesToScore
} else {
percentage = sched.percentageOfNodesToScore
}
if percentage == 0 {
// 如果没有提供百分比,则使用默认的计算方式
percentage = int32(50) - numAllNodes/125
if percentage < minFeasibleNodesPercentageToFind {
// 确保百分比不低于预设的最小值
percentage = minFeasibleNodesPercentageToFind
}
}
// 计算基于总节点数和百分比的节点数
numNodes = numAllNodes * percentage / 100
if numNodes < minFeasibleNodesToFind {
// 如果计算出的节点数小于最小可行节点数,则返回最小值
return minFeasibleNodesToFind
}
// 返回计算出的可行节点数
return numNodes
}然后定义了内部的checkNode函数,其输入是要检查的node 的id相对于sched.nextStartNodeIndex的偏移。注意这里使用了k8s内部定义的并行函数fwk.Parallelizer().Until,其定义如下,在pkg/scheduler/framework/parallelize/parallelism.go:56和staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/util/workqueue/parallelizer.go:46中:
go
// Until is a wrapper around workqueue.ParallelizeUntil to use in scheduling algorithms.
// A given operation will be a label that is recorded in the goroutine metric.
func (p Parallelizer) Until(ctx context.Context, pieces int, doWorkPiece workqueue.DoWorkPieceFunc, operation string) {
goroutinesMetric := metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(operation)
withMetrics := func(piece int) {
goroutinesMetric.Inc()
doWorkPiece(piece)
goroutinesMetric.Dec()
}
workqueue.ParallelizeUntil(ctx, p.parallelism, pieces, withMetrics, workqueue.WithChunkSize(chunkSizeFor(pieces, p.parallelism)))
}
// ParallelizeUntil is a framework that allows for parallelizing N
// independent pieces of work until done or the context is canceled.
func ParallelizeUntil(ctx context.Context, workers, pieces int, doWorkPiece DoWorkPieceFunc, opts ...Options) {
if pieces == 0 {
return
}
o := options{}
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(&o)
}
chunkSize := o.chunkSize
if chunkSize < 1 {
chunkSize = 1
}
chunks := ceilDiv(pieces, chunkSize)
toProcess := make(chan int, chunks)
for i := 0; i < chunks; i++ {
toProcess <- i
}
close(toProcess)
var stop <-chan struct{}
if ctx != nil {
stop = ctx.Done()
}
if chunks < workers {
workers = chunks
}
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
wg.Add(workers)
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go func() {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer wg.Done()
for chunk := range toProcess {
start := chunk * chunkSize
end := start + chunkSize
if end > pieces {
end = pieces
}
for p := start; p < end; p++ {
select {
case <-stop:
return
default:
doWorkPiece(p)
}
}
}
}()
}
wg.Wait()
}checkNode函数内部检查对应的node是否能通过所有filter插件的过滤(RunFilterPluginsWithNominatedPods)如果通过就将筛选过的node数量+1,并记录相关的值,同时还会检查是否已经筛选到了足够的node,如果足够了,那么就发送取消信号,停止并行进程,不再继续筛选。
对于每个node进行筛选的函数RunFilterPluginsWithNominatedPods在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:816中,如下
go
func (f *frameworkImpl) RunFilterPluginsWithNominatedPods(
ctx context.Context, // 调度上下文
state *framework.CycleState, // 当前周期状态
pod *v1.Pod, // 待调度的 Pod
info *framework.NodeInfo, // 节点信息
) *framework.Status {
var status *framework.Status
podsAdded := false
// We run filters twice in some cases. If the node has greater or equal priority
// nominated pods, we run them when those pods are added to PreFilter state and nodeInfo.
// If all filters succeed in this pass, we run them again when these
// nominated pods are not added. This second pass is necessary because some
// filters such as inter-pod affinity may not pass without the nominated pods.
// If there are no nominated pods for the node or if the first run of the
// filters fail, we don't run the second pass.
// We consider only equal or higher priority pods in the first pass, because
// those are the current "pod" must yield to them and not take a space opened
// for running them. It is ok if the current "pod" take resources freed for
// lower priority pods.
// Requiring that the new pod is schedulable in both circumstances ensures that
// we are making a conservative decision: filters like resources and inter-pod
// anti-affinity are more likely to fail when the nominated pods are treated
// as running, while filters like pod affinity are more likely to fail when
// the nominated pods are treated as not running. We can't just assume the
// nominated pods are running because they are not running right now and in fact,
// they may end up getting scheduled to a different node.
// 我们可能需要两次运行过滤插件。如果节点上有优先级更高或相等的被提名的 Pods,
// 我们会在这些 Pods 被添加到 PreFilter 状态和 nodeInfo 时运行它们。
// 如果所有过滤插件在这一轮通过,我们会在这些被提名的 Pods 没有被添加的情况下再次运行它们。
// 第二轮运行是必要的,因为一些过滤插件(如 Pod 亲和性)可能在没有被提名的 Pods 的情况下无法通过。
// 如果节点没有被提名的 Pods 或者第一轮过滤插件失败,我们不会进行第二轮。
// 我们只考虑第一轮中优先级相等或更高的 Pods,因为当前的 "pod" 必须为它们让路,而不是占用为它们运行而开放的空间。
// 如果当前的 "pod" 占用了为低优先级 Pods 释放的资源,这是可以的。
// 要求新的 Pod 在这两种情况下都是可调度的,确保我们做出的是保守的决定:
// 像资源和 Pod 反亲和性这样的过滤器在将被提名的 Pods 视为运行时更有可能失败,
// 而像 Pod 亲和性这样的过滤器在将被提名的 Pods 视为未运行时更有可能失败。
// 我们不能仅仅假设被提名的 Pods 正在运行,因为它们现在并没有运行,事实上,
// 它们最终可能会被调度到一个不同的节点上。
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ {
stateToUse := state
nodeInfoToUse := info
if i == 0 {
// 第一轮:添加被提名的 Pods 到周期状态和节点信息
var err error
podsAdded, stateToUse, nodeInfoToUse, err = addNominatedPods(ctx, f, pod, state, info)
if err != nil {
return framework.AsStatus(err)
}
} else if !podsAdded || !status.IsSuccess() {
break
}
// 运行过滤插件
status = f.RunFilterPlugins(ctx, stateToUse, pod, nodeInfoToUse)
if !status.IsSuccess() && !status.IsUnschedulable() {
return status
}
}
return status
}注意到这里执行了两遍筛选,主要是考虑到这个node上面可能存在一些预计要被调度过来的pod,在第一轮中会假设这些pod真的会被调度过来,然后查看是否满足pod筛选需求,在第二列会假设这些pod最后没有被调度过来,然后检查是否满足pod的筛选需求。因为在第一轮中可能会存在反亲和性要求,导致无法通过筛选,在第二轮中可能会存在亲和性要求,导致无法通过筛选,这是一种很保守的筛选方式。
利用各个插件进行筛选的函数(RunFilterPlugins)在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:725中,如下
go
// RunFilterPlugins runs the set of configured Filter plugins for pod on
// the given node. If any of these plugins doesn't return "Success", the
// given node is not suitable for running pod.
// Meanwhile, the failure message and status are set for the given node.
func (f *frameworkImpl) RunFilterPlugins(
ctx context.Context,
state *framework.CycleState,
pod *v1.Pod,
nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo,
) *framework.Status {
for _, pl := range f.filterPlugins {
if state.SkipFilterPlugins.Has(pl.Name()) {
continue
}
metrics.PluginEvaluationTotal.WithLabelValues(pl.Name(), metrics.Filter, f.profileName).Inc()
if status := f.runFilterPlugin(ctx, pl, state, pod, nodeInfo); !status.IsSuccess() {
if !status.IsUnschedulable() {
// Filter plugins are not supposed to return any status other than
// Success or Unschedulable.
status = framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("running %q filter plugin: %w", pl.Name(), status.AsError()))
}
status.SetFailedPlugin(pl.Name())
return status
}
}
return nil
}这里的逻辑很简单,就是遍历各个筛选的插件,依次检查是否符合要求。
可以继续看runFilterPlugin这运行一个筛选插件进行检查的函数,在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:750中。
go
func (f *frameworkImpl) runFilterPlugin(ctx context.Context, pl framework.FilterPlugin, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) *framework.Status {
if !state.ShouldRecordPluginMetrics() {
return pl.Filter(ctx, state, pod, nodeInfo)
}
startTime := time.Now()
status := pl.Filter(ctx, state, pod, nodeInfo)
f.metricsRecorder.ObservePluginDurationAsync(metrics.Filter, pl.Name(), status.Code().String(), metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
return status
}主要也就是调用插件的Filter函数,具体插件的介绍后面再补充。
打分过程
打分的函数prioritizeNodes 在pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go 中,如下,补充了部分注释
go
func prioritizeNodes(
ctx context.Context,
extenders []framework.Extender,
fwk framework.Framework,
state *framework.CycleState,
pod *v1.Pod,
nodes []*v1.Node,
) ([]framework.NodePluginScores, error) {
// 如果没有提供优先级配置,则所有节点的分数都设为 1。
// 这是为了在所需的格式中生成优先级列表
if len(extenders) == 0 && !fwk.HasScorePlugins() {
result := make([]framework.NodePluginScores, 0, len(nodes))
for i := range nodes {
result = append(result, framework.NodePluginScores{
Name: nodes[i].Name,
TotalScore: 1,
})
}
return result, nil
}
// 运行 PreScore 插件。
preScoreStatus := fwk.RunPreScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !preScoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, preScoreStatus.AsError()
}
// 运行 Score 插件。
nodesScores, scoreStatus := fwk.RunScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !scoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, scoreStatus.AsError()
}
// 如果启用了详细日志记录,记录每个插件对每个节点的打分
klogV := klog.V(10)
if klogV.Enabled() {
for _, nodeScore := range nodesScores {
for _, pluginScore := range nodeScore.Scores {
klogV.InfoS("Plugin scored node for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "plugin", pluginScore.Name, "node", nodeScore.Name, "score", pluginScore.Score)
}
}
}
// 如果有扩展器并且有节点,运行扩展器
if len(extenders) != 0 && nodes != nil {
allNodeExtendersScores := make(map[string]*framework.NodePluginScores, len(nodes))
var mu sync.Mutex
var wg sync.WaitGroup
// 并发运行每个扩展器的优先级函数
for i := range extenders {
if !extenders[i].IsInterested(pod) {
continue
}
wg.Add(1)
go func(extIndex int) {
defer wg.Done()
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.PrioritizingExtender).Inc()
metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.PrioritizingExtender).Inc()
defer func() {
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.PrioritizingExtender).Dec()
metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.PrioritizingExtender).Dec()
}()
prioritizedList, weight, err := extenders[extIndex].Prioritize(pod, nodes)
if err != nil {
klog.V(5).InfoS("Failed to run extender's priority function. No score given by this extender.", "error", err, "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "extender", extenders[extIndex].Name())
return
}
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
for i := range *prioritizedList {
nodename := (*prioritizedList)[i].Host
score := (*prioritizedList)[i].Score
klogV.InfoS("Extender scored node for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "extender", extenders[extIndex].Name(), "node", nodename, "score", score)
// 将扩展器的分数转换为调度器使用的分数范围
finalscore := score * weight * (framework.MaxNodeScore / extenderv1.MaxExtenderPriority)
if allNodeExtendersScores[nodename] == nil {
allNodeExtendersScores[nodename] = &framework.NodePluginScores{
Name: nodename,
Scores: make([]framework.PluginScore, 0, len(extenders)),
}
}
allNodeExtendersScores[nodename].Scores = append(allNodeExtendersScores[nodename].Scores, framework.PluginScore{
Name: extenders[extIndex].Name(),
Score: finalscore,
})
allNodeExtendersScores[nodename].TotalScore += finalscore
}
}(i)
}
wg.Wait() // 等待所有扩展器完成
// 将扩展器的分数添加到节点分数中
for i := range nodesScores {
if score, ok := allNodeExtendersScores[nodes[i].Name]; ok {
nodesScores[i].Scores = append(nodesScores[i].Scores, score.Scores...)
nodesScores[i].TotalScore += score.TotalScore
}
}
}
// 记录每个节点的最终分数
if klogV.Enabled() {
for i := range nodesScores {
klogV.InfoS("Calculated node's final score for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "node", nodesScores[i].Name, "score", nodesScores[i].TotalScore)
}
}
return nodesScores, nil
}主要流程包括:
- 如果没有提供任何扩展器或打分插件,则为所有节点设置默认分数,并返回。
- 运行 PreScore 插件,为打分阶段做准备。
- 运行 Score 插件,获取每个节点的分数。
- 如果有扩展器并且有节点,则并发运行每个扩展器的优先级函数,获取扩展器为节点分配的分数。
- 将扩展器的分数转换为调度器使用的分数范围,并添加到节点分数中。
- 记录每个节点的最终分数。
这里补充一下其记录节点分数的结构体NodePluginScores,在文件pkg/scheduler/framework/interface.go:55中,其定义如下:
go
// NodePluginScores is a struct with node name and scores for that node.
type NodePluginScores struct {
// Name is node name.
Name string
// Scores is scores from plugins and extenders.
Scores []PluginScore
// TotalScore is the total score in Scores.
TotalScore int64
}
// PluginScore is a struct with plugin/extender name and score.
type PluginScore struct {
// Name is the name of plugin or extender.
Name string
Score int64
}可以看到每个插件给node打分都是一个int64的类型,一个节点可能会被多个插件进行打分,最后再汇总。
再回到插件打分,这里我们主要关注关键的打分插件RunScorePlugins ,在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:931中,如下,补充了部分注释
go
func (f *frameworkImpl) RunScorePlugins(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodes []*v1.Node) (ns []framework.NodePluginScores, status *framework.Status) {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
// 记录打分扩展点的持续时间
metrics.FrameworkExtensionPointDuration.WithLabelValues(metrics.Score, status.Code().String(), f.profileName).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
}()
allNodePluginScores := make([]framework.NodePluginScores, len(nodes))
numPlugins := len(f.scorePlugins) - state.SkipScorePlugins.Len()
plugins := make([]framework.ScorePlugin, 0, numPlugins)
pluginToNodeScores := make(map[string]framework.NodeScoreList, numPlugins)
// 为每个插件创建一个节点分数列表
for _, pl := range f.scorePlugins {
if state.SkipScorePlugins.Has(pl.Name()) {
continue
}
plugins = append(plugins, pl)
pluginToNodeScores[pl.Name()] = make(framework.NodeScoreList, len(nodes))
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
errCh := parallelize.NewErrorChannel()
if len(plugins) > 0 {
// 并行地为每个节点运行每个插件的 Score 方法
f.Parallelizer().Until(ctx, len(nodes), func(index int) {
nodeName := nodes[index].Name
for _, pl := range plugins {
s, status := f.runScorePlugin(ctx, pl, state, pod, nodeName)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
err := fmt.Errorf("plugin %q failed with: %w", pl.Name(), status.AsError())
errCh.SendErrorWithCancel(err, cancel)
return
}
pluginToNodeScores[pl.Name()][index] = framework.NodeScore{
Name: nodeName,
Score: s,
}
}
}, metrics.Score)
if err := errCh.ReceiveError(); err != nil {
return nil, framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("running Score plugins: %w", err))
}
}
// 并行地为每个打分插件运行 NormalizeScore 方法
f.Parallelizer().Until(ctx, len(plugins), func(index int) {
pl := plugins[index]
if pl.ScoreExtensions() == nil {
return
}
nodeScoreList := pluginToNodeScores[pl.Name()]
status := f.runScoreExtension(ctx, pl, state, pod, nodeScoreList)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
err := fmt.Errorf("plugin %q failed with: %w", pl.Name(), status.AsError())
errCh.SendErrorWithCancel(err, cancel)
return
}
}, metrics.Score)
if err := errCh.ReceiveError(); err != nil {
return nil, framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("running Normalize on Score plugins: %w", err))
}
// 并行地为每个打分插件应用分数权重,并构建 allNodePluginScores
f.Parallelizer().Until(ctx, len(nodes), func(index int) {
nodePluginScores := framework.NodePluginScores{
Name: nodes[index].Name,
Scores: make([]framework.PluginScore, len(plugins)),
}
for i, pl := range plugins {
weight := f.scorePluginWeight[pl.Name()]
nodeScoreList := pluginToNodeScores[pl.Name()]
score := nodeScoreList[index].Score
if score > framework.MaxNodeScore || score < framework.MinNodeScore {
err := fmt.Errorf("plugin %q returns an invalid score %v, it should in the range of [%v, %v] after normalizing", pl.Name(), score, framework.MinNodeScore, framework.MaxNodeScore)
errCh.SendErrorWithCancel(err, cancel)
return
}
weightedScore := score * int64(weight)
nodePluginScores.Scores[i] = framework.PluginScore{
Name: pl.Name(),
Score: weightedScore,
}
nodePluginScores.TotalScore += weightedScore
}
allNodePluginScores[index] = nodePluginScores
}, metrics.Score)
if err := errCh.ReceiveError(); err != nil {
return nil, framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("applying score defaultWeights on Score plugins: %w", err))
}
// 返回所有节点的插件分数
return allNodePluginScores, nil
}主要流程包括:
- 为每个插件创建一个节点分数列表。
- 使用并行处理为每个节点运行每个插件的
Score方法。 - 为每个插件运行
NormalizeScore方法,以标准化分数。 - 应用每个插件的分数权重,构建最终的节点分数。
- 返回各个节点的分数
查看插件打分的函数runScorePlugin,在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:1025 中,如下。
go
func (f *frameworkImpl) runScorePlugin(ctx context.Context, pl framework.ScorePlugin, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *framework.Status) {
if !state.ShouldRecordPluginMetrics() {
return pl.Score(ctx, state, pod, nodeName)
}
startTime := time.Now()
s, status := pl.Score(ctx, state, pod, nodeName)
f.metricsRecorder.ObservePluginDurationAsync(metrics.Score, pl.Name(), status.Code().String(), metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
return s, status
}可以看到主要是调用插件的Score方法。
一般调度的后期处理
PostFilter插件
在schedulingCycle中可以看到如果上述的一般调度没有为Pod找到合适的node,并且错误不是没有合适的node,即ErrNoNodesAvailable 的话,就会检查是否存在有PostFilterPlugins,如果有就运行,即运行RunPostFilterPlugins函数,来进行相关的处理,例如释放一些资源,从而希望使得该pod在下一次调度时有机会成功调度,当然这被释放的资源也可能被其他不同的pod给占用了,但是这对系统是无害的,所以也不管。
该RunPostFilterPlugins函数在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:762中,如下所示
go
// RunPostFilterPlugins runs the set of configured PostFilter plugins until the first
// Success, Error or UnschedulableAndUnresolvable is met; otherwise continues to execute all plugins.
func (f *frameworkImpl) RunPostFilterPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, filteredNodeStatusMap framework.NodeToStatusMap) (_ *framework.PostFilterResult, status *framework.Status) {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
metrics.FrameworkExtensionPointDuration.WithLabelValues(metrics.PostFilter, status.Code().String(), f.profileName).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
}()
// `result` records the last meaningful(non-noop) PostFilterResult.
var result *framework.PostFilterResult
var reasons []string
var failedPlugin string
for _, pl := range f.postFilterPlugins {
r, s := f.runPostFilterPlugin(ctx, pl, state, pod, filteredNodeStatusMap)
if s.IsSuccess() {
return r, s
} else if s.Code() == framework.UnschedulableAndUnresolvable {
return r, s.WithFailedPlugin(pl.Name())
} else if !s.IsUnschedulable() {
// Any status other than Success, Unschedulable or UnschedulableAndUnresolvable is Error.
return nil, framework.AsStatus(s.AsError()).WithFailedPlugin(pl.Name())
} else if r != nil && r.Mode() != framework.ModeNoop {
result = r
}
reasons = append(reasons, s.Reasons()...)
// Record the first failed plugin unless we proved that
// the latter is more relevant.
if len(failedPlugin) == 0 {
failedPlugin = pl.Name()
}
}
return result, framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable, reasons...).WithFailedPlugin(failedPlugin)
}可以看到他就是遍历了所有的postFilter插件,然后使用函数runPostFilterPlugin运行这些插件,其在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:796中
func (f *frameworkImpl) runPostFilterPlugin(ctx context.Context, pl framework.PostFilterPlugin, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, filteredNodeStatusMap framework.NodeToStatusMap) (*framework.PostFilterResult, *framework.Status) {
if !state.ShouldRecordPluginMetrics() {
return pl.PostFilter(ctx, state, pod, filteredNodeStatusMap)
}
startTime := time.Now()
r, s := pl.PostFilter(ctx, state, pod, filteredNodeStatusMap)
f.metricsRecorder.ObservePluginDurationAsync(metrics.PostFilter, pl.Name(), s.Code().String(), metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
return r, s
}Reserve插件
得到想要调度到的pod后,可能需要执行一些资源预留的操作,就需要定义在reserve插件中,该插件对应的调用函数为RunReservePluginsReserve,在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:1144 中
go
// RunReservePluginsReserve runs the Reserve method in the set of configured
// reserve plugins. If any of these plugins returns an error, it does not
// continue running the remaining ones and returns the error. In such a case,
// the pod will not be scheduled and the caller will be expected to call
// RunReservePluginsUnreserve.
func (f *frameworkImpl) RunReservePluginsReserve(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (status *framework.Status) {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
metrics.FrameworkExtensionPointDuration.WithLabelValues(metrics.Reserve, status.Code().String(), f.profileName).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
}()
for _, pl := range f.reservePlugins {
status = f.runReservePluginReserve(ctx, pl, state, pod, nodeName)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
err := status.AsError()
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed running Reserve plugin", "plugin", pl.Name(), "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("running Reserve plugin %q: %w", pl.Name(), err))
}
}
return nil
}这里也是遍历所有的reserve插件,如果有任意一个插件失败了那么就失败了。单个插件的调用函数在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:1160中,如下
go
func (f *frameworkImpl) runReservePluginReserve(ctx context.Context, pl framework.ReservePlugin, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *framework.Status {
if !state.ShouldRecordPluginMetrics() {
return pl.Reserve(ctx, state, pod, nodeName)
}
startTime := time.Now()
status := pl.Reserve(ctx, state, pod, nodeName)
f.metricsRecorder.ObservePluginDurationAsync(metrics.Reserve, pl.Name(), status.Code().String(), metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
return status
}Permit插件
找到了要调度的pod后还需要运行permit插件,该插件主要用来查看记录是否还需要等待一下其他操作,例如抢占某个pod的资源,那么就需要等待被抢占pod的资源释放掉。
该插件对应的函数RunPermitPlugins 在pkg/scheduler/framework/runtime/framework.go:1200中,如下
go
// RunPermitPlugins runs the set of configured permit plugins. If any of these
// plugins returns a status other than "Success" or "Wait", it does not continue
// running the remaining plugins and returns an error. Otherwise, if any of the
// plugins returns "Wait", then this function will create and add waiting pod
// to a map of currently waiting pods and return status with "Wait" code.
// Pod will remain waiting pod for the minimum duration returned by the permit plugins.
func (f *frameworkImpl) RunPermitPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (status *framework.Status) {
startTime := time.Now() // 记录permit插件开始运行的时间
defer func() {
// 记录permit插件的运行时间和最终状态
metrics.FrameworkExtensionPointDuration.WithLabelValues(metrics.Permit, status.Code().String(), f.profileName).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startTime))
}()
pluginsWaitTime := make(map[string]time.Duration) // 存储每个插件的等待时间
statusCode := framework.Success // 初始化状态码为成功
for _, pl := range f.permitPlugins {
// 运行当前permit插件
status, timeout := f.runPermitPlugin(ctx, pl, state, pod, nodeName)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
if status.IsUnschedulable() {
// 如果插件返回不可调度的状态,则记录日志并返回该状态
klog.V(4).InfoS("Pod rejected by permit plugin", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "plugin", pl.Name(), "status", status.Message())
status.SetFailedPlugin(pl.Name()) // 设置失败的插件名称
return status
}
if status.IsWait() {
// 如果插件返回等待的状态,则记录等待时间,但不立即返回
// 允许的最长等待时间由 maxTimeout 限制
if timeout > maxTimeout {
timeout = maxTimeout
}
pluginsWaitTime[pl.Name()] = timeout
statusCode = framework.Wait // 更新状态码为等待
} else {
// 如果插件返回错误状态,则记录错误日志并返回错误状态
err := status.AsError()
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed running Permit plugin", "plugin", pl.Name(), "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("running Permit plugin %q: %w", pl.Name(), err)).WithFailedPlugin(pl.Name())
}
}
}
if statusCode == framework.Wait {
// 如果任何插件返回等待状态,则创建并添加等待中的 Pod 到映射中,并返回等待状态
waitingPod := newWaitingPod(pod, pluginsWaitTime)
f.waitingPods.add(waitingPod)
msg := fmt.Sprintf("one or more plugins asked to wait and no plugin rejected pod %q", pod.Name)
klog.V(4).InfoS("One or more plugins asked to wait and no plugin rejected pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return framework.NewStatus(framework.Wait, msg)
}
// 如果所有插件都成功或返回等待,且没有插件拒绝 Pod,则返回 nil 表示没有错误
return nil
}主要流程包括:
- 记录开始运行许可插件的时间。
- 使用
defer语句确保无论函数如何结束,都记录许可插件的运行时间和状态。 - 遍历所有的permit插件。
- 运行当前插件,并将结果状态保存到
status。 - 检查状态:
- 如果状态是成功的,则继续运行下一个插件。
- 如果状态是不可调度的,则记录日志并返回该状态。
- 如果状态是等待的,则记录等待时间,并更新状态码为等待,然后继续运行下一个插件。
- 如果状态是错误,则记录错误日志,并返回错误状态。
- 如果任何插件返回等待状态,则创建等待中的 Pod 并添加到映射中,然后返回等待状态。
- 如果所有插件都成功或返回等待,且没有插件拒绝 Pod,则返回
nil。