文章目录
- 膨胀卷积
- 从零开始手动实现一个1D膨胀卷积,不使用PyTorch的`nn.Conv1d`
-
-
- [1. 基本概念](#1. 基本概念)
- [2. 手动实现1D膨胀卷积](#2. 手动实现1D膨胀卷积)
-
- TCN结构
- 如何使用TCN
膨胀卷积
什么是膨胀卷积
膨胀卷积(Dilated Convolution),也称为空洞卷积(Atrous Convolution),是在标准卷积的基础上通过引入膨胀因子(dilation factor)来扩展感受野,而不增加参数数量或计算复杂度。膨胀卷积通过在滤波器的每两个元素之间插入空洞(即,零值)来实现这一点。
膨胀卷积公式
膨胀卷积的数学公式如下:
F ( s ) = ( x ∗ d f ) ( s ) = ∑ i = 0 k − 1 f ( i ) ⋅ x s − d ⋅ i F(s) = (x *d f)(s) = \sum{i=0}^{k-1} f(i) \cdot x_{s - d \cdot i} F(s)=(x∗df)(s)=i=0∑k−1f(i)⋅xs−d⋅i
其中:
- (x) 是输入信号。
- (f) 是卷积滤波器。
- (s) 是输出信号的位置。
- (d) 是膨胀因子,表示滤波器元素之间的间隔。
- (k) 是滤波器的大小。
当 (d=1) 时,膨胀卷积退化为标准卷积。
PyTorch代码
下面是一个使用PyTorch实现膨胀卷积的示例:
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class DilatedConv1D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, dilation):
super(DilatedConv1D, self).__init__()
self.dilated_conv = nn.Conv1d(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
dilation=dilation,
padding=(kernel_size - 1) * dilation // 2
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.dilated_conv(x)
# 示例输入
batch_size = 1
in_channels = 1
seq_length = 10
x = torch.randn(batch_size, in_channels, seq_length)
# 创建膨胀卷积层
dilated_conv_layer = DilatedConv1D(in_channels=1, out_channels=1, kernel_size=3, dilation=2)
# 前向传播
output = dilated_conv_layer(x)
print(output)从零开始手动实现一个1D膨胀卷积,不使用PyTorch的nn.Conv1d
1. 基本概念
膨胀卷积的公式为:
y [ t ] = ∑ k x [ t − k ⋅ d ] ⋅ w [ k ] y[t] = \sum_{k} x[t - k \cdot d] \cdot w[k] y[t]=k∑x[t−k⋅d]⋅w[k]
其中:
- y [ t ] y[t] y[t] 是输出信号。
- x [ t ] x[t] x[t] 是输入信号。
- w [ k ] w[k] w[k] 是卷积核的权重。
- d d d 是膨胀率。
2. 手动实现1D膨胀卷积
下面是手动实现1D膨胀卷积的Python代码:
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class ManualDilatedConv1D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, dilation=1):
super(ManualDilatedConv1D, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.dilation = dilation
# 初始化卷积核权重
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(out_channels, in_channels, kernel_size))
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(out_channels))
def forward(self, x):
batch_size, in_channels, length = x.shape
assert in_channels == self.in_channels
# 计算输出的长度
out_length = length - (self.kernel_size - 1) * self.dilation
# 初始化输出张量
out = torch.zeros(batch_size, self.out_channels, out_length)
# 对每个输出通道进行卷积
for b in range(batch_size):
for o in range(self.out_channels):
for i in range(out_length):
sum = 0
for k in range(self.kernel_size):
sum += x[b, :, i + k * self.dilation] * self.weight[o, :, k]
out[b, o, i] = sum + self.bias[o]
return out
# 示例参数
in_channels = 1
out_channels = 1
kernel_size = 3
dilation = 2
# 创建一个输入张量 (batch_size, channels, length)
input_tensor = torch.randn(1, in_channels, 10)
# 创建手动膨胀卷积层
manual_dilated_conv = ManualDilatedConv1D(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, dilation)
# 前向传播
output_tensor = manual_dilated_conv(input_tensor)
print(output_tensor)TCN结构
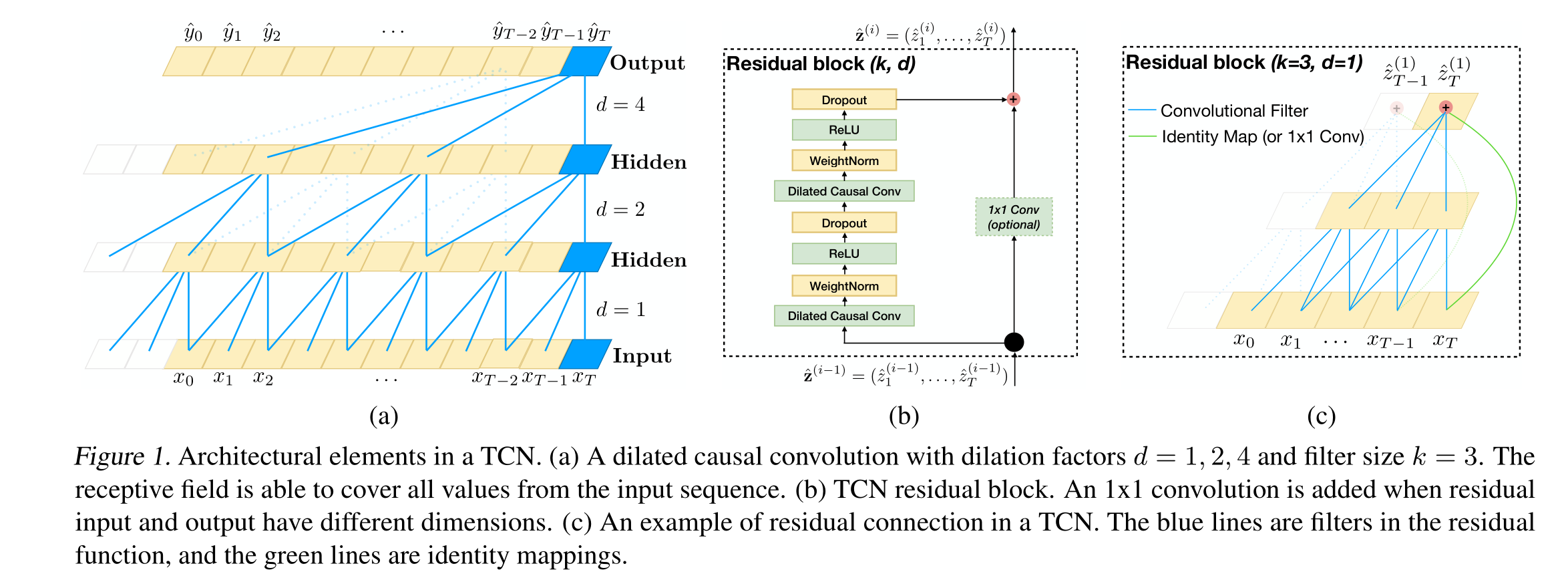
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn.utils import weight_norm
class Chomp1d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, chomp_size):
super(Chomp1d, self).__init__()
self.chomp_size = chomp_size
def forward(self, x):
return x[:, :, :-self.chomp_size].contiguous()
class TemporalBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_inputs, n_outputs, kernel_size, stride, dilation, padding, dropout=0.2):
super(TemporalBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = weight_norm(nn.Conv1d(n_inputs, n_outputs, kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation))
self.chomp1 = Chomp1d(padding)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.conv2 = weight_norm(nn.Conv1d(n_outputs, n_outputs, kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation))
self.chomp2 = Chomp1d(padding)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.net = nn.Sequential(self.conv1, self.chomp1, self.relu1, self.dropout1,
self.conv2, self.chomp2, self.relu2, self.dropout2)
self.downsample = nn.Conv1d(n_inputs, n_outputs, 1) if n_inputs != n_outputs else None
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.init_weights()
def init_weights(self):
self.conv1.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
self.conv2.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
if self.downsample is not None:
self.downsample.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.net(x)
res = x if self.downsample is None else self.downsample(x)
return self.relu(out + res)
class TemporalConvNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_inputs, num_channels, kernel_size=2, dropout=0.2):
super(TemporalConvNet, self).__init__()
layers = []
num_levels = len(num_channels)
for i in range(num_levels):
dilation_size = 2 ** i
in_channels = num_inputs if i == 0 else num_channels[i-1]
out_channels = num_channels[i]
layers += [TemporalBlock(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=dilation_size,
padding=(kernel_size-1) * dilation_size, dropout=dropout)]
self.network = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
return self.network(x)如何使用TCN
以下是如何使用上述Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) 代码的详细讲解和步骤:
源码说明
1. Chomp1d 类
Chomp1d类用于从输入的末端裁剪指定大小的时间步长。
python
class Chomp1d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, chomp_size):
super(Chomp1d, self).__init__()
self.chomp_size = chomp_size
def forward(self, x):
return x[:, :, :-self.chomp_size].contiguous()2. TemporalBlock 类
TemporalBlock类构建了一个基础的时间卷积模块,包括两个卷积层,每个卷积层后都有一个Chomp1d、ReLU激活函数和Dropout。
python
class TemporalBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_inputs, n_outputs, kernel_size, stride, dilation, padding, dropout=0.2):
super(TemporalBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = weight_norm(nn.Conv1d(n_inputs, n_outputs, kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation))
self.chomp1 = Chomp1d(padding)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.conv2 = weight_norm(nn.Conv1d(n_outputs, n_outputs, kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation))
self.chomp2 = Chomp1d(padding)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.net = nn.Sequential(self.conv1, self.chomp1, self.relu1, self.dropout1,
self.conv2, self.chomp2, self.relu2, self.dropout2)
self.downsample = nn.Conv1d(n_inputs, n_outputs, 1) if n_inputs != n_outputs else None
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.init_weights()
def init_weights(self):
self.conv1.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
self.conv2.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
if self.downsample is not None:
self.downsample.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.net(x)
res = x if self.downsample is None else self.downsample(x)
return self.relu(out + res)3. TemporalConvNet 类
TemporalConvNet类将多个TemporalBlock组合在一起,形成完整的TCN模型。
python
class TemporalConvNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_inputs, num_channels, kernel_size=2, dropout=0.2):
super(TemporalConvNet, self).__init__()
layers = []
num_levels = len(num_channels)
for i in range(num_levels):
dilation_size = 2 ** i
in_channels = num_inputs if i == 0 else num_channels[i-1]
out_channels = num_channels[i]
layers += [TemporalBlock(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=dilation_size,
padding=(kernel_size-1) * dilation_size, dropout=dropout)]
self.network = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
return self.network(x)使用方法
-
准备输入数据 :
TCN适用于一维序列数据,如时间序列。输入数据的形状应该是
(batch_size, num_inputs, sequence_length)。 -
初始化模型 :
定义模型的输入通道数
num_inputs,每一层的输出通道数列表num_channels,卷积核大小kernel_size和dropout比例。
python
num_inputs = 10 # 输入通道数,例如10个特征
num_channels = [16, 32, 64] # 每个TemporalBlock的输出通道数
kernel_size = 2
dropout = 0.2
model = TemporalConvNet(num_inputs, num_channels, kernel_size, dropout)- 训练模型 :
使用PyTorch常规的训练步骤,定义损失函数和优化器,然后进行前向传播、计算损失、反向传播和参数更新。
python
# 示例:随机生成输入数据
batch_size = 8
sequence_length = 30
input_data = torch.randn(batch_size, num_inputs, sequence_length)
# 模型输出
output = model(input_data)
print(output.shape) # 输出形状为(batch_size, num_channels[-1], sequence_length)batch_size, num_inputs, 和 sequence_length 是与输入数据和模型有关的参数。以下是对它们的详细解释:
-
batch_size:
- 表示每次输入模型的样本数量。
- 例如,如果你有1000个样本数据,并且你希望每次输入模型进行训练时处理32个样本,那么
batch_size将是32。 - 这个参数通常用于加速训练过程,并使得计算更高效,因为可以利用并行计算。
-
num_inputs:
- 表示输入数据的特征数量或通道数。
- 在时间序列数据中,通常每个时间步可能包含多个特征。例如,如果你的时间序列数据在每个时间步包含温度和湿度两个特征,那么
num_inputs将是2。 - 对于一维时间序列数据,如果每个时间步只有一个值(如单变量时间序列),则
num_inputs为1。
-
sequence_length:
- 表示时间序列的长度,即每个样本中包含的时间步数。
- 例如,如果你有一个每天记录温度的时间序列数据,记录了30天的数据,那么
sequence_length将是30。 - 这个参数决定了输入数据的时间维度长度。
- 定义损失函数和优化器 :
可以使用MSELoss或其他适合具体任务的损失函数。
python
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 示例:随机生成目标数据
target_data = torch.randn(batch_size, num_channels[-1], sequence_length)
# 前向传播
output = model(input_data)
# 计算损失
loss = criterion(output, target_data)
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('Loss:', loss.item())以上是如何使用Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN)代码的详细步骤和示例。通过这些步骤,你可以定义并训练一个TCN模型来处理一维序列数据。