引言
倒排索引(Inverted Index)是一种索引数据结构,用于存储某个单词(词项)在一组文档中的所有出现情况的映射。它是搜索引擎执行快速全文搜索的核心技术,也广泛用于数据库中进行文本搜索。我们熟知的 ElasticSearch 最核心底层原理便就是倒排索引。
倒排索引的基本原理是将文档中的词汇进行反转,形成倒排列表。 在倒排列表中,每个词汇都对应一个文档标识符的列表,这些标识符指明了该词汇出现在哪些文档中。 通过查询倒排列表,可以快速地找到包含特定词汇的文档。
本文将使用 Rust 语言来实现一个简单的倒排索引,包括倒排索引的构建和搜索过程。在下一篇文章中,笔者会基于《Rust 程序设计(第二版)》并发编程篇章,解读该书作者是如何基于 Rust 通道实现更优秀、更高性能的倒排索引。
可以学到
- 倒排索引的原理、优势和使用
- 常用 crate:
colored、regex - Rust HashMap
- Rust 迭代器
开发思路
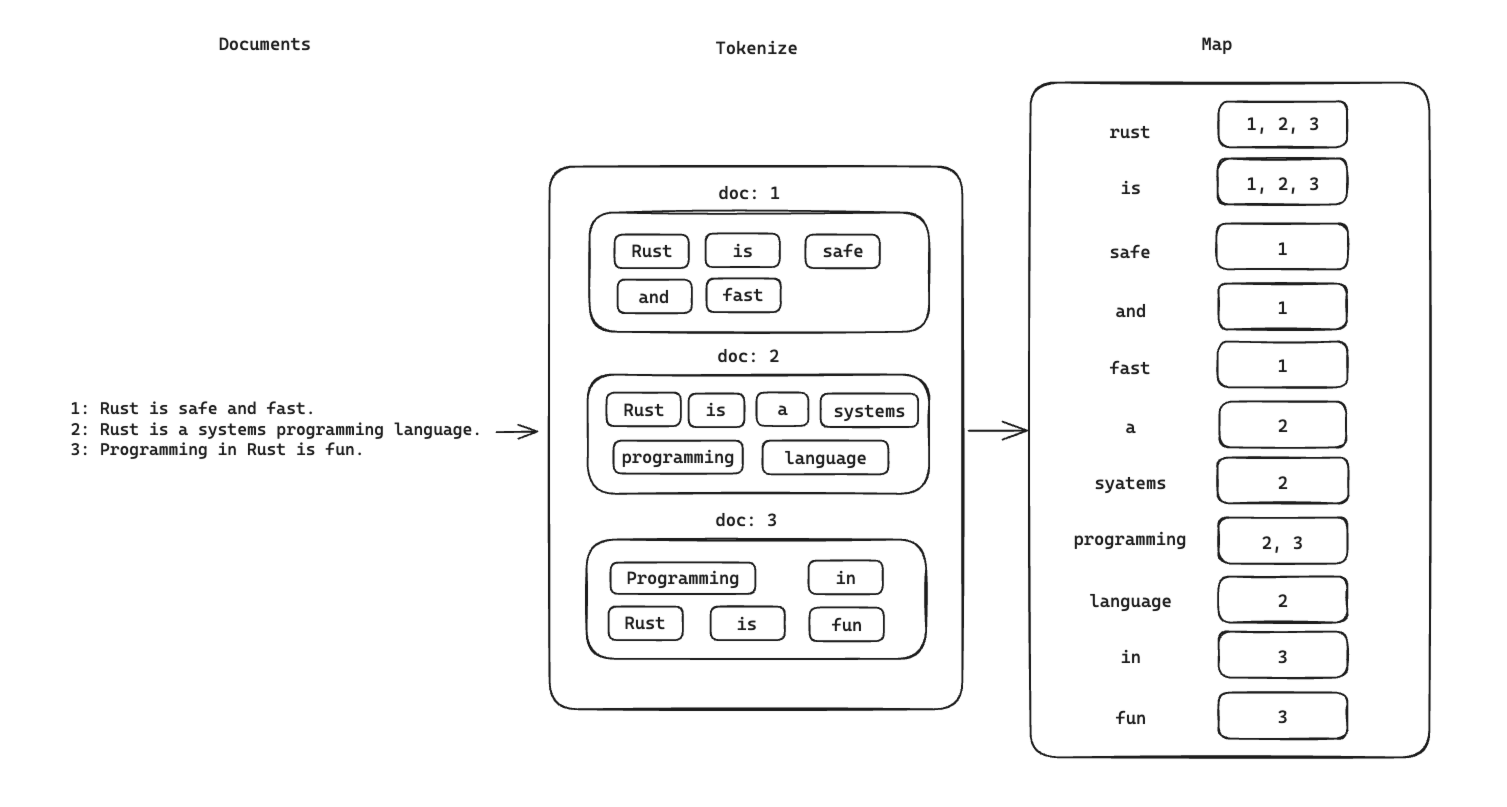
一个简单的倒排索引开发思路大概如上图所示:
- 读取文档
- 分词
- 构建每个词到每个文档的映射
开发过程
完整源码位于:inverted_index。
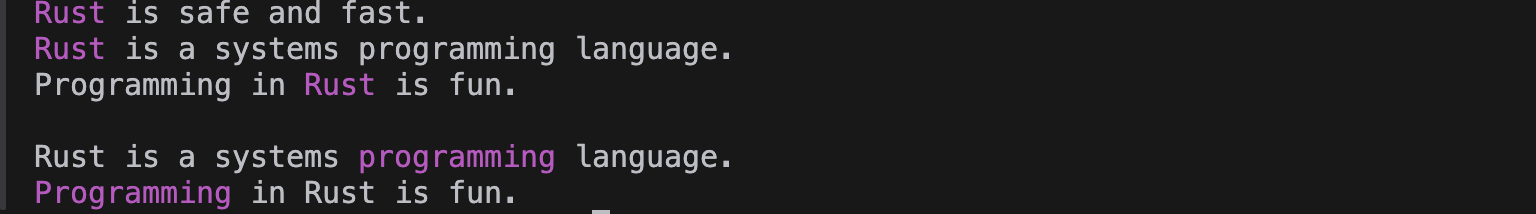
最终效果
rust
fn main() {
let mut index = InvertedIndex::new();
index.add(1, "Rust is safe and fast.");
index.add(2, "Rust is a systems programming language.");
index.add(3, "Programming in Rust is fun.");
// query "Rust"
let results = index.query("Rust");
for result in results {
println!("{}", result);
}
println!("");
// query "Programming"
let results = index.query("Programming");
for result in results {
println!("{}", result);
}
}执行:
bash
cargo run输出:
版本声明
toml
[package]
name = "inverted_index"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
[dependencies]
colored = "2.1.0"
regex = "1.10.4"项目准备
首先我们创建项目:
bash
cargo new inverted_index准备依赖:
bash
cargo add regex
cargo add colored- colored: 终端高亮,后面我们将实现搜索词的高亮显示,使结果更美观。
- regex: 正则库,用于实现不区分大小写替换匹配到的搜索词。
实现过程
首先我们定义两个数据结构:
rust
struct Document {
id: usize,
content: String,
}
struct InvertedIndex {
indexes: HashMap<String, Vec<usize>>,
documents: HashMap<usize, Document>,
}
impl InvertedIndex {
fn new() -> InvertedIndex {
InvertedIndex {
indexes: HashMap::new(),
documents: HashMap::new(),
}
}
}- Document: 封装原始文档
- IndexedIndex: 我们将构建的倒排索引
接下来我们要实现 2 个辅助函数,一个是 tokenize,用于将原始的文档信息拆分成独立的词(word/term),另一个是 hightlight,用于将匹配到的文本进行替换,使其在中断可以以紫色输出。
tokenize 实现如下:
rust
fn tokenize(text: &str) -> Vec<&str> {
text.split(|ch: char| !ch.is_alphanumeric())
.filter(|c| !c.is_empty())
.collect()
}
#[test]
fn tokenize_test() {
assert_eq!(
tokenize("This is\nhedon's tokenize function."),
vec!["This", "is", "hedon", "s", "tokenize", "function"]
)
}highlight 实现如下:
rust
fn highlight(term: &str, content: &str) -> String {
let regex = Regex::new(&format!(r"(?i){}", term)).unwrap();
let highlighted_content = regex
.replace_all(content, |caps: ®ex::Captures| {
caps[0].to_string().purple().to_string()
})
.to_string();
highlighted_content
}
#[test]
fn highlight_test() {
assert_eq!(
highlight("programming", "I like programming with Rust Programming"),
"I like \u{1b}[35mprogramming\u{1b}[0m with Rust \u{1b}[35mProgramming\u{1b}[0m"
);
}现在我们可以为 InvertedIndex 实现构建索引的方法 add 了,它会接收原始文档,对其进行分词,并将记录每个分词和文档 id 的映射。
rust
impl InvertedIndex {
fn add(&mut self, doc_id: usize, content: &str) {
let content_lowercase = content.to_lowercase();
let words = tokenize(&content_lowercase);
for word in words {
self.indexes
.entry(word.to_string())
.or_insert(vec![])
.push(doc_id)
}
self.documents.insert(
doc_id,
Document {
id: doc_id,
content: content.to_string(),
},
);
}
}然后我们再实现对应的根据分词 term 搜索原始文档的方法:
rust
impl InvertedIndex {
fn query(&self, term: &str) -> Vec<String> {
let term_lowercase = term.to_lowercase();
if let Some(doc_ids) = self.indexes.get(&term_lowercase) {
doc_ids
.iter()
.filter_map(|doc_id| {
self.documents
.get(doc_id)
.map(|doc| highlight(&term_lowercase, &doc.content))
})
.collect()
} else {
Vec::new()
}
}
}这样一个简单的倒排索引构建和搜索功能就完成了,具体的执行效果你可以回到前面的「最终效果」进行查阅。
总结预告
本文实现的倒排索引虽然非常简单,但是也基本体现了倒排索引的最核心思想和应用方式了。在《Rust 程序设计(第二版)》的并发编程篇章中,该书提出了使用通道 channel 来并发构建倒排索引,同时给出了更加丰富和优雅的实现。在下篇文章中,笔者将阅读这部分的源码,解析并重现当中的实战过程,并进行适当扩展。
peace! enjoy coding~