一、Netty编解码器
1.Java的编解码
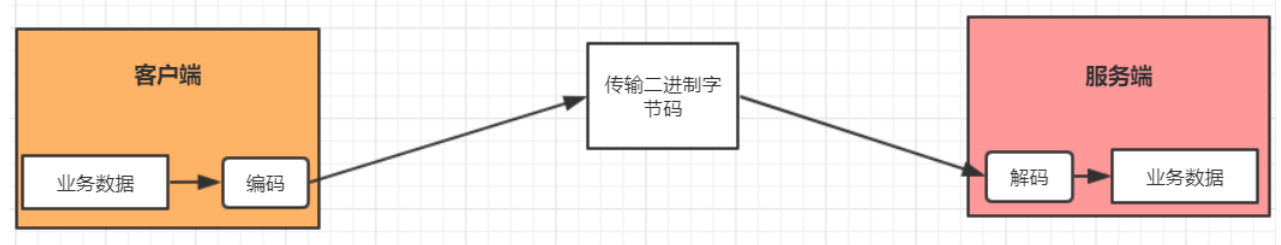
- 编码(Encode)称为序列化,它将对象序列化为字节数组,用于网络传输、数据持久化或者其它用途
- 解码(Decode)称为反序列化,它把从网络、磁盘等读取的字节数组还原成原始对象(通常是原始对象的拷贝),以方便后续的业务逻辑操作。
J
ava序列化对象只需要实现java.io.Serializable接口并生成序列化ID,这个类就能够通过java.io.ObjectInput和java.io.ObjectOutput序列化和反序列化
Java序列化目的:1.网络传输。2.对象持久化
Java序列化缺点:1.无法跨语言。2.序列化后码流太大。3.序列化性能太低
Java序列化仅仅是Java编解码技术的一种,由于它的种种缺陷,衍生出了多种编解码技术和框架,这些编解码框架实现消息的高效序列化。
2.Netty编解码器
1)概念
在网络应用中需要实现某种编解码器,将原始字节数据与自定义的消息对象进行互相转换。网络中都是以字节码的数据形式来传输数据的,服务器编码数据后发送到客户端,客户端需要对数据进行解码。
对于Netty而言,编解码器由两部分组成:编码器、解码器
- 解码器:负责将消息从字节或其他序列形式转成指定的消息对象
- 编码器:将消息对象转成字节或其他序列形式在网络上传输
Netty的编(解)码器实现了ChannelHandlerAdapter,也是一种特殊的ChannelHandler,所以依赖于ChannelPipeline,可以将多个编(解)码器链接在一起,以实现复杂的转换逻辑。
Netty里面的编解码:
- 解码器:负责处理"入站 InboundHandler"数据
- 编码器:负责"出站Out波UN他Handler"数据
2)解码器(Decoder)
解码器负责解码"入站"数据从一种格式到另一种格式,解码器处理入站数据是抽象ChannelInboundHandler的实现。需要将解码器放在ChannelPipeline中。对于解码器,Netty中主要提供了抽象基类ByteToMessageDecoder和MessageToMessageDecoder

- ByteToMessageDecoder:用于将字节转为消息,需要检查缓冲区是否有足够的字节
- ReplayingDecoder:继承ByteToMessageDecoder,不需要检查缓冲区是否有足够的字节,但是ReplayingDecoder速度略慢于ByteToMessageDecoder,同时不是所有的ByteBuf都支持。项目复杂性高则使用ReplayingDecoder,否则使用ByteToMessageDecoder
- MessageToMessageDecoder:用于从一种消息解码为另外一种消息
核心方法:
java
decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,ByteBuf msg,List<Object> out)代码实现:
解码器:
java
public class MessageDecoder extends MessageToMessageDecoder {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, List out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("正在进行消息解码 ");
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
out.add(byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));//传递到下一个handler
}
}使用
java
//4. 设置bossGroup线程组和workerGroup线程组
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//5. 设置服务端通道实现为NIO
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)//6. 参数设置
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,Boolean.TRUE)//6. 参数设置
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//7. 创建一个通道初始化对象
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
//添加解码器,需要在自定义业务处理handler之前
channel.pipeline().addLast("messageDecoder",new MessageDecoder());
//8. 向Pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler
channel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});这样在自定义业务处理handler中,消息就已经是解码之后的了,不需要再解码了。
3)编码器(Encoder)
与ByteToMessageDecoder和MessageToMessageDecoder相对应,Netty提供了对应的编码器实现MessageToMessageEncoder和MessageToMessageEncoder,二者都实现ChannelOutboundHandler接口。

抽象编码器:
- MessageToByteEncoder:将消息转化成字节
- MessageToMessageEncoder:用于从一种消息编码为另外一种消息
核心代码:
java
encoder(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,String msg,List<Object> out)编码:
java
public class MessageEncoder extends MessageToMessageEncoder {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, List out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("消息正在进行编码。。。");
String str = (String) msg;
out.add(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}使用
java
//4. 设置bossGroup线程组和workerGroup线程组
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//5. 设置服务端通道实现为NIO
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)//6. 参数设置
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,Boolean.TRUE)//6. 参数设置
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//7. 创建一个通道初始化对象
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
//添加解码器,需要在自定义业务处理handler之前
channel.pipeline().addLast("messageDecoder",new MessageDecoder());
//添加编码器
channel.pipeline().addLast("messageEncoder",new MessageEncoder());
//8. 向Pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler
channel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});4)编码解码器Codec
编码解码器:同时具有编码与解码功能,特点同时实现了ChannelInboundHandler和ChannelOutboundHandler接口,因此在数据输入和输出时都能进行处理。

代码:
编解码器
java
public class MessageCodec extends MessageToMessageCodec {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, List out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("消息正在进行编码。。。");
String str = (String) msg;
out.add(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, List out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("正在进行消息解码 ");
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
out.add(byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));//传递到下一个handler
}
}使用:
java
//4. 设置bossGroup线程组和workerGroup线程组
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//5. 设置服务端通道实现为NIO
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)//6. 参数设置
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,Boolean.TRUE)//6. 参数设置
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//7. 创建一个通道初始化对象
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
// //添加解码器,需要在自定义业务处理handler之前
// channel.pipeline().addLast("messageDecoder",new MessageDecoder());
// //添加编码器
// channel.pipeline().addLast("messageEncoder",new MessageEncoder());
//添加编解码器
channel.pipeline().addLast(new MessageCodec());
//8. 向Pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler
channel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});二、Netty案例-群聊天室
1.聊天室服务端
服务端代码:
java
public class NettyChatServer {
//端口号
private int port;
public NettyChatServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
//1. 创建bossGroup线程组:处理网络事件--连接事件
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = null;
//2. 创建workerGroup线程组:处理网络事件--读写事件 2*处理器线程数
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = null;
try {
//1. 创建bossGroup线程组:处理网络事件--连接事件
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
//2. 创建workerGroup线程组:处理网络事件--读写事件 2*处理器线程数
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//3. 创建服务端启动助手
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//4. 设置bossGroup线程组和workerGroup线程组
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//5. 设置服务端通道实现为NIO
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)//6. 参数设置
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,Boolean.TRUE)//6. 参数设置
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//7. 创建一个通道初始化对象
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
//8. 向Pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler
//添加编码器
channel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
channel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
//todo
channel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyChatServerHandler());
}
});
//9. 启动服务端并绑定端口,同时将异步改为同步
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()){
System.out.println("端口绑定成功");
}else {
System.out.println("端口绑定失败");
}
}
});
System.out.println("聊天室服务端启动成功");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
// 10. 关闭通道(并不是真正意义上的关闭,而是监听通道关闭的状态)和关闭连接池
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.isShuttingDown();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new NettyChatServer(999).run();
}
}服务端业务处理类代码:
java
public class NettyChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
public static List<Channel> channelList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @Author liufj
* @Description //通道就绪事件
* @Date 22:13 2024/6/11
**/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//当有新的客户端连接的时候,将通道放入集合
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelList.add(channel);
System.out.println("[Server]: "+channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1)+"在线.");
}
/**
* @Author liufj
* @Description //通道读取事件
* @Date 22:13 2024/6/11
**/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
//当前发送消息的通道,当前发送的客户端连接
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
for (Channel channel1 : channelList) {
//排除自身通道
if (channel!=channel1){
channel1.writeAndFlush("["+channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1)+"]说:"+msg);
}
}
}
/**
* @Author liufj
* @Description //通道未就绪事件--channel下线
* @Date 22:13 2024/6/11
**/
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//当有客户端断开连接的时候,就移除对应的通道
channelList.remove(channel);
System.out.println("[Server]: "+channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1)+"下线.");
}
/**
* @Author liufj
* @Description //异常处理时间
* @Date 22:13 2024/6/11
**/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("[Server]: "+channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1)+"异常.");
}
}2.聊天室客户端
客户端代码:
java
public class NettyChatClient {
//服务端ip
private String ip;
//服务端端口号
private int port;
public NettyChatClient(String ip, int port) {
this.ip = ip;
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup group = null;
try {
//1. 创建线程组
group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//2. 创建客户端启动助手
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//3. 设置线程组
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//4. 创建客户端通道实现为NIO
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//5. 创建一个通道初始化对象
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//6. 向Pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler
//添加编码器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
//添加客户端处理类
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyChatClientHandler());
}
});
//7. 启动客户端,等待连接服务端,同时将异步改为同步
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(ip,port).sync();
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
System.out.println("----------"+channel.localAddress().toString().substring(1)+"----------");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
//向服务端发送消息
channel.writeAndFlush(msg);
}
//8. 关闭通道和关闭连接池
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new NettyChatClient("127.0.0.1",9998).run();
}
}客户端handler处理类
java
public class NettyChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
/**
* @Author liufj
* @Description //通道就绪事件
* @Date 22:13 2024/6/11
**/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}三、基于Netty的Http服务器开发
1.介绍
Nettt的HTTP协议栈无论在性能还是在可靠性上,都表现优异,非常适合在非Web容器的场景下应用,相比传统的Tomcat、Jetty等Web容器,它更加轻量和小巧,灵活性和定制性也更好。
2.功能需求
- Netty服务器在8080端口监听
- 浏览器发出请求 "http://localhost:8080/"
- 服务器可以回复消息给客户端"Hello!这里是Netty服务器",并对特定请求资源进行过滤
3.服务端代码实现
服务器代码:
java
public class NettyHttpServer {
//端口号
private int port;
public NettyHttpServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
//1. 创建bossGroup线程组:处理网络事件--连接事件
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = null;
//2. 创建workerGroup线程组:处理网络事件--读写事件 2*处理器线程数
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = null;
try {
//1. 创建bossGroup线程组:处理网络事件--连接事件
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
//2. 创建workerGroup线程组:处理网络事件--读写事件 2*处理器线程数
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//3. 创建服务端启动助手
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//4. 设置bossGroup线程组和workerGroup线程组
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//5. 设置服务端通道实现为NIO
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)//6. 参数设置
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,Boolean.TRUE)//6. 参数设置
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//7. 创建一个通道初始化对象
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
//8. 向Pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler
//添加编码器
channel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
//自定义业务处理类
channel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyHttpServerHandler());
}
});
//9. 启动服务端并绑定端口,同时将异步改为同步
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()){
System.out.println("端口绑定成功");
}else {
System.out.println("端口绑定失败");
}
}
});
System.out.println("服务器启动成功");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
// 10. 关闭通道(并不是真正意义上的关闭,而是监听通道关闭的状态)和关闭连接池
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.isShuttingDown();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new NettyHttpServer(8080).run();
}
}http服务器处理类:
java
public class NettyHttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> {
/**
* @Author liufj
* @Description //读取就绪事件
* @Date 22:55 2024/6/11
**/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception {
//1.判断请求是不是http请求
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest){
DefaultHttpRequest request = (DefaultHttpRequest) msg;
System.out.println("浏览器请求路径:"+request.uri());
if ("/favicon.ico".equals(request.uri())){
System.out.println("图标不响应");
return;
}
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello!这里是Netty服务器", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
//2.给浏览器进行响应
DefaultHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(
HttpVersion.HTTP_1_0,
HttpResponseStatus.OK,
byteBuf
);
//3.设置响应头
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE,"text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,byteBuf.readableBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}四、Netty中的粘包和拆包
1.粘包和拆包简介
粘包和拆包是TCP网络编程中不可避免的,无论是服务端还是客户端,当我们读取或者发送消息的时候,都需要考虑TCP底层的粘包/拆包机制。
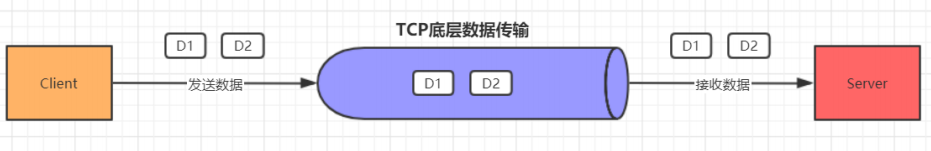
TCP是个"流"协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数据。TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分,所以在业务上认为,一个完整的包可能会被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也有可能把多个小的包封装成一个大的数据包发送,这就是所谓的TCP粘包和拆包问题。
如图所示,假设客户端分别发送了两个数据包D1和D2给服务端,由于服务端一次读取到的字节数是不确定的,故可能存在以下4种情况。
1)服务端分两次读取到了两个独立的数据包,分别是D1和D2,没有粘包和拆包
2)服务端一次接受到了两个数据包,D1和D2沾合在一起,被称为TCP粘包

3)如果D2的数据包比较大,服务端分两次读取到了两个数据包,第一次读取到了完整的D1包和D2包的部分内容,第二次读取到了D2包的剩余内容,这被称为TCP拆包

4)如果D1,D2的数据包都很大,服务端分多次才能将D1和D2包接收完全,期间发生多次拆包

TCP粘包和拆包产生的原因:
数据从发送方到接收方需要经过操作系统的缓冲区,而造成粘包和拆包的主要原因就在于这个缓冲区上。粘包可以理解为缓冲区数据堆积,导致多个请求数据粘在一起,而拆包可以理解为发送的数据大于缓冲区,进行拆分处理。
2.粘包和拆包代码演示
1)粘包
客户端
java
/**
* 通道就绪事件
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("你好呀.我是Netty客户端" + i,
CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}服务端:
java
public int count = 0;
/**
* 通道读取事件
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("客户端发送过来的消息:" +byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("读取次数:"+(++count));
}
服务端一次读取了客户端发送过来的消息,应该读取10次,因此发生了粘包
2)拆包
客户端
java
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//一次发送102400字节数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[102400];
Arrays.fill(bytes, (byte) 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(bytes));
}
}服务端
java
public int count = 0;
/**
* 通道读取事件
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("长度是:" + byteBuf.readableBytes());
System.out.println("读取次数 = " + (++count));
}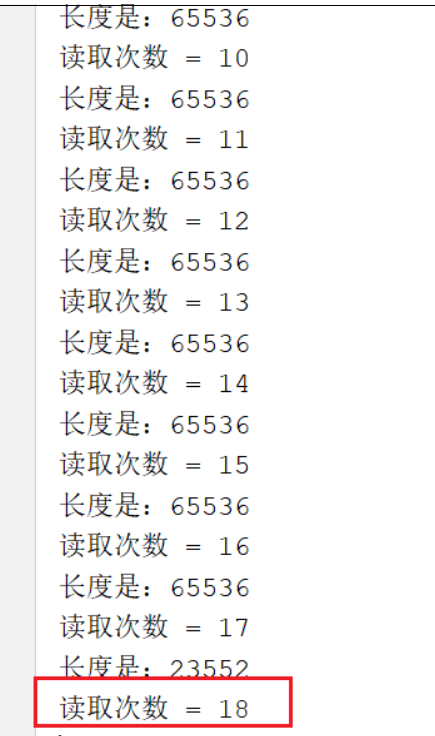
当客户端发送的数据包比较大的时候,就发生了拆包事件。
3.粘包和拆包的解决方法
1)业内解决方案
由于底层的TCP无法理解上层的业务数据,所在在底层是无法保证数据包不被拆分和重组的,这个问题只能通过上层的应用协议栈设计来解决,根据业界的主流协议的解决方案,可以归纳如下:
- 消息长度固定,累计读取到长度和为定长LEN的报文后,就认为读取到了一个完整的信息
- 将换行符作为消息结束符
- 将特殊的分隔符作为消息的结束标志,回车换行符就是一种特殊的结束分割符
- 通过在消息头中定义长度字段来标识消息的总长度
2)Netty中的粘包和拆包解决方案
Netty提供了4中解码器来解决,分别如下:
- 固定长度的拆包器FixedLengthFrameDecoder,每个应用层数据包都拆分成固定长度的大小
- 行拆包器LineBasedFrameDecoder,每个应用层数据包,都以换行符作为分隔符,进行分割拆分
- 分隔符拆包器DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder,每个应用数据包,都通过自定义的分隔符,进行分割拆分
- 基于数据包长度的拆包器LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,将应用层数据包的长度,作为接收端应用层数据包的拆分依据。按照应用层数据包的大小,拆包。这个拆包器,有一个要求,就是应用层协议中包含数据包的长度