数据结构之树
树
本篇讲的树也就是多叉树
普通树(多叉树)
概念:
- 树 就是由根节点(父亲)分出多个分支节点(儿子) ,然后分支又分出多个分支,我们将这种结构称为树,树也可以这么定义:一棵树由称作根的节点r以及0个或多个非空的(子)树T1,T2,T3...Tk组成 ,这些子树每一棵的根都被来自根r的一条有向的边所连接。
- 从递归定义中我们发现 ,一颗树是N个节点 和N-1条边 的集合,其中的一个节点叫做根 。每条边都将某个节点连接到它的父亲,而除去根接待你外每一个节点都有一个父亲。没有子节点的节点叫做树叶(叶节点) ,具有相同父节点称为兄弟节点 。节点深度 就是该节点到根节点的长度是多少,节点高度就是该节点到最近叶节点的长度。
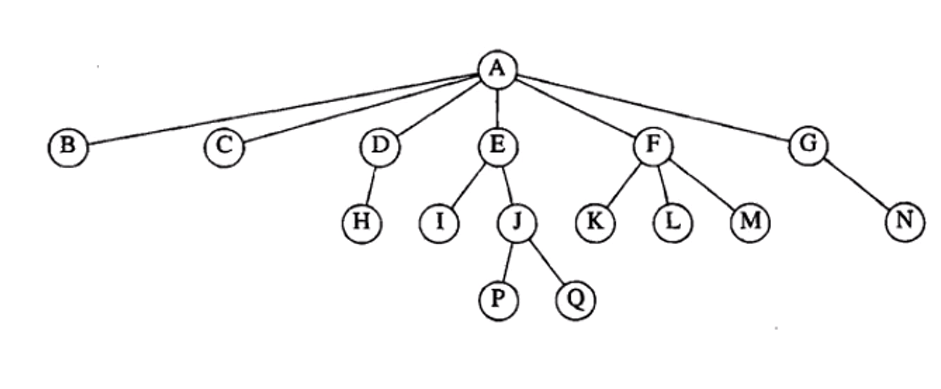
代码:
cpp
//通过链表的形式,表头就是根节点,通过找到第一个子节点,就能找到其他的子节点。
struct treeNode{
int data;
treeNode* firstchild; //用于指向该节点的第一个子节点
treeNode* nextsibling; //用于指向该节点的下一个兄弟节点
};
treeNode* createNode(int data){
auto p=new treeNode;
p->data=data;
p->firstchild=NULL;
p->nextsibling=NULL;
return p;
}
//插入节点
void addChild(treeNode* &root,int data){
treeNode* add=createNode(data);
if(root==NULL){
root=add;
}else{
if(root->firstchild==NULL){
root->firstchild=add;
}else{
treeNode* p=root->firstchild;
while(p->nextsibling!=NULL){
p=p->nextsibling;
}
p->nextsibling=add;
}
}
}
//先序查找
treeNode* preorderSearch(treeNode* root,int data){
if(root==NULL){
return NULL;
}
if(root->data==data){
return root;
}
treeNode* res;
res=preorderSearch(root->firstchild,data);
if(res!=NULL){
return res;
}
res=preorderSearch(root->nextsibling,data);
if(res!=NULL){
return res;
}
return NULL;
}
//后序查找
treeNode* postorderSearch(treeNode* root,int data){
if(root==NULL){
return NULL;
}
treeNode* res;
res=postorderSearch(root->firstchild,data);
if(res!=NULL){
return res;
}
res=postorderSearch(root->nextsibling,data);
if(res!=NULL){
return res;
}
if(root->data==data){
return root;
}
return NULL;
}
//删除节点
void del(treeNode* &root,int data){
if(root==NULL){
return NULL;
}
treeNode* p=NULL;
treeNode* tail=root->firstchild;
while(tail!=NULL){
if(tail->data==data){
if(p==NULL){
root->firstchild=tail->nextsibling;
}else{
p->nextsibling=tail->nextsibling;
}
delete tail;
return;
}
del(tail,data);
p=tail;
tail=tail->nextsibling;
}
return NULL;
}
//先序遍历
void preorderprint(treeNode *root){
if(root==NULL){
return;
}
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preorderprint(root->firstchild);
preorderprint(root->nextsibling);
}
//后序遍历
void postorderprint(treeNode* root){
if(root==NULL){
return;
}
postorderprint(root->firstchild);
postorderprint(root->nextsibling);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
}
//清空树
void destroy(treeNode* root){
if(root==NULL){
return;
}
destroy(root->firstchild);
destroy(root->nextsibling);
delete root;
}树的遍历
树有很多应用。流行的用法之一是包括UNIX、VAX/VMS和DOS在内的许多常用操作中的目录结构。
核心思想:
- 树的遍历的核心是递归
- 树的遍历的核心思想还有遍历的方式(先序遍历,后序遍历...)
先序遍历:
- 先从根节点,处理完根节点,再去处理子树
- 先处理子树的根节点,才处理子节点
- 先序遍历总是处理根节点,再处理子节点
后序遍历:
- 先处理子树的子节点,再处理子树的根节点
- 把全部小子树处理完,就处理树的根节点
- 后序遍历总是先处理子节点,再处理根节点
尾言
完整版笔记也就是数据结构与算法专栏完整版可到我的博客进行查看,或者在github库中自取(包含源代码)
- 博客1: codebooks.xyz
- 博客2:moonfordream.github.io
- github项目地址:Data-Structure-and-Algorithms