大家好!我是你们的老朋友------想不明白的过度思考者!今天我们要一起探索Java中两个神奇的数据结构:Map和Set!准备好了吗?让我们开始这场魔法之旅吧!🎩
🎯 先来点开胃菜:二叉搜索树(BST)
🌳 什么是二叉搜索树?
想象一下,你有一棵神奇的树,左边的果子都比树根小,右边的果子都比树根大!这就是我们的二叉搜索树!
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
java
package Tree;
//表示树的节点
class Node {
public int key;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"key=" + key +
", left=" + left +
", right=" + right +
'}';
}
}
public class BinarySearchTree {
private Node root = null;
//把新的元素插入到树中
public void insert(int key) {
//如果当前是空树,那就直接用root指向新节点即可
Node newNode = new Node(key);
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
}
// 如果是普通的树,需要找到哦插入位置,再去进行插入
//cur用来找待插入元素的位置
//parent记录cur的父元素
Node cur = root;
Node parent = null;
while (cur != null) {
if(key<cur.key) {
//往左找
parent = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}else if(key>cur.key) {
//往右找
parent = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}else {
//对于相等的情况,存在不同的解决方式
//当前不允许重复key存在,并且是Set只保存key,直接return
return;
}
}
//通过上述循环最终得到的结果就是cur为空
//此时的parent就是叶子节点,也就是新插入元素的父亲,此时就是要把newNode插入到parent的子节点上
//新节点,应该在parent的左子树还是右子树呢??直接比较大小
if (key> parent.key){
parent.right = newNode;
}else {
parent.left = newNode;
}
}
public void remove(int key) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//查找要删除节点的位置,记录其父节点
Node cur = root;
Node parent = null;
while (cur != null) {
if(key<cur.key) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}else if(key>cur.key) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}else {
//找到了
removeNode(parent, cur);
return;
}
}
}
private void removeNode(Node parent, Node cur) {
//具体删除节点要考虑四种情况
//1.没有子树
if(cur.right == null && cur.left == null) {
//1.1如果cur就是root,需要对root进行调整
if(cur == root) {
//说明整棵树只有root一个节点,直接把root设置为空
root = null;
}
//1.2如果cur不是root,同时cur是parent的左子树
if (cur == parent.left) {
parent.left = null;
return;
}
//1.3如果cur不是root,同时cur是parent的右子树
if (cur == parent.right) {
parent.right = null;
return;
}
//稳妥起见加个return
return;
}
//2.只有左子树
if(cur.left != null && cur.right == null) {
//2.1cur为root
if(cur == root){
root = cur.left;
return;
}
//2.2cur不为root,且cur是parent的左子树
if (cur == parent.left) {
parent.left = cur.left;
return;
}
//2.3cur不为root,且cur是parent的右子树
if (cur == parent.right) {
parent.right = cur.left;
return;
}
}
//3.只有右子树
if(cur.left == null && cur.right != null) {
//3.1只有root
if(cur == root){
root = cur.right;
return;
}
//3.2cur不是root,且cur是parent的左子树
if (cur == parent.left) {
parent.left = cur.right;
return;
}
//3.3cur不是root,且cur是parent的右子树
if (cur == parent.right) {
parent.right = cur.right;
return;
}
}
//4.左右都有子树
if(cur.left != null && cur.right != null) {
// 这种情况下,不需要考虑 cur 是不是 root的情况,并没有真正的删除 cur指向的节点,即使 cur 是 root,也无需修改 root 的指向
//因为实际删除的是"替罪羊节点"
//4.1首先需要找到右子树中的最小值 =>替罪羊,
//后续要删除替罪羊,也顺便把替罪羊的父亲,记录一下.
Node goat = cur.right;
Node goatParent= cur;
while (goat.left != null) {
goatParent = goat;
goat = goat.left;
}
//循环结束后。goat指向的就是cur右子树的最左侧元素
//4.2移花接木,把替罪羊节点的值复制到cur节点中
cur.key = goat.key;
//4.3真正删除goat节点,因为goat是没有左子树的,让goatParent直接连上goat的右子树即可
// 即使goat的右子树也是空也不影响
if(goat == goatParent.left){
goatParent.left = goat.right;
}else {
goatParent.right = goat.right;
}
}
}
//查找key是否在树中,如果存在则返回对应节点位置,如果不存在则返回null
private Node find(int key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if(key<cur.key) {
cur = cur.left;
}
else if(key>cur.key) {
cur = cur.right;
}else {
//相等,找到了
return cur;
}
}
return null;
}
//先序遍历
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
//中序遍历
private static void inOrder(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
public void print(){
//先打印先序遍历
System.out.println("先序遍历结果:");
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
//在打印中序遍历
System.out.println("中序遍历结果:");
inOrder(root);
//有了先序和中序就能够画出树的结构
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 3, 2, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 0};
//BinarySearchTree也总被缩写成BST
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
//循环插入
for(int key: arr){
tree.insert(key);
}
tree.print();
System.out.println();
System.out.println(tree.find(7));
}
}🎭 BST的表演时刻
| 操作 | 最佳情况(完全二叉树) | 最差情况(单支树) |
|---|---|---|
| 查找 | O(logN) | O(N) |
| 插入 | O(logN) | O(N) |
| 删除 | O(logN) | O(N) |
💡 小贴士:Java中的TreeMap和TreeSet就是用红黑树(BST的升级版)实现的哦!
🎩 主角登场:Map和Set
🗺️ Map:你的万能字典
Map就像你的通讯录,名字(Key)对应电话(Value),而且名字不能重复!
java
Map<String, String> heroNicknames = new HashMap<>();
heroNicknames.put("林冲", "豹子头");
heroNicknames.put("李逵", "黑旋风");
heroNicknames.put("宋江", "及时雨");
// 获取外号
System.out.println(heroNicknames.get("林冲")); // 输出:豹子头
// 遍历所有英雄
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : heroNicknames.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "的外号是:" + entry.getValue());
}
- Tip :使用put方法时:
若key不同 ,value相同 则新增键值对
若key相同 ,value不同则为修改对应的value
🎭 Map的两种实现对比
| 特性 | TreeMap(红黑树) | HashMap(哈希表) |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 时间复杂度 | O(logN) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | Key有序 | 无序 |
| 允许null | Key不能为null | Key和Value都可以为null |
🎪 Set:独一无二的马戏团
Set就像一个不允许重复演员的马戏团,每个演员都是独一无二的!
java
Set<String> fruitSet = new HashSet<>();
fruitSet.add("苹果");
fruitSet.add("香蕉");
fruitSet.add("橙子");
fruitSet.add("苹果"); // 这个不会被添加进去
System.out.println(fruitSet.contains("香蕉")); // 输出:true
System.out.println(fruitSet.size()); // 输出:3🎭 Set的两种实现对比
| 特性 | TreeSet(红黑树) | HashSet(哈希表) |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 时间复杂度 | O(logN) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | Key有序 | 无序 |
| 允许null | 不允许 | 允许 |
🔮 哈希表:数据结构的魔法帽
🎩 哈希函数:魔法咒语
哈希函数就像把名字变成数字的咒语:
java
int hashCode = "魔法".hashCode(); // 返回一个魔法数字⚡ 哈希冲突:当两个咒语撞车了
当不同的Key计算出相同的哈希值,就发生了冲突!我们有几种解决办法:
-
开放地址法(线性探测/二次探测)
- 线性探测:h(key) = (h(key) + i) % size
- 二次探测:h(key) = (h(key) + i²) % size
-
链地址法(哈希桶)
- 每个位置放一个链表,冲突的元素都挂在链表上
🌟 哈希桶实现:我们的魔法实验室
java
public class HashBucket {
static class Node {
int key, value;
Node next;
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private Node[] array;
private int size;
private static final double LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75;
public HashBucket() {
array = new Node[8];
size = 0;
}
public int put(int key, int value) {
int index = key % array.length;
// 查找key是否已存在
for (Node cur = array[index]; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
if (key == cur.key) {
int oldValue = cur.value;
cur.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// 插入新节点
Node node = new Node(key, value);
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
size++;
// 检查是否需要扩容
if ((double)size / array.length >= LOAD_FACTOR) {
resize();
}
return -1;
}
private void resize() {
Node[] newArray = new Node[array.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node next;
for (Node cur = array[i]; cur != null; cur = next) {
next = cur.next;
int index = cur.key % newArray.length;
cur.next = newArray[index];
newArray[index] = cur;
}
}
array = newArray;
}
public int get(int key) {
int index = key % array.length;
for (Node cur = array[index]; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
if (key == cur.key) return cur.value;
}
return -1;
}
}📊 哈希表性能分析
| 因素 | 影响 |
|---|---|
| 哈希函数设计 | 决定冲突率高低 |
| 负载因子 | 通常控制在0.75以下 |
| 冲突解决方法 | 影响查找效率和内存使用 |
| 扩容机制 | 影响性能和内存使用的平衡 |
🎯 实战演练:OJ题目解析
1. 只出现一次的数字
题目:给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
魔法解法:使用异或运算的特性!
java
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int result = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
result ^= num;
}
return result;
}2. 宝石与石头
题目:给定字符串J代表宝石的类型,S代表你拥有的石头。你想知道你拥有的石头中有多少是宝石。
魔法解法:使用HashSet!
java
public int numJewelsInStones(String J, String S) {
Set<Character> jewels = new HashSet<>();
for (char c : J.toCharArray()) {
jewels.add(c);
}
int count = 0;
for (char c : S.toCharArray()) {
if (jewels.contains(c)) count++;
}
return count;
}🎓 知识总结:思维导图
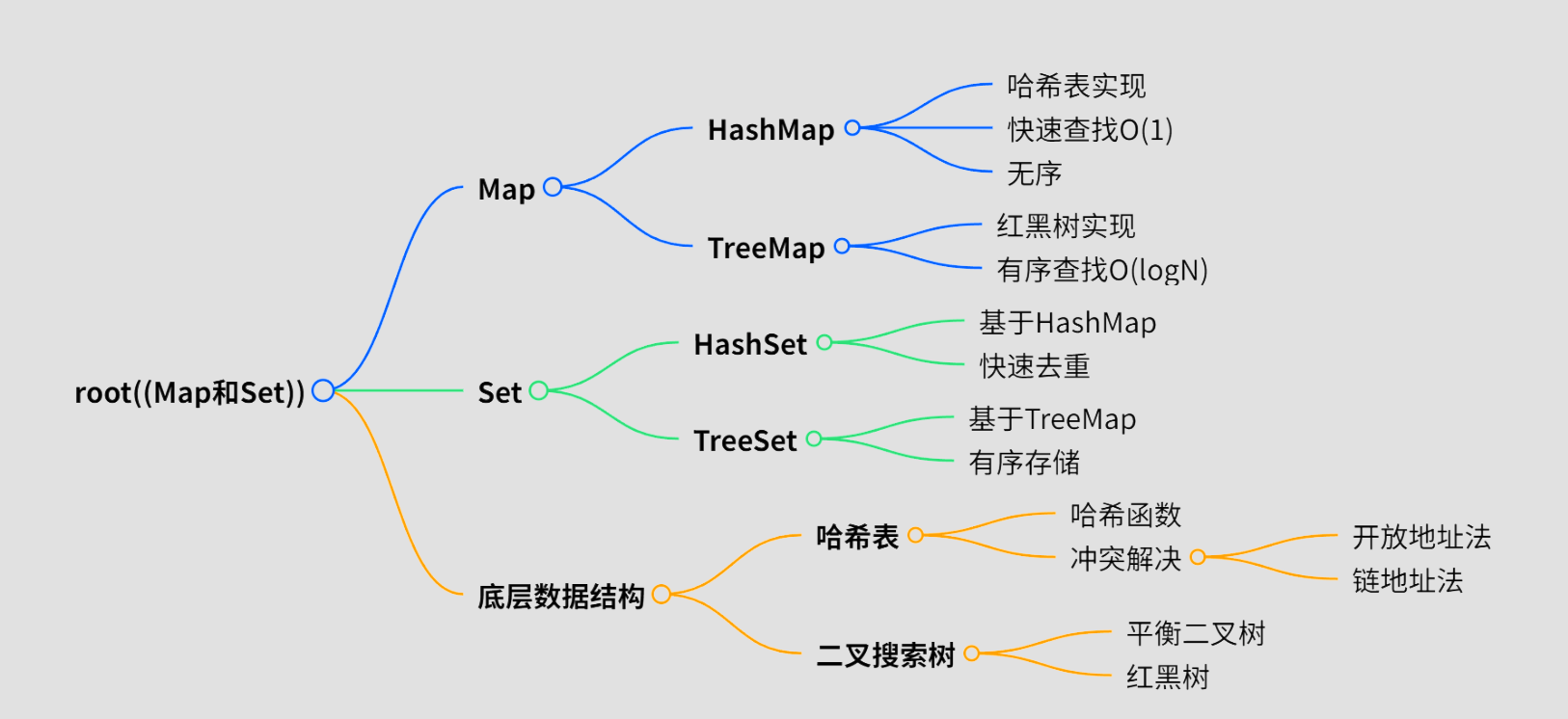
🎉 结语:选择你的魔法武器
今天我们一起探索了Map和Set的魔法世界,从二叉搜索树到哈希表,从TreeMap到HashMap,每个数据结构都有它独特的魔法特性!
记住:
- 需要快速查找?选HashMap/HashSet!
- 需要有序存储?选TreeMap/TreeSet!
- 遇到哈希冲突?试试链地址法!
希望这篇博客能像魔法一样帮助你理解这些数据结构!