文章目录
基础IO
文件描述符
系统底层提供打开文件(open),读(read),写(write),关闭文件(close)的系统调用,如果想详细了解可以复制以下命令仔细阅读使用方法,这里不做赘述。
打开文件
shell
man 2 open读
shell
man 2 read写
shell
man 2 write关闭文件
shell
man close文件描述符fd,是file descriptor的简写,数据类型是int
这里我们新建4个文件

然后打开这4个文件,用4个文件描述符去接收返回值
代码如下
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fd1 = open("test1.txt", O_RDONLY);
int fd2 = open("test2.txt", O_RDONLY);
int fd3 = open("test3.txt", O_RDONLY);
int fd4 = open("test4.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (-1 == fd1)
{
perror("open file:");
_exit(1);
}
if (-1 == fd2)
{
perror("open file:");
_exit(1);
}
if (-1 == fd3)
{
perror("open file:");
_exit(1);
}
if (-1 == fd4)
{
perror("open file:");
_exit(1);
}
printf("%d\n", fd1);
printf("%d\n", fd2);
printf("%d\n", fd3);
printf("%d\n", fd4);
return 0;
}运行结果如下:
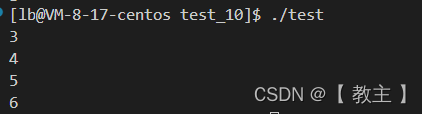
看起来是按顺序递增,这是什么意思?难道跟数组下标有关?
open打开文件失败会返回-1,成功则会返回一个非负整数,可是这里为什么是从3开始递增?0,1,2呢?
0,1,2是预留给标准输入,标准输出,标准错误的,在进程创建时就已经被操作系统打开。
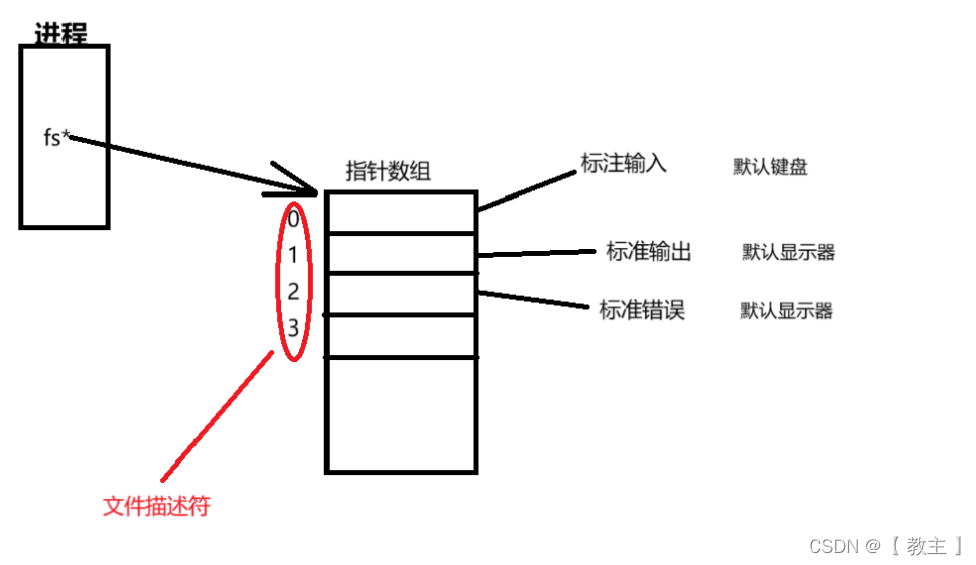
在进程打开文件时,进程内部会有一个数组指针,指向该进程的文件指针数组,而默认打开的标准输入,标准输出,标准错误就是该数组的0,1,2下标,在我们新打开文件时,这时就会从头开始扫描该数组,找到第一个为空的,存放内存中该文件地址,文件描述符就是该数组下标。
文件描述符本质:数组下标
原理图如下
重定向
重定向将输入或输出从标准位置改变到其他位置。
输出重定向
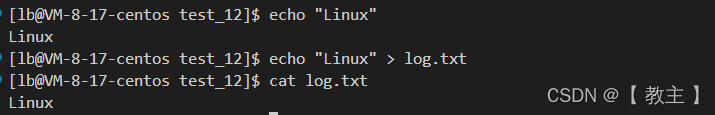
将原本输出到显示器改为输出到文件,打印文件内容即可查看信息
输入重定向
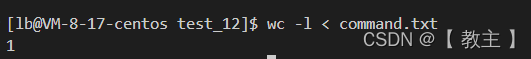
将原本从键盘读取输入改为从文件中读取输入,这就是输入重定向
重定向本质
输入重定向本质,将标准输入改为别的文件,就可以从该文件中读取输入,而不是从键盘读取输入。
输出重定向本质,将标准输出改为别的文件,就可以输出到该文件,而不是输出到显示器。
输入重定向验证
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
close(0);
int fd = open("input.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (-1 == fd)
{
perror("open file:");
_exit(1);
}
char buffer[64];
memset(buffer, '\0', sizeof buffer);
read(0, buffer, sizeof buffer);
write(1, buffer, strlen(buffer));
close(fd);
return 0;
}因为标准输入认准的就是0号下标,所以我们就让input.txt文件描述符成为0,原本从键盘读取输入变为从input.txt中读取数据,这就是输入重定向本质。
结果如下

输出重定向验证
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
close(1);
int fd = open("output.txt", O_WRONLY | O_APPEND);
if (-1 == fd)
{
perror("open file:");
_exit(1);
}
char buffer[64];
fgets(buffer, sizeof buffer, stdin);
write(1, buffer, strlen(buffer));
close(fd);
return 0;
}运行起来之后,命令行会等待输入,我们输入字符串后,结果并没有显示在显示器上,打印output.txt文件后可以看到输入的字符串。
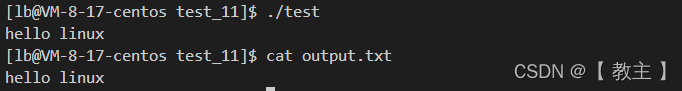
重定向系统调用
上面的代码只是为了验证重定向底层原理,如果想让实现重定向可以使用系统调用,可以查看下使用手册
shell
man dup这里使用dup2
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main() {
// 打开文件 "output.txt" 并获取文件描述符
int file_fd = open("output.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (file_fd < 0) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 使用 dup2 将标准输出 (file descriptor 1) 重定向到文件描述符 file_fd
if (dup2(file_fd, STDOUT_FILENO) < 0) {
perror("dup2");
close(file_fd);
return 1;
}
printf("hello linux\n");
close(file_fd);
return 0;
}原本打印到标准输出的内容就会被重定向到显示器