说明
- @author blog.jellyfishmix.com / JellyfishMIX - github
- LICENSE GPL-2.0
获取泛型,泛型擦除
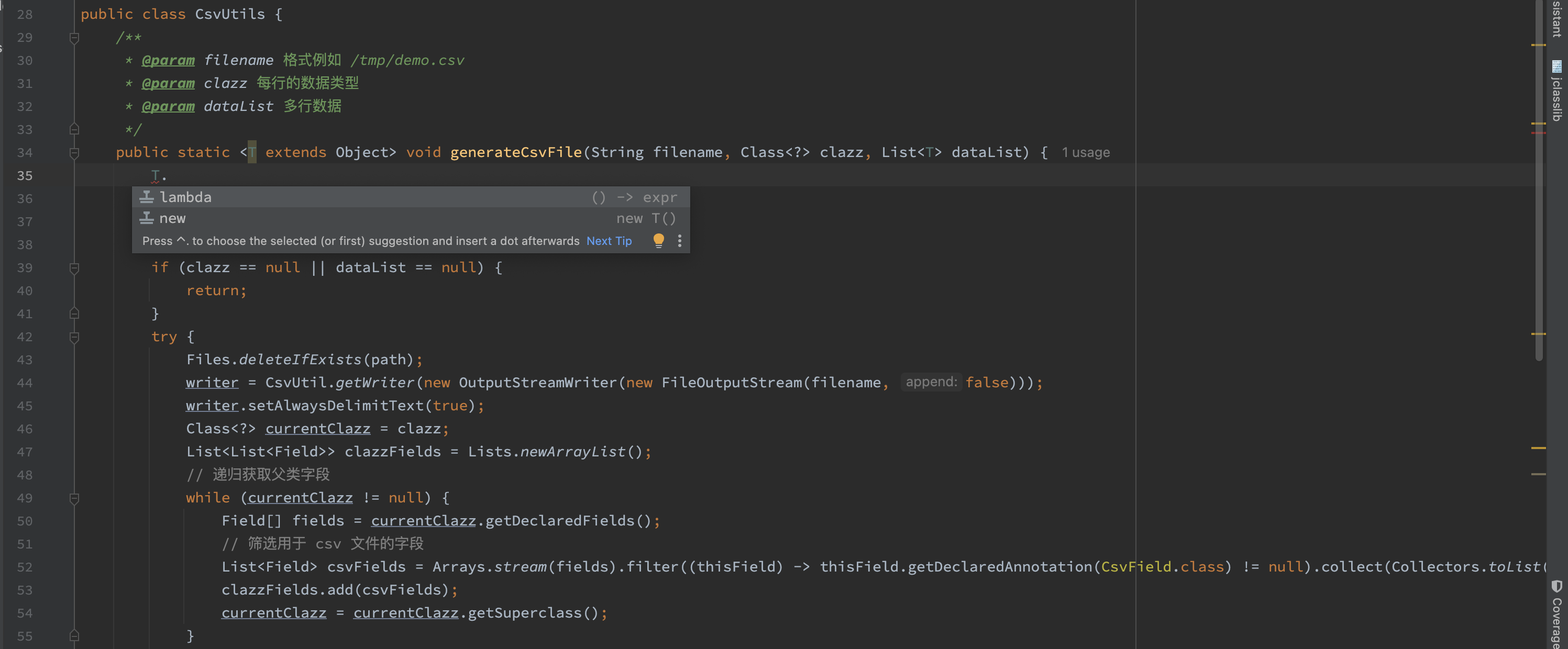
- 下图中示例代码是一个工具类用于生成 csv 文件,需要拿到数据的类型,使用反射感知数据类型的字段,来填充表字段名。
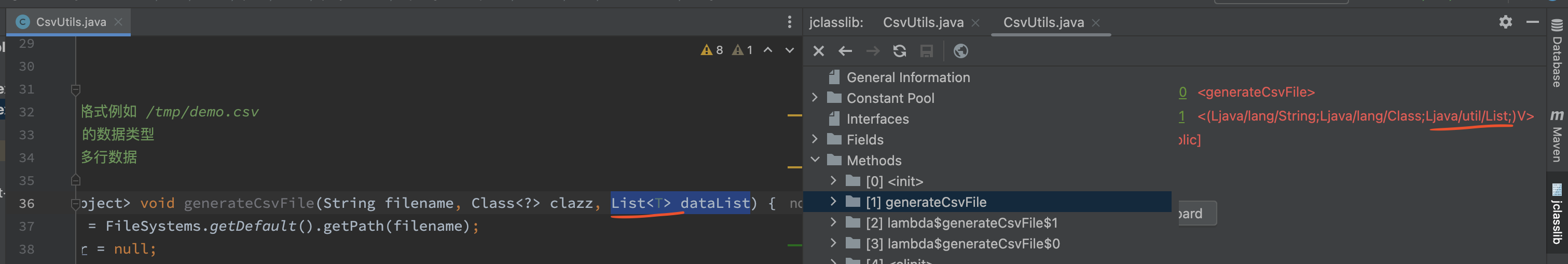
- 可以看到泛型 T 没有类似 getClass() 的方法,因为编译后泛型 T 会被擦除,在字节码中不存在 T 这个类型,所以没办法通过 T 来获取某些信息。方法签名中的
java.util.List<T>编译后会变成java.util.List。 - 解决方式是显式传入
Class<?> clazz来指定数据类型。
泛型嵌套
Class<?> clazz只能传递一层数据类型,无法解决泛型嵌套时的数据类型传递问题。- 对于泛型嵌套,例如
List<List<Map<String, Person>>>,这样的类型。如果使用Class<?> clazz来传递,只能感知到最外层的List.class,内层泛型还是会出现泛型擦除的情况。 - 完整地传递泛型嵌套,还是需要感知到具体的泛型。
TypeReference 原理分析--感知具体泛型
- 出现泛型嵌套情况时,获取完整的泛型,也是序列化组件需要面对的问题。解决方法例如 jackson 提供的 TypeReference。
泛型没有完全擦除
- javac 编译后没有把所有持有泛型的位置都做擦除。
- 编译后的字节码中,子类的类签名显式指定了传递给父类的泛型。
根据子类获取向父类传递的泛型理论基础
作为 TypeReference 的替代品,定义一个 CustomTypeHandler,通过演义来展示 TypeReference 的原理,
java
public abstract class CustomTypeHandler<T extends Object> {
}再定义一个 ChildCustomTypeHandler 子类,继承父类时声明泛型。
java
public class ChildCustomTypeHandler extends CustomTypeHandler<List<List<Map<String, Person>>>> {
private String tag;
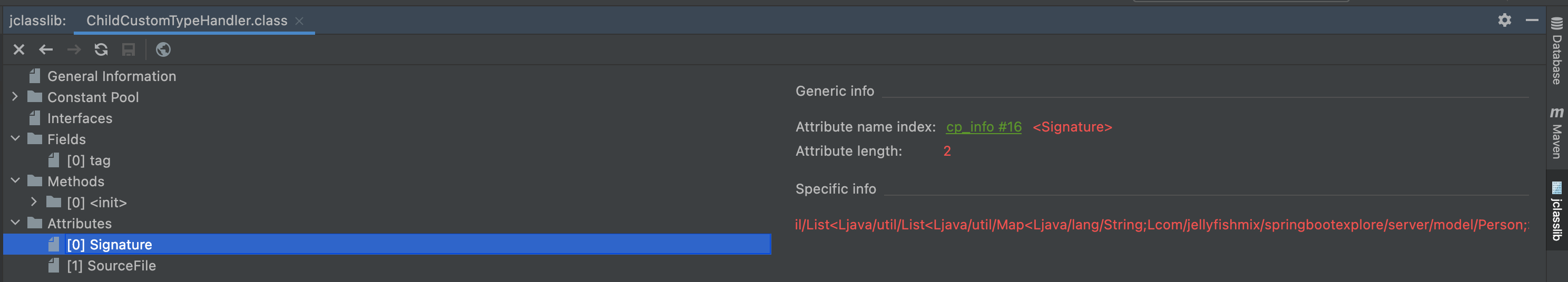
}编译项目后,使用 jclasslib(一个 IDEA 查看字节码的插件) 查看 ChildCustomTypeHandler.class 字节码,发现 Attributes -> Signature 属性中,记录了类签名,类签名显式指定了传递给父类的泛型。
class 文件结构
jvm 定义了 u1, u2, u4 三种数据结构来表示 1, 2, 4 字节无符号整数。class 文件采用类似 C 语言的结构体来存储数据,如下所示:
ClassFile {
u4 magic;
u2 minor_version;
u2 major_version;
u2 constant_pool_count;
cp_info constant_pool[constant_pool_count-1];
u2 access_flags;
u2 this_class;
u2 super_class;
u2 interfaces_count;
u2 interfaces[interfaces_count];
u2 fields_count;
field_info fields[fields_count];
u2 methods_count;
method_info methods[methods_count];
u2 attributes_count;
attribute_info attributes[attributes_count];
}中文说明:
魔数(Magic Number)
版本号(Minor&Major Version)
常量池(Constant Pool)
类访问标记(Access Flags)
类索引(This Class)
超类索引(Super Class)
接口表索引(Interfaces)
字段表(Fields)
方法表(Methods)
属性表(Attributes)类的字节码 Attributes -> Signature 属性中,记录了类签名,类签名会显式指定传递给父类的泛型 。这是根据子类获取向父类传递的泛型的理论基础 ,及 TypeReference 的理论基础。
根据子类获取向父类传递的泛型 demo
- getActualTypeArguments 可能会存在多个泛型,例如 Map<K,V> 所以会返回 Type[] 数组。
- 根据 CustomTypeHandler 的约定,只能向 CustomTypeHandler 传递一个最外层 T,因此这里直接通过[0]拿 T。
- 这里拿到的 T 是包含泛型嵌套的。例如子类声明 extends CustomTypeHandler<List<List<Map<String, Person>>>>,这里会拿到 List<List<Map<String, Person>>>
- 如果想继续拿嵌套的内层泛型,可以继续调用 ParameterizedType#getActualTypeArguments
java
public abstract class CustomTypeHandler<T extends Object> {
protected final Type _type;
/**
* 此方法实际由子类调用
*/
protected CustomTypeHandler() {
Type superClass = getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
// sanity check, should never happen
if (superClass instanceof Class<?>) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Internal error: TypeReference constructed without actual type information");
}
/*
* getActualTypeArguments 可能会存在多个泛型,例如 Map<K,V> 所以会返回 Type[] 数组
* 根据 CustomTypeHandler 的约定,只能向 CustomTypeHandler 传递一个最外层 T,因此这里直接通过[0]拿 T。
* 这里拿到的 T 是包含泛型嵌套的。例如子类声明 extends CustomTypeHandler<List<List<Map<String, Person>>>>,这里会拿到 List<List<Map<String, Person>>>
* 如果想继续拿嵌套的内层泛型,可以继续调用 ParameterizedType#getActualTypeArguments
*/
_type = ((ParameterizedType) superClass).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
}
public Type getType() {
return this._type;
}
}扩展阅读
