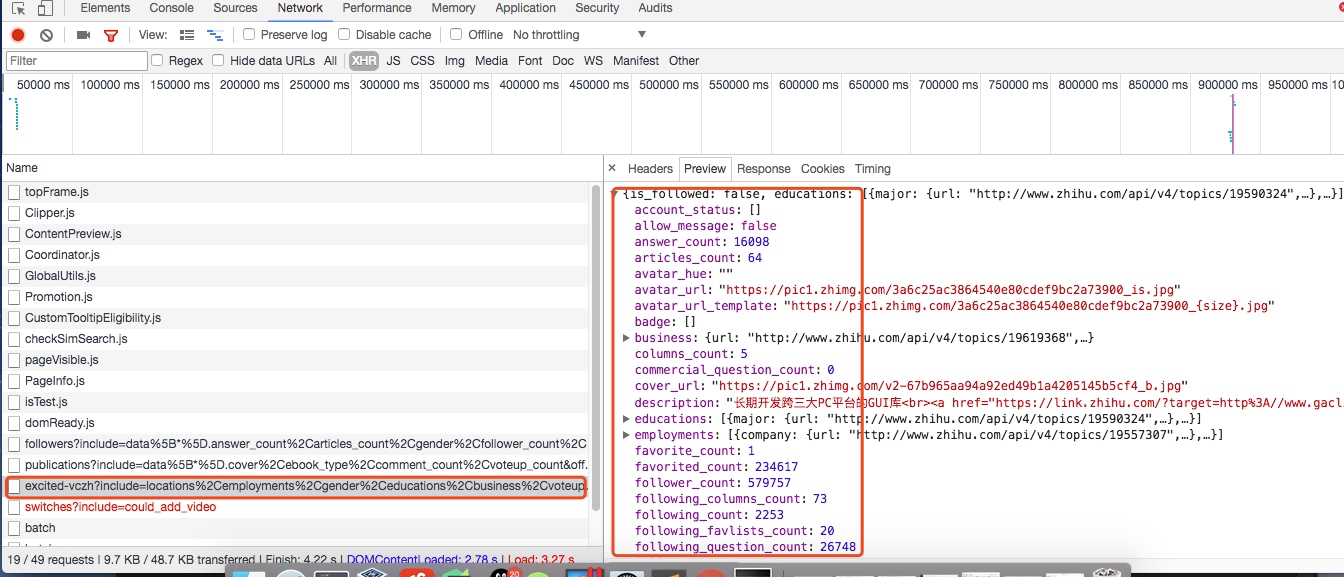
items中的代码主要是我们要爬取的字段的定义
class UserItem(scrapy.Item):
id \= Field()
name \= Field()
account\_status \= Field()
allow\_message\= Field()
answer\_count \= Field()
articles\_count \= Field()
avatar\_hue \= Field()
avatar\_url \= Field()
avatar\_url\_template \= Field()
badge \= Field()
business \= Field()
employments \= Field()
columns\_count \= Field()
commercial\_question\_count \= Field()
cover\_url \= Field()
description \= Field()
educations \= Field()
favorite\_count \= Field()
favorited\_count \= Field()
follower\_count \= Field()
following\_columns\_count \= Field()
following\_favlists\_count \= Field()
following\_question\_count \= Field()
following\_topic\_count \= Field()
gender \= Field()
headline \= Field()
hosted\_live\_count \= Field()
is\_active \= Field()
is\_bind\_sina \= Field()
is\_blocked \= Field()
is\_advertiser \= Field()
is\_blocking \= Field()
is\_followed \= Field()
is\_following \= Field()
is\_force\_renamed \= Field()
is\_privacy\_protected \= Field()
locations \= Field()
is\_org \= Field()
type \= Field()
url \= Field()
url\_token \= Field()
user\_type \= Field()
logs\_count \= Field()
marked\_answers\_count \= Field()
marked\_answers\_text \= Field()
message\_thread\_token \= Field()
mutual\_followees\_count \= Field()
participated\_live\_count \= Field()
pins\_count \= Field()
question\_count \= Field()
show\_sina\_weibo \= Field()
thank\_from\_count \= Field()
thank\_to\_count \= Field()
thanked\_count \= Field()
type \= Field()
vote\_from\_count \= Field()
vote\_to\_count \= Field()
voteup\_count \= Field()这些字段的是在用户详细信息里找到的,如下图所示,这里一共有58个字段,可以详细研究每个字段代表的意思:
关于spiders中爬虫文件zhihu.py中的主要代码
这段代码是非常重要的,主要的处理逻辑其实都是在这里
class ZhihuSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name \= "zhihu"
allowed\_domains \= \["www.zhihu.com"\]
start\_urls \= \['http://www.zhihu.com/'\]
#这里定义一个start\_user存储我们找的大V账号
start\_user = "excited-vczh"
#这里把查询的参数单独存储为user\_query,user\_url存储的为查询用户信息的url地址
user\_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/api/v4/members/{user}?include={include}"
user\_query \= "locations,employments,gender,educations,business,voteup\_count,thanked\_Count,follower\_count,following\_count,cover\_url,following\_topic\_count,following\_question\_count,following\_favlists\_count,following\_columns\_count,avatar\_hue,answer\_count,articles\_count,pins\_count,question\_count,columns\_count,commercial\_question\_count,favorite\_count,favorited\_count,logs\_count,marked\_answers\_count,marked\_answers\_text,message\_thread\_token,account\_status,is\_active,is\_bind\_phone,is\_force\_renamed,is\_bind\_sina,is\_privacy\_protected,sina\_weibo\_url,sina\_weibo\_name,show\_sina\_weibo,is\_blocking,is\_blocked,is\_following,is\_followed,mutual\_followees\_count,vote\_to\_count,vote\_from\_count,thank\_to\_count,thank\_from\_count,thanked\_count,description,hosted\_live\_count,participated\_live\_count,allow\_message,industry\_category,org\_name,org\_homepage,badge\[?(type=best\_answerer)\].topics"
#follows\_url存储的为关注列表的url地址,fllows\_query存储的为查询参数。这里涉及到offset和limit是关于翻页的参数,0,20表示第一页
follows\_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/api/v4/members/{user}/followees?include={include}&offset={offset}&limit={limit}"
follows\_query \= "data%5B\*%5D.answer\_count%2Carticles\_count%2Cgender%2Cfollower\_count%2Cis\_followed%2Cis\_following%2Cbadge%5B%3F(type%3Dbest\_answerer)%5D.topics"
#followers\_url是获取粉丝列表信息的url地址,followers\_query存储的为查询参数。
followers\_url = "https://www.zhihu.com/api/v4/members/{user}/followers?include={include}&offset={offset}&limit={limit}"
followers\_query \= "data%5B\*%5D.answer\_count%2Carticles\_count%2Cgender%2Cfollower\_count%2Cis\_followed%2Cis\_following%2Cbadge%5B%3F(type%3Dbest\_answerer)%5D.topics"
def start\_requests(self):
'''
这里重写了start\_requests方法,分别请求了用户查询的url和关注列表的查询以及粉丝列表信息查询
:return:
'''
yield Request(self.user\_url.format(user=self.start\_user,include=self.user\_query),callback=self.parse\_user)
yield Request(self.follows\_url.format(user=self.start\_user,include=self.follows\_query,offset=0,limit=20),callback=self.parse\_follows)
yield Request(self.followers\_url.format(user=self.start\_user,include=self.followers\_query,offset=0,limit=20),callback=self.parse\_followers)
def parse\_user(self, response):
'''
因为返回的是json格式的数据,所以这里直接通过json.loads获取结果
:param response:
:return:
'''
result \= json.loads(response.text)
item \= UserItem()
#这里循环判断获取的字段是否在自己定义的字段中,然后进行赋值
for field in item.fields:
if field in result.keys():
item\[field\] \= result.get(field)
#这里在返回item的同时返回Request请求,继续递归拿关注用户信息的用户获取他们的关注列表
yield item
yield Request(self.follows\_url.format(user = result.get("url\_token"),include=self.follows\_query,offset=0,limit=20),callback=self.parse\_follows)
yield Request(self.followers\_url.format(user = result.get("url\_token"),include=self.followers\_query,offset=0,limit=20),callback=self.parse\_followers)
def parse\_follows(self, response):
'''
用户关注列表的解析,这里返回的也是json数据 这里有两个字段data和page,其中page是分页信息
:param response:
:return:
'''
results \= json.loads(response.text)
if 'data' in results.keys():
for result in results.get('data'):
yield Request(self.user\_url.format(user = result.get("url\_token"),include=self.user\_query),callback=self.parse\_user)
#这里判断page是否存在并且判断page里的参数is\_end判断是否为False,如果为False表示不是最后一页,否则则是最后一页
if 'page' in results.keys() and results.get('is\_end') == False:
next\_page \= results.get('paging').get("next")
#获取下一页的地址然后通过yield继续返回Request请求,继续请求自己再次获取下页中的信息
yield Request(next\_page,self.parse\_follows)
def parse\_followers(self, response):
'''
这里其实和关乎列表的处理方法是一样的
用户粉丝列表的解析,这里返回的也是json数据 这里有两个字段data和page,其中page是分页信息
:param response:
:return:
'''
results \= json.loads(response.text)
if 'data' in results.keys():
for result in results.get('data'):
yield Request(self.user\_url.format(user = result.get("url\_token"),include=self.user\_query),callback=self.parse\_user)
#这里判断page是否存在并且判断page里的参数is\_end判断是否为False,如果为False表示不是最后一页,否则则是最后一页
if 'page' in results.keys() and results.get('is\_end') == False:
next\_page \= results.get('paging').get("next")
#获取下一页的地址然后通过yield继续返回Request请求,继续请求自己再次获取下页中的信息
yield Request(next\_page,self.parse\_followers)上述的代码的主要逻辑用下图分析表示:
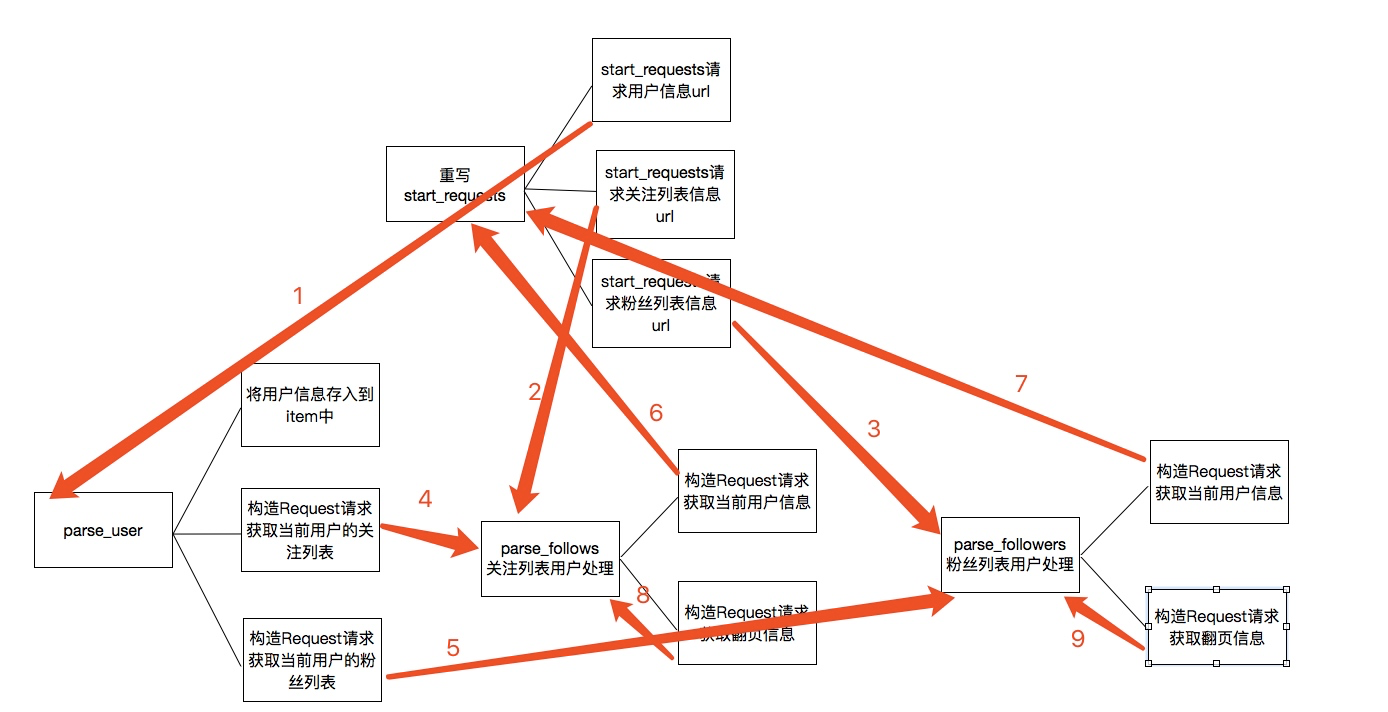
关于上图的一个简单描述:
-
当重写start_requests,一会有三个yield,分别的回调函数调用了parse_user,parse_follows,parse_followers,这是第一次会分别获取我们所选取的大V的信息以及关注列表信息和粉丝列表信息
-
而parse分别会再次回调parse_follows和parse_followers信息,分别递归获取每个用户的关注列表信息和分析列表信息
-
parse_follows获取关注列表里的每个用户的信息回调了parse_user,并进行翻页获取回调了自己parse_follows
-
parse_followers获取粉丝列表里的每个用户的信息回调了parse_user,并进行翻页获取回调了自己parse_followers
通过上面的步骤实现所有用户信息的爬取,最后是关于数据的存储
关于数据存储到mongodb
这里主要是item中的数据存储到mongodb数据库中,这里主要的一个用法是就是插入的时候进行了一个去重检测
class MongoPipeline(object):
def \_\_init\_\_(self, mongo\_uri, mongo\_db):
self.mongo\_uri \= mongo\_uri
self.mongo\_db \= mongo\_db
@classmethod
def from\_crawler(cls, crawler):
return cls(
mongo\_uri\=crawler.settings.get('MONGO\_URI'),
mongo\_db\=crawler.settings.get('MONGO\_DATABASE', 'items')
)
def open\_spider(self, spider):
self.client \= pymongo.MongoClient(self.mongo\_uri)
self.db \= self.client\[self.mongo\_db\]
def close\_spider(self, spider):
self.client.close()
def process\_item(self, item, spider):
#这里通过mongodb进行了一个去重的操作,每次更新插入数据之前都会进行查询,判断要插入的url\_token是否已经存在,如果不存在再进行数据插入,否则放弃数据
self.db\['user'\].update({'url\_token':item\["url\_token"\]},{'$set':item},True)
return item
仅作项目练习,切勿商用!!!由于文章篇幅有限,文档资料内容较多,需要这些文档的朋友,可以加小助手微信免费获取,【保证100%免费】,中国人不骗中国人。

全套Python学习资料分享:
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向路线就是把Python常用的技术点做整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。

二、学习软件
工欲善其事必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,还有环境配置的教程,给大家节省了很多时间。

三、全套PDF电子书
书籍的好处就在于权威和体系健全,刚开始学习的时候你可以只看视频或者听某个人讲课,但等你学完之后,你觉得你掌握了,这时候建议还是得去看一下书籍,看权威技术书籍也是每个程序员必经之路。
四、入门学习视频全套
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。
五、实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
好了今天的分享就到这里了