文章目录
- [1. 前言](#1. 前言)
- [2. MAC Address](#2. MAC Address)
-
- [2.1 MAC 地址格式](#2.1 MAC 地址格式)
- [2.2 Locally Administered MAC Address](#2.2 Locally Administered MAC Address)
-
- [2.3 MAC 单播 和 多播](#2.3 MAC 单播 和 多播)
- [3. 参考资料](#3. 参考资料)
1. 前言
限于作者能力水平,本文可能存在谬误,因此而给读者带来的损失,作者不做任何承诺。
2. MAC Address
2.1 MAC 地址格式
网络设备的 MAC 地址格式如下图:
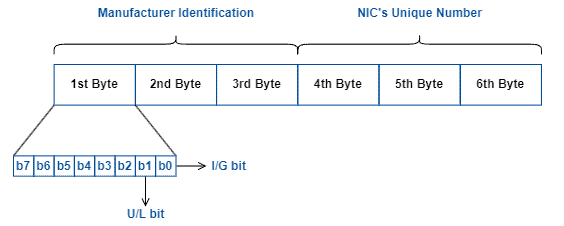
MAC 共 6 个字节,前 3 个字节为制造商 ID,从 OUI 组织申请,后 3 个字节为厂商网络设备的唯一标识。
2.2 Locally Administered MAC Address
Locally Administered Address 是一类特殊的 MAC 地址,类似于 LAN IP 地址,如 10.0.0.0/8,192.168.0.0/16,172.16.0.0/16 等局域网地址。Locally Administered Address 是系统管理员自定义的网络设备 MAC,不会和各大厂商注册的 MAC 冲突,通常用于虚拟网卡(如网桥)等设备。
MAC 地址的第一个字节的第 2 位,即上图中的 U/L bit ,如果该 bit 为 0,则为 OUI 组织分配的各大厂商 MAC;否则为 Locally Administered Address 。看下对 Locally Administered Address 的说明:
c
locally administered address
A locally administered MAC address is similar to a LAN IP address (10.0.0.0/8,
172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16). You can make up your own locally administered
address and can be sure that it will not collide with any hardware on your network that
use a factory burned-in MAC address. Locally administered addresses are useful when
creating virtual machines or virtual network interfaces.
The second bit of the first byte of a MAC address determines the type of OUI. If the bit
is 0 then it is an OUI globally assigned by the IEEE; if the bit is 1 then it is a locally
administered MAC address.
Create a OUI by whatever scheme you like, then logically OR it with 02:00:00:00:00:00, and
then logically AND it with fe:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, and you will have a locally administered
address. The first OR pattern sets bit 2 of the first byte; the second AND pattern clears
bit 1 of the first byte (unicast, not multicast).
The following MAC address pattern satisfies the OUI requirements:
4e:4f:41:48:00:002.3 MAC 单播 和 多播

上图中,MAC 的最高字节的 bit 0,如果该 bit 为 0,则是单播 MAC;否则为多播 MAC。看下面的描述:
bash
universally administered address
The original IEEE 802 MAC address comes from the original Xerox Ethernet addressing scheme.
This 48-bit address space contains potentially 248 or 281,474,976,710,656 possible MAC
addresses.
All three numbering systems use the same format and differ only in the length of the
identifier. Addresses can either be "universally administered addresses" or "locally
administered addresses".
A universally administered address is uniquely assigned to a device by its manufacturer;
these are sometimes called "burned-in addresses" (BIA). The first three octets (in
transmission order) identify the organization that issued the identifier and are known as
the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI). The following three (MAC-48 and EUI-48) or
five (EUI-64) octets are assigned by that organization in nearly any manner they please,
subject to the constraint of uniqueness. The IEEE expects the MAC-48 space to be
exhausted no sooner than the year 2100; EUI-64s are not expected to run out in the
foreseeable future.
A locally administered address is assigned to a device by a network administrator,
overriding the burned-in address. Locally administered addresses do not contain OUIs.
Universally administered and locally administered addresses are distinguished by setting
the second least significant bit of the most significant byte of the address. If the bit
is 0, the address is universally administered. If it is 1, the address is locally
administered. In the example address 06-00-00-00-00-01 the most significant byte is
06 (hex), the binary form of which is 00000110, where the second least significant bit is
1. Therefore, it is a locally administered address. Consequently, this bit is 0 in all
OUIs.
If the least significant bit of the most significant octet of an address is set to 0
(zero), the frame is meant to reach only one receiving NIC. This type of transmission
is calledunicast . A unicast frame is transmitted to all nodes within the collision
domain , which typically ends at the nearest network switch or router . Only the node
with the matching hardware MAC address will accept the frame; network frames with
non-matching MAC-addresses are ignored, unless the device is in promiscuous mode.
If the least significant bit of the most significant address octet is set to 1, the packet
will still be sent only once; however, NICs will choose to accept it based on different
criteria than a matching MAC address: for example, based on a configurable list of
accepted multicast MAC addresses. This is called multicast addressing.3. 参考资料
1\] [Understanding MAC Addresses](https://www.baeldung.com/cs/understanding-mac-addresses) \[2\] [Identify a randomised (locally administered) MAC Address](https://richardatkin.com/post/2022/01/14/MAC-Address-Randomisation.html) \[3\] [给自己分一个 MAC地址--locally administered address](https://blog.csdn.net/rainharder/article/details/45025147) \[4\] [MAC 地址格式](https://blog.csdn.net/rainharder/article/details/45025147) \[5\] [Organizationally unique identifier](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organizationally_Unique_Identifier) \[6\] [MAC address](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAC_address)