一、简介
在前面的文章中,我们已经分析了 MyBatis 配置文件的解析过程。由于上一篇文章的篇幅比较大,加之映射文件解析过程也比较复杂的原因。所以将映射文件解析过程的分析内容从上一篇文章中抽取出来,独立成文,于是就有了本篇文章。在本篇文章中,将分析解析配置文件中的<mapper>标签以继SQL映射文件中出现的一些节点,比如 <cache>,<cache-ref>,<resultMap>, <select | insert | update | delete> 等。除了分析常规的 XML 解析过程外,还会向大家介绍 Mapper 接口的绑定过程等。综上所述,本篇文章内容会比较丰富,如果大家对此感兴趣,不妨花点时间读一读,会有新的收获。当然,本篇文章通篇是关于源码分析的,所以阅读本文需要大家对 MyBatis 有一定的了解。如果大家对 MyBatis 还不是很了解,建议阅读一下 MyBatis 的官方文档。
二、 映射文件解析过程分析
映射文件的解析过程是 MyBatis 配置文件解析过程的一部分。MyBatis 的配置文件由 XMLConfigBuilder 的 parseConfiguration 进行解析,该方法依次解析了 <properties>、<settings>、<typeAliases> 等节点。至于 <mappers> 节点,parseConfiguration 则是在方法的结尾对其进行了解析。该部分的解析逻辑封装在 mapperElement 方法中。
2.0 解析全局配置文件中的 <mappers> 标签
所以Mapper 映射文件的解析是从XMLConfigBuilder类的对全局配置文件的mappers节点解析开始的,mappers节点的配置有很多形式,主要有以下四种:
XML
<!-- 1.使用类路径 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
<!-- 2.使用绝对url路径 -->
<mappers>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
<!-- 3.使用java类名 -->
<mappers>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/>
</mappers>
<!-- 4.自动扫描包下所有映射器 -->
<mappers>
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
</mappers>- 可通过package标签批量注册Mapper接口
- 通过mapper标签的resource****属性配置具体的xml****文件
- 通过mapper标签的url****属性配置网络上的xml****文件
- 通过mapper标签的class****属性配置具体的Mapper****接口。
下面我们就从全局配置文件中mappers标签的解析入口方法mapperElement()开始,作为源码分析的入口:
java
// -☆- XMLConfigBuilder
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// 遍历解析mappers节点下的所有mapper子节点
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 判断mapper是否通过批量注册的<package name="com.eleven.mapper"></package>
// 1、自动扫描包下所有映射器
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 获取 <package> 节点中的 name 属性
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 从指定包中查找 mapper 接口,并根据 mapper 接口解析映射配置
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
// 获取 resource/url/class 等属性
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// 2、resource 不为空,且其他两者为空,则从指定路径中加载SQL映射文件
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
// 把文件读取出一个流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 创建读取XmlMapper构建器对象,用于来解析mapper.xml文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 解析映射文件
mapperParser.parse();
// 3、url 不为空,且其他两者为空,则通过 url 加载SQL映射文件
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 解析映射文件
mapperParser.parse();
// 4、mapperClass 不为空,且其他两者为空,则通过 mapperClass 解析映射文件(直接通过Mapper接口解析映射文件,一般这种就是将SQL写到了注解中)
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
// 以上条件不满足,则抛出异常
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}上面的代码比较简单,主要逻辑是遍历 mappers 的子节点,并根据节点属性值判断通过什么方式加载映射文件或映射信息。这里,我把配置在注解中的内容称为映射信息,以 XML 为载体的配置称为映射文件。在 MyBatis 中,共有四种加载映射文件或信息的方式:
- 第一种是通过包扫描的方式获取到某个包下的所有类,并使用第四种方式为每个类解析映射信息。
- 第二种是从文件系统中加载映射文件;
- 第三种是通过 URL 的方式加载和解析映射文件;
- 第四种是通过 mapper 接口加载映射信息,映射信息可以配置在注解中,也可以配置在映射文件中(如果映射文件的路径写在了Mapper接口中的注解中,就仍然会建立Mapper接口和XML文件的映射关系)。
上述解析方法的主要流程如下流程图所示:
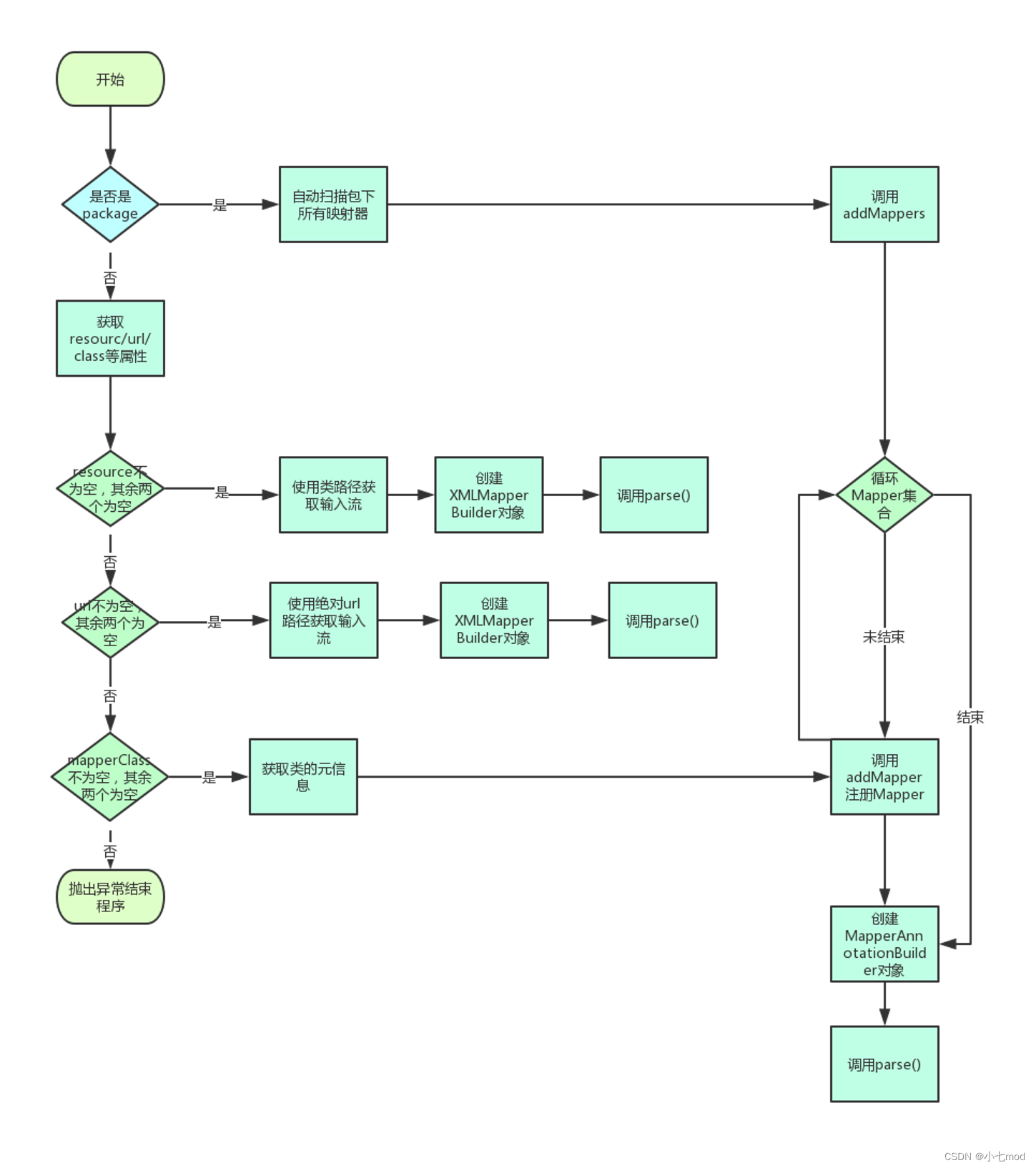
如上流程图,mappers节点的解析还是比较复杂的,这里我挑几个部分说下。其中:
- configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage)还是利用ResolverUtil找出包下所有的类,然后循环调用MapperRegistry类的addMapper方法。
- 配置resource或者url的因为是要解析XML映射文件,所以都需要先创建一个XMLMapperBuilder对象(专门用来解析XML的类)。然后调用XMLMapperBuilder的parse方法。
2.1 解析 SQL 映射信息(解析 Mapper 接口映射器)
我们这一篇文章我们主要是以解析XML的SQL映射文件为例来进行源码分析的,因为只要是搞懂了XML的解析流程,那么解析Mapper接口映射器(对注解进行解析)和扫描包下的所有映射器的解析(本质还是对Mapper接口的解析)就会很好理解。这里我们就先简单介绍一下解析Mapper映射的源码,也就是上面说的第四种解析分支。
java
//* MapperRegistry 添加映射的方法
// 传入的是Mapper接口类型Class对象
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// mapper必须是接口!才会添加
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
// 如果重复添加了,报错
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 将映射器的class对象(mapper接口类型),以及其代理类工厂设置到集合中,采用的是JDK代理。建立起了目标对象和代理对象工厂的映射关系
// 在这里就将接口和其代理对象工厂的映射关系,添加到了knownMappers中
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// 在运行解析器之前添加类型是很重要的,否则,可能会自动尝试绑定映射器解析器。如果类型已经知道,则不会尝试。
// 创建注解解析器。在 MyBatis 中,有 XML 和 注解两种配置方式可选
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 这里就用的注解解析器MapperAnnotationBuilder 进行解析的,但是上面其他的分支是使用的XML解析器XMLMapperBuilder进行解析的,后面源码分析也是以XML解析为例讲解的。关于注解解析器的源码这里就不分析了,我们在下面主要分析XML解析器的源码,两者的思路是基本一致的,只不过一个是解析注解,一个是解析XML文件而已。
// 解析注解中的信息
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
// 如果加载过程中出现异常需要再将这个mapper从mybatis中删除,
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
//* MapperProxyFactory
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 代理工厂就可以用JDK自带的动态代理生成映射器
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}需要注意的是,在 MyBatis 中,通过注解配置映射信息的方式是有一定局限性的,这一点 MyBatis 官方文档中描述的比较清楚。这里引用一下:
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| |--------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | 🛈 | 因为最初设计时,MyBatis 是一个 XML 驱动的框架。配置信息是基于 XML 的,而且映射语句也是定义在 XML 中的。而到了 MyBatis 3,就有新选择了。MyBatis 3 构建在全面且强大的基于 Java 语言的配置 API 之上。这个配置 API 是基于 XML 的 MyBatis 配置的基础,也是新的基于注解配置的基础。注解提供了一种简单的方式来实现简单映射语句,而不会引入大量的开销。 注意: 不幸的是,Java 注解的的表达力和灵活性十分有限 。尽管很多时间都花在调查、设计和试验上,最强大的 MyBatis 映射并不能用注解来构建------并不是在开玩笑,的确是这样。 | |
如上所示,重点语句我用黑体标注了出来。限于 Java 注解的表达力和灵活性,通过注解的方式并不能完全发挥 MyBatis 的能力。所以,对于一些较为复杂的配置信息,我们还是应该通过 XML 的方式进行配置。正因此,在接下的章节中,我会重点分析基于 XML 的映射文件的解析过程。如果能弄懂此种配置方式的解析过程,那么基于注解的解析过程也不在话下。
2.2 解析 SQL 映射文件(解析 XML 映射文件 )
下面开始分析映射文件的解析过程,在展开分析之前,先来看一下映射文件解析入口。如下:
java
// -☆- XMLMapperBuilder类
public void parse() {
// 检测映射文件是否已经被解析过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 2.2.1 解析 mapper 节点,这个mapper节点是指的映射文件里的mapper节点
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 添加资源路径到"已解析资源集合"中,即把mapper.xml全限定名保存到已被加载列表
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 2.2.2 根据命名空间绑定 Mapper 接口(将XML映射文件和对应的Mapper接口绑定起来),如果接口中有注解,则解析Mapper接口中SQL注解
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 2.2.3 处理未完成解析的节点
parsePendingResultMaps();// 处理未完成解析的ResultMaps节点
parsePendingCacheRefs();// 处理未完成解析的CacheRefs节点
parsePendingStatements();// 处理未完成解析的Statements节点
}如上,映射文件解析入口逻辑包含三个核心操作,分别如下:
- 解析 mapper 节点(这个mapper节点是指的映射文件里的mapper节点)
- 添加资源路径到"已解析资源集合"中
- 通过命名空间绑定 Mapper 接口
- 处理未完成解析的节点
Mapper是通过XML****配置文件的方法配置的,首先会通过parse方法先去解析mapper.xml文件内容,然后再通过调用bindMapperForNamespace从而调用configuration#addMapper去触发解析Mapper接口中的注解。
这三个操作对应的逻辑,我将会在随后的章节中依次进行分析。下面,先来分析第一个操作对应的逻辑。
2.2.1 解析映射文件
在 MyBatis 映射文件中,可以配置多种节点。比如 <cache>,<resultMap>,<sql> 以及 <select | insert | update | delete> 等。下面我们来看一个映射文件配置示例。
XML
<!-- namespace用于设置命名空间 -->
<mapper namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.AuthorDao">
<cache/>
<resultMap id="authorResult" type="Author">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<!-- ... -->
</resultMap>
<sql id="table">
author
</sql>
<select id="findOne" resultMap="authorResult">
SELECT
id, name, age, sex, email
FROM
<include refid="table"/>
WHERE
id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- <insert|update|delete/> -->
</mapper>上面是一个比较简单的映射文件,还有一些的节点没有出现在上面。以上每种配置中的每种节点的解析逻辑都封装在了相应的方法中,这些方法由 XMLMapperBuilder 类的 configurationElement 方法统一调用。该方法的逻辑如下:
java
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 获取 mapper 命名空间
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 设置命名空间到 builderAssistant 中
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 解析 <cache-ref> 节点
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 解析 <cache> 节点
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 已废弃配置,这里不做分析
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// 解析 <resultMap> 节点
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析 <sql> 节点
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析 <select>、<update>、<insert>、<delete> 等节点
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}上面代码的执行流程清晰明了。在阅读源码时,我们可以按部就班的分析每个方法调用即可。不过在写文章进行叙述时,需要做一些调整。下面我将会先分析 <cache> 节点的解析过程,然后再分析 <cache-ref> 节点,之后会按照顺序分析其他节点的解析过程。接下来,我们来看看 <cache> 节点的解析过程。
2.2.1.1 解析 <cache> 节点
MyBatis 提供了一、二级缓存,其中一级缓存是 SqlSession 级别的,默认为开启状态。二级缓存配置在映射文件中,使用者需要显示配置才能开启(全局配置文件和SQL映射文件都要配置一下才能开启二级缓存。全局配置文件的二级缓存配置也需要设置为true,这个开启标签默认就是true,但还是要自己配置一下这个标签才行)。如果没有特殊要求,二级缓存的配置很容易。如下:
<cache/>
如果我们想修改缓存的一些属性,可以像下面这样配置。
XML
<cache
eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>根据上面的配置创建出的缓存有以下特点:
- 按先进先出的策略淘汰缓存项
- 缓存的容量为 512 个对象引用
- 缓存每隔60秒刷新一次
- 缓存会被视为读/写缓存,这意味着获取到的对象并不是共享的,缓存返回的对象是写安全的,可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
除了上面两种配置方式,我们还可以给 MyBatis 配置第三方缓存或者自己实现的缓存等。比如,我们将 Ehcache 缓存整合到 MyBatis 中,可以这样配置。
XML
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
<property name="timeToIdleSeconds" value="3600"/>
<property name="timeToLiveSeconds" value="3600"/>
<property name="maxEntriesLocalHeap" value="1000"/>
<property name="maxEntriesLocalDisk" value="10000000"/>
<property name="memoryStoreEvictionPolicy" value="LRU"/>
</cache>以上简单介绍了几种缓存配置方式。
二级缓存在结构设计上采用装饰器****+**责任链模式。从最内层到最外层依次是PerpetualCache**、LruCache、ScheduledCache、SerializedCache、LoggingCache、SynchronizedCache、BlockingCache。
构建好的Cache缓存对象会被设置到MapperBuilderAssistant的currentCache属性,最后Mapper解析完成后通过MapperBuilderAssistant的addMappedStatement方法将缓存对象设置到对应的MappedStatement的cache属性中。在执行查询操作时会通过判断MappedStatement的cache属性是否为****null从而判断是否走二级缓存。关于 MyBatis 缓存更多的知识,后面我会独立成文进行分析,这里就不深入说明了。下面我们来分析一下缓存配置的解析逻辑,如下:
java
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 获取各种属性
// 解析cache节点的type属性
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
// 根据type的String获取class类型
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
// 获取缓存过期策略:默认是LRU
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
// flushInterval刷新间隔,可被设置为任意正整数,设置的值应该是一个以毫秒为单位的合理时间量。默认不设置即没有刷新间隔,缓存仅在调用语句时刷新
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
// size引用数目,可被设置为任意正整数,要注意缓存对象的大小和运行环境中可用的内存资源。默认值是1024
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
// readOnly只读,可被设置为true或false。只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些对象不能被修改。
// 而可读写的缓存会通过序列化返回缓存对象的拷贝,速度上会慢一些,但更安全默认值false
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
// 获取子节点配置
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 构建缓存对象,把缓存节点加入到Configuration中
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}上面代码中,大段代码用来解析 <cache> 节点的属性和子节点,这些代码没什么好说的。缓存的构建逻辑封装在 BuilderAssistant 类的 useNewCache 方法中,下面我们来看一下该方法的逻辑。
java
// -☆- MapperBuilderAssistant
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,Long flushInterval,
Integer size,boolean readWrite,boolean blocking,Properties props) {
// 使用建造模式构建缓存实例
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
// 添加缓存到 Configuration 对象中
configuration.addCache(cache);
// 设置 currentCache 遍历,即当前使用的缓存
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}如上,useNewCache 方法的主要有如下逻辑:
- 调用CacheBuilder构建cache,id=currentNamespace(使用建造者模式构建缓存实例)
- 添加缓存到Configuration对象中
- 设置currentCache遍历,即当前使用的缓存
上面使用了建造模式构建 Cache 实例,Cache 实例的构建过程略为复杂,我们跟下去看看。
java
// -☆- CacheBuilder
public Cache build() {
// 设置默认的缓存类型(PerpetualCache)和缓存装饰器(LruCache)
setDefaultImplementations();
// 通过反射创建缓存
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);
// 仅对内置缓存 PerpetualCache 应用装饰器
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
// 遍历装饰器集合,应用装饰器
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
// 通过反射创建装饰器实例
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
// 设置属性值到缓存实例中
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
// 应用标准的装饰器,比如 LoggingCache、SynchronizedCache
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
// 应用具有日志功能的缓存装饰器
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}上面的构建过程流程较为复杂,这里总结一下。如下:
- 设置默认的缓存类型(PerpetualCache)和缓存装饰器(LruCache)
- 应用装饰器到 PerpetualCache 对象上
- 遍历装饰器类型集合,并通过反射创建装饰器实例
- 将属性设置到实例中
- 应用一些标准的装饰器,装饰者模式一个个包装cache,仅针对内置缓存PerpetualCache应用装饰器
- 对非 LoggingCache 类型的缓存应用 LoggingCache 装饰器
在以上4个步骤中,最后一步的逻辑很简单,无需多说。下面按顺序分析前3个步骤对应的逻辑,如下:
java
private void setDefaultImplementations() {
if (implementation == null) {
// 设置默认的缓存实现类
implementation = PerpetualCache.class;
if (decorators.isEmpty()) {
// 添加 LruCache 装饰器
decorators.add(LruCache.class);
}
}
}以上逻辑比较简单,主要做的事情是在 implementation 为空的情况下,为它设置一个默认值。如果大家仔细看前面的方法,会发现 MyBatis 做了不少判空的操作。比如:
java
// 判空操作1,若用户未设置 cache 节点的 type 和 eviction 属性,这里设置默认值 PERPETUAL
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
// 判空操作2,若 typeClass 或 evictionClass 为空,valueOrDefault 方法会为它们设置默认值
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
// 省略部分代码
.build();既然前面已经做了两次判空操作,implementation 不可能为空,那么 setDefaultImplementations 方法似乎没有存在的必要了。其实不然,如果有人不按套路写代码。比如:
java
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
// 忘记设置 implementation
.build();这里忘记设置 implementation,或人为的将 implementation 设为空。如果不对 implementation 进行判空,会导致 build 方法在构建实例时触发空指针异常,对于框架来说,出现空指针异常是很尴尬的,这是一个低级错误。这里以及之前做了这么多判空,就是为了避免出现空指针的情况,以提高框架的健壮性(鲁棒性)。好了,关于 setDefaultImplementations 方法的分析先到这,继续往下分析。
我们在使用 MyBatis 内置缓存时,一般不用为它们配置自定义属性。但使用第三方缓存时,则应按需进行配置。比如前面演示 MyBatis 整合 Ehcache 时,就为 Ehcache 配置了一些必要的属性。下面我们来看一下这部分配置是如何设置到缓存实例中的。
java
private void setCacheProperties(Cache cache) {
if (properties != null) {
/*
* 为缓存实例生成一个"元信息"实例,forObject 方法调用层次比较深,但最终调用了
* MetaClass 的 forClass 方法。关于 MetaClass 的源码,我在上一篇文章中已经
* 详细分析过了,这里不再赘述。
*/
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String name = (String) entry.getKey();
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
if (metaCache.hasSetter(name)) {
// 获取 setter 方法的参数类型
Class<?> type = metaCache.getSetterType(name);
/*
* 根据参数类型对属性值进行转换,并将转换后的值
* 通过 setter 方法设置到 Cache 实例中
*/
if (String.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, value);
} else if (int.class == type || Integer.class == type) {
/*
* 此处及以下分支包含两个步骤:
* 1.类型转换 → Integer.valueOf(value)
* 2.将转换后的值设置到缓存实例中 → metaCache.setValue(name, value)
*/
metaCache.setValue(name, Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if (long.class == type || Long.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Long.valueOf(value));
}
else if (short.class == type || Short.class == type) {...}
else if (byte.class == type || Byte.class == type) {...}
else if (float.class == type || Float.class == type) {...}
else if (boolean.class == type || Boolean.class == type) {...}
else if (double.class == type || Double.class == type) {...}
else {
throw new CacheException("Unsupported property type for cache: '" + name + "' of type " + type);
}
}
}
}
// 如果缓存类实现了 InitializingObject 接口,则调用 initialize 方法执行初始化逻辑
if (InitializingObject.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
try {
((InitializingObject) cache).initialize();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Failed cache initialization for '" +
cache.getId() + "' on '" + cache.getClass().getName() + "'", e);
}
}
}上面的大段代码用于对属性值进行类型转换,和设置转换后的值到 Cache 实例中。关于上面代码中出现的 MetaObject,大家可以自己尝试分析一下。最后,我们来看一下设置标准装饰器的过程。如下:
java
private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) {
try {
// 创建"元信息"对象
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) {
// 设置 size 属性,
metaCache.setValue("size", size);
}
if (clearInterval != null) {
// clearInterval 不为空,应用 ScheduledCache 装饰器
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval);
}
if (readWrite) {
// readWrite 为 true,应用 SerializedCache 装饰器
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
}
/*
* 应用 LoggingCache,SynchronizedCache 装饰器,
* 使原缓存具备打印日志和线程同步的能力
*/
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
if (blocking) {
// blocking 为 true,应用 BlockingCache 装饰器
cache = new BlockingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}以上代码用于为缓存应用一些基本的装饰器,除了 LoggingCache 和 SynchronizedCache 这两个是必要的装饰器,其他的装饰器应用与否,取决于用户的配置。
到此,关于缓存的解析过程就分析完了。这一块的内容比较多,不过好在代码逻辑不是很复杂,耐心看还是可以弄懂的。其他的就不多说了,进入下一节的分析。
2.2.1.2 解析 <cache-ref> 节点
在 MyBatis 中,二级缓存是可以被不同的mapper.xml映射文件共用的。这需要使用 <cache-ref> 节点配置参照缓存,比如像下面这样。
XML
<!-- Mapper1.xml -->
<mapper namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.Mapper1">
<!-- Mapper1 与 Mapper2 共用一个二级缓存 -->
<cache-ref namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.Mapper2"/>
</mapper>
<!-- Mapper2.xml -->
<mapper namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.Mapper2">
<cache/>
</mapper>接下来,我们对照上面的配置分析 cache-ref 的解析过程。如下:
java
private void cacheRefElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
configuration.addCacheRef(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
// 创建 CacheRefResolver 实例
CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver(builderAssistant, context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
try {
// 解析参照缓存
cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
/*
* 这里对 IncompleteElementException 异常进行捕捉,并将 cacheRefResolver
* 存入到 Configuration 的 incompleteCacheRefs 集合中
*/
configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver);
}
}
}如上所示,<cache-ref> 节点的解析逻辑封装在了 CacheRefResolver 的 resolveCacheRef 方法中。下面,我们一起看一下这个方法的逻辑。
java
// -☆- CacheRefResolver
public Cache resolveCacheRef() {
// 调用 builderAssistant 的 useNewCache(namespace) 方法
return assistant.useCacheRef(cacheRefNamespace);
}
// -☆- MapperBuilderAssistant
public Cache useCacheRef(String namespace) {
if (namespace == null) {
throw new BuilderException("cache-ref element requires a namespace attribute.");
}
try {
unresolvedCacheRef = true;
// 根据命名空间从全局配置对象(Configuration)中查找相应的缓存实例
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
/*
* 若未查找到缓存实例,此处抛出异常。这里存在两种情况导致未查找到 cache 实例,
* 分别如下:
* 1.使用者在 <cache-ref> 中配置了一个不存在的命名空间,
* 导致无法找到 cache 实例
* 2.使用者所引用的缓存实例还未创建
*/
if (cache == null) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.");
}
// 设置 cache 为当前使用缓存
currentCache = cache;
unresolvedCacheRef = false;
return cache;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.", e);
}
}以上是 cache-ref 的解析过程,逻辑并不复杂。不过这里要注意 cache 为空的情况,我在代码中已经注释了可能导致 cache 为空的两种情况。第一种情况比较好理解,第二种情况稍微复杂点,但是也不难理解。我会在 2.3 节进行解释说明,这里先不说。
到此,关于 <cache-ref> 节点的解析过程就分析完了。本节的内容不是很难理解,就不多说了。
2.2.1.3 解析 <resultMap> 节点
resultMap 是 MyBatis 框架中常用的特性,主要用于映射结果。resultMap 是 MyBatis 提供的一个强力武器,这一点官方文档中有所描述,这里引用一下。
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| |--------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | 🛈 | resultMap 元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素。它可以让你从 90% 的 JDBC ResultSets 数据提取代码中解放出来, 并在一些情形下允许你做一些 JDBC 不支持的事情。 实际上,在对复杂语句进行联合映射的时候,它很可能可以代替数千行的同等功能的代码。 ResultMap 的设计思想是,简单的语句不需要明确的结果映射,而复杂一点的语句只需要描述它们的关系就行了。 | |
如上描述,resultMap 元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素,它可以把大家从 JDBC ResultSets 数据提取的工作中解放出来。通过 resultMap 和自动映射,可以让 MyBatis 帮助我们完成 ResultSet → Object 的映射,这将会大大提高了开发效率。关于 resultMap 的用法,我相信大家都比较熟悉了,所以这里我就不介绍了。当然,如果大家不熟悉也没关系,MyBatis 的官方文档上对此进行了详细的介绍,大家不妨去看看。
XML
<resultMap id="authorResult" type="Author">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<!-- ... -->
</resultMap>好了,其他的就不多说了,下面开始分析 resultMap 配置的解析过程。
java
// -☆- XMLMapperBuilder
private void resultMapElements(List<XNode> list) throws Exception {
// 遍历 <resultMap> 节点列表
for (XNode resultMapNode : list) {
try {
// 解析 resultMap 节点
resultMapElement(resultMapNode);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// ignore, it will be retried
}
}
}
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode) throws Exception {
// 调用重载方法
return resultMapElement(resultMapNode, Collections.<ResultMapping>emptyList());
}
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取 id 和 type 属性
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id", resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// 获取 extends 和 autoMapping
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
// 解析 type 属性对应的类型
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
Discriminator discriminator = null;
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
// 获取并遍历 <resultMap> 的子节点列表
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析 constructor 节点,并生成相应的 ResultMapping
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析 discriminator 节点
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<ResultFlag>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 添加 ID 到 flags 集合中
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
// 解析 id 和 property 节点,并生成相应的 ResultMapping
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend,
discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
// 根据前面获取到的信息构建 ResultMap 对象
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
/*
* 如果发生 IncompleteElementException 异常,
* 这里将 resultMapResolver 添加到 incompleteResultMaps 集合中
*/
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}上面的代码比较多,看起来有点复杂,这里总结一下:
- 获取 <resultMap> 节点的各种属性
- 遍历 <resultMap> 的子节点,并根据子节点名称执行相应的解析逻辑,生成相应的ResultMapping
- 构建 ResultMap 对象
- 若构建过程中发生异常,则将 resultMapResolver 添加到 incompleteResultMaps 集合中
如上流程,第1步和最后一步都是一些常规操作,无需过多解释。第2步和第3步则是接下来需要重点分析的操作,这其中,鉴别器 discriminator 不是很常用的特性,我觉得大家知道它有什么用就行了,所以就不分析了。下面先来分析 <id> 和 <result> 节点的解析逻辑。
2.2.1.3.1 解析 <id> 和 <result> 节点
在 <resultMap> 节点中,子节点 <id> 和 <result> 都是常规配置,比较常见。相信大家对此也比较熟悉了,我就不多说了。下面我们直接分析这两个节点的解析过程。如下:
java
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception {
String property;
// 根据节点类型获取 name 或 property 属性
if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
property = context.getStringAttribute("name");
} else {
property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
}
// 获取其他各种属性
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
/*
* 解析 resultMap 属性,该属性出现在 <association> 和 <collection> 节点中。
* 若这两个节点不包含 resultMap 属性,则调用 processNestedResultMappings 方法
* 解析嵌套 resultMap。
*/
String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap", processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.<ResultMapping>emptyList()));
String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn");
String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix");
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
String resultSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet");
String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn");
boolean lazy = "lazy".equals(context.getStringAttribute("fetchType", configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager"));
// 解析 javaType、typeHandler 的类型以及枚举类型 JdbcType
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
// 构建 ResultMapping 对象
return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping(resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect,
nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resultSet, foreignColumn, lazy);
}上面的方法主要用于获取 <id> 和 <result> 节点的属性,其中,resultMap 属性的解析过程要相对复杂一些。该属性存在于 <association> 和 <collection> 节点中。下面以 <association> 节点为例,演示该节点的两种配置方式,分别如下:
第一种配置方式是通过 resultMap 属性引用其他的 <resultMap> 节点,配置如下:
XML
<resultMap id="articleResult" type="Article">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="title" column="article_title"/>
<!-- 引用 authorResult -->
<association property="article_author" column="article_author_id" javaType="Author" resultMap="authorResult"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="authorResult" type="Author">
<id property="id" column="author_id"/>
<result property="name" column="author_name"/>
</resultMap>第二种配置方式是采取 resultMap 嵌套的方式进行配置,如下:
XML
<resultMap id="articleResult" type="Article">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="title" column="article_title"/>
<!-- resultMap 嵌套 -->
<association property="article_author" javaType="Author">
<id property="id" column="author_id"/>
<result property="name" column="author_name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>如上配置,<association> 的子节点是一些结果映射配置,这些结果配置最终也会被解析成 ResultMap。我们可以看看解析过程是怎样的,如下:
java
private String processNestedResultMappings(XNode context, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception {
// 判断节点名称
if ("association".equals(context.getName())
|| "collection".equals(context.getName())
|| "case".equals(context.getName())) {
if (context.getStringAttribute("select") == null) {
// resultMapElement 是解析 ResultMap 入口方法
ResultMap resultMap = resultMapElement(context, resultMappings);
// 返回 resultMap id
return resultMap.getId();
}
}
return null;
}如上,<association> 的子节点由 resultMapElement 方法解析成 ResultMap,并在最后返回 resultMap.id。对于 <resultMap> 节点,id 的值配置在该节点的 id 属性中。但 <association> 节点无法配置 id 属性,那么该 id 如何产生的呢?答案在 XNode 类的 getValueBasedIdentifier 方法中,这个方法具体逻辑我就不分析了。下面直接看一下以上配置中的 <association> 节点解析成 ResultMap 后的 id 值,如下:
id = mapper_resultMap[articleResult]_association[article_author]
关于嵌套 resultMap 的解析逻辑就先分析到这,下面分析 ResultMapping 的构建过程。
java
public ResultMapping buildResultMapping(Class<?> resultType, String property, String column, Class<?> javaType,JdbcType jdbcType,
String nestedSelect, String nestedResultMap, String notNullColumn, String columnPrefix,Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandler,
List<ResultFlag> flags, String resultSet, String foreignColumn, boolean lazy) {
/*
* 若 javaType 为空,这里根据 property 的属性进行解析。关于下面方法中的参数,
* 这里说明一下:
* - resultType:即 <resultMap type="xxx"/> 中的 type 属性
* - property:即 <result property="xxx"/> 中的 property 属性
*/
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveResultJavaType(resultType, property, javaType);
// 解析 TypeHandler
TypeHandler<?> typeHandlerInstance = resolveTypeHandler(javaTypeClass, typeHandler);
/*
* 解析 column = {property1=column1, property2=column2} 的情况,
* 这里会将 column 拆分成多个 ResultMapping
*/
List<ResultMapping> composites = parseCompositeColumnName(column);
// 通过建造模式构建 ResultMapping
return new ResultMapping.Builder(configuration, property, column, javaTypeClass)
.jdbcType(jdbcType)
.nestedQueryId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedSelect, true))
.nestedResultMapId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedResultMap, true))
.resultSet(resultSet)
.typeHandler(typeHandlerInstance)
.flags(flags == null ? new ArrayList<ResultFlag>() : flags)
.composites(composites)
.notNullColumns(parseMultipleColumnNames(notNullColumn))
.columnPrefix(columnPrefix)
.foreignColumn(foreignColumn)
.lazy(lazy)
.build();
}
// -☆- ResultMapping.Builder
public ResultMapping build() {
// 将 flags 和 composites 两个集合变为不可修改集合
resultMapping.flags = Collections.unmodifiableList(resultMapping.flags);
resultMapping.composites = Collections.unmodifiableList(resultMapping.composites);
// 从 TypeHandlerRegistry 中获取相应 TypeHandler
resolveTypeHandler();
validate();
return resultMapping;
}ResultMapping 的构建过程不是很复杂,首先是解析 javaType 类型,并创建 typeHandler 实例。然后处理复合 column。最后通过建造器构建 ResultMapping 实例。关于上面方法中出现的一些方法调用,这里接不跟下去分析了,大家可以自己看看。
到此关于 ResultMapping 的解析和构建过程就分析完了,总的来说,还是比较复杂的。不过再难也是人写的,静下心都可以看懂。好了,其他就不多说了,继续往下分析。
2.2.1.3.2 解析 <constructor> 节点
一般情况下,我们所定义的实体类都是简单的 Java 对象,即 POJO。这种对象包含一些私有属性和相应的 getter/setter 方法,通常这种 POJO 可以满足大部分需求。但如果你想使用不可变类存储查询结果,则就需要做一些改动。比如把 POJO 的 setter 方法移除,增加构造方法用于初始化成员变量。对于这种不可变的 Java 类,需要通过带有参数的构造方法进行初始化(反射也可以达到同样目的)。下面举个例子说明一下:
java
public class ArticleDO {
// ...
public ArticleDO(Integer id, String title, String content) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
// ...
}如上,ArticleDO 的构造方法对应的配置如下:
XML
<constructor>
<idArg column="id" name="id"/>
<arg column="title" name="title"/>
<arg column="content" name="content"/>
</constructor>下面,分析 constructor 节点的解析过程。如下:
java
private void processConstructorElement(XNode resultChild, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception {
// 获取子节点列表
List<XNode> argChildren = resultChild.getChildren();
for (XNode argChild : argChildren) {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<ResultFlag>();
// 向 flags 中添加 CONSTRUCTOR 标志
flags.add(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR);
if ("idArg".equals(argChild.getName())) {
// 向 flags 中添加 ID 标志
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
// 构建 ResultMapping,上一节已经分析过
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(argChild, resultType, flags));
}
}如上,上面方法的逻辑并不复杂。首先是获取并遍历子节点列表,然后为每个子节点创建 flags 集合,并添加 CONSTRUCTOR 标志。对于 idArg 节点,额外添加 ID 标志。最后一步则是构建 ResultMapping,该步逻辑前面已经分析过,这里就不多说了。
分析完 <resultMap> 的子节点 <id>,<result> 以及 <constructor> 的解析过程,下面来看看 ResultMap 实例的构建过程。
2.2.1.3.3 ResultMap 对象构建过程分析
前面用了不少的篇幅来分析 <resultMap> 子节点的解析过程。通过前面的分析,我们可知 <id>,<result> 等节点最终都被解析成了 ResultMapping。在得到这些 ResultMapping 后,紧接着要做的事情是构建 ResultMap。如果说 ResultMapping 与单条结果映射相对应,那 ResultMap 与什么对应呢?答案是...。答案暂时还不能说,我们到源码中去找寻吧。下面,让我们带着这个疑问开始本节的源码分析。
前面分析了很多源码,大家可能都忘了 ResultMap 构建的入口了。这里再贴一下,如下:
java
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
// 获取 resultMap 节点中的属性
// ...
// 解析 resultMap 对应的类型
// ...
// 遍历 resultMap 节点的子节点,构建 ResultMapping 对象
// ...
// 创建 ResultMap 解析器
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend,
discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
// 根据前面获取到的信息构建 ResultMap 对象
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}如上,ResultMap 的构建逻辑分装在 ResultMapResolver 的 resolve 方法中,下面我从该方法进行分析。
java
// -☆- ResultMapResolver
public ResultMap resolve() {
return assistant.addResultMap(this.id, this.type, this.extend, this.discriminator, this.resultMappings, this.autoMapping);
}上面的方法将构建 ResultMap 实例的任务委托给了 MapperBuilderAssistant 的 addResultMap,我们跟进到这个方法中看看。
java
// -☆- MapperBuilderAssistant
public ResultMap addResultMap(
String id, Class<?> type, String extend, Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings, Boolean autoMapping) {
// 为 ResultMap 的 id 和 extend 属性值拼接命名空间
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
if (extend != null) {
if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find a parent resultmap with id '" + extend + "'");
}
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend);
List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>(resultMap.getResultMappings());
// 为拓展 ResultMappings 取出重复项
extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings);
boolean declaresConstructor = false;
// 检测当前 resultMappings 集合中是否包含 CONSTRUCTOR 标志的元素
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) {
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
declaresConstructor = true;
break;
}
}
/*
* 如果当前 <resultMap> 节点中包含 <constructor> 子节点,
* 则将拓展 ResultMapping 集合中的包含 CONSTRUCTOR 标志的元素移除
*/
if (declaresConstructor) {
Iterator<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappingsIter = extendedResultMappings.iterator();
while (extendedResultMappingsIter.hasNext()) {
if (extendedResultMappingsIter.next().getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
extendedResultMappingsIter.remove();
}
}
}
// 将扩展 resultMappings 集合合并到当前 resultMappings 集合中
resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings);
}
// 构建 ResultMap
ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping)
.discriminator(discriminator)
.build();
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
}上面的方法主要用于处理 resultMap 节点的 extend 属性,extend 不为空的话,这里将当前 resultMappings 集合和扩展 resultMappings 集合合二为一。随后,通过建造模式构建 ResultMap 实例。过程如下:
java
// -☆- ResultMap
public ResultMap build() {
if (resultMap.id == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ResultMaps must have an id");
}
resultMap.mappedColumns = new HashSet<String>();
resultMap.mappedProperties = new HashSet<String>();
resultMap.idResultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>();
resultMap.constructorResultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>();
resultMap.propertyResultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>();
final List<String> constructorArgNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMap.resultMappings) {
/*
* 检测 <association> 或 <collection> 节点
* 是否包含 select 和 resultMap 属性
*/
resultMap.hasNestedQueries = resultMap.hasNestedQueries || resultMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null;
resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps =
resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps || (resultMapping.getNestedResultMapId() != null && resultMapping.getResultSet() == null);
final String column = resultMapping.getColumn();
if (column != null) {
// 将 colum 转换成大写,并添加到 mappedColumns 集合中
resultMap.mappedColumns.add(column.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
} else if (resultMapping.isCompositeResult()) {
for (ResultMapping compositeResultMapping : resultMapping.getComposites()) {
final String compositeColumn = compositeResultMapping.getColumn();
if (compositeColumn != null) {
resultMap.mappedColumns.add(compositeColumn.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
}
}
}
// 添加属性 property 到 mappedProperties 集合中
final String property = resultMapping.getProperty();
if (property != null) {
resultMap.mappedProperties.add(property);
}
// 检测当前 resultMapping 是否包含 CONSTRUCTOR 标志
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
// 添加 resultMapping 到 constructorResultMappings 中
resultMap.constructorResultMappings.add(resultMapping);
// 添加属性(constructor 节点的 name 属性)到 constructorArgNames 中
if (resultMapping.getProperty() != null) {
constructorArgNames.add(resultMapping.getProperty());
}
} else {
// 添加 resultMapping 到 propertyResultMappings 中
resultMap.propertyResultMappings.add(resultMapping);
}
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.ID)) {
// 添加 resultMapping 到 idResultMappings 中
resultMap.idResultMappings.add(resultMapping);
}
}
if (resultMap.idResultMappings.isEmpty()) {
resultMap.idResultMappings.addAll(resultMap.resultMappings);
}
if (!constructorArgNames.isEmpty()) {
// 获取构造方法参数列表,篇幅原因,这个方法不分析了
final List<String> actualArgNames = argNamesOfMatchingConstructor(constructorArgNames);
if (actualArgNames == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Error in result map '" + resultMap.id
+ "'. Failed to find a constructor in '"
+ resultMap.getType().getName() + "' by arg names " + constructorArgNames
+ ". There might be more info in debug log.");
}
// 对 constructorResultMappings 按照构造方法参数列表的顺序进行排序
Collections.sort(resultMap.constructorResultMappings, new Comparator<ResultMapping>() {
public int compare(ResultMapping o1, ResultMapping o2) {
int paramIdx1 = actualArgNames.indexOf(o1.getProperty());
int paramIdx2 = actualArgNames.indexOf(o2.getProperty());
return paramIdx1 - paramIdx2;
}
});
}
// 将以下这些集合变为不可修改集合
resultMap.resultMappings = Collections.unmodifiableList(resultMap.resultMappings);
resultMap.idResultMappings = Collections.unmodifiableList(resultMap.idResultMappings);
resultMap.constructorResultMappings = Collections.unmodifiableList(resultMap.constructorResultMappings);
resultMap.propertyResultMappings = Collections.unmodifiableList(resultMap.propertyResultMappings);
resultMap.mappedColumns = Collections.unmodifiableSet(resultMap.mappedColumns);
return resultMap;
}以上代码看起来很复杂,实际上这是假象。以上代码主要做的事情就是将 ResultMapping 实例及属性分别存储到不同的集合中,仅此而已。ResultMap 中定义了五种不同的集合,下面分别介绍一下这几种集合。
|---------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 集合名称 | 用途 |
| mappedColumns | 用于存储 <id>、<result>、<idArg>、<arg> 节点 column 属性 |
| mappedProperties | 用于存储 <id> 和 <result> 节点的 property 属性,或 <idArgs> 和 <arg> 节点的 name 属性 |
| idResultMappings | 用于存储 <id> 和 <idArg> 节点对应的 ResultMapping 对象 |
| propertyResultMappings | 用于存储 <id> 和 <result> 节点对应的 ResultMapping 对象 |
| constructorResultMappings | 用于存储 <idArgs> 和 <arg> 节点对应的 ResultMapping 对象 |
上面干巴巴的描述不够直观。下面我们写点代码测试一下,并把这些集合的内容打印到控制台上,大家直观感受一下。先定义一个映射文件,如下:
XML
<mapper namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.ArticleDao">
<resultMap id="articleResult" type="xyz.coolblog.model.Article">
<constructor>
<idArg column="id" name="id"/>
<arg column="title" name="title"/>
<arg column="content" name="content"/>
</constructor>
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="author" column="author"/>
<result property="createTime" column="create_time"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>测试代码如下:
java
public class ResultMapTest {
public void printResultMapInfo() throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
String resource = "mapper/ArticleMapper.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder builder = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
builder.parse();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap("articleResult");
System.out.println("\n-------------------+✨ mappedColumns ✨+--------------------");
System.out.println(resultMap.getMappedColumns());
System.out.println("\n------------------+✨ mappedProperties ✨+------------------");
System.out.println(resultMap.getMappedProperties());
System.out.println("\n------------------+✨ idResultMappings ✨+------------------");
resultMap.getIdResultMappings().forEach(rm -> System.out.println(simplify(rm)));
System.out.println("\n---------------+✨ propertyResultMappings ✨+---------------");
resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings().forEach(rm -> System.out.println(simplify(rm)));
System.out.println("\n-------------+✨ constructorResultMappings ✨+--------------");
resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings().forEach(rm -> System.out.println(simplify(rm)));
System.out.println("\n-------------------+✨ resultMappings ✨+-------------------");
resultMap.getResultMappings().forEach(rm -> System.out.println(simplify(rm)));
inputStream.close();
}
/** 简化 ResultMapping 输出结果 */
private String simplify(ResultMapping resultMapping) {
return String.format("ResultMapping{column='%s', property='%s', flags=%s, ...}",
resultMapping.getColumn(), resultMapping.getProperty(), resultMapping.getFlags());
}
}这里,我们把5个集合转给你的内容都打印出来,结果如下:
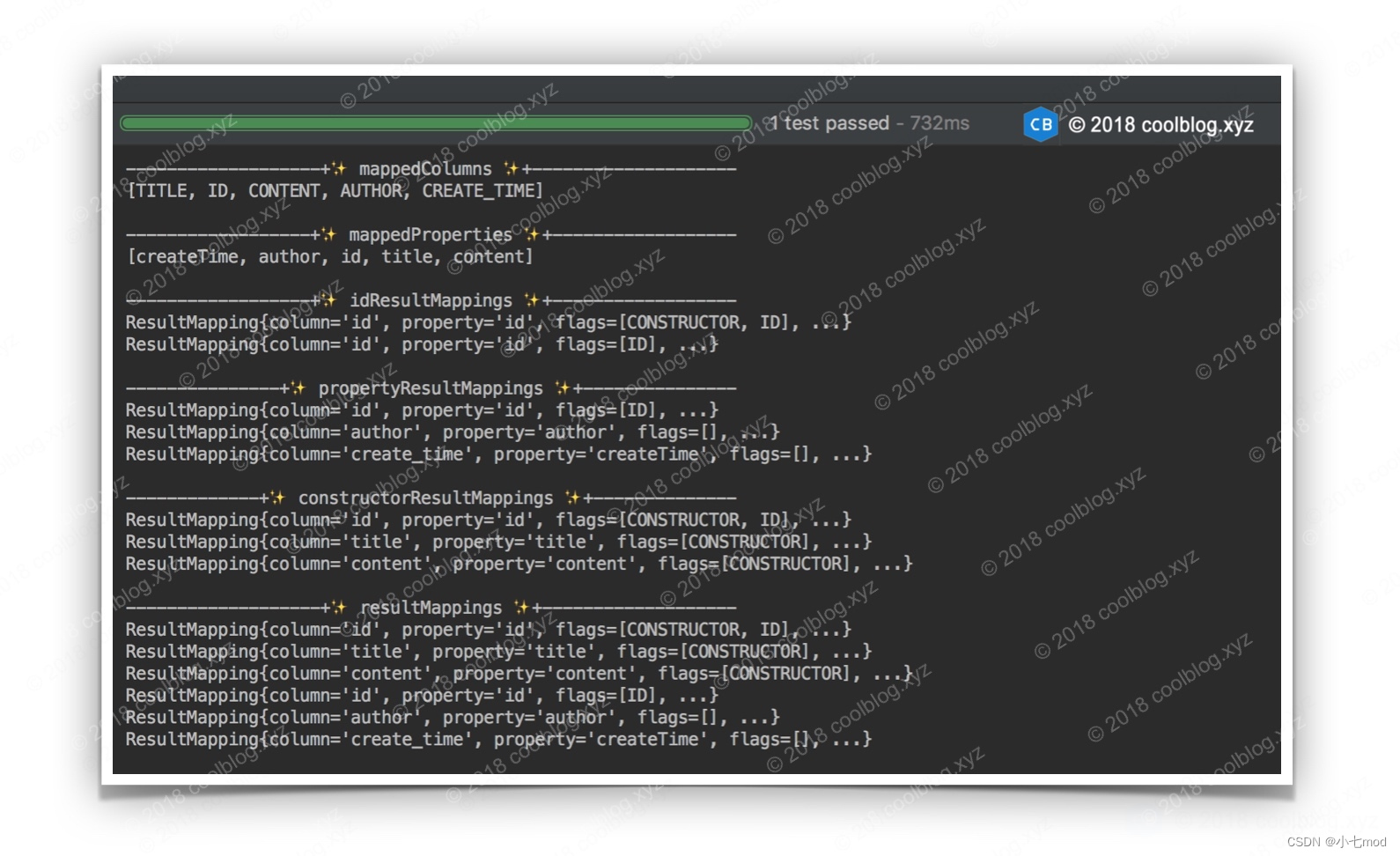
如上,结果比较清晰明了,不需要过多解释了。我们参照上面配置文件及输出的结果,把 ResultMap 的大致轮廓画出来。如下:

到这里,<resultMap> 节点的解析过程就分析完了。总的来说,该节点的解析过程还是比较复杂的。好了,其他的就不多说了,继续后面的分析。
2.2.1.4 解析 <sql> 节点
<sql> 节点用来定义一些可重用的 SQL 语句片段,比如表名,或表的列名等。在映射文件中,我们可以通过 <include> 节点引用 <sql> 节点定义的内容。下面我来演示一下 <sql> 节点的使用方式,如下:
XML
<sql id="table">
article
</sql>
<select id="findOne" resultType="Article">
SELECT id, title FROM <include refid="table"/> WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<update id="update" parameterType="Article">
UPDATE <include refid="table"/> SET title = #{title} WHERE id = #{id}
</update>如上,上面配置中,<select> 和 <update> 节点通过 <include> 引入定义在 <sql> 节点中的表名。上面的配置比较常规,除了静态文本,<sql> 节点还支持属性占位符 ${}。比如:
XML
<sql id="table">
${table_prefix}_article
</sql>如果属性 table_prefix = blog,那么 <sql> 节点中的内容最终为 blog_article。
上面介绍了 <sql> 节点的用法,比较容易。下面分析一下 sql 节点的解析过程,如下:
java
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list) throws Exception {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
// 调用 sqlElement 解析 <sql> 节点
sqlElement(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
// 再次调用 sqlElement,不同的是,这次调用,该方法的第二个参数为 null
sqlElement(list, null);
}这个方法需要大家注意一下,如果 Configuration 的 databaseId 不为空,sqlElement 方法会被调用了两次。第一次传入具体的 databaseId,用于解析带有 databaseId 属性,且属性值与此相等的 <sql> 节点。第二次传入的 databaseId 为空,用于解析未配置 databaseId 属性的 <sql> 节点。这里是个小细节,大家注意一下就好。我们继续往下分析。
java
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) throws Exception {
for (XNode context : list) {
// 获取 id 和 databaseId 属性
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// id = currentNamespace + "." + id
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
// 检测当前 databaseId 和 requiredDatabaseId 是否一致
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) {
// 将 <id, XNode> 键值对缓存到 sqlFragments 中
sqlFragments.put(id, context);
}
}
}这个方法逻辑比较简单,首先是获取 <sql> 节点的 id 和 databaseId 属性,然后为 id 属性值拼接命名空间。最后,通过检测当前 databaseId 和 requiredDatabaseId 是否一致,来决定保存还是忽略当前的 <sql> 节点。下面,我们来看一下 databaseId 的匹配逻辑是怎样的。
java
private boolean databaseIdMatchesCurrent(String id, String databaseId, String requiredDatabaseId) {
if (requiredDatabaseId != null) {
// 当前 databaseId 和目标 databaseId 不一致时,返回 false
if (!requiredDatabaseId.equals(databaseId)) {
return false;
}
} else {
// 如果目标 databaseId 为空,但当前 databaseId 不为空。两者不一致,返回 false
if (databaseId != null) {
return false;
}
/*
* 如果当前 <sql> 节点的 id 与之前的 <sql> 节点重复,且先前节点
* databaseId 不为空。则忽略当前节点,并返回 false
*/
if (this.sqlFragments.containsKey(id)) {
XNode context = this.sqlFragments.get(id);
if (context.getStringAttribute("databaseId") != null) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}下面总结一下 databaseId 的匹配规则。
- databaseId 与 requiredDatabaseId 不一致,即失配,返回 false
- 当前节点与之前的节点出现 id 重复的情况,若之前的 <sql> 节点 databaseId 属性不为空,返回 false
- 若以上两条规则均匹配失败,此时返回 true
在上面三条匹配规则中,第二条规则稍微难理解一点。这里简单分析一下,考虑下面这种配置。
XML
<!-- databaseId 不为空 -->
<sql id="table" databaseId="mysql">
article
</sql>
<!-- databaseId 为空 -->
<sql id="table">
article
</sql>在上面配置中,两个 <sql> 节点的 id 属性值相同,databaseId 属性不一致。假设 configuration.databaseId = mysql,第一次调用 sqlElement 方法,第一个 <sql> 节点对应的 XNode 会被放入到 sqlFragments 中。第二次调用 sqlElement 方法时,requiredDatabaseId 参数为空。由于 sqlFragments 中已包含了一个 id 节点,且该节点的 databaseId 不为空,此时匹配逻辑返回 false,第二个节点不会被保存到 sqlFragments。
上面的分析内容涉及到了 databaseId,关于 databaseId 的用途,这里简单介绍一下。databaseId 用于标明数据库厂商的身份,不同厂商有自己的 SQL 方言,MyBatis 可以根据 databaseId 执行不同 SQL 语句。databaseId 在 <sql> 节点中有什么用呢?这个问题也不难回答。<sql> 节点用于保存 SQL 语句片段,如果 SQL 语句片段中包含方言的话,那么该 <sql> 节点只能被同一 databaseId 的查询语句或更新语句引用。关于 databaseId,这里就介绍这么多。
好了,本节内容先到这里。继续往下分析。
2.2.1.5 解析 SQL 语句节点
前面分析了 <cache>、<cache-ref>、<resultMap> 以及 <sql> 节点,从这一节开始,我们要分析映射文件中剩余的几个节点,分别是 <select>、<insert>、<update> 以及 <delete> 等。这几个节点中存储的是相同的内容,都是 SQL 语句,所以这几个节点的解析过程也是相同的。在进行代码分析之前,这里需要特别说明一下:为了避免和 <sql> 节点混淆,同时也为了描述方便,这里把 <select>、<insert>、<update> 以及 <delete> 等节点统称为 SQL 语句节点。
对于select、delete、insert、update等标签的解析是通过buildStatementFromContext中创建XMLStatementBuilder来完成解析的。下面我们就来分析一下它的解析过程。
java
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
// 调用重载方法构建 Statement
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
// 调用重载方法构建 Statement,requiredDatabaseId 参数为空
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
// 循环select | delte | insert | update节点
for (XNode context : list) {
// 创建 Statement 建造类
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
/*
* 解析 Statement 节点,并将解析结果存储到
* configuration 的 mappedStatements 集合中
*/
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 解析失败,将解析器放入 configuration 的 incompleteStatements 集合中
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}上面的解析方法没有什么实质性的解析逻辑,我们继续往下分析。
java
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 获取 id 和 databaseId 属性
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
// 根据 databaseId 进行检测,检测逻辑和上一节基本一致,这里不再赘述
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
// 获取各种属性
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// 通过别名解析 resultType 对应的类型
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
// 解析 Statement 类型,默认为 PREPARED
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
// 解析 ResultSetType
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
// 获取节点的名称,比如 <select> 节点名称为 select
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 根据节点名称解析 SqlCommandType
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// 解析 <include> 节点
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// 解析 <selectKey> 节点
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// 解析 SQL 语句
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
// 获取 KeyGenerator 实例
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
// 创建 KeyGenerator 实例
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType)) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
/*
* 构建 MappedStatement 对象,并将该对象存储到
* Configuration 的 mappedStatements 集合中
*/
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}上面的代码比较长,看起来有点复杂。不过如果大家耐心看一下源码,会发现,上面的代码中起码有一半的代码都是用来获取节点属性,以及解析部分属性等。抛去这部分代码,以上代码做的事情如下。
- 解析 <include> 节点
- 解析 <selectKey> 节点
- 解析 SQL,获取 SqlSource
- 构建 MappedStatement 实例
以上流程对应的代码比较复杂,每个步骤都能分析出一些东西来。下面我会每个步骤都进行分析,首先来分析 <include> 节点的解析过程。
2.2.1.5.1 解析 <include> 节点
<include> 节点的解析逻辑封装在 applyIncludes 中,该方法的代码如下:
java
public void applyIncludes(Node source) {
Properties variablesContext = new Properties();
Properties configurationVariables = configuration.getVariables();
if (configurationVariables != null) {
// 将 configurationVariables 中的数据添加到 variablesContext 中
variablesContext.putAll(configurationVariables);
}
// 调用重载方法处理 <include> 节点
applyIncludes(source, variablesContext, false);
}上面代码创建了一个新的 Properties 对象,并将全局 Properties 添加到其中。这样做的原因是 applyIncludes 的重载方法会向 Properties 中添加新的元素,如果直接将全局 Properties 传给重载方法,会造成全局 Properties 被污染。这是个小细节,一般容易被忽视掉。其他没什么需要注意的了,我们继续往下看。
java
private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) {
// ⭐️ 第一个条件分支
if (source.getNodeName().equals("include")) {
/*
* 获取 <sql> 节点。若 refid 中包含属性占位符 ${},
* 则需先将属性占位符替换为对应的属性值
*/
Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(getStringAttribute(source, "refid"), variablesContext);
/*
* 解析 <include> 的子节点 <property>,并将解析结果与 variablesContext 融合,
* 然后返回融合后的 Properties。若 <property> 节点的 value 属性中存在占位符 ${},
* 则将占位符替换为对应的属性值
*/
Properties toIncludeContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext);
/*
* 这里是一个递归调用,用于将 <sql> 节点内容中出现的属性占位符 ${} 替换为对应的
* 属性值。这里要注意一下递归调用的参数:
*
* - toInclude:<sql> 节点对象
* - toIncludeContext:<include> 子节点 <property> 的解析结果与
* 全局变量融合后的结果
*/
applyIncludes(toInclude, toIncludeContext, true);
/*
* 如果 <sql> 和 <include> 节点不在一个文档中,
* 则从其他文档中将 <sql> 节点引入到 <include> 所在文档中
*/
if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) {
toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true);
}
// 将 <include> 节点替换为 <sql> 节点
source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source);
while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) {
// 将 <sql> 中的内容插入到 <sql> 节点之前
toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude);
}
/*
* 前面已经将 <sql> 节点的内容插入到 dom 中了,
* 现在不需要 <sql> 节点了,这里将该节点从 dom 中移除
*/
toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude);
// ⭐️ 第二个条件分支
} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
if (included && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
NamedNodeMap attributes = source.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attr = attributes.item(i);
// 将 source 节点属性中的占位符 ${} 替换成具体的属性值
attr.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(attr.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
NodeList children = source.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
// 递归调用
applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included);
}
// ⭐️ 第三个条件分支
} else if (included && source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// 将文本(text)节点中的属性占位符 ${} 替换成具体的属性值
source.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}上面的代码如果从上往下读,不太容易看懂。因为上面的方法由三个条件分支,外加两个递归调用组成,代码的执行顺序并不是由上而下。要理解上面的代码,我们需要定义一些配置,并将配置带入到具体代码中,逐行进行演绎。不过,更推荐的方式是使用 IDE 进行单步调试。为了便于讲解,我把上面代码中的三个分支都用 ⭐️ 标记了出来,这个大家注意一下。好了,必要的准备工作做好了,下面开始演绎代码的执行过程。演绎所用的测试配置如下:
XML
<mapper namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.ArticleDao">
<sql id="table">
${table_name}
</sql>
<select id="findOne" resultType="xyz.coolblog.dao.ArticleDO">
SELECT
id, title
FROM
<include refid="table">
<property name="table_name" value="article"/>
</include>
WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>我们先来看一下 applyIncludes 方法第一次被调用时的状态,如下:
参数值:
source = <select> 节点
节点类型:ELEMENT_NODE
variablesContext = [ ] // 无内容
included = false
执行流程:
1.进入条件分支2
2.获取 <select> 子节点列表
3.遍历子节点列表,将子节点作为参数,进行递归调用
第一次调用 applyIncludes 方法,source = <select>,代码进入条件分支2。在该分支中,首先要获取 <select> 节点的子节点列表。可获取到的子节点如下:
|--------|----------------------------|--------------|--------|
| 编号 | 子节点 | 类型 | 描述 |
| 1 | SELECT id, title FROM | TEXT_NODE | 文本节点 |
| 2 | <include refid="table"/> | ELEMENT_NODE | 普通节点 |
| 3 | WHERE id = #{id} | TEXT_NODE | 文本节点 |
在获取到子节点类列表后,接下来要做的事情是遍历列表,然后将子节点作为参数进行递归调用。在上面三个子节点中,子节点1和子节点3都是文本节点,调用过程一致。因此,下面我只会演示子节点1和子节点2的递归调用过程。先来演示子节点1的调用过程,如下:

节点1的调用过程比较简单,只有两层调用。然后我们在看一下子节点2的调用过程,如下:

上面是子节点2的调用过程,共有四层调用,略为复杂。大家自己也对着配置,把源码走一遍,然后记录每一次调用的一些状态,这样才能更好的理解 applyIncludes 方法的逻辑。
好了,本节内容先到这里,继续往下分析。
2.2.1.5.2 解析 <selectKey> 节点
对于一些不支持自增主键的数据库来说,我们在插入数据时,需要明确指定主键数据。以 Oracle 数据库为例,Oracle 数据库不支持自增主键,但它提供了自增序列工具。我们每次向数据库中插入数据时,可以先通过自增序列获取主键数据,然后再进行插入。这里涉及到两次数据库查询操作,我们不能在一个 <select> 节点中同时定义两个 select 语句,否者会导致 SQL 语句出错。对于这个问题,MyBatis 的 <selectKey> 可以很好的解决。下面我们看一段配置:
XML
<insert id="saveAuthor">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="BEFORE">
select author_seq.nextval from dual
</selectKey>
insert into Author
(id, name, password)
values
(#{id}, #{username}, #{password})
</insert>在上面的配置中,查询语句会先于插入语句执行,这样我们就可以在插入时获取到主键的值。关于 <selectKey> 的用法,这里不过多介绍了。下面我们来看一下 <selectKey> 节点的解析过程。
java
private void processSelectKeyNodes(String id, Class<?> parameterTypeClass, LanguageDriver langDriver) {
List<XNode> selectKeyNodes = context.evalNodes("selectKey");
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
// 解析 <selectKey> 节点,databaseId 不为空
parseSelectKeyNodes(id, selectKeyNodes, parameterTypeClass, langDriver, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
// 解析 <selectKey> 节点,databaseId 为空
parseSelectKeyNodes(id, selectKeyNodes, parameterTypeClass, langDriver, null);
// 将 <selectKey> 节点从 dom 树中移除
removeSelectKeyNodes(selectKeyNodes);
}从上面的代码中可以看出,<selectKey> 节点在解析完成后,会被从 dom 树中移除。这样后续可以更专注的解析 <insert> 或 <update> 节点中的 SQL,无需再额外处理 <selectKey> 节点。继续往下看。
java
private void parseSelectKeyNodes(String parentId, List<XNode> list, Class<?> parameterTypeClass,
LanguageDriver langDriver, String skRequiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode nodeToHandle : list) {
// id = parentId + !selectKey,比如 saveUser!selectKey
String id = parentId + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
// 获取 <selectKey> 节点的 databaseId 属性
String databaseId = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
// 匹配 databaseId
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, skRequiredDatabaseId)) {
// 解析 <selectKey> 节点
parseSelectKeyNode(id, nodeToHandle, parameterTypeClass, langDriver, databaseId);
}
}
}
private void parseSelectKeyNode(String id, XNode nodeToHandle, Class<?> parameterTypeClass,
LanguageDriver langDriver, String databaseId) {
// 获取各种属性
String resultType = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
String keyProperty = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
boolean executeBefore = "BEFORE".equals(nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("order", "AFTER"));
// 设置默认值
boolean useCache = false;
boolean resultOrdered = false;
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
boolean flushCache = false;
String parameterMap = null;
String resultMap = null;
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = null;
// 创建 SqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, nodeToHandle, parameterTypeClass);
/*
* <selectKey> 节点中只能配置 SELECT 查询语句,
* 因此 sqlCommandType 为 SqlCommandType.SELECT
*/
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.SELECT;
/*
* 构建 MappedStatement,并将 MappedStatement
* 添加到 Configuration 的 mappedStatements map 中
*/
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, null);
// id = namespace + "." + id
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
MappedStatement keyStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(id, false);
// 创建 SelectKeyGenerator,并添加到 keyGenerators map 中
configuration.addKeyGenerator(id, new SelectKeyGenerator(keyStatement, executeBefore));
}上面的源码比较长,但大部分代码都是一些基础代码,不是很难理解。以上代码比较重要的步骤如下:
- 创建 SqlSource 实例
- 构建并缓存 MappedStatement 实例
- 构建并缓存 SelectKeyGenerator 实例
在这三步中,第1步和第2步调用的是公共逻辑,其他地方也会调用,这两步对应的源码后续会分两节进行讲解。第3步则是创建一个 SelectKeyGenerator 实例,SelectKeyGenerator 创建的过程本身没什么好说的,所以就不多说了。下面分析一下 SqlSource 和 MappedStatement 实例的创建过程。
2.2.1.5.3 解析 SQL 语句
前面分析了 <include> 和 <selectKey> 节点的解析过程,这两个节点解析完成后,都会以不同的方式从 dom 树中消失。所以目前的 SQL 语句节点由一些文本节点和普通节点组成,比如 <if>、<where> 等。那下面我们来看一下移除掉 <include> 和 <selectKey> 节点后的 SQL 语句节点是如何解析的。
java
// -☆- XMLLanguageDriver
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
// -☆- XMLScriptBuilder
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 解析 SQL 语句节点
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource = null;
// 根据 isDynamic 状态创建不同的 SqlSource
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}如上,SQL 语句的解析逻辑被封装在了 XMLScriptBuilder 类的 parseScriptNode 方法中。首先会调用 parseDynamicTags方法 解析 SQL 语句节点,通过这个方法获取当前节点的所有子节点列表,判断子节点类型是否是动态标签节点:
- 如果这个节点就是个动态标签节点(<if>、<foreach>等),就说明这个一定是动态SQL,那么我们就获取对应处理的handler,handler列表是在XMLScriptBuilder****构造函数中调用initNodeHandlerMap就已初始化完成,对于各种动态标签因为可以嵌套,所以handleNode内部也是递归处理的,然后将isDynamic 设为 true。
- 若不是动态标签节点,再去判断文本中是否包含${}动态标识,若包含这些标识则说明这个也是动态SQL,将isDynamic 设为 true,如果不包含就是说明这是一个静态SQL,则直接获取节点中的SQL文本。
后续会根据isDynamic 创建不同的 SqlSource,将动态SQL文本封装到TextSqlNode中添加到结果列表中,将静态封装为StaticTextSqlNode添加到结果列表中。
总的来说,对于select、delete、insert、update等标签内容具体解析是通过LanguageDriver#createSqlSource中创建XMLScriptBuilder来完成的,最终将解析出的sqlNode根据是否是动态****SQL将其封装成DynamicSqlSource或RawSqlSource。判断是否是动态****SQL是根据SQL中是否包含**${}以及是否包含动态标签**。MyBatis解析动态SQL原理分析
下面,我们来看一下 parseDynamicTags 方法的逻辑。
java
/** 该方法用于初始化 nodeHandlerMap 集合,该集合后面会用到 */
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());
}
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<SqlNode>();
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
// 遍历子节点
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
// 获取文本内容
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// 若文本中包含 ${} 占位符,也被认为是动态节点
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
// 设置 isDynamic 为 true
isDynamic = true;
} else {
// 创建 StaticTextSqlNode
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
// child 节点是 ELEMENT_NODE 类型,比如 <if>、<where> 等
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
// 获取节点名称,比如 if、where、trim 等
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 根据节点名称获取 NodeHandler
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
/*
* 如果 handler 为空,表明当前节点对与 MyBatis 来说,是未知节点。
* MyBatis 无法处理这种节点,故抛出异常
*/
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
// 处理 child 节点,生成相应的 SqlNode
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
// 设置 isDynamic 为 true
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}上面方法的逻辑我前面已经说过,主要是用来判断节点是否包含一些动态标记,比如 ${} 占位符以及动态 SQL 节点(<if>、<foreach>等)。这里,不管是动态 SQL 节点还是静态 SQL 节点,我们都可以把它们看成是 SQL 片段,一个 SQL 语句由多个 SQL 片段组成。在解析过程中,这些 SQL 片段被存储在 contents 集合中。最后,该集合会被传给 MixedSqlNode 构造方法,用于创建 MixedSqlNode 实例。从 MixedSqlNode 类名上可知,它会存储多种类型的 SqlNode。除了上面代码中已出现的几种 SqlNode 实现类,还有一些 SqlNode 实现类未出现在上面的代码中。但它们也参与了 SQL 语句节点的解析过程,这里我们来看一下这些幕后的 SqlNode 类。
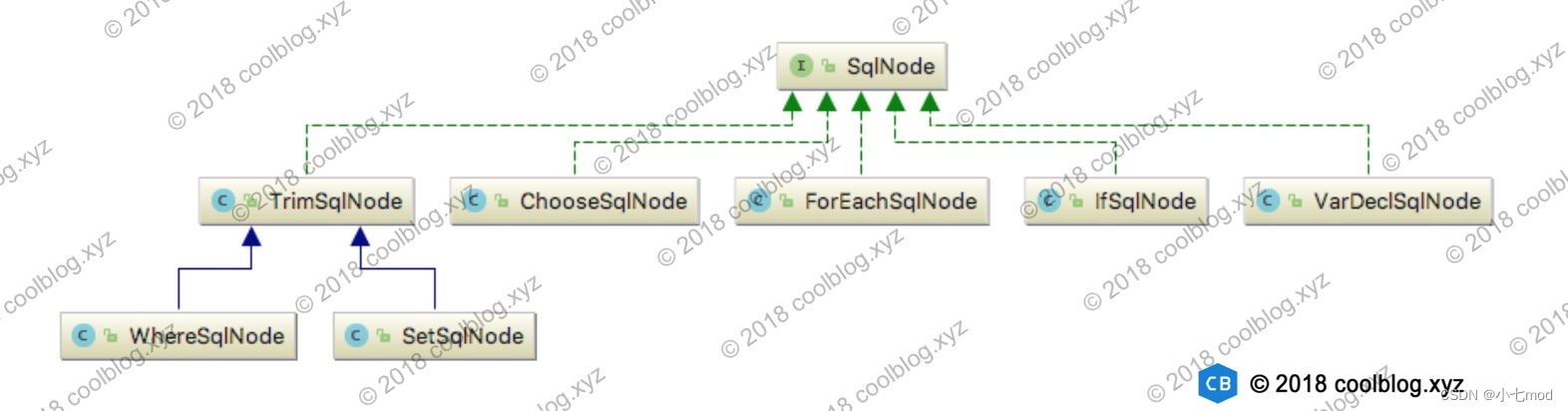
上面的 SqlNode 实现类用于处理不同的动态 SQL 逻辑,这些 SqlNode 是如何生成的呢?答案是由各种 NodeHandler 生成。我们再回到上面的代码中,可以看到这样一句代码:
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
该代码用于处理动态 SQL 节点,并生成相应的 SqlNode。下面来简单分析一下 WhereHandler 的代码。
java
/** 定义在 XMLScriptBuilder 中 */
private class WhereHandler implements NodeHandler {
public WhereHandler() {
}
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
// 调用 parseDynamicTags 解析 <where> 节点
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
// 创建 WhereSqlNode
WhereSqlNode where = new WhereSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode);
// 添加到 targetContents
targetContents.add(where);
}
}如上,handleNode 方法内部会再次调用 parseDynamicTags 解析 <where> 节点中的内容,这样又会生成一个 MixedSqlNode 对象。最终,整个 SQL 语句节点会生成一个具有树状结构的 MixedSqlNode。如下图:

到此,SQL 语句的解析过程就分析完了。现在,我们已经将 XML 中的SQL语句信息解析到了 SqlSource中,每一个SQL语句都对应一个SqlSource,但这还没有结束。SqlSource 中只能记录 SQL 语句信息,除此之外,这里还有一些额外的信息需要记录。因此,我们需要一个类能够同时存储 SqlSource 和其他的信息。这个类就是 MappedStatement。下面我们来看一下它的构建过程。
2.2.1.5.4 构建 MappedStatement
SQL 语句节点可以定义很多属性,这些属性和属性值最终存储在 MappedStatement 中。每一个SQL语句标签对应了一个MappedStatement 对象(例如一个select标签的语句就对应一个MappedStatement对象)。
下面我们看一下 MappedStatement 的构建过程是怎样的。
java
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id, SqlSource sqlSource, StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,Integer fetchSize, Integer timeout,
String parameterMap, Class<?> parameterType,String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType, ResultSetType resultSetType, boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache, boolean resultOrdered, KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,String keyColumn, String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang, String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 创建建造器,设置各种属性
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource).fetchSize(fetchSize).timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType).keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty).keyColumn(keyColumn).databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang).resultOrdered(resultOrdered).resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.resultSetType(resultSetType).useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
// 获取或创建 ParameterMap
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
// 构建 MappedStatement,没有什么复杂逻辑,不跟下去了
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
// 添加 MappedStatement 到 configuration 的 mappedStatements 集合中
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}上面就是 MappedStatement,没什么复杂的地方,就不多说了。
将每个增删改查SQL解析完成后都封装成一个MappedStatement并添加到Configuration#mappedStatements属性中(最终还是将解析出来的SQL映射信息存到了Configuration对象中,这个对象后面就会用于创建SqlSessionFactory对象),依次遍历解析完所有的XML文件中的SQL,到此XML解析完成。
解析完XML后就该解析Mapper接口中的注解了,首先解析**@CacheNamespace**、@CacheNamespaceRef注解。然后解析方法上的SQL注解。在parseStatement中通过getSqlSourceFromAnnotations然后通过LanguageDriver去将注解上的SQL解析成SQLNode列表封装成DynamicSqlSource或RawSqlSource。
对于**@SelectProvider**、@InsertProvider、@UpdateProvider、@DeleteProvider注解的方法解析最终会封装成一个ProviderSqlSource。
2.2.1.6 小节
本章分析了映射文件的解析过程,总的来说,本章的内容还是比较复杂的,逻辑太多。不过如果大家自己也能把映射文件的解析过程认真分析一遍,会对 MyBatis 有更深入的理解。分析过程很累,但是在此过程中会收获了很多东西,还是很开心的。好了,本章内容先到这里。后面还有一些代码需要分析,我们继续往后看。
2.2.2 Mapper 接口绑定过程分析
映射文件解析完成后,并不意味着整个解析过程就结束了。此时还需要通过命名空间将解析出来的映射文件绑定上对应的 mapper 接口,这样才能将映射文件中的 SQL 语句和 mapper 接口中的方法绑定在一起,后续即可通过调用 mapper 接口方法执行与之对应的 SQL 语句。下面我们来分析一下 mapper 接口的绑定过程。
java
// -☆- XMLMapperBuilder
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
// 获取映射文件的命名空间
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// 根据命名空间找到对应的mapper接口,去解析出 mapper接口 的类型
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (boundType != null) {
// 检测当前 mapper接口 类是否被绑定过
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// 绑定 mapper接口 类
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
// -☆- Configuration
// 传入的Mapper接口类型的Class对象,其实这个流程在前面将解析映射器接口那一节中的内容差不多
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 通过 MapperRegistry 绑定 mapper接口 类
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
// -☆- MapperRegistry
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 判断传入进来的type类型是不是接口
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 判断的缓存中有没有该类型
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
/*
* 将 type(原目标接口类型) 和 MapperProxyFactory(该接口类的代理类工厂) 进行绑定,将映射信息添加到了knownMappers中
* MapperProxyFactory 为 mapper 接口生成代理类
*/
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// 创建注解解析器。在 MyBatis 中,有 XML 和 注解两种配置方式可选
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析注解中的信息
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
// 如果加载过程中出现异常需要再将这个mapper从mybatis中删除,
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}以上就是 Mapper 接口的绑定过程。这里简单一下:
- 获取命名空间,并根据命名空间解析 mapper 类型
- 将 type 和 MapperProxyFactory 工厂类实例的映射关系存入 knownMappers 中
- 解析注解中的信息
总的来说,对于Mapper****接口的配置以及上面的bindMapperForNamespace,都是通过MapperAnnotationBuilder对注解进行解析,解析注解前会先去判断XML文件是否被解析,若没有被解析会先解析XML文件,若解析过了则直接解析SQL注解。
以上步骤中,第3步的逻辑较多。如果大家看懂了映射文件的解析过程,那么注解的解析过程也就不难理解了,这里就不深入分析了。好了,Mapper 接口的绑定过程就先分析到这。
2.2.3 处理未完成解析的节点
在解析某些节点的过程中,如果这些节点引用了其他一些未被解析的配置,会导致当前节点解析工作无法进行下去。对于这种情况,MyBatis 的做法是抛出 IncompleteElementException 异常。外部逻辑会捕捉这个异常,并将节点对应的解析器放入 incomplet* 集合中。这个我在分析映射文件解析的过程中进行过相应注释,不知道大家有没有注意到。没注意到也没关系,待会我会举例说明。下面我们来看一下 MyBatis 是如何处理未完成解析的节点。
java
// -☆- XMLMapperBuilder
public void parse() {
// 省略部分代码
// 解析 mapper 节点
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 处理未完成解析的节点
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}如上,parse 方法是映射文件的解析入口。在本章的开始位置,我贴过这个源码。从上面的源码中可以知道有三种节点在解析过程中可能会出现不能完成解析的情况。由于上面三个以 parsePending 开头的方法逻辑一致,所以下面我只会分析其中一个方法的源码。简单起见,这里选择分析 parsePendingCacheRefs 的源码。下面看一下如何配置映射文件会导致 <cache-ref> 节点无法完成解析。
XML
<!-- 映射文件1 -->
<mapper namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.Mapper1">
<!-- 引用映射文件2中配置的缓存 -->
<cache-ref namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.Mapper2"/>
</mapper>
<!-- 映射文件2 -->
<mapper namespace="xyz.coolblog.dao.Mapper2">
<cache/>
</mapper>如上,假设 MyBatis 先解析映射文件1,然后再解析映射文件2。按照这样的解析顺序,映射文件1中的 <cache-ref> 节点就无法完成解析,因为它所引用的缓存还未被解析。当映射文件2解析完成后,MyBatis 会调用 parsePendingCacheRefs 方法处理在此之前未完成解析的 <cache-ref> 节点。具体的逻辑如下:
java
private void parsePendingCacheRefs() {
// 获取 CacheRefResolver 列表
Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = configuration.getIncompleteCacheRefs();
synchronized (incompleteCacheRefs) {
Iterator<CacheRefResolver> iter = incompleteCacheRefs.iterator();
// 通过迭代器遍历列表
while (iter.hasNext()) {
try {
/*
* 尝试解析 <cache-ref> 节点,若解析失败,则抛出 IncompleteElementException,
* 此时下面的删除操作不会被执行
*/
iter.next().resolveCacheRef();
/*
* 移除 CacheRefResolver 对象。如果代码能执行到此处,
* 表明已成功解析了 <cache-ref> 节点
*/
iter.remove();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
/*
* 如果再次发生 IncompleteElementException 异常,表明当前映射文件中并没有
* <cache-ref> 所引用的缓存。有可能所引用的缓存在后面的映射文件中,所以这里
* 不能将解析失败的 CacheRefResolver 从集合中删除
*/
}
}
}
}关于未完成解析节点的解析过程就分析到这。
相关文章: 【MyBatis】MyBatis的介绍和基本使用_dbutil mybaits-CSDN博客
【MyBatis】MyBatis的日志实现_mybatis 日志-CSDN博客
【MyBatis】MyBatis解析全局配置文件源码详解_mybatis解析配置文件源码-CSDN博客
【MyBatis】MyBatis内置数据源-CSDN博客