- 数据读取
wine葡萄酒数据集是来自UCI的公开数据集,也scikit-learn库自带的数据集,它是对意大利同一地区种植的葡萄酒进行化学分析的结果,这些葡萄酒来自三个不同的品种。该分析确定了三种葡萄酒中每种葡萄酒中含有的13种成分的数量。
每行代表一种酒的样本,共有178个样本;一共有14列,其中,第一个属性是类标识符,分别是1/2/3来表示,代表葡萄酒的三个分类。后面的13列为每个样本的对应属性的样本值,分别是酒精、苹果酸、灰、灰分的碱度、镁、总酚、黄酮类化合物、非黄烷类酚类、原花色素、颜色强度、色调、稀释葡萄酒的OD280/OD315、脯氨酸。其中第1类有59个样本,第2类有71个样本,第3类有48个样本。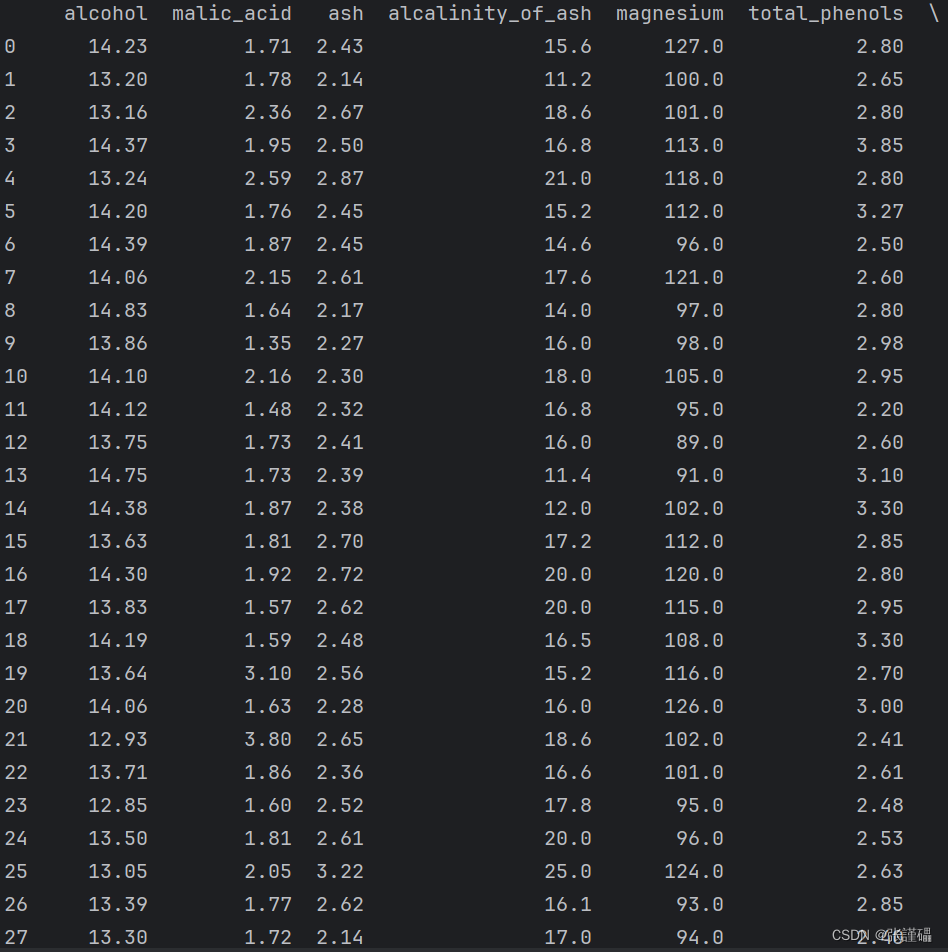
数据读取方法:
- 特征选择
单变量过滤法:
- 请使用方差阈值法对wine数据集进行特征选择,阈值设置为1。
python
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold
# 设置pandas的显示选项,使输出不被省略
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
# 读取wine数据集
wine = load_wine()
X = pd.DataFrame(wine.data, columns=wine.feature_names)
# 使用方差阈值法进行特征选择
selector = VarianceThreshold(threshold=1)
X_selected = selector.fit_transform(X)
# 显示选择后的特征数量
print("方差阈值法特征选择后的特征数量:", X_selected.shape[1])
print(X_selected)
- 请使用卡方统计量法对wine数据集进行特征选择,选择的特征子集的大小为5。
python
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
# 设置pandas的显示选项,使输出不被省略
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
# 读取wine数据集
wine = load_wine()
X = pd.DataFrame(wine.data, columns=wine.feature_names)
y = wine.target
# 使用卡方统计量法进行特征选择
selector = SelectKBest(chi2, k=5)
X_selected = selector.fit_transform(X, y)
# 显示选择后的特征数量
print("卡方统计量法特征选择后的特征数量:", X_selected.shape[1])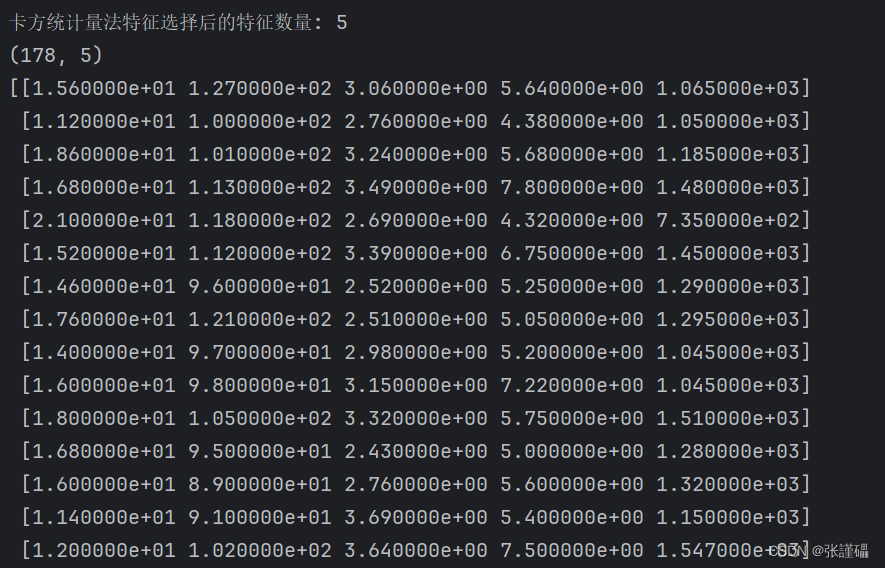
- 请使用互信息法wine数据集进行特征选择,选择的特征子集的大小为5。
python
from sklearn.feature_selection import mutual_info_classif
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
# 设置pandas的显示选项,使输出不被省略
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
# 读取wine数据集
wine = load_wine()
X = pd.DataFrame(wine.data, columns=wine.feature_names)
y = wine.target
# 使用互信息法进行特征选择
selector = SelectKBest(mutual_info_classif, k=5)
X_selected = selector.fit_transform(X, y)
# 显示选择后的特征数量
print("互信息法特征选择后的特征数量:", X_selected.shape[1])
print(X_selected.shape)
print(X_selected)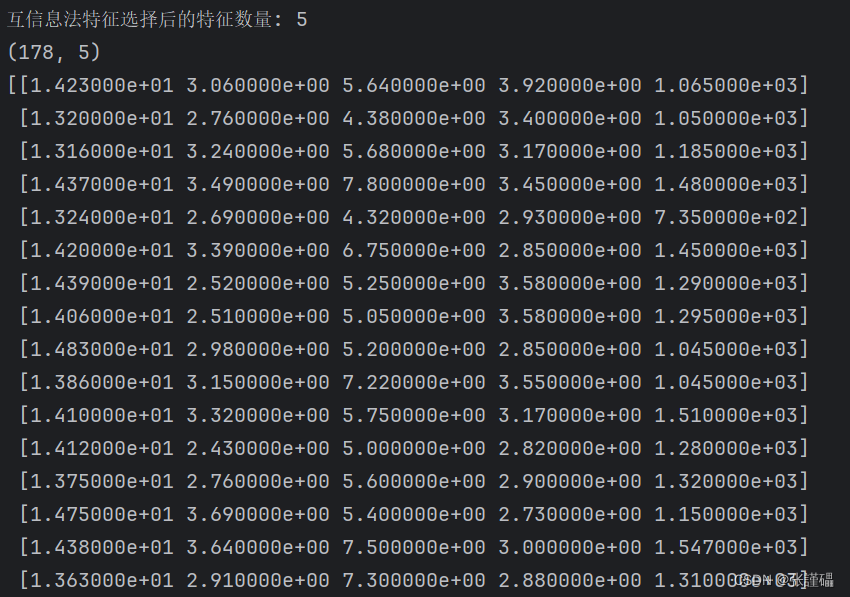
嵌入法:
- 对wine数据集进行标准规范化。
- 对标准化后的数据集进行训练集和测试集的划分。
- 使用L1正则化的逻辑回归模型进行嵌入法特征选择。
python
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 设置pandas的显示选项,使输出不被省略
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
# 读取wine数据集
wine = load_wine()
X = pd.DataFrame(wine.data, columns=wine.feature_names)
y = wine.target
# 对数据集进行标准规范化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_scaled, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 使用L1正则化的逻辑回归模型进行嵌入法特征选择
model = LogisticRegression(penalty='l1', solver='liblinear')
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 输出选择的特征数量
print("L1正则化逻辑回归模型选择的特征数量:", sum(model.coef_[0] != 0))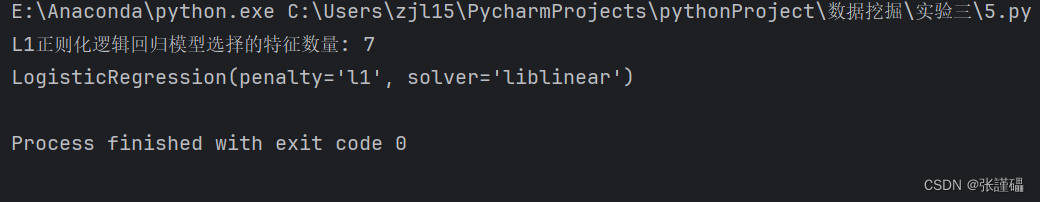
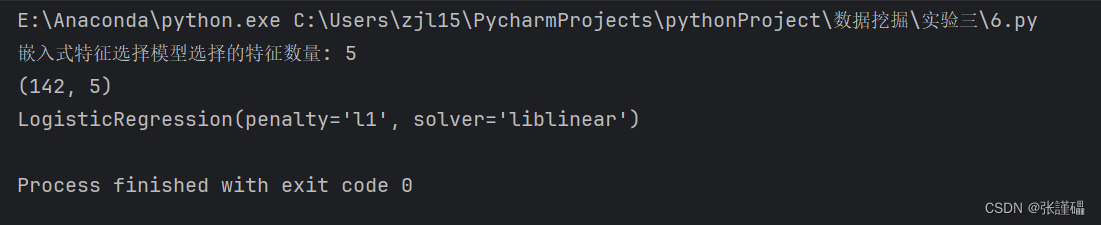
- 嵌入式特征选择模型,选择的特征子集的大小为5。
- 嵌入式特征选择模型。
python
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 设置pandas的显示选项,使输出不被省略
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
# 读取wine数据集
wine = load_wine()
X = pd.DataFrame(wine.data, columns=wine.feature_names)
y = wine.target
# 对数据集进行标准规范化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_scaled, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
model = LogisticRegression(penalty='l1', solver='liblinear')
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 使用嵌入式特征选择模型,选择的特征子集的大小为5
selector = SelectFromModel(model, max_features=5)
X_selected = selector.fit_transform(X_train, y_train)
# 显示选择后的特征数量
print("嵌入式特征选择模型选择的特征数量:", X_selected.shape[1])
print(X_selected.shape)
print(model)