整体架构如下所示:
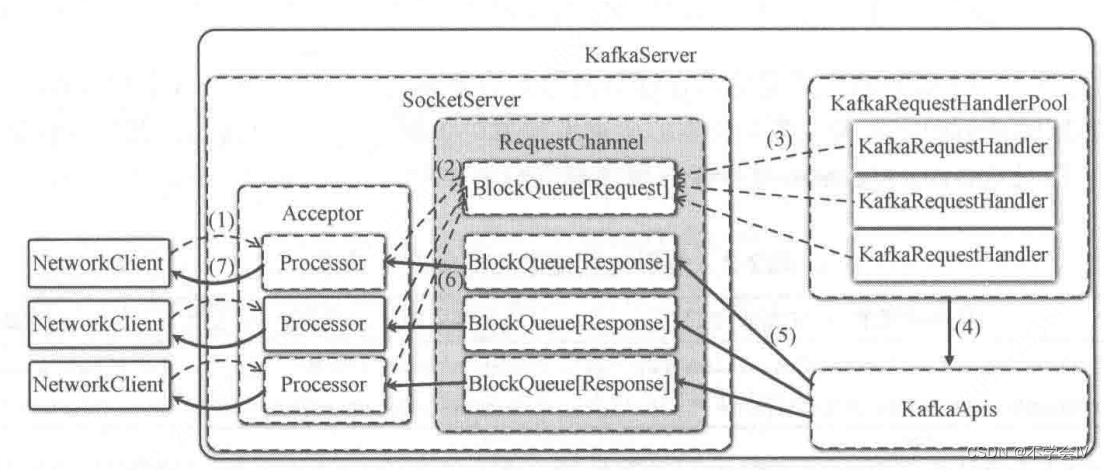
responseQueue不在RequestChannel中,在Processor中,每个Processor内部有一个responseQueue
- 客户端发送的请求被Acceptor转发给Processor处理
- 处理器将请求放到RequestChannel的requestQueue中
- KafkaRequestHandler取出requestQueue中的请求
- 调用KafkaApis进行业务逻辑处理
- KafkaApis将响应结果放到对应的Processor的responseQueue中
- processor从responseQueue中取出响应结果
- processor将响应结果返回给客户端
KafkaServer是Kafka服务端的主类,KafkaServer中和网络成相关的服务组件包括SocketServer、KafkaApis和KafkaRequestHandlerPool。SocketServer主要关注网络层的通信协议,具体的业务处理逻辑则交给KafkaRequestHandler和KafkaApis来完成。
scala
class KafkaServer(val config: KafkaConfig) {
def startup() {
socketServer = new SocketServer(config, metrics, time, credentialProvider)
socketServer.startup(startupProcessors = false)
/* start processing requests */
apis = new KafkaApis(socketServer.requestChannel, ...)
requestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.brokerId, ...)
}
}SocketServer
scala
def startup(startupProcessors: Boolean = true) {
this.synchronized {
...
createAcceptorAndProcessors(config.numNetworkThreads, config.listeners)
if (startupProcessors) {
startProcessors()
}
}
private def createAcceptorAndProcessors(processorsPerListener: Int,
endpoints: Seq[EndPoint]): Unit = synchronized {
...
endpoints.foreach { endpoint =>
...
val acceptor = new Acceptor(endpoint, ...)
addProcessors(acceptor, endpoint, processorsPerListener)
KafkaThread.nonDaemon(s"kafka-socket-acceptor-$listenerName-$securityProtocol-${endpoint.port}", acceptor).start()
acceptor.awaitStartup()
acceptors.put(endpoint, acceptor)
}
}可以看出SocketServer.startup()中会根据listener的个数创建相同个数的acceptor,每个acceptor关联数个processor。这是一种典型的Reactor模式,acceptor负责与客户端建立连接,并将连接分发给processor,processor负责所分连接后续的所有读写交互。
Acceptor
scala
def run() {
serverChannel.register(nioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)
startupComplete()
try {
var currentProcessor = 0
while (isRunning) {
try {
val ready = nioSelector.select(500)
if (ready > 0) {
val keys = nioSelector.selectedKeys()
val iter = keys.iterator()
while (iter.hasNext && isRunning) {
try {
val key = iter.next
iter.remove()
if (key.isAcceptable) {
val processor = synchronized {
currentProcessor = currentProcessor % processors.size
processors(currentProcessor)
}
accept(key, processor)
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized key state for acceptor thread.")
// round robin to the next processor thread, mod(numProcessors) will be done later
currentProcessor = currentProcessor + 1
} catch {
case e: Throwable => error("Error while accepting connection", e)
}
}
}
}
catch {
// We catch all the throwables to prevent the acceptor thread from exiting on exceptions due
// to a select operation on a specific channel or a bad request. We don't want
// the broker to stop responding to requests from other clients in these scenarios.
case e: ControlThrowable => throw e
case e: Throwable => error("Error occurred", e)
}
}
} finally {
debug("Closing server socket and selector.")
CoreUtils.swallow(serverChannel.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
CoreUtils.swallow(nioSelector.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
shutdownComplete()
}
}上面是Acceptor的run()方法,可以看出,Acceptor在通道上注册了SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT事件(OP_READ、OP_WRITE、OP_CONNECT、OP_ACCEPT,客户端监听OP_CONNECT事件,负责发起连接,服务端监听OP_CONNECT事件,负责建立连接),负责与客户端建立连接。并将建立的连接通过轮询的方式指派给processor。
Processor
每个Processor都会分到数个与客户端的连接。Processor的处理逻辑如下所示:
scala
override def run() {
startupComplete()
try {
while (isRunning) {
try {
// 在新分到的客户端连接上注册OP_READ事件
configureNewConnections()
// 从responseQueue中取响应,赋值给KafkaChannel的send,等待poll时发送
processNewResponses()
// selector轮询各种事件,读取请求或者发送响应
poll()
// 封装selector.completedReceives中的请求,放入requestQueue
processCompletedReceives()
// 处理selector.completedSends响应(移除inflightResponses中的记录;执行响应的回调函数)
processCompletedSends()
processDisconnected()
} catch {
...
}
}
} finally {
...
}
}Processor线程的名字中有kafka-network字样,可以通过jstack -l pid | grep kafka-network进行筛选。
KafkaRequestHandlerPool
KafkaServer会创建请求处理线程池(KafkaRequestHandlerPool),在请求处理线程池中会创建并启动多个请求处理线程(KafkaRequestHandler)。KafkaRequestHandler会获取RequestChannel.requestQueue中的请求进行处理,在内部实际处理会交给KafkaApis完成。
scala
class KafkaRequestHandlerPool(val brokerId: Int, ...) {
...
for (i <- 0 until numThreads) {
createHandler(i)
}
def createHandler(id: Int): Unit = synchronized {
runnables += new KafkaRequestHandler(..., requestChannel, apis, time)
KafkaThread.daemon("kafka-request-handler-" + id, runnables(id)).start()
}
}KafkaRequestHandler的run()方法如下:
scala
class KafkaRequestHandler(id: Int,...) extends Runnable with Logging {
...
def run() {
while (!stopped) {
val req = requestChannel.receiveRequest(300)
req match {
case RequestChannel.ShutdownRequest =>
shutdownComplete.countDown()
return
case request: RequestChannel.Request =>
try {
request.requestDequeueTimeNanos = endTime
apis.handle(request)
} catch {
case e: FatalExitError =>
shutdownComplete.countDown()
Exit.exit(e.statusCode)
case e: Throwable => error("Exception when handling request", e)
} finally {
request.releaseBuffer()
}
case null => // continue
}
}
shutdownComplete.countDown()
}
}