文章目录
一、分离模板的声明与定义方法一
在模板定义的cpp文件中声明其特化版本
other.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
void show(T t);oher.cpp
cpp
#include "other.h"
template<typename T>
void show(T t)
{
cout<<"t"<<'\n';
}
template void show<int>(int);
template void show<double>(double);
template void show<string>(string);二、分离模板的声明与定义方法二
使用variant(C++17语法)代替上述的方式
other.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <variant>
using namespace std;
void show(variant<int , double, string> t);other.cpp
cpp
#include "other.h"
void show(variant<int , double, string> t)
{
cout << t.index() <<endl;
/*
visit内部的实现方式可能就是通过index()选择的;
auto visitor = [](auto&& arg){cout<<arg<<endl;};
if (t.index() == 0)
{
visitor(get<int>(t));
}
else if (t.index() == 1)
{
visitor(get<double>(t));
}
else if(t.index() == 2)
{
visitor(get<string>(t));
}
or
if (holds_alternative<int>(t))
{
visitor(get<int>(t));
}
else if (holds_alternative<double>(t))
{
visitor(get<double>(t));
}
else if(holds_alternative<string>(t))
{
visitor(get<string>(t));
}
*/
visit([](auto&& arg){cout<<args<<endl;},t);
}解决了分离模板的声明与实现后,如果想要把每个variant对象保存至vector,出现的问题是:每个variant=32+8,string bytes+index bytes。每次占用内存过大,需要优化。所以使用data-oriented design进行改造
other.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <variant>
using namespace std;
using Object = variant<int, double, string>;
void add_object(Object o);
void print_objects();other.cpp
cpp
#include "other.h"
#Include <vector>
static vector<variant<int.double.string>> objects;
static vector<int> int_objects;
static vector<double> double_objects;
static vector<string> string_objects;
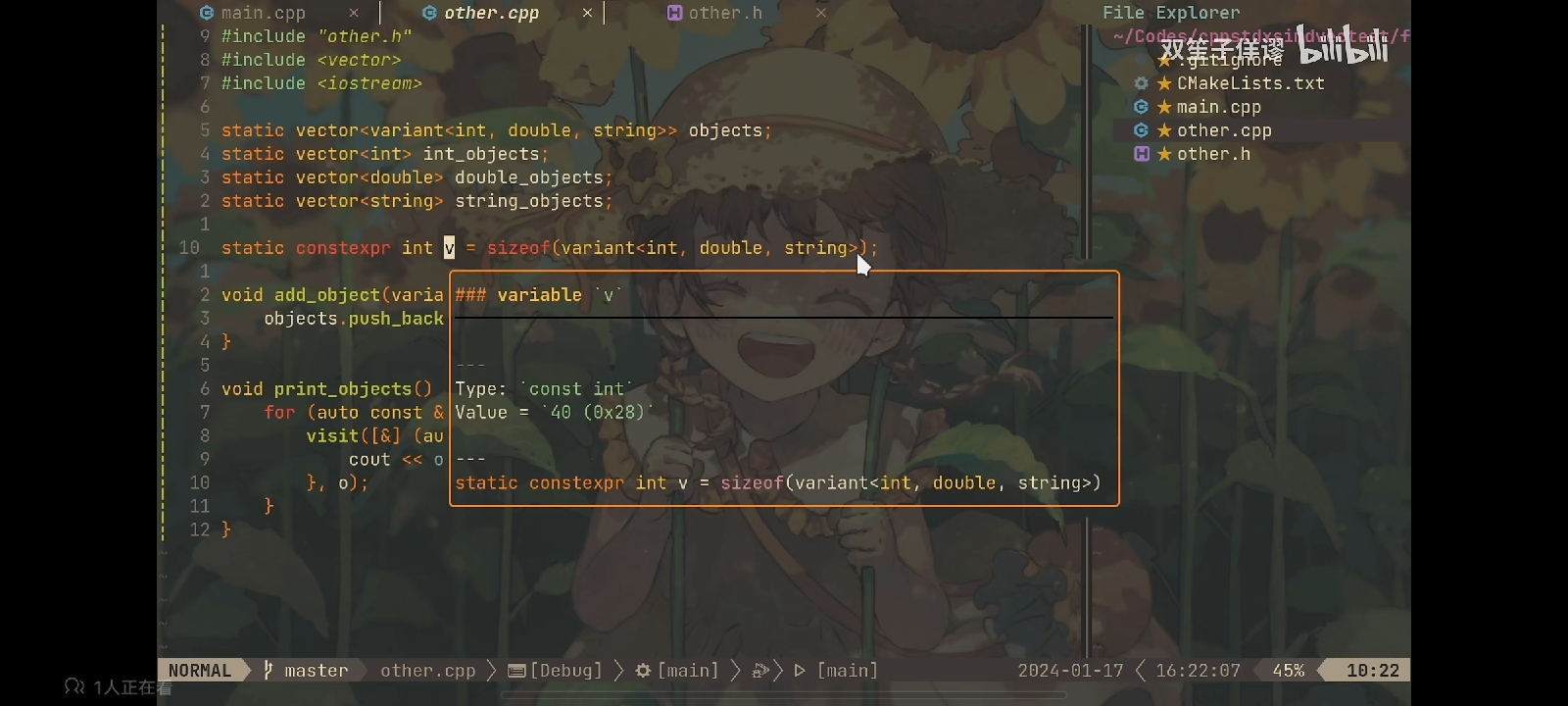
static constexpr int v = sizeof(variant<int.double.string>);
void add_object(variant<int.double.string> o)
{
objects.push_back(o);objects
}
void print_objects()
{
for(auto&& o : objects)
{
visit([](auto&& arg){std::cout<<arg<<std::endl;},o);
}
}
other.cpp
cpp
#include "other.h"
#Include <vector>
static vector<int> int_objects;
static vector<double> double_objects;
static vector<string> string_objects;
void add_object(variant<int,double,string> o)
{
if(holds_alternatibe<int>(o))
{
int_objects.push_back(get<int>(o));
}
else if(holds_alternatibe<double>(o))
{
double_objects.push_back(get<double>(o));
}
else if(holds_alternatibe<string>(o))
{
string_objects.push_back(get<string>(o));
}
}
void print_objects()
{
for(auto&& o: int_objects)
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
for(auto&& o: double_objects)
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
for(auto&& o: string_objects)
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
}使用编译器for循环以及tuple简化代码
cpp
static tuple<vector<int>. vector<double>, vector<string>> objects;
void add_object(variant<int, double, string> o)
{
if (o.index() == 0)
{
std::get<0>(objects).push_back(std::get<0>(o));
}
else if (o.index() == 1)
{
std::get<1>(objects).push_back(std::get<1>(o));
}
else if (o.index() == 2)
{
std::get<2>(objects).push_back(std::get<2>(o));
}
}
void print_objects()
{
for(auto&& o: std::get<0>(objects))
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
for(auto&& o: std::get<1>(objects))
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
for(auto&& o: std::get<2>(objects))
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
}other.cpp
cpp
static tuple<vector<int>. vector<double>, vector<string>> objects;
template<int N>
struct int_constant{
static constexpr int value = N;
};
template <int N, typename Lambda>
void static_for(Lambda&& lambda)
{
if constexpr (N > 0)
{
static_for<N-1>(lambda);
int_constant<N-1> ic;
lambda(ic);
}
}
void add_objects(variant<int, double, string> o)
{
static_for<3>([&](auto ic){
std::get<ic.value>(objects).push_vack(std::get<ic.value>(o));
});
}
void print_objects()
{
static_for<3>([&](auto ic){
for(auto&& o: std::get<ic.value>(objects))
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
});
}取出variant中的所有类型,以vector<x>,vector<y>的形式放在tuple中的类型中。即Object类型->Objects类型
other.cpp
cpp
template <class V>
struct variant_to_tuple_of_vector
{
}
template <class ...Ts>
struct variant_to_tuple_of_vector<variant<Ts...>> {
using type = tuple<vector<Ts>...>;
};
static variant_to_tuple_of_vector<Object>::type objects;自动提取variant中所有参数的个数,优化lambda只在输入的variant变量中插入
other.cpp
cpp
void add_objects(variant<int, double, string> o)
{
static_for<std::variant_size_v<decltype(o)>>([&](auto ic){
if (o.index() == ic.value)
{
std::get<ic.value>(objects).push_vack(std::get<ic.value>(o));
}
});
}
void print_objects()
{
static_for<std::variant_size_v<decltype(o)>([&](auto ic){
for(auto&& o: std::get<ic.value>(objects))
{
cout<<o<<endl;
}
});
}