注:机翻,未校对。
7 Types of Routing Protocols
七种路由协议类型
Routing is the process of moving information from a source to a destination across the internetwork. Typically, at least one intermediary node is encountered along the path. Routing takes place at Layer 3 (the network layer) of the OSI model. Typically, networks employ a combination of static and dynamic routing. Static routing is preferable for small networks, whereas dynamic routing is ideal for large networks.
路由是通过互联网络将信息从源移动到目标的过程。通常,沿路径至少会遇到一个中间节点。路由发生在 OSI 模型的第 3 层(网络层)。通常,网络采用静态和动态路由的组合。静态路由更适合小型网络,而动态路由非常适合大型网络。
Routing protocols are mechanisms for exchanging routing information between routers to make routing decisions. Routing protocols can facilitate effective and efficient communication between computer networks. Regardless of the scale of the network, these protocols facilitate the secure delivery of data to its destination. Understanding the various categories and types helps determine which routing method will best meet your goals.
路由协议是在路由器之间交换路由信息以做出路由决策的机制。路由协议可以促进计算机网络之间的有效和高效通信。无论网络规模如何,这些协议都有助于将数据安全地传送到目的地。了解各种类别和类型有助于确定哪种路由方法最能满足您的目标。
Depending on their properties, routing protocols can be categorized into distinct classes. In particular, routing protocols can be categorized according to their:
根据其属性,路由协议可以分为不同的类。具体而言,路由协议可以根据其分类:
- Behavior: Classful (legacy) or classless protocol.
行为:有类(旧版)或无类协议。 - Purpose: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) or Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP).
用途:内部网关协议 (IGP) 或外部网关协议 (EGP)。 - Operation: Path-vector protocol, distance vector protocol, and link-state protocol.
操作:路径向量协议、距离向量协议和链路状态协议。
IPv4 routing protocols are categorized as follows:
IPv4 路由协议分类如下:
- RIPv1 (legacy): IGP, distance vector, classful protocol
RIPv1(旧版):IGP、距离向量、经典协议 - RIPv2: IGP, distance vector, classless protocol
RIPv2:IGP、距离向量、无类别协议 - OSPF: IGP, link-state, classless protocol
OSPF:IGP、链路状态、无类别协议 - IGRP: IGRP (legacy) is Cisco's IGP, distance vector, classy protocol (deprecated from 12.2 IOS and later)
IGRP:IGRP(旧版)是思科的IGP,距离向量,经典协议(从12.2 IOS及更高版本中弃用) - EIGRP: IGP, distance vector, classless protocol
EIGRP:IGP、距离向量、无类别协议 - EGP
- BGP: EGP, classless path-vector protocol
BGP:EGP,无类路径向量协议 - IS-IS: Internet Protocol, link-state, classless
IS-IS:互联网协议,链路状态,无类别
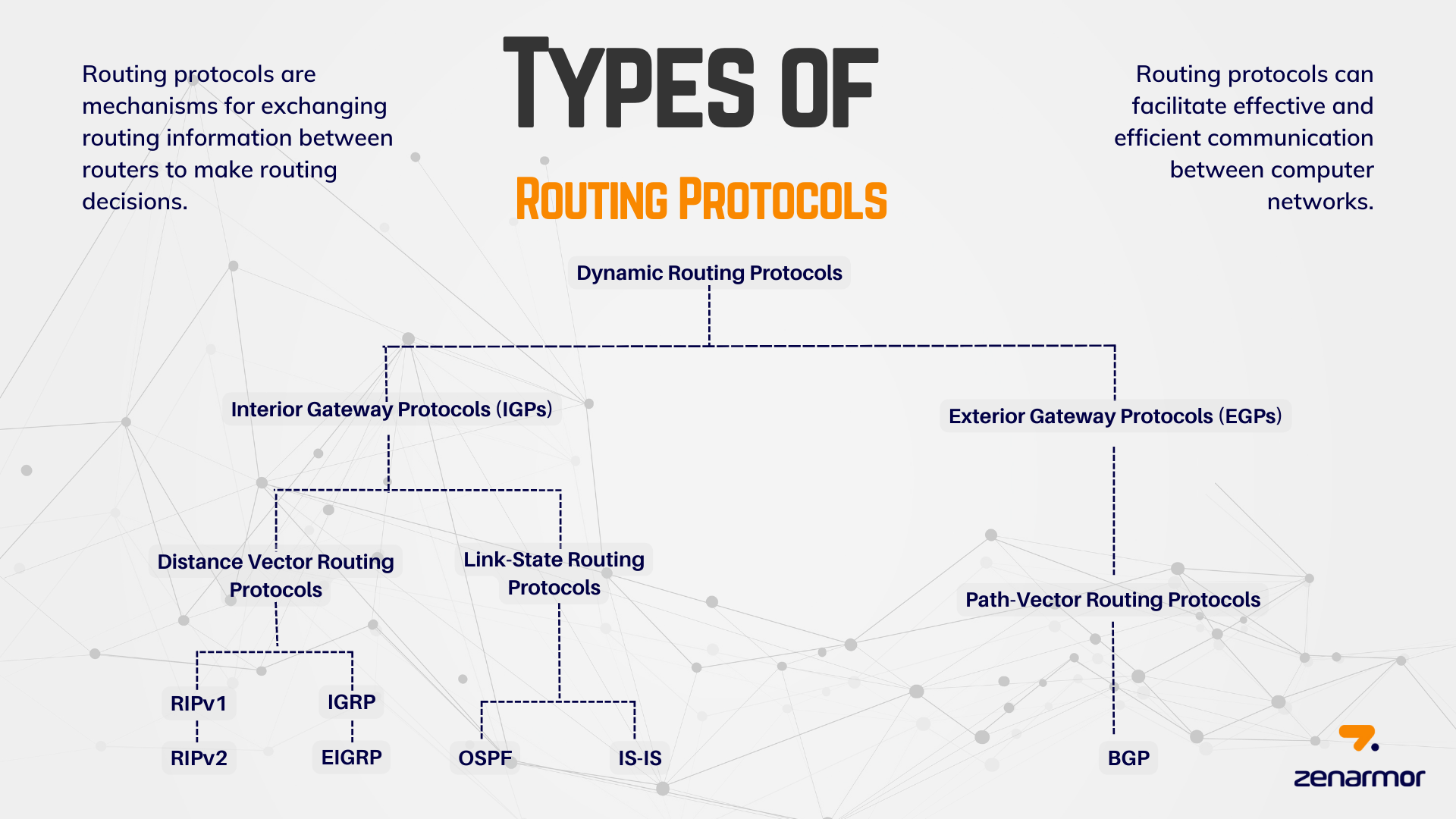
Figure 1. Types of Routing Protocols
图 1.路由协议的类型
This article describes the seven dynamic routing protocol types.
本文介绍七种动态路由协议类型。
1. Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
1. 路由信息协议 (RIP)
The Routing Information System (RIP) was first defined in RFC 1058 as a first-generation routing protocol for IPv4. RIP is a distance-vector routing protocol that uses the metric hop count. RIP is straightforward to configure, making it an excellent option for small networks.
路由信息系统 (RIP) 在 RFC 1058 中首次定义为 IPv4 的第一代路由协议。RIP 是一种使用指标跃点计数的距离向量路由协议。RIP 易于配置,使其成为小型网络的绝佳选择。
RIPv1 possesses the following qualities:
RIPv1 具有以下特性:
- The number of hops is utilized as the path selection metric.
跃点数用作路径选择指标。 - Every 30 seconds, routing updates are transmitted (255.255.255.255).
每 30 秒传输一次路由更新 (255.255.255.255)。 - Greater than 15 hops is considered infinite (too far). This 15th hop router would not transmit the routing update to the following router.
大于 15 个跃点被视为无限(太远)。此第 15 跳路由器不会将路由更新传输到以下路由器。
In 1993, RIPv1 evolved into RIP version 2, a classless routing protocol (RIPv2). RIPv2 brought the subsequent enhancements:
1993 年,RIPv1 演变为 RIP 版本 2,这是一种无类别路由协议 (RIPv2)。RIPv2 带来了后续增强功能:
- Security: It includes an authentication mechanism for securing routing table update communications between neighbors.
安全性:它包括一种身份验证机制,用于保护邻居之间的路由表更新通信。 - Classless routing protocol support: It supports VLSM and CIDR because routing updates include the subnet mask.
无类别路由协议支持:它支持 VLSM 和 CIDR,因为路由更新包含子网掩码。 - Improved efficiency: It forwards updates to the multicast address 224.0.0.9 rather than the broadcast address 255.255.255.255.
提高效率:它将更新转发到组播地址 224.0.0.9,而不是广播地址 255.255.255.255。 - Reduced routing entries: Manual route summarization on any interface is supported.
减少路由条目:支持在任何接口上手动路由汇总。
RIP updates are contained in a UDP segment with both the source and destination ports set to UDP port 520.
RIP 更新包含在 UDP 分段中,源端口和目标端口都设置为 UDP 端口 520。
The IPv6-enabled version of RIP was introduced in 1997. RIPng is an extension of RIPv2 restricted to 15 hops, the administrative distance is 120. This hop count limitation renders RIP unsuitable for larger networks.
支持 IPv6 的 RIP 版本于 1997 年推出。RIPng 是 RIPv2 的扩展,限制为 15 个跃点,管理距离为 120。此跃点计数限制使 RIP 不适合大型网络。
2. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
2. 首先开放最短路径 (OSPF)
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is the most prevalent link-state routing protocol. OSPF is the most common protocol that routers use to determine the optimal path to forward traffic. The OSPF Working Group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) designed it. OSPF development began in 1987, and there are currently two active versions:
开放最短路径优先 (OSPF) 是最流行的链路状态路由协议。OSPF 是路由器用于确定转发流量的最佳路径的最常用协议。互联网工程任务组 (IETF) 的 OSPF 工作组设计了它。OSPF 开发始于 1987 年,目前有两个活动版本:
- OSPFv2: OSPF for IPv4 networks (RFC 1247 and RFC 2328)
OSPFv2:用于 IPv4 网络的 OSPF(RFC 1247 和 RFC 2328) - OSPFv3: OSPFv3 is the IPv6 version of OSPF (RFC 2740)
OSPFv3:OSPFv3 是 OSPF (RFC 2740) 的 IPv6 版本
OSPFv3 now supports both IPv4 and IPv6 thanks to the Address Families functionality.
OSPFv3 现在支持 IPv4 和 IPv6,这要归功于地址系列功能。
OSPF implements the link state routing algorithm and is utilized in medium- to large-sized networks. OSPF is an intradomain routing protocol that only operates within a specific routing domain. OSPF is also a hierarchical routing protocol that may be used in a single autonomous system. OSPF emerged from the intermediate-system-to-system (IS-IS) routing protocol of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. OSPF enables multipath routing and uses one or more routing metrics, including dependability, bandwidth, latency, load, and maximum transmission unit (MTU). If OSPF utilizes many metrics, it also allows type-of-service (TOS) requests for traffic differentiation.
OSPF实现了链路状态路由算法,并用于大中型网络。OSPF 是一种域内路由协议,仅在特定路由域内运行。OSPF 也是一种分层路由协议,可用于单个自治系统。OSPF 源于开放系统互连 (OSI) 参考模型的中间系统到系统 (IS-IS) 路由协议。OSPF 支持多路径路由,并使用一个或多个路由指标,包括可靠性、带宽、延迟、负载和最大传输单元 (MTU)。如果 OSPF 使用许多指标,它还允许服务类型 (TOS) 请求以实现流量差异化。
OSPF, is a link-state, interior gateway, and classless protocol that uses the shortest path first (SPF) algorithm to ensure efficient data transmission. Internally, this type maintains numerous databases containing topology tables and network-wide information. Typically, the data is derived from link state advertising transmitted by individual routers. The advertising, which resembles reports, provides thorough details of the path's length and the resources that may be necessary.
OSPF 是一种链路状态、内部网关和无类别协议,它使用最短路径优先 (SPF) 算法来确保高效的数据传输。在内部,此类型维护大量包含拓扑表和网络范围信息的数据库。通常,数据来自单个路由器传输的链路状态通告。该广告类似于报告,提供了路径长度和可能需要的资源的详尽细节。
OSPF utilizes the Dijkstra algorithm to recalculate paths when topology changes occur. It also employs authentication procedures to maintain the security of its data throughout network modifications and intrusions. Due to its scalability, OSPF may be advantageous for both small and large network enterprises.
OSPF 利用 Dijkstra 算法在发生拓扑更改时重新计算路径。它还采用身份验证程序来在整个网络修改和入侵过程中维护其数据的安全性。由于其可扩展性,OSPF 可能对小型和大型网络企业都有优势。
3. Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
3. 内部网关路由协议 (IGRP)
In 1984, Cisco created the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) to address issues with RIP in large networks. IGRP is a distance vector protocol, however, it employs several routing metrics (not just hop count) to compute the destination's distance. Hold-downs, split horizons, and poison-reverse updates are IGRP features aimed at improving network stability. IGRP should only be utilized if your current environment consists solely of IGRP and you do not wish to add another routing protocol.
1984 年,思科创建了内部网关路由协议 (IGRP),以解决大型网络中的 RIP 问题。IGRP 是一种距离向量协议,但是,它使用多个路由指标(而不仅仅是跳数)来计算目的地的距离。保持、分割水平和毒物反向更新是旨在提高网络稳定性的 IGRP 功能。仅当当前环境仅由 IGRP 组成且不希望添加其他路由协议时,才应使用 IGRP。
The IGRP protocol offers the following routing goals:
IGRP 协议提供以下路由目标:
- The capacity to manage many "types of services" with a single set of data
使用一组数据管理多种"服务类型"的能力 - Routing loop prevention
路由环路防护 - Routing stability, even in extremely large or complex networks
路由稳定性,即使在非常大或复杂的网络中也是如此 - Low overhead, indicating that IGRP should not consume more bandwidth than it needs for its own operation
开销低,表明 IGRP 消耗的带宽不应超过其自身操作所需的带宽 - Rapid reaction to varying network structure
对不同的网络结构做出快速反应 - Split traffic along parallel routes when their desirability is equal.
当流量的可取性相等时,沿平行路由拆分流量。 - Consideration of error rates and traffic levels on various paths
考虑各种路径上的错误率和流量级别
IGRP is a distance-vector protocol in which routers (commonly referred to as gateways) only exchange routing information with neighboring routers. IGRP outperforms RIP in terms of metrics. It utilizes many of RIP's fundamental functionalities but increases the maximum number of hops supported to 100. Consequently, it may function better on larger networks. IGRP compares network parameters such as capacity, dependability, and load to function. This type automatically updates when modifications, such as route modifications, occur. This aids in the prevention of routing loops, which are faults that result in an infinite loop of data transfer. The new IGRP measures include the following:
IGRP 是一种距离矢量协议,其中路由器(通常称为网关)仅与相邻路由器交换路由信息。IGRP 在指标方面优于 RIP。它利用了 RIP 的许多基本功能,但将支持的最大跃点数增加到 100。因此,它可能在较大的网络上运行得更好。IGRP 将容量、可靠性和负载等网络参数与功能进行比较。当发生修改(如路径修改)时,此类型会自动更新。这有助于防止路由环路,路由环路是导致数据传输无限循环的故障。新的IGRP措施包括以下内容:
-
Bandwidth of the path section with the smallest bandwidth. The transmission rate in bits per second.
带宽最小的路径段的带宽。以比特/秒为单位的传输速率。
-
Topological delay time. The time it would take for a packet to reach its destination if the network were not crowded. If there is network traffic on the network, you may experience additional delays.
拓扑延迟时间。如果网络不拥挤,数据包到达目的地所需的时间。如果网络上有网络流量,您可能会遇到额外的延迟。
-
Dependability of the route. Indicates the path's reliability based on the number of packets that really arrive at the destination, relative to the total number of packets transmitted.
路线的可靠性。根据实际到达目的地的数据包数(相对于传输的数据包总数)指示路径的可靠性。
-
Path occupancy of the channel. Indicates the percentage of bandwidth currently in use. This value will fluctuate frequently as network traffic fluctuates.
通道的路径占用率。指示当前正在使用的带宽的百分比。此值将随着网络流量的波动而频繁波动。
Using a complex algorithm, IGRP evaluates these parameters and determines the optimal route, as represented by the smallest metric value.
IGRP使用复杂的算法评估这些参数并确定最佳路线,由最小指标值表示。
Hold-downs, Split horizons, and Poison-reverse updates are further significant stability characteristics of IGRP.
压紧、分裂地平线和毒物反向更新是 IGRP 的进一步重要稳定性特征。
-
Hold-downs: Used to prevent a regular update message from reestablishing a route that may have previously become invalid. When a network link fails, surrounding routers will detect the absence of regularly scheduled updates and determine that the link is no longer operational. The network will subsequently begin to propagate messages informing users that this router is not operating. If this convergence takes too long, another router on the network may indicate that this router is still operating normally. This gadget may be broadcasting inaccurate route information. A hold-down instructs the network's routers to delay for a period of time any modifications that could disrupt the routes. The hold-down duration is calculated to be only marginally longer than the time required to update the entire network with a route change.
Hold-downs:用于防止定期更新消息重新建立以前可能已失效的路由。当网络链路发生故障时,周围的路由器将检测到没有定期计划的更新,并确定该链路不再运行。随后,网络将开始传播消息,通知用户此路由器未运行。如果此收敛时间过长,网络上的另一台路由器可能指示此路由器仍在正常运行。此小工具可能正在广播不准确的路线信息。按住指示网络的路由器将任何可能中断路由的修改延迟一段时间。按住时间计算,仅略长于通过路由更改更新整个网络所需的时间。
-
Split horizons: Used to prevent routing loops from occurring between two routers. It is never advantageous to relay route information back in the direction from whence a packet was sent.
分割水平:用于防止在两个路由器之间发生路由环路。将路由信息中继回发送数据包的方向绝不是有利的。 -
Poison-reverse updates: Used to reduce loops between many routers. When the metric rises dramatically, it may suggest a routing loop. The router is subsequently placed on hold-down by sending it a poison-reverse update.
毒反向更新:用于减少许多路由器之间的环路。当指标急剧上升时,它可能表明存在路由循环。路由器随后通过向路由器发送毒药反向更新将其置于按压状态。
Utilizing timers and variables containing time intervals is another characteristic of IGRP's stability. Included among the timers are as follows:
利用计时器和包含时间间隔的变量是 IGRP 稳定性的另一个特征。计时器包括如下:
-
Update Timer: The update timer specifies how frequently update messages are transmitted. The IGRP default update interval is 90 seconds.
更新计时器:更新计时器指定更新消息的传输频率。IGRP 默认更新间隔为 90 秒。 -
Invalid Timer: The invalid timer specifies how long a router will wait before declaring a route invalid if it is not receiving routing update messages. The default value for the IGRP invalid timer is three times the update timer.
无效计时器:无效计时器指定路由器在未接收路由更新消息时在宣布路由无效之前将等待多长时间。IGRP 无效计时器的默认值是更新计时器的三倍。 -
Hold-time Period: The hold-time period (also known as the hold-down period) will indicate the duration of the hold-down period. The default hold-time for IGRP is three times the update interval plus ten seconds.
保持时间段:保持时间段(也称为保持期)将表示保持时间的持续时间。IGRP 的默认保持时间为更新间隔的三倍加上 10 秒。 -
Flush Timer: The flush timer specifies the amount of time that must elapse before a route is removed from a routing database. The default value of the IGRP flush timer is seven times the update interval.
刷新计时器:刷新计时器指定从路由数据库中删除路由之前必须经过的时间量。IGRP 刷新计时器的默认值是更新间隔的七倍。 -
Sleep Timer: The sleep timer specifies how long update messages will be delayed. The sleep value should be less than the update timer; otherwise, the routing tables will never be synchronized.
睡眠定时器:睡眠定时器指定更新消息的延迟时间。睡眠值应小于更新计时器;否则,路由表将永远不会同步。
4. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
4. 增强型内部网关路由协议 (EIGRP)
EIGRP, or Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol, is a distance vector routing protocol used in IP, AppleTalk, and NetWare networks. EIGRP is a proprietary Cisco protocol that was developed to succeed the earlier IGRP protocol in 1992. Similar to RIPv2, EIGRP added support for VLSM and CIDR. EIGRP enhances productivity, lowers routing changes, and facilitates secure message exchange.
EIGRP(增强型内部网关路由协议)是 IP、AppleTalk 和 NetWare 网络中使用的距离矢量路由协议。EIGRP 是一种专有的 Cisco 协议,旨在接替 1992 年的早期 IGRP 协议。与 RIPv2 类似,EIGRP 增加了对 VLSM 和 CIDR 的支持。EIGRP 可提高工作效率、减少路由更改并促进安全消息交换。
EIGRP presents the following features:
EIGRP具有以下特点:
- Rapid convergence: In the majority of instances, it is the quickest IGP to converge since it maintains other pathways, allowing for nearly instantaneous convergence. If a primary route fails, the router might use an alternate route. The changeover to the alternate route is instantaneous and requires no interaction with other routers.
快速收敛:在大多数情况下,它是收敛速度最快的 IGP,因为它保持其他路径,允许几乎瞬时收敛。如果主路由发生故障,路由器可能会使用备用路由。到备用路由的转换是即时的,不需要与其他路由器交互。 - Bounded triggered updates: This type of update does not transmit frequent updates. Only updates to the routing table are propagated whenever a change occurs. This decreases the network load imposed by the routing protocol. Bound triggered updates allow EIGRP to only deliver updates to neighbors that require them. It uses less bandwidth, particularly in big networks with several routes.
有界触发的更新:此类型的更新不会传输频繁的更新。每当发生更改时,只会传播对路由表的更新。这样可以减少路由协议施加的网络负载。绑定触发的更新允许 EIGRP 仅将更新交付给需要更新的邻居。它使用更少的带宽,特别是在具有多个路由的大型网络中。 - Management of the topology table: Maintains in a topology table all routes received from neighbors, not only the optimal ones. DUAL can inject backup routes into the EIGRP topology table.
拓扑表管理:在拓扑表中维护从邻居接收的所有路由,而不仅仅是最佳路由。DUAL可以将备份路由注入EIGRP拓扑表。 - Hello keepalive mechanism: A periodic exchange of a short Hello message is used to maintain adjacencies between routers. This results in a minimal utilization of network resources during regular operation, as opposed to frequent updates.
Hello keepalive 机制:定期交换短 Hello 消息,用于维护路由器之间的邻接关系。这会导致在常规操作期间对网络资源的利用率降至最低,而不是频繁更新。 - Multiple network layer protocol support: EIGRP is the only protocol that supports protocols other than IPv4 and IPv6, including legacy IPX and AppleTalk, because it employs Protocol Dependent Modules (PDM).
多网络层协议支持:EIGRP 是唯一支持 IPv4 和 IPv6 以外的协议的协议,包括传统 IPX 和 AppleTalk,因为它采用协议相关模块 (PDM)。
EIGRP possesses a variety of characteristics that make it an effective, intelligent, and potent routing protocol, such as the Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) and a Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL). To accelerate the convergence process, routes are adjusted. to improve the efficiency of packet transmissions. The downside of EIGRP is that it is a Cisco-proprietary protocol. Only Cisco routers will be able to interact via EIGRP if your network has routers from multiple suppliers. Non-Cisco routers will be unable to use or understand EIGRP.
EIGRP 具有多种特性,使其成为一种有效、智能和强大的路由协议,例如可靠传输协议 (RTP) 和扩散更新算法 (DUAL)。为了加速收敛过程,对路线进行了调整。提高数据包传输的效率。EIGRP的缺点是它是思科专有的协议。如果您的网络具有来自多个供应商的路由器,则只有 Cisco 路由器能够通过 EIGRP 进行交互。非思科路由器将无法使用或理解EIGRP。
5. Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP)
5. 外部网关协议 (EGP)
The Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) was a routing protocol used to connect autonomous systems on the Internet from the mid-1980s to the mid-1990s when it was replaced by the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). EGP was created by Bolt, Beranek, and Newman in the early 1980s. It was first mentioned in RFC 827 and stated formally in RFC 904. RFC 1772 outlined an EGP to BGP migration path. EGP does not utilize routing metrics; instead, it merely tracks which networks are currently accessible via a given router.
外部网关协议 (EGP) 是一种路由协议,用于连接 1980 年代中期至 1990 年代中期的 Internet 上的自治系统,当时它被边界网关协议 (BGP) 取代。EGP 由 Bolt、Beranek 和 Newman 在 1980 年代初期创建。它首先在 RFC 827 中被提及,并在 RFC 904 中正式声明。RFC 1772 概述了 EGP 到 BGP 的迁移路径。EGP 不使用路由指标;相反,它只是跟踪当前可以通过给定路由器访问的网络。
Included in the routing table for the EGP protocol are:
EGP 协议的路由表中包括:
- Network addresses of nearby devices
附近设备的网络地址 - Route costs 路线费用
- Identified routers 已识别的路由器
EGP maintains network databases close to one another to route the various paths data may travel to reach its destination. The databases then distribute the information to the connected routers so that all routers' tables are current. The updated routing tables can assist in determining the optimal data route.
EGP 维护彼此靠近的网络数据库,以路由数据可能到达目的地的各种路径。然后,数据库将信息分发到连接的路由器,以便所有路由器的表都是最新的。更新后的路由表有助于确定最佳数据路由。
This protocol has gone out of favor since it cannot operate in multipath networking situations. The EGP protocol functions by maintaining a database of neighboring networks and the possible routing pathways to reach them. These route details are transmitted to connected routers. Once it comes, the devices can update their routing tables and select network paths based on more accurate information.
该协议已经失宠,因为它不能在多路径网络情况下运行。EGP 协议通过维护相邻网络的数据库和到达它们的可能路由路径来发挥作用。这些路由详细信息将传输到连接的路由器。一旦它到来,设备可以更新其路由表并根据更准确的信息选择网络路径。
6. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
6. 边界网关协议 (BGP)
BGP is an alternative exterior gateway protocol that was created to replace EGP. BGP is the routing protocol used to exchange routes between internet service providers and autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. BGP employs the optimal path selection technique for data package transfers, making it a distance vector protocol. To automatically find the optimal route, BGP refers to the following variables:
BGP 是为取代 EGP 而创建的替代外部网关协议。BGP 是用于在 Internet 服务提供商和 Internet 上的自治系统 (AS) 之间交换路由的路由协议。BGP采用最优路径选择技术进行数据包传输,使其成为距离向量协议。为了自动找到最佳路由,BGP 引用了以下变量:
- Adjacent IP addresses
相邻 IP 地址 - Router designation 路由器名称
- Path distance 路径距离
- Origin type 原产地类型
The BGP Best Path Selection Algorithm is utilized to determine the optimal paths for data packet transfers. If no special parameters have been configured, BGP will select routes with the shortest path to the destination.
BGP最佳路径选择算法用于确定数据包传输的最佳路径。如果未配置特殊参数,BGP 将选择到达目的地路径最短的路由。
BGP enables administrators to modify transfer routes based on their requirements and provides extensive security measures to ensure that only authorized routers can exchange data and information. The algorithm for selecting the optimal route path can be modified by modifying the BGP cost community attribute. BGP is able to make routing decisions based on factors including weight, local preference, locally generated, AS Path length, origin type, multi-exit discriminator, eBGP over iBGP, IGP metric, router ID, cluster list, and neighbor IP address.
BGP使管理员能够根据自己的要求修改传输路由,并提供广泛的安全措施,以确保只有授权的路由器才能交换数据和信息。选择最优路由路径的算法可以通过修改 BGP 成本社区属性进行修改。BGP 能够根据权重、本地首选项、本地生成、AS 路径长度、源类型、多出口鉴别器、基于 iBGP 的 eBGP、IGP 指标、路由器 ID、集群列表和邻居 IP 地址等因素做出路由决策。
BGP only transmits updated routing table data when a change occurs. Therefore, there is no auto-discovery of topology changes, and the user must manually set up BGP. Regarding security, the BGP protocol can be verified so that only authorized routers can exchange data.
BGP 仅在发生更改时传输更新的路由表数据。因此,不会自动发现拓扑更改,用户必须手动设置 BGP。在安全性方面,可以验证BGP协议,以便只有授权的路由器才能交换数据。
BGP was chosen over OSPF because BGP allows device designers and owners greater flexibility and control than OSPF. BGP processes include options for which routes should be broadcast and which alerts the device will accept. It provides extra options for route choosing. This allows us greater flexibility to avoid overloading specific lines that OSPF would automatically presume to be the fastest path.
之所以选择 BGP 而不是 OSPF,是因为 BGP 允许设备设计人员和所有者比 OSPF 具有更大的灵活性和控制力。BGP 进程包括应广播哪些路由以及设备将接受哪些警报的选项。它为路线选择提供了额外的选项。这使我们能够更灵活地避免 OSPF 自动假定为最快路径的特定线路过载。
7. Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS)
7. 中间系统到中间系统(IS-IS)
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) designed IS-IS, which is documented in ISO 10589. The original version of this link-state routing protocol, known as DECnet Phase V, was created by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). Radia Perlman was the IS-IS routing protocol's principal designer.
国际标准化组织 (ISO) 设计了 IS-IS,该 IS-IS 记录在 ISO 10589 中。此链路状态路由协议的原始版本(称为 DECnet 第五阶段)由 Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) 创建。Radia Perlman 是 IS-IS 路由协议的首席设计者。
IS-IS was originally built for the OSI protocol suite and not TCP/IP. Later, Integrated IS-IS or Dual IS-IS added IP network capability. IS-IS was formerly known as the routing protocol used mostly by ISPs and carriers, although enterprise networks are increasingly adopting it.
IS-IS 最初是为 OSI 协议套件而不是 TCP/IP 构建的。后来,集成 IS-IS 或双 IS-IS 增加了 IP 网络功能。IS-IS以前被称为主要由ISP和运营商使用的路由协议,尽管企业网络越来越多地采用它。
IS-IS protocol employs a modified form of the Dijkstra algorithm. Typically, the protocol groups routers together to build bigger domains and connects routers for data transport. IS-IS employs these two network types frequently:
IS-IS 协议采用 Dijkstra 算法的修改形式。通常,该协议将路由器组合在一起以构建更大的域,并连接路由器进行数据传输。IS-IS经常使用以下两种网络类型:
- Network Service Access Point (NSAP): Similar to an IP address, a network service access point (NSAP) identifies a service access point in systems that employ the open system interconnection (OSI) concept.
网络服务接入点 (NSAP):与 IP 地址类似,网络服务接入点 (NSAP) 用于标识采用开放系统互连 (OSI) 概念的系统中的服务接入点。 - Network Entity Title(NET): This facilitates the identification of specific network routers within bigger computer networks.
网络实体标题 (NET):这有助于在更大的计算机网络中识别特定的网络路由器。
What is a Routing Protocol?
什么是路由协议?
A protocol that is used for identifying or publicizing network paths is referred to as a "routing protocol." A routing protocol specifies how routers exchange information that enables them to pick routes between network nodes. Routers direct Internet traffic so that data packets are sent from router to router through the Internet's networks until they reach their destination machine. Algorithms governing routing determine the precise route chosen. Each router is only aware of networks that are physically connected to it. A routing protocol distributes this information initially with its close neighbors and later with the rest of the network. Thus, routers obtain information about the network topology. A routing protocol enables the network to dynamically adapt to changing conditions; without it, all routing decisions must be made statically in advance. Thanks to the capacity of routing protocols to dynamically adapt to changing conditions, the Internet offers fault tolerance and high availability.
用于标识或公开网络路径的协议称为"路由协议"。路由协议指定路由器如何交换信息,使它们能够在网络节点之间选择路由。路由器定向 Internet 流量,以便数据包通过 Internet 网络从路由器发送到路由器,直到它们到达目标计算机。控制路由的算法决定了所选的精确路由。每个路由器只知道物理连接到它的网络。路由协议最初将此信息分发给其近邻,然后分发给网络的其余部分。因此,路由器获取有关网络拓扑的信息。路由协议使网络能够动态地适应不断变化的条件;没有它,所有路由决策都必须提前静态做出。由于路由协议能够动态适应不断变化的条件,互联网提供了容错和高可用性。
Routers utilize dynamic routing protocols to allow the transmission of routing information between routers. The objective of dynamic routing protocols comprises the discovery of remote networks, the maintenance of up-to-date routing information, the selection of the optimal way to destination networks, and the capacity to discover a new optimal path if the present path is no longer available. While dynamic routing protocols require less administrative overhead than static routing, they nonetheless demand a portion of a router's resources, including CPU time and network link bandwidth, for protocol execution.
路由器利用动态路由协议在路由器之间传输路由信息。动态路由协议的目标包括发现远程网络、维护最新的路由信息、选择到达目标网络的最佳路径,以及在当前路径不再可用时发现新的最佳路径的能力。虽然动态路由协议比静态路由需要更少的管理开销,但它们仍然需要路由器的一部分资源,包括 CPU 时间和网络链路带宽来执行协议。
The discovery of remote networks and the maintenance of reliable network information are the responsibilities of routing protocols. When there is a change in topology, routing protocols notify the entire routing domain. Convergence is the process of bringing all routing tables to a consistent state when all routers in the same routing domain or area have complete and accurate network information. Certain routing protocols converge more quickly than others.
发现远程网络和维护可靠的网络信息是路由协议的职责。当拓扑发生更改时,路由协议会通知整个路由域。收敛是当同一路由域或区域中的所有路由器都具有完整准确的网络信息时,使所有路由表保持一致状态的过程。某些路由协议比其他路由协议收敛得更快。
Classifications for routing protocols include classful or classless, distance vector or link-state, and Interior Gateway Protocol or Exterior Gateway Protocol.
路由协议的分类包括有类或无类、距离向量或链路状态,以及内部网关协议或外部网关协议。
Distance vector protocols utilize routers as "sign posts" on the way to the final destination. The only information a router has about a distant network is the distance or metric required to reach it, as well as the way or interface used to reach it. Distance vector routing techniques lack a true network topology diagram.
距离矢量协议利用路由器作为通往最终目的地的"路标"。路由器拥有的关于远程网络的唯一信息是到达它所需的距离或指标,以及用于到达它的方式或接口。距离矢量路由技术缺乏真正的网络拓扑图。
By collecting data from all of the other routers, a router configured with a link-state routing protocol is able to construct a comprehensive network topology by collecting data from all of the other routers.
通过从所有其他路由器收集数据,配置了链路状态路由协议的路由器能够通过从所有其他路由器收集数据来构建全面的网络拓扑。
Routing protocols use metrics to identify the optimal or shortest path to a destination network. Various routing protocols may have distinct metrics. Generally, a lower metric indicates a superior path. Hops, bandwidth, delay, reliability, and load can be used to determine a metric's value.
路由协议使用指标来标识到目标网络的最佳或最短路径。各种路由协议可能具有不同的指标。通常,指标越低表示路径越好。跃点、带宽、延迟、可靠性和负载可用于确定指标的值。
Multiple routes to the same network may be learned by routers via both static and dynamic routing protocols. When multiple routing sources provide information on a target network, routers use the administrative distance value to select which source to use. Along with static routes and directly connected networks, each dynamic routing protocol has a distinct administrative value. The less administrative value a route source has, the more desired it is. Directly connected networks are always preferable over static and dynamic routing methods.
路由器可以通过静态和动态路由协议学习到同一网络的多个路由。当多个路由源提供有关目标网络的信息时,路由器使用管理距离值来选择要使用的源。除了静态路由和直接连接的网络外,每个动态路由协议都具有不同的管理值。路由源的管理价值越小,它就越受欢迎。直接连接的网络始终优于静态和动态路由方法。
Among the objectives of dynamic routing protocols are as follows:
动态路由协议的目标如下:
-
Maintaining current route information
维护当前路线信息
-
Discovering distant networks
发现远程的网络
-
Locating a new optimal path if the present one is no longer accessible
如果当前路径不再可访问,则查找新的最佳路径
-
Determining the optimal route to destination networks
确定通往目标网络的最佳路由
The principal components of dynamic routing protocols are listed below:
动态路由协议的主要组件如下:
- Algorithm: An algorithm is a finite list of steps that are utilized to complete a task. Routing protocols utilize algorithms to facilitate routing information and to determine the optimal path.
算法:算法是用于完成任务的有限步骤列表。路由协议利用算法来促进路由信息并确定最佳路径。 - Routing Protocol Messages: Messages are used by routing protocols to discover neighboring routers, communicate routing information, and conduct other network-related duties, such as learning and maintaining accurate network information.
路由协议消息:路由协议使用消息来发现相邻路由器、通信路由信息以及执行其他与网络相关的职责,例如学习和维护准确的网络信息。 - Data Structures: Routing protocols generally utilize tables or databases to perform their tasks. This data is maintained in RAM.
数据结构:路由协议通常利用表或数据库来执行其任务。此数据保存在 RAM 中。
In general, the following describes the operations of a dynamic routing protocol:
一般而言,动态路由协议的操作如下:
- The router transmits and receives routing messages on its interfaces.
路由器在其接口上发送和接收路由消息。 - The router exchanges routing messages and routing data with other routers employing the same routing protocol.
路由器与采用相同路由协议的其他路由器交换路由消息和路由数据。 - Routers share routing information to gain knowledge of distant networks.
路由器共享路由信息以获取远程网络的知识。 - When a router detects a change in topology, the routing protocol might broadcast this information to other routers.
当路由器检测到拓扑更改时,路由协议可能会将此信息广播到其他路由器。
Dynamic routing protocols are more expensive in terms of CPU and bandwidth usage and less secure as compared to default and static routing.
与默认路由和静态路由相比,动态路由协议在 CPU 和带宽使用方面成本更高,安全性更低。
| Features | RIP V1 | RIP V2 | IGRP | OSPF | EIGRP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classful/Classless | Classful | Classless | Classful | Classless | Classless |
| Metric | Hop | Hop | Composite Bandwidth, Delay | Bandwidth | Composite, Bandwidth, Delay |
| Periodic | 30 seconds | 30 seconds | 90 seconds | None | 30 seconds |
| Advertising Address | 255.255.255.255.255 | 223.0.0.9 | 255.255.255.255.255 | 224.0.0.5 224.0.0.6 | 224.0.0.10 |
| Category | Distance Vector | Distance Vector | Distance Vector | Link State | Hybrid |
| Default Distance | 120 | 120 | 200 | 110 | 170 |
Table 1. Features of Dynamic Routing Protocols
表 1.动态路由协议的功能
The Routing Protocols Timeline is given below:
路由协议时间表如下:
- 1982 - EGP
- 1985 - IGRP
- 1988 - RIPv1
- 1990 - IS-IS
- 1991 - OSPFv2
- 1992 - EIGRP
- 1994 - RIPv2
- 1995 - BGP
- 1997 - RIPng
- 1999 - BGPv6 and OSPFv3
- 2000 - IS-ISv6
What is a Protocol in Networking?
什么是网络协议?
A network protocol is an agreed collection of rules that govern the transmission of data between devices on the same network. A network protocol enables connected devices to communicate despite internal processes, structure, or design variances. Network protocols play a crucial part in current digital communications because they make it possible to communicate with people all over the world.
网络协议是商定的规则集合,用于管理同一网络上的设备之间的数据传输。网络协议使连接的设备能够进行通信,尽管内部流程、结构或设计存在差异。网络协议在当前的数字通信中起着至关重要的作用,因为它们使与世界各地的人们进行通信成为可能。
The Internet protocols are the most widely used open-system (nonproprietary) protocol suite in the world because they can be used to communicate across any set of interconnected networks and are suitable for both LAN and WAN communications. The two most well-known Internet protocols are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP). The Internet protocols are a suite of communication protocols, of which the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) are the best. In addition to lower-layer protocols (such as TCP and IP), the Internet protocol suite also specifies typical applications such as electronic mail, terminal emulation, and file transfer.
互联网协议是世界上使用最广泛的开放系统(非专有)协议套件,因为它们可用于跨任何一组互连网络进行通信,并且适用于LAN和WAN通信。两种最著名的 Internet 协议是传输控制协议 (TCP) 和 Internet 协议 (IP)。互联网协议是一套通信协议,其中传输控制协议(TCP)和互联网协议(IP)是最好的。除了较低层协议(如 TCP 和 IP)之外,Internet 协议套件还指定了典型的应用程序,例如电子邮件、终端仿真和文件传输。
What Is the Importance of Routing Protocols?
路由协议的重要性是什么?
The data networks we use to learn, play and work in our daily lives ranging from small, local networks to enormous, global networks. Multiple routers and switches may serve the data connectivity needs of hundreds or thousands of PCs within an enterprise.
我们在日常生活中用来学习、娱乐和工作的数据网络,从小型的本地网络到巨大的全球网络。多个路由器和交换机可以满足企业内数百或数千台 PC 的数据连接需求。
Routing protocols enable routers to dynamically share information about external networks and add it to their routing tables. Routers forward packets using the routing table's information. The router can discover routes to faraway networks in two ways: statically and dynamically. The optimal route to each network is determined by routing protocols.
路由协议使路由器能够动态共享有关外部网络的信息,并将其添加到其路由表中。路由器使用路由表的信息转发数据包。路由器可以通过两种方式发现到遥远网络的路由:静态和动态。每个网络的最佳路由由路由协议确定。
In a big network consisting of several networks and subnets, designing and maintaining static routes between these networks takes a substantial amount of administrative and operational overhead. This operational burden is particularly burdensome when network changes occur, such as a downlink or the implementation of a new subnet. Implementing dynamic routing protocols can lighten the load of configuration and maintenance duties and provide scalability to the network.
在由多个网络和子网组成的大型网络中,设计和维护这些网络之间的静态路由需要大量的管理和运营开销。当发生网络更改(例如下行链路或新子网的实施)时,这种操作负担尤其繁重。实施动态路由协议可以减轻配置和维护职责的负担,并为网络提供可扩展性。
A fundamental advantage of dynamic routing protocols is that routers share routing information whenever there is a change in network topology. This exchange enables routers to automatically discover new networks and find alternate routes in the event of a network link loss.
动态路由协议的一个基本优点是,每当网络拓扑发生变化时,路由器都会共享路由信息。这种交换使路由器能够在网络链路丢失时自动发现新网络并找到备用路由。
Dynamic routing protocols demand less administrative work than static routing. However, dynamic routing protocols require a portion of a router's resources, including CPU time and network link bandwidth, for protocol execution. Despite the advantages of dynamic routing, there is still a role for static routing. There are instances where static routing is preferable and others when dynamic routing is preferable. In networks with a modest degree of complexity, both static and dynamic routing may be established.
与静态路由相比,动态路由协议需要更少的管理工作。但是,动态路由协议需要路由器的一部分资源,包括 CPU 时间和网络链路带宽。尽管动态路由具有优点,但静态路由仍然有其作用。在某些情况下,静态路由更可取,而在其他情况下,动态路由更可取。在具有适度复杂程度的网络中,可以同时建立静态和动态路由。
In summary, routing protocols are important technologies in the communication world because of the following:
总之,路由协议是通信领域的重要技术,原因如下:
- A rapid convergence 快速融合
- Easy to configure 易于配置
- Permits optimal route selection
允许最佳路线选择 - Minimize update traffic
最大限度减少更新流量 - Provides for loop-free routing
提供无环路路由 - Adapts to alterations
适应变化 - Supports vary in length
支架的长度各不相同 - Compatible with established hosts and routers
与已建立的主机和路由器兼容 - Scales to a substantial size
缩放到相当大的尺寸
What are the IGP and EGP Routing Protocols?
什么是 IGP 和 EGP 路由协议?
An autonomous system (AS) is a collection of routers administered by a single entity, such as a business or organization. An AS may also be referred to as a route domain. An AS often consists of a company's internal network and an ISP's network.
自治系统 (AS) 是由单个实体(如企业或组织)管理的路由器集合。AS 也可以称为路由域。AS 通常由公司的内部网络和 ISP 的网络组成。
Due to the fact that the Internet is based on the AS idea, two types of routing protocols are required:
由于 Internet 是基于 AS 思想的,因此需要两种类型的路由协议:
- Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP): These are protocols used for routing within an AS. This is also known as the intra-AS route. Internal networks of businesses, organizations and even service providers use an IGP. RIP, IGRP, EIGRP, OSPF, and IS-IS are IGPs.
内部网关协议 (IGP):这些是用于在 AS 内路由的协议。这也称为 AS 内路由。企业、组织甚至服务提供商的内部网络都使用 IGP。RIP、IGRP、EIGRP、OSPF 和 IS-IS 是 IGP。 - Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGP): Used for routing between autonomous systems. This is also known as the inter-AS route. Using an EGP, service providers and huge corporations can interconnect. The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the Internet's official routing protocol and the only EGP that is currently operational. Since BGP is the sole available EGP, the word EGP is rarely used; instead, engineers typically refer to BGP.
外部网关协议 (EGP):用于自治系统之间的路由。这也称为 AS 间路由。使用 EGP,服务提供商和大公司可以互连。边界网关协议 (BGP) 是互联网的官方路由协议,也是当前唯一运行的 EGP。由于 BGP 是唯一可用的 EGP,因此很少使用 EGP 一词;相反,工程师通常使用 BGP。
What are Routing Protocol Metrics?
什么是路由协议度量?
There are instances in which a routing protocol discovers many routes to the same destination. For the routing protocol to select the optimal path, it must be able to analyze and differentiate amongst the available paths. This is achieved with the use of routing metrics.
在某些情况下,路由协议会发现到同一目标的多个路由。为了使路由协议选择最佳路径,它必须能够分析和区分可用路径。这是通过使用路由指标来实现的。
A metric is a quantitative value assigned to different routes by the routing protocol based on the usefulness of that route. In instances where numerous paths exist to the same remote network, routing metrics are used to calculate the "cost" of a path from source to destination. Routing protocols find the optimal path based on the least expensive route.
指标是路由协议根据路由的有用性分配给不同路由的定量值。在存在多个路径到同一远程网络的情况下,路由指标用于计算从源到目标的路径的"成本"。路由协议根据最便宜的路由找到最佳路径。
Various routing protocols employ distinct metrics. One routing protocol's metric cannot be compared to the metric of another routing protocol. Two distinct routing protocols may select distinct routes to the same destination.
各种路由协议采用不同的指标。一个路由协议的指标不能与另一个路由协议的指标进行比较。两种不同的路由协议可以选择到同一目的地的不同路由。
Below are the most typical routing protocol metric values:
以下是最典型的路由协议指标值:
- Reliability: Reliability is a metric factor that may be given a constant value. Its value is dynamically measured and is dependent on the network links. Some networks experience outages more frequently than others. Some network links are easier to repair than others after a network breakdown. Any dependability element may be considered when assigning reliability ratings, which are typically issued by the system administrator as numeric values.
可靠性:可靠性是一个指标因素,可以给出一个恒定的值。它的值是动态测量的,并且取决于网络链路。某些网络比其他网络更频繁地出现中断。在网络故障后,某些网络链接比其他网络链接更容易修复。在分配可靠性评级时,可以考虑任何可靠性元素,这些评级通常由系统管理员以数值形式发布。 - Delay: The amount of time a router needs to process, queue, and transmit a datagram to an interface. This measure is used by the protocols to determine the delay values for all links along the end-to-end path. The route with the lowest delay value will be considered the optimal route.
延迟:路由器处理、排队和将数据报传输到接口所需的时间。协议使用此度量值来确定端到端路径上所有链路的延迟值。延迟值最低的路线将被视为最佳路线。 - Hop count: Hop count is a measure that specifies the number of internetworking devices, such as a router, through which a packet must pass in order to go from source to destination. If the hop is considered a major metric value by the routing protocol, then the path with the fewest hops will be deemed the optimal way from source to destination.
跳数:跳数是一种度量值,用于指定网际网络设备(如路由器)的数量,数据包必须通过这些设备才能从源到达目的地。如果路由协议将跃点视为主要指标值,则跃点最少的路径将被视为从源到目标的最佳方式。 - Load: Load is the degree to which a network resource, such as a router or network link, is utilized. A load can be determined in numerous ways, including CPU use and packets processed per second. If the volume of traffic increases, so will the load value. The load value adapts to the fluctuating volume of traffic.
负载:负载是网络资源(如路由器或网络链路)的利用程度。负载可以通过多种方式确定,包括 CPU 使用率和每秒处理的数据包数。如果流量增加,负载值也会增加。负载值适应流量的波动。 - Bandwidth: The capacity of the link is referred to as its bandwidth. The bandwidth is quantified in bits per second. The connection with a higher transfer rate, such as gigabit, is chosen over the connection with a smaller capacity, such as 56 kb. The protocol will assess the bandwidth capacity of each link along the route, and the route with the highest bandwidth will be deemed the optimal one.
带宽:链路的容量称为其带宽。带宽以每秒比特数为单位进行量化。选择具有较高传输速率(如千兆位)的连接,而不是具有较小容量(如 56 kb)的连接。该协议将评估沿路由的每个链路的带宽容量,带宽最高的路由将被视为最佳路由。
Comparison of Routing Protocols
路由协议的比较
Routing protocols are compared based on the following characteristics:
根据以下特征比较路由协议:
- Implementation and maintenance : Implementation and maintenance describe the level of knowledge necessary for a network administrator to install and maintain the network by the routing protocol adopted.
实施和维护:实施和维护描述了网络管理员通过所采用的路由协议安装和维护网络所需的知识水平。 - Speed of convergence : The speed of convergence is the rate at which the routers in a network architecture share routing information and attain a state of consistent knowledge. The more rapidly a protocol converges, the more desirable it is. When inconsistent routing tables are not updated due to poor convergence in a dynamic network, routing loops can arise.
收敛速度:收敛速度是网络架构中的路由器共享路由信息并达到一致知识状态的速率。协议收敛得越快,就越可取。当由于动态网络中的收敛性差而未更新不一致的路由表时,可能会出现路由环路。 - Classful vs Classless : Classful routing protocols do not include the subnet mask and cannot support variable-length subnet mask (VLSM). Updates for classless routing protocols include the subnet mask. Classless routing techniques support VLSM and provide for improved route summarization.
有类与无类:有类路由协议不包括子网掩码,并且不支持可变长度子网掩码 (VLSM)。无类路由协议的更新包括子网掩码。无类别路由技术支持 VLSM,并提供改进的路由汇总。 - Scalability :Scalability defines the maximum size of a network based on the deployed routing system. The routing protocol must be more scalable as the network size increases.
可伸缩性:可伸缩性根据部署的路由系统定义网络的最大大小。随着网络规模的增加,路由协议必须更具可伸缩性。 - Resource usage : Resource usage consists of the requirements of a routing protocol, including memory space (RAM), CPU utilization, and link bandwidth usage. In addition to packet forwarding activities, the operation of the routing protocol necessitates more robust hardware due to its increased resource demands.
资源使用:资源使用由路由协议的要求组成,包括内存空间 (RAM)、CPU 使用率和链路带宽使用率。除了数据包转发活动外,路由协议的运行还需要更强大的硬件,因为它增加了资源需求。
Comparisons of the routing protocols are given in the following table:
下表给出了路由协议的比较:
| RIPv1 | RIPv2 | IGRP | EIGRP | OSPF | IS-IS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Converge | Slow | Slow | Slow | Fast | Fast | Fast |
| Scalibility/Size of Network | Small | Small | Small | Large | Large | Large |
| Use of VLSM | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Resource Usage | Low | Low | Low | Medium | High | High |
| Implementation & Maintenance | Simple | Simple | Simple | Complex | Complex | Complex |
Table 2. Comparisons of the Dynamic Routing Protocols
表 2.动态路由协议的比较
Which Network Protocol is Used to Route IP Addresses?
使用哪种网络协议来路由 IP 地址?
Internet Protocol is used to route IP addresses. An Internet Protocol (IP) assigns the network-participating system a unique address known as an IP address. These IP addresses are used to route data packets between the source and destination systems.
Internet 协议用于路由 IP 地址。Internet 协议 (IP) 为参与网络的系统分配一个称为 IP 地址的唯一地址。这些 IP 地址用于在源系统和目标系统之间路由数据包。
The IP address is accountable for identifying and routing network systems. Each device has a unique Internet protocol address.
IP 地址负责识别和路由网络系统。每个设备都有一个唯一的 Internet 协议地址。
Is VPN a Routing Protocol?
VPN是路由协议吗?
No . VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, which enables a user to connect to a private network securely and privately over the Internet. VPN creates an encrypted connection known as a VPN tunnel, through which all Internet traffic and conversation are routed. Some VPN protocols are as follows:
不。VPN 代表虚拟专用网络,它使用户能够通过 Internet 安全、私密地连接到专用网络。VPN 创建一个称为 VPN 隧道的加密连接,所有 Internet 流量和对话都通过该隧道进行路由。一些VPN协议如下:
Does VPN Improve Routing?
VPN 会改善路由吗?
No. If you install a VPN on your router, you might anticipate speed and performance issues. Since deploying a VPN on your router imposes new network management responsibilities such as traffic encryption/decryption that is memory-intensive and CPU-intensive operations. Additionally, the router must periodically connect to a certain VPN server, which requires processing power.
不。如果您在路由器上安装 VPN,您可能会遇到速度和性能问题。由于在路由器上部署 VPN 会带来新的网络管理责任,例如流量加密/解密,这是内存密集型和 CPU 密集型操作。此外,路由器必须定期连接到某个 VPN 服务器,这需要处理能力。
Do NGFWs Support Routing Protocols?
NGFW 是否支持路由协议?
Yes , next-generation firewall(NGFW) solutions support IPv4 and IPv6 routing protocols. For instance, OPNsense powered with Zenarmor next-generation firewall plugin offers dynamic routing protocols, like RIP v1 and v2, OSPFv2 and v3, and BGPv4. In order to use one or more of the dynamic routing protocols included, OPNsense firewall administrators must install os-frr, FRRouting Protocol Suite plugin.
是的,下一代防火墙 (NGFW) 解决方案支持 IPv4 和 IPv6 路由协议。例如,由 Zenarmor 下一代防火墙插件提供支持的 OPNsense 提供动态路由协议,如 RIP v1 和 v2、OSPFv2 和 v3 以及 BGPv4。为了使用所包含的一个或多个动态路由协议,OPNsense 防火墙管理员必须安装 os-frr,FRRouting 协议套件插件。
What is the Most Used Routing Protocol?
最常用的路由协议是什么?
OSPF and EIGRP are the most used Interior routing protocols. And the most used Exterior routing protocol is BGP .
OSPF 和 EIGRP 是最常用的内部路由协议。最常用的外部路由协议是 BGP。
via:
-
7 Types of Routing Protocols - Last updated on Jun 20, 2024 by Zenarmor
https://www.zenarmor.com/docs/network-basics/types-of-routing-protocols