一、简介
遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm, GA)是一种用于解决优化和搜索问题的进化算法。它基于自然选择和遗传学原理,通过模拟生物进化过程来寻找最优解。
以下是遗传算法的主要步骤和概念:
初始化种群(Initialization):随机生成一组可能的解(个体),形成初始种群。
适应度评估(Fitness Evaluation) :根据适应度函数评估每个个体的质量,即其解问题的效果。
选择(Selection) :根据适应度选择较优的个体进行繁殖。常见的选择方法包括轮盘赌选择、锦标赛选择和排序选择。
交叉(Crossover):将两个个体的部分基因组合生成新的个体(子代)。交叉操作模拟生物的基因重组,常见的交叉方法有单点交叉和多点交叉。
变异(Mutation):随机改变个体的部分基因,以增加种群的多样性,防止算法陷入局部最优。变异操作模拟生物的基因突变。
替换(Replacement):将子代个体加入种群中,通常会替换掉适应度较低的个体,以保持种群规模恒定。
终止条件(Termination Condition):当达到预定的终止条件时(如运行一定代数、适应度达到某个阈值),算法停止,输出最优解。
遗传算法通常用于解决以下类型的问题:
- 优化问题,例如函数优化、路径优化(如旅行商问题)。
- 搜索问题,例如求解数独、密码破解。
- 机器学习中的参数优化,例如神经网络权重优化。
优点
- 遗传算法具有全局搜索能力,能够在较大的搜索空间中找到全局最优解。
- 适用于复杂的、多维的、非线性的优化问题。
- 不依赖于问题的具体数学性质,可以处理各种类型的目标函数和约束条件。
缺点
- 计算代价较高,尤其是适应度评估过程可能耗时。
- 需要精心设计适应度函数、选择方法、交叉和变异操作,才能获得好的效果。
- 对于某些问题,可能会收敛到局部最优解,而非全局最优解。
二、算法介绍
(1)适应度函数

(2)轮盘赌选择

(3)锦标赛选择

(4)排序选择


(5)单点交叉


应用场景
单点交叉适用于问题规模较小或基因序列较短的情况。
对于复杂问题或基因序列较长的情况,可以考虑多点交叉或均匀交叉等更复杂的交叉方法,以提高解的多样性和质量。
(6) 多点交叉


(7)均匀交叉


(8)变异
通常设置较低的变异率(如 0.1% 到 1%)
三、遗传算法解TSP
python
import copy
import random
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
N = 20000 # 最大迭代次数
city_num = 31
pop_size = 100 # 种群数量
pc = 0.8 # 交叉概率
pm = 0.05 # 变异概率
# 城市坐标
city_position = [(1304, 2312), (3639, 1315), (4177, 2244), (3712, 1399), (3488, 1535),
(3326, 1556), (3238, 1229), (4196, 1004), (4312, 790), (4380, 570),
(3007, 1970), (2562, 1756), (2788, 1491), (2381, 1676), (1332, 695),
(3715, 1678), (3918, 2179), (4061, 2370), (3780, 2212), (3676, 2578),
(4029, 2838), (4263, 2931), (3429, 1908), (3507, 2367), (3394, 2643),
(3439, 3201), (2935, 3240), (3140, 3550), (2545, 2357), (2778, 2826), (2370, 2975)]
# 距离矩阵,城市之间的距离
dis = np.zeros((31, 31))
for i in range(31):
for j in range(31):
if i != j:
dis[i][j] = ((city_position[i][0] - city_position[j][0]) ** 2 + (city_position[i][1] - city_position[j][1]) ** 2) ** 0.5
# 初始化种群并去重
def init(pop_size, city_num):
population = []
while len(population) < pop_size:
temp = random.sample(range(city_num), city_num)
if temp not in population:
population.append((temp))
return population
# 适应度函数
def fitness(population, dis):
fitness = []
for i in range(len(population)):
distance = 0
for j in range(city_num - 1):
distance += dis[population[i][j]][population[i][j + 1]]
distance += dis[population[i][-1]][population[i][0]]
if distance == 0:
f = float('inf')
else:
f = 1 / (distance ** 2)
fitness.append(f)
return fitness
# 选择函数:轮盘赌选择
def select(population, fitness):
index = random.randint(0, pop_size - 1)
num = 0
r = random.uniform(0, sum(fitness))
for i in range(len(population)):
num += fitness[i]
if num >= r:
index = i
break
return population[index]
# 交叉函数
def cross(fa1, fa2):
if random.random() < pc:
chrom1 = fa1[:]
chrom2 = fa2[:]
cpoint1 = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)
cpoint2 = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)
if cpoint1 > cpoint2:
temp = cpoint1
cpoint1 = cpoint2
cpoint2 = temp
temp1 = []
temp2 = []
for i in range(cpoint1, len(chrom1)):
temp1.append(chrom1[i])
temp2.append(chrom2[i])
for i in range(cpoint1, cpoint2 + 1):
chrom1[i] = fa2[i]
chrom2[i] = fa1[i]
new_chrom1 = []
new_chrom2 = []
for i in range(cpoint2 + 1):
new_chrom1.append(chrom1[i])
new_chrom2.append(chrom2[i])
new_chrom1.extend(temp1)
new_chrom2.extend(temp2)
ans1 = []
ans2 = []
for i in range(len(new_chrom1)):
if new_chrom1[i] not in ans1:
ans1.append(new_chrom1[i])
for i in range(len(new_chrom2)):
if new_chrom2[i] not in ans2:
ans2.append(new_chrom2[i])
return ans1, ans2
else:
return fa1[:], fa2[:]
# 变异函数
def mutate(chrom):
if random.random() < pm:
mpoint1 = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)
mpoint2 = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)
temp = chrom[mpoint1]
chrom[mpoint1] = chrom[mpoint2]
chrom[mpoint2] = temp
return chrom
def show(lx, ly, fit_history):
# 画出每代最好适应值的图像
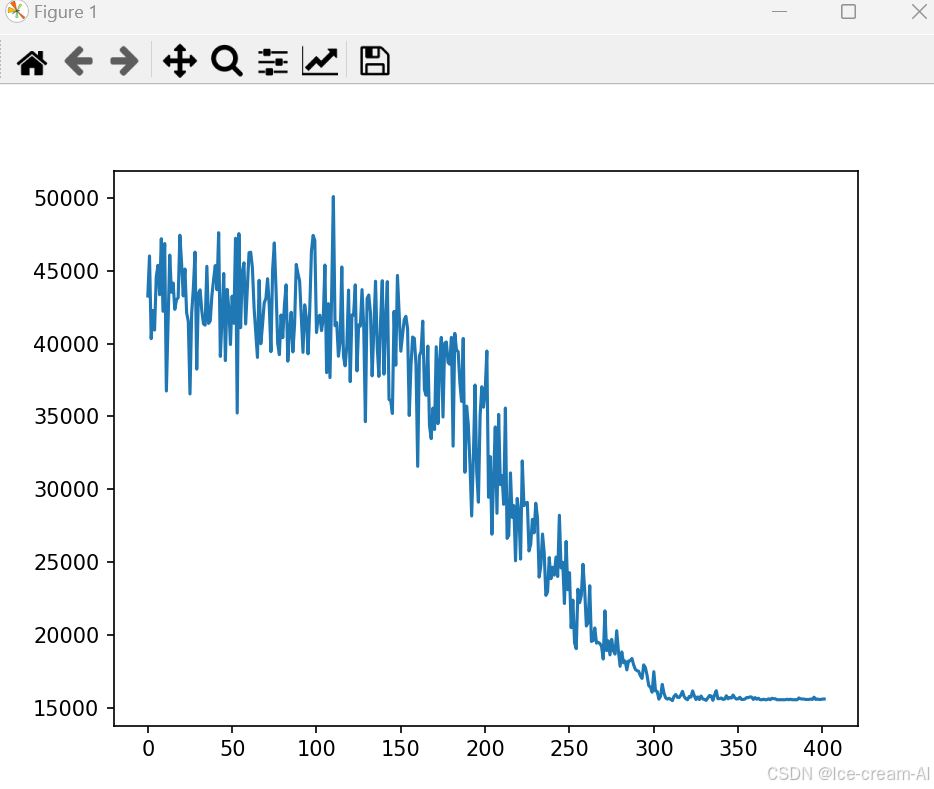
plt.plot(range(len(fit_history)), fit_history)
plt.xlabel("Generation")
plt.ylabel("Fitness")
plt.show()
# 画出最短路径大小的变化图
a = []
for i in range(len(fit_history)):
a.append(math.sqrt(1 / fit_history[i]))
plt.plot(range(len(a)), a)
plt.xlabel("Generation")
plt.ylabel("Best_path_size")
plt.show()
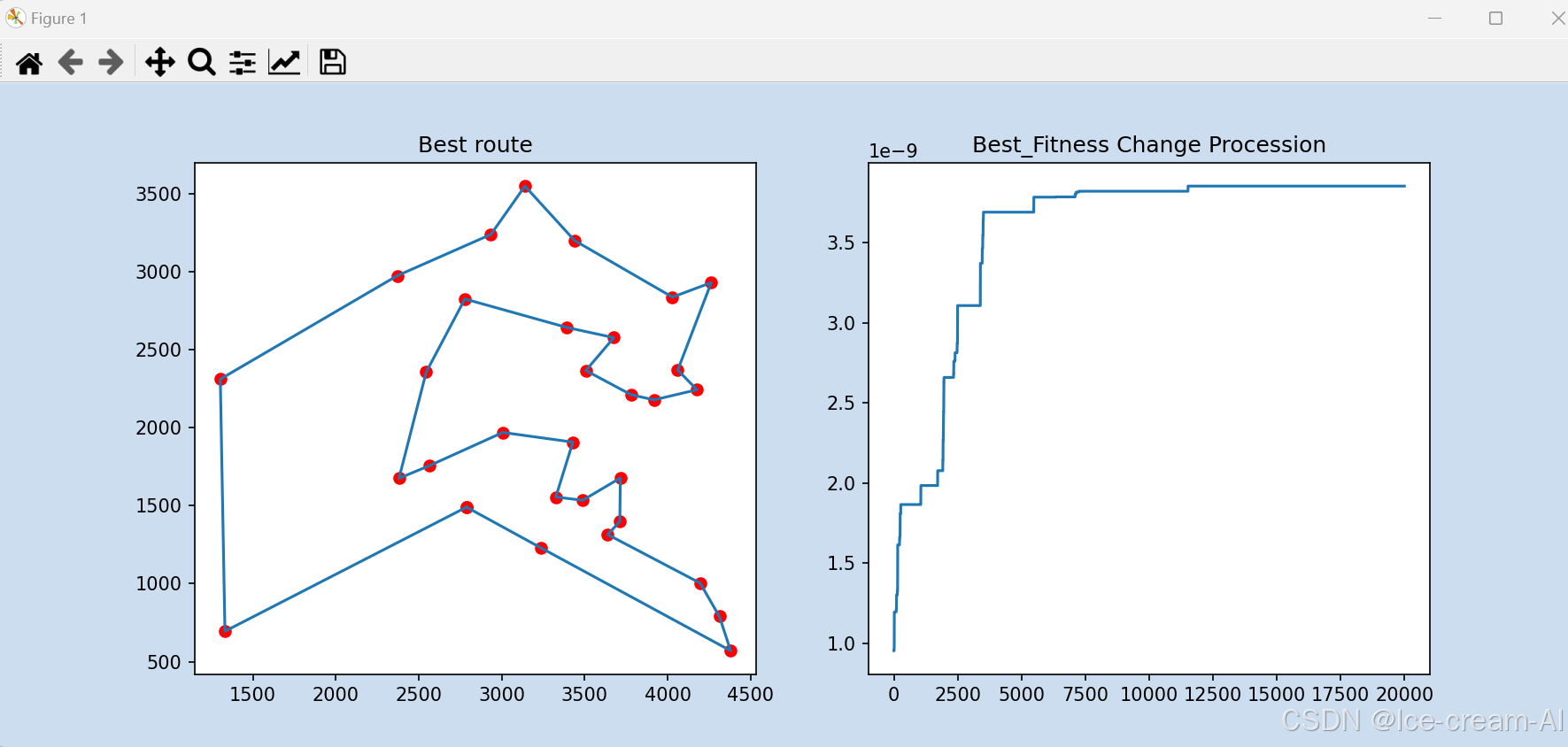
def best_show(x, y, Best_Fitness):
# 定义两个子图
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5), facecolor='#ccddef')
# 定义子图1标题
ax[0].set_title("Best route")
# 定义子图2标题
ax[1].set_title("Best_Fitness Change Procession")
# 画线
ax[0].plot(x, y)
# 画点(第一个子图)
ax[0].scatter(x, y, color='r')
# 画线(第二个子图)
ax[1].plot(range(len(Best_Fitness)), [Best_Fitness[i] for i in range(len(Best_Fitness))])
plt.show()
# 主程序
if __name__ == '__main__':
best_fit = 0.0
ans = []
best_path = []
population = init(pop_size, city_num) # 初始化种群,pop_size:种群个数
for i in range(N):
fit = fitness(population, dis) # 计算适应度列表
max_fit = max(fit) # 因为适应度是采用距离和的平方的倒数,故最大的适应度代表距离最小
max_index = fit.index(max_fit) # 最大适应度的方案索引
lx = []
ly = []
for j in population[max_index][:]:
j = int(j) # 保证整数
lx.append(city_position[j][0])
ly.append(city_position[j][1])
if max_fit > best_fit: # 假如路径更短
best_fit = max_fit # 修正了这里的错别字
ans = population[max_index][:]
x = copy.copy(lx)
y = copy.copy(ly)
best_path.append(best_fit) # 记录适应度变化,为画图准备
# 变异、交叉
new_population = []
n = 0
while n < pop_size:
p1 = select(population, fit)
p2 = select(population, fit)
while p2 == p1:
p2 = select(population, fit)
# 交叉
chrom1, chrom2 = cross(p1, p2)
# 变异
chrom1 = mutate(chrom1)
chrom2 = mutate(chrom2)
new_population.append(chrom1)
new_population.append(chrom2)
n += 2
population = new_population
print("######################################################")
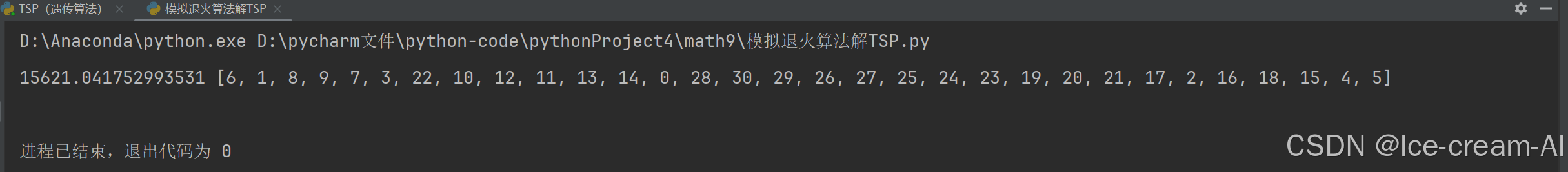
print(f"第{i + 1}代的最优路径为:", ans)
print("最短路径为:", (1 / best_fit) ** 0.5)
show(lx,ly,best_path)
x.append(x[0])
y.append(y[0])
best_show(x,y,best_path)结果:
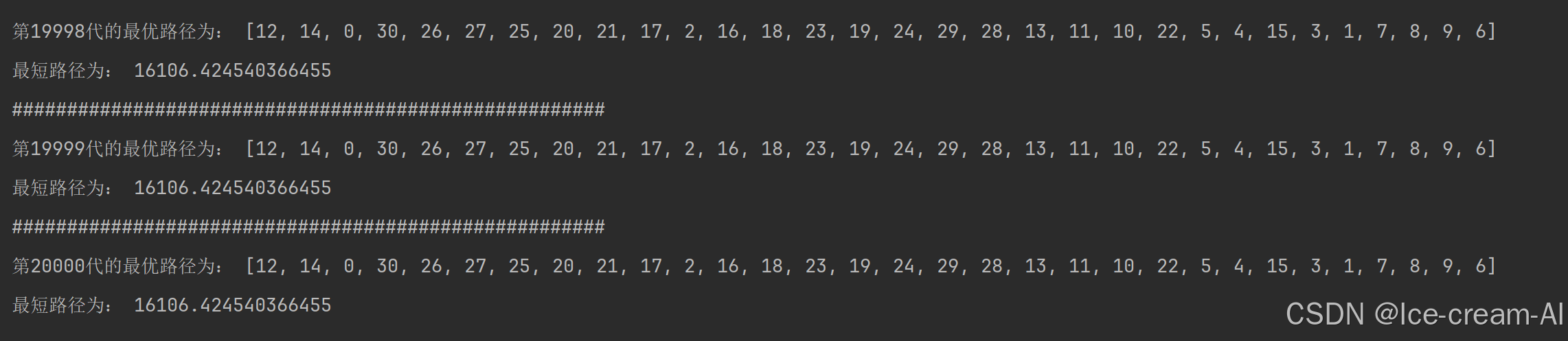
对比模拟退火算法的结果:
(以下是模拟退火算法的结果)