1.迭代器模式概念
用于顺序访问集合对象中的元素,而无需暴露底层的数据结构。这种模式提供了一种访问集合元素的方法,同时隐藏了集合内部的实现细节。
2.举个栗子
正常遍历和迭代器模式遍历模式,如下图
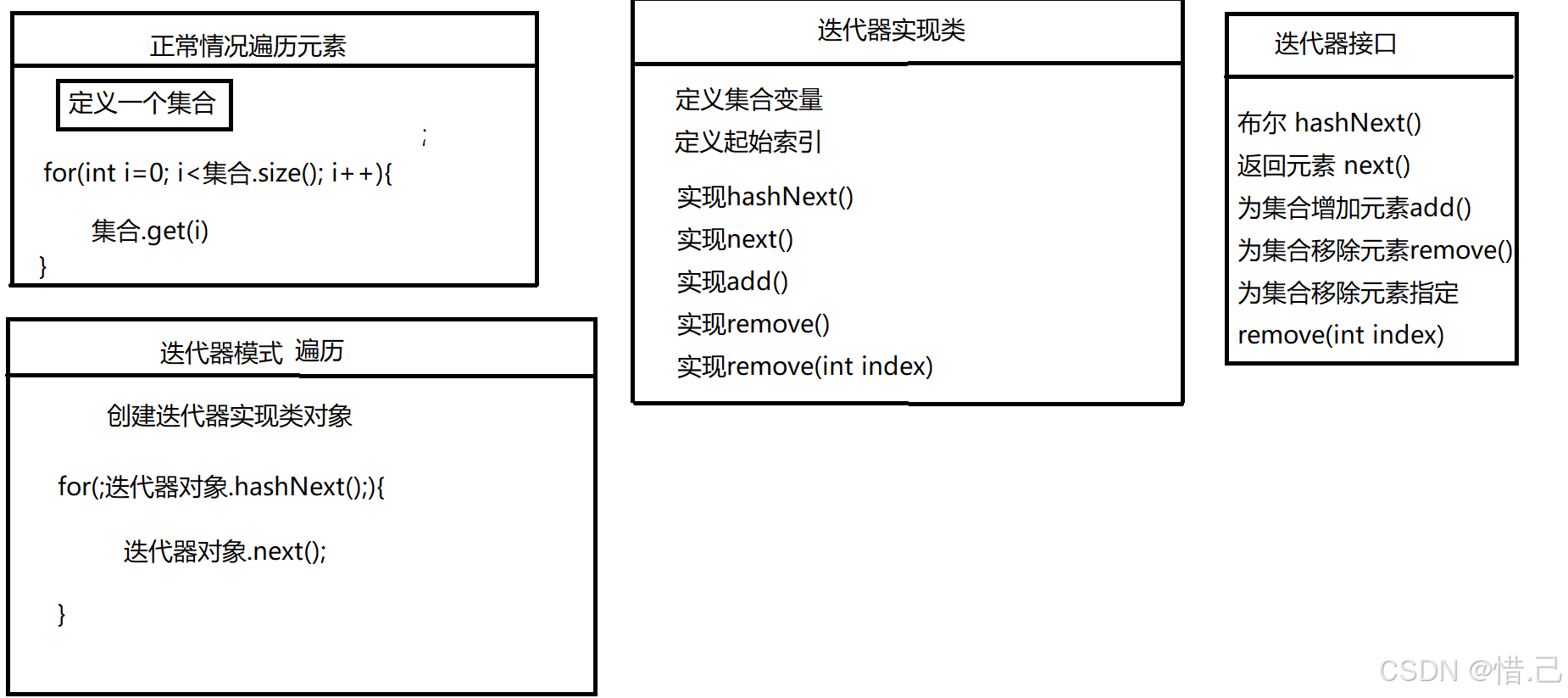
可以看出我们只要遍历迭代器对象,不关注集合本身,依旧可以获取元素,遍历元素
3.代码实现
1)Iterator接口代码
java
package org.xiji.iterator;
/**
* 定义迭代器的行为
*/
public interface Iterator<T> {
/**
* 判断下一个元素是否存在
*
*/
boolean hasNext();
/**
* 获取下一个元素
*
*/
T next();
/**
* 增加一个元素
*/
void add(T t);
/**
* 减少末尾的怨怒是
*/
void remove();
/**
* 通过索引移除元素
*/
void remove(int index);
}2)迭代器实现类
注:迭代器中的index变量相当于C中的指针,当我们遍历失败的时候需要重置为0,否则,下遍历该对象时还会从当前索引继续遍历
java
package org.xiji.iterator;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 定义自己的 列表迭代器
*/
public class MyList<T> implements Iterator<T> {
/***
* 定义遍历元素集合
*/
private List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
/**
*
* 定义起始变量
*/
private int index=0;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (this.index < list.size() || this.index<=0) {
return true;
}
this.index = 0;//指针归零
return false;
}
@Override
public T next() {
//如果遍历的元素在正常范围内继续遍历
if(!hasNext()){
throw new RuntimeException("指针异常");
}
return list.get(this.index++);
}
//为迭代器实现集合添加元素对象
@Override
public void add(T t) {
this.list.add(t);
}
//移除迭代器最后对象
@Override
public void remove() {
if (this.list.size() <= 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("指针超出范围");
}
//移除最后一个元素
this.list.remove(this.list.size() - 1);
}
//移除迭代器指定元素
@Override
public void remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.list.size()) {
throw new RuntimeException("指针超出范围");
}
this.list.remove(index);
}
}3)迭代器测试类
注:使用while循环实现,for循环上面已经给了
java
package org.xiji.iterator;
/**
* 迭代器测试类
*/
public class IteratorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyList<String> stringMyList = new MyList<>();
//字符串迭代器类
stringMyList.add("张三");
stringMyList.add("李四");
stringMyList.add("王五");
while (stringMyList.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(stringMyList.next());
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------- ");
stringMyList.remove();
while (stringMyList.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(stringMyList.next());
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------");
stringMyList.add("小久");
while (stringMyList.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(stringMyList.next());
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------");
stringMyList.remove(1);
while (stringMyList.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(stringMyList.next());
}
}
}4)运行结果
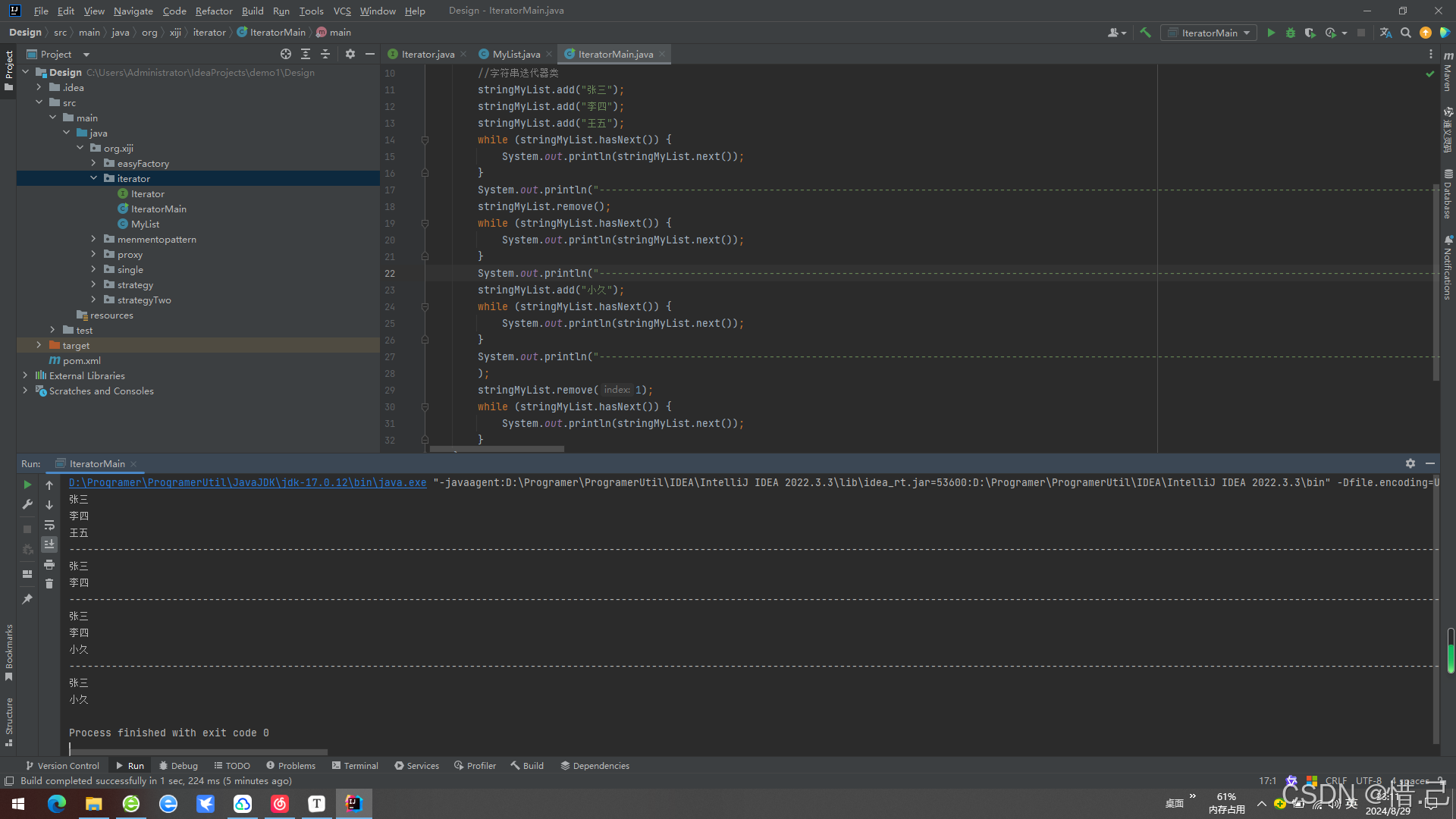
4.个人理解
感觉就是对集合的操作的二次封装,简化操作,不关心内部实现