1. 简介
方案概述
我们使用 Filebeat 作为日志收集器,接入到 Redis 队列,然后消费队列中的日志数据流转到 Logstash 中进行解析处理,最后输出到 Elasticsearch 中,再由 Kibana 展示到页面上。我们采用 Elasticsearch 3 节点集群来确保高可用性和扩展性。
系统架构
- Filebeat:日志收集器,负责从各个日志源收集日志并发送到 Redis。
- Redis:消息队列,暂存日志数据,确保日志数据的可靠传输。
- Logstash:日志处理器,从 Redis 中消费日志数据,进行解析和处理,然后发送到 Elasticsearch。
- Elasticsearch:分布式搜索和分析引擎,存储和索引日志数据。
- Kibana:数据可视化工具,展示 Elasticsearch 中的日志数据。
部署架构
Elasticsearch
- 节点数量:3 个节点,组成一个高可用集群。
- 配置:每个节点都配置为主节点和数据节点,确保集群的高可用性和数据冗余。
Logstash
- 实例数量:实现高可用性和负载均衡至少需要 2 个 Logstash 实例。
- 负载均衡 :可以使用 Redis 的
list数据结构来实现负载均衡,多个 Logstash 实例可以同时从 Redis 中消费日志数据。
Redis
- 部署方式 :可以根据业务需求选择单机或集群模式。
- 单机模式:适用于日志量较小的场景,配置简单。
- 集群模式:适用于日志量较大的场景,提供更高的可用性和扩展性。
- 数据结构 :使用
list数据结构来暂存日志数据,确保数据的有序性和可靠传输。
Filebeat
- 部署方式:Filebeat 部署在每个日志源服务器上,负责收集本地日志并发送到 Redis。Kubernetes 中使用 Dasemonset 部署 Filebeat 在每一个节点,收集日志可以实现指定命名空间和指定应用 pod。
- 配置 :配置 Filebeat 发送日志到 Redis 的
list中。
Kibana
- 实例数量:通常部署 1 个实例即可,除非有高并发访问需求,可以考虑部署多个实例并使用负载均衡器进行流量分发。
- 配置:配置 Kibana 连接到 Elasticsearch 集群。
方案示意图
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+
| | | | | | | |
| Filebeat | --> | Redis | --> | Logstash | --> | Elasticsearch |
| | | (list) | | | | |
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+总结
- Elasticsearch:3 个节点组成高可用集群。
- Logstash:至少部署 2 个实例,实现高可用性和负载均衡。
- Redis:根据业务需求选择单机或集群模式。
- Filebeat:部署在每个日志源服务器上,负责收集日志并发送到 Redis。
- Kibana:通常部署 1 个实例,除非有高并发访问需求。
通过这种部署架构,可以确保日志收集、处理、存储和展示的高可用性和扩展性。
但是经过测试,使用了 redis 效率有些低,后面我们又把 redis 停用了,再加上 filebeat 是推荐直接接入 es,logstash 可以需要的时候使用。
2. 安装
因为涉及到证书生成,我们使用单机把 es 集群拉起,然后再把数据目录和证书目录同步到其它物理节点上。
docker 和 docker-compose 环境准备,略。
hosts:
10.1.205.165 elk-node1
10.1.205.166 elk-node2
10.1.205.167 elk-node32.1 单机启动 es 集群
bash
mkdir -p /data/docker/elk
cd /data/docker/elk
mkdir -p es01/data es02/data es03/data kibana
chown 1000.1000 -R es01/data es02/data es03/data kibana
vim .env.env 内容如下:
# Password for the 'elastic' user (at least 6 characters)
ELASTIC_PASSWORD=changeme
# Password for the 'kibana_system' user (at least 6 characters)
KIBANA_PASSWORD=changeme
# Version of Elastic products
STACK_VERSION=8.15.0
# Set the cluster name
CLUSTER_NAME=docker-cluster
# Set to 'basic' or 'trial' to automatically start the 30-day trial
LICENSE=basic
#LICENSE=trial
# Port to expose Elasticsearch HTTP API to the host
ES_PORT=9200
#ES_PORT=127.0.0.1:9200
# Port to expose Kibana to the host
KIBANA_PORT=5601
#KIBANA_PORT=80
# Increase or decrease based on the available host memory (in bytes)
MEM_LIMIT=1073741824
# Project namespace (defaults to the current folder name if not set)
#COMPOSE_PROJECT_NAME=myprojectdocker-compose.yml 如下(下面证书生成中最好把 IP 也加上),
yaml
version: "2.2"
services:
setup:
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
user: "0"
command: >
bash -c '
if [ x${ELASTIC_PASSWORD} == x ]; then
echo "Set the ELASTIC_PASSWORD environment variable in the .env file";
exit 1;
elif [ x${KIBANA_PASSWORD} == x ]; then
echo "Set the KIBANA_PASSWORD environment variable in the .env file";
exit 1;
fi;
if [ ! -f config/certs/ca.zip ]; then
echo "Creating CA";
bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca --silent --pem -out config/certs/ca.zip;
unzip config/certs/ca.zip -d config/certs;
fi;
if [ ! -f config/certs/certs.zip ]; then
echo "Creating certs";
echo -ne \
"instances:\n"\
" - name: es01\n"\
" dns:\n"\
" - es01\n"\
" - localhost\n"\
" ip:\n"\
" - 127.0.0.1\n"\
" - name: es02\n"\
" dns:\n"\
" - es02\n"\
" - localhost\n"\
" ip:\n"\
" - 127.0.0.1\n"\
" - name: es03\n"\
" dns:\n"\
" - es03\n"\
" - localhost\n"\
" ip:\n"\
" - 127.0.0.1\n"\
> config/certs/instances.yml;
bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --silent --pem -out config/certs/certs.zip --in config/certs/instances.yml --ca-cert config/certs/ca/ca.crt --ca-key config/certs/ca/ca.key;
unzip config/certs/certs.zip -d config/certs;
fi;
echo "Setting file permissions"
chown -R root:root config/certs;
find . -type d -exec chmod 750 \{\} \;;
find . -type f -exec chmod 640 \{\} \;;
echo "Waiting for Elasticsearch availability";
until curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://es01:9200 | grep -q "missing authentication credentials"; do sleep 30; done;
echo "Setting kibana_system password";
until curl -s -X POST --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt -u "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://es01:9200/_security/user/kibana_system/_password -d "{\"password\":\"${KIBANA_PASSWORD}\"}" | grep -q "^{}"; do sleep 10; done;
echo "All done!";
'
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "[ -f config/certs/es01/es01.crt ]"]
interval: 1s
timeout: 5s
retries: 120
es01:
depends_on:
setup:
condition: service_healthy
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
- ./es01/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:rw
ports:
- ${ES_PORT}:9200
restart: always
environment:
- node.name=es01
- cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME}
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- discovery.seed_hosts=es02,es03
- ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- xpack.security.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es01/es01.key
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es01/es01.crt
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es01/es01.key
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es01/es01.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate
- xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE}
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120
es02:
depends_on:
- es01
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
- ./es02/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:rw
restart: always
environment:
- node.name=es02
- cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME}
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es03
- ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- xpack.security.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es02/es02.key
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es02/es02.crt
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es02/es02.key
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es02/es02.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate
- xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE}
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120
es03:
depends_on:
- es02
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
- ./es03/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:rw
restart: always
environment:
- node.name=es03
- cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME}
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es02
- ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- xpack.security.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es03/es03.key
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es03/es03.crt
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es03/es03.key
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es03/es03.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate
- xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE}
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120
kibana:
depends_on:
es01:
condition: service_healthy
es02:
condition: service_healthy
es03:
condition: service_healthy
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/kibana/config/certs
- ./kibana/data:/usr/share/kibana/data:rw
ports:
- ${KIBANA_PORT}:5601
environment:
- SERVERNAME=kibana
- ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=https://es01:9200
- ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME=kibana_system
- ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD=${KIBANA_PASSWORD}
- ELASTICSEARCH_SSL_CERTIFICATEAUTHORITIES=config/certs/ca/ca.crt
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s -I http://localhost:5601 | grep -q 'HTTP/1.1 302 Found'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120先拉起来:
bash
docker-compose up -d启动成功后,浏览器访问进去,看看能否正常访问。用户使用 elastic,密码使用 .env 中设置的 ELASTIC_PASSWORD
没有问题后,我们关闭 es 集群:
bash
docker-compose down2.2 启动 es node1 节点
因为刚刚是单机启动了 3 个节点的 es 集群,先把文件和数据目录同步到其它节点:
bash
# 同步之前先在节点 2、3 创建 /data/docker/elk 目录
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/.env elk-node2:/data/docker/elk/.env
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/docker-compose.yml elk-node2:/data/docker/elk/docker-compose.yml
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/certs/ elk-node2:/data/docker/elk/certs/
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/es02/ elk-node2:/data/docker/elk/es02/
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/.env elk-node3:/data/docker/elk/.env
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/docker-compose.yml elk-node3:/data/docker/elk/docker-compose.yml
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/certs/ elk-node3:/data/docker/elk/certs/
rsync -avz /data/docker/elk/es03/ elk-node3:/data/docker/elk/es03/现在修改 elk-node1 的 docker-compose.yml:
因为证书不需要再处理了,把 setup 段注释,并且以下段注释
yaml
depends_on:
setup:
condition: service_healthy
yaml
version: "2.2"
services:
# setup:
# image: 10.1.205.109/library/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
# volumes:
# - ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
# user: "0"
# network_mode: host
# extra_hosts:
# - "es01:10.1.205.165"
# - "es02:10.1.205.166"
# - "es03:10.1.205.167"
# command: >
# bash -c '
# if [ x${ELASTIC_PASSWORD} == x ]; then
# echo "Set the ELASTIC_PASSWORD environment variable in the .env file";
# exit 1;
# elif [ x${KIBANA_PASSWORD} == x ]; then
# echo "Set the KIBANA_PASSWORD environment variable in the .env file";
# exit 1;
# fi;
# if [ ! -f config/certs/ca.zip ]; then
# echo "Creating CA";
# bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca --silent --pem -out config/certs/ca.zip;
# unzip config/certs/ca.zip -d config/certs;
# fi;
# if [ ! -f config/certs/certs.zip ]; then
# echo "Creating certs";
# echo -ne \
# "instances:\n"\
# " - name: es01\n"\
# " dns:\n"\
# " - es01\n"\
# " - localhost\n"\
# " ip:\n"\
# " - 127.0.0.1\n"\
# " - name: es02\n"\
# " dns:\n"\
# " - es02\n"\
# " - localhost\n"\
# " ip:\n"\
# " - 127.0.0.1\n"\
# " - name: es03\n"\
# " dns:\n"\
# " - es03\n"\
# " - localhost\n"\
# " ip:\n"\
# " - 127.0.0.1\n"\
# > config/certs/instances.yml;
# bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --silent --pem -out config/certs/certs.zip --in config/certs/instances.yml --ca-cert config/certs/ca/ca.crt --
ca-key config/certs/ca/ca.key;
# unzip config/certs/certs.zip -d config/certs;
# fi;
# echo "Setting file permissions"
# chown -R root:root config/certs;
# find . -type d -exec chmod 750 \{\} \;;
# find . -type f -exec chmod 640 \{\} \;;
# echo "Waiting for Elasticsearch availability";
# until curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://es01:9200 | grep -q "missing authentication credentials"; do sleep 30; done;
# echo "Setting kibana_system password";
# until curl -s -X POST --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt -u "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://es01:9200/_se
curity/user/kibana_system/_password -d "{\"password\":\"${KIBANA_PASSWORD}\"}" | grep -q "^{}"; do sleep 10; done;
# echo "All done!";
# '
# healthcheck:
# test: ["CMD-SHELL", "[ -f config/certs/es01/es01.crt ]"]
# interval: 1s
# timeout: 5s
# retries: 120
es01:
# depends_on:
# setup:
# condition: service_healthy
container_name: es01
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
- ./es01/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:rw
ports:
- ${ES_PORT}:9200
- 9300:9300
restart: always
network_mode: host
# 添加 hosts
extra_hosts:
- "es01:10.1.205.165"
- "es02:10.1.205.166"
- "es03:10.1.205.167"
environment:
- node.name=es01
- cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME}
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- discovery.seed_hosts=es02,es03
- ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- xpack.security.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es01/es01.key
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es01/es01.crt
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es01/es01.key
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es01/es01.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate
- xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE}
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120
kibana:
depends_on:
es01:
condition: service_healthy
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/kibana/config/certs
- ./kibana/data:/usr/share/kibana/data:rw
ports:
- ${KIBANA_PORT}:5601
environment:
- SERVERNAME=kibana
- ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=https://es01:9200
- ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME=kibana_system
- ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD=${KIBANA_PASSWORD}
- ELASTICSEARCH_SSL_CERTIFICATEAUTHORITIES=config/certs/ca/ca.crt
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s -I http://localhost:5601 | grep -q 'HTTP/1.1 302 Found'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 1202.3 启动 es node2 节点
docker-compose.yml
yml
version: "2.2"
services:
test_es01:
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
user: "0"
extra_hosts:
- "es01:10.1.205.165"
- "es02:10.1.205.166"
- "es03:10.1.205.167"
restart: always
network_mode: host
command: >
bash -c '
sleep infinity
'
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://es01:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120
es02:
depends_on:
test_es01:
condition: service_healthy
container_name: es02
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
extra_hosts:
- "es01:10.1.205.165"
- "es02:10.1.205.166"
- "es03:10.1.205.167"
ports:
- ${ES_PORT}:9200
- 9300:9300
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
- ./es02/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:rw
restart: always
environment:
- node.name=es02
- cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME}
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es03
- ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- xpack.security.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es02/es02.key
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es02/es02.crt
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es02/es02.key
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es02/es02.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate
- xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE}
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120启动:
bash
docker-compose up -d2.4 启动 es node3 节点
docker-compose.yml
yml
version: "2.2"
services:
test_es02:
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
user: "0"
extra_hosts:
- "es01:10.1.205.165"
- "es02:10.1.205.166"
- "es03:10.1.205.167"
restart: always
network_mode: host
command: >
bash -c '
sleep infinity
'
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://es02:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120
es03:
depends_on:
test_es02:
condition: service_healthy
container_name: es03
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION}
volumes:
- ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs
- ./es03/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:rw
restart: always
environment:
- node.name=es03
- cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME}
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es02
- ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- xpack.security.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es03/es03.key
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es03/es03.crt
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es03/es03.key
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es03/es03.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate
- xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE}
mem_limit: ${MEM_LIMIT}
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
healthcheck:
test:
[
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'",
]
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120启动:
bash
docker-compose up -d
# 最好是 3 个节点都试下
# 如果不行,进一个节点 `elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic`,再测试`
curl -X GET "https://es01:9200/_cluster/health?pretty" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-u elastic:密码" \
--cacert certs/ca/ca.crt启动后浏览器访问 https://10.1.205.165:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
验证的话,输入 elastic 的用户和密码。
3. 安装 kibana
上面已经有安装 kibana了,略。
报错:
-response-actions] with timeout of [5m] and run interval of [60s]
[2024-08-27T10:09:54.254+00:00][ERROR][elasticsearch-service] Unable to retrieve version information from Elasticsearch nodes. Request timed out
[2024-08-27T10:09:54.753+00:00][ERROR][elasticsearch-service] Unable to retrieve version information from Elasticsearch nodes. security_exception
Root causes:
security_exception: unable to authenticate user [kibana_system] for REST request [/_nodes?filter_path=nodes.*.version%2Cnodes.*.http.publish_address%2Cnodes.*.ip]
[2024-08-27T10:09:54.908+00:00][INFO ][plugins.screenshotting.chromium] Browser executable: /usr/share/kibana/node_modules/@kbn/screenshotting-plugin/chromium/headless_shell-linux_x64/headless_shell可能是因为你清理了目录和数据,没有执行打开 setup 这个初始化一次。
4. 安装 logstash
将以下段添加到 docker-compose.yml 中
logstash:
image: docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:8.15.0
restart: always
extra_hosts:
- "es01:10.1.205.165"
- "es02:10.1.205.166"
- "es03:10.1.205.167"
network_mode: host
volumes:
- ./logstash/pipeline:/usr/share/logstash/pipeline/
bash
cd /data/docker/elk
docker-compose up -d
docker cp elk-logstash-1:/usr/share/logstash/config logstash/
chown 1000.1000 -R logstash
yaml
volumes:
- ./logstash/data:/usr/share/logstash/data/
- ./logstash/pipeline:/usr/share/logstash/pipeline/
- ./logstash/config:/usr/share/logstash/config/
bash
cd /data/docker/elk
chown 1000.1000 -R certs在浏览器中进入 kibana,点左边的 "management" -> "Stack Managerment",然后在 "Security" 那点击 "Users",选择 "logstash_system",修改它的密码,下面用得到。
编辑 logstash/config/logstash.yml,把刚才获取到的密码替换进去:
yaml
http.host: "0.0.0.0"
xpack.monitoring.enabled: true
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.hosts: [ "https://es01:9200" ]
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: "logstash_system"
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: "logstash_passowrd"
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authority: "/usr/share/logstash/certs/ca/ca.crt"这里给 2 个 pipeline:
k8s-filebeat.conf:
yaml
#
input {
beats {
port => 5044
}
}
filter {
}
output {
# 处理解析成功的事件
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["https://es01:9200", "https://es02:9200", "https://es03:9200"]
index => "logstash-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
user => "logstash_writer"
password => "logstash_password"
ssl => true
cacert => "/usr/share/logstash/certs/ca/ca.crt"
}
# stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}k8s-filebeat-redis.conf:
yaml
#
input {
redis {
host => "10.1.205.167" # Redis 服务器的 IP 地址
port => 6379 # Redis 服务器的端口
data_type => "list" # 数据类型为列表
key => "filebeat" # Redis 列表的键名
password => "redispwd" # 如果 Redis 设置了密码,请在此处填写
}
}
filter {
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["https://es01:9200", "https://es02:9200", "https://es03:9200"]
index => "logstash-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
user => "logstash_writer"
password => "logstash_password"
ssl => true
cacert => "/usr/share/logstash/certs/ca/ca.crt"
}
# stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}创建用户和角色:
bash
cd /data/docker/elk
curl -X POST "https://127.0.0.1:9200/_security/user/logstash_writer" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-u elastic:$ELASTIC_PASSWORD \
--cacert certs/ca/ca.crt \
-d '{
"password" : "logstash_password",
"roles" : [ "logstash_writer_role" ]
}'
curl -X POST "https://127.0.0.1:9200/_security/role/logstash_writer_role" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-u elastic:$ELASTIC_PASSWORD \
--cacert certs/ca/ca.crt \
-d '{
"description": "Role for Logstash to write data to Elasticsearch",
"cluster": ["monitor", "manage_index_templates", "manage"],
"indices": [
{
"names": [ "logstash-*" ],
"privileges": ["write", "create", "create_index", "manage"]
}
]
}'然后可以尝试启动,docker-compose up -d
5. 安装 redis
根据 elk 需求,我这里使用单机 redis 即可。
在 es03 上 /data/docker/elk/docker-compose.yml 中添加以下段
yaml
redis:
restart: always
image: redis:7.4
command: redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
volumes:
- ./redis/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
- ./redis/data:/data
ports:
- "6379:6379"下面是 redis.conf
protected-mode yes
port 6379
tcp-backlog 511
timeout 0
tcp-keepalive 300
daemonize no
pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
loglevel notice
logfile ""
databases 16
always-show-logo no
set-proc-title yes
proc-title-template "{title} {listen-addr} {server-mode}"
locale-collate ""
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes
rdbcompression yes
rdbchecksum yes
dbfilename dump.rdb
rdb-del-sync-files no
dir /data
replica-serve-stale-data yes
replica-read-only yes
repl-diskless-sync yes
repl-diskless-sync-delay 5
repl-diskless-sync-max-replicas 0
repl-diskless-load disabled
repl-disable-tcp-nodelay no
replica-priority 100
acllog-max-len 128
lazyfree-lazy-eviction no
lazyfree-lazy-expire no
lazyfree-lazy-server-del no
replica-lazy-flush no
lazyfree-lazy-user-del no
lazyfree-lazy-user-flush no
oom-score-adj no
oom-score-adj-values 0 200 800
disable-thp yes
appendonly no
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
appenddirname "appendonlydir"
appendfsync everysec
no-appendfsync-on-rewrite no
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
aof-load-truncated yes
aof-use-rdb-preamble yes
aof-timestamp-enabled no
slowlog-log-slower-than 10000
slowlog-max-len 128
latency-monitor-threshold 0
notify-keyspace-events ""
hash-max-listpack-entries 512
hash-max-listpack-value 64
list-max-listpack-size -2
list-compress-depth 0
set-max-intset-entries 512
set-max-listpack-entries 128
set-max-listpack-value 64
zset-max-listpack-entries 128
zset-max-listpack-value 64
hll-sparse-max-bytes 3000
stream-node-max-bytes 4096
stream-node-max-entries 100
activerehashing yes
client-output-buffer-limit normal 0 0 0
client-output-buffer-limit replica 256mb 64mb 60
client-output-buffer-limit pubsub 32mb 8mb 60
hz 10
dynamic-hz yes
aof-rewrite-incremental-fsync yes
rdb-save-incremental-fsync yes
jemalloc-bg-thread yes
# 设置 Redis 访问密码
requirepass redispwd
# 设置 最大内存,避免撑爆
maxmemory 2gb启动
bash
cd /data/docker/elk
docker-compose up -d6. 安装 filebeat
6.1 k8s 安装 filebeat
k8s 使用的 filebeat-kubernetes.yaml:
yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: filebeat
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources:
- namespaces
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources:
- replicasets
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources:
- jobs
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat
# should be the namespace where filebeat is running
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups:
- coordination.k8s.io
resources:
- leases
verbs: ["get", "create", "update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- configmaps
resourceNames:
- kubeadm-config
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: filebeat-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
data:
filebeat.yml: |-
# filebeat.inputs:
# - type: filestream
# id: kubernetes-container-logs
# paths:
# - /var/log/containers/*.log
# parsers:
# - container: ~
# prospector:
# scanner:
# fingerprint.enabled: true
# symlinks: true
# file_identity.fingerprint: ~
# processors:
# - add_kubernetes_metadata:
# host: ${NODE_NAME}
# matchers:
# - logs_path:
# logs_path: "/var/log/containers/"
# To enable hints based autodiscover, remove `filebeat.inputs` configuration and uncomment this:
filebeat.autodiscover:
providers:
- type: kubernetes
node: ${NODE_NAME}
hints.enabled: true
hints.default_config:
type: filestream
id: kubernetes-container-logs-${data.kubernetes.pod.name}-${data.kubernetes.container.id}
paths:
- /var/log/containers/*-${data.kubernetes.container.id}.log
parsers:
- container: ~
prospector:
scanner:
fingerprint.enabled: true
symlinks: true
file_identity.fingerprint: ~
ignore_older: 48h
clean_inactive: 72h
close_inactive: 5m
scan_frequency: 10s
processors:
- add_cloud_metadata:
- add_host_metadata:
output.redis:
hosts: ["10.1.205.167:6379"]
key: "filebeat"
datatype: "list"
db: 0
timeout: 10
password: "redispwd"
logging.level: warning
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: filebeat
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
serviceAccountName: filebeat
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
hostNetwork: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
containers:
- name: filebeat
image: docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:8.15.0
args: [
"-c", "/etc/filebeat.yml",
"-e",
]
env:
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
# If using Red Hat OpenShift uncomment this:
#privileged: true
resources:
limits:
memory: 300Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/filebeat.yml
readOnly: true
subPath: filebeat.yml
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/filebeat/data
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
defaultMode: 0640
name: filebeat-config
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
# data folder stores a registry of read status for all files, so we don't send everything again on a Filebeat pod restart
- name: data
hostPath:
# When filebeat runs as non-root user, this directory needs to be writable by group (g+w).
path: /var/lib/filebeat-data
type: DirectoryOrCreate
---6.2 普通服务器安装 filebeat
使用二进制安装,解压后即可使用。
我放在了 /usr/local/filebeat-8.15.0-linux-x86_64,然后做了个软链接。
bash
cd /usr/local/
ln -s filebeat-8.15.0-linux-x86_64 filebeat先弄 2 个启停脚本 start.sh:
bash
#!/usr/bin/env bash
cd "$(dirname "$0")" || return 1
SH_DIR=$(pwd)
nohup $SH_DIR/filebeat 2>&1 &stop.sh:
bash
pkill filebeat filebeat.yml:
yaml
filebeat.config.modules:
# Glob pattern for configuration loading
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
#output.elasticsearch:
# hosts: ["https://10.1.205.165:9200"]
# username: "filebeat_internal"
# password: "YOUR_PASSWORD"
# ssl:
# enabled: true
# # fingerprint=$(openssl x509 -fingerprint -sha256 -noout -in certs/ca/ca.crt | awk -F"=" '{print $2}' | sed 's/://g')
# ca_trusted_fingerprint: "33CB5A3B3ECCA59FDF7333D9XXXXXXXXFD34D5386FF9205AB8E1"
# certs/ca 目录从 es 中拷过来
# certificate_authorities: ["certs/ca/ca.crt"]
output.logstash:
hosts: ["10.1.205.165:5044", "10.1.205.166:5044"]
setup.kibana:
host: "10.1.205.165:5601"
logging.level: warning6.3 导入 filebeat 模板
因为 filebeat 没有直连 es 集群,所以需要创建角色和用户,让 filebeat 直连 es 一次集群创建模板。
PUT /_security/role/filebeat_writer
{
"cluster": ["manage_index_templates", "monitor", "manage_ilm"],
"indices": [
{
"names": ["filebeat-*"],
"privileges": ["write", "create_index", "manage"]
}
],
"applications": [
{
"application": "kibana-.kibana",
"privileges": ["read", "write"],
"resources": ["*"]
}
]
}使用 Dev Tools 创建:
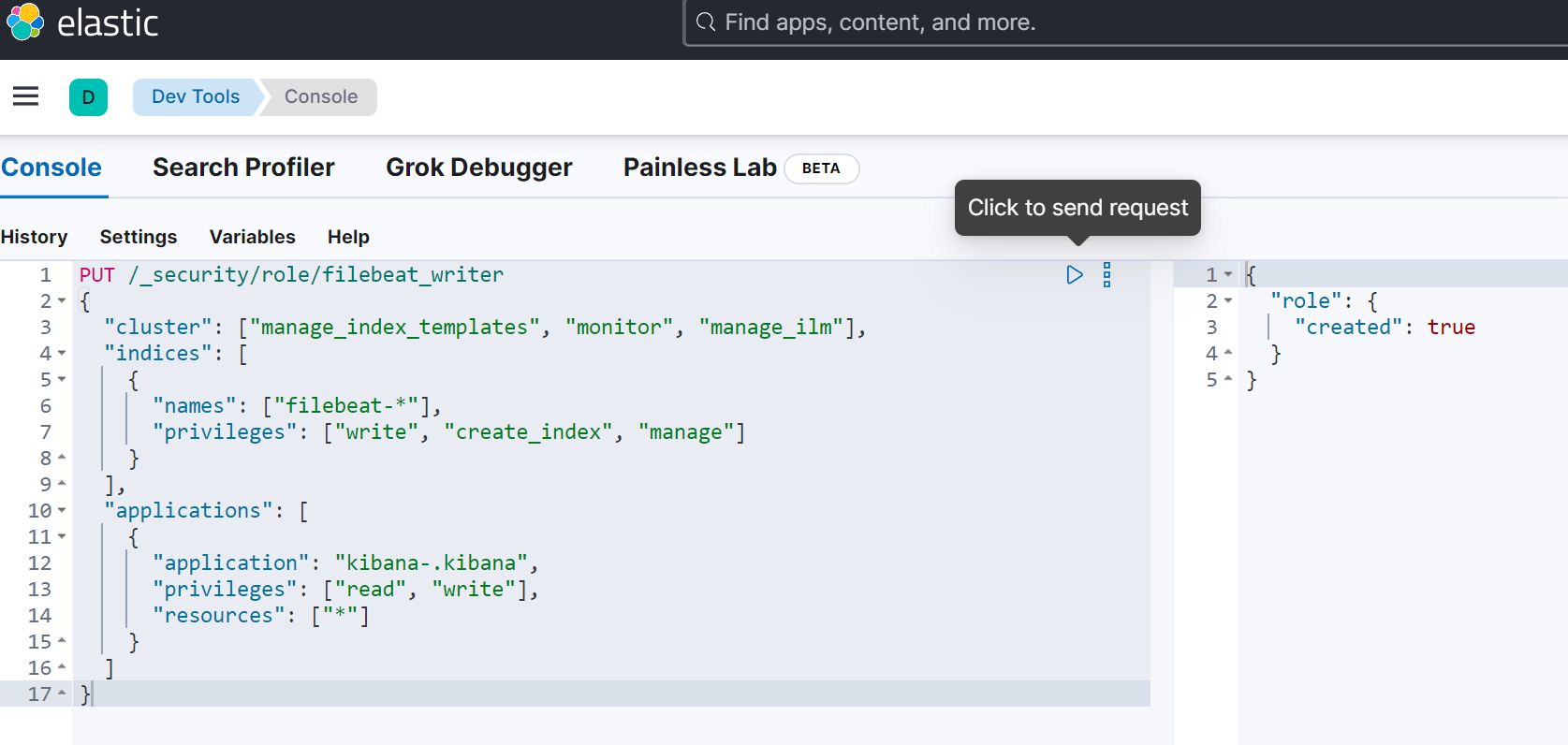
创建角色:
PUT /_security/role/kibana_dashboard_manager
{
"cluster": ["monitor"],
"indices": [
{
"names": ["filebeat-*"],
"privileges": ["read", "view_index_metadata", "create_index"]
}
],
"applications": [
{
"application": "kibana-.kibana",
"privileges": ["all"],
"resources": ["*"]
}
]
}创建用户:
POST /_security/user/filebeat_internal
{
"password" : "YOUR_PASSWORD",
"roles" : [ "filebeat_writer", "kibana_dashboard_manager" ],
"full_name" : "Filebeat Internal User",
"email" : "filebeat_internal@example.com",
"enabled": true
}连接 es 导入模板数据:
bash
cd /data/docker/elk
fingerprint=$(openssl x509 -fingerprint -sha256 -noout -in certs/ca/ca.crt | awk -F"=" '{print $2}' | sed 's/://g')
docker run --net="host" --rm \
-v $(pwd)/certs:/usr/share/filebeat/certs \
10.1.205.109/library/beats/filebeat:8.15.0 setup -e \
-E output.logstash.enabled=false \
-E output.elasticsearch.hosts=['https://10.1.205.165:9200'] \
-E output.elasticsearch.username=filebeat_internal \
-E output.elasticsearch.password=YOUR_PASSWORD \
-E output.elasticsearch.ssl.enabled=true \
-E output.elasticsearch.ssl.ca_trusted_fingerprint=${fingerprint} \
-E output.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authorities=["/usr/share/filebeat/certs/ca/ca.crt"] \
-E setup.kibana.host=10.1.205.165:56017. 问题处理
logstash 写入权限问题
全部启动后,logstash 启动发现老是退出,通过查看日志发现权限问题,
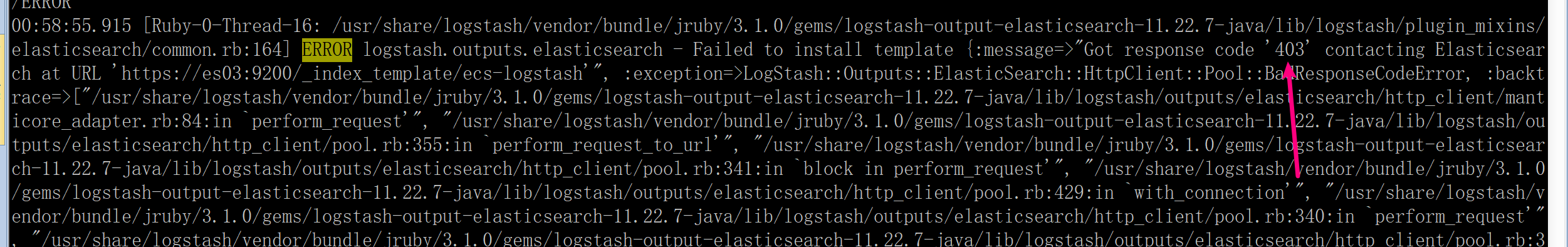
有权限提示:
dle/jruby/3.1.0/gems/logstash-output-elasticsearch-11.22.7-java/lib/logstash/plugin_mixins/elasticsearch/common.rb:172:in `block in after_successful_conn
ection'"], :body=>"{\"error\":{\"root_cause\":[{\"type\":\"security_exception\",\"reason\":\"action [indices:admin/index_template/put] is unauthorized fo
r user [logstash_writer] with effective roles [logstash_writer_role], this action is granted by the cluster privileges [manage_index_templates,manage,all
]\"}],\"type\":\"security_exception\",\"reason\":\"action [indices:admin/index_template/put] is unauthorized for user [logstash_writer] with effective ro
les [logstash_writer_role], this action is granted by the cluster privileges [manage_index_templates,manage,all]\"},\"status\":403}"}完整的权限是(上文已更新):
PUT /_security/role/logstash_writer_role
{
"cluster": ["manage_index_templates", "manage"],
"indices": [
{
"names": ["logstash-*"],
"privileges": ["write", "create", "create_index", "manage"]
}
]
}用了 redis 效率低
filebeat 直接输出日志到 logstash,效率高很多。
8. 索引模式创建
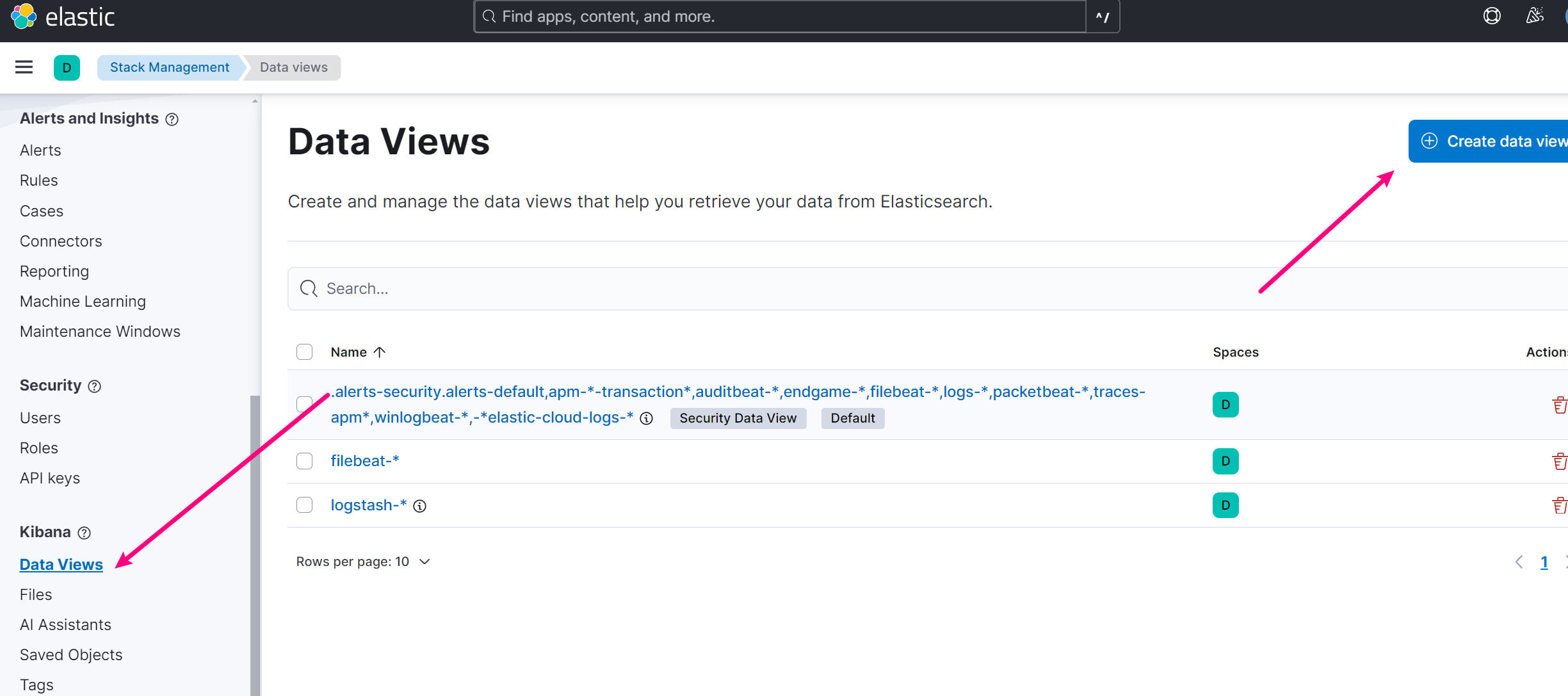
8.1 创建 Data View
新版本 kibana 叫 Data Views了,按如图创建。
8.2 配置 ILM 策略
ILM 有些复杂,需要多熟悉和测试。
以下是一个示例 ILM 策略,配置为在索引创建 15 天后自动删除索引:
- 创建 ILM 策略
你可以在 Kibana 的 Dev Tools 中运行以下命令来创建 ILM 策略:
json
PUT _ilm/policy/delete-after-15-days
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": {
"actions": {
"rollover": {
"max_age": "1d"
}
}
},
"delete": {
"min_age": "15d",
"actions": {
"delete": {}
}
}
}
}
}这个策略定义了两个阶段:
- hot:在索引达到 1 天时进行滚动。
- delete:在索引达到 15 天时删除索引。
- 应用 ILM 策略到索引模板
接下来,你需要将这个 ILM 策略应用到你的索引模板。假设你有一个名为 logstash 的索引模板:
json
PUT _template/logstash_template
{
"index_patterns": ["logstash-*"],
"settings": {
"index.lifecycle.name": "delete-after-15-days",
"index.lifecycle.rollover_alias": "logstash"
}
}这个模板将 delete-after-15-days 策略应用到所有匹配 logstash-* 模式的索引。
- 创建索引并设置别名
json
PUT /logstash-000001
{
"aliases": {
"logstash": {
"is_write_index": true
}
}
}- 验证配置
你可以通过以下命令验证 ILM 策略是否正确应用:
json
GET logstash-*/_ilm/explain这个命令将显示每个索引的 ILM 状态和当前阶段。
通过配置 Elasticsearch 的 Index Lifecycle Management (ILM) 策略,你可以自动管理和清理索引。
参考资料:
1\] https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/docker.html \[2\] https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/docker.html \[3\] https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/docker-config.html \[4\] https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/docker.html \[5\] https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/running-on-kubernetes.html