Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
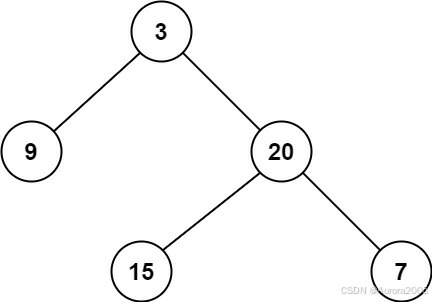
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 2Example 2:
Input: root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Output: 5Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 105]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
递归:
后序:
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode*node){
if(node==NULL)return 0;
int leftDepth=getDepth(node->left);
int rightDepth=getDepth(node->right);
if(node->left==NULL && node->right!=NULL){
return 1+rightDepth;
}
if(node->left!=NULL && node->right==NULL){
return 1+leftDepth;
}
int result=1+min(leftDepth,rightDepth);
return result;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};思路:
1,最小深度需要在中间加上判断左右子树是否一个为空,一个不为空,因为最小深度是指到叶节点的最小深度
2,记得加1
前序:
class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getDepth(TreeNode*node,int depth){
if(node==NULL)return;
if(node->left==NULL && node->right==NULL){
result=min(result,depth);
}
if(node->left){
getDepth(node->left,depth+1);
}
if(node->right){
getDepth(node->right,depth+1);
}
return;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)return 0;
result=INT_MAX;
getDepth(root,1);
return result;
}
};思路:
1,中(result=min(result,depth))左(递归)右(递归),找到最后没有左右子树的叶节点。
2,递归回去时,Depth+1
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)return 0;
int depth=0;
queue<TreeNode*>que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
depth++;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode*node=que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left)que.push(node->left);
if(node->right)que.push(node->right);
if(node->left==NULL && node->right==NULL)return depth;
}
}
return depth;
}
};思路:
1,别忘了每一层遍历depth++
2,TreeNode*node=que.front();
que.pop();这两行代码需要再for循环中用,这样,每次下一层遍历的时候都能刚好把上一层的pop掉