大白话
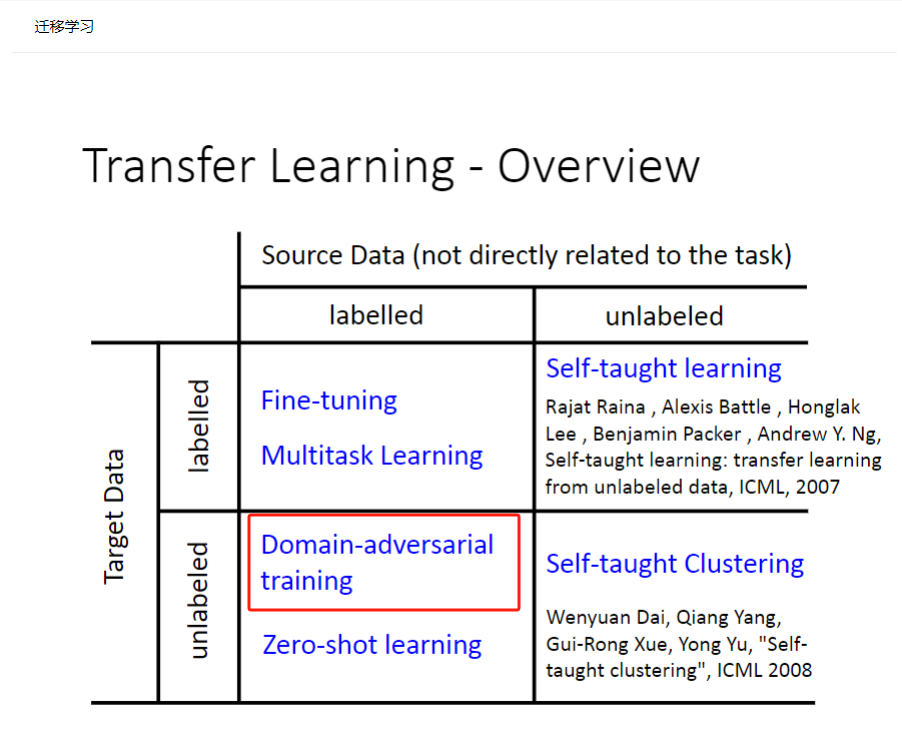
迁移学习就是用不太相同但又有一些联系的A和B数据,训练同一个网络。比如,先用A数据训练一下网络,然后再用B数据训练一下网络,那么就说最后的模型是从A迁移到B的。
迁移学习的具体形式是多种多样的,比如先用A训练好一个网络,然后复制这个网络的某几个层的参数到一个新的网络作为初始化的参数,然后用B数据去训练这个新网络。又或者,面对中文翻译的问题,中文翻译成英文和中文翻译成火星文,前几层在提取特征,可以共享参数层,后面几层由于任务不同就可以各自私有训练。
案例来源:李宏毅课程-机器学习-迁移学习
A数据:是源数据,量大效果好,并且有标签。

B数据:量少,没标签。

目的:希望用A数据先训练网络提取到关键特征,然后预测B数据的标签。但是把他们当作两个任务效果不佳,于是以一种迁移的方法解决--域对抗(先用A训练好模型,再直接用B测试,这样效果不佳;而是希望以一种"迁移"的方法,把A数据的知识拿到B上面用)
直接上代码
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def no_axis_show(img, title='', cmap=None):
# imshow, 缩放模式为nearest。
fig = plt.imshow(img, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
# 不要显示axis。
fig.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
fig.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.title(title)
titles = ['horse', 'bed', 'clock', 'apple', 'cat', 'plane', 'television', 'dog', 'dolphin', 'spider']
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 18))
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(1, 10, i+1)
fig = no_axis_show(plt.imread(f'work/real_or_drawing/train_data/{i}/{500*i}.bmp'), title=titles[i])
python
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 18))
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(1, 10, i+1)
fig = no_axis_show(plt.imread(f'work/real_or_drawing/test_data/0/' + str(i).rjust(5, '0') + '.bmp'))
python
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
titles = ['horse', 'bed', 'clock', 'apple', 'cat', 'plane', 'television', 'dog', 'dolphin', 'spider']
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 18))
original_img = plt.imread(f'work/real_or_drawing/train_data/0/0.bmp')
plt.subplot(1, 5, 1)
no_axis_show(original_img, title='original')
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(original_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
plt.subplot(1, 5, 2)
no_axis_show(gray_img, title='gray scale', cmap='gray')
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(original_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
plt.subplot(1, 5, 2)
no_axis_show(gray_img, title='gray scale', cmap='gray')
canny_50100 = cv2.Canny(gray_img, 50, 100)
plt.subplot(1, 5, 3)
no_axis_show(canny_50100, title='Canny(50, 100)', cmap='gray')
canny_150200 = cv2.Canny(gray_img, 150, 200)
plt.subplot(1, 5, 4)
no_axis_show(canny_150200, title='Canny(150, 200)', cmap='gray')
canny_250300 = cv2.Canny(gray_img, 250, 300)
plt.subplot(1, 5, 5)
no_axis_show(canny_250300, title='Canny(250, 300)', cmap='gray')
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import paddle
import paddle.optimizer as optim
from paddle.io import DataLoader
from paddle.vision.datasets import DatasetFolder
from paddle.nn import Sequential, Conv2D, BatchNorm1D, BatchNorm2D, ReLU, MaxPool2D, Linear
from paddle.vision.transforms import Compose, Grayscale, Transpose, RandomHorizontalFlip, RandomRotation, Resize, ToTensor
python
class Canny(paddle.vision.transforms.transforms.BaseTransform):
def __init__(self, low, high, keys=None):
super(Canny, self).__init__(keys)
self.low = low
self.high = high
def _apply_image(self, img):
Canny = lambda img: cv2.Canny(np.array(img), self.low, self.high)
return Canny(img)
python
source_transform = Compose([
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
RandomRotation(15),
Grayscale(),
Canny(low=170, high=300),
# Transpose(),
ToTensor()
])
target_transform = Compose([
Grayscale(),
Resize((32, 32)),
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
RandomRotation(15, fill=(0,)),
ToTensor()
])
source_dataset = DatasetFolder('work/real_or_drawing/train_data', transform=source_transform)
target_dataset = DatasetFolder('work/real_or_drawing/test_data', transform=target_transform)
source_dataloader = DataLoader(source_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
target_dataloader = DataLoader(target_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(target_dataset, batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
python
class FeatureExtractor(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(FeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
self.conv = Sequential(
Conv2D(1, 64, 3, 1, 1),
BatchNorm2D(64),
ReLU(),
MaxPool2D(2),
Conv2D(64, 128, 3, 1, 1),
BatchNorm2D(128),
ReLU(),
MaxPool2D(2),
Conv2D(128, 256, 3, 1, 1),
BatchNorm2D(256),
ReLU(),
MaxPool2D(2),
Conv2D(256, 256, 3, 1, 1),
BatchNorm2D(256),
ReLU(),
MaxPool2D(2),
Conv2D(256, 512, 3, 1, 1),
BatchNorm2D(512),
ReLU(),
MaxPool2D(2)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x).squeeze()
return x
class LabelPredictor(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(LabelPredictor, self).__init__()
self.layer = Sequential(
Linear(512, 512),
ReLU(),
Linear(512, 512),
ReLU(),
Linear(512, 10),
)
def forward(self, h):
c = self.layer(h)
return c
class DomainClassifier(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(DomainClassifier, self).__init__()
self.layer = Sequential(
Linear(512, 512),
BatchNorm1D(512),
ReLU(),
Linear(512, 512),
BatchNorm1D(512),
ReLU(),
Linear(512, 512),
BatchNorm1D(512),
ReLU(),
Linear(512, 512),
BatchNorm1D(512),
ReLU(),
Linear(512, 1),
)
def forward(self, h):
y = self.layer(h)
return y
python
feature_extractor = FeatureExtractor()
label_predictor = LabelPredictor()
domain_classifier = DomainClassifier()
class_criterion = paddle.nn.loss.CrossEntropyLoss()
domain_criterion = paddle.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
optimizer_F = optim.Adam(parameters=feature_extractor.parameters())
optimizer_C = optim.Adam(parameters=label_predictor.parameters())
optimizer_D = optim.Adam(parameters=domain_classifier.parameters())
python
def train_epoch(source_dataloader, target_dataloader, lamb):
'''
Args:
source_dataloader: source data的dataloader
target_dataloader: target data的dataloader
lamb: 调控adversarial的loss系数。
'''
# D loss: Domain Classifier的loss
# F loss: Feature Extrator & Label Predictor的loss
# total_hit: 计算目前对了几笔 total_num: 目前经过了几笔
running_D_loss, running_F_loss = 0.0, 0.0
total_hit, total_num = 0.0, 0.0
for i, ((source_data, source_label), (target_data, _)) in enumerate(zip(source_dataloader, target_dataloader)):
# source_data = source_data.cuda()
# source_label = source_label.cuda()
# target_data = target_data.cuda()
# 我们把source data和target data混在一起,否则batch_norm可能会算错 (两边的data的mean/var不太一样)
mixed_data = paddle.concat([source_data, target_data], axis=0)
domain_label = paddle.zeros([source_data.shape[0] + target_data.shape[0], 1])
# 设定source data的label为1
domain_label[:source_data.shape[0]] = 1
# Step 1 : 训练Domain Classifier
feature = feature_extractor(mixed_data)
# 因为我们在Step 1不需要训练Feature Extractor,所以把feature detach避免loss backprop上去。
domain_logits = domain_classifier(feature.detach())
# print('domain_logits.shape:', domain_logits.shape, 'domain_label.shape:', domain_label.shape)
loss = domain_criterion(domain_logits, domain_label)
# running_D_loss+= loss.numpy()[0]
running_D_loss+= loss.numpy()
# print('loss:', loss)
loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
# Step 2 : 训练Feature Extractor和Domain Classifier
class_logits = label_predictor(feature[:source_data.shape[0]])
domain_logits = domain_classifier(feature)
# loss为原本的class CE - lamb * domain BCE,相减的原因同GAN中的Discriminator中的G loss。
loss = class_criterion(class_logits, source_label) - lamb * domain_criterion(domain_logits, domain_label)
# running_F_loss+= loss.numpy()[0]
running_F_loss+= loss.numpy()
loss.backward()
optimizer_F.step()
optimizer_C.step()
optimizer_D.clear_grad()
optimizer_F.clear_grad()
optimizer_C.clear_grad()
# print('class_logits.shape:', class_logits.shape, 'source_label.shape:', source_label.shape)
# print('class_logits[0]:', class_logits[0], 'source_label[0]:', source_label[0])
total_hit += np.sum((paddle.argmax(class_logits, axis=1) == source_label).numpy())
total_num += source_data.shape[0]
print(i, end='\r')
return running_D_loss / (i+1), running_F_loss / (i+1), total_hit / total_num
# 训练200 epochs
for epoch in range(200):
train_D_loss, train_F_loss, train_acc = train_epoch(source_dataloader, target_dataloader, lamb=0.1)
paddle.save(feature_extractor.state_dict(), f'extractor_model.pdparams')
paddle.save(label_predictor.state_dict(), f'predictor_model.pdparams')
print('epoch {:>3d}: train D loss: {:6.4f}, train F loss: {:6.4f}, acc {:6.4f}'.format(epoch, train_D_loss, train_F_loss, train_acc))训练结束,预测一波
python
result = []
label_predictor.eval()
feature_extractor.eval()
for i, (test_data, _) in enumerate(test_dataloader):
test_data = test_data
class_logits = label_predictor(feature_extractor(test_data))
x = paddle.argmax(class_logits, axis=1).detach().numpy()
result.append(x)
import pandas as pd
result = np.concatenate(result)
# Generate your submission
df = pd.DataFrame({'id': np.arange(0,len(result)), 'label': result})
df.to_csv('work/DaNN_submission.csv',index=False)训练比较慢,还得是把代码转到cuda上才行,demo可以把epoch减小一点。