目录
[1. 二叉树的前序遍历(简单)](#1. 二叉树的前序遍历(简单))
[1.1. 题目描述](#1.1. 题目描述)
[1.2. 解题思路](#1.2. 解题思路)
[2. 二叉树的中序遍历(中等)](#2. 二叉树的中序遍历(中等))
[2.1. 题目描述](#2.1. 题目描述)
[2.2. 解题思路](#2.2. 解题思路)
[3. 二树的后序遍历(简单)](#3. 二树的后序遍历(简单))
[3.1. 题目描述](#3.1. 题目描述)
[3.2. 解题思路](#3.2. 解题思路)
[4. 求二叉树的层序遍历](#4. 求二叉树的层序遍历)
[4.1. 题目描述](#4.1. 题目描述)
[4.2. 解题思路](#4.2. 解题思路)
[5. 按之字形顺序打印二叉树](#5. 按之字形顺序打印二叉树)
[5.1. 题目描述](#5.1. 题目描述)
[5.2. 解题思路](#5.2. 解题思路)
[6. 二叉树的最大深度](#6. 二叉树的最大深度)
[6.1. 题目描述](#6.1. 题目描述)
[6.2. 解题思路](#6.2. 解题思路)
[7. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)](#7. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一))
[7.1. 题目描述](#7.1. 题目描述)
[7.2. 解题思路](#7.2. 解题思路)
[8. 二叉搜索树与双向链表](#8. 二叉搜索树与双向链表)
[8.1. 题目描述](#8.1. 题目描述)
[8.2. 解题思路](#8.2. 解题思路)
[9. 对称的二叉树](#9. 对称的二叉树)
[9.1. 题目描述](#9.1. 题目描述)
[9.2. 解题思路](#9.2. 解题思路)
[10. 合并二叉树](#10. 合并二叉树)
[10.1. 题目描述](#10.1. 题目描述)
[10.2. 解题思路](#10.2. 解题思路)
[11. 二叉树的镜像](#11. 二叉树的镜像)
[11.1. 题目描述](#11.1. 题目描述)
[11.2. 解题思路](#11.2. 解题思路)
[12. 判断是不是二叉搜索树](#12. 判断是不是二叉搜索树)
[12.1. 题目描述](#12.1. 题目描述)
[12.2. 解题思路](#12.2. 解题思路)
[13. 判断是不是完全二叉树](#13. 判断是不是完全二叉树)
[13.1. 题目描述](#13.1. 题目描述)
[13.2. 解题思路](#13.2. 解题思路)
[14. 判断是不是平衡二叉树](#14. 判断是不是平衡二叉树)
[14.1. 题目描述](#14.1. 题目描述)
[14.2. 解题思路](#14.2. 解题思路)
[15. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](#15. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先)
[15.1. 题目描述](#15.1. 题目描述)
[15.2. 解题思路](#15.2. 解题思路)
[16. 在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先](#16. 在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先)
[16.1. 题目描述](#16.1. 题目描述)
[16.2. 解题思路](#16.2. 解题思路)
[17. 序列化二叉树](#17. 序列化二叉树)
[17.1. 题目描述](#17.1. 题目描述)
[17.2. 解题思路](#17.2. 解题思路)
[18. 重建二叉树](#18. 重建二叉树)
[18.1. 题目描述](#18.1. 题目描述)
[18.2. 解题思路](#18.2. 解题思路)
[19. 输出二叉树的右视图](#19. 输出二叉树的右视图)
[19.1. 题目描述](#19.1. 题目描述)
[19.2. 解题思路](#19.2. 解题思路)
[20. 相同的树](#20. 相同的树)
[20.1. 题目描述](#20.1. 题目描述)
[20.2. 解题思路](#20.2. 解题思路)
[21. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树](#21. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树)
[21.1. 题目描述](#21.1. 题目描述)
[21.2. 解题思路](#21.2. 解题思路)
[22. 二叉树的层序遍历 II](#22. 二叉树的层序遍历 II)
[22.1. 题目描述](#22.1. 题目描述)
[22.2. 解题思路](#22.2. 解题思路)
[23. 平衡二叉树](#23. 平衡二叉树)
[23.1. 题目描述](#23.1. 题目描述)
[23.2. 解题思路](#23.2. 解题思路)
[24. 路径总和](#24. 路径总和)
[24.1. 题目描述](#24.1. 题目描述)
[24.2. 解题思路](#24.2. 解题思路)
[25. 路径总和 II](#25. 路径总和 II)
[25.1. 题目描述](#25.1. 题目描述)
[25.2. 解题思路](#25.2. 解题思路)
[26. 将N叉树编码为二叉树](#26. 将N叉树编码为二叉树)
[26.1. 题目描述](#26.1. 题目描述)
[26.2. 解题思路](#26.2. 解题思路)
[27. 翻转二叉树(简单)](#27. 翻转二叉树(简单))
[27.1. 题目描述](#27.1. 题目描述)
[27.2. 解题思路](#27.2. 解题思路)
[28. 二叉树的直径](#28. 二叉树的直径)
[28.1. 题目描述](#28.1. 题目描述)
[28.2. 解题思路](#28.2. 解题思路)
[29. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](#29. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树)
[29.1. 题目描述](#29.1. 题目描述)
[29.2. 解题思路](#29.2. 解题思路)
[30. 验证二叉搜索树](#30. 验证二叉搜索树)
[30.1. 题目描述](#30.1. 题目描述)
[30.2. 解题思路](#30.2. 解题思路)
[方法一: 递归](#方法一: 递归)
[31. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素](#31. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素)
[31.1. 题目描述](#31.1. 题目描述)
[31.2. 解题思路](#31.2. 解题思路)
[32. 二叉树的右视图](#32. 二叉树的右视图)
[32.1. 题目描述](#32.1. 题目描述)
[32.2. 解题思路](#32.2. 解题思路)
[33. 二叉树展开为链表](#33. 二叉树展开为链表)
[33.1. 题目描述](#33.1. 题目描述)
[33.2. 解题思路](#33.2. 解题思路)
[34. 路径总和 III](#34. 路径总和 III)
[34.1. 题目描述](#34.1. 题目描述)
[34.2. 解题思路](#34.2. 解题思路)
[方法二: 前缀和](#方法二: 前缀和)
[35. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](#35. 二叉树的最近公共祖先)
[35.1. 题目描述](#35.1. 题目描述)
[35.2. 解题思路](#35.2. 解题思路)
[36. 二叉树中的最大路径和(困难)](#36. 二叉树中的最大路径和(困难))
[36.1. 题目描述](#36.1. 题目描述)
[36.2. 解题思路](#36.2. 解题思路)
[37. 叶子相似的树](#37. 叶子相似的树)
[37.1. 题目描述](#37.1. 题目描述)
[37.2. 解题思路](#37.2. 解题思路)
[38. 统计二叉树中好节点的数目](#38. 统计二叉树中好节点的数目)
[38.1. 题目描述](#38.1. 题目描述)
[38.2. 解题思路](#38.2. 解题思路)
[39. 二叉树中的最长交错路径](#39. 二叉树中的最长交错路径)
[39.1. 题目描述](#39.1. 题目描述)
[39.2. 解题思路](#39.2. 解题思路)
[40. 最大层内元素和](#40. 最大层内元素和)
[40.1. 题目描述](#40.1. 题目描述)
[40.2. 解题思路](#40.2. 解题思路)
[41. 二叉搜索树中的搜索](#41. 二叉搜索树中的搜索)
[41.1. 题目描述](#41.1. 题目描述)
[41.2. 解题思路](#41.2. 解题思路)
[42. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点](#42. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点)
[42.1. 题目描述](#42.1. 题目描述)
[42.2 解题思路](#42.2 解题思路)
[43. 数组中的第K个最大元素](#43. 数组中的第K个最大元素)
[43.1. 题目描述](#43.1. 题目描述)
[43.2. 解题思路](#43.2. 解题思路)
[44. 前 K 个高频元素](#44. 前 K 个高频元素)
[44.1. 题目描述](#44.1. 题目描述)
[44.2. 解题思路](#44.2. 解题思路)
[45. 数据流的中位数](#45. 数据流的中位数)
[45.1. 题目描述](#45.1. 题目描述)
[45.2. 解题思路](#45.2. 解题思路)
[方法二:有序集合 + 双指针](#方法二:有序集合 + 双指针)
[46. 无限集中的最小数字](#46. 无限集中的最小数字)
[46.1. 题目描绘](#46.1. 题目描绘)
[46.2. 解题思路](#46.2. 解题思路)
[47. 最大子序列的分数](#47. 最大子序列的分数)
[47.1. 题目描述](#47.1. 题目描述)
[47.2. 解题思路](#47.2. 解题思路)
[48. 雇佣 K 位工人的总代价](#48. 雇佣 K 位工人的总代价)
[48.1. 题目描述](#48.1. 题目描述)
[48.2. 解题思路](#48.2. 解题思路)
[方法一: 双堆简单模拟](#方法一: 双堆简单模拟)
1. 二叉树的前序遍历(简单)
1.1. 题目描述
1.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)


import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public void preorder(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root){
//遇到空节点则返回
if(root == null)
return;
//先遍历根节点
list.add(root.val);
//再去左子树
preorder(list, root.left);
//最后去右子树
preorder(list, root.right);
}
public int[] preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
//添加遍历结果的数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
//递归前序遍历
preorder(list, root);
//返回的结果
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
res[i] = list.get(i);
return res;
}
}

方法二:非递归(扩展思路)


Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
//添加遍历结果的数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//空树返回空数组
if(root == null)
return new int[0];
//根节点先进栈
s.push(root);
while(!s.isEmpty()){
//每次栈顶就是访问的元素
TreeNode node = s.pop();
list.add(node.val);
//如果右边还有右子节点进栈
if(node.right != null)
s.push(node.right);
//如果左边还有左子节点进栈
if(node.left != null)
s.push(node.left);
}
//返回的结果
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
res[i] = list.get(i);
return res;
}
}

2. 二叉树的中序遍历(中等)
2.1. 题目描述
2.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public void inorder(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root){
//遇到空节点则返回
if(root == null)
return;
//先去左子树
inorder(list, root.left);
//再访问根节点
list.add(root.val);
//最后去右子树
inorder(list, root.right);
}
public int[] inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
//添加遍历结果的数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
//递归中序遍历
inorder(list, root);
//返回的结果
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
res[i] = list.get(i);
return res;
}
}
方法二:非递归(扩展思路)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
//添加遍历结果的数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//空树返回空数组
if(root == null)
return new int[0];
//当树节点不为空或栈中有节点时
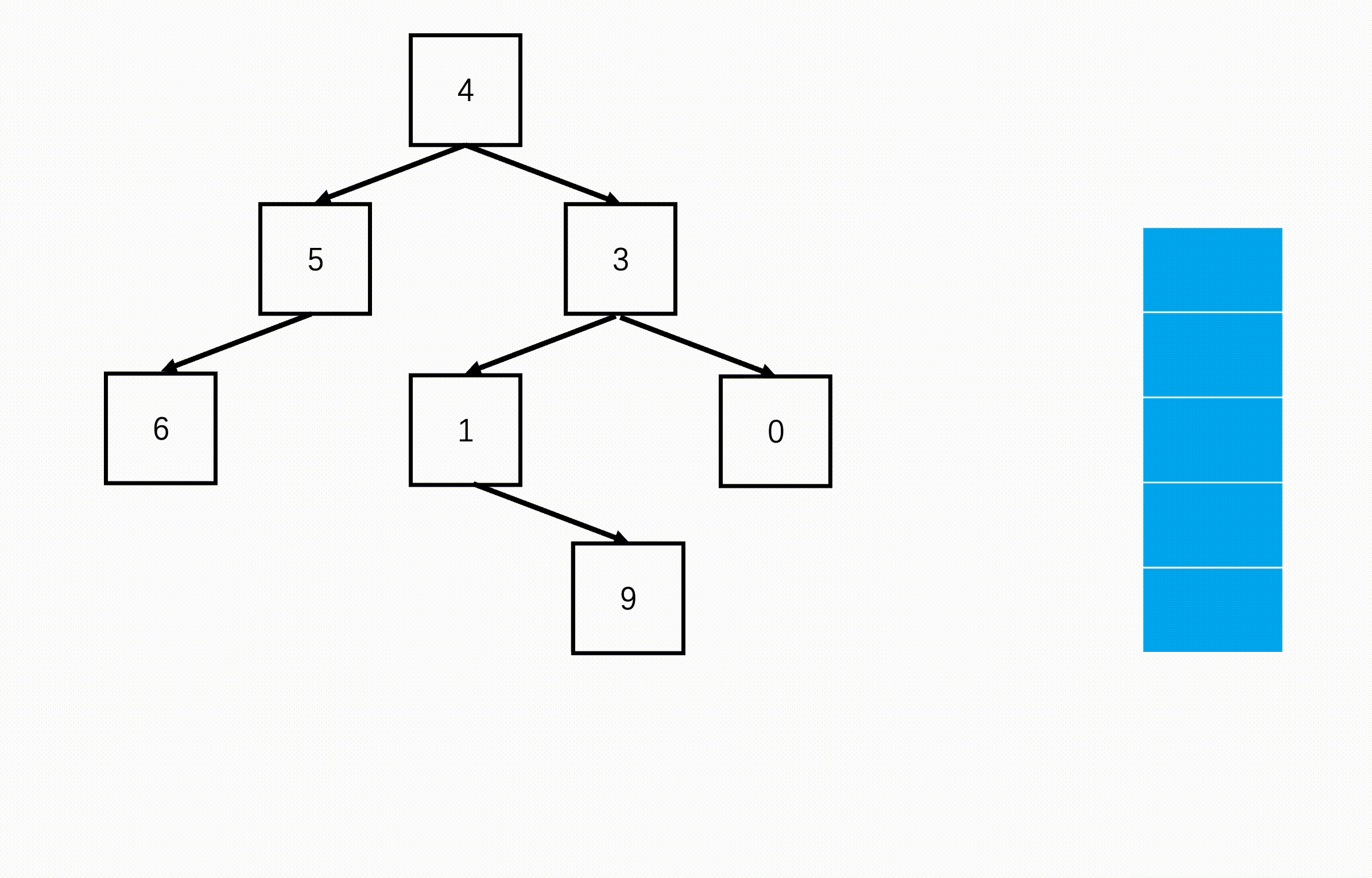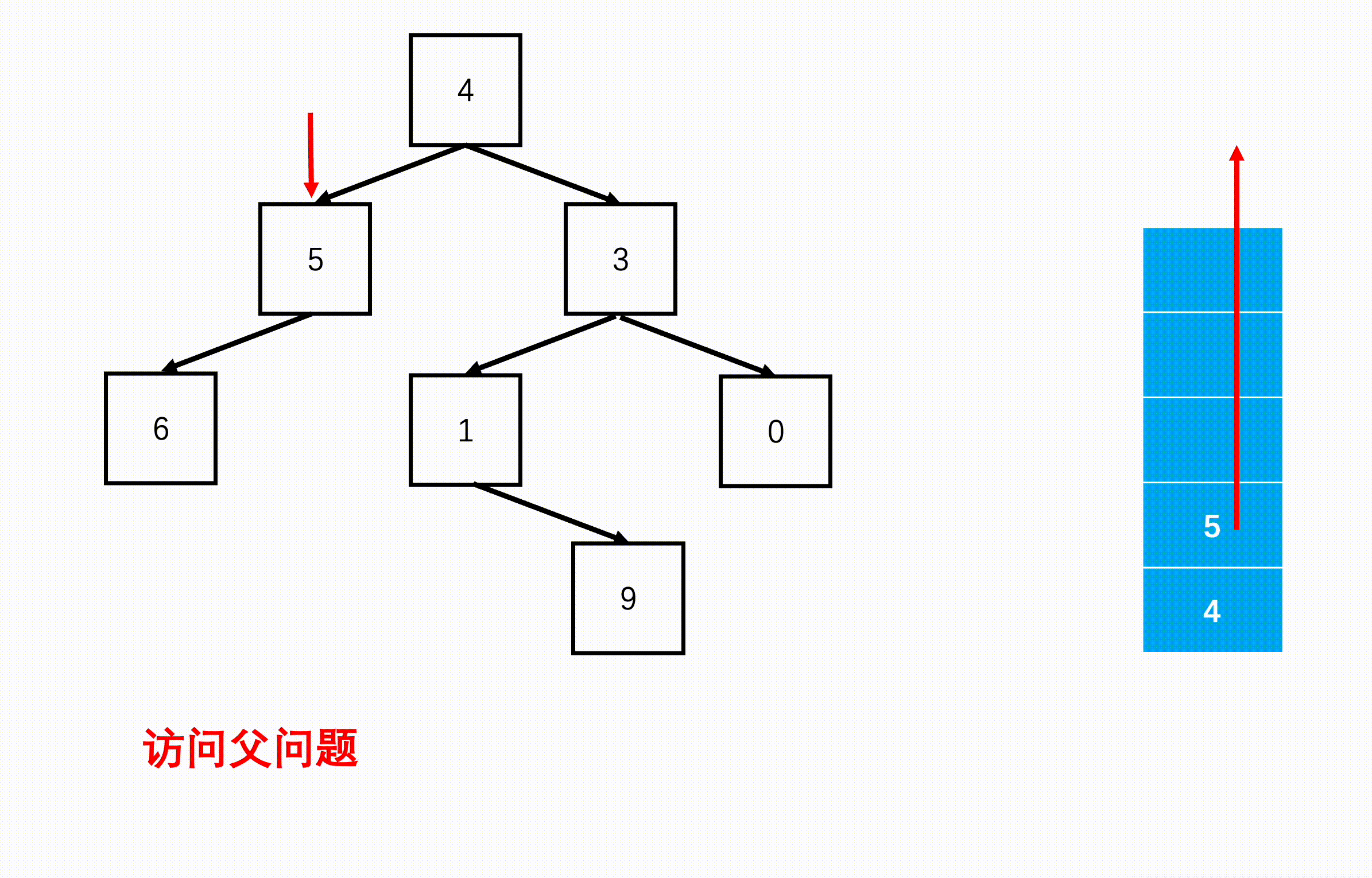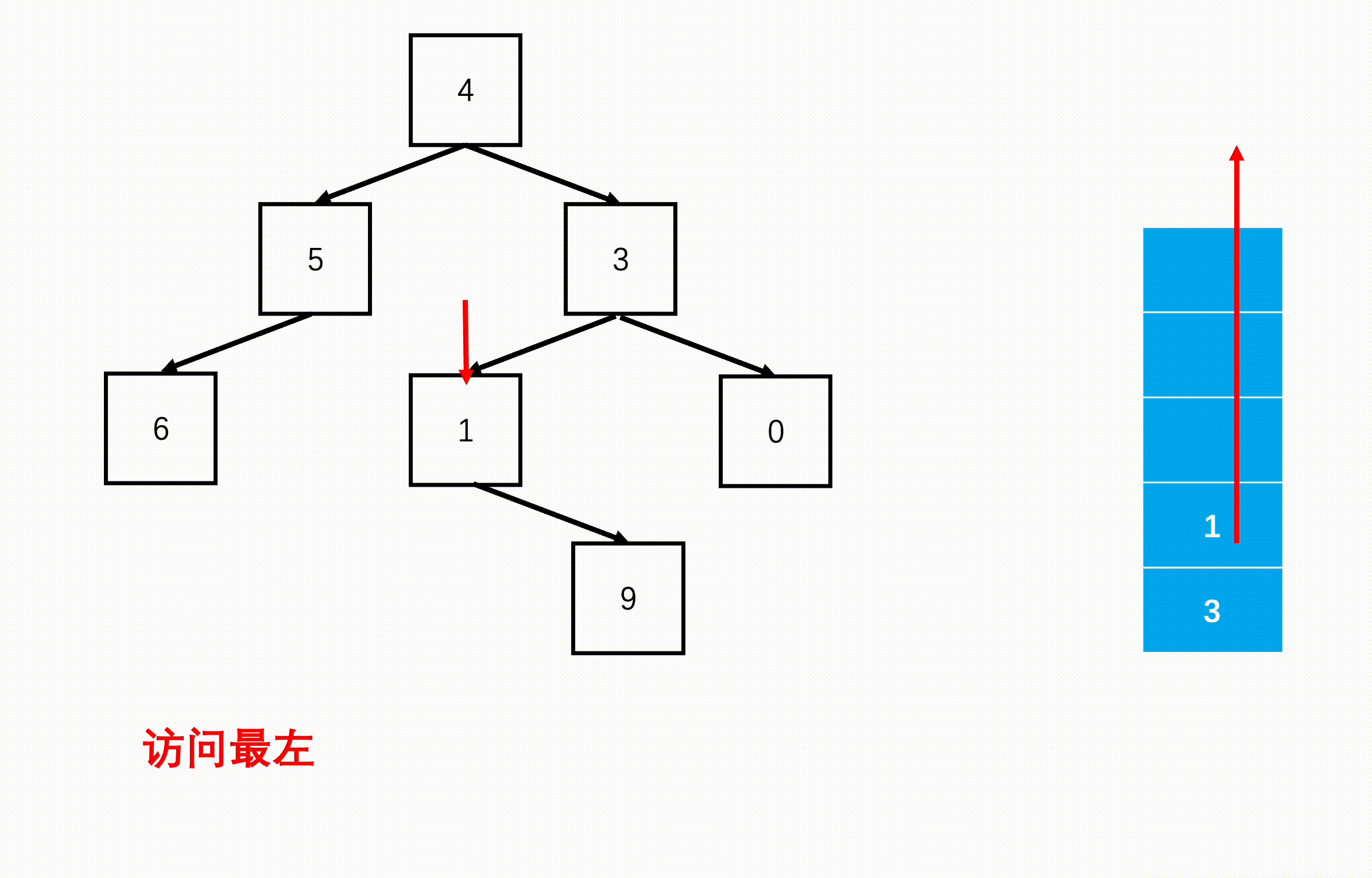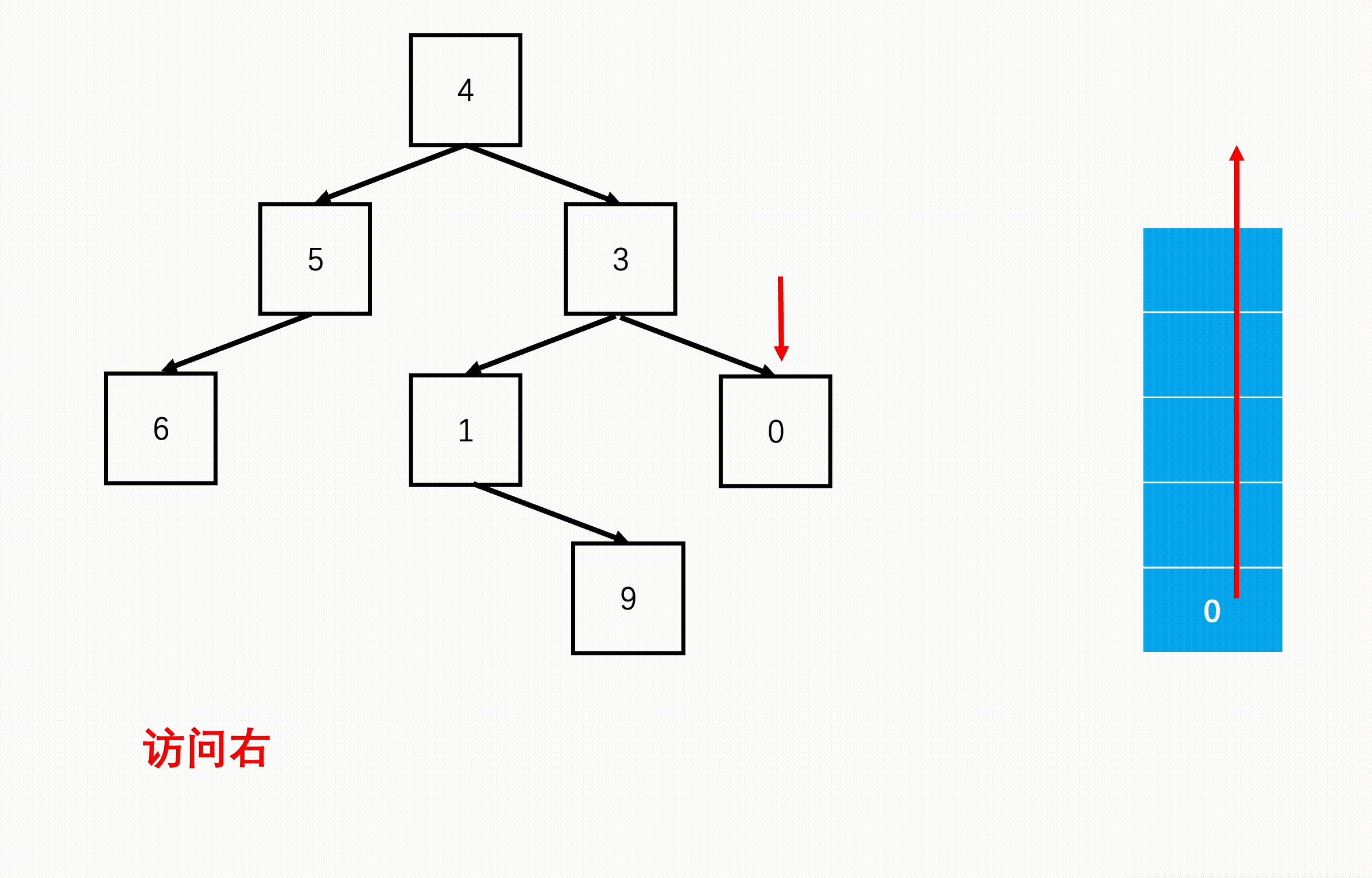
while(root != null || !s.isEmpty()){
//每次找到最左节点
while(root != null){
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
//访问该节点
TreeNode node = s.pop();
list.add(node.val);
//进入右节点
root = node.right;
}
//返回的结果
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
res[i] = list.get(i);
return res;
}
}

3. 二树的后序遍历(简单)
3.1. 题目描述

3.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public void postorder(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root){
//遇到空节点则返回
if(root == null)
return;
//先去左子树
postorder(list, root.left);
//再去右子树
postorder(list, root.right);
//最后访问根节点
list.add(root.val);
}
public int[] postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
//添加遍历结果的数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
//递归后序遍历
postorder(list, root);
//返回的结果
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
res[i] = list.get(i);
return res;
}
}
方法二:非递归(扩展思路)

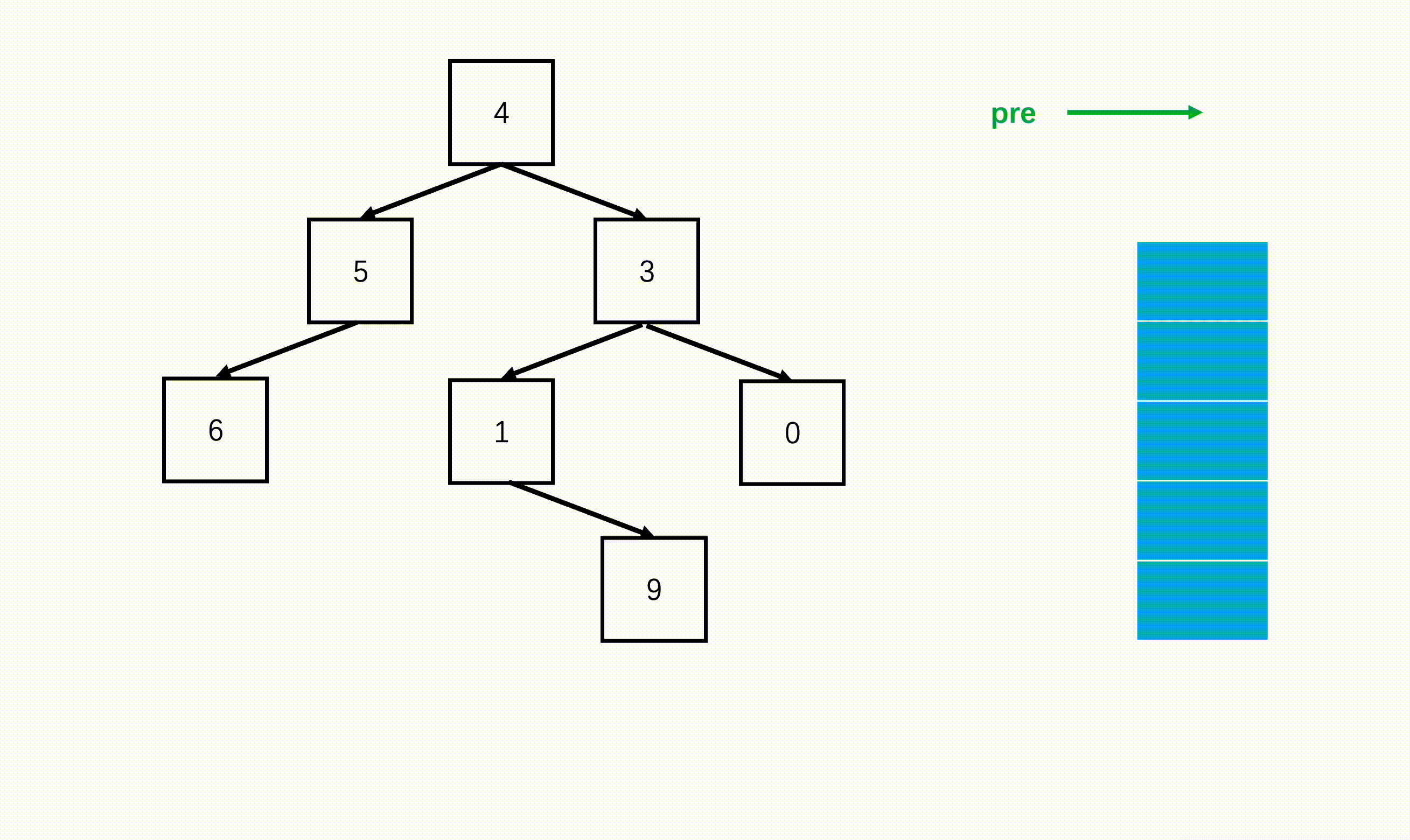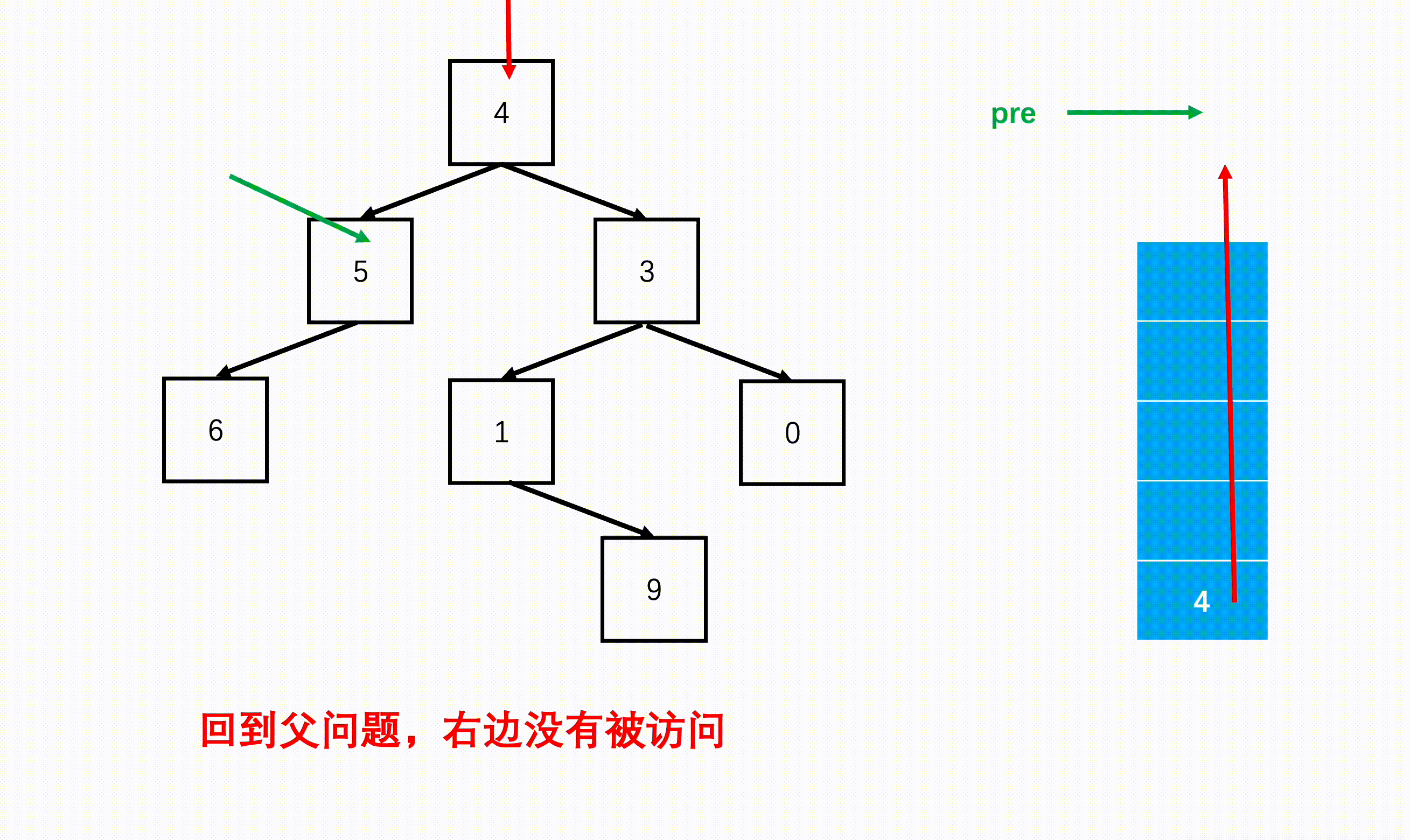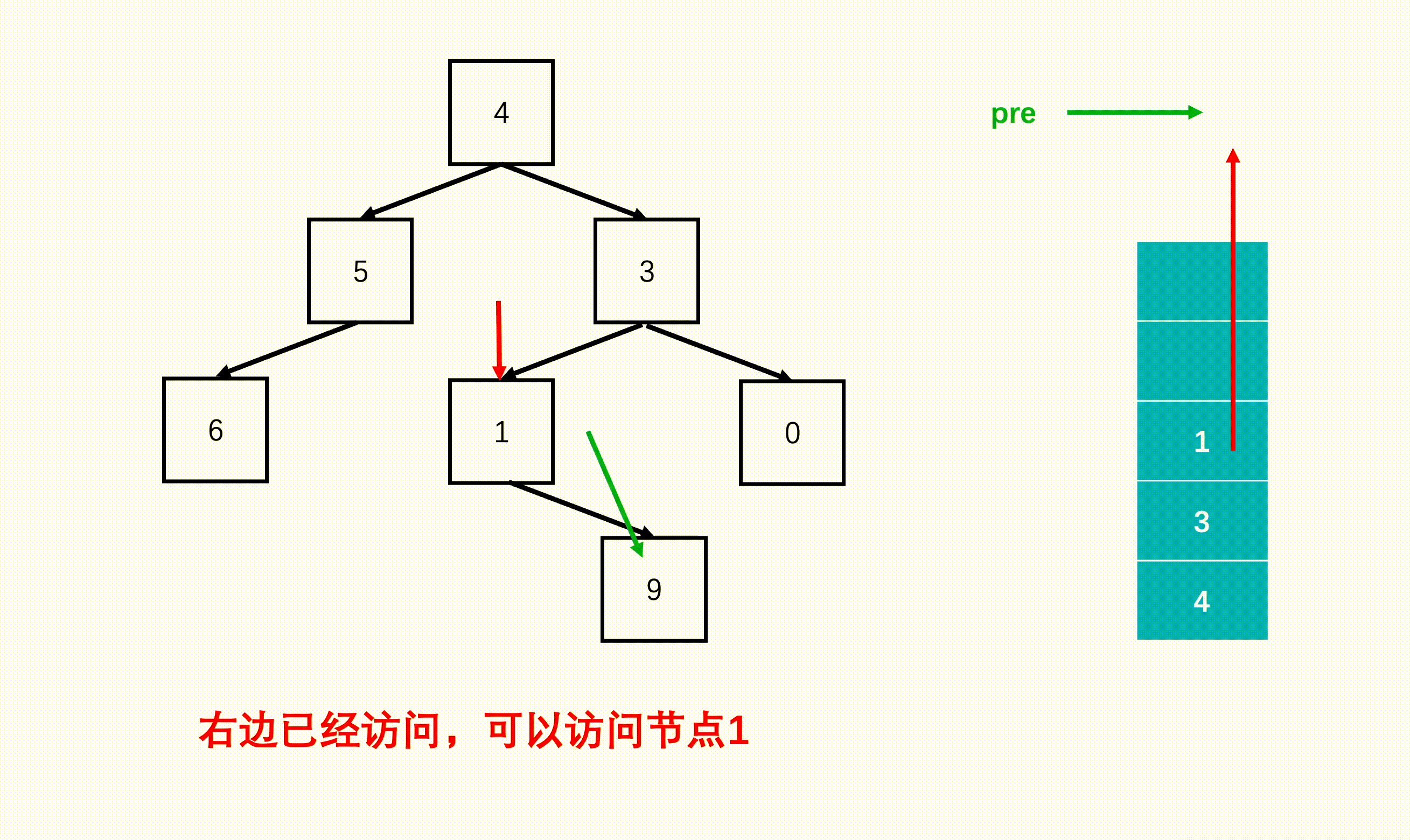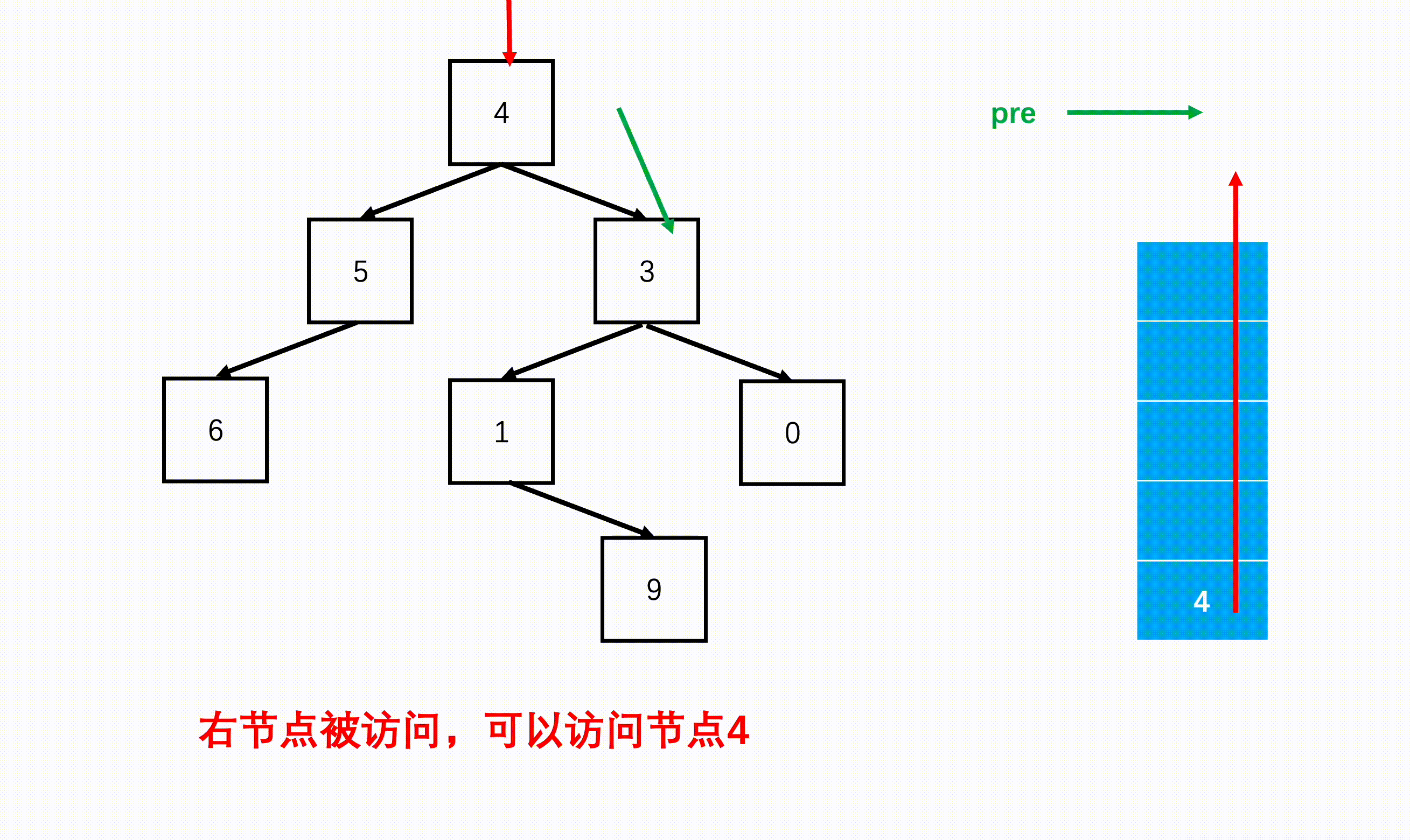
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
//添加遍历结果的数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while(root != null || !s.isEmpty()){
//每次先找到最左边的节点
while(root != null){
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
//弹出栈顶
TreeNode node = s.pop();
//如果该元素的右边没有或是已经访问过
if(node.right == null || node.right == pre){
//访问中间的节点
list.add(node.val);
//且记录为访问过了
pre = node;
}else{
//该节点入栈
s.push(node);
//先访问右边
root = node.right;
}
}
//返回的结果
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
res[i] = list.get(i);
return res;
}
}
4. 求二叉树的层序遍历
4.1. 题目描述
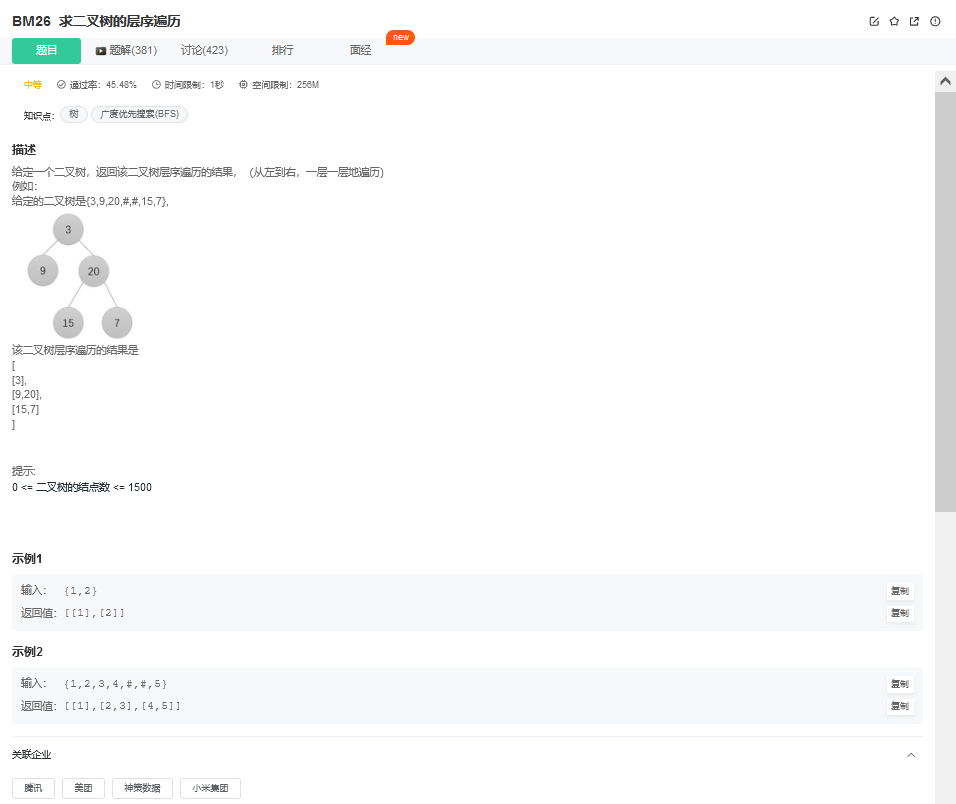
4.2. 解题思路
方法一:非递归(推荐使用)

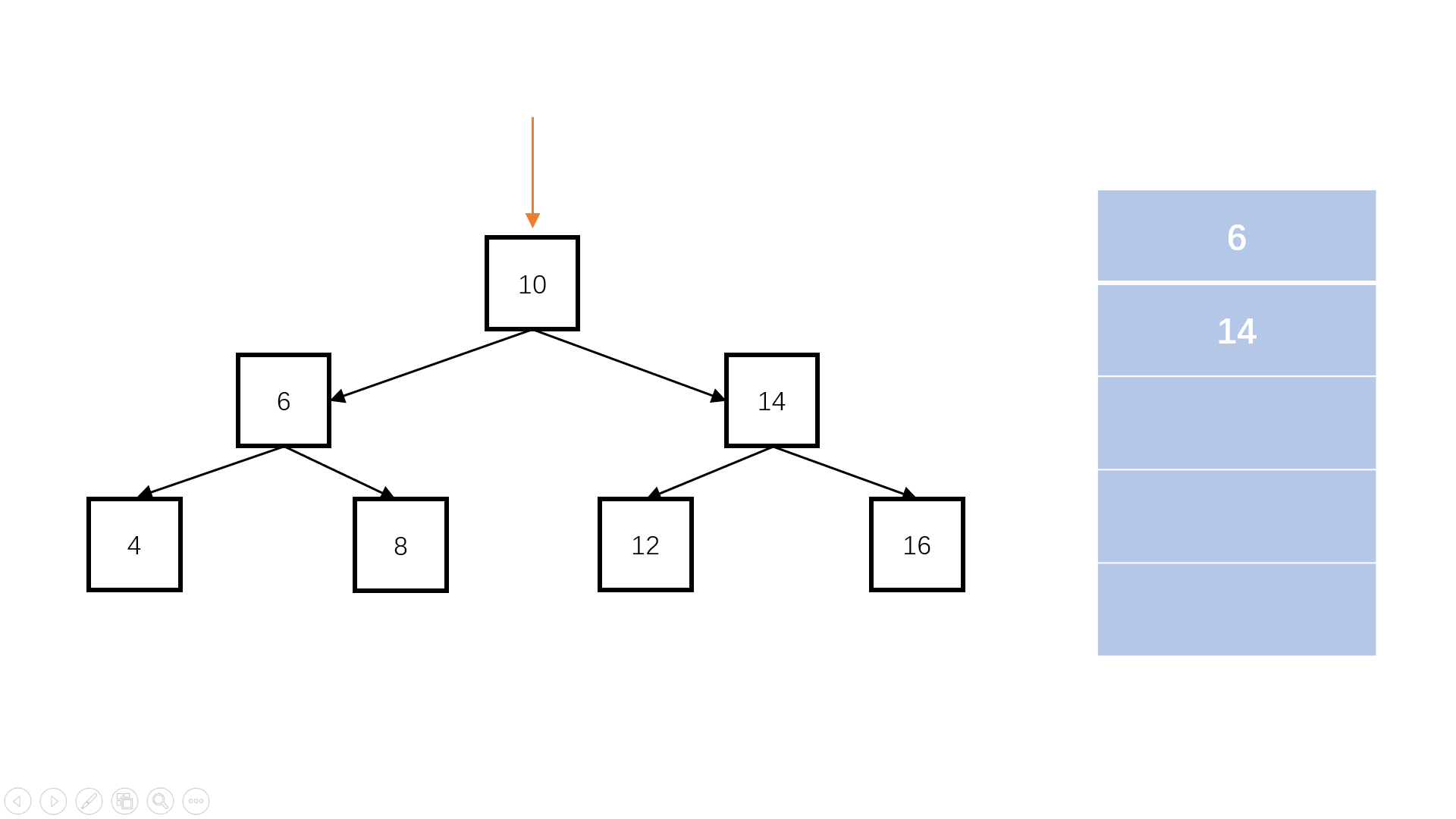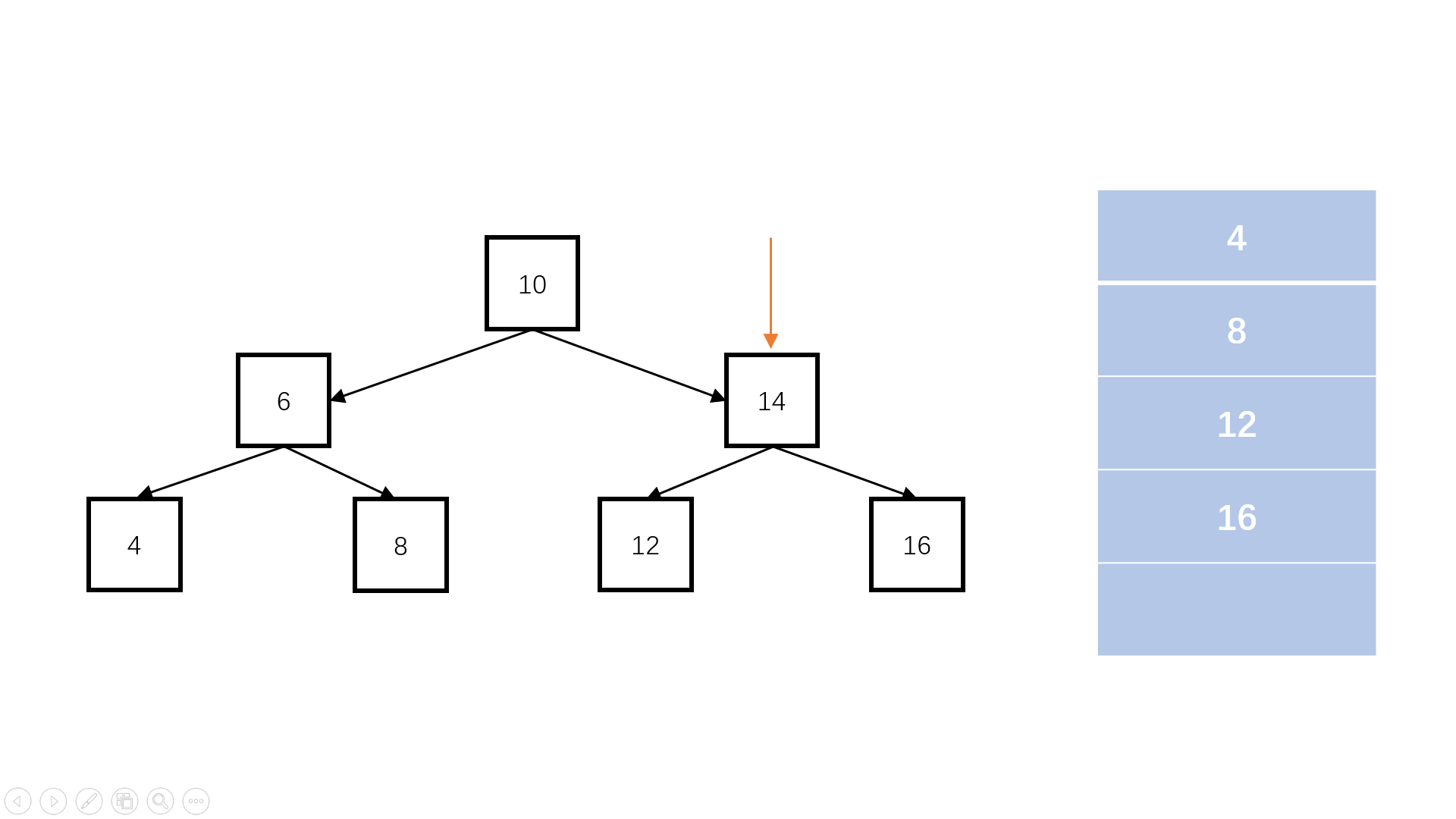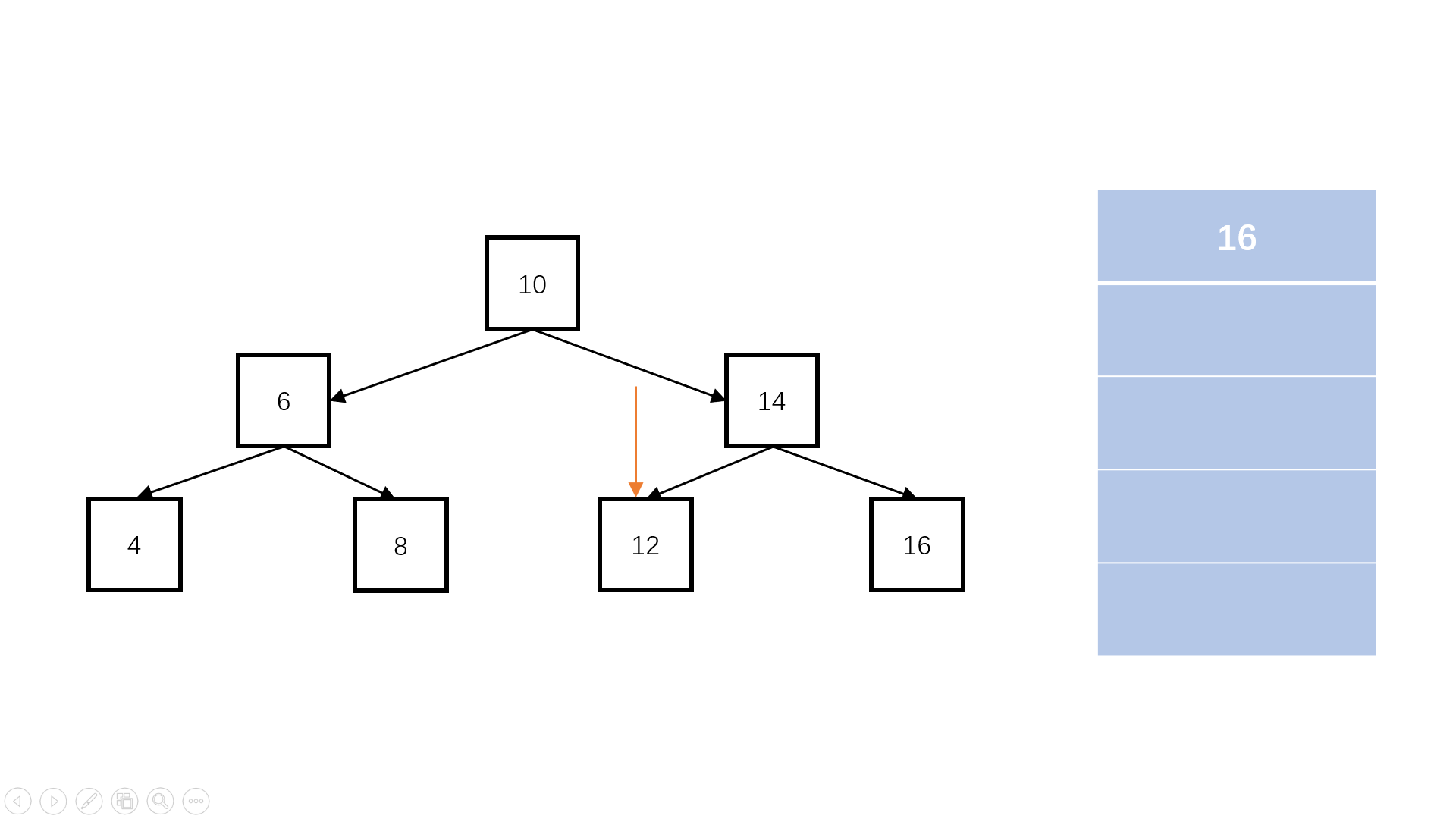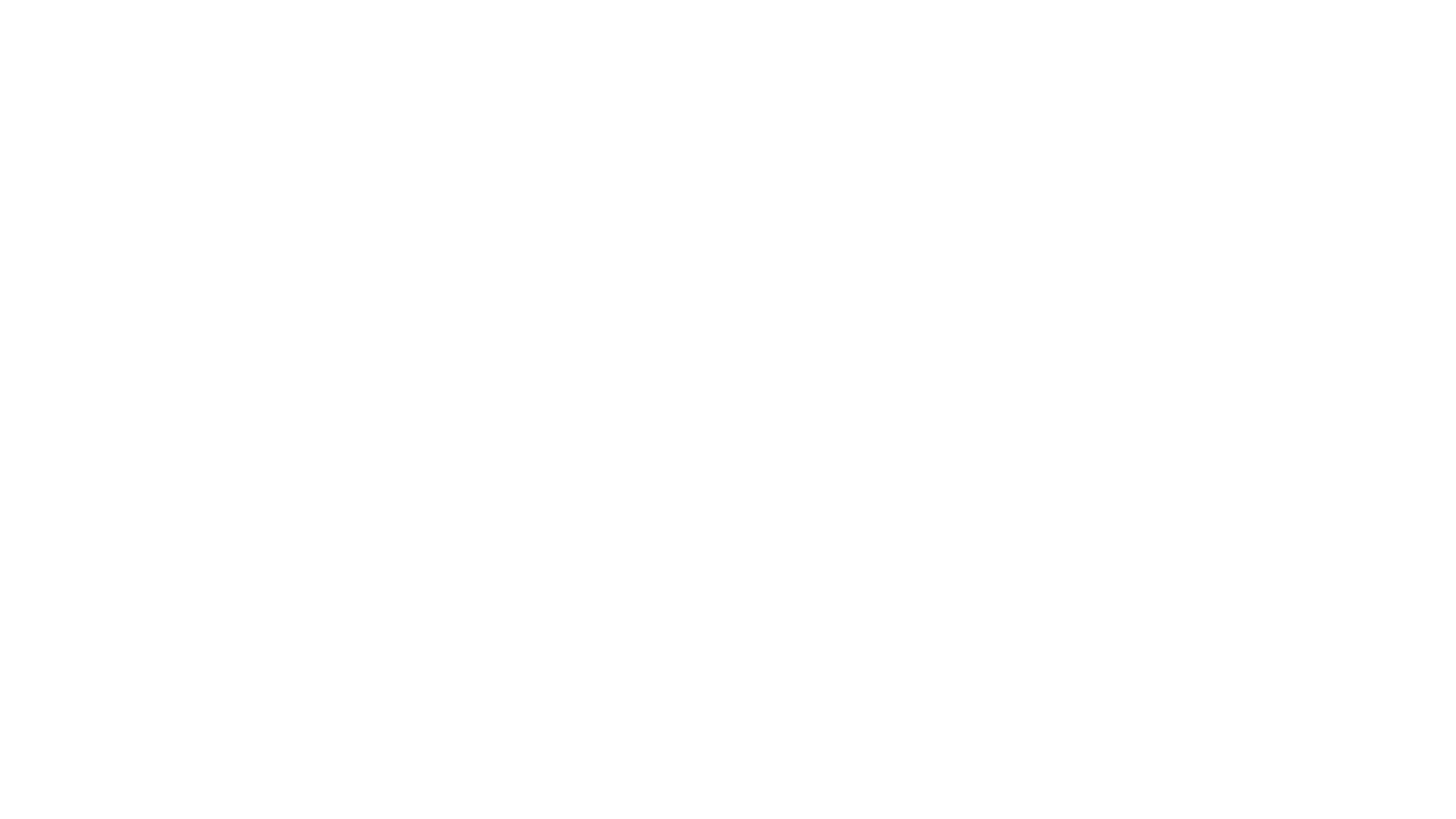
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > res = new ArrayList();
if(root == null)
//如果是空,则直接返回空数组
return res;
//队列存储,进行层次遍历
Queue<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
//记录二叉树的某一行
ArrayList<Integer> row = new ArrayList();
int n = q.size();
//因先进入的是根节点,故每层节点多少,队列大小就是多少
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
row.add(cur.val);
//若是左右孩子存在,则存入左右孩子作为下一个层次
if(cur.left != null)
q.add(cur.left);
if(cur.right != null)
q.add(cur.right);
}
//每一层加入输出
res.add(row);
}
return res;
}
}
方法二:递归(扩展思路)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//记录输出
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > res = new ArrayList();
void traverse(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if(root != null){
//新的一层
if(res.size() < depth){
ArrayList<Integer> row = new ArrayList();
res.add(row);
row.add(root.val);
//读取该层的一维数组,将元素加入末尾
}else{
ArrayList<Integer> row = res.get(depth - 1);
row.add(root.val);
}
}
else
return;
//递归左右时深度记得加1
traverse(root.left, depth + 1);
traverse(root.right, depth + 1);
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
//如果是空,则直接返回
return res;
//递归层次遍历
traverse(root, 1);
return res;
}
}
5. 按之字形顺序打印二叉树
5.1. 题目描述
5.2. 解题思路
方法一:非递归层次遍历(推荐使用)

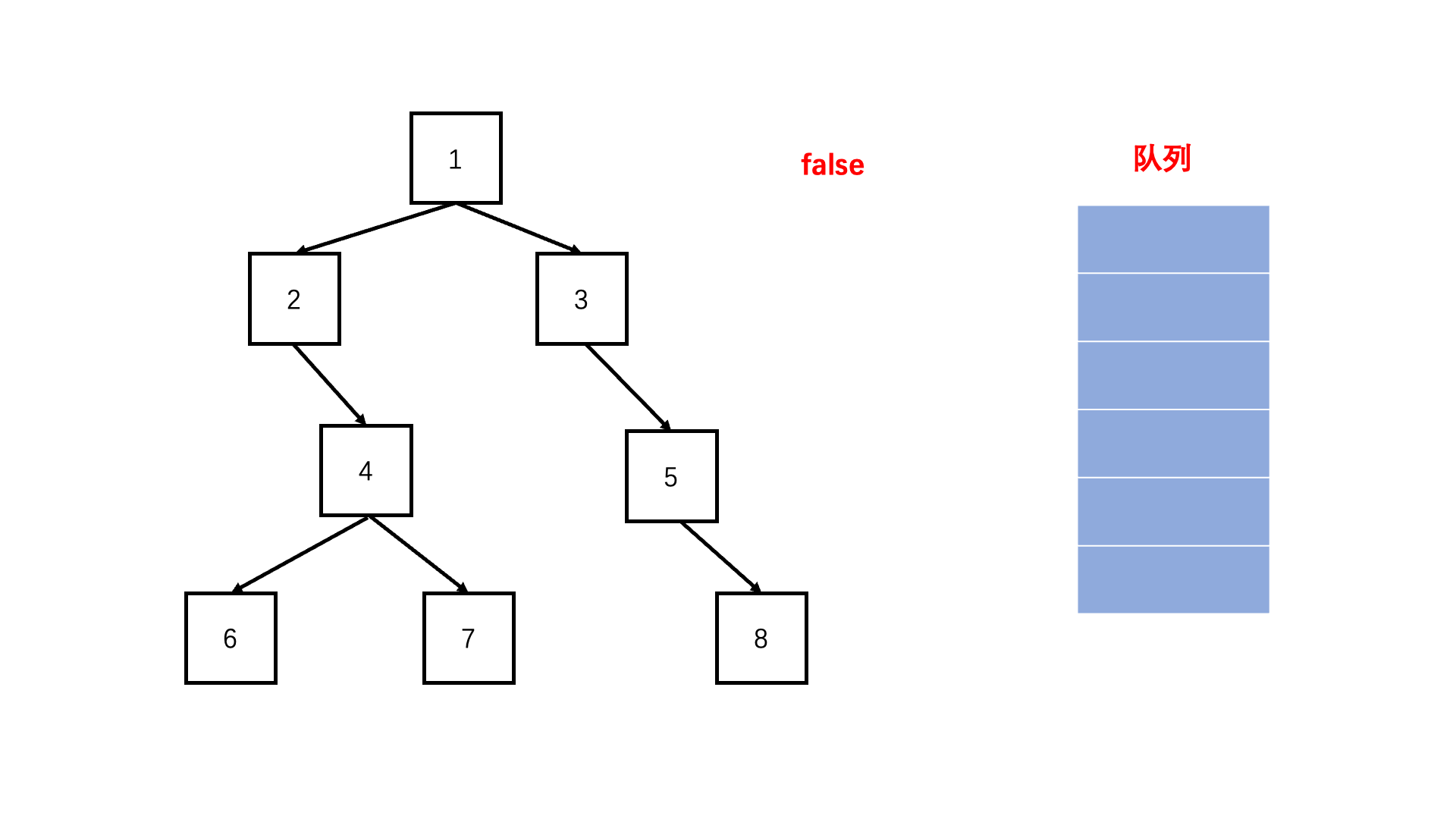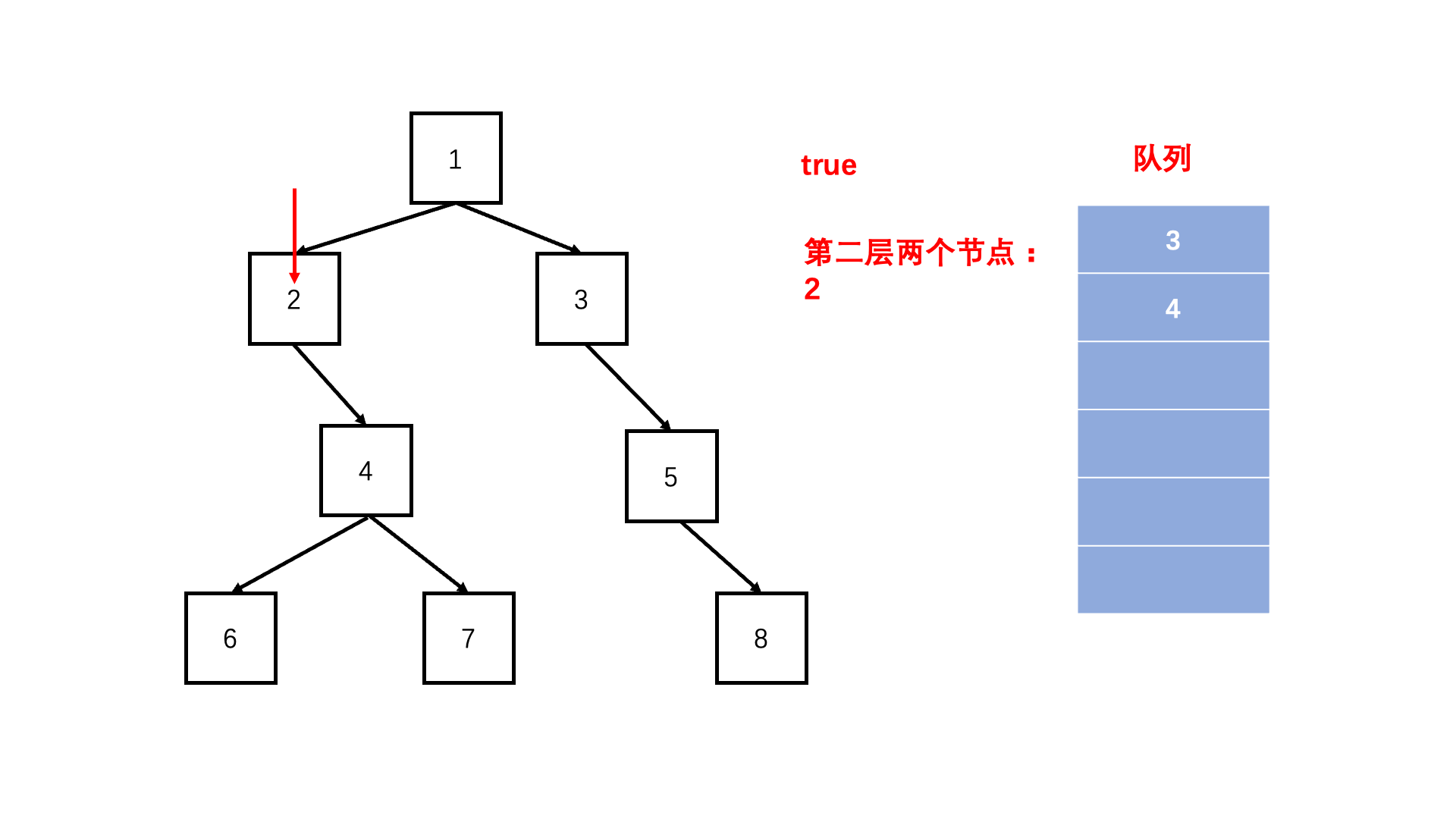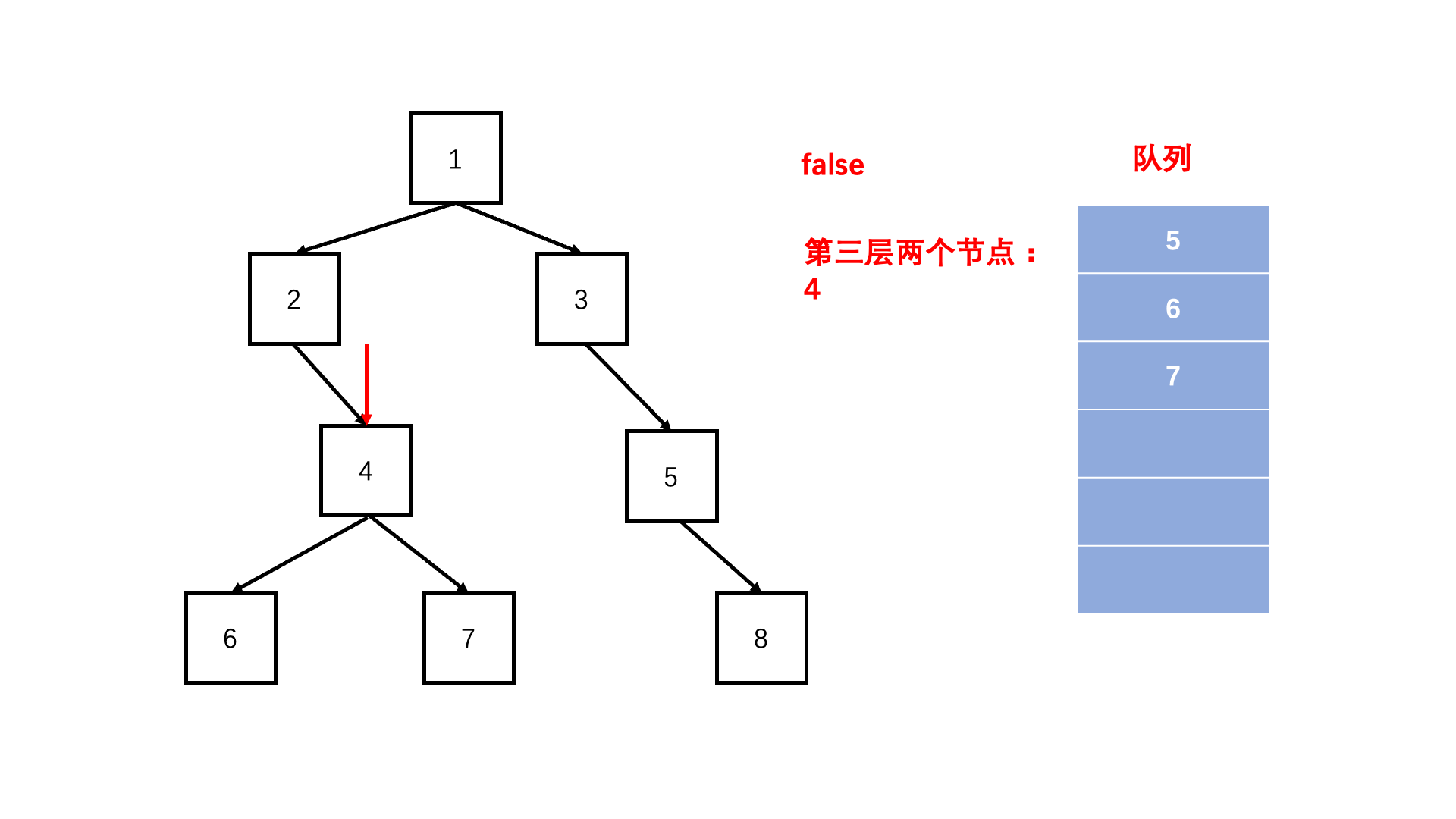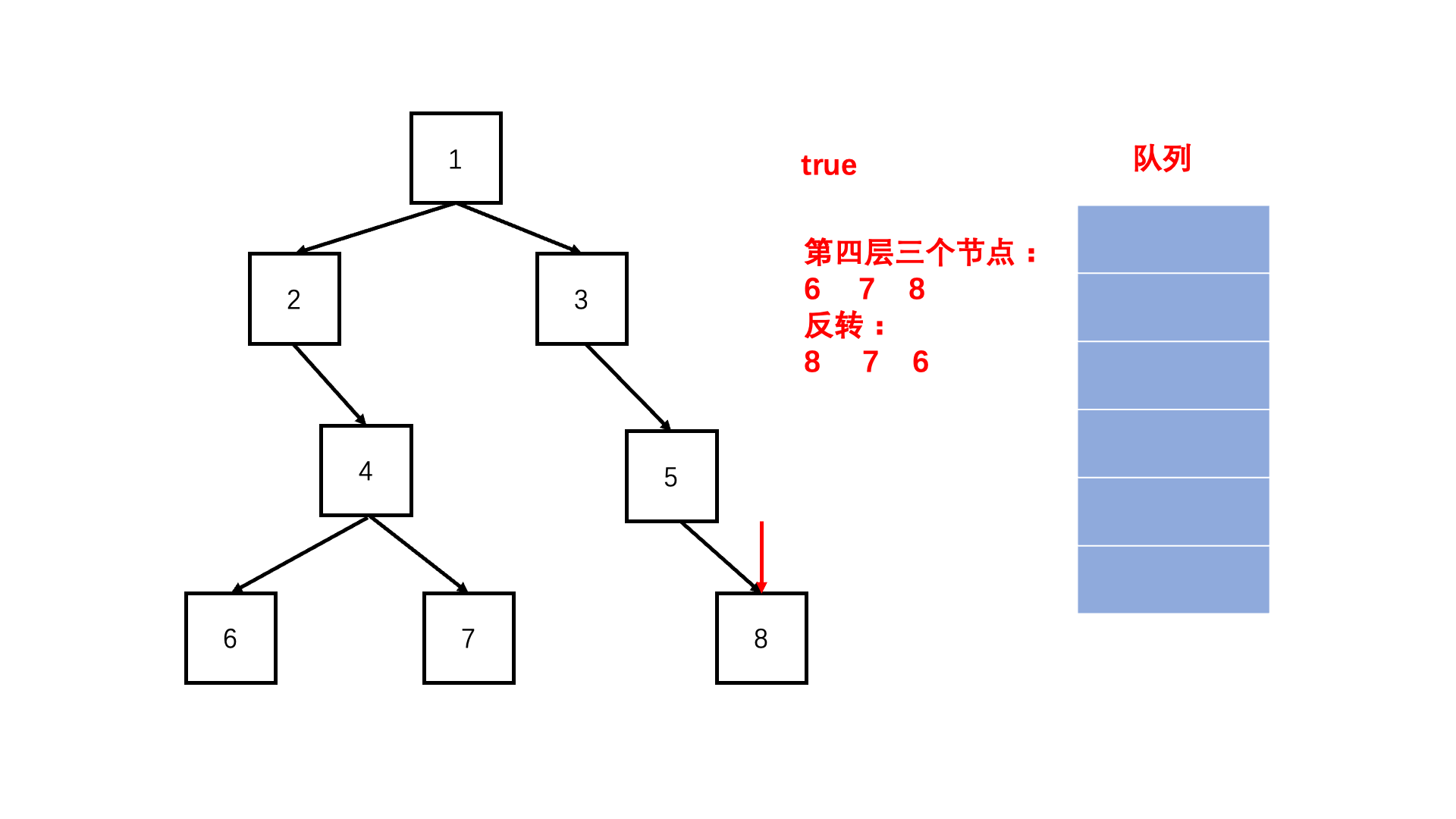
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
TreeNode head = pRoot;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(head == null)
//如果是空,则直接返回空list
return res;
//队列存储,进行层次遍历
Queue<TreeNode> temp = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
temp.offer(head);
TreeNode p;
boolean flag = true;
while(!temp.isEmpty()){
//记录二叉树的某一行
ArrayList<Integer> row = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int n = temp.size();
//奇数行反转,偶数行不反转
flag = !flag;
//因先进入的是根节点,故每层节点多少,队列大小就是多少
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
p = temp.poll();
row.add(p.val);
//若是左右孩子存在,则存入左右孩子作为下一个层次
if(p.left != null)
temp.offer(p.left);
if(p.right != null)
temp.offer(p.right);
}
//奇数行反转,偶数行不反转
if(flag)
Collections.reverse(row);
res.add(row);
}
return res;
}
}
方法二:双栈法(扩展思路)

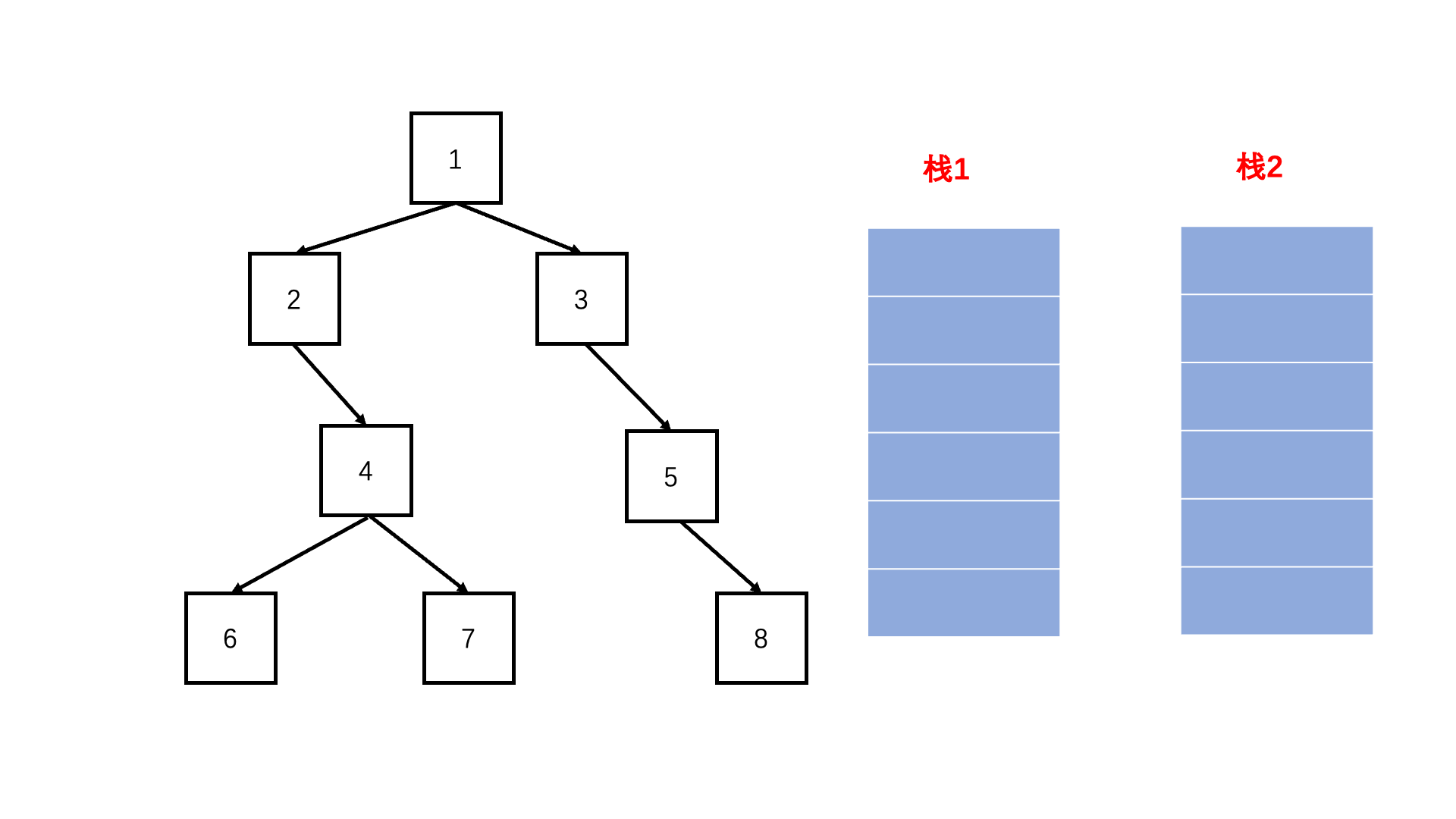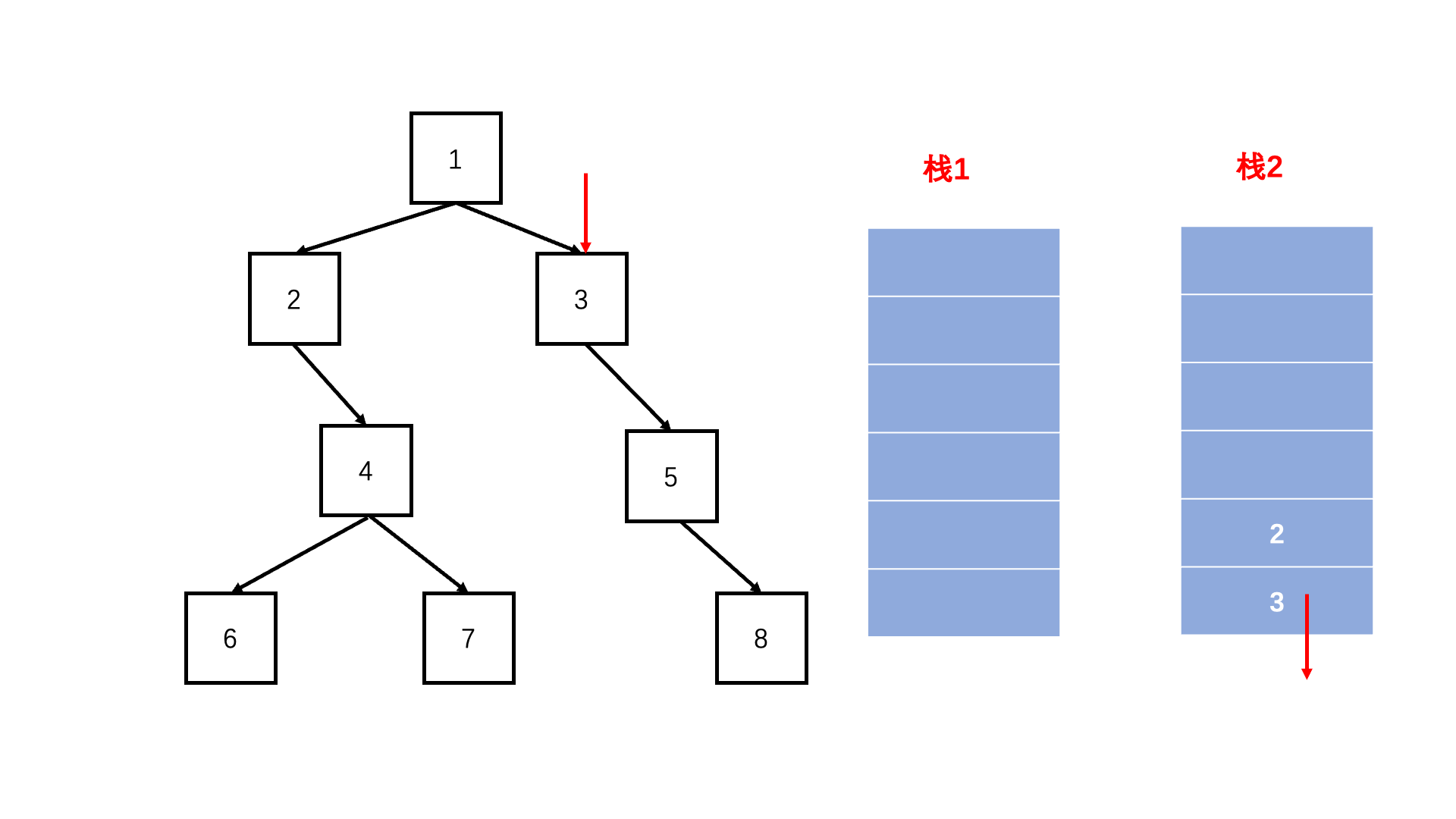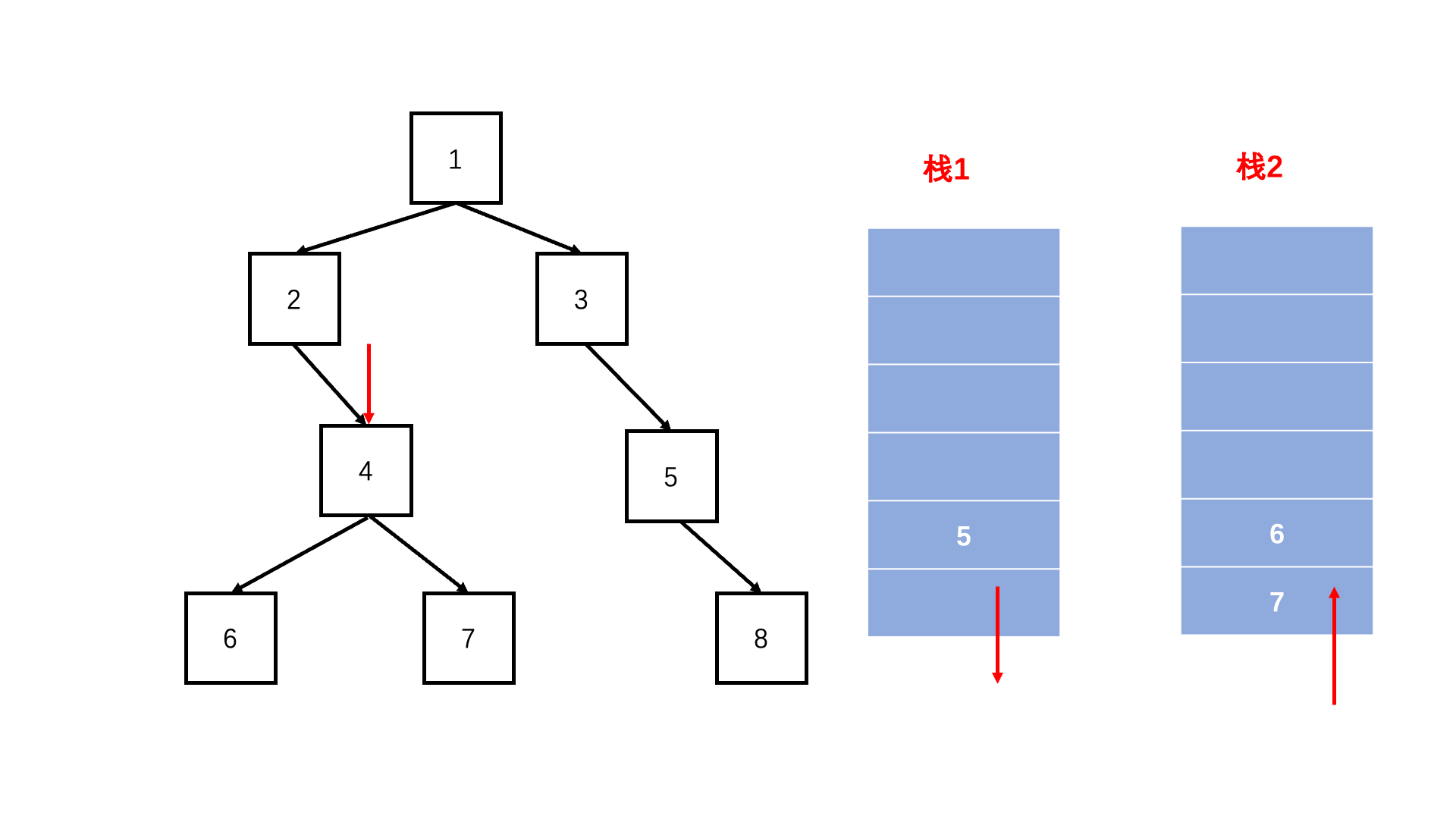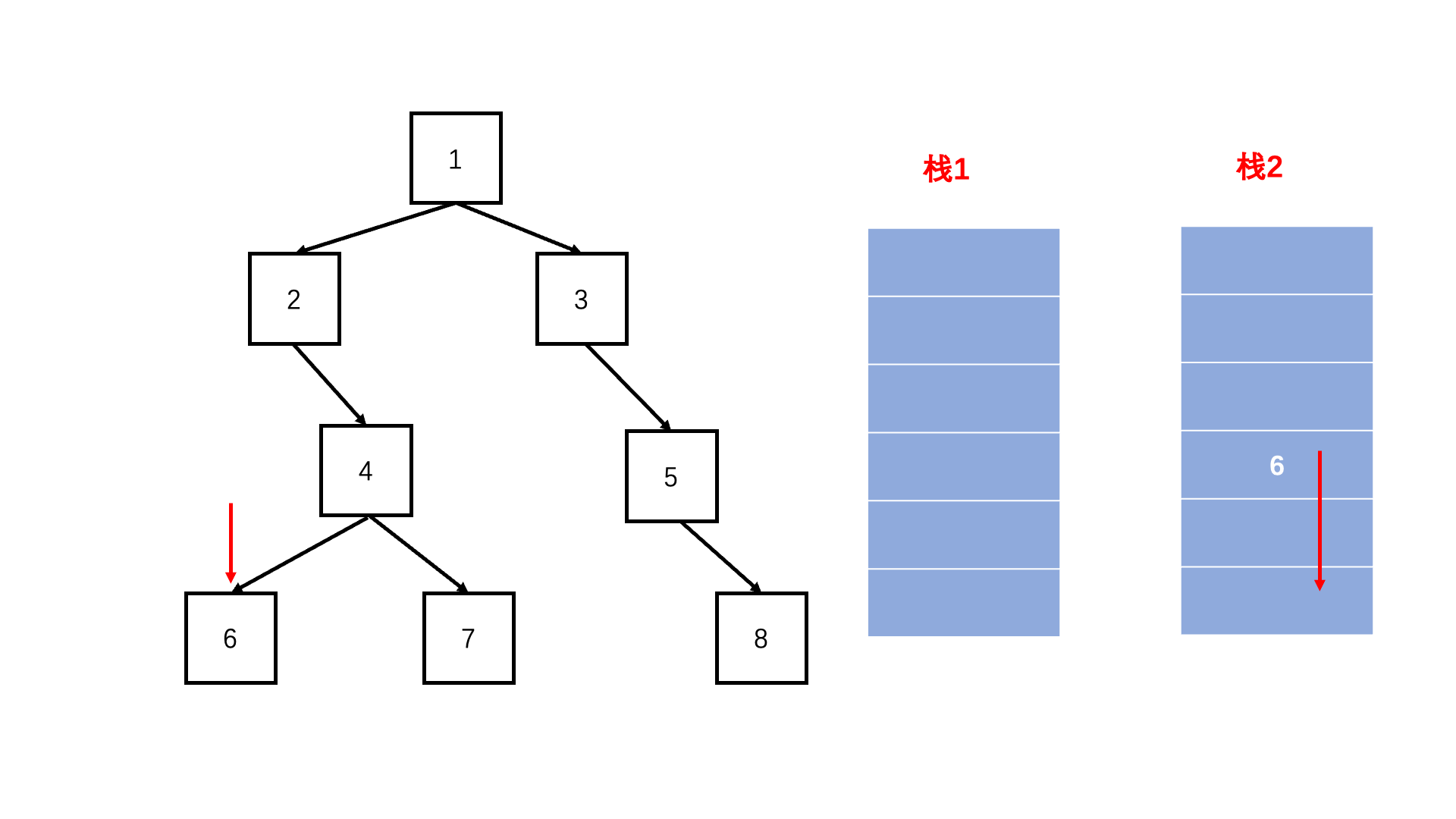
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
TreeNode head = pRoot;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(head == null)
//如果是空,则直接返回空list
return res;
Stack<TreeNode> s1 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode> s2 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//放入第一次
s1.push(head);
while(!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//遍历奇数层
while(!s1.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = s1.pop();
//记录奇数层
temp.add(node.val);
//奇数层的子节点加入偶数层
if(node.left != null)
s2.push(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
s2.push(node.right);
}
//数组不为空才添加
if(temp.size() != 0)
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
//清空本层数据
temp.clear();
//遍历偶数层
while(!s2.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = s2.pop();
//记录偶数层
temp.add(node.val);
//偶数层的子节点加入奇数层
if(node.right != null)
s1.push(node.right);
if(node.left != null)
s1.push(node.left);
}
//数组不为空才添加
if(temp.size() != 0)
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
//清空本层数据
temp.clear();
}
return res;
}
}
6. 二叉树的最大深度
6.1. 题目描述

6.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)

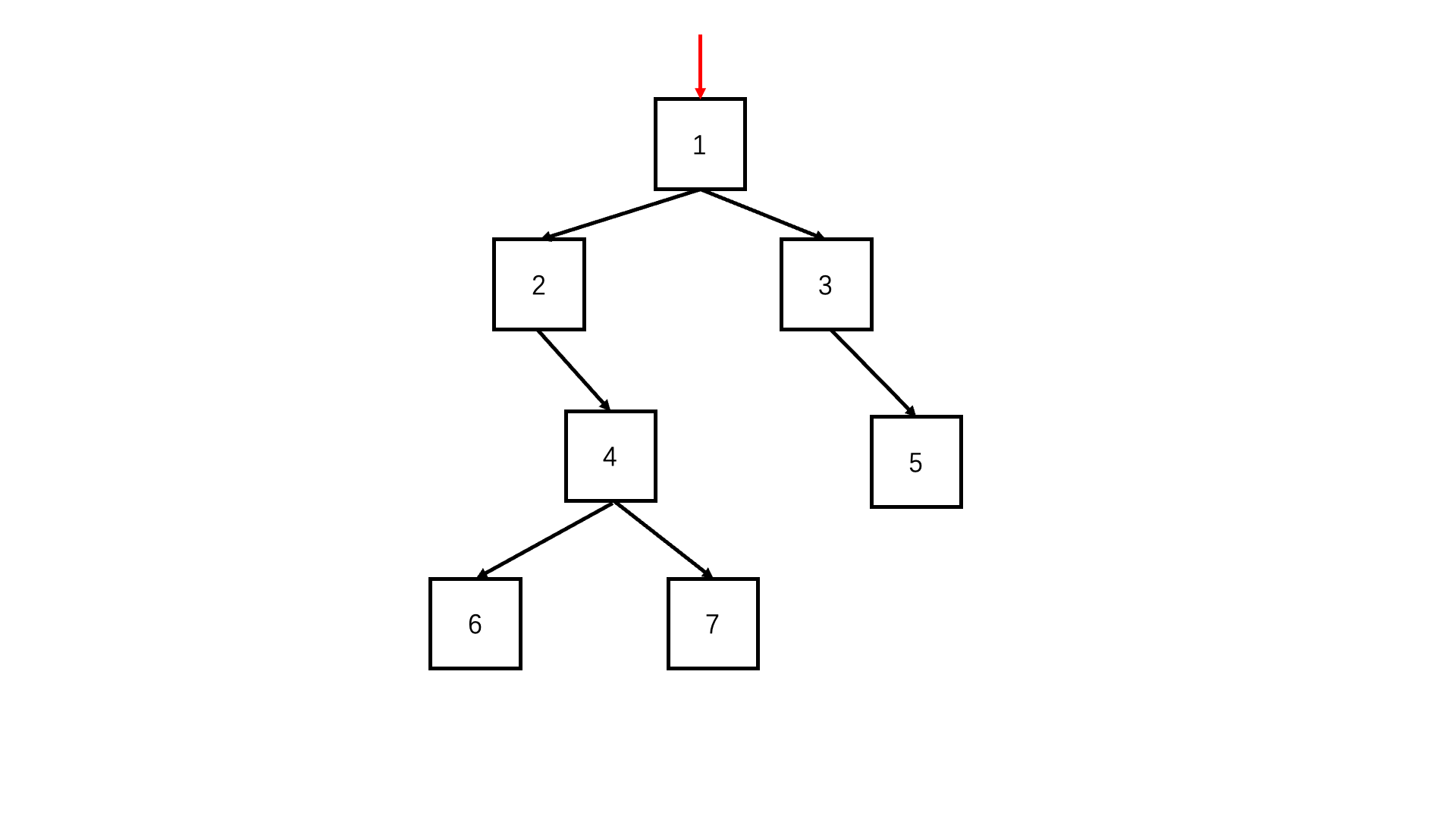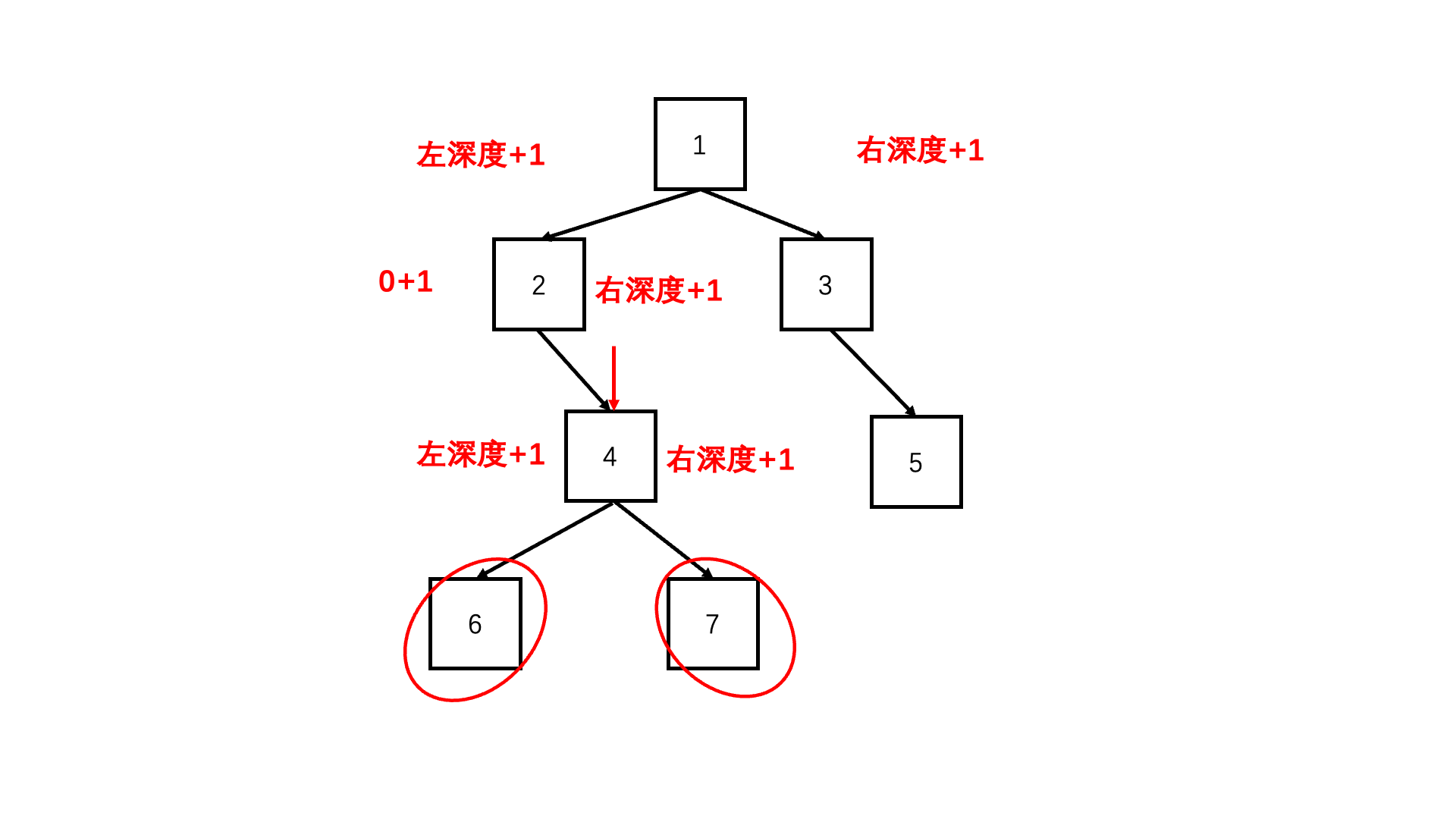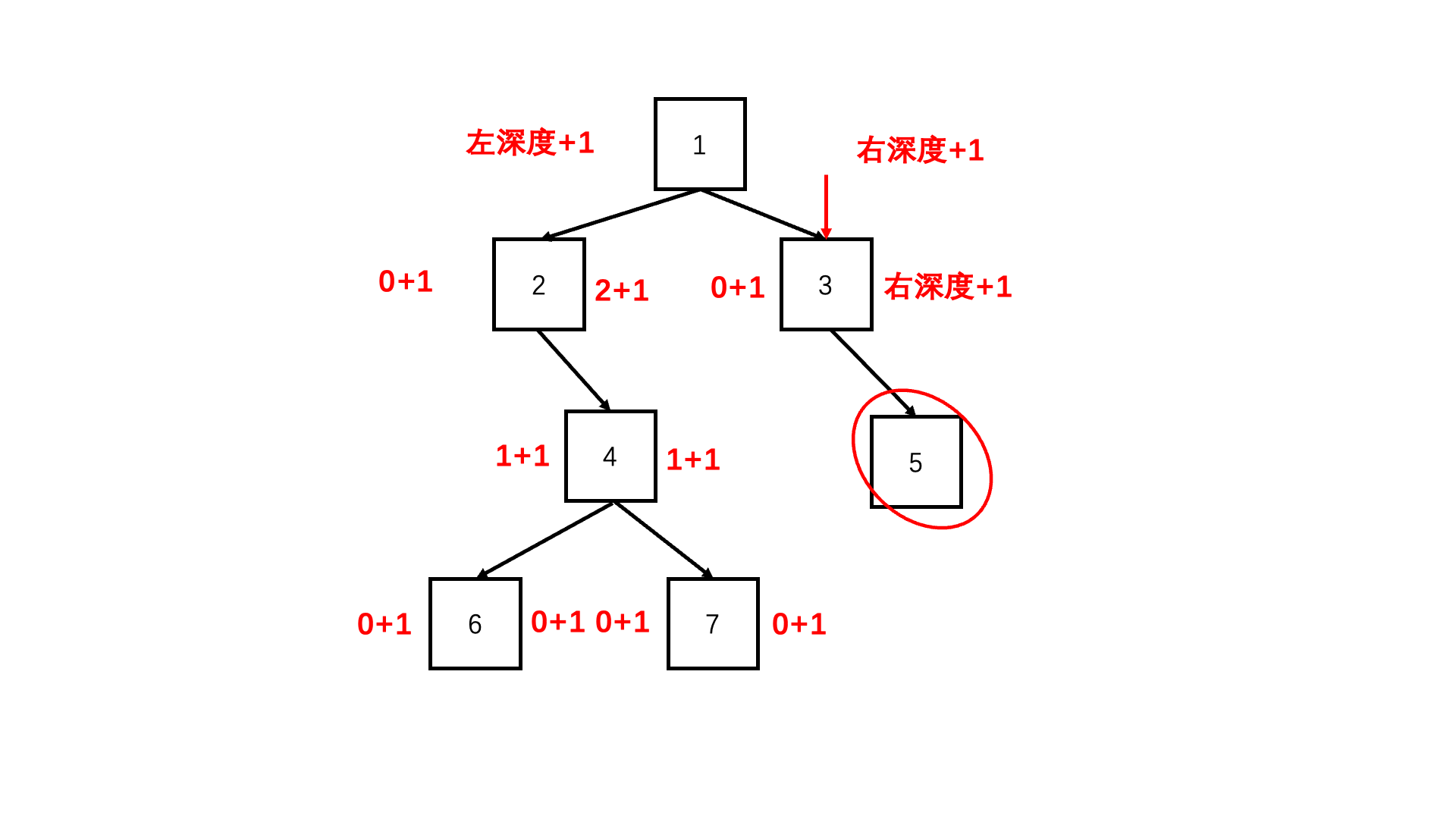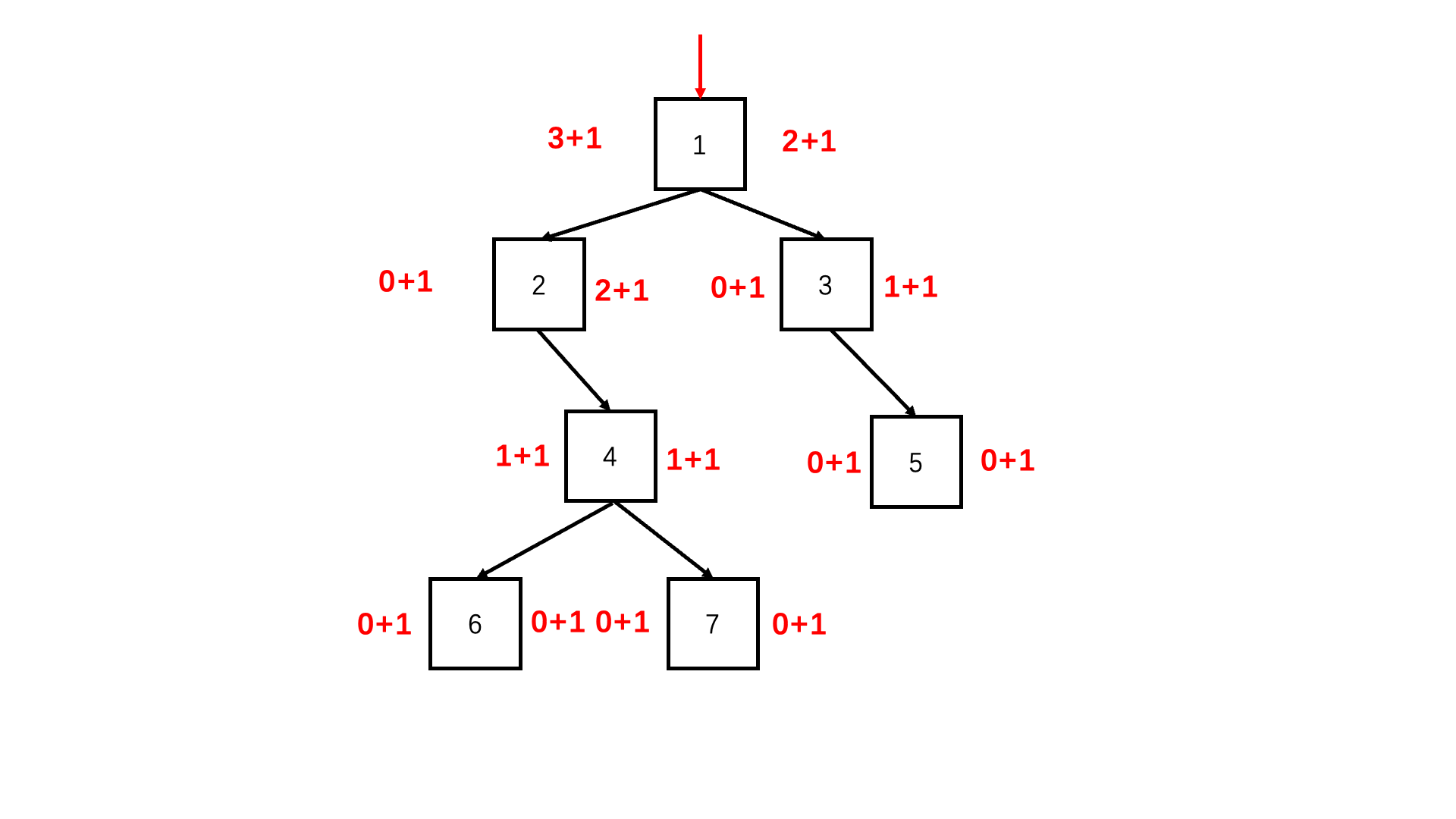
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {
//空节点没有深度
if(root == null)
return 0;
//返回子树深度+1
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
方法二:层次遍历(扩展思路)

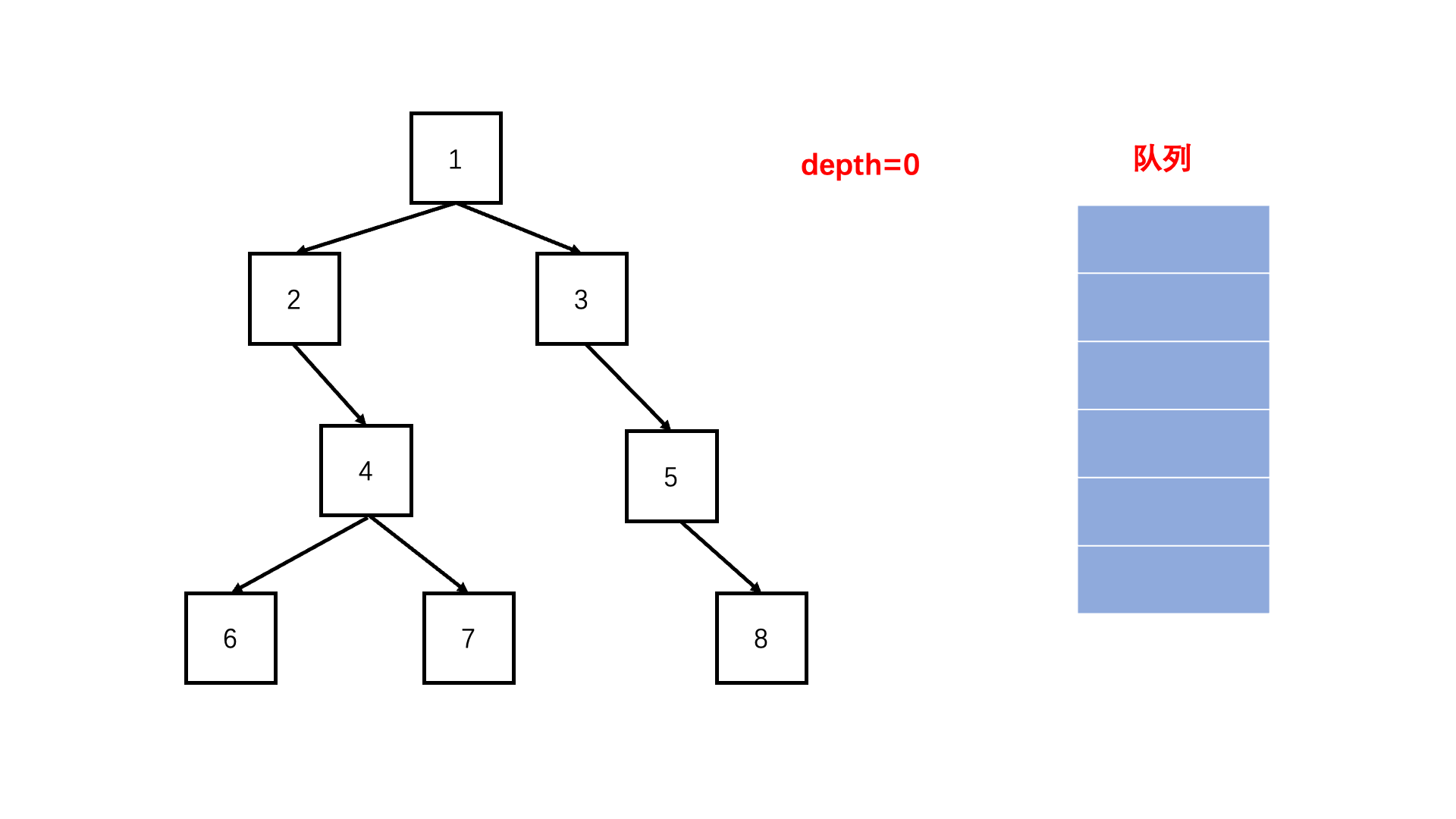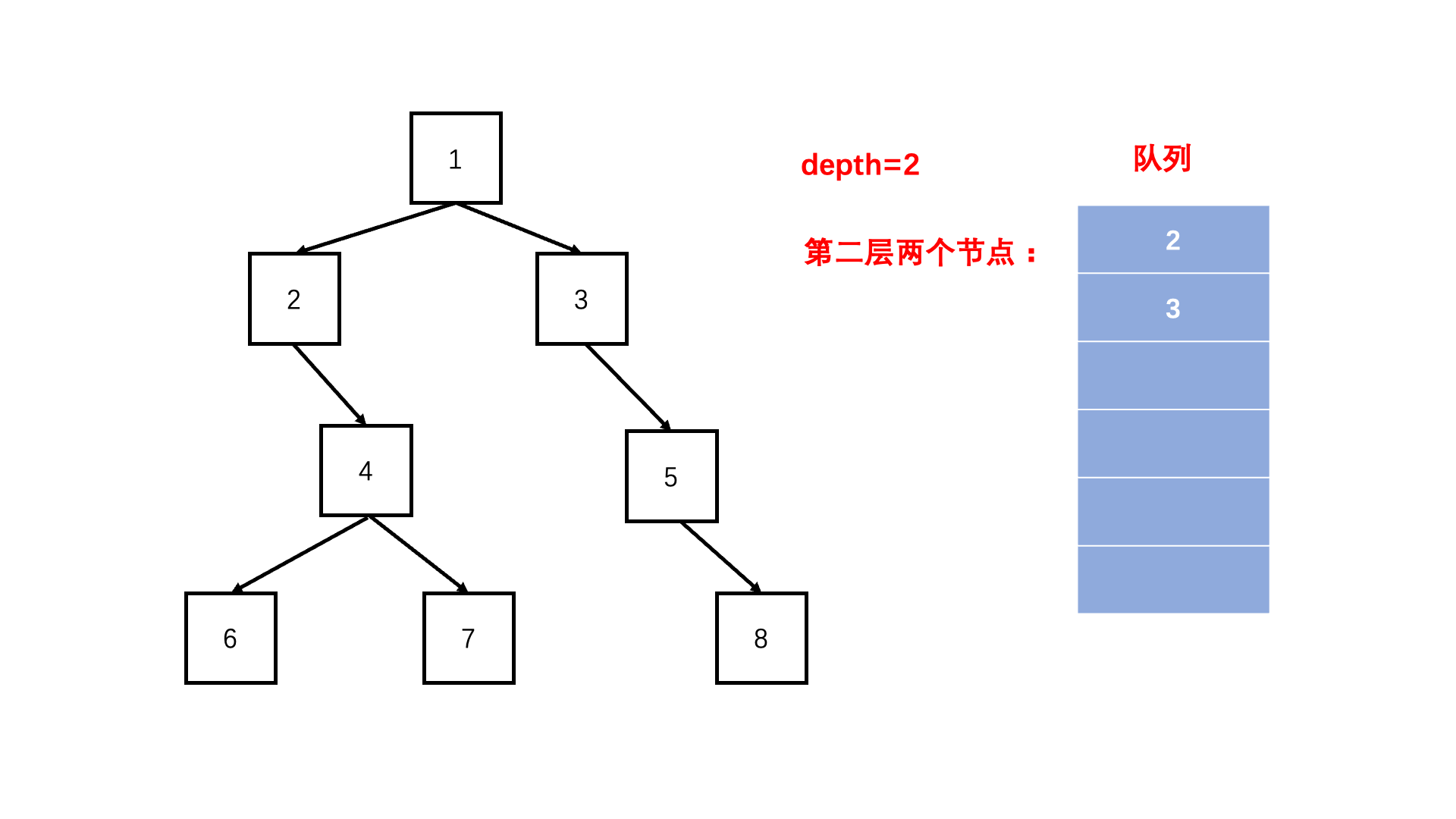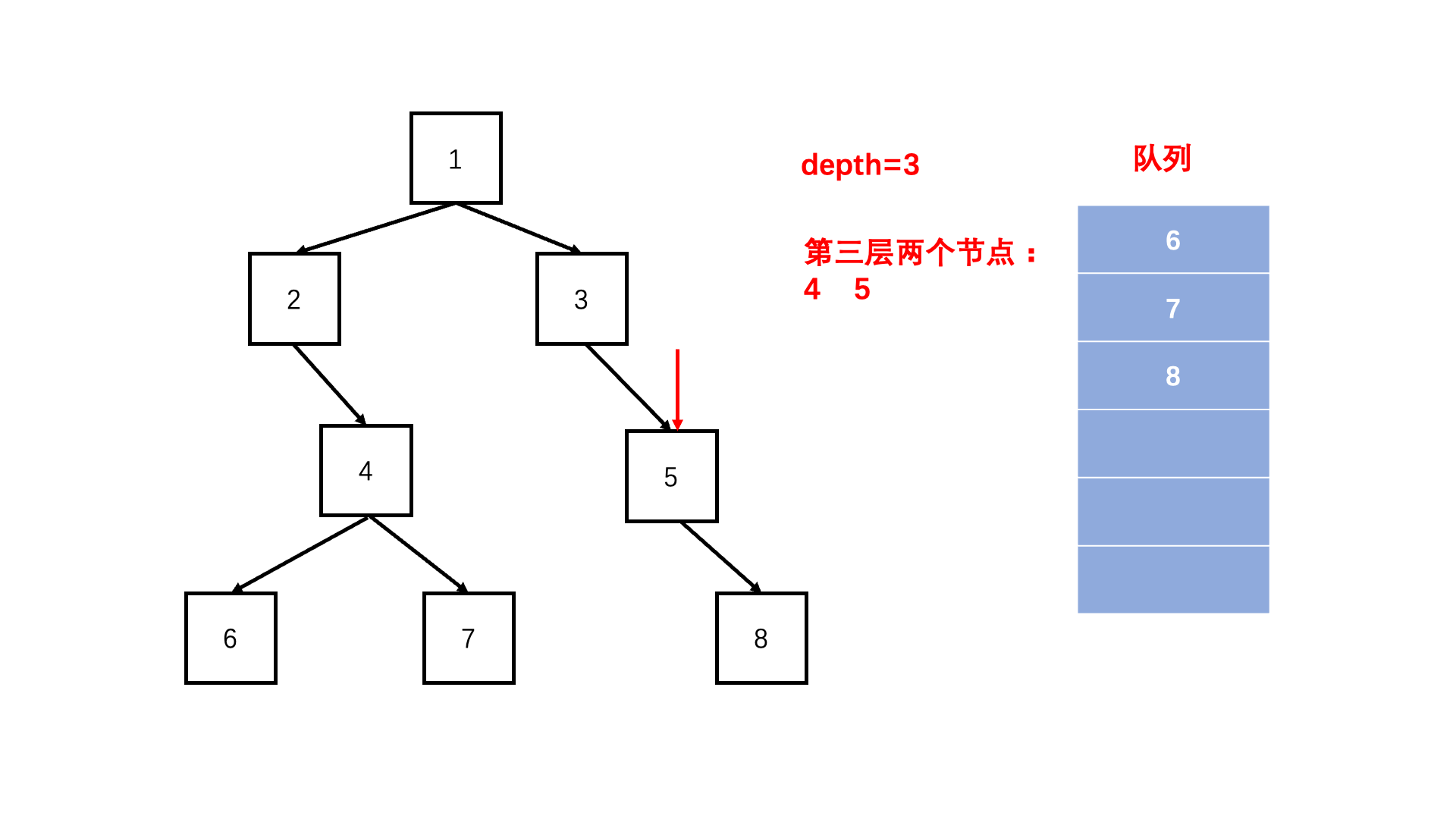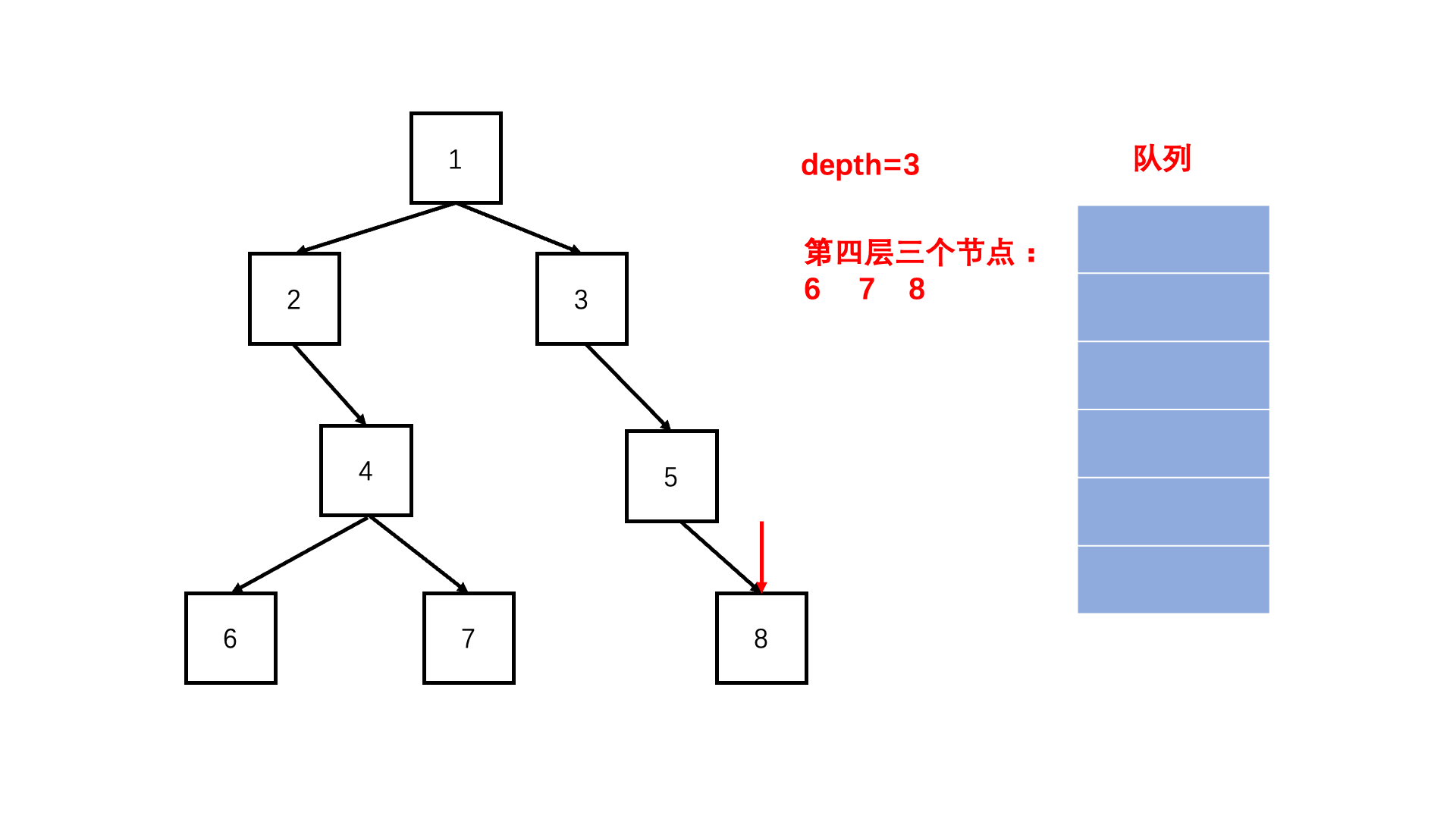
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {
//空节点没有深度
if(root == null)
return 0;
//队列维护层次后续节点
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
//根入队
q.offer(root);
//记录深度
int res = 0;
//层次遍历
while(!q.isEmpty()){
//记录当前层有多少节点
int n = q.size();
//遍历完这一层,再进入下一层
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
TreeNode node = q.poll();
//添加下一层的左右节点
if(node.left != null)
q.offer(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
q.offer(node.right);
}
//深度加1
res++;
}
return res;
}
}
7. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
7.1. 题目描述
7.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {
//空节点找不到路径
if(root == null)
return false;
//叶子节点,且路径和为sum
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && sum - root.val == 0)
return true;
//递归进入子节点
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
}
方法二:非递归(扩展思路)

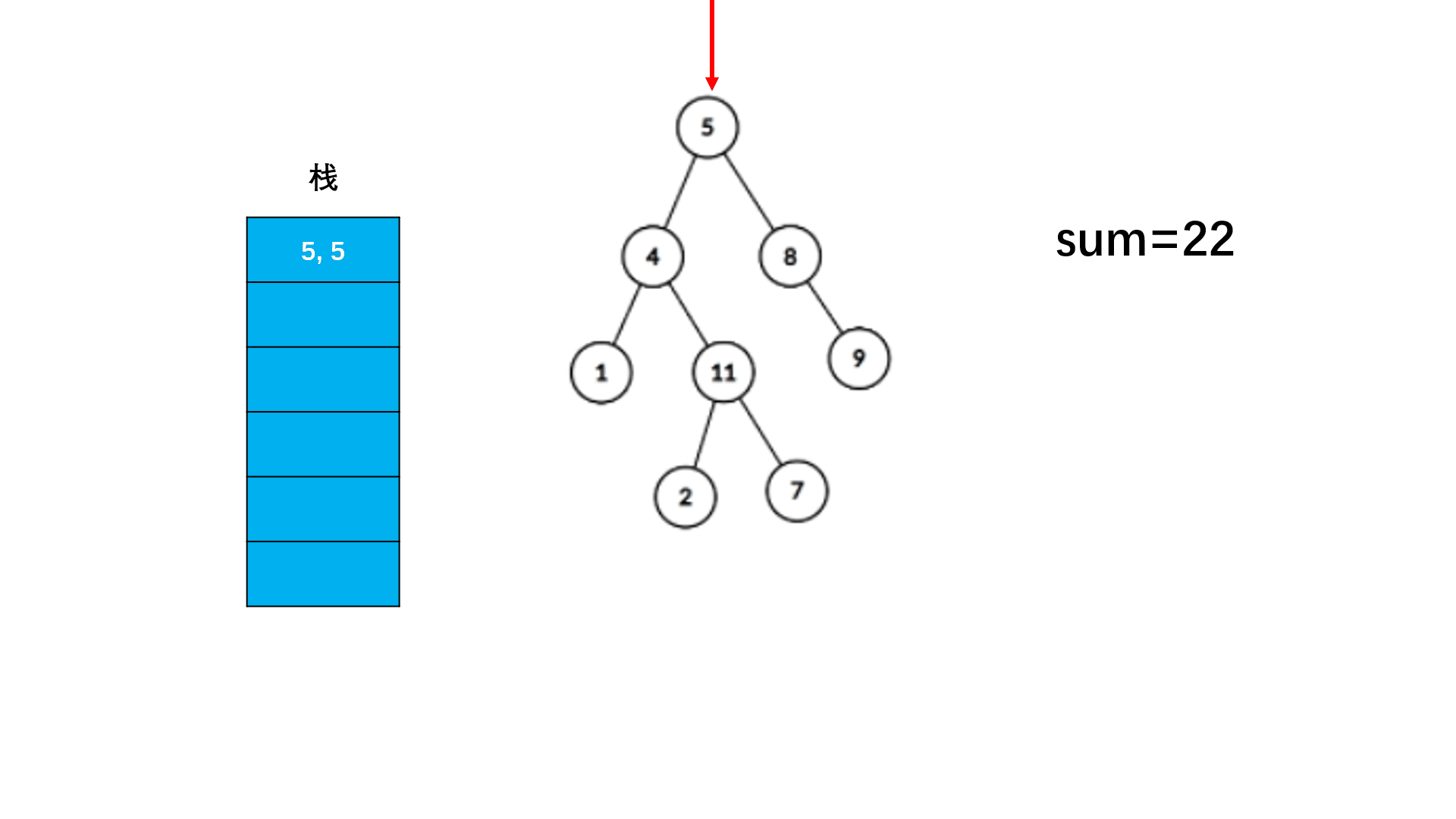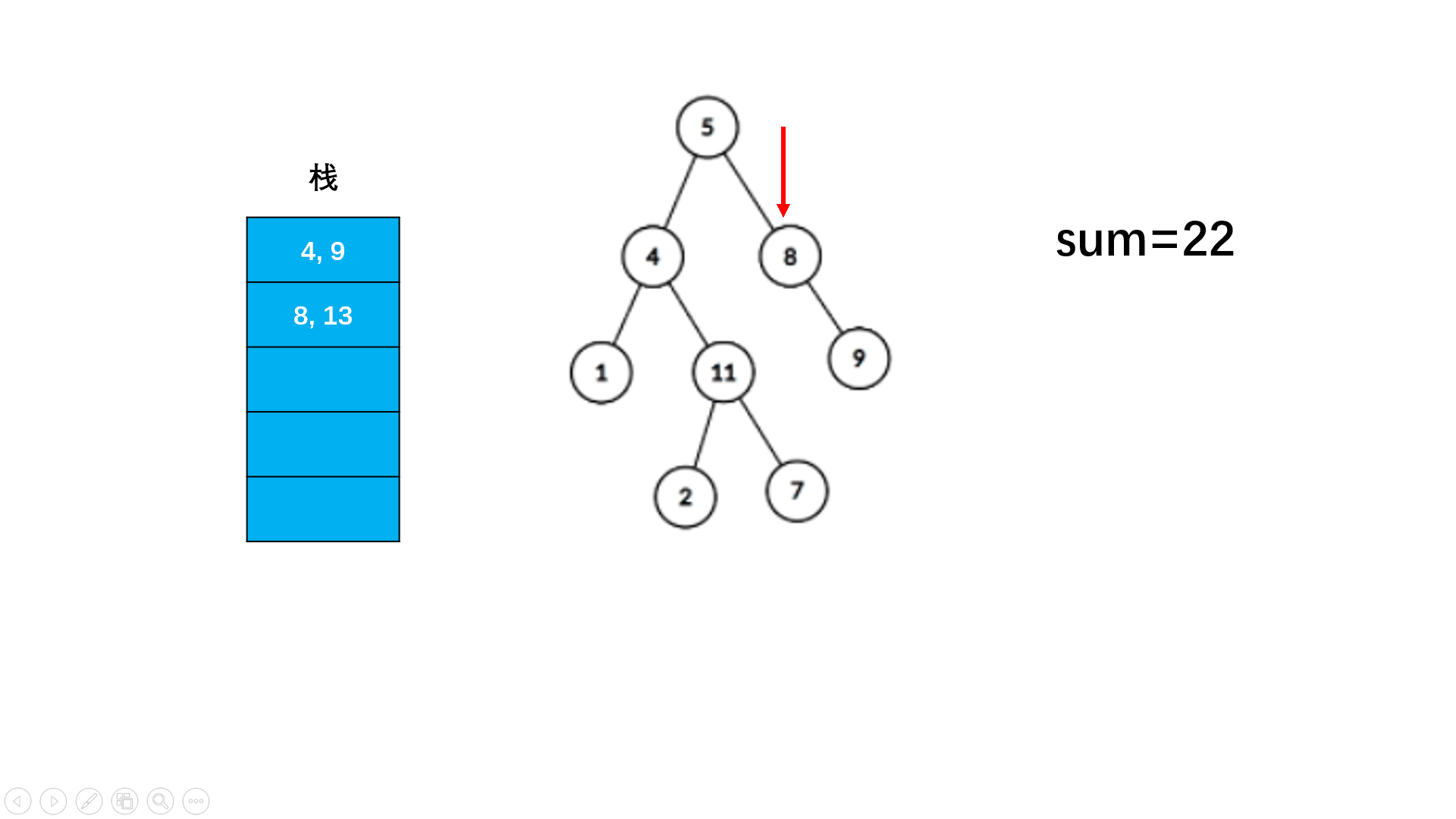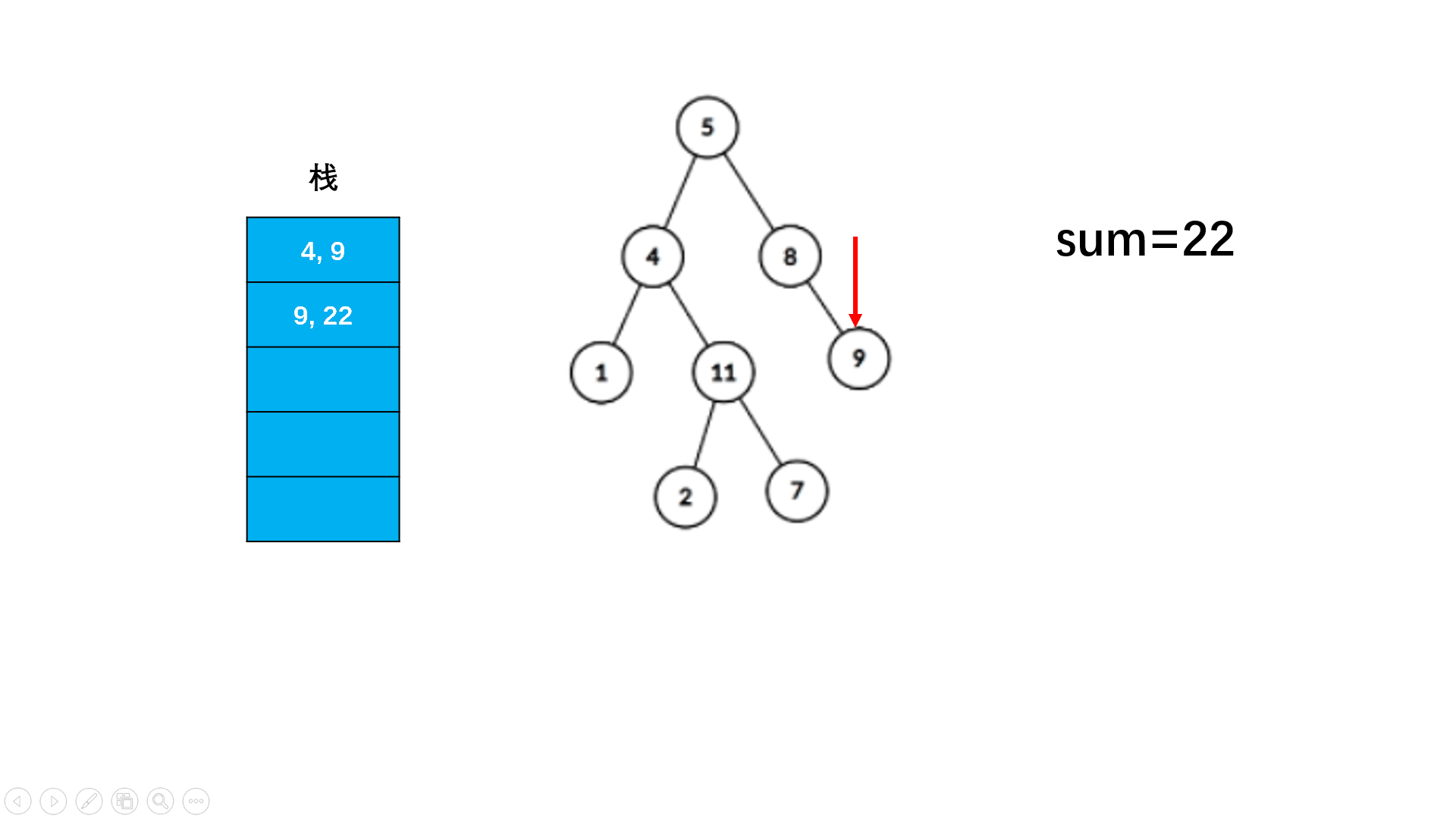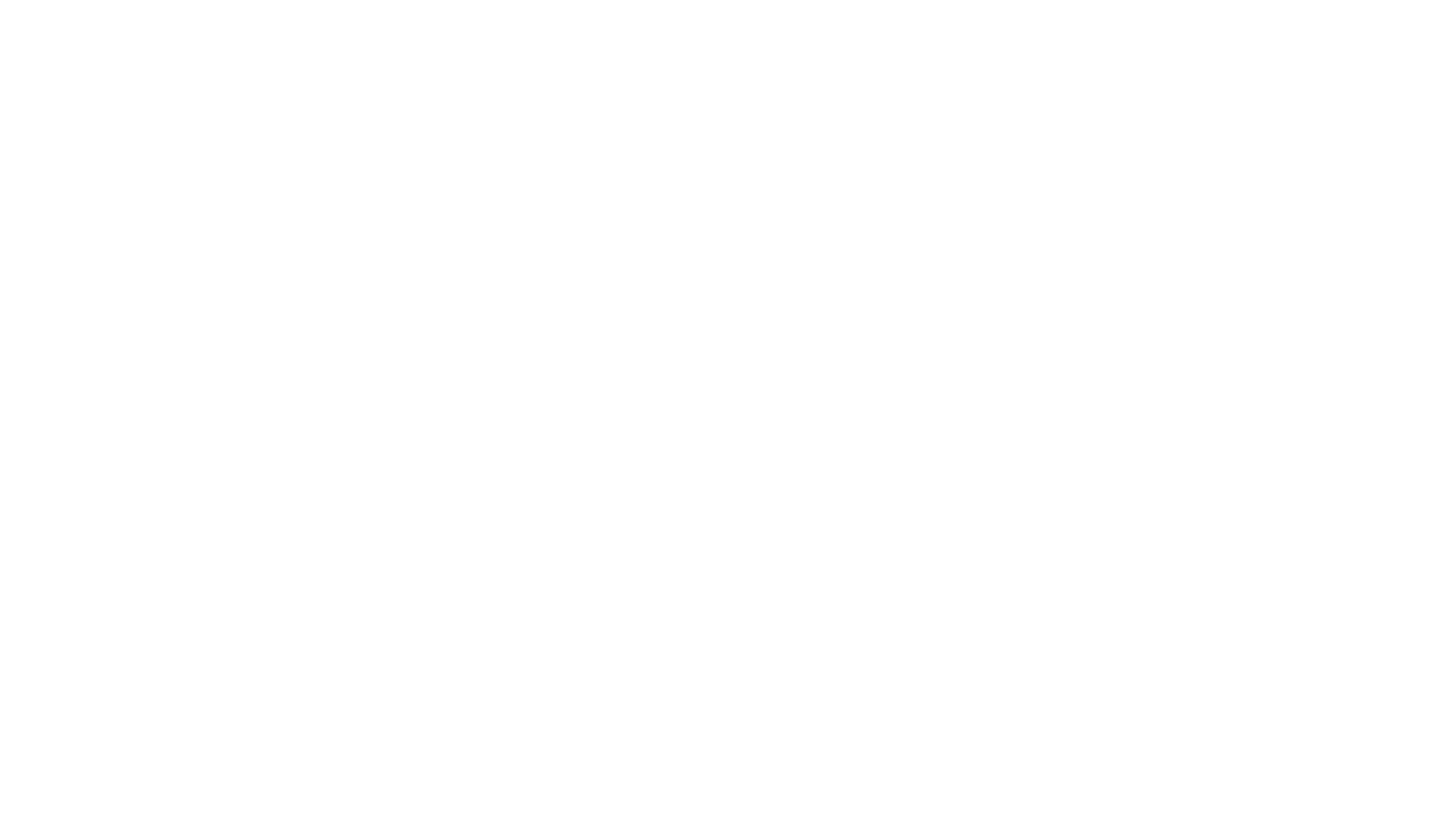
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {
//空节点找不到路径
if(root == null)
return false;
//栈辅助深度优先遍历
Stack<TreeNode> s1 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//跟随s1记录到相应节点为止的路径和
Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<Integer>();
s1.push(root);
s2.push(root.val);
while(!s1.isEmpty()){
//弹出相应节点
TreeNode temp = s1.pop();
//弹出到该点为止的当前路径和
int cur_sum = s2.pop();
//叶子节点且当前路径和等于sum
if(temp.left == null && temp.right == null && cur_sum == sum)
return true;
//左节点及路径和入栈
if(temp.left != null){
s1.push(temp.left);
s2.push(cur_sum + temp.left.val);
}
//右节点及路径和入栈
if(temp.right != null){
s1.push(temp.right);
s2.push(cur_sum + temp.right.val);
}
}
return false;
}
}8. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
8.1. 题目描述
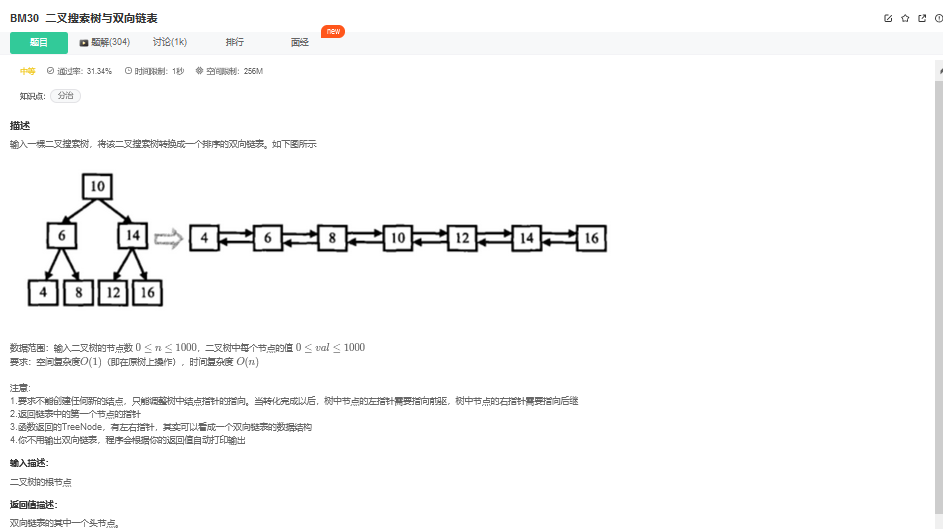
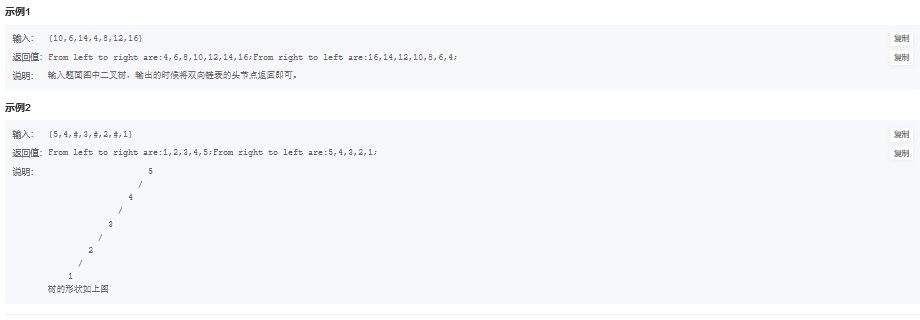
8.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归中序遍历(推荐使用)


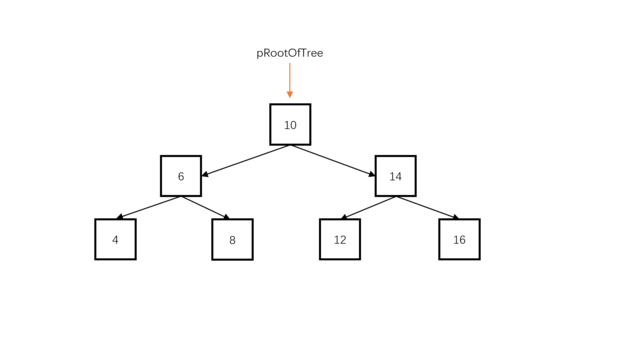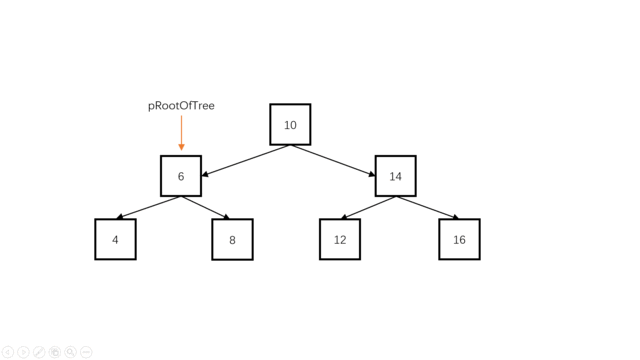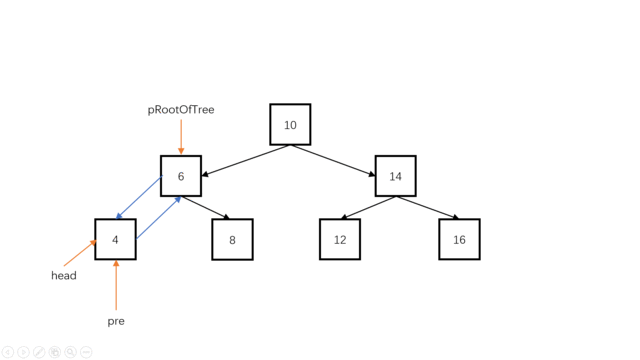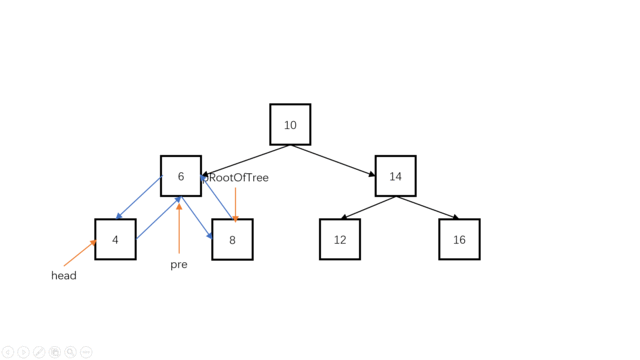
Java实现代码:
public class Solution {
//返回的第一个指针,即为最小值,先定为null
public TreeNode head = null;
//中序遍历当前值的上一位,初值为最小值,先定为null
public TreeNode pre = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null)
//中序递归,叶子为空则返回
return null;
//首先递归到最左最小值
Convert(pRootOfTree.left);
//找到最小值,初始化head与pre
if(pre == null){
head = pRootOfTree;
pre = pRootOfTree;
}
//当前节点与上一节点建立连接,将pre设置为当前值
else{
pre.right = pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree.left = pre;
pre = pRootOfTree;
}
Convert(pRootOfTree.right);
return head;
}
}
方法二:非递归中序遍历(扩展思路)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if (pRootOfTree == null)
return null;
//设置栈用于遍历
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode head = null;
TreeNode pre = null;
//确认第一个遍历到最左,即为首位
boolean isFirst = true;
while(pRootOfTree != null || !s.isEmpty()){
//直到没有左节点
while(pRootOfTree != null){
s.push(pRootOfTree);
pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.left;
}
pRootOfTree = s.pop();
//最左元素即表头
if(isFirst){
head = pRootOfTree;
pre = head;
isFirst = false;
//当前节点与上一节点建立连接,将pre设置为当前值
}else{
pre.right = pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree.left = pre;
pre = pRootOfTree;
}
pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.right;
}
return head;
}
}
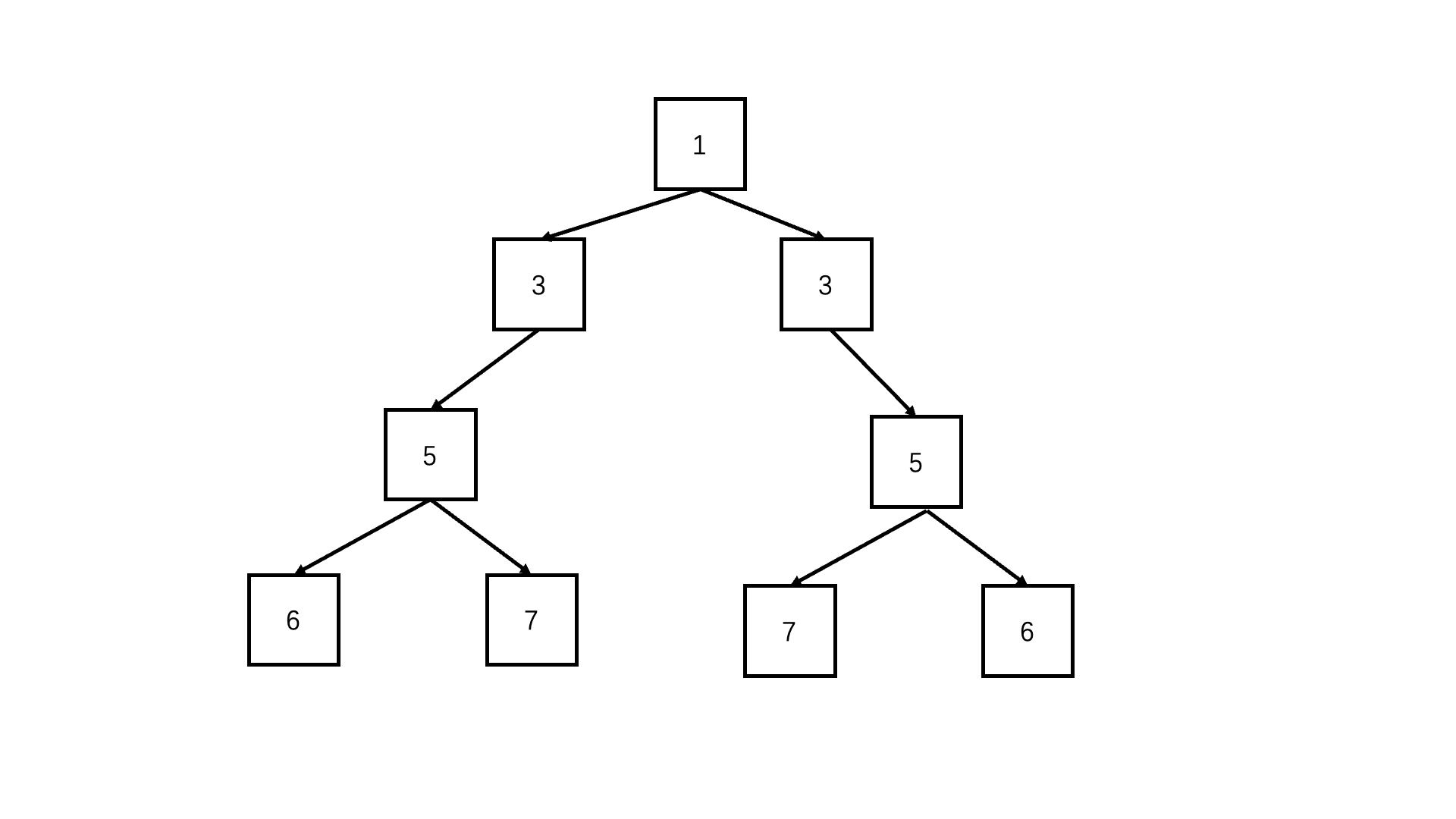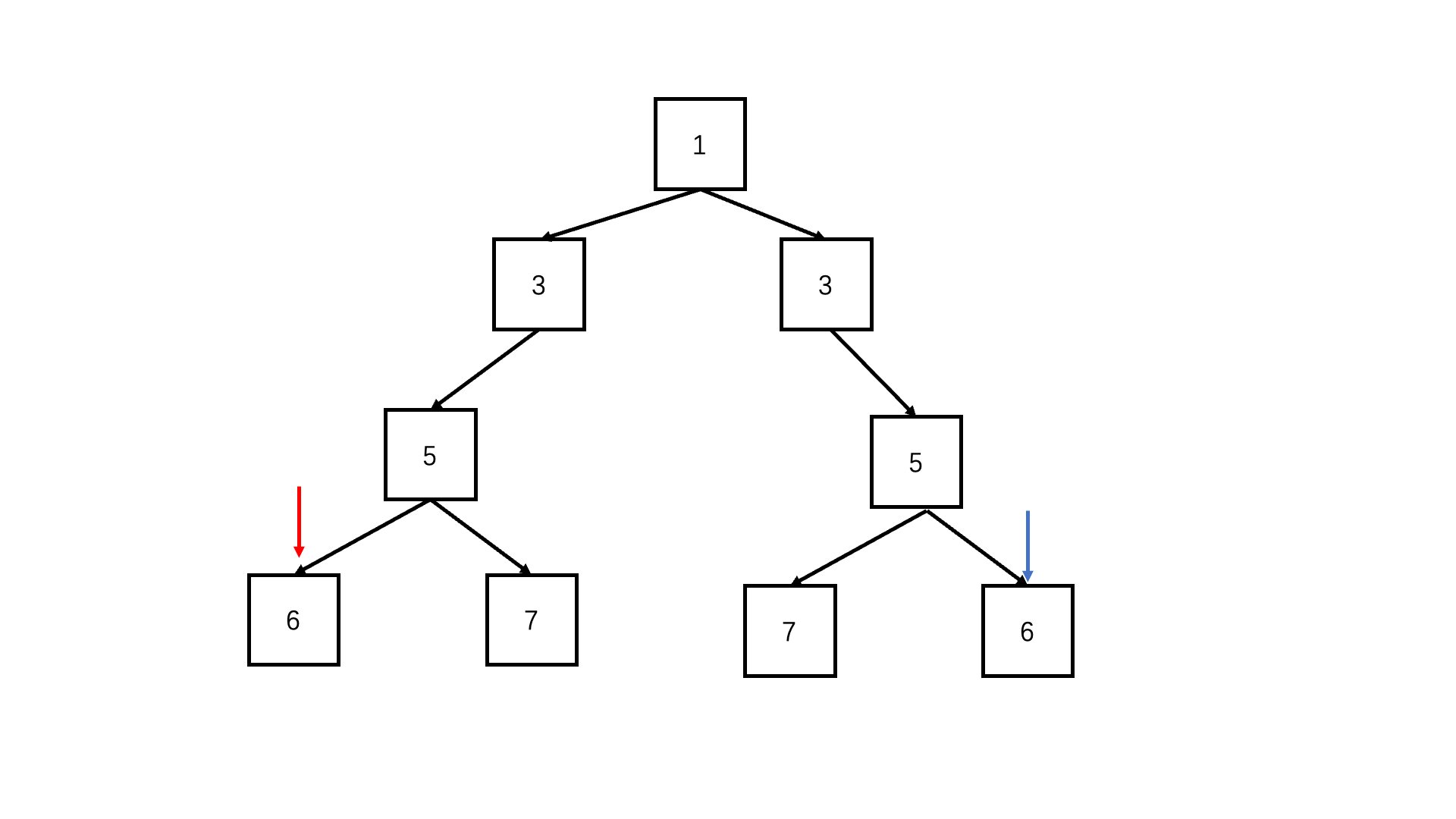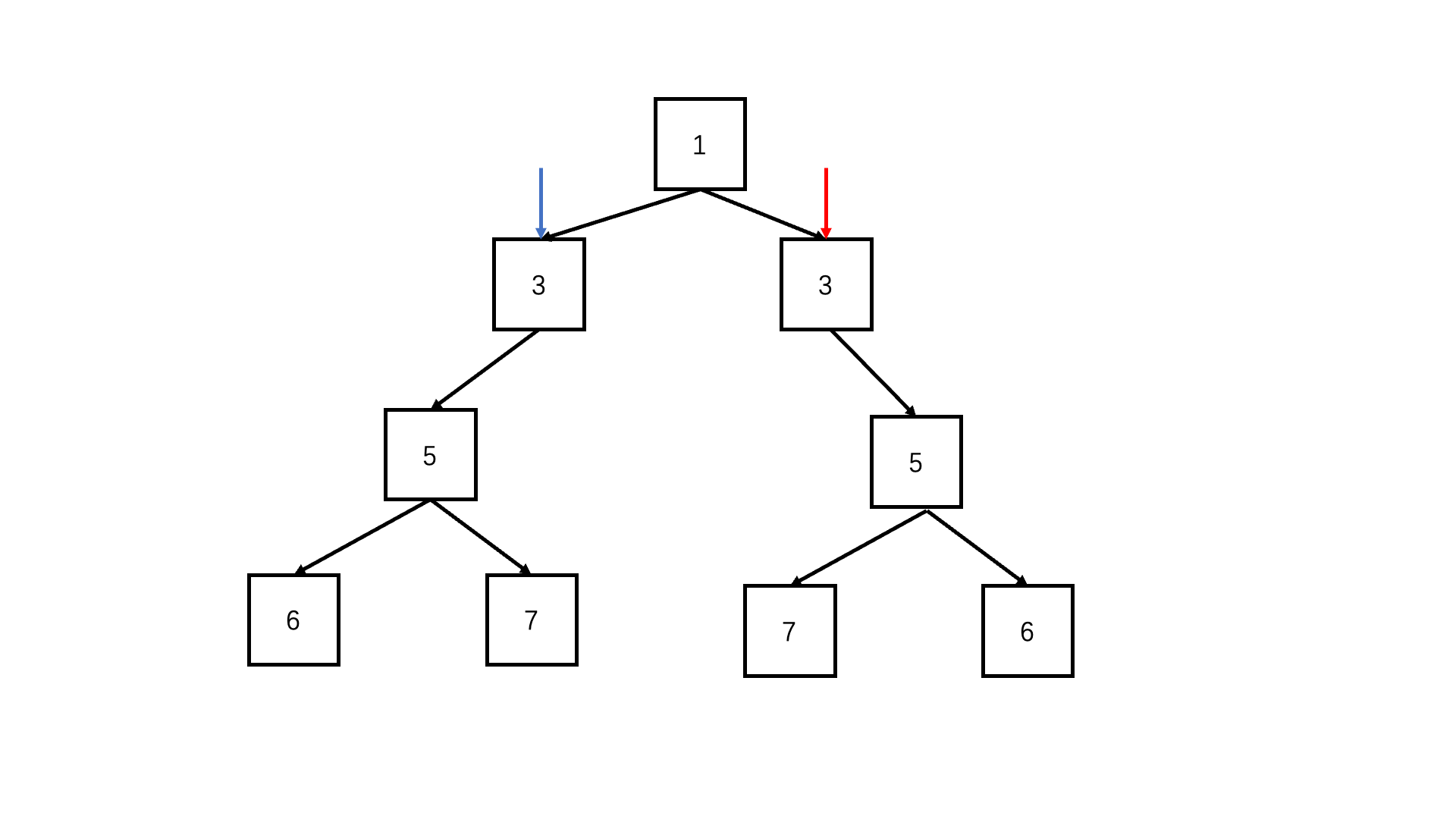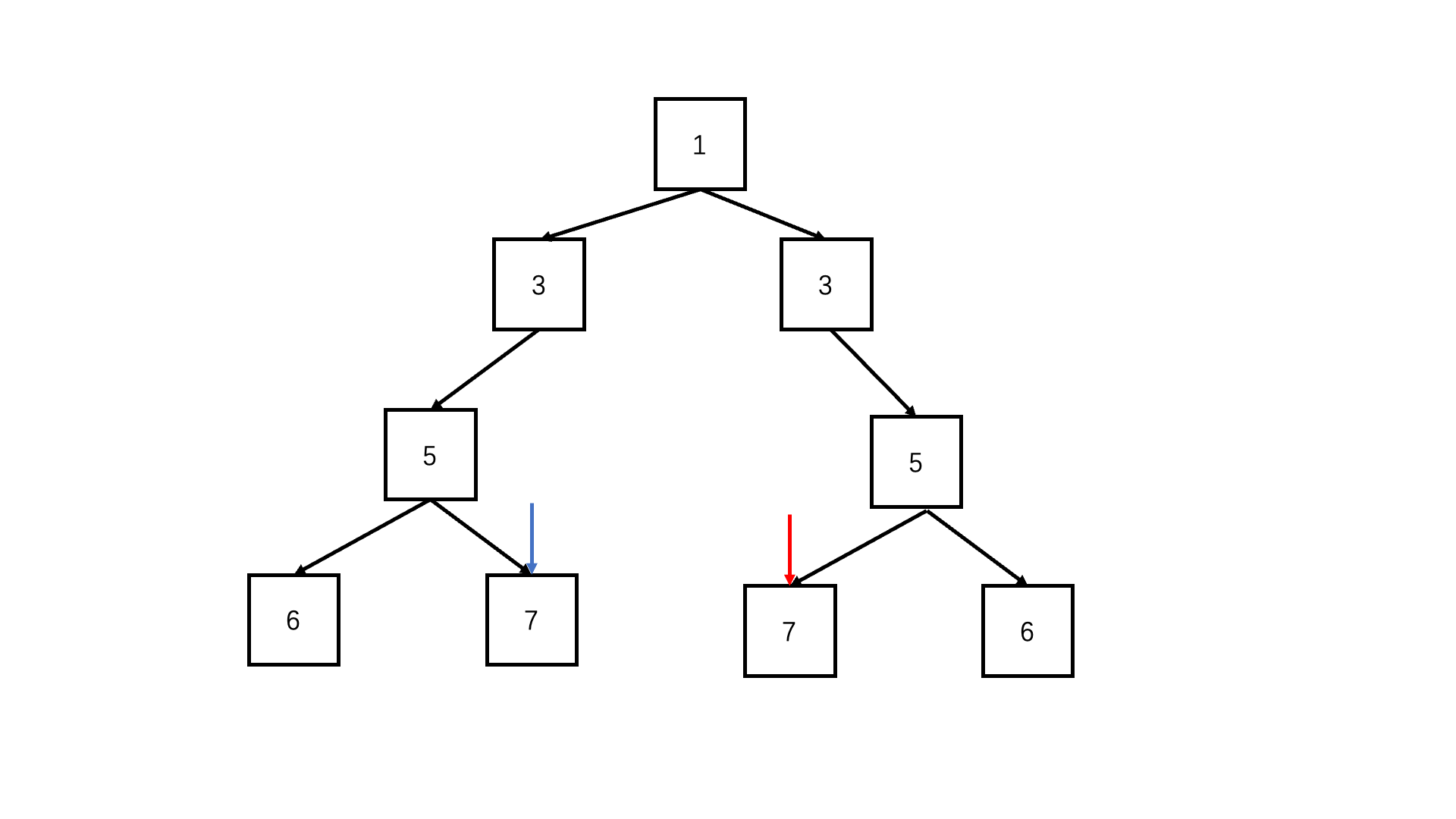
9. 对称的二叉树
9.1. 题目描述
9.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)

Java实现代码:
public class Solution {
boolean recursion(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2){
//可以两个都为空
if(root1 == null && root2 == null)
return true;
//只有一个为空或者节点值不同,必定不对称
if(root1 == null || root2 == null || root1.val != root2.val)
return false;
//每层对应的节点进入递归比较
return recursion(root1.left, root2.right) && recursion(root1.right, root2.left);
}
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
return recursion(pRoot, pRoot);
}
}
方法二:层次遍历(扩展思路)

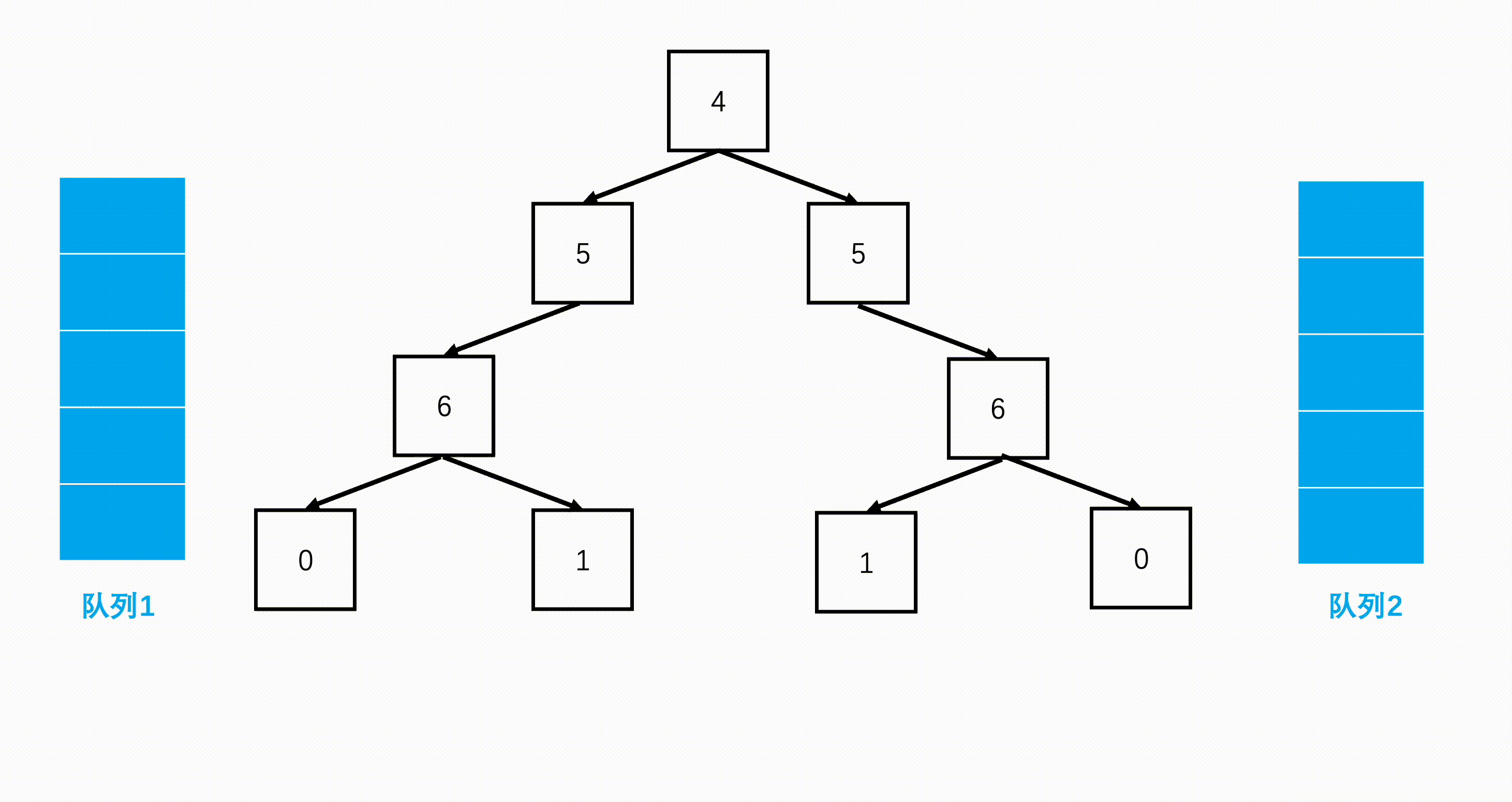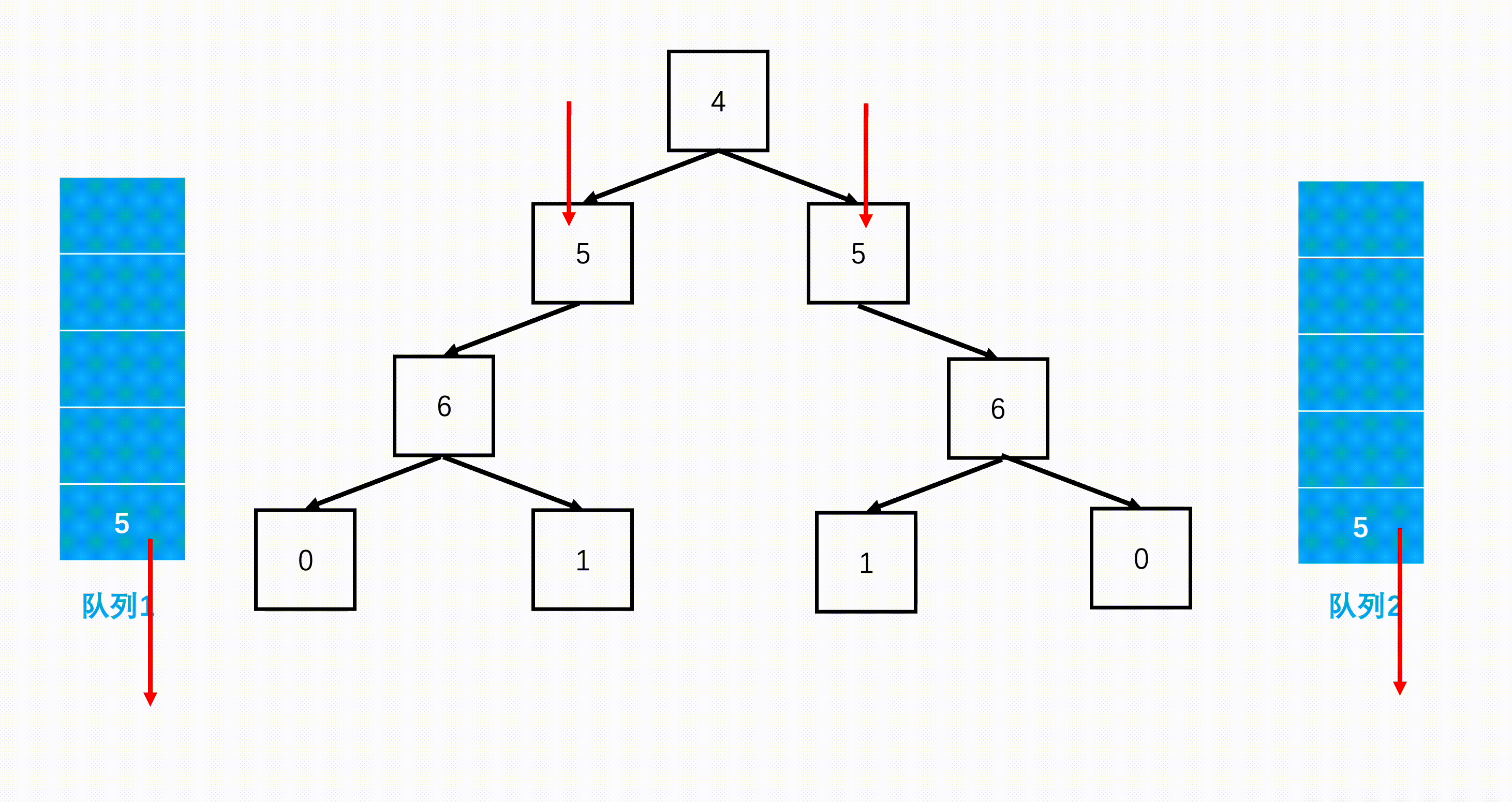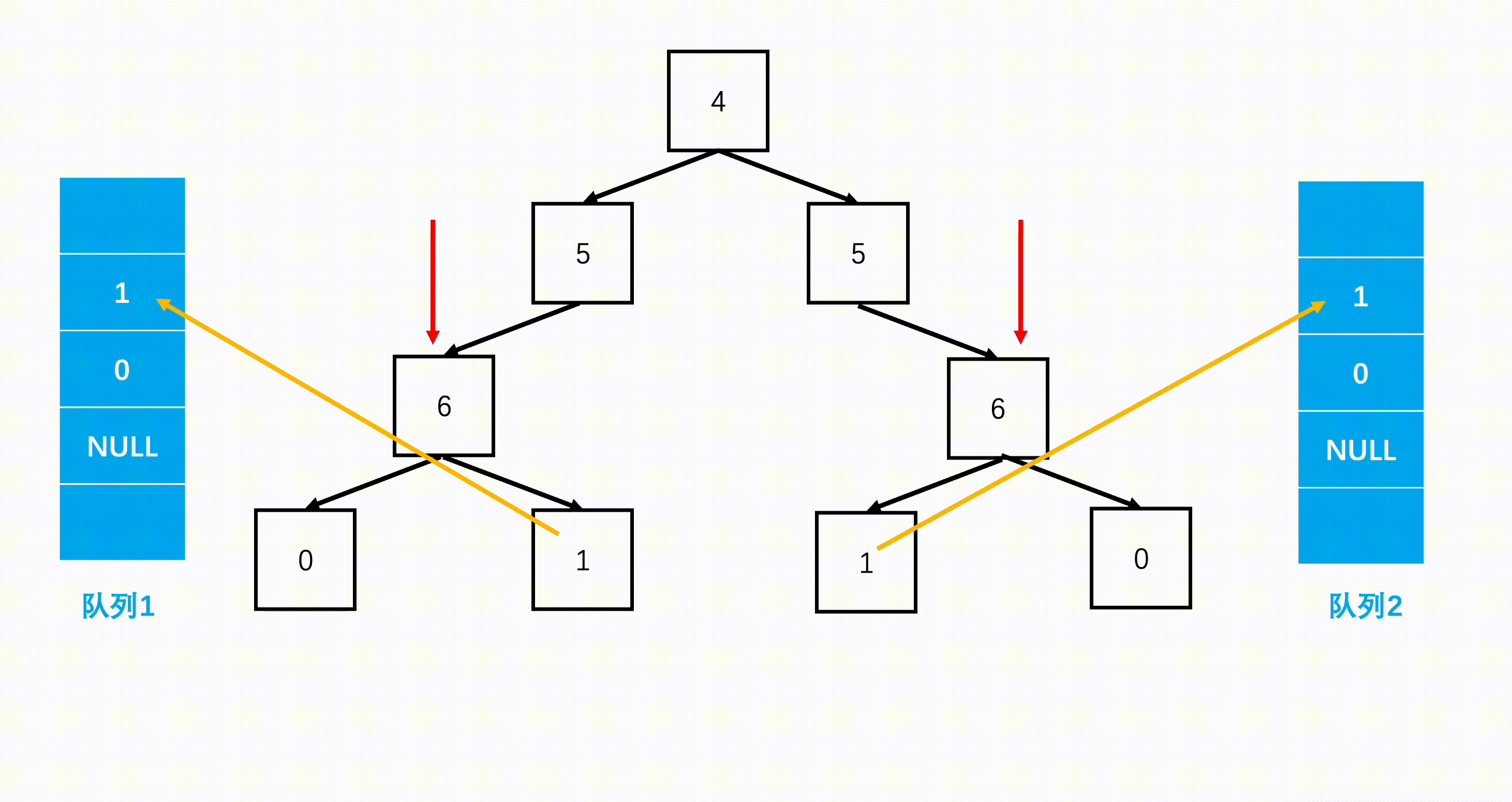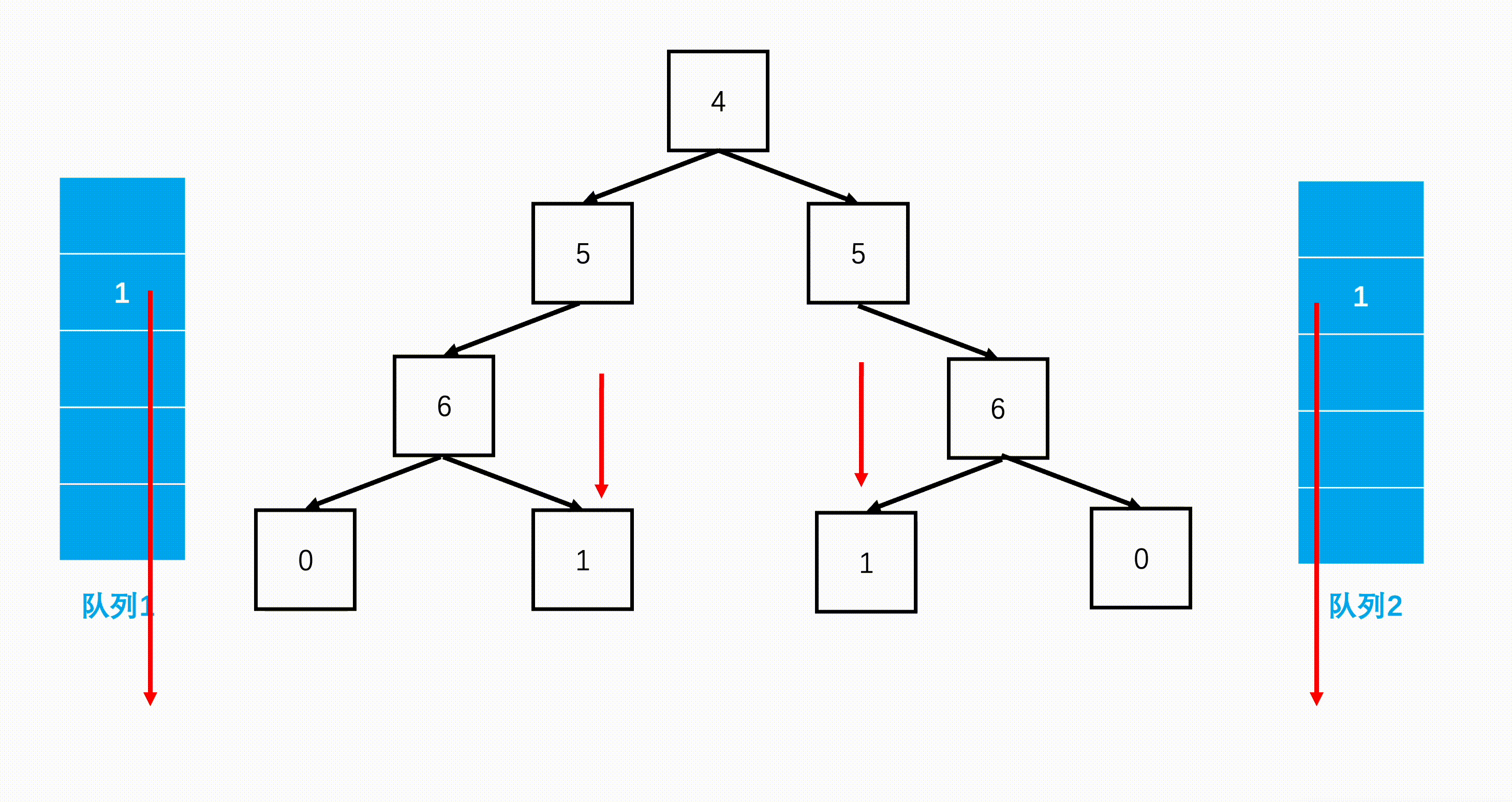
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
//空树为对称的
if(pRoot == null)
return true;
//辅助队列用于从两边层次遍历
Queue<TreeNode> q1 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> q2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q1.offer(pRoot.left);
q2.offer(pRoot.right);
while(!q1.isEmpty() && !q2.isEmpty()){
//分别从左边和右边弹出节点
TreeNode left = q1.poll();
TreeNode right = q2.poll();
//都为空暂时对称
if(left == null && right == null)
continue;
//某一个为空或者数字不相等则不对称
if(left == null || right == null || left.val != right.val)
return false;
//从左往右加入队列
q1.offer(left.left);
q1.offer(left.right);
//从右往左加入队列
q2.offer(right.right);
q2.offer(right.left);
}
//都检验完都是对称的
return true;
}
}
10. 合并二叉树
10.1. 题目描述
10.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归前序遍历(推荐使用)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
//若只有一个节点返回另一个,两个都为null自然返回null
if (t1 == null)
return t2;
if (t2 == null)
return t1;
//根左右的方式递归
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
head.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
head.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
return head;
}
}
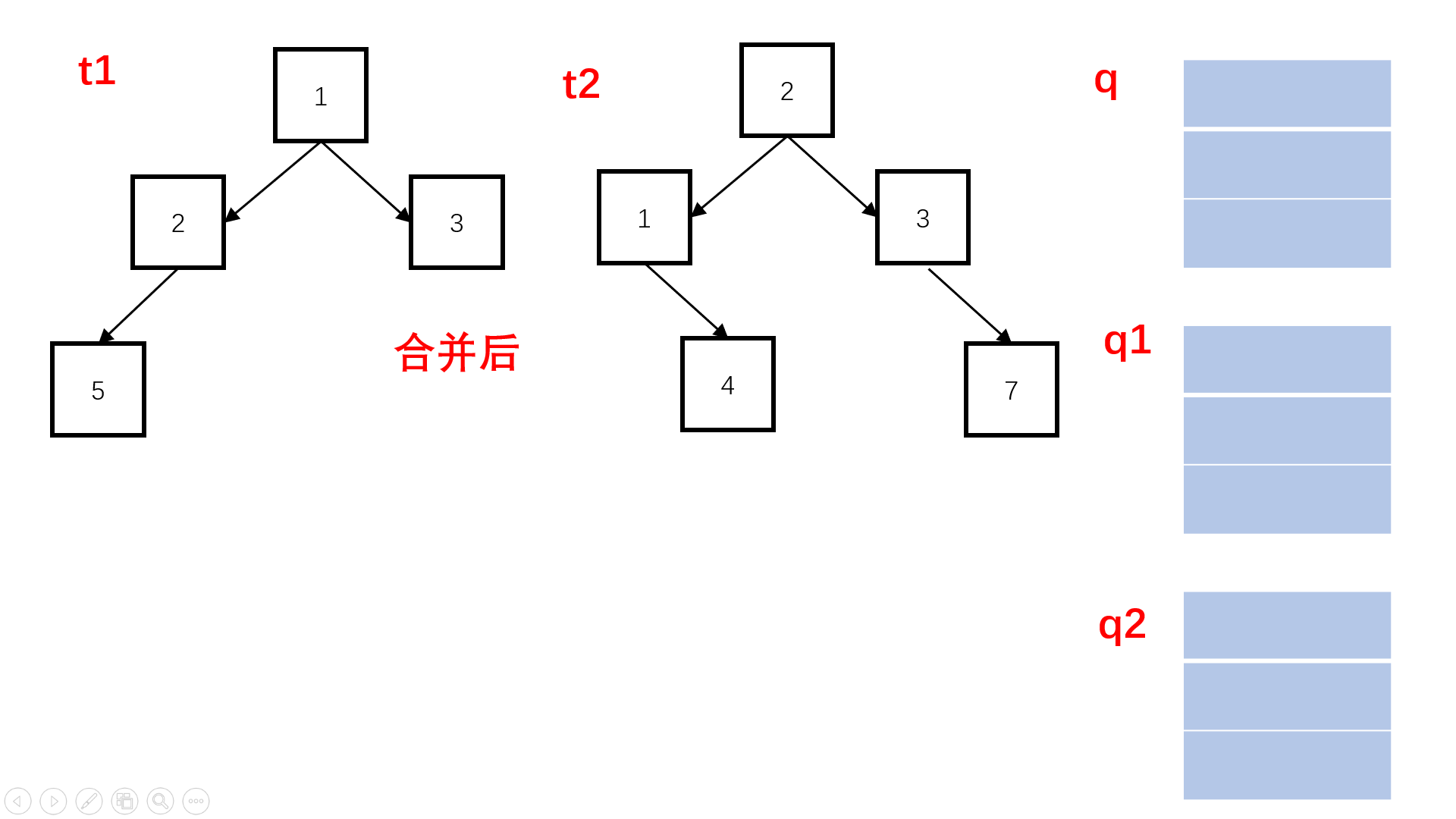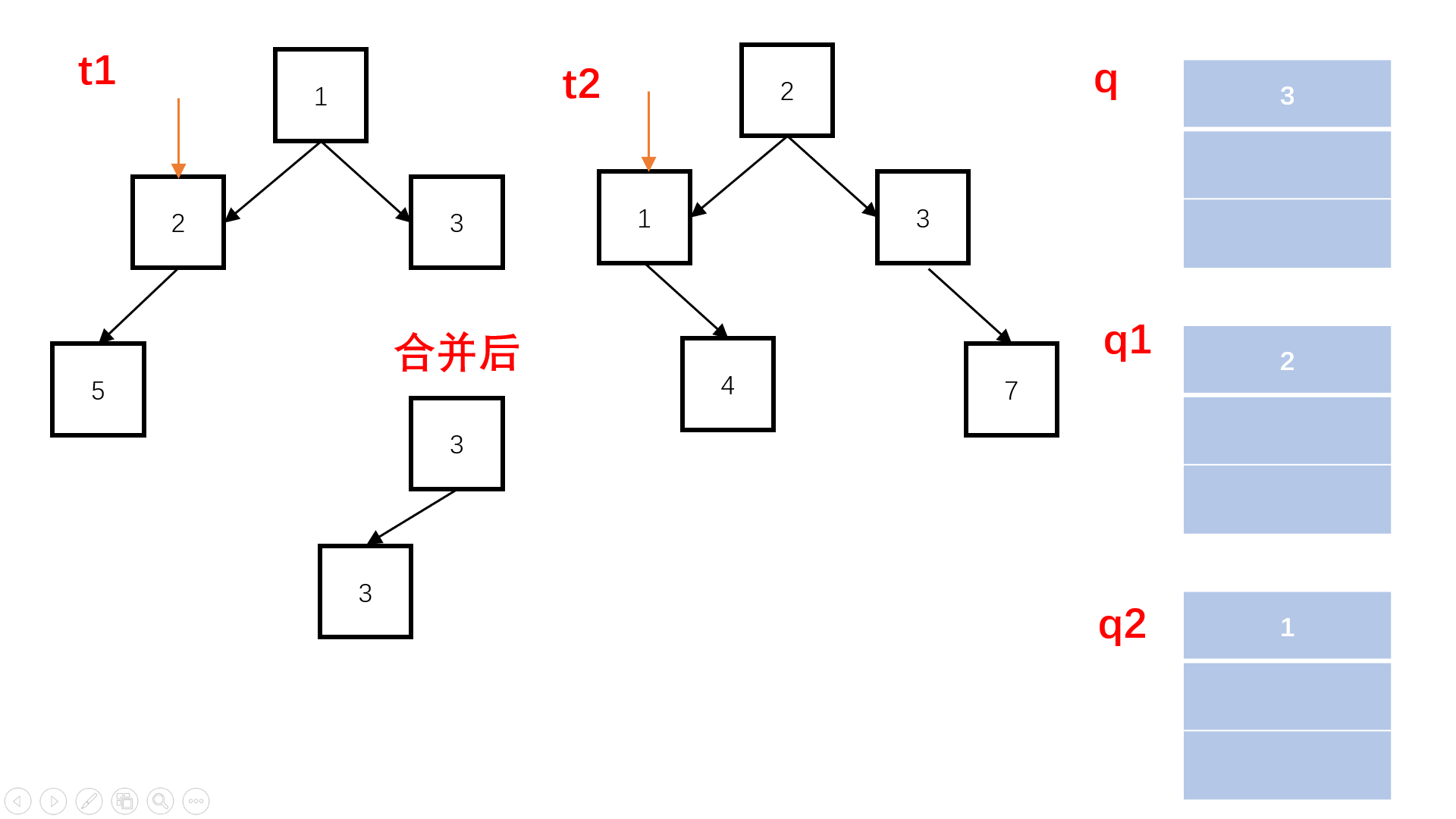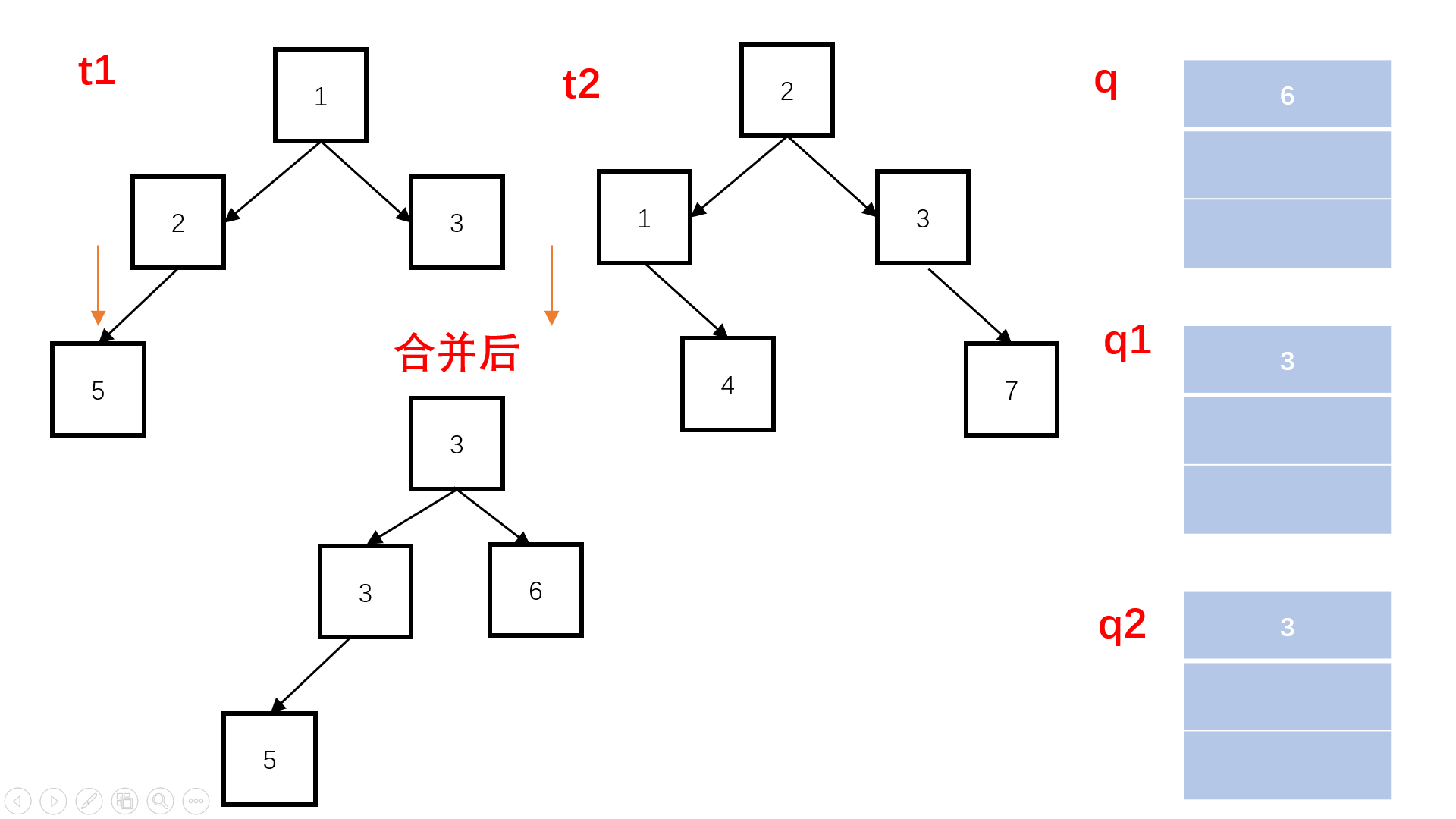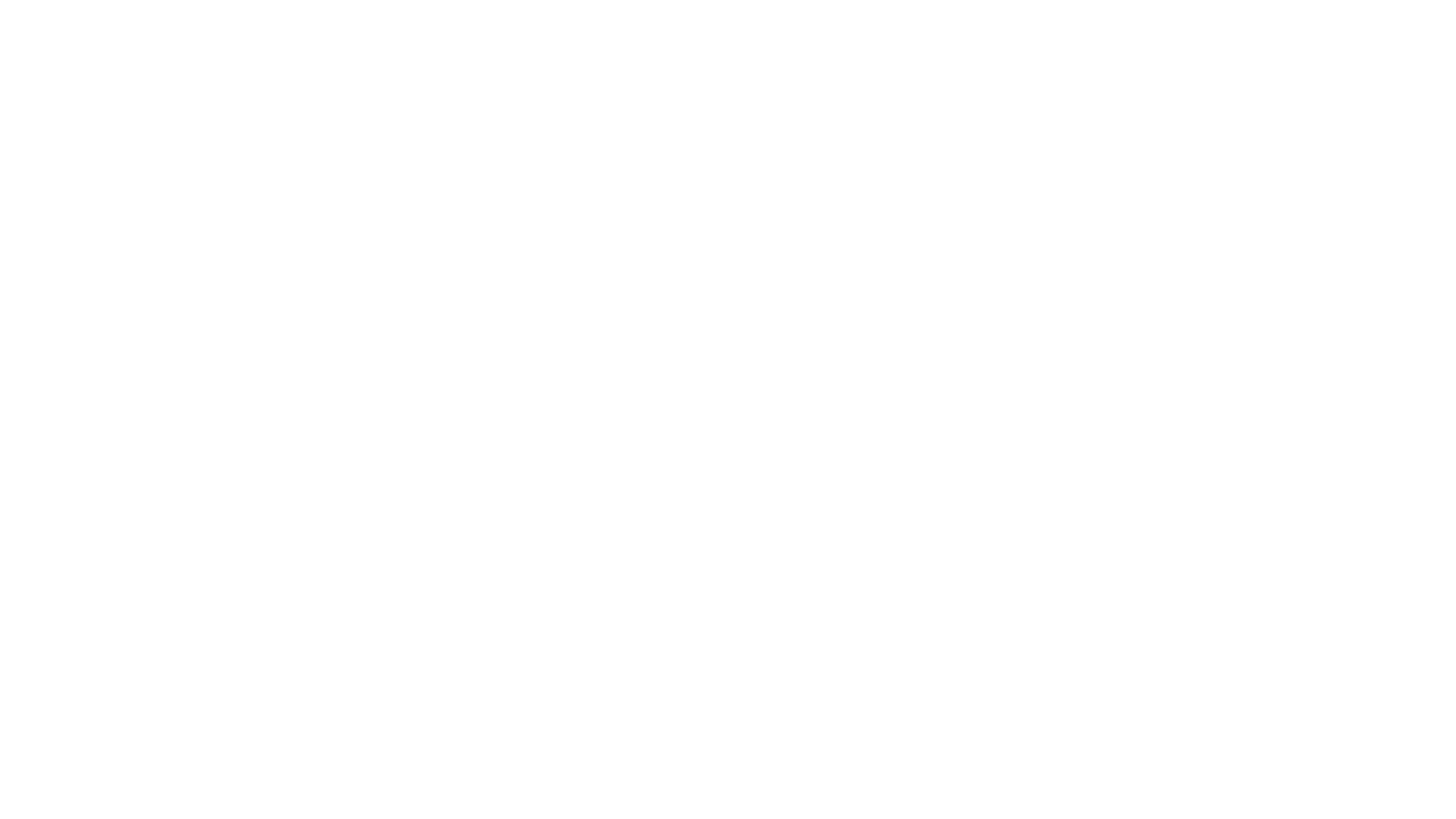
方法二:非递归层次遍历(扩展思路)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
//若只有一个节点返回另一个,两个都为null自然返回null
if (t1 == null)
return t2;
if (t2 == null)
return t1;
//合并根节点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
//连接后的树的层次遍历节点
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
//分别存两棵树的层次遍历节点
Queue<TreeNode> q1 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> q2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.offer(head);
q1.offer(t1);
q2.offer(t2);
while (!q1.isEmpty() && !q2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
TreeNode node1 = q1.poll();
TreeNode node2 = q2.poll();
TreeNode left1 = node1.left;
TreeNode left2 = node2.left;
TreeNode right1 = node1.right;
TreeNode right2 = node2.right;
if(left1 != null || left2 != null){
//两个左节点都存在
if(left1 != null && left2 != null){
TreeNode left = new TreeNode(left1.val + left2.val);
node.left = left;
//新节点入队列
q.offer(left);
q1.offer(left1);
q2.offer(left2);
//只连接一个节点
}else if(left1 != null)
node.left = left1;
else
node.left = left2;
}
if(right1 != null || right2 != null){
//两个右节点都存在
if(right1 != null && right2 != null) {
TreeNode right = new TreeNode(right1.val + right2.val);
node.right = right;
//新节点入队列
q.offer(right);
q1.offer(right1);
q2.offer(right2);
//只连接一个节点
}else if(right1 != null)
node.right = right1;
else
node.right = right2;
}
}
return head;
}
}

11. 二叉树的镜像
11.1. 题目描述

11.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)


Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {
//空树返回
if(pRoot == null)
return null;
//先递归子树
TreeNode left = Mirror(pRoot.left);
TreeNode right = Mirror(pRoot.right);
//交换
pRoot.left = right;
pRoot.right = left;
return pRoot;
}
}

方法二:栈(扩展思路)

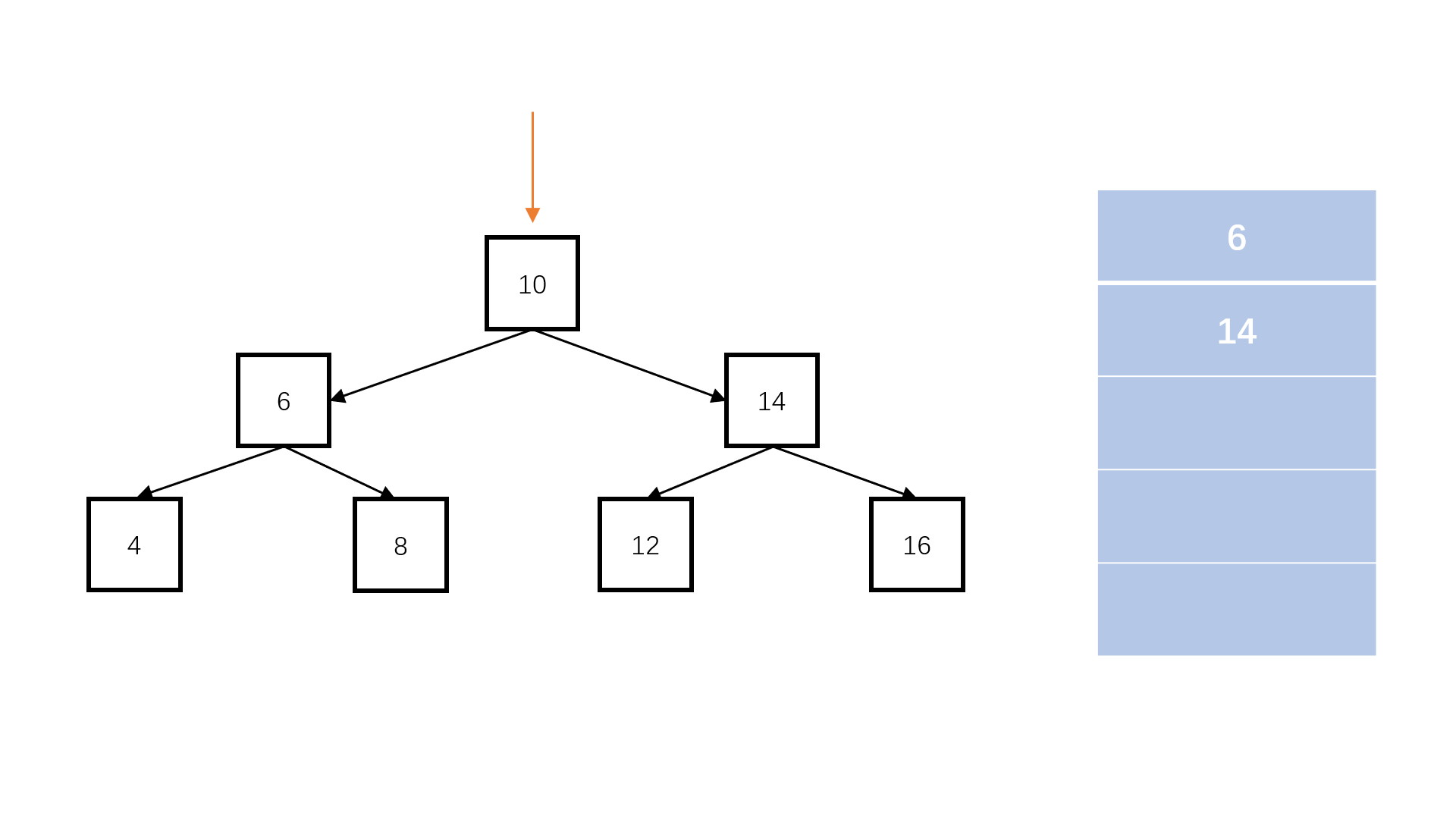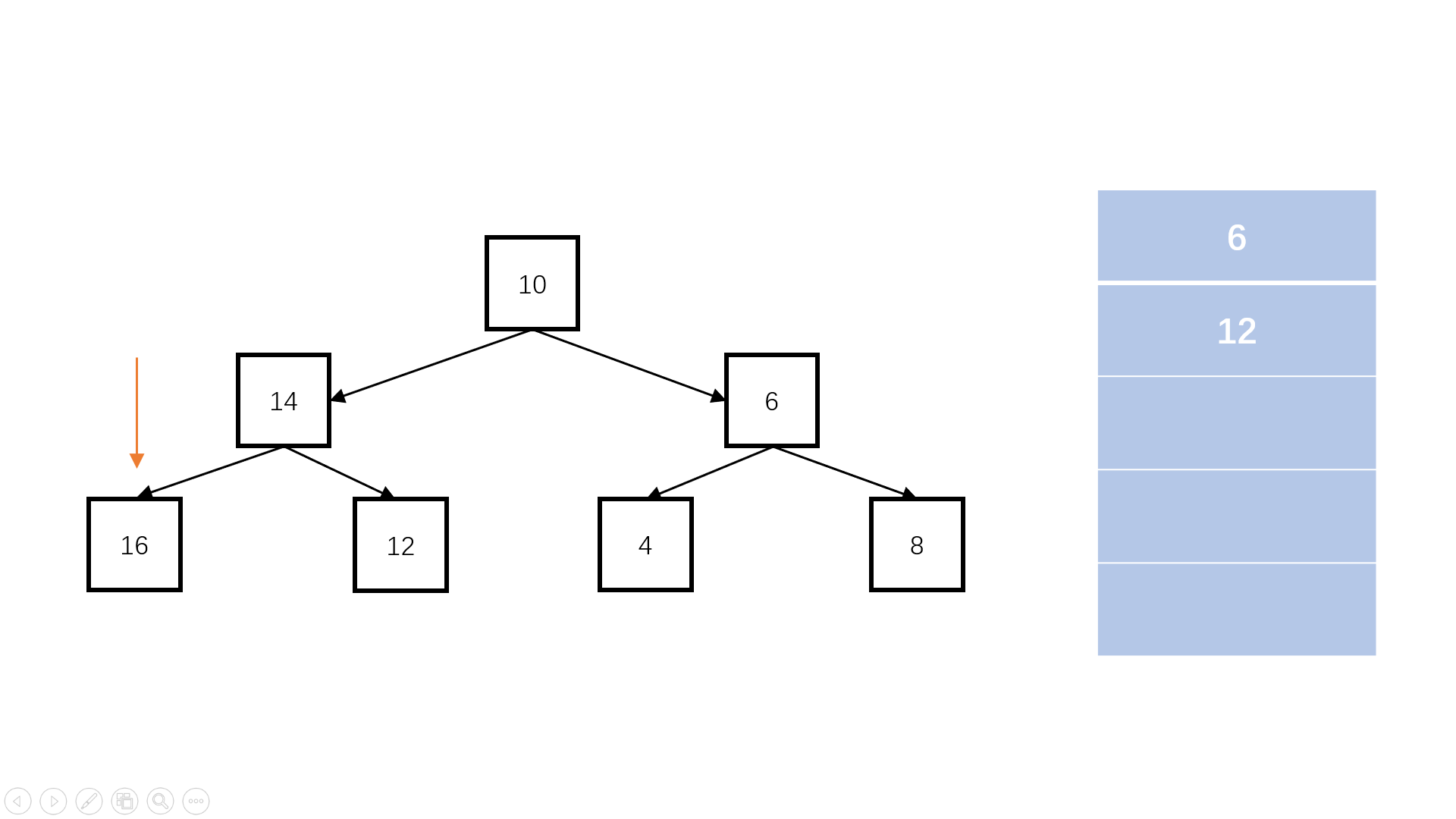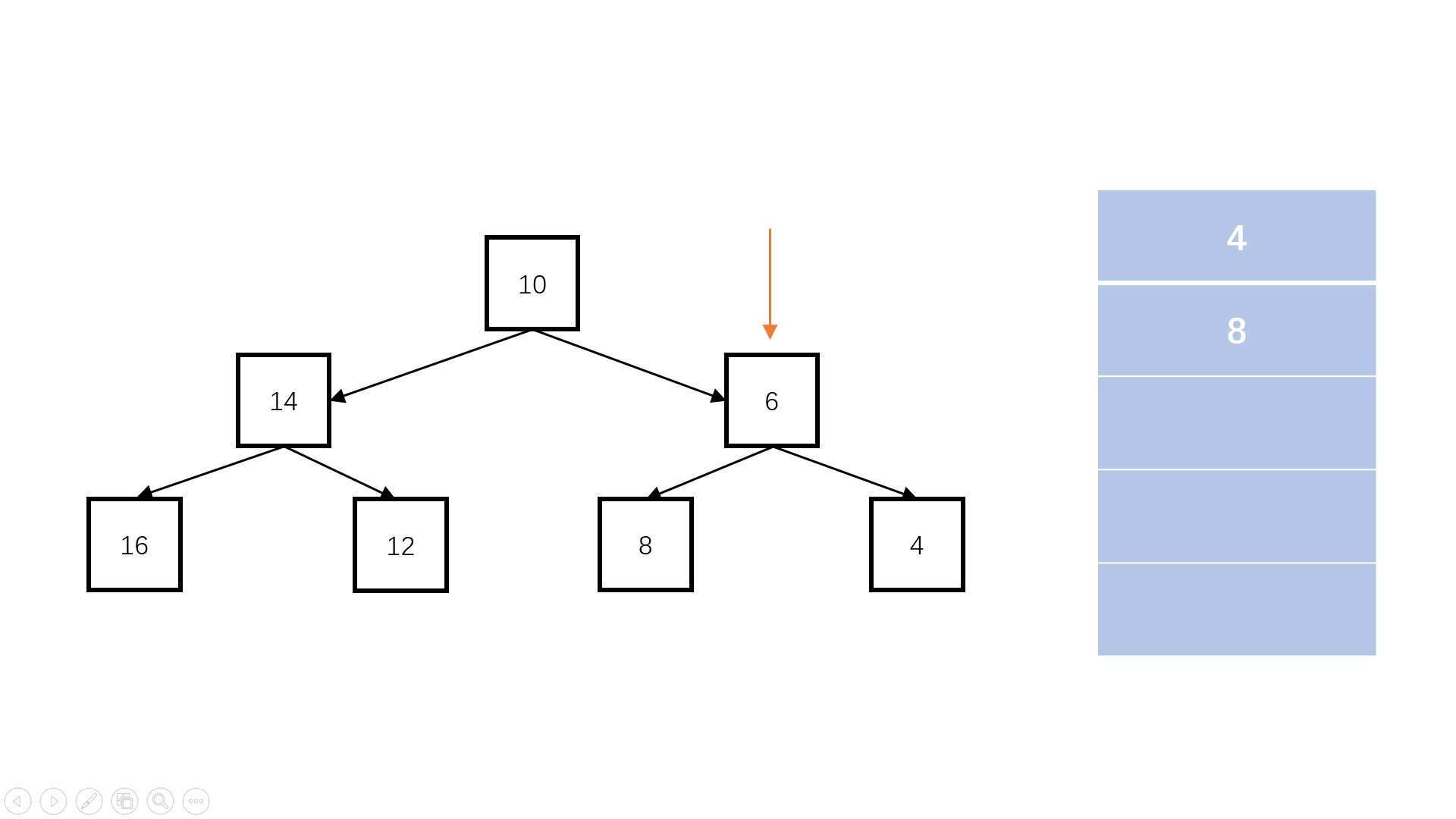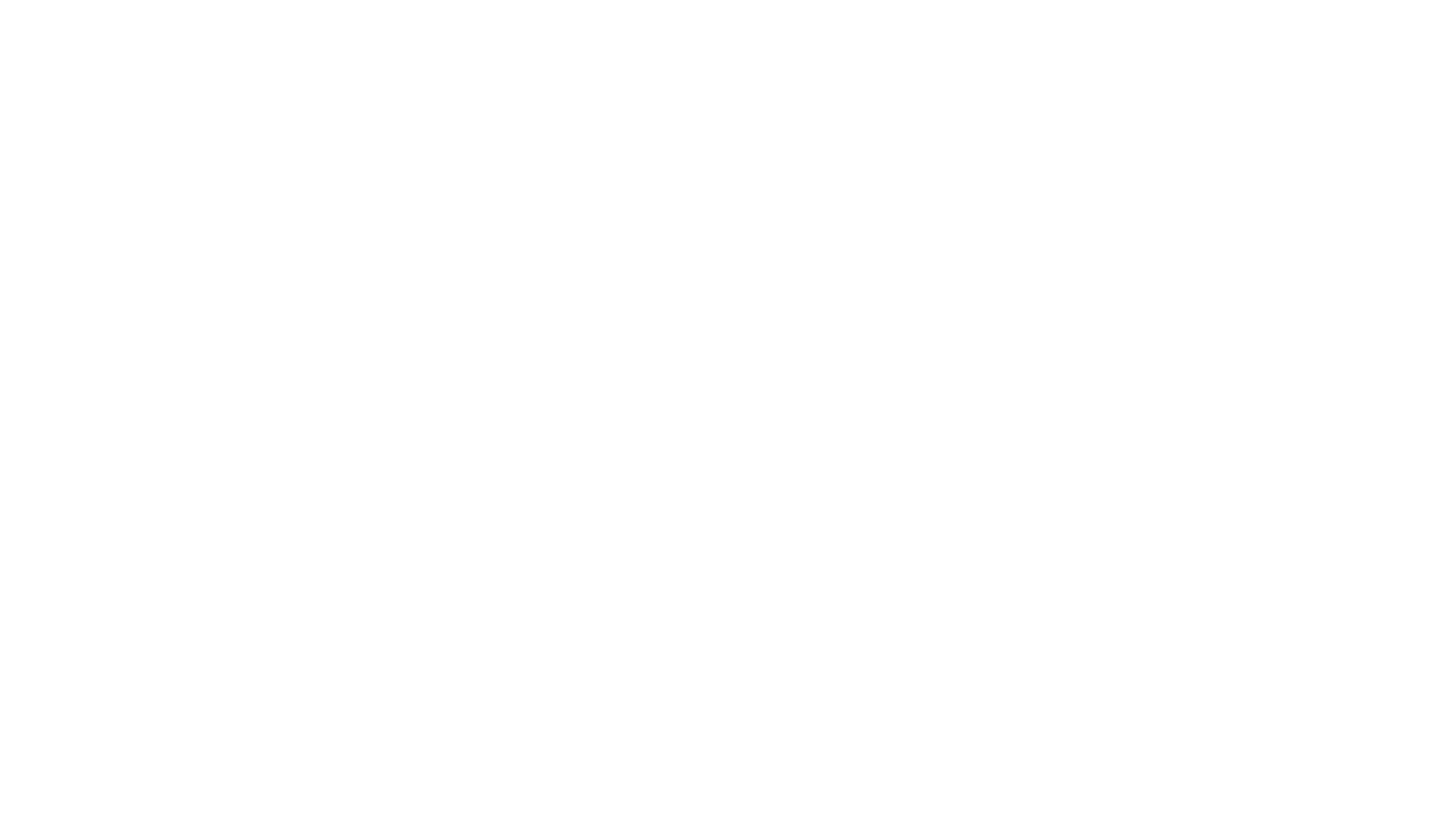
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {
//空树
if(pRoot == null)
return null;
//辅助栈
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//根节点先进栈
s.push(pRoot);
while (!s.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = s.pop();
//左右节点入栈
if(node.left != null)
s.push(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
s.push(node.right);
//交换左右
TreeNode temp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = temp;
}
return pRoot;
}
}
12. 判断是不是二叉搜索树
12.1. 题目描述
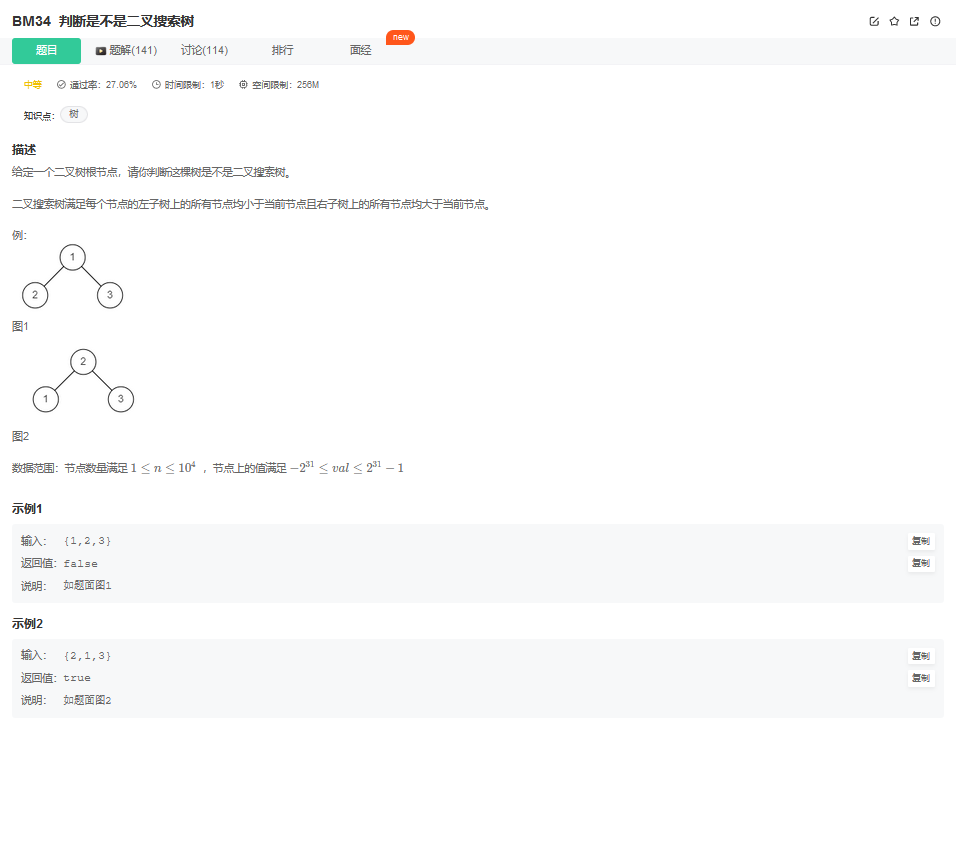
12.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//中序遍历
public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return true;
//先进入左子树
if(!isValidBST(root.left))
return false;
if(root.val < pre)
return false;
//更新最值
pre = root.val;
//再进入右子树
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
方法二:非递归(扩展思路)

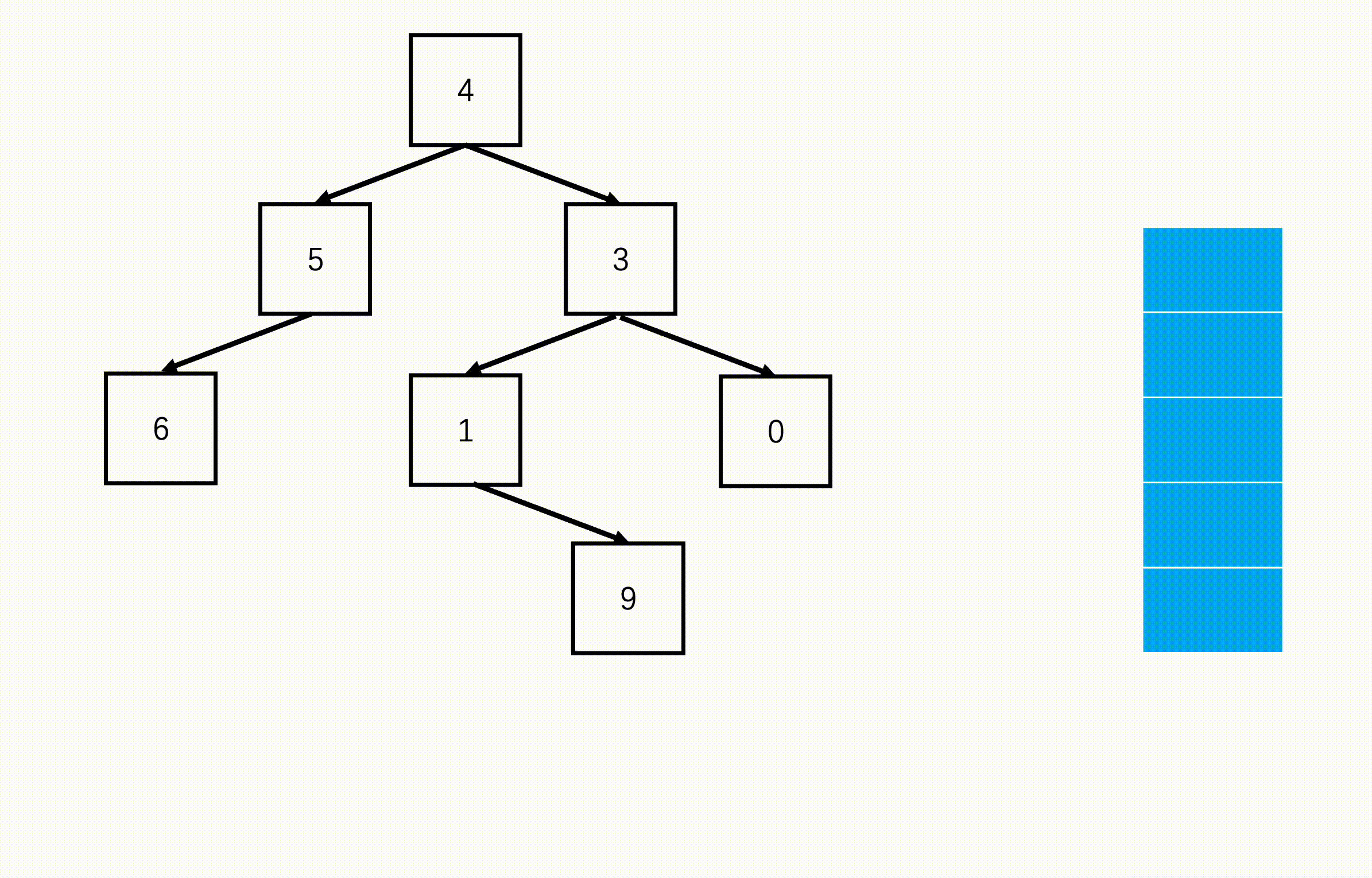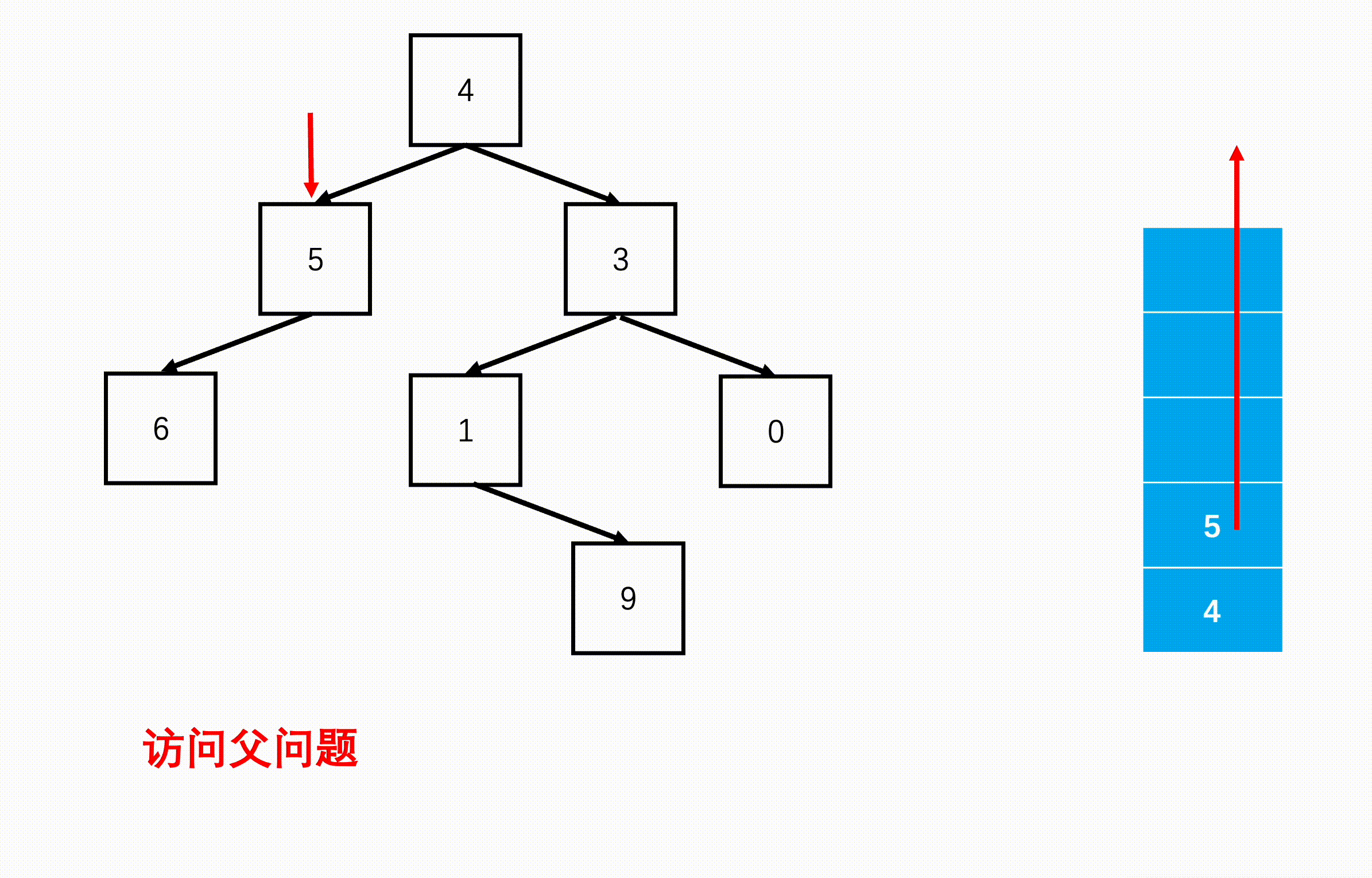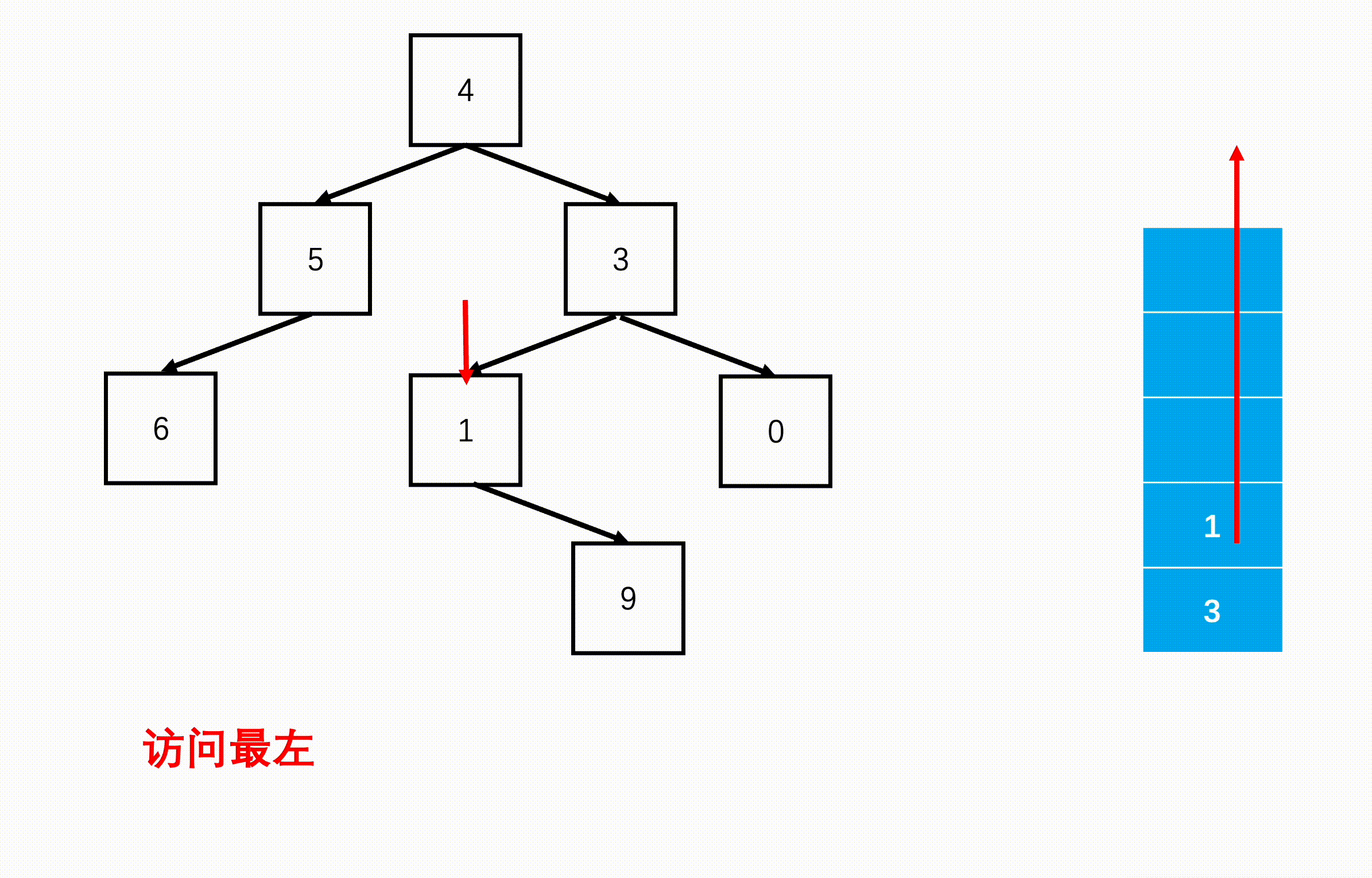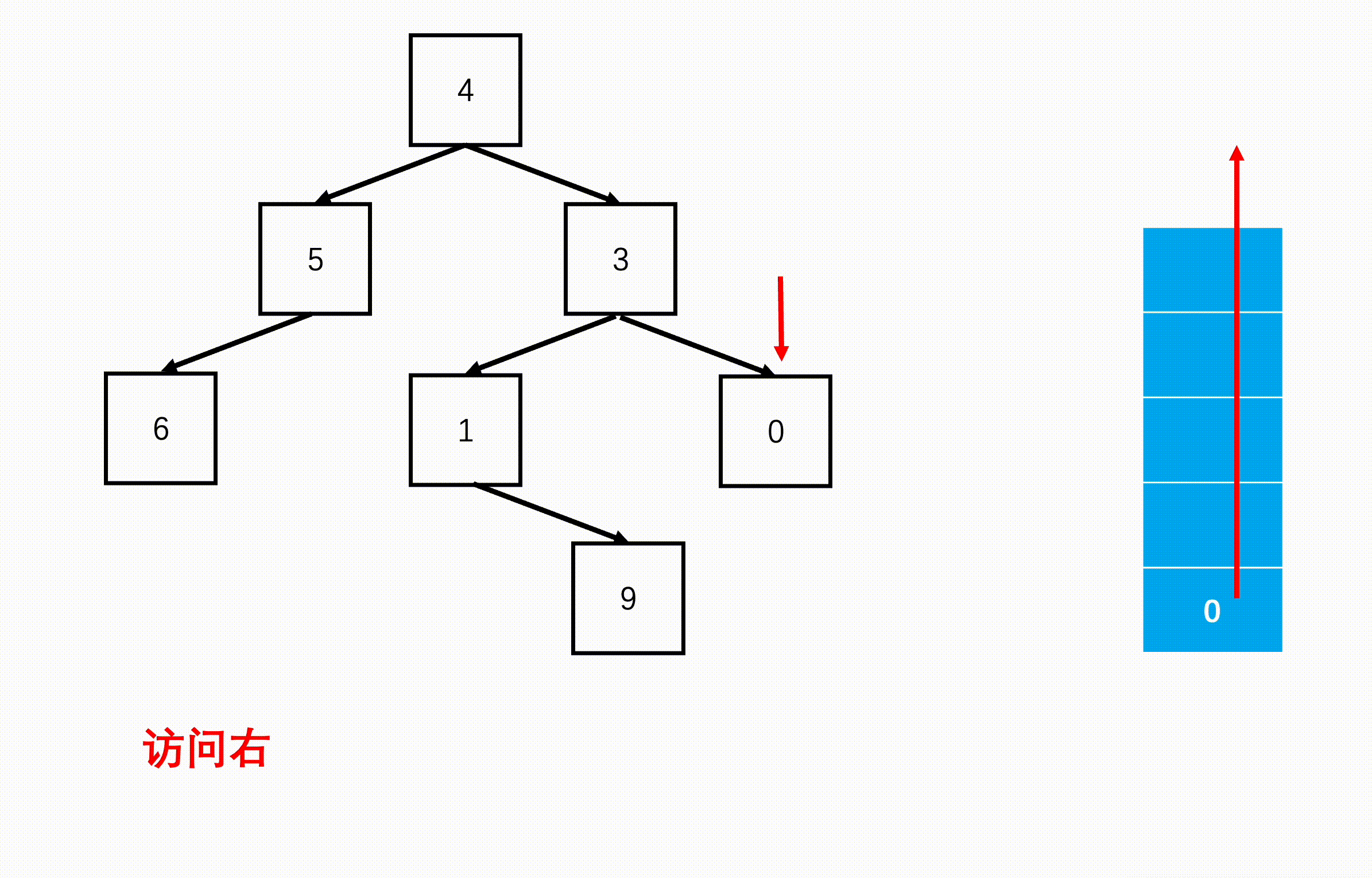
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root){
//设置栈用于遍历
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode head = root;
//记录中序遍历的数组
ArrayList<Integer> sort = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(head != null || !s.isEmpty()){
//直到没有左节点
while(head != null){
s.push(head);
head = head.left;
}
head = s.pop();
//访问节点
sort.add(head.val);
//进入右边
head = head.right;
}
//遍历中序结果
for(int i = 1; i < sort.size(); i++){
//一旦有降序,则不是搜索树
if(sort.get(i - 1) > sort.get(i))
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
13. 判断是不是完全二叉树
13.1. 题目描述
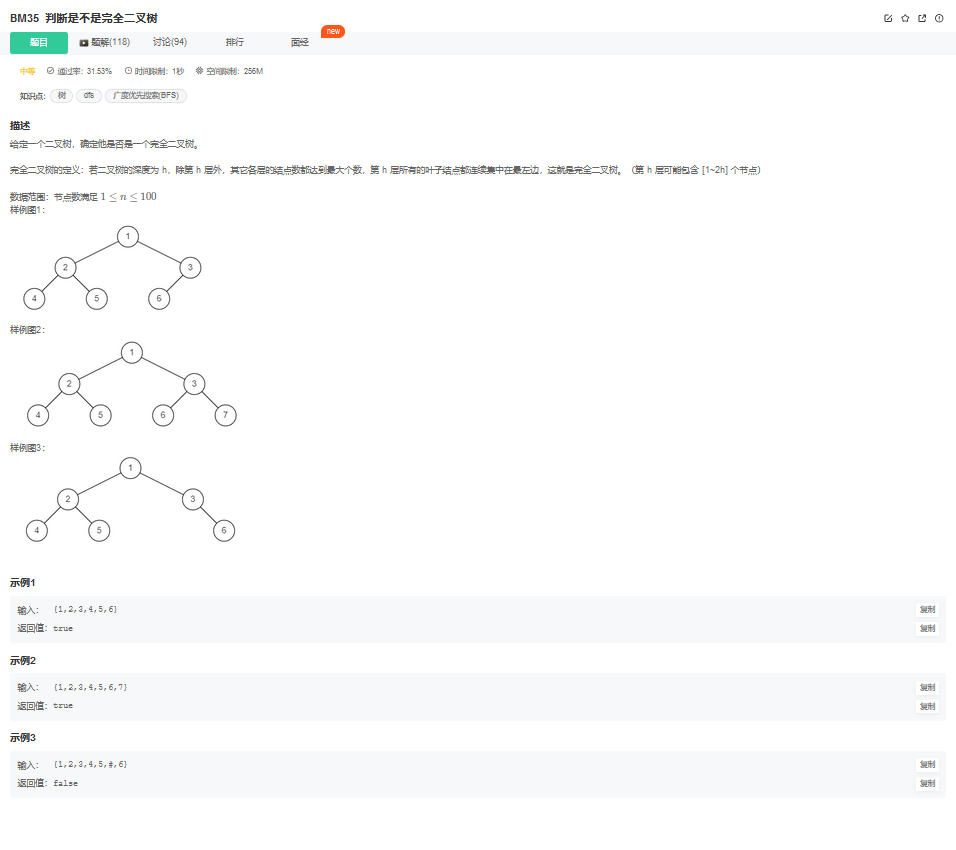
13.2. 解题思路
方法:层次遍历(推荐使用)

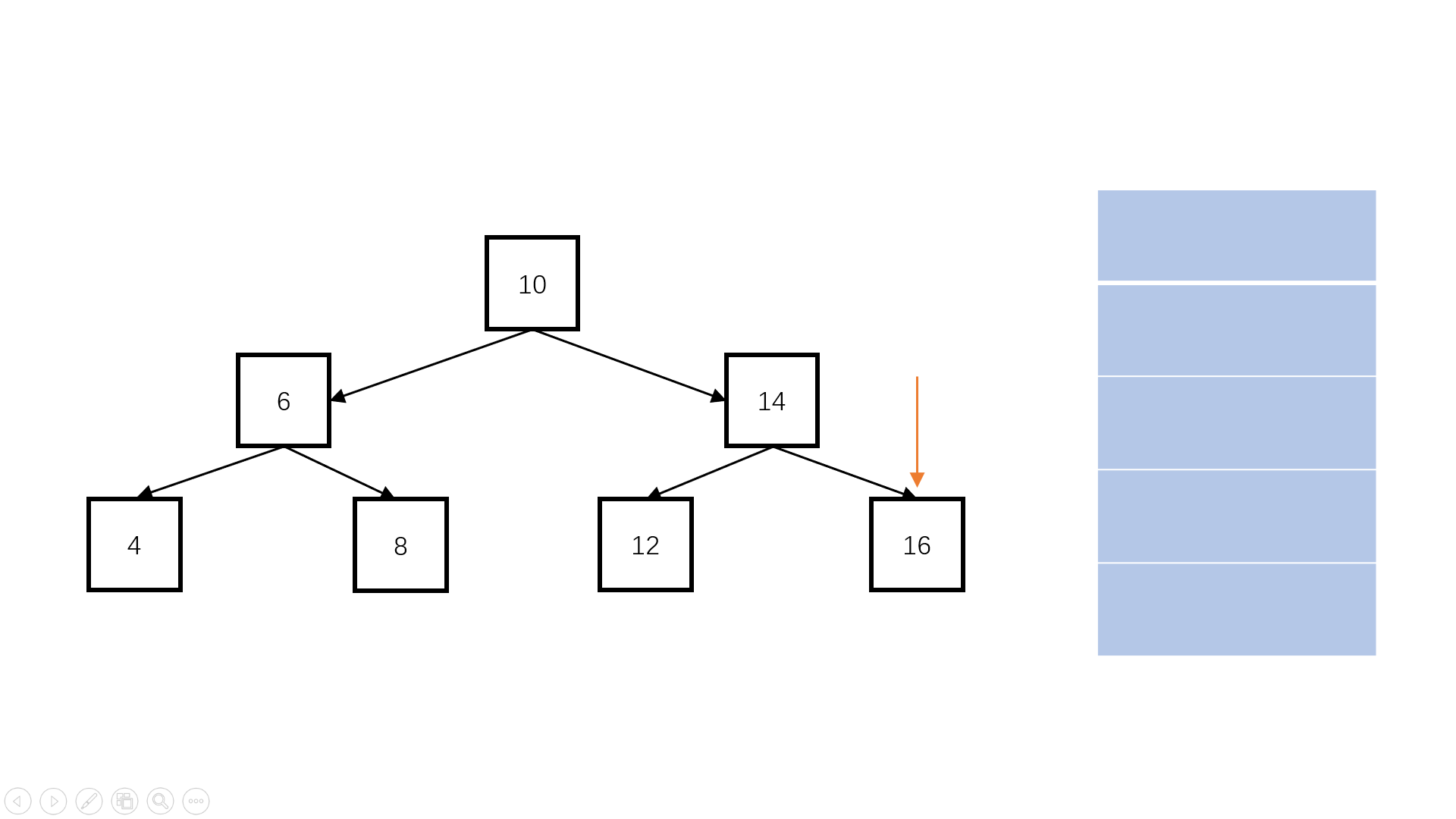
Java代码实现:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean isCompleteTree (TreeNode root) {
//空树一定是完全二叉树
if(root == null)
return true;
//辅助队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
TreeNode cur;
//定义一个首次出现的标记位
boolean notComplete = false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
cur = queue.poll();
//标记第一次遇到空节点
if(cur == null){
notComplete = true;
continue;
}
//后续访问已经遇到空节点了,说明经过了叶子
if(notComplete)
return false;
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
return true;
}
}
14. 判断是不是平衡二叉树
14.1. 题目描述
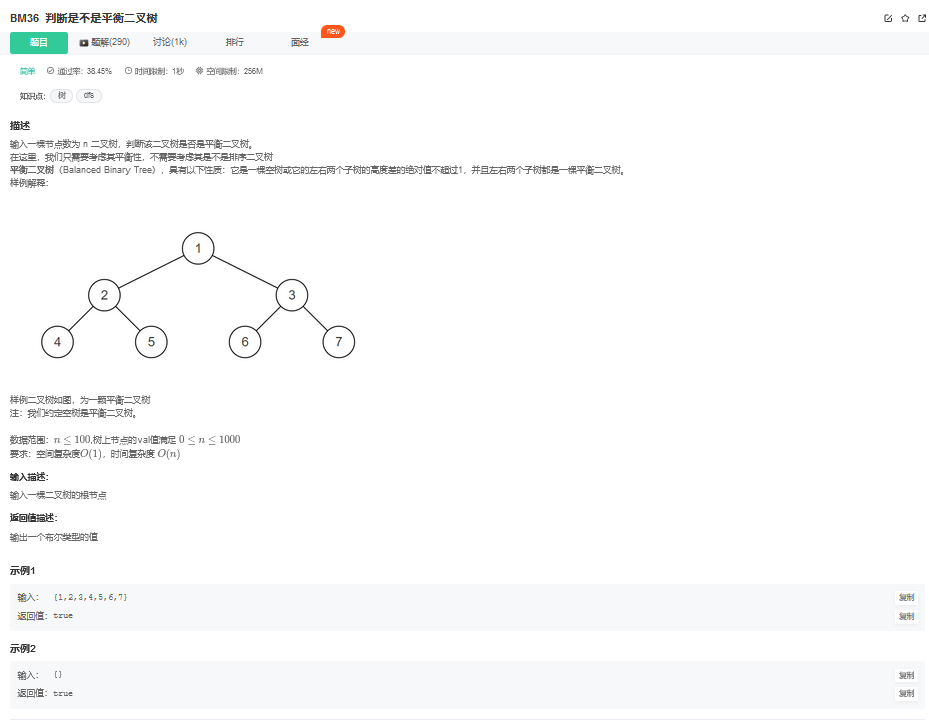
14.2. 解题思路
方法一:自顶向下(推荐使用)

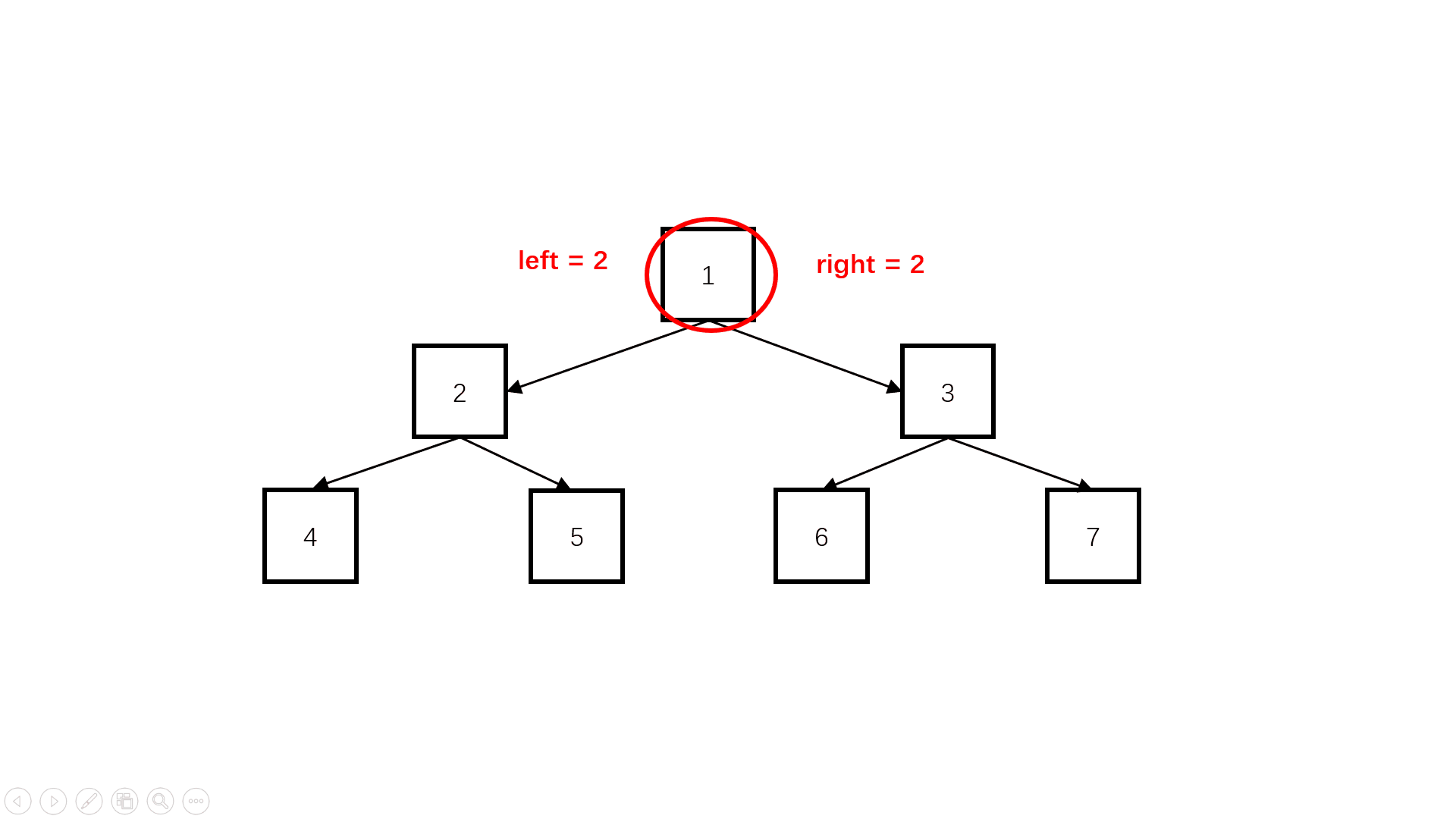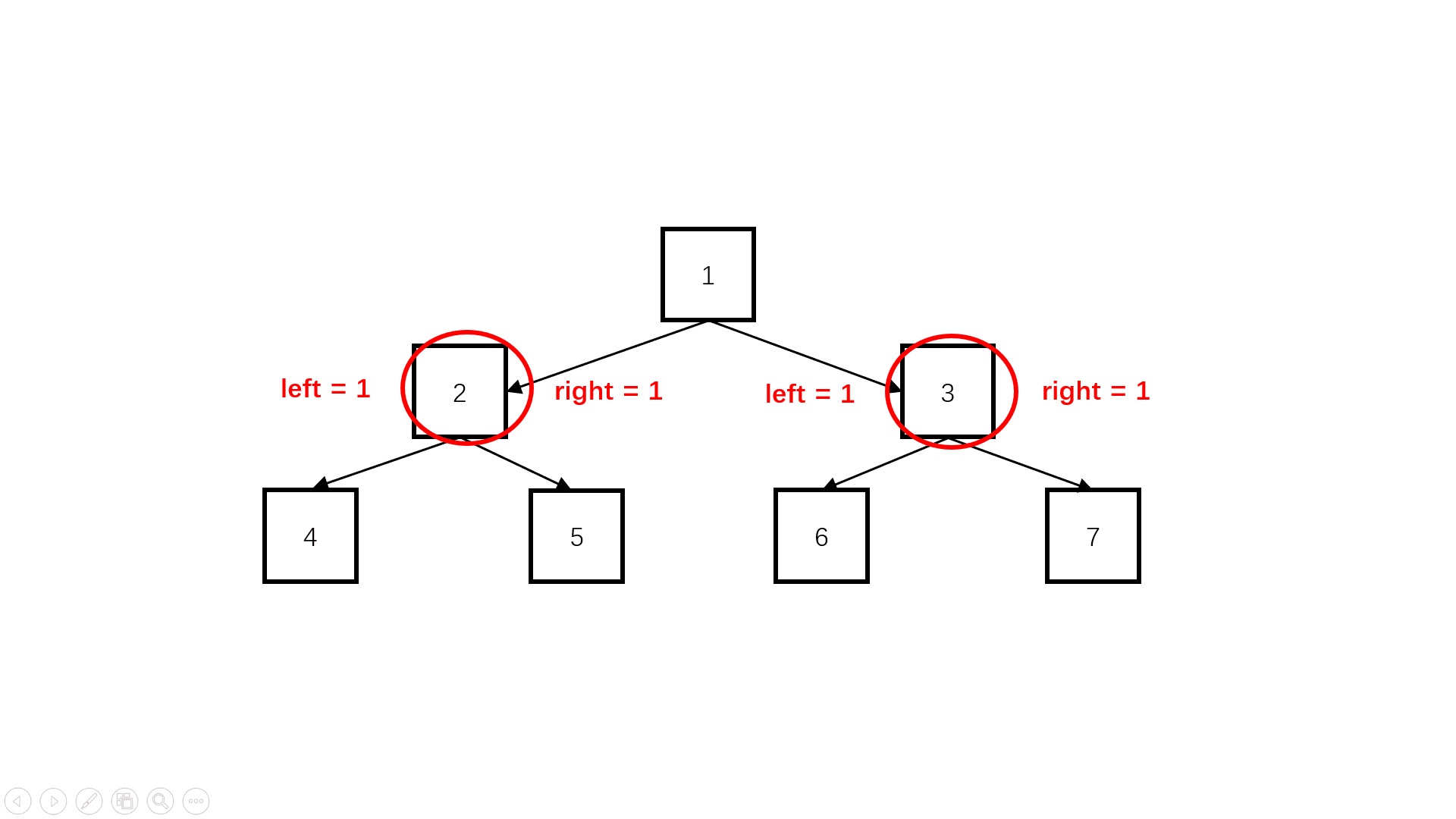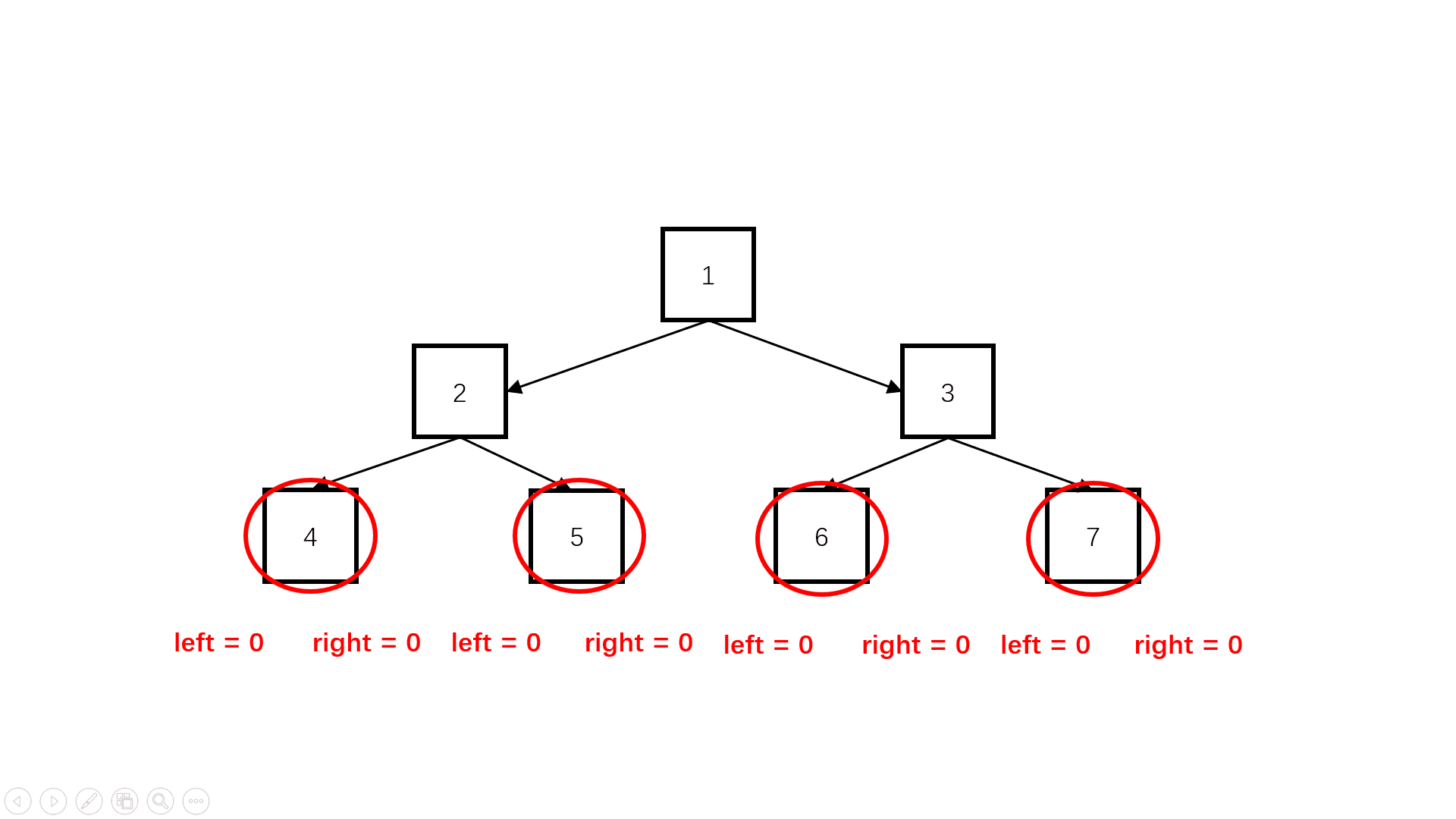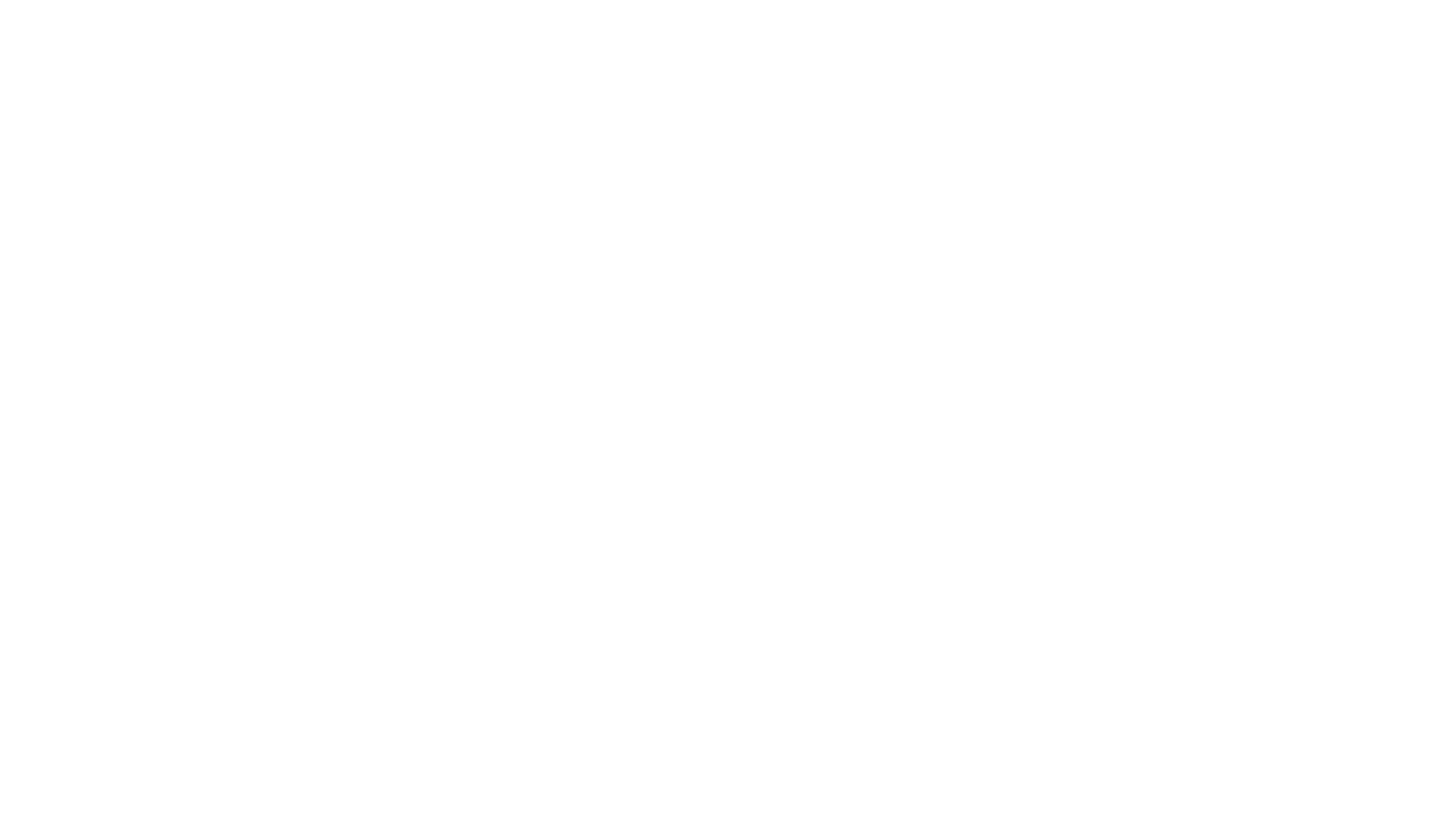
Java实现代码:
public class Solution {
//计算该子树深度函数
public int deep(TreeNode root){
//空节点深度为0
if(root == null)
return 0;
//递归算左右子树的深度
int left = deep(root.left);
int right = deep(root.right);
//子树最大深度加上自己
return (left > right) ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
//空树为平衡二叉树
if (root == null)
return true;
int left = deep(root.left);
int right = deep(root.right);
//左子树深度减去右子树相差绝对值大于1
if(left - right > 1 || left - right < -1)
return false;
//同时,左右子树还必须是平衡的
return IsBalanced_Solution(root.left) && IsBalanced_Solution(root.right);
}
}
方法二:自底向上(扩展思路)

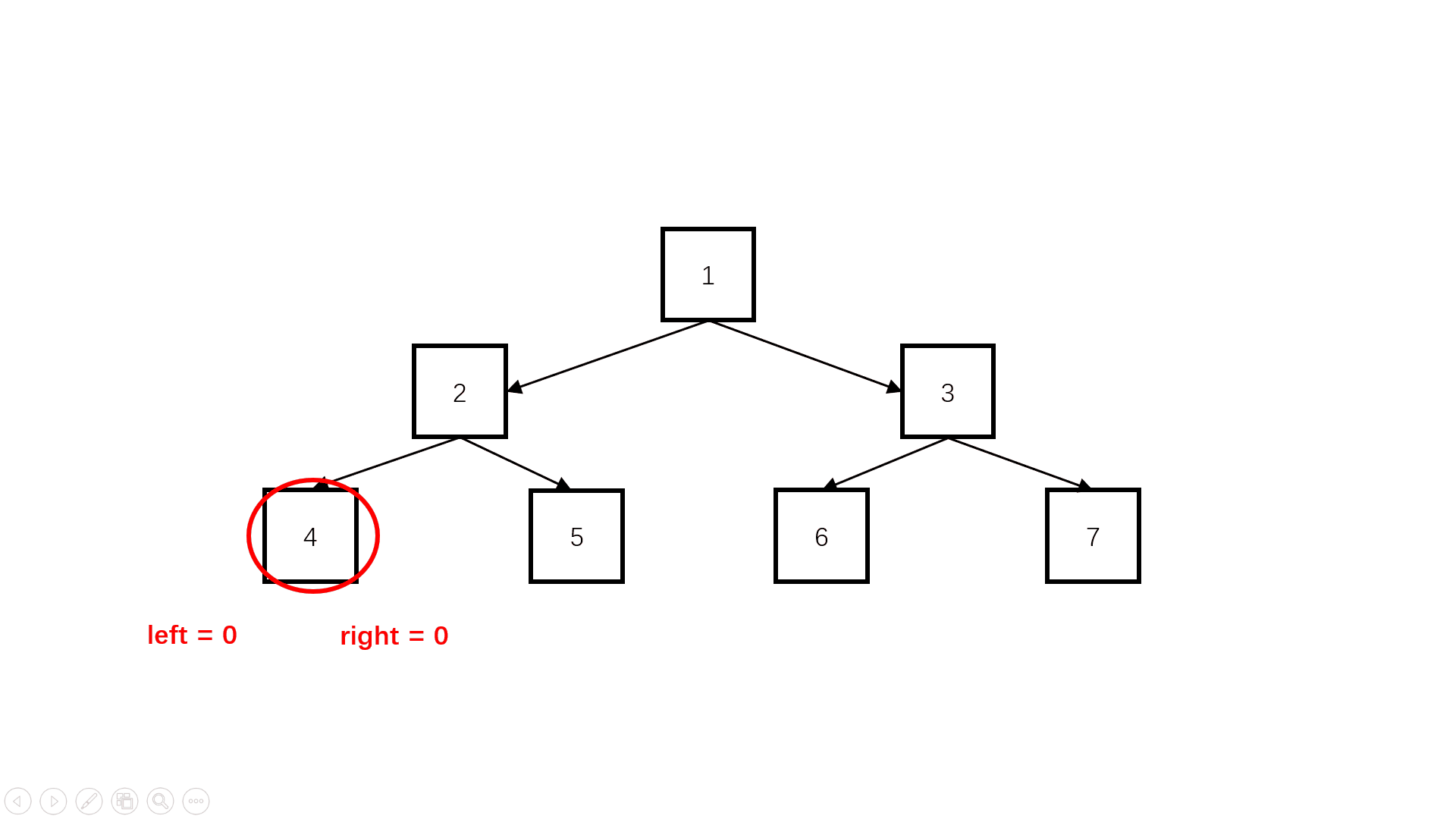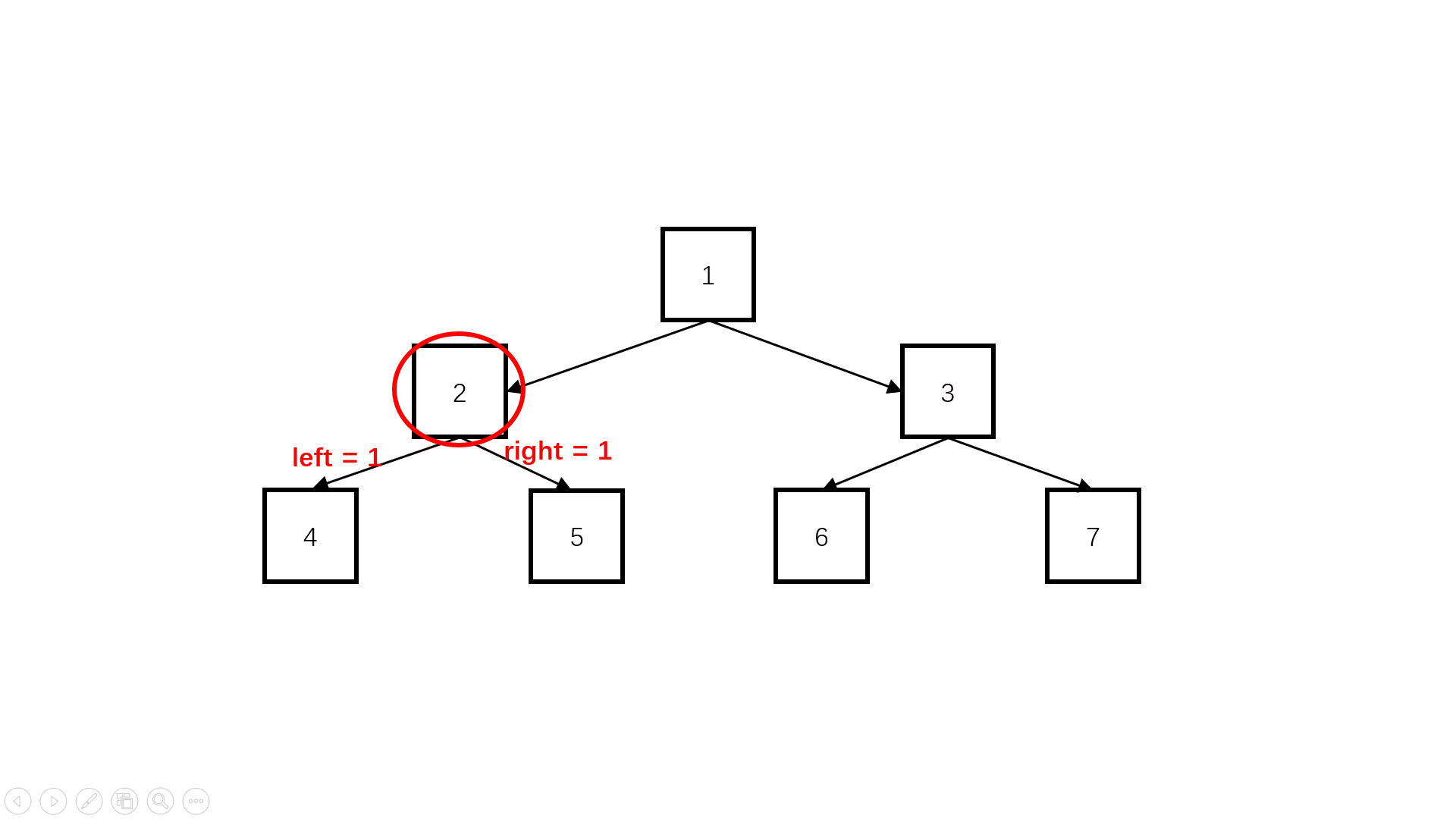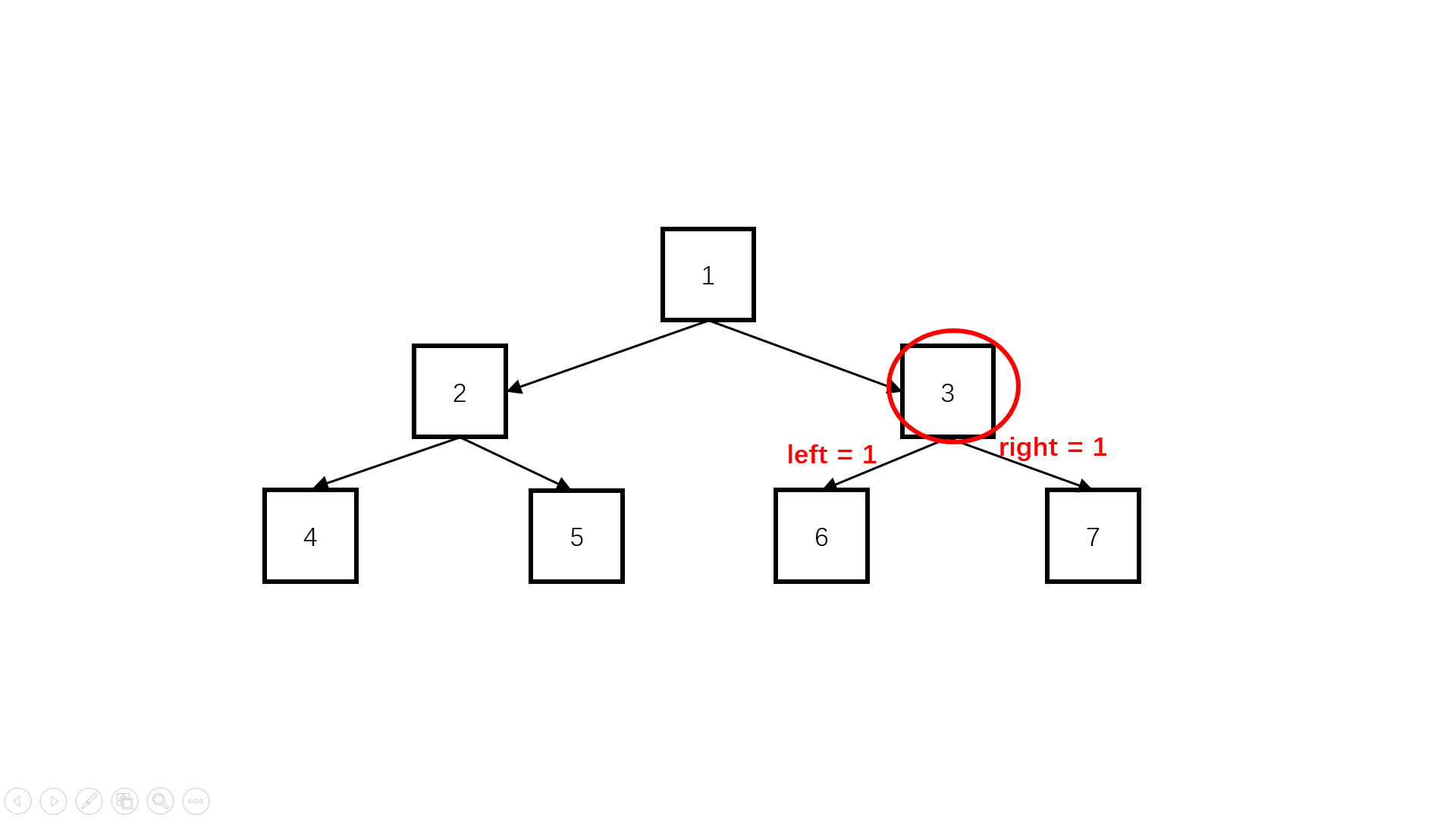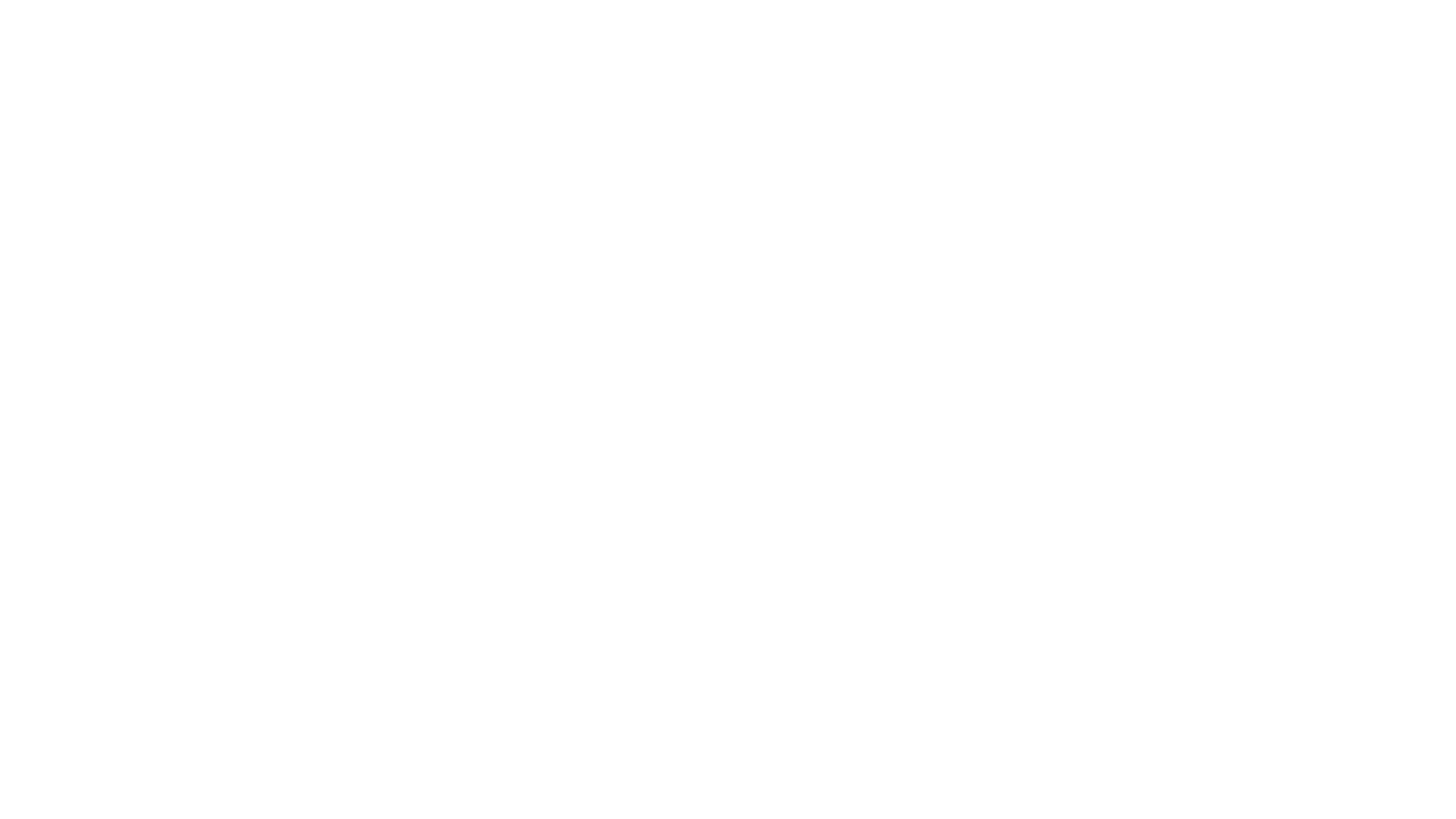
Java实现代码:
public class Solution {
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
//空树也是平衡二叉树
if(root == null)
return true;
return getdepth(root) != -1;
}
public int getdepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
//递归计算当前root左右子树的深度差
int left = getdepth(root.left);
//当前节点左子树不平衡,则该树不平衡
if(left < 0)
return -1;
int right = getdepth(root.right);
//当前节点右子树不平衡,则该树不平衡
if(right < 0)
return -1;
//计算深度差
return Math.abs(left - right) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + Math.max(left, right);
}
}
15. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
15.1. 题目描述
15.2. 解题思路
方法一:搜索路径比较(推荐使用)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
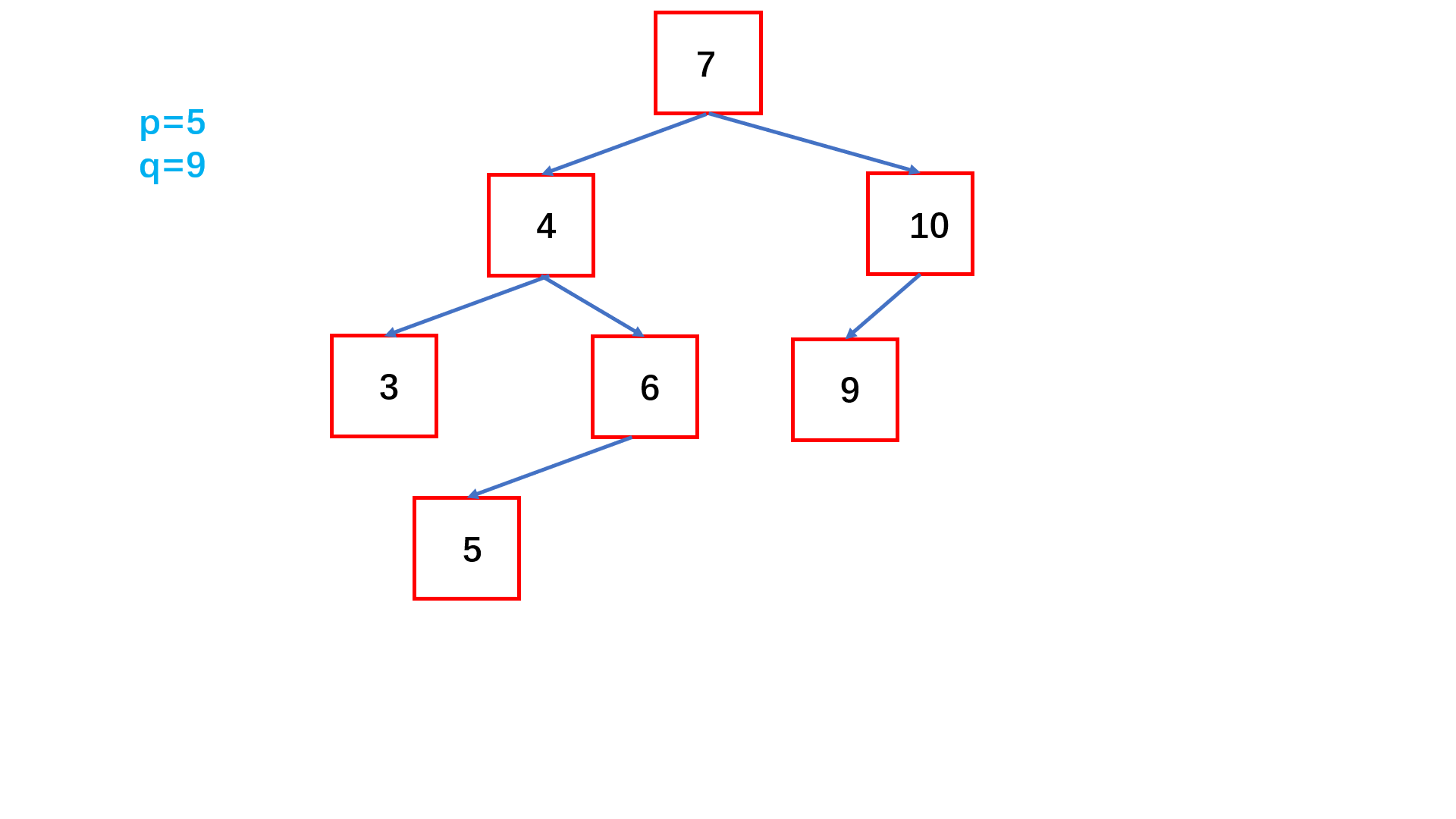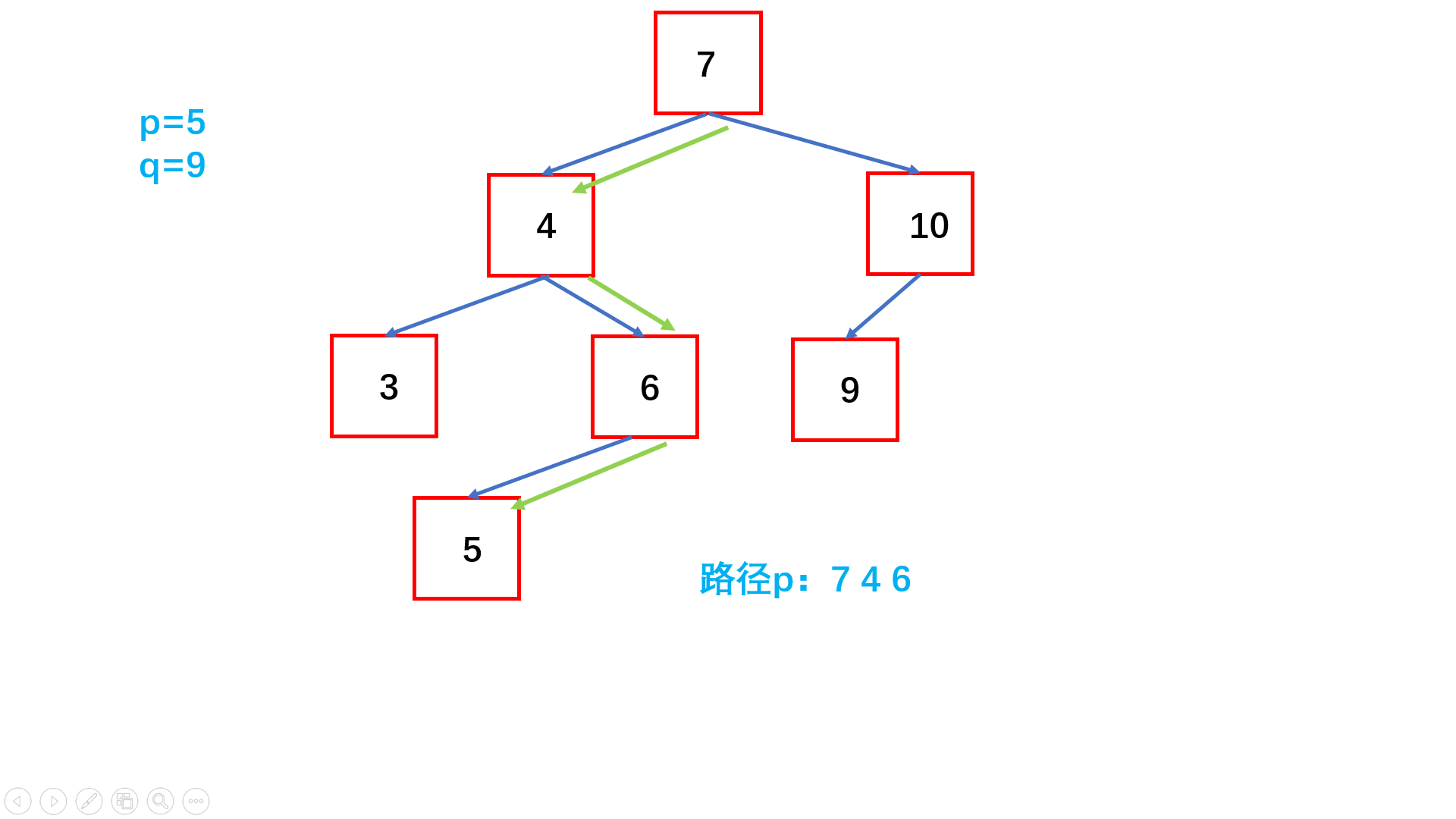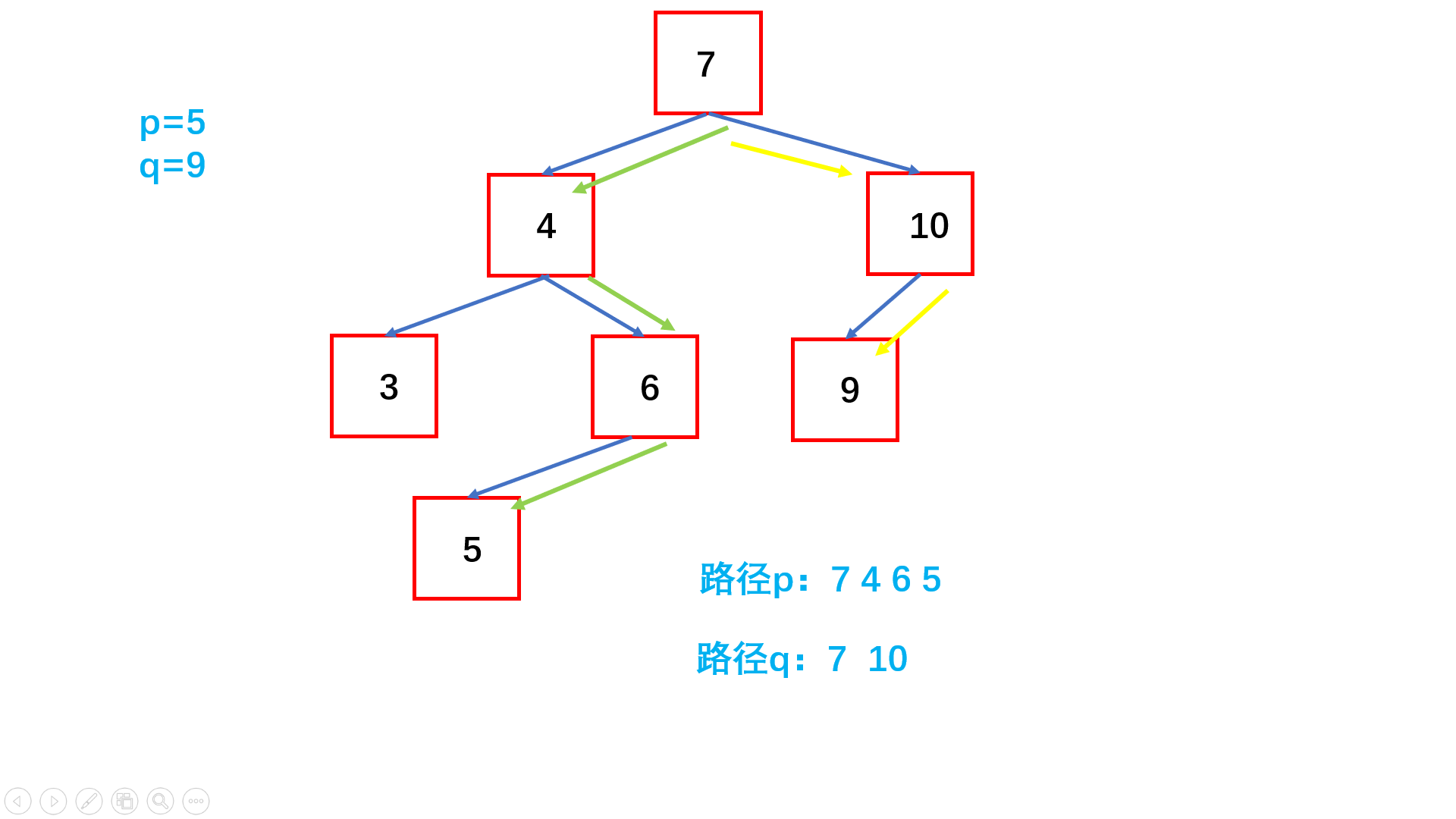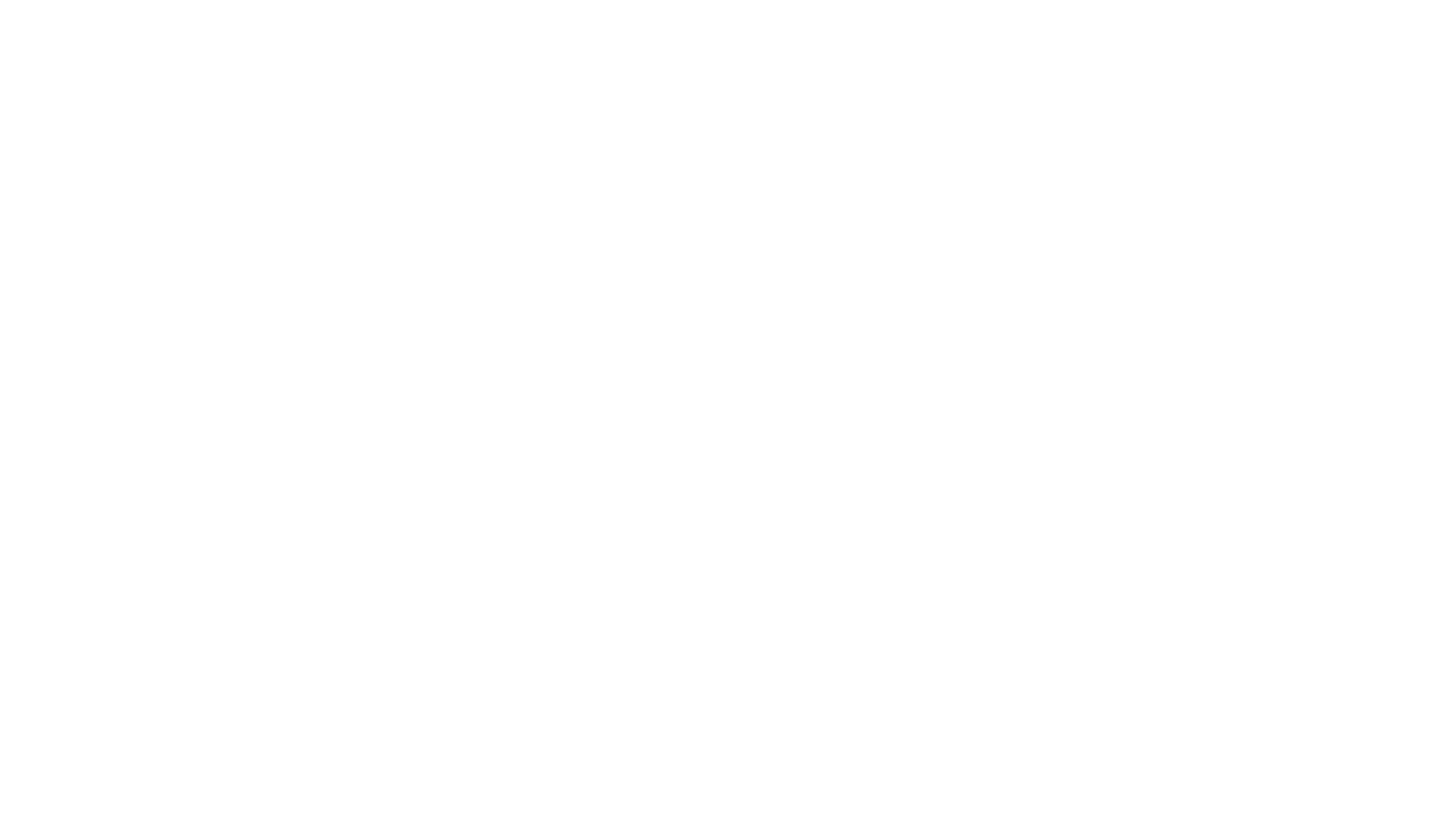
//求得根节点到目标节点的路径
public ArrayList<Integer> getPath(TreeNode root, int target) {
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
TreeNode node = root;
//节点值都不同,可以直接用值比较
while(node.val != target){
path.add(node.val);
//小的在左子树
if(target < node.val)
node = node.left;
//大的在右子树
else
node = node.right;
}
path.add(node.val);
return path;
}
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
//求根节点到两个节点的路径
ArrayList<Integer> path_p = getPath(root, p);
ArrayList<Integer> path_q = getPath(root, q);
int res = 0;
//比较两个路径,找到第一个不同的点
for(int i = 0; i < path_p.size() && i < path_q.size(); i++){
int x = path_p.get(i);
int y = path_q.get(i);
//最后一个相同的节点就是最近公共祖先
if(x == y)
res = path_p.get(i);
else
break;
}
return res;
}
}
方法二:一次遍历(扩展思路)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
//空树找不到公共祖先
if(root == null)
return -1;
//pq在该节点两边说明这就是最近公共祖先
if((p >= root.val && q <= root.val) || (p <= root.val && q >= root.val))
return root.val;
//pq都在该节点的左边
else if(p <= root.val && q <= root.val)
//进入左子树
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
//pq都在该节点的右边
else
//进入右子树
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
}
}
16. 在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先
16.1. 题目描述
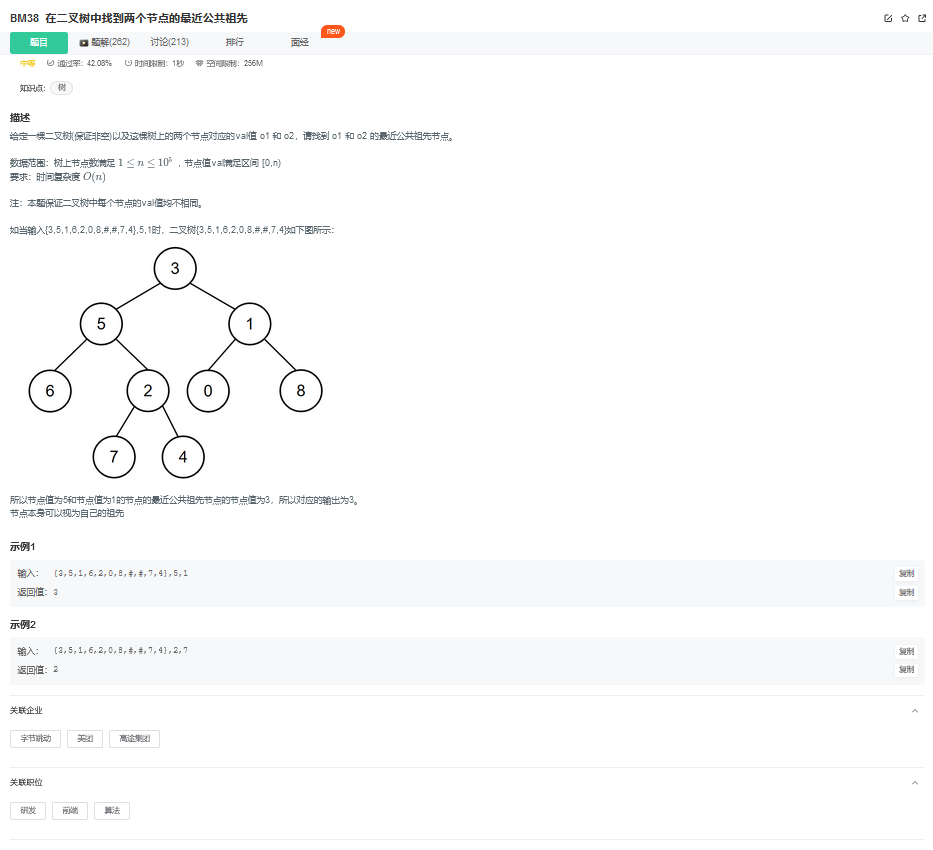
16.2. 解题思路
方法一:路径比较法(推荐使用)

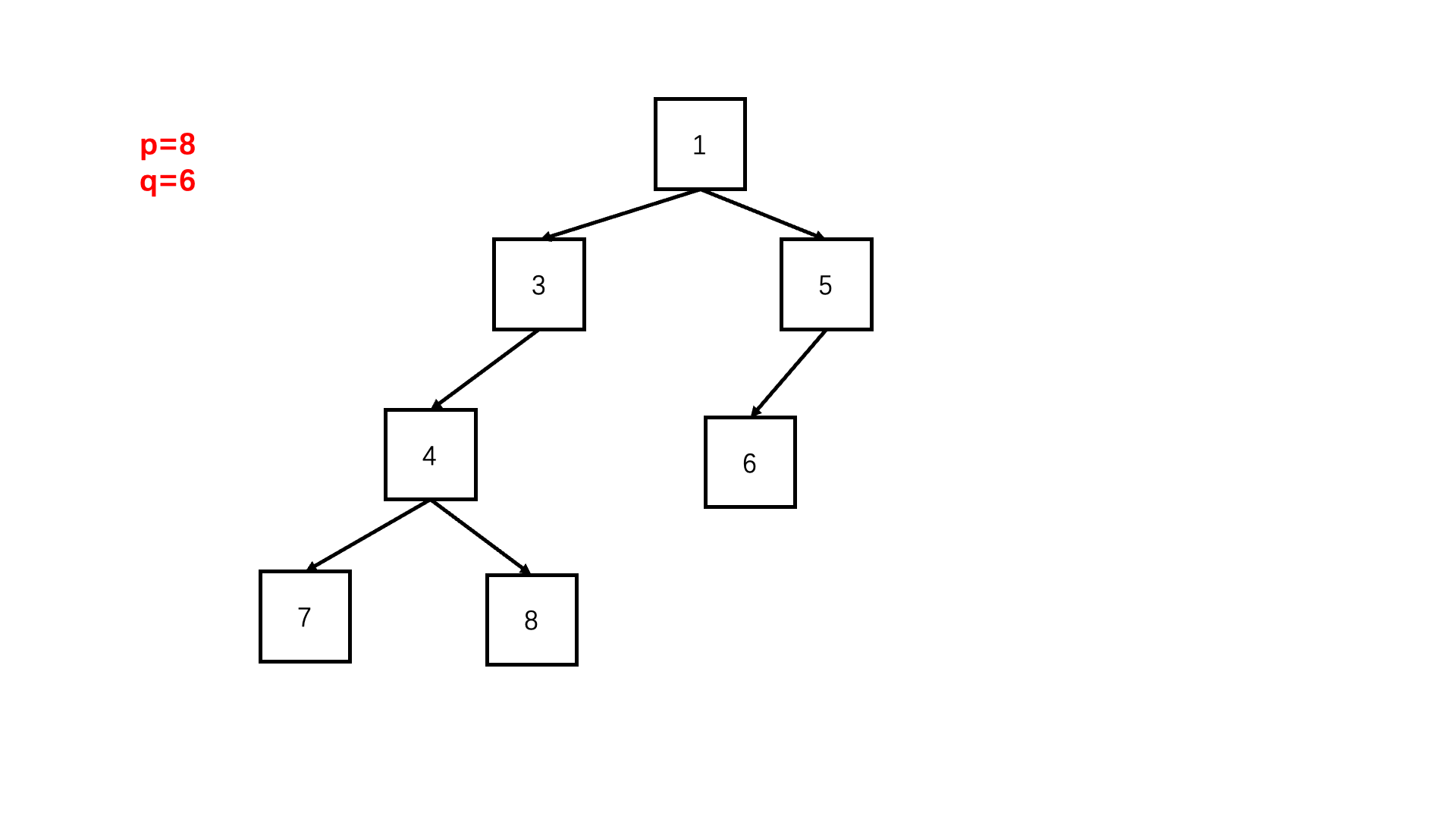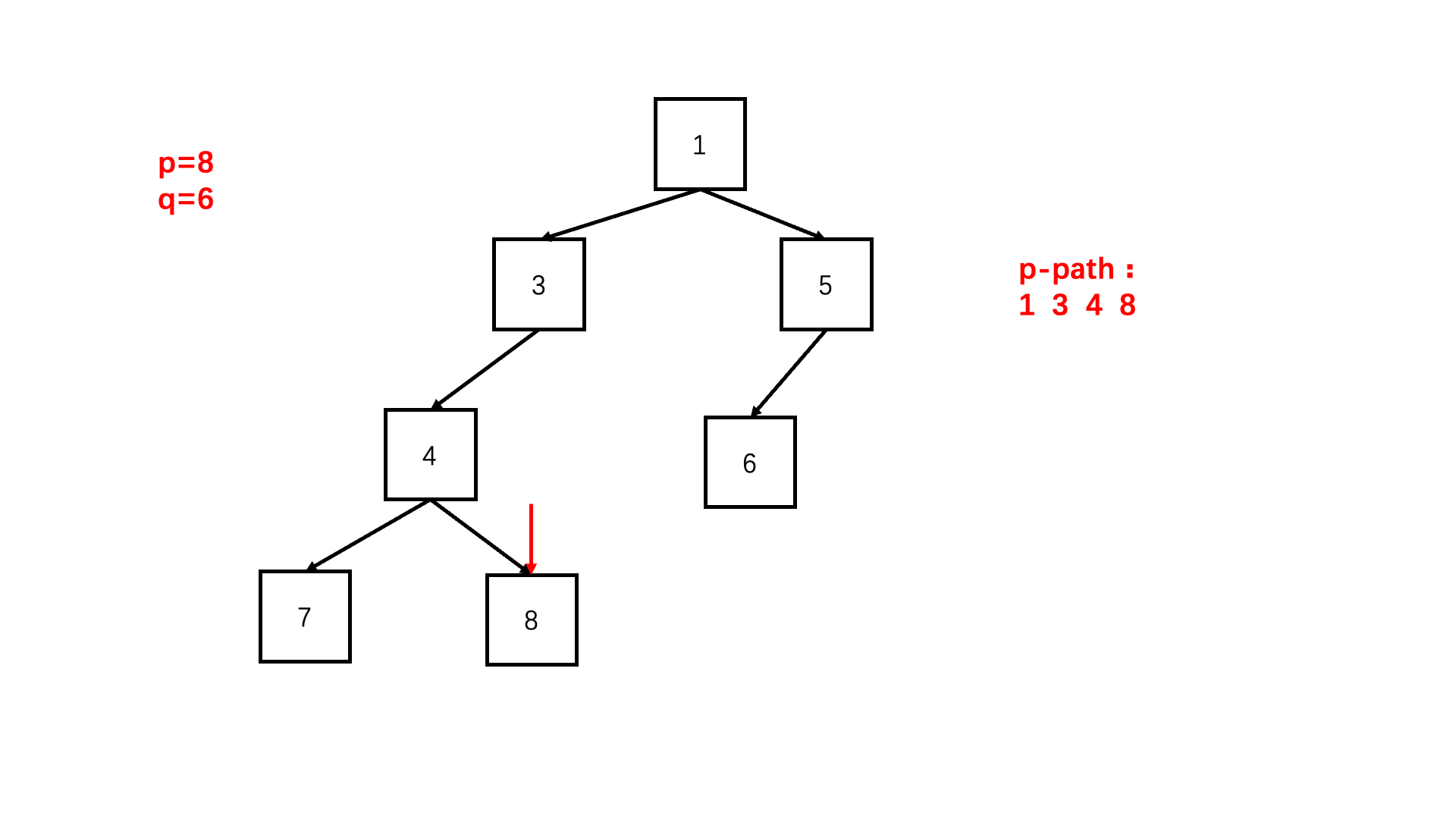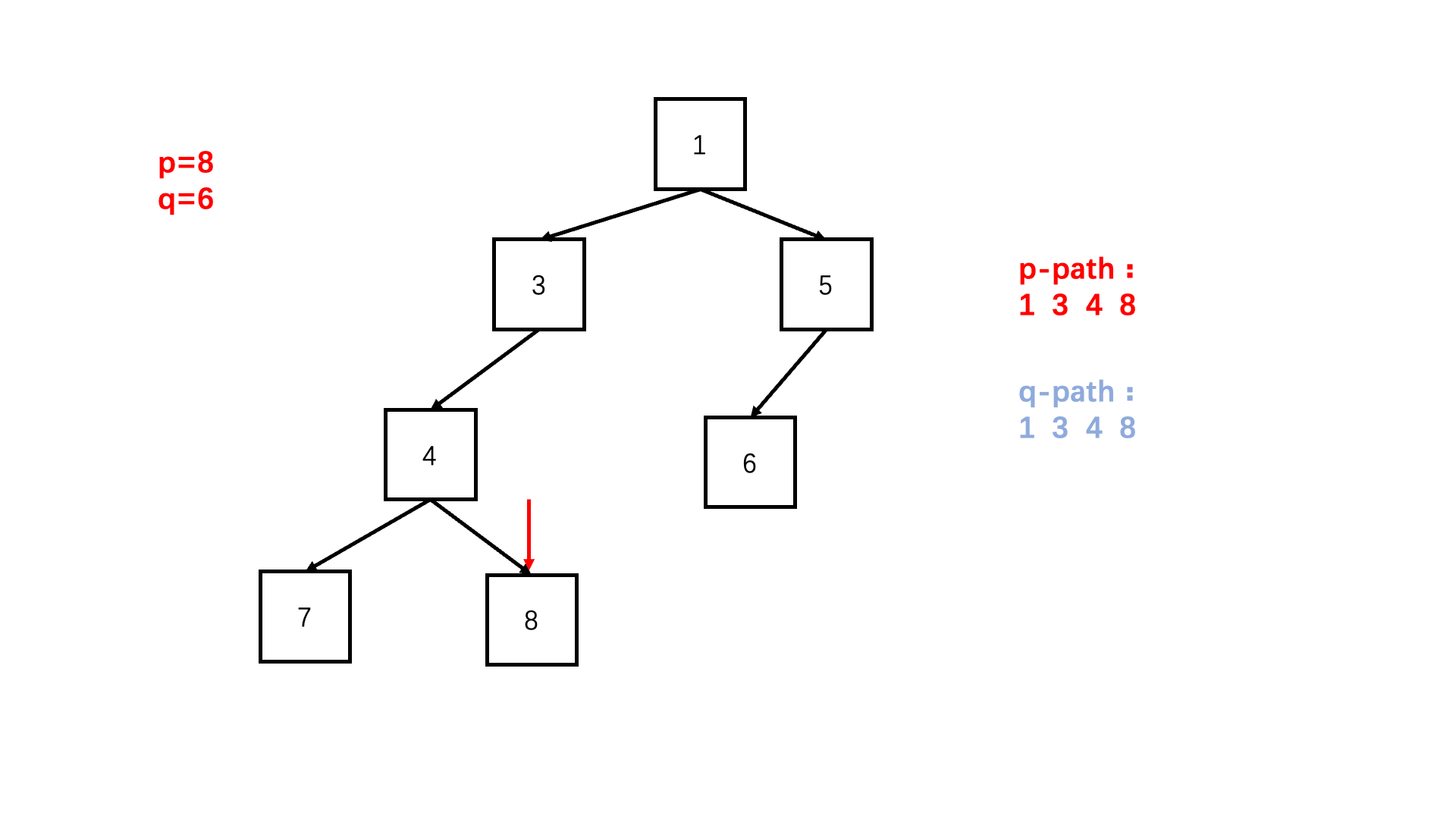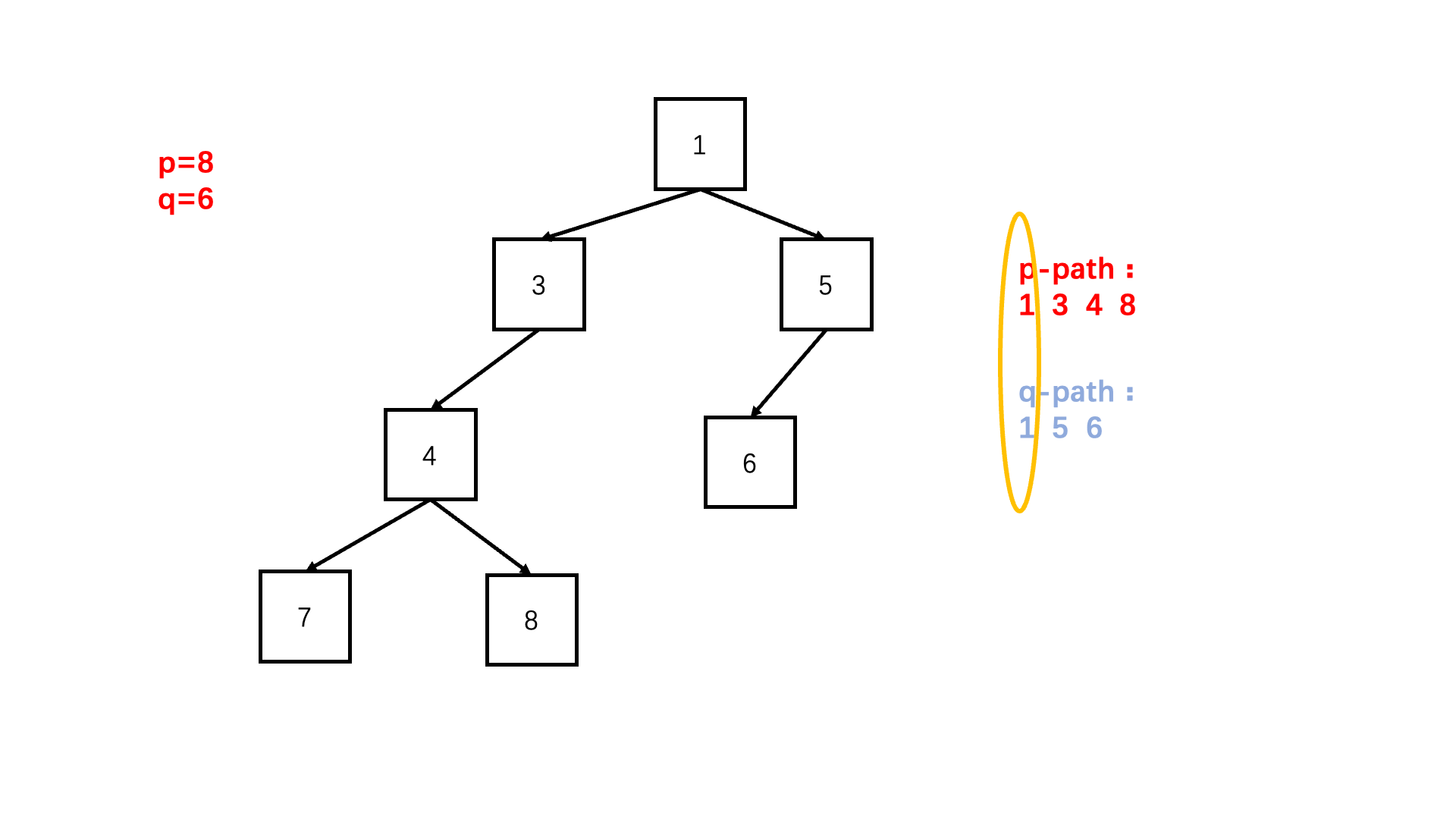
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//记录是否找到到o的路径
public boolean flag = false;
//求得根节点到目标节点的路径
public void dfs(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> path, int o){
if(flag || root == null)
return;
path.add(root.val);
//节点值都不同,可以直接用值比较
if(root.val == o){
flag = true;
return;
}
//dfs遍历查找
dfs(root.left, path, o);
dfs(root.right, path, o);
//找到
if(flag)
return;
//回溯
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
ArrayList<Integer> path1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> path2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//求根节点到两个节点的路径
dfs(root, path1, o1);
//重置flag,查找下一个
flag = false;
dfs(root, path2, o2);
int res = 0;
//比较两个路径,找到第一个不同的点
for(int i = 0; i < path1.size() && i < path2.size(); i++){
int x = path1.get(i);
int y = path2.get(i);
if(x == y)
//最后一个相同的节点就是最近公共祖先
res = x;
else
break;
}
return res;
}
}
方法二:递归(扩展思路)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
//该子树没找到,返回-1
if(root == null)
return -1;
//该节点是其中某一个节点
if(root.val == o1 || root.val == o2)
return root.val;
//左子树寻找公共祖先
int left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, o1, o2);
//右子树寻找公共祖先
int right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, o1, o2);
//左子树为没找到,则在右子树中
if(left == -1)
return right;
//右子树没找到,则在左子树中
if(right == -1)
return left;
//否则是当前节点
return root.val;
}
}
17. 序列化二叉树
17.1. 题目描述
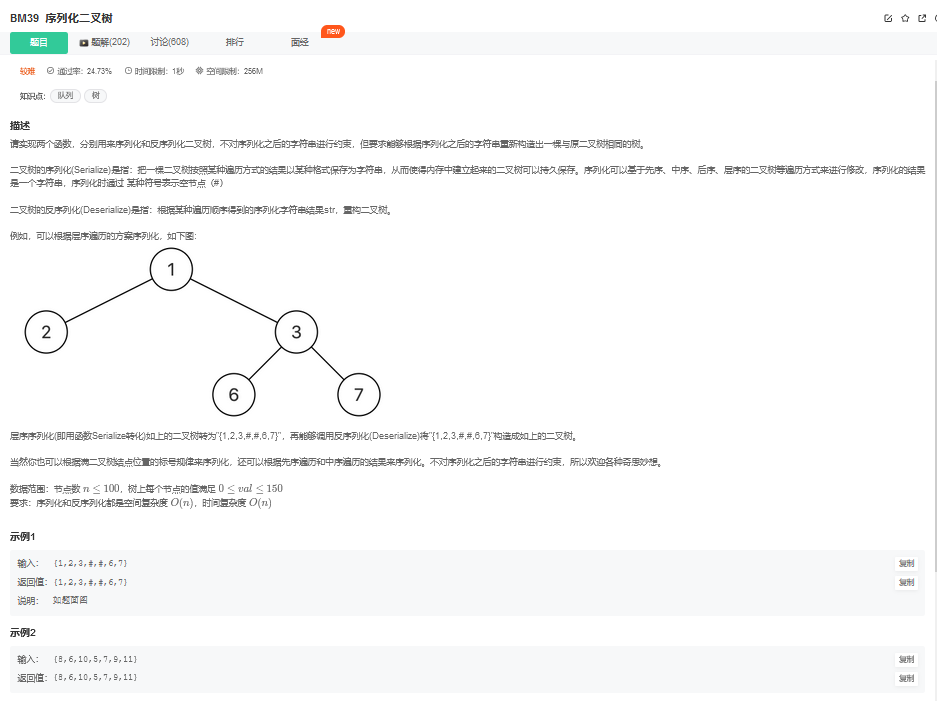
17.2. 解题思路
方法:前序遍历(推荐使用)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//序列的下标
public int index = 0;
//处理序列化的功能函数(递归)
private void SerializeFunction(TreeNode root, StringBuilder str){
//如果节点为空,表示左子节点或右子节点为空,用#表示
if(root == null){
str.append('#');
return;
}
//根节点
str.append(root.val).append('!');
//左子树
SerializeFunction(root.left, str);
//右子树
SerializeFunction(root.right, str);
}
public String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
//处理空树
if(root == null)
return "#";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
SerializeFunction(root, res);
//把str转换成char
return res.toString();
}
//处理反序列化的功能函数(递归)
private TreeNode DeserializeFunction(String str){
//到达叶节点时,构建完毕,返回继续构建父节点
//空节点
if(str.charAt(index) == '#'){
index++;
return null;
}
//数字转换
int val = 0;
//遇到分隔符或者结尾
while(str.charAt(index) != '!' && index != str.length()){
val = val * 10 + ((str.charAt(index)) - '0');
index++;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(val);
//序列到底了,构建完成
if(index == str.length())
return root;
else
index++;
//反序列化与序列化一致,都是前序
root.left = DeserializeFunction(str);
root.right = DeserializeFunction(str);
return root;
}
public TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
//空序列对应空树
if(str == "#")
return null;
TreeNode res = DeserializeFunction(str);
return res;
}
}
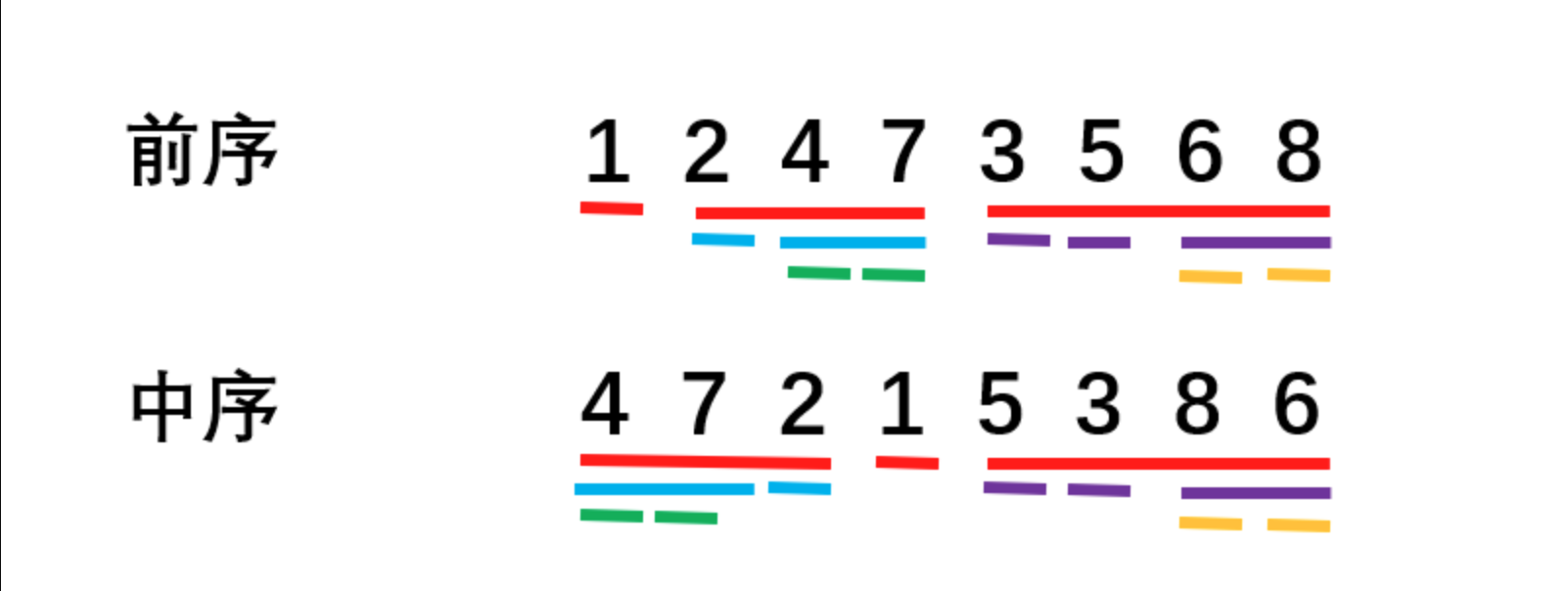
18. 重建二叉树
18.1. 题目描述
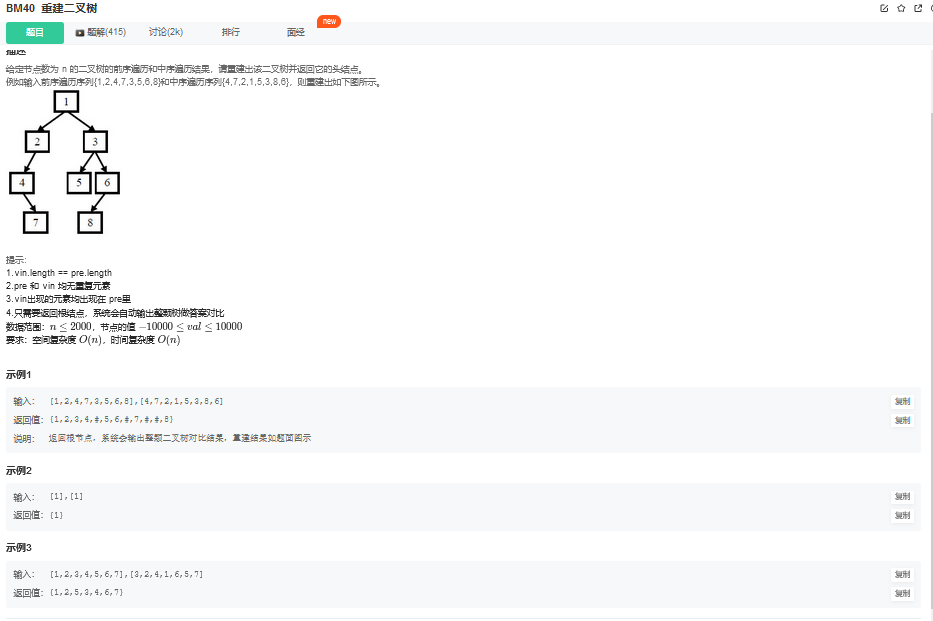
18.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归(推荐使用)


Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] vin) {
int n = pre.length;
int m = vin.length;
//每个遍历都不能为0
if(n == 0 || m == 0)
return null;
//构建根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
for(int i = 0; i < vin.length; i++){
//找到中序遍历中的前序第一个元素
if(pre[0] == vin[i]){
//构建左子树
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, i + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(vin, 0, i));
//构建右子树
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, i + 1, pre.length), Arrays.copyOfRange(vin, i + 1, vin.length));
break;
}
}
return root;
}
}
方法二:栈(思路扩展)

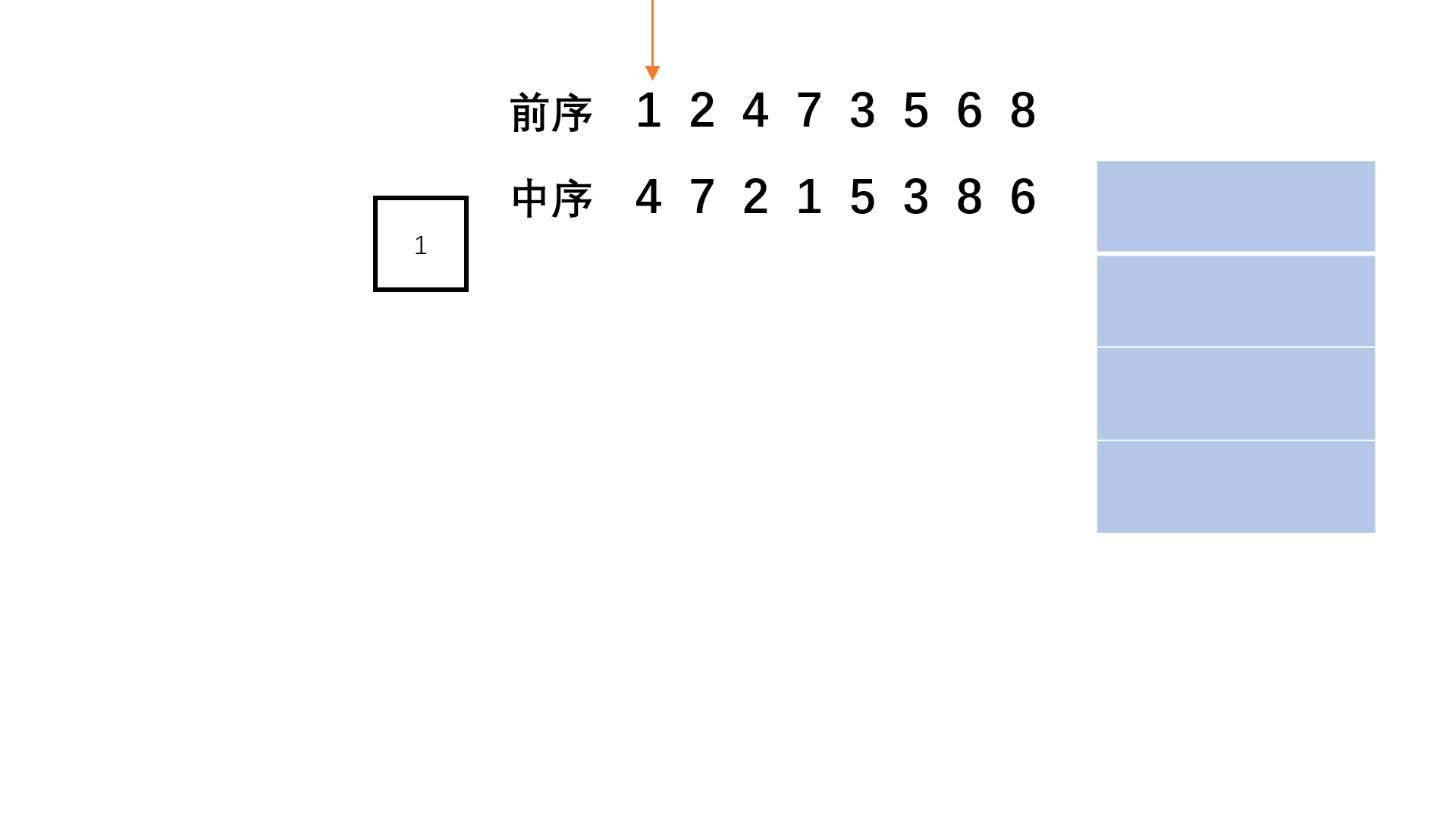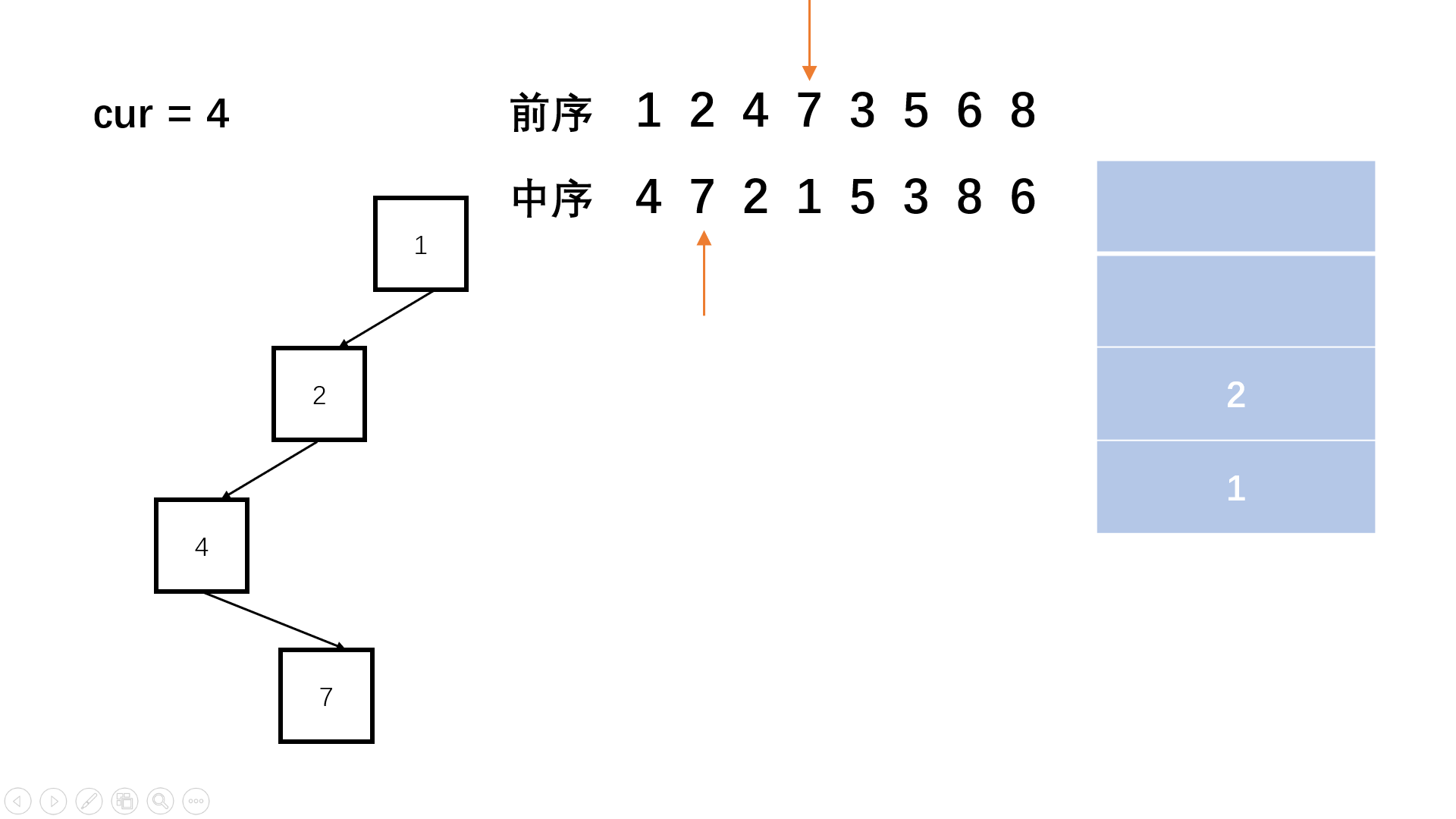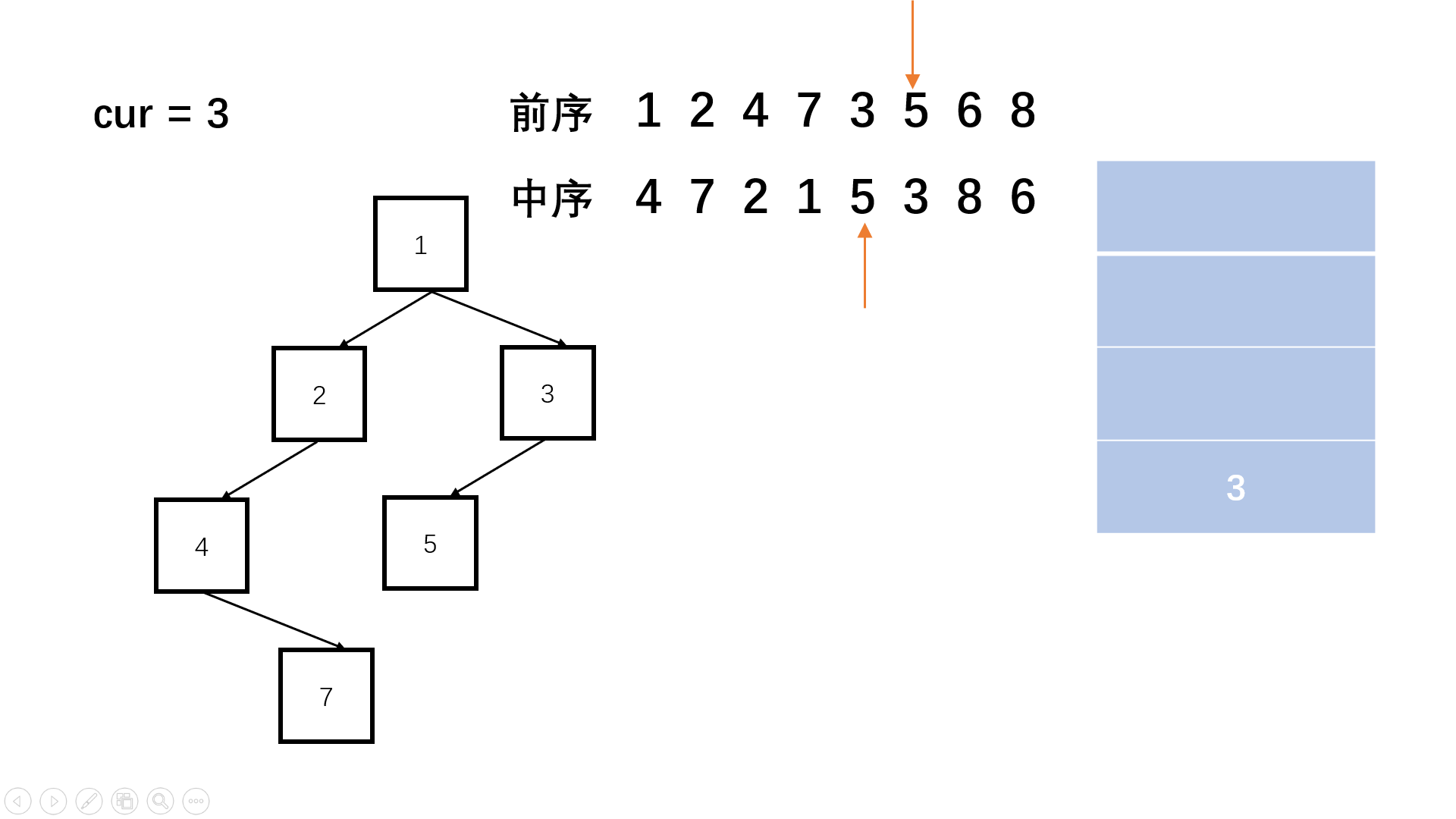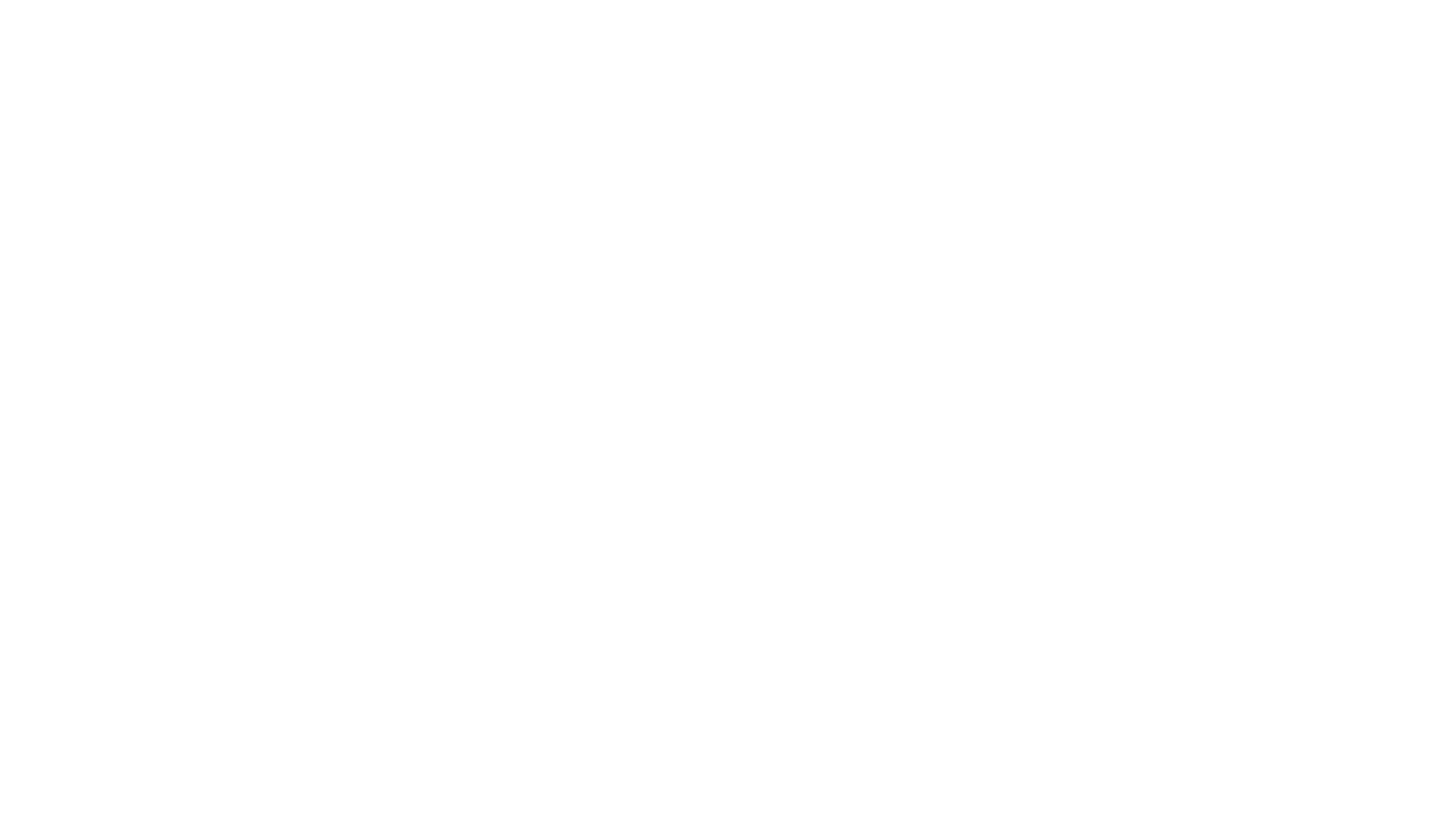
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] vin) {
int n = pre.length;
int m = vin.length;
//每个遍历都不能为0
if(n == 0 || m == 0)
return null;
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//首先建立前序第一个即根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
TreeNode cur = root;
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < n; i++){
//要么旁边这个是它的左节点
if(cur.val != vin[j]){
cur.left = new TreeNode(pre[i]);
s.push(cur);
//要么旁边这个是它的右节点,或者祖先的右节点
cur = cur.left;
}else{
j++;
//弹出到符合的祖先
while(!s.isEmpty() && s.peek().val == vin[j]){
cur = s.pop();
j++;
}
//添加右节点
cur.right = new TreeNode(pre[i]);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return root;
}
}
19. 输出二叉树的右视图
19.1. 题目描述
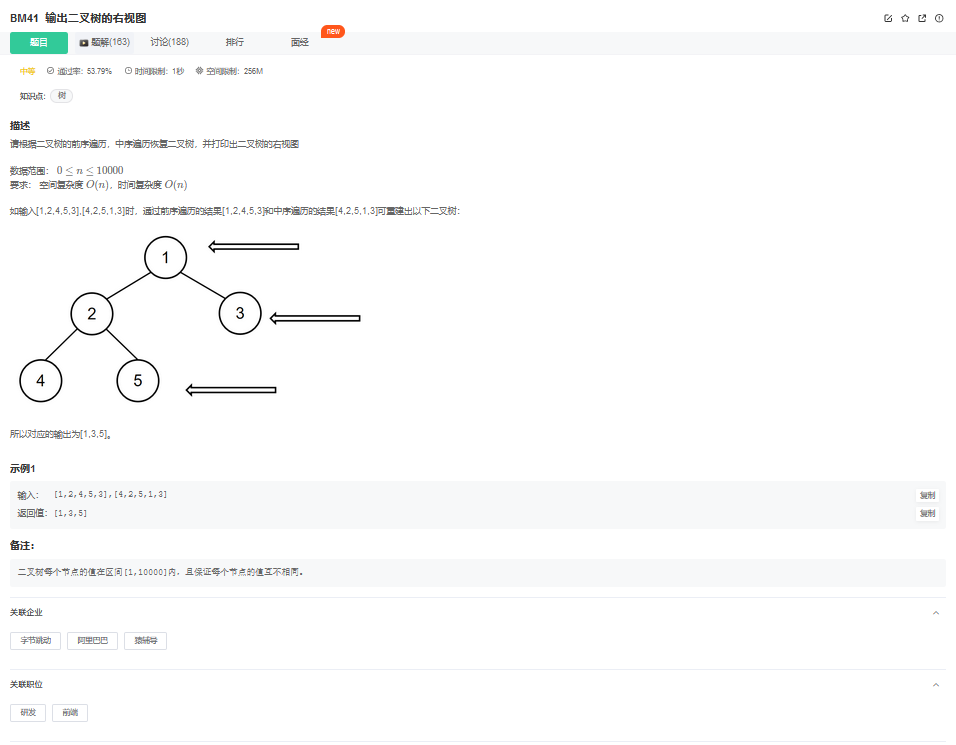
19.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归建树+深度优先搜索(推荐使用)

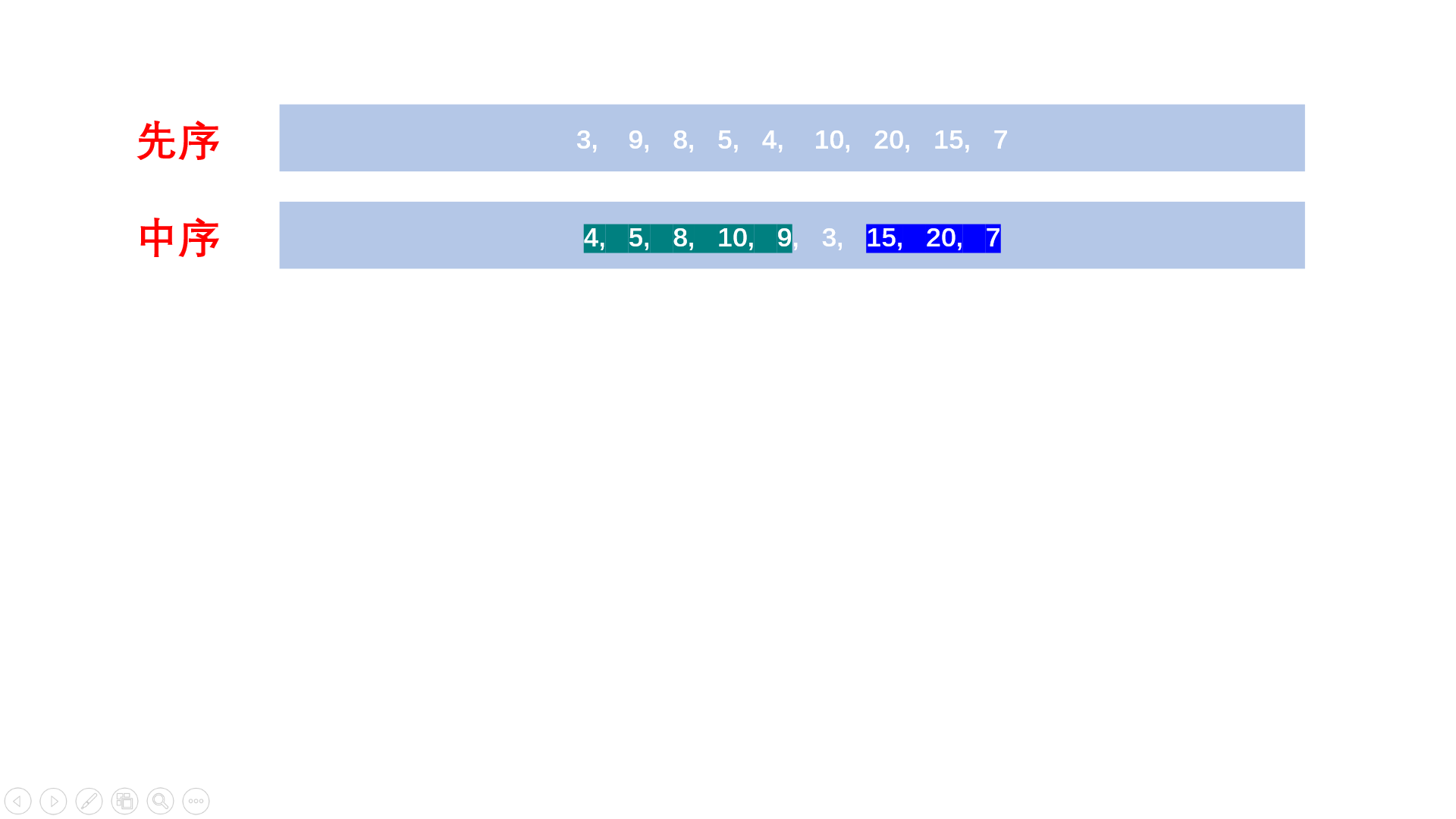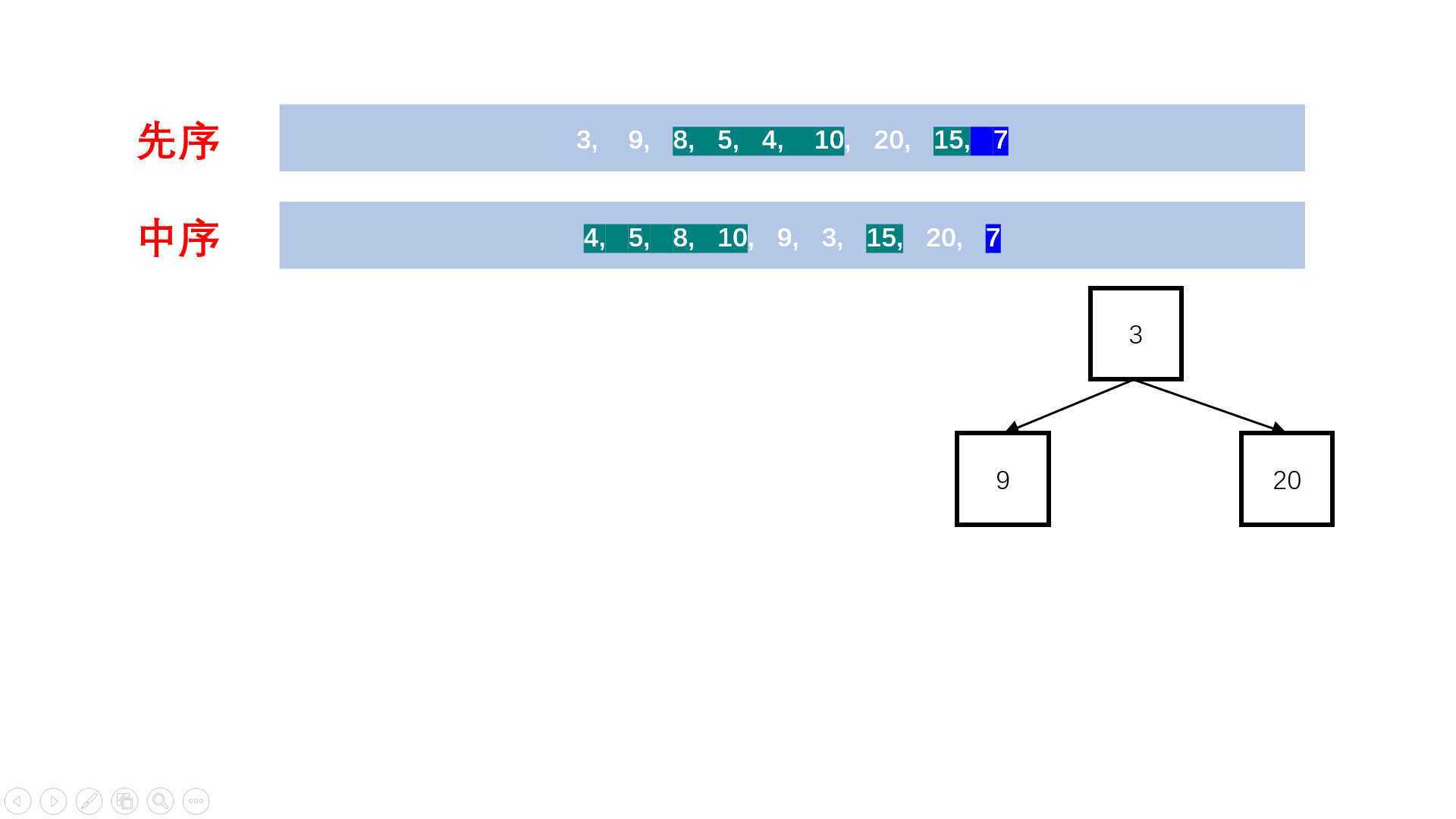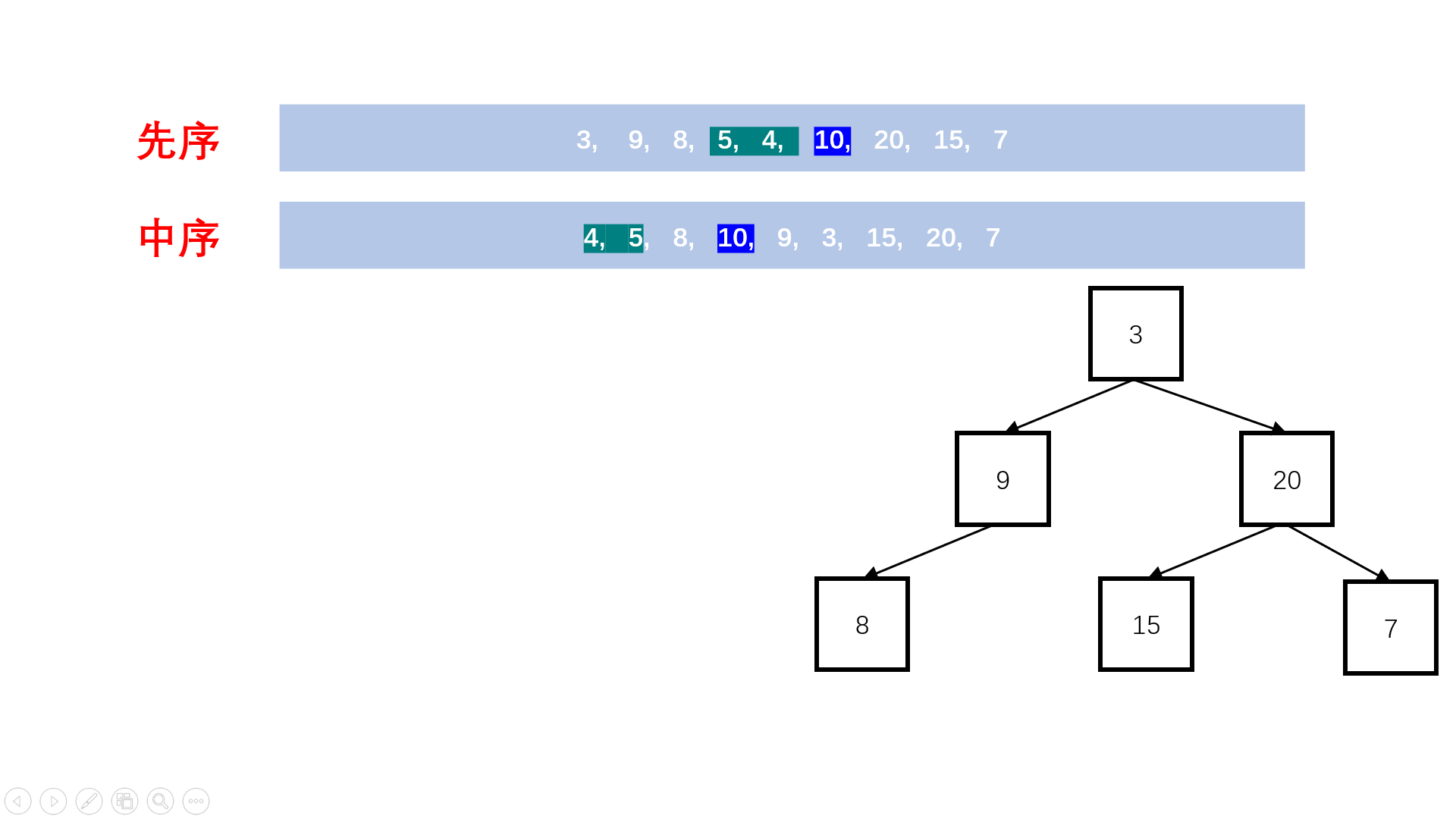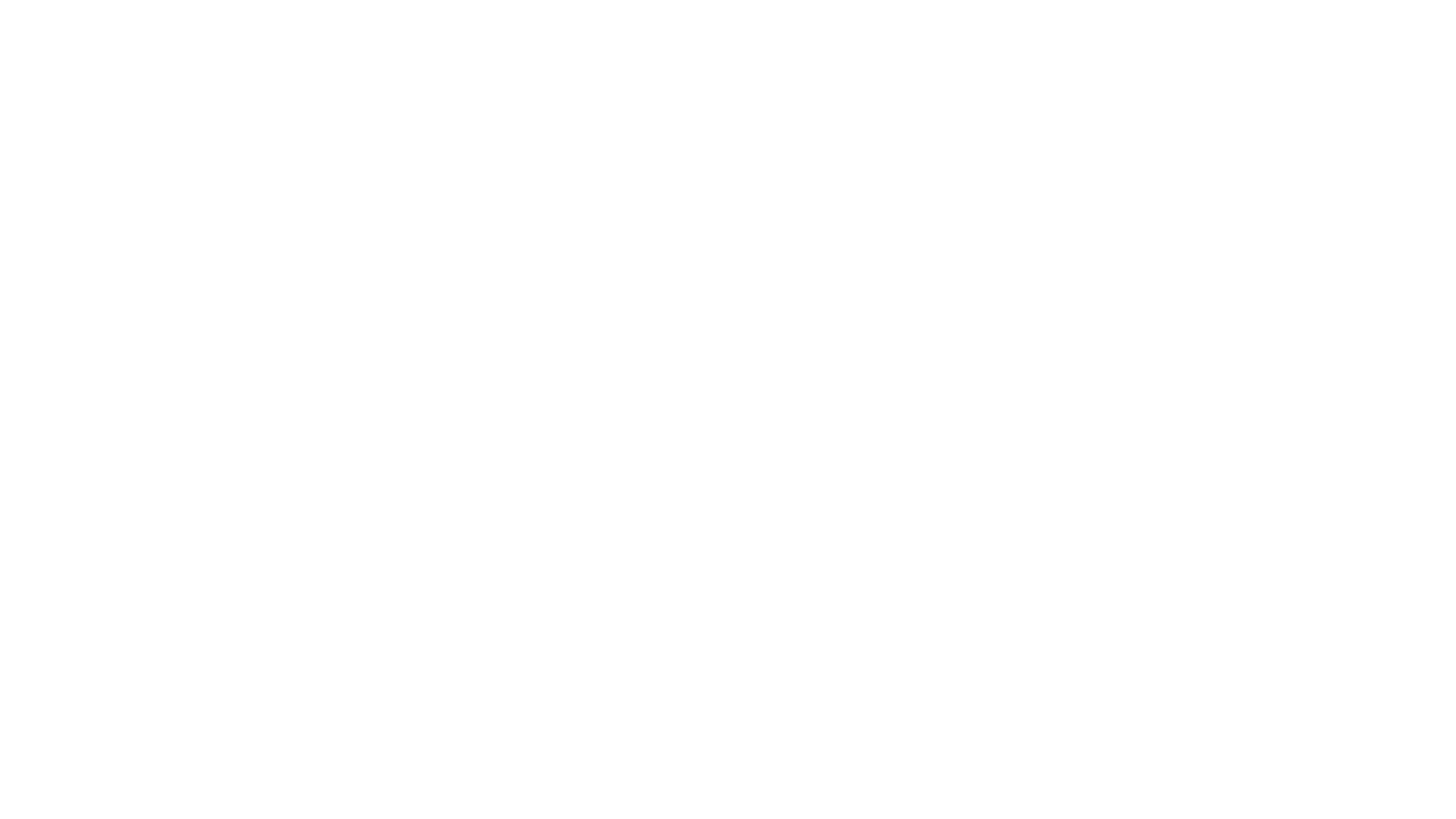
Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//建树函数
//四个int参数分别是前序最左节点下标,前序最右节点下标
//中序最左节点下标,中序最右节点坐标
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] xianxu, int l1, int r1, int[] zhongxu, int l2, int r2){
if(l1 > r1 || l2 > r2)
return null;
//构建节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(xianxu[l1]);
//用来保存根节点在中序遍历列表的下标
int rootIndex = 0;
//寻找根节点
for(int i = l2; i <= r2; i++){
if(zhongxu[i] == xianxu[l1]){
rootIndex = i;
break;
}
}
//左子树大小
int leftsize = rootIndex - l2;
//右子树大小
int rightsize = r2 - rootIndex;
//递归构建左子树和右子树
root.left = buildTree(xianxu, l1 + 1, l1 + leftsize, zhongxu, l2 , l2 + leftsize - 1);
root.right = buildTree(xianxu, r1 - rightsize + 1, r1, zhongxu, rootIndex + 1, r2);
return root;
}
//深度优先搜索函数
public ArrayList<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
//右边最深处的值
Map<Integer, Integer> mp = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
//记录最大深度
int max_depth = -1;
//维护深度访问节点
Stack<TreeNode> nodes = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//维护dfs时的深度
Stack<Integer> depths = new Stack<Integer>();
nodes.push(root);
depths.push(0);
while(!nodes.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = nodes.pop();
int depth = depths.pop();
if(node != null){
//维护二叉树的最大深度
max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, depth);
//如果不存在对应深度的节点我们才插入
if(mp.get(depth) == null)
mp.put(depth, node.val);
nodes.push(node.left);
nodes.push(node.right);
depths.push(depth + 1);
depths.push(depth + 1);
}
}
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//结果加入链表
for(int i = 0; i <= max_depth; i++)
res.add(mp.get(i));
return res;
}
public int[] solve (int[] xianxu, int[] zhongxu) {
//空节点
if(xianxu.length == 0)
return new int[0];
//建树
TreeNode root = buildTree(xianxu, 0, xianxu.length - 1, zhongxu, 0, zhongxu.length - 1);
//获取右视图输出
ArrayList<Integer> temp = rightSideView(root);
//转化为数组
int[] res = new int[temp.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++)
res[i] = temp.get(i);
return res;
}
}
方法二:哈希表优化的递归建树+层次遍历(扩展思路)

Java实现代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public Map<Integer, Integer> index;
//建树函数
//四个int参数分别是前序最左节点下标,前序最右节点下标
//中序最左节点下标,中序最右节点坐标
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] xianxu, int l1, int r1, int[] zhongxu, int l2, int r2){
if(l1 > r1 || l2 > r2)
return null;
//前序遍历中的第一个节点就是根节点
int xianxu_root = l1;
//在中序遍历中定位根节点
int zhongxu_root = index.get(xianxu[xianxu_root]);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(xianxu[xianxu_root]);
//得到左子树中的节点数目
int leftsize = zhongxu_root - l2;
root.left = buildTree(xianxu, l1 + 1, l1 + leftsize, zhongxu, l2, zhongxu_root - 1);
root.right = buildTree(xianxu, l1 + leftsize + 1, r1, zhongxu, zhongxu_root + 1, r2);
return root;
}
//层次遍历
public ArrayList<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
//队列中的大小即是这一层的节点树
int size = q.size();
while(size-- != 0){
TreeNode temp = q.poll();
if(temp.left != null)
q.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null)
q.offer(temp.right);
//最右元素
if(size == 0)
res.add(temp.val);
}
}
return res;
}
public int[] solve (int[] xianxu, int[] zhongxu) {
index = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
//空节点
if(xianxu.length == 0)
return new int[0];
//用哈希表标记中序节点在前序中的位置
for(int i = 0; i < xianxu.length; i++)
index.put(zhongxu[i], i);
//建树
TreeNode root = buildTree(xianxu, 0, xianxu.length - 1, zhongxu, 0, zhongxu.length - 1);
//获取右视图输出
ArrayList<Integer> temp = rightSideView(root);
//转化为数组
int[] res = new int[temp.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++)
res[i] = temp.get(i);
return res;
}
}
20. 相同的树
20.1. 题目描述
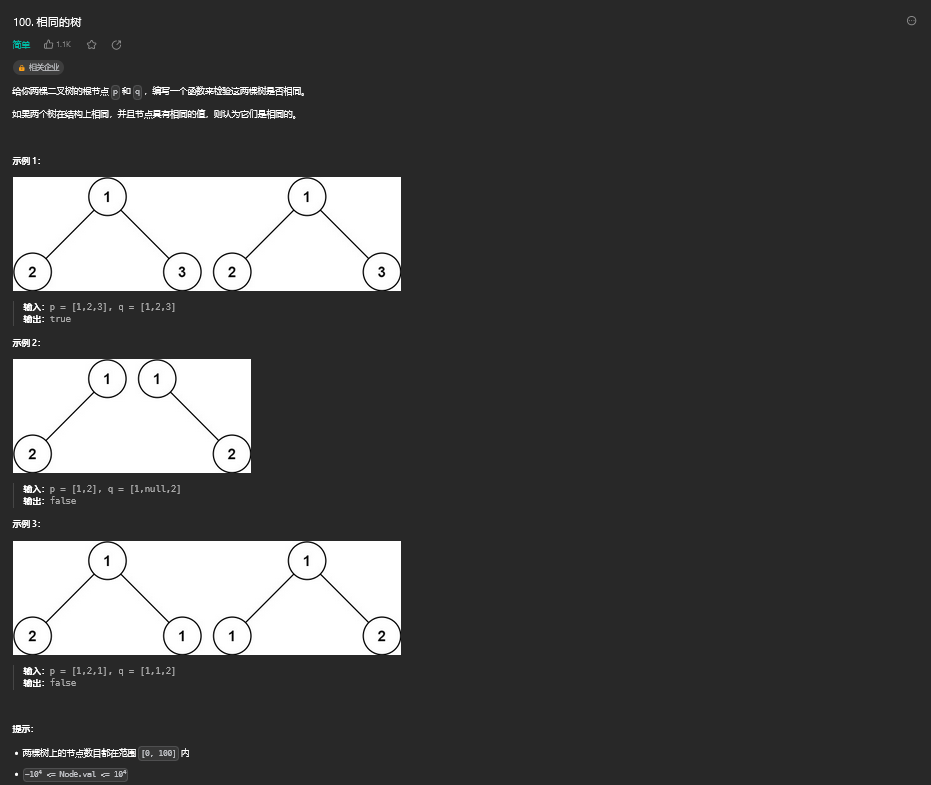
20.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先搜索

class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
} else if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
} else if (p.val != q.val) {
return false;
} else {
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}
}
方法二:广度优先搜索


class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
} else if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue1.offer(p);
queue2.offer(q);
while (!queue1.isEmpty() && !queue2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node1 = queue1.poll();
TreeNode node2 = queue2.poll();
if (node1.val != node2.val) {
return false;
}
TreeNode left1 = node1.left, right1 = node1.right, left2 = node2.left, right2 = node2.right;
if (left1 == null ^ left2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (right1 == null ^ right2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (left1 != null) {
queue1.offer(left1);
}
if (right1 != null) {
queue1.offer(right1);
}
if (left2 != null) {
queue2.offer(left2);
}
if (right2 != null) {
queue2.offer(right2);
}
}
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}

21. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
21.1. 题目描述

21.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归

class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> indexMap;
public TreeNode myBuildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder, int preorder_left, int preorder_right, int inorder_left, int inorder_right) {
if (preorder_left > preorder_right) {
return null;
}
// 前序遍历中的第一个节点就是根节点
int preorder_root = preorder_left;
// 在中序遍历中定位根节点
int inorder_root = indexMap.get(preorder[preorder_root]);
// 先把根节点建立出来
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_root]);
// 得到左子树中的节点数目
int size_left_subtree = inorder_root - inorder_left;
// 递归地构造左子树,并连接到根节点
// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1 开始的 size_left_subtree」个元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 左边界 开始到 根节点定位-1」的元素
root.left = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + 1, preorder_left + size_left_subtree, inorder_left, inorder_root - 1);
// 递归地构造右子树,并连接到根节点
// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1+左子树节点数目 开始到 右边界」的元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 根节点定位+1 到 右边界」的元素
root.right = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + size_left_subtree + 1, preorder_right, inorder_root + 1, inorder_right);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int n = preorder.length;
// 构造哈希映射,帮助我们快速定位根节点
indexMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
indexMap.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, 0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
}
}
方法二:迭代



class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if (preorder == null || preorder.length == 0) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
stack.push(root);
int inorderIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < preorder.length; i++) {
int preorderVal = preorder[i];
TreeNode node = stack.peek();
if (node.val != inorder[inorderIndex]) {
node.left = new TreeNode(preorderVal);
stack.push(node.left);
} else {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().val == inorder[inorderIndex]) {
node = stack.pop();
inorderIndex++;
}
node.right = new TreeNode(preorderVal);
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
22. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
22.1. 题目描述

22.2. 解题思路
方法一:广度优先搜索

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> levelOrder = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null) {
return levelOrder;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
TreeNode left = node.left, right = node.right;
if (left != null) {
queue.offer(left);
}
if (right != null) {
queue.offer(right);
}
}
levelOrder.add(0, level);
}
return levelOrder;
}
}
23. 平衡二叉树
23.1. 题目描述

23.2. 解题思路
方法一:自顶向下的递归

class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
} else {
return Math.abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
}
public int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
}
方法二:自底向上的递归

class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return height(root) >= 0;
}
public int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(root.left);
int rightHeight = height(root.right);
if (leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return -1;
} else {
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}
24. 路径总和
24.1. 题目描述

24.2. 解题思路
方法一:广度优先搜索

class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queNode = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> queVal = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queNode.offer(root);
queVal.offer(root.val);
while (!queNode.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode now = queNode.poll();
int temp = queVal.poll();
if (now.left == null && now.right == null) {
if (temp == sum) {
return true;
}
continue;
}
if (now.left != null) {
queNode.offer(now.left);
queVal.offer(now.left.val + temp);
}
if (now.right != null) {
queNode.offer(now.right);
queVal.offer(now.right.val + temp);
}
}
return false;
}
}
方法二:递归

class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum == root.val;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
}
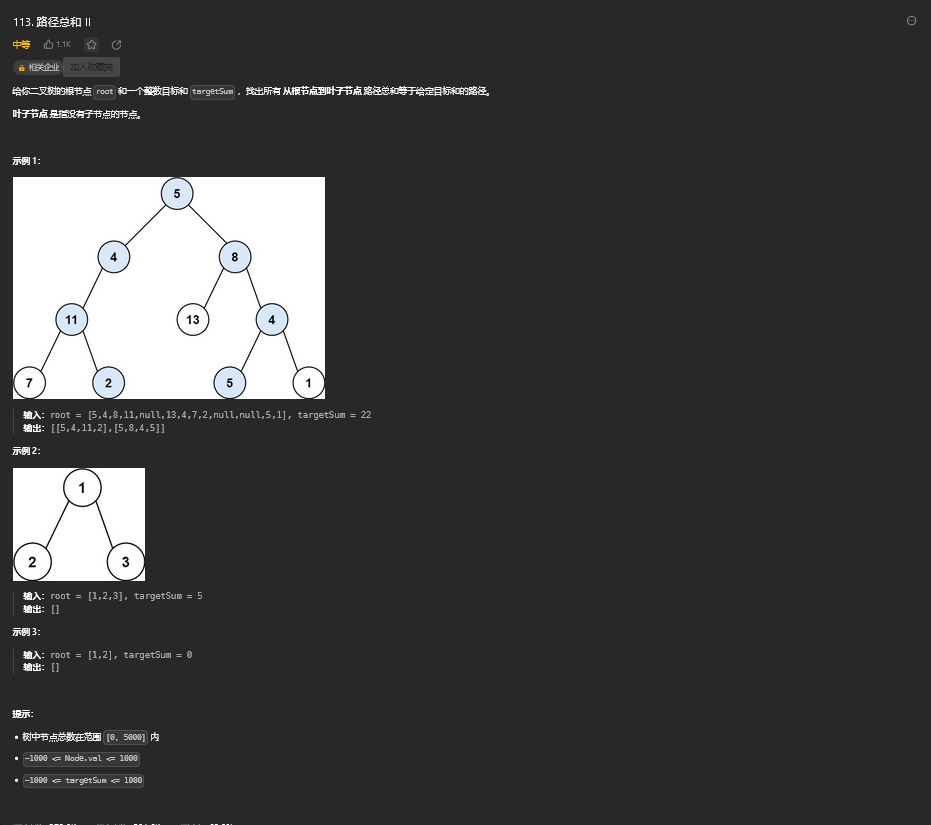
25. 路径总和 II
25.1. 题目描述
25.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先搜索

class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
path.offerLast(root.val);
targetSum -= root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0) {
ret.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
}
dfs(root.left, targetSum);
dfs(root.right, targetSum);
path.pollLast();
}
}

方法二:广度优先搜索

class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> map = new HashMap<TreeNode, TreeNode>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return ret;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queueNode = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> queueSum = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queueNode.offer(root);
queueSum.offer(0);
while (!queueNode.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queueNode.poll();
int rec = queueSum.poll() + node.val;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
if (rec == targetSum) {
getPath(node);
}
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
map.put(node.left, node);
queueNode.offer(node.left);
queueSum.offer(rec);
}
if (node.right != null) {
map.put(node.right, node);
queueNode.offer(node.right);
queueSum.offer(rec);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
public void getPath(TreeNode node) {
List<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while (node != null) {
temp.add(node.val);
node = map.get(node);
}
Collections.reverse(temp);
ret.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(temp));
}
}
26. 将N叉树编码为二叉树
26.1. 题目描述
26.2. 解题思路
// 本题测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/encode-n-ary-tree-to-binary-tree
public class d14_EncodeNaryTreeToBinaryTree {
// 提交时不要提交这个类
public static class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
// 提交时不要提交这个类
public static class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
// 只提交这个类即可
class Codec {
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
public TreeNode encode(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(root.val);
head.left = en(root.children);
return head;
}
private TreeNode en(List<Node> children) {
TreeNode head = null;
TreeNode cur = null;
for (Node child : children) {
TreeNode tNode = new TreeNode(child.val);
if (head == null) {
head = tNode;
} else {
cur.right = tNode;
}
cur = tNode;
cur.left = en(child.children);
}
return head;
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
public Node decode(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return new Node(root.val, de(root.left));
}
public List<Node> de(TreeNode root) {
List<Node> children = new ArrayList<>();
while (root != null) {
Node cur = new Node(root.val, de(root.left));
children.add(cur);
root = root.right;
}
return children;
}
}
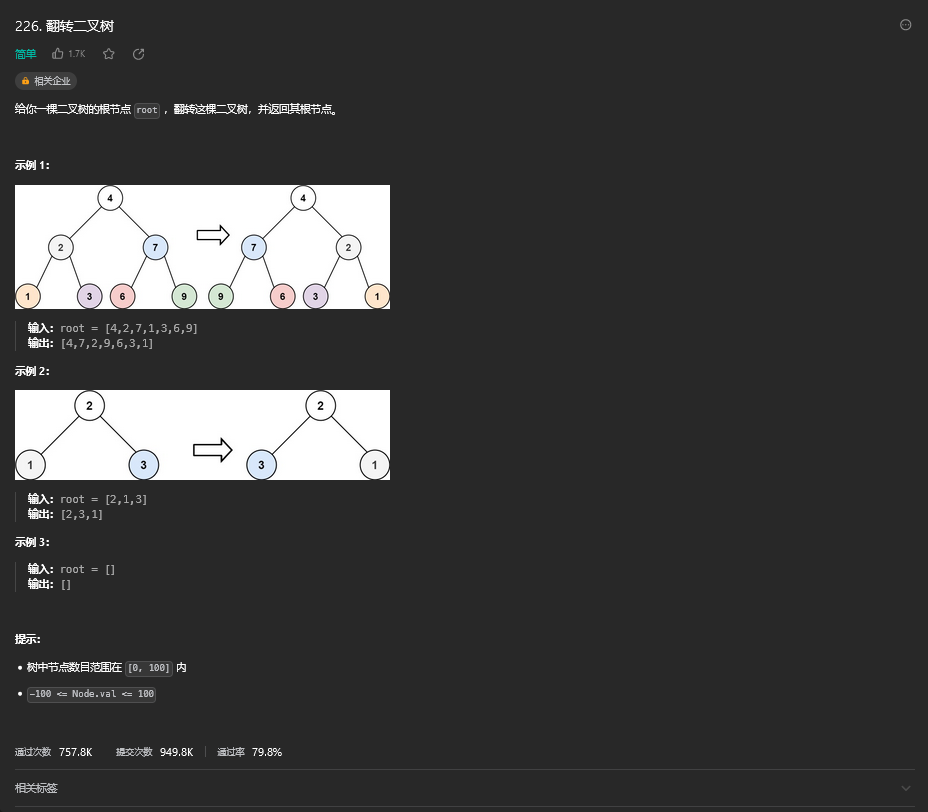
}27. 翻转二叉树(简单)
27.1. 题目描述
27.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归

class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
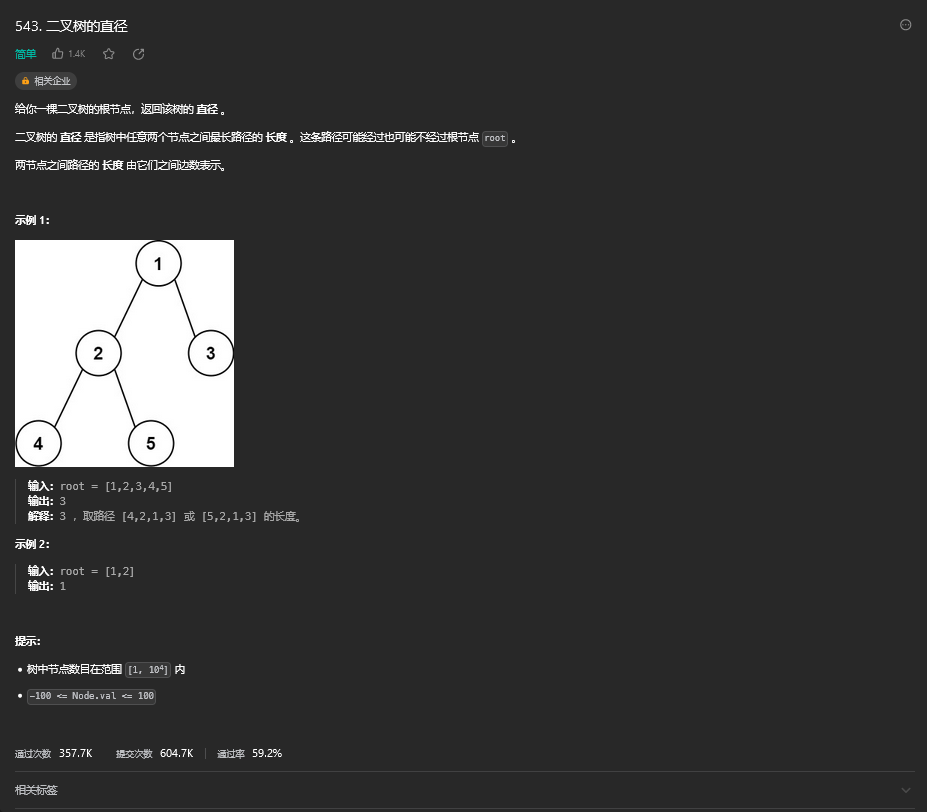
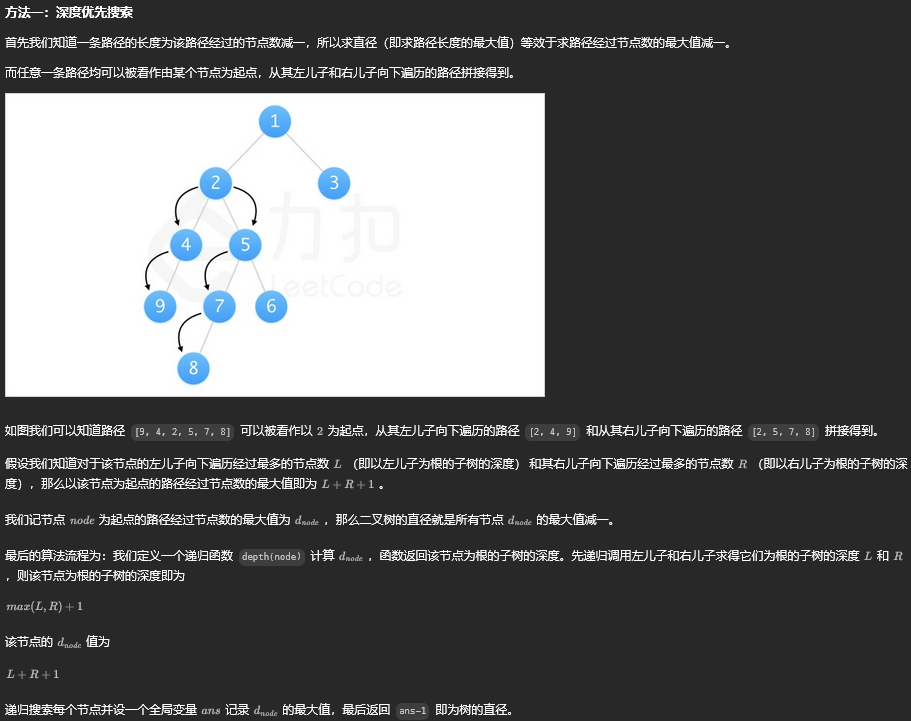
28. 二叉树的直径
28.1. 题目描述
28.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先搜索
class Solution {
int ans;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
ans = 1;
depth(root);
return ans - 1;
}
public int depth(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0; // 访问到空节点了,返回0
}
int L = depth(node.left); // 左儿子为根的子树的深度
int R = depth(node.right); // 右儿子为根的子树的深度
ans = Math.max(ans, L+R+1); // 计算d_node即L+R+1 并更新ans
return Math.max(L, R) + 1; // 返回该节点为根的子树的深度
}
}
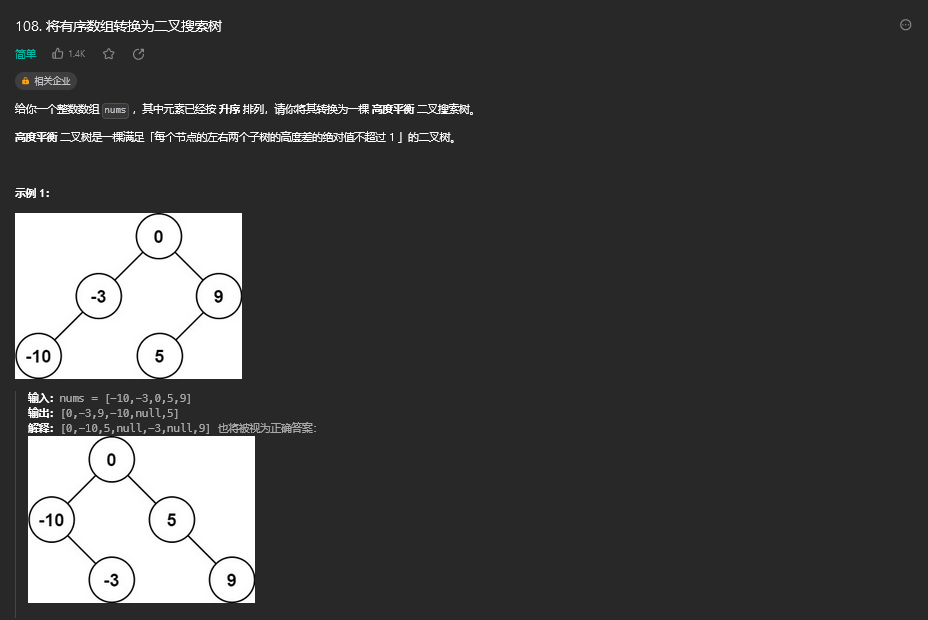
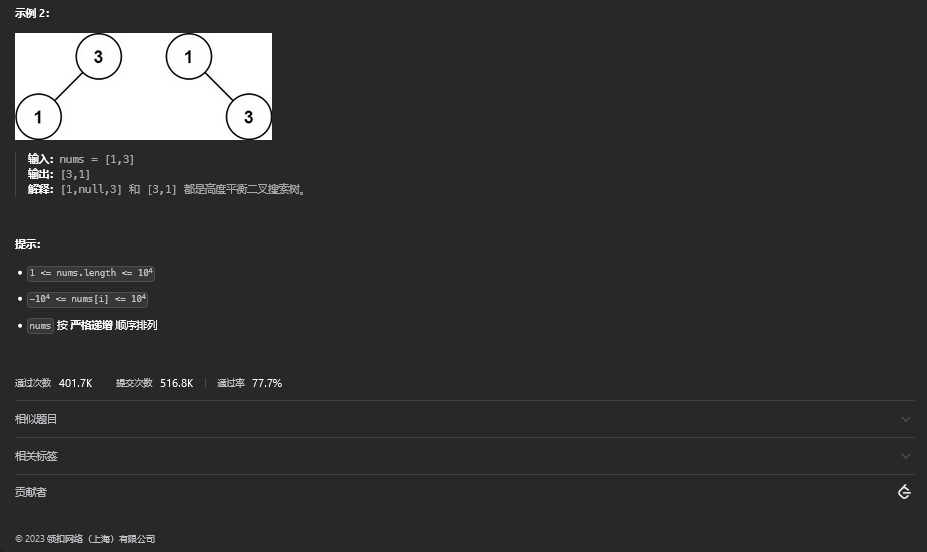
29. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
29.1. 题目描述
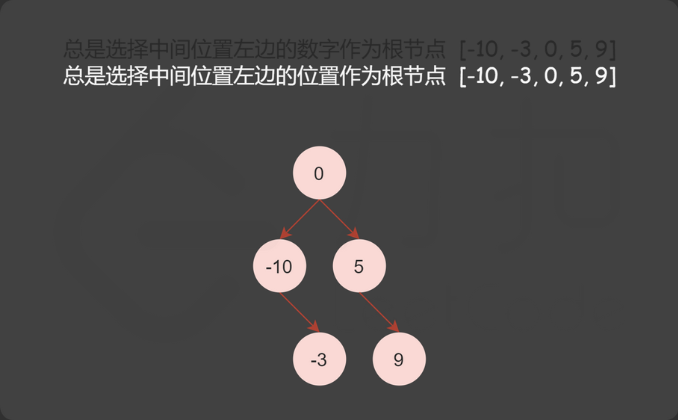
29.2. 解题思路
方法一:中序遍历,总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点

class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
// 总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
方法二:中序遍历,总是选择中间位置右边的数字作为根节点


class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
// 总是选择中间位置右边的数字作为根节点
int mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
方法三:中序遍历,选择任意一个中间位置数字作为根节点

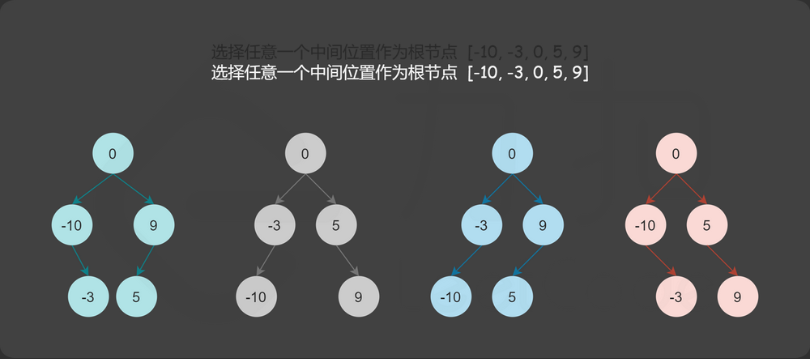
class Solution {
Random rand = new Random();
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
// 选择任意一个中间位置数字作为根节点
int mid = (left + right + rand.nextInt(2)) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
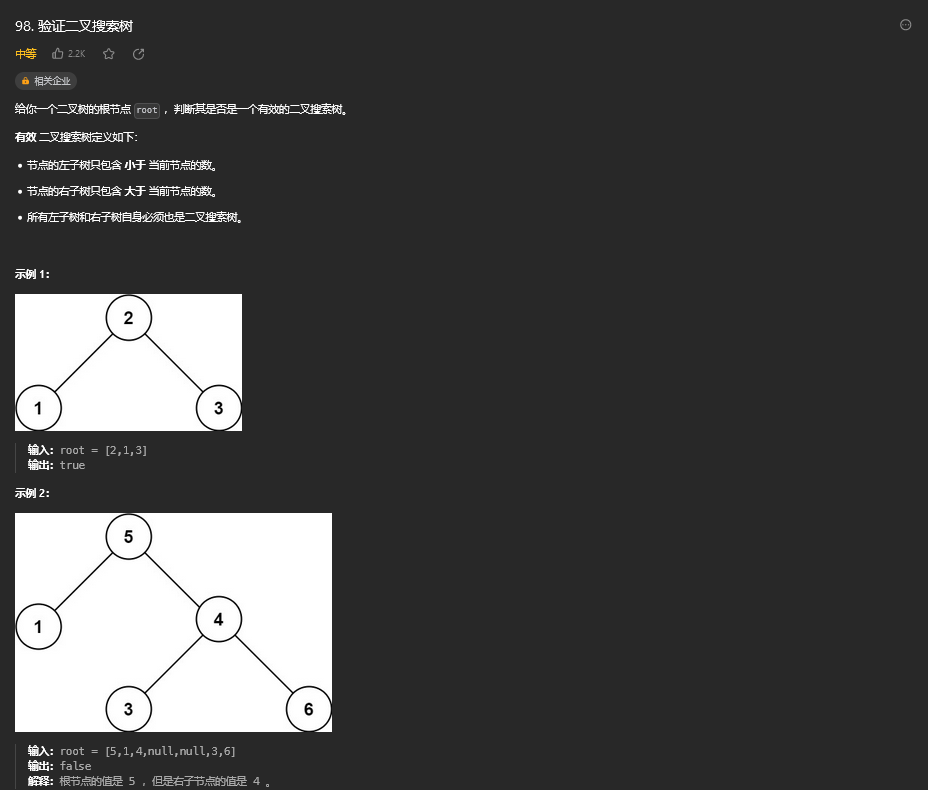
30. 验证二叉搜索树
30.1. 题目描述
30.2. 解题思路
方法一: 递归

class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode node, long lower, long upper) {
if (node == null) {
return true;
}
if (node.val <= lower || node.val >= upper) {
return false;
}
return isValidBST(node.left, lower, node.val) && isValidBST(node.right, node.val, upper);
}
}
方法二:中序遍历


class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
double inorder = -Double.MAX_VALUE;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
// 如果中序遍历得到的节点的值小于等于前一个 inorder,说明不是二叉搜索树
if (root.val <= inorder) {
return false;
}
inorder = root.val;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}
}
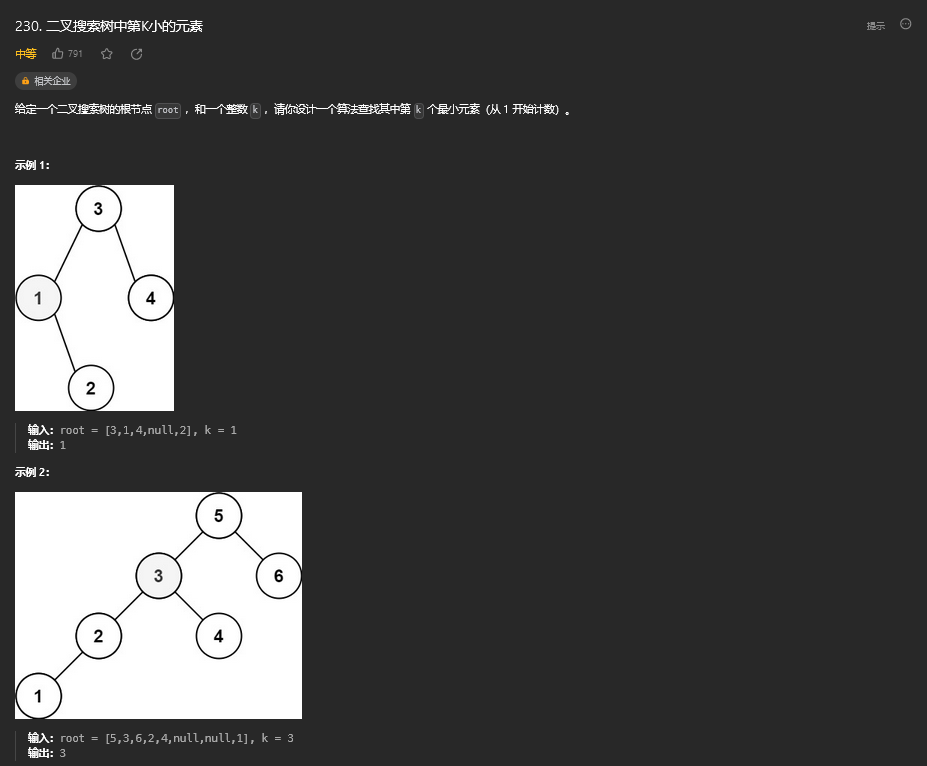
31. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
31.1. 题目描述
31.2. 解题思路
方法一:中序遍历
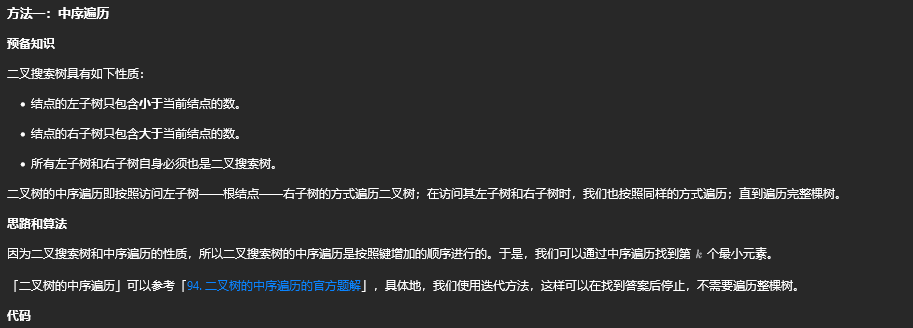
class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
--k;
if (k == 0) {
break;
}
root = root.right;
}
return root.val;
}
}
方法二:记录子树的结点数

class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
MyBst bst = new MyBst(root);
return bst.kthSmallest(k);
}
}
class MyBst {
TreeNode root;
Map<TreeNode, Integer> nodeNum;
public MyBst(TreeNode root) {
this.root = root;
this.nodeNum = new HashMap<TreeNode, Integer>();
countNodeNum(root);
}
// 返回二叉搜索树中第k小的元素
public int kthSmallest(int k) {
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
int left = getNodeNum(node.left);
if (left < k - 1) {
node = node.right;
k -= left + 1;
} else if (left == k - 1) {
break;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
return node.val;
}
// 统计以node为根结点的子树的结点数
private int countNodeNum(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
nodeNum.put(node, 1 + countNodeNum(node.left) + countNodeNum(node.right));
return nodeNum.get(node);
}
// 获取以node为根结点的子树的结点数
private int getNodeNum(TreeNode node) {
return nodeNum.getOrDefault(node, 0);
}
}
方法三:平衡二叉搜索树
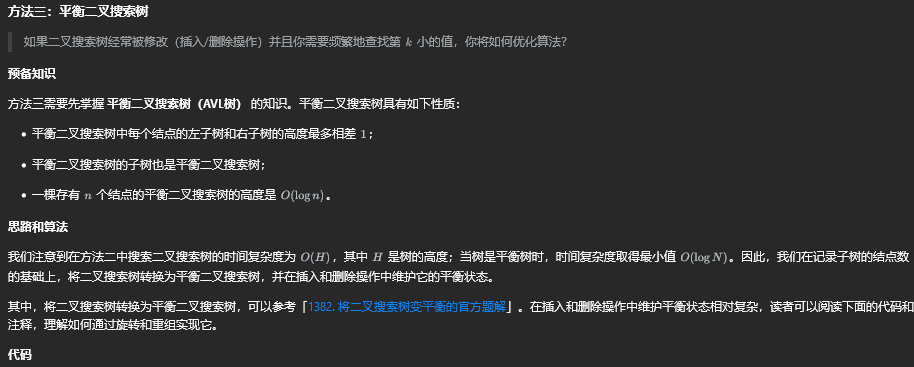
class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
// 中序遍历生成数值列表
List<Integer> inorderList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, inorderList);
// 构造平衡二叉搜索树
AVL avl = new AVL(inorderList);
// 模拟1000次插入和删除操作
int[] randomNums = new int[1000];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
randomNums[i] = random.nextInt(10001);
avl.insert(randomNums[i]);
}
shuffle(randomNums); // 列表乱序
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
avl.delete(randomNums[i]);
}
return avl.kthSmallest(k);
}
private void inorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> inorderList) {
if (node.left != null) {
inorder(node.left, inorderList);
}
inorderList.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
inorder(node.right, inorderList);
}
}
private void shuffle(int[] arr) {
Random random = new Random();
int length = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int randIndex = random.nextInt(length);
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[randIndex];
arr[randIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
// 平衡二叉搜索树(AVL树):允许重复值
class AVL {
Node root;
// 平衡二叉搜索树结点
class Node {
int val;
Node parent;
Node left;
Node right;
int size;
int height;
public Node(int val) {
this(val, null);
}
public Node(int val, Node parent) {
this(val, parent, null, null);
}
public Node(int val, Node parent, Node left, Node right) {
this.val = val;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.height = 0; // 结点高度:以node为根节点的子树的高度(高度定义:叶结点的高度是0)
this.size = 1; // 结点元素数:以node为根节点的子树的节点总数
}
}
public AVL(List<Integer> vals) {
if (vals != null) {
this.root = build(vals, 0, vals.size() - 1, null);
}
}
// 根据vals[l:r]构造平衡二叉搜索树 -> 返回根结点
private Node build(List<Integer> vals, int l, int r, Node parent) {
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
Node node = new Node(vals.get(m), parent);
if (l <= m - 1) {
node.left = build(vals, l, m - 1, node);
}
if (m + 1 <= r) {
node.right = build(vals, m + 1, r, node);
}
recompute(node);
return node;
}
// 返回二叉搜索树中第k小的元素
public int kthSmallest(int k) {
Node node = root;
while (node != null) {
int left = getSize(node.left);
if (left < k - 1) {
node = node.right;
k -= left + 1;
} else if (left == k - 1) {
break;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
return node.val;
}
public void insert(int v) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(v);
} else {
// 计算新结点的添加位置
Node node = subtreeSearch(root, v);
boolean isAddLeft = v <= node.val; // 是否将新结点添加到node的左子结点
if (node.val == v) { // 如果值为v的结点已存在
if (node.left != null) { // 值为v的结点存在左子结点,则添加到其左子树的最右侧
node = subtreeLast(node.left);
isAddLeft = false;
} else { // 值为v的结点不存在左子结点,则添加到其左子结点
isAddLeft = true;
}
}
// 添加新结点
Node leaf = new Node(v, node);
if (isAddLeft) {
node.left = leaf;
} else {
node.right = leaf;
}
rebalance(leaf);
}
}
// 删除值为v的结点 -> 返回是否成功删除结点
public boolean delete(int v) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
Node node = subtreeSearch(root, v);
if (node.val != v) { // 没有找到需要删除的结点
return false;
}
// 处理当前结点既有左子树也有右子树的情况
// 若左子树比右子树高度低,则将当前结点替换为右子树最左侧的结点,并移除右子树最左侧的结点
// 若右子树比左子树高度低,则将当前结点替换为左子树最右侧的结点,并移除左子树最右侧的结点
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
Node replacement = null;
if (node.left.height <= node.right.height) {
replacement = subtreeFirst(node.right);
} else {
replacement = subtreeLast(node.left);
}
node.val = replacement.val;
node = replacement;
}
Node parent = node.parent;
delete(node);
rebalance(parent);
return true;
}
// 删除结点p并用它的子结点代替它,结点p至多只能有1个子结点
private void delete(Node node) {
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
return;
// throw new Exception("Node has two children");
}
Node child = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
if (child != null) {
child.parent = node.parent;
}
if (node == root) {
root = child;
} else {
Node parent = node.parent;
if (node == parent.left) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
}
node.parent = node;
}
// 在以node为根结点的子树中搜索值为v的结点,如果没有值为v的结点,则返回值为v的结点应该在的位置的父结点
private Node subtreeSearch(Node node, int v) {
if (node.val < v && node.right != null) {
return subtreeSearch(node.right, v);
} else if (node.val > v && node.left != null) {
return subtreeSearch(node.left, v);
} else {
return node;
}
}
// 重新计算node结点的高度和元素数
private void recompute(Node node) {
node.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.left), getHeight(node.right));
node.size = 1 + getSize(node.left) + getSize(node.right);
}
// 从node结点开始(含node结点)逐个向上重新平衡二叉树,并更新结点高度和元素数
private void rebalance(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
int oldHeight = node.height, oldSize = node.size;
if (!isBalanced(node)) {
node = restructure(tallGrandchild(node));
recompute(node.left);
recompute(node.right);
}
recompute(node);
if (node.height == oldHeight && node.size == oldSize) {
node = null; // 如果结点高度和元素数都没有变化则不需要再继续向上调整
} else {
node = node.parent;
}
}
}
// 判断node结点是否平衡
private boolean isBalanced(Node node) {
return Math.abs(getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right)) <= 1;
}
// 获取node结点更高的子树
private Node tallChild(Node node) {
if (getHeight(node.left) > getHeight(node.right)) {
return node.left;
} else {
return node.right;
}
}
// 获取node结点更高的子树中的更高的子树
private Node tallGrandchild(Node node) {
Node child = tallChild(node);
return tallChild(child);
}
// 重新连接父结点和子结点(子结点允许为空)
private static void relink(Node parent, Node child, boolean isLeft) {
if (isLeft) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
if (child != null) {
child.parent = parent;
}
}
// 旋转操作
private void rotate(Node node) {
Node parent = node.parent;
Node grandparent = parent.parent;
if (grandparent == null) {
root = node;
node.parent = null;
} else {
relink(grandparent, node, parent == grandparent.left);
}
if (node == parent.left) {
relink(parent, node.right, true);
relink(node, parent, false);
} else {
relink(parent, node.left, false);
relink(node, parent, true);
}
}
// trinode操作
private Node restructure(Node node) {
Node parent = node.parent;
Node grandparent = parent.parent;
if ((node == parent.right) == (parent == grandparent.right)) { // 处理需要一次旋转的情况
rotate(parent);
return parent;
} else { // 处理需要两次旋转的情况:第1次旋转后即成为需要一次旋转的情况
rotate(node);
rotate(node);
return node;
}
}
// 返回以node为根结点的子树的第1个元素
private static Node subtreeFirst(Node node) {
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
// 返回以node为根结点的子树的最后1个元素
private static Node subtreeLast(Node node) {
while (node.right != null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node;
}
// 获取以node为根结点的子树的高度
private static int getHeight(Node node) {
return node != null ? node.height : 0;
}
// 获取以node为根结点的子树的结点数
private static int getSize(Node node) {
return node != null ? node.size : 0;
}
}
32. 二叉树的右视图
32.1. 题目描述

32.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先搜索

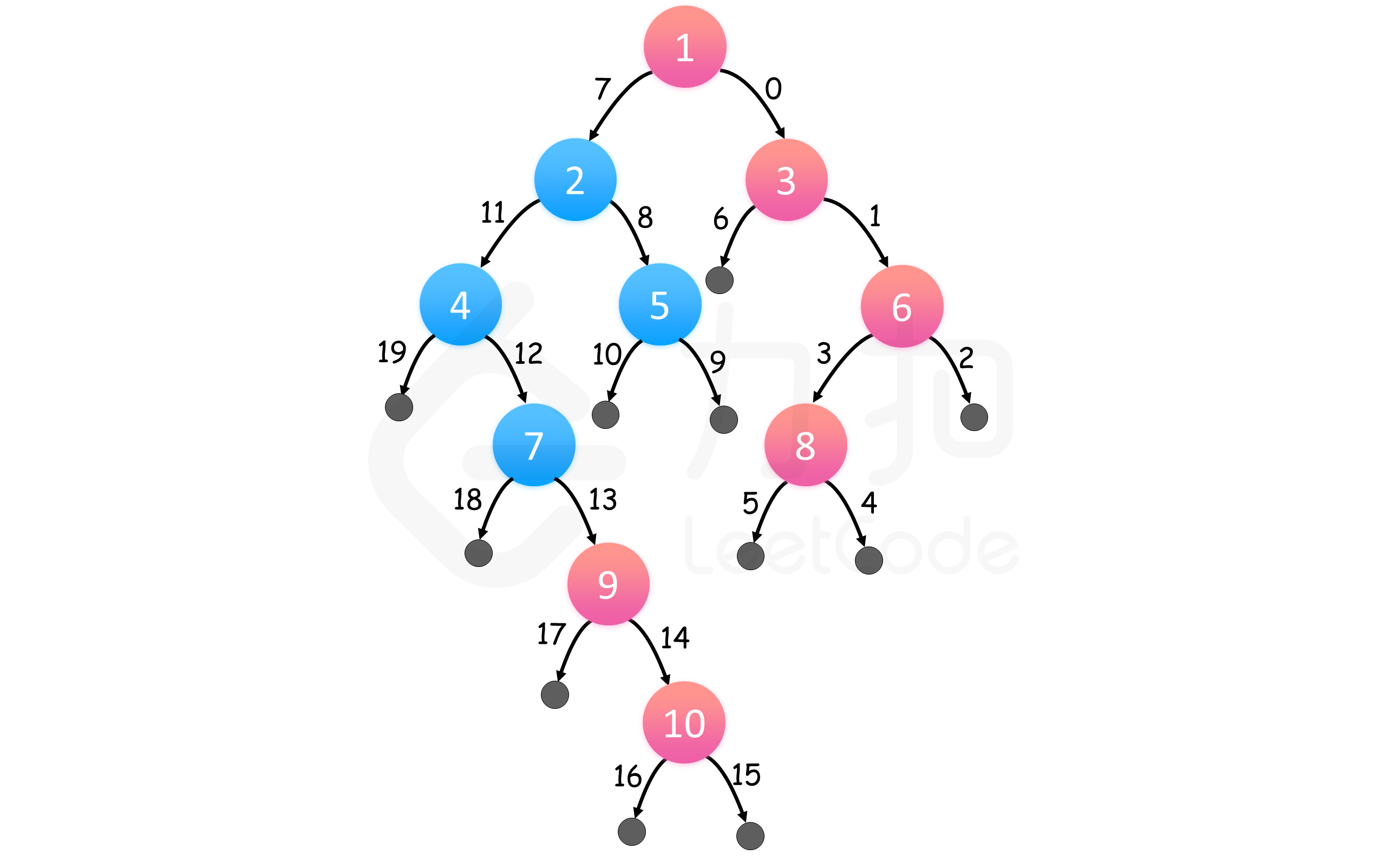
上图表示了问题的一个实例。红色结点自上而下组成答案,边缘以访问顺序标号。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> rightmostValueAtDepth = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int max_depth = -1;
Deque<TreeNode> nodeStack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Deque<Integer> depthStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
nodeStack.push(root);
depthStack.push(0);
while (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeStack.pop();
int depth = depthStack.pop();
if (node != null) {
// 维护二叉树的最大深度
max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, depth);
// 如果不存在对应深度的节点我们才插入
if (!rightmostValueAtDepth.containsKey(depth)) {
rightmostValueAtDepth.put(depth, node.val);
}
nodeStack.push(node.left);
nodeStack.push(node.right);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
}
}
List<Integer> rightView = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int depth = 0; depth <= max_depth; depth++) {
rightView.add(rightmostValueAtDepth.get(depth));
}
return rightView;
}
}方法二:广度优先搜索

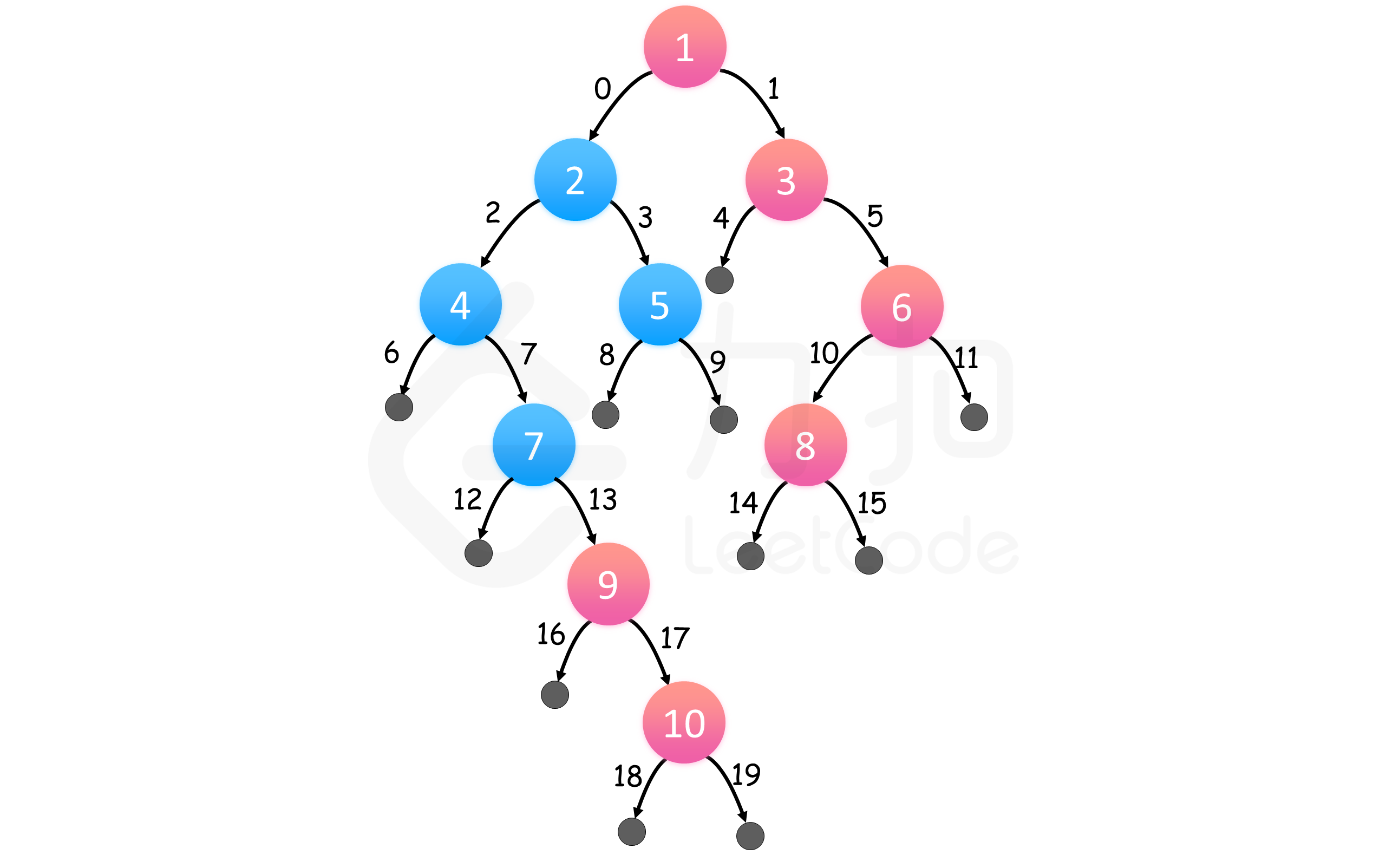
上图表示了同一个示例,红色结点自上而下组成答案,边缘以访问顺序标号。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> rightmostValueAtDepth = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int max_depth = -1;
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> depthQueue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
nodeQueue.add(root);
depthQueue.add(0);
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.remove();
int depth = depthQueue.remove();
if (node != null) {
// 维护二叉树的最大深度
max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, depth);
// 由于每一层最后一个访问到的节点才是我们要的答案,因此不断更新对应深度的信息即可
rightmostValueAtDepth.put(depth, node.val);
nodeQueue.add(node.left);
nodeQueue.add(node.right);
depthQueue.add(depth + 1);
depthQueue.add(depth + 1);
}
}
List<Integer> rightView = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int depth = 0; depth <= max_depth; depth++) {
rightView.add(rightmostValueAtDepth.get(depth));
}
return rightView;
}
}
33. 二叉树展开为链表
33.1. 题目描述
33.2. 解题思路
方法一:前序遍历

class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
preorderTraversal(root, list);
int size = list.size();
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode prev = list.get(i - 1), curr = list.get(i);
prev.left = null;
prev.right = curr;
}
}
public void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<TreeNode> list) {
if (root != null) {
list.add(root);
preorderTraversal(root.left, list);
preorderTraversal(root.right, list);
}
}
}以下代码通过迭代实现前序遍历。
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (node != null) {
list.add(node);
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
node = node.right;
}
int size = list.size();
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode prev = list.get(i - 1), curr = list.get(i);
prev.left = null;
prev.right = curr;
}
}
}
方法二:前序遍历和展开同步进行

class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
stack.push(root);
TreeNode prev = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.pop();
if (prev != null) {
prev.left = null;
prev.right = curr;
}
TreeNode left = curr.left, right = curr.right;
if (right != null) {
stack.push(right);
}
if (left != null) {
stack.push(left);
}
prev = curr;
}
}
}
方法三:寻找前驱节点

class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode curr = root;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.left != null) {
TreeNode next = curr.left;
TreeNode predecessor = next;
while (predecessor.right != null) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
predecessor.right = curr.right;
curr.left = null;
curr.right = next;
}
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
34. 路径总和 III
34.1. 题目描述
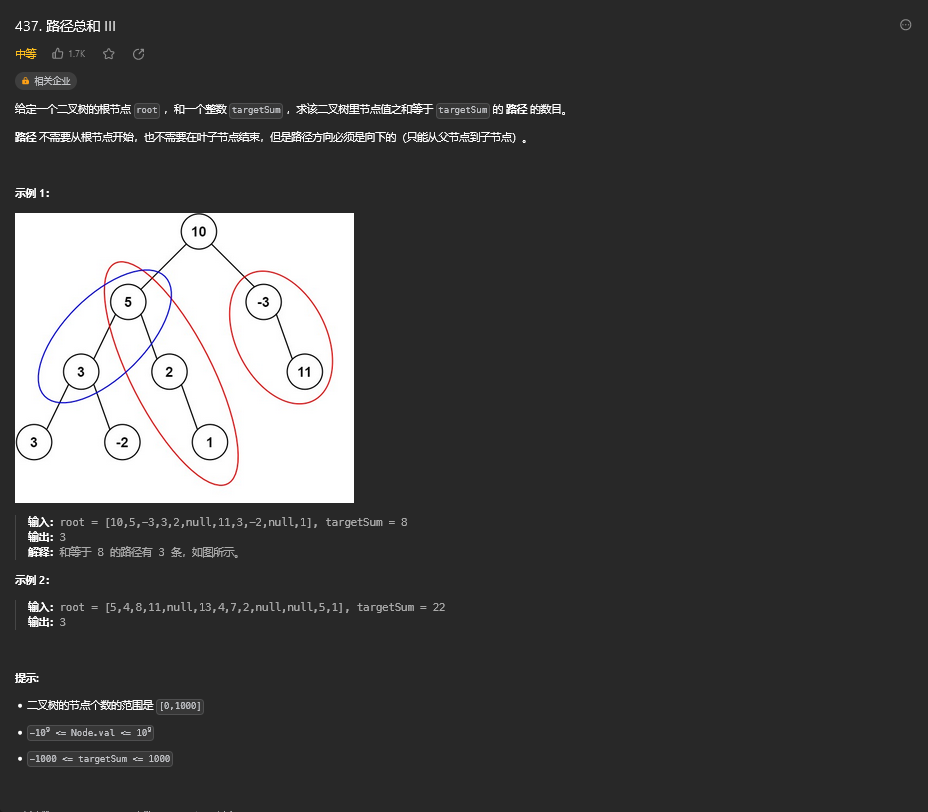
34.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先搜索

class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int ret = rootSum(root, targetSum);
ret += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);
ret += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);
return ret;
}
public int rootSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
int ret = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int val = root.val;
if (val == targetSum) {
ret++;
}
ret += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - val);
ret += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - val);
return ret;
}
}
方法二: 前缀和

class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
Map<Long, Integer> prefix = new HashMap<Long, Integer>();
prefix.put(0L, 1);
return dfs(root, prefix, 0, targetSum);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, Map<Long, Integer> prefix, long curr, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int ret = 0;
curr += root.val;
ret = prefix.getOrDefault(curr - targetSum, 0);
prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) + 1);
ret += dfs(root.left, prefix, curr, targetSum);
ret += dfs(root.right, prefix, curr, targetSum);
prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) - 1);
return ret;
}
}
35. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
35.1. 题目描述
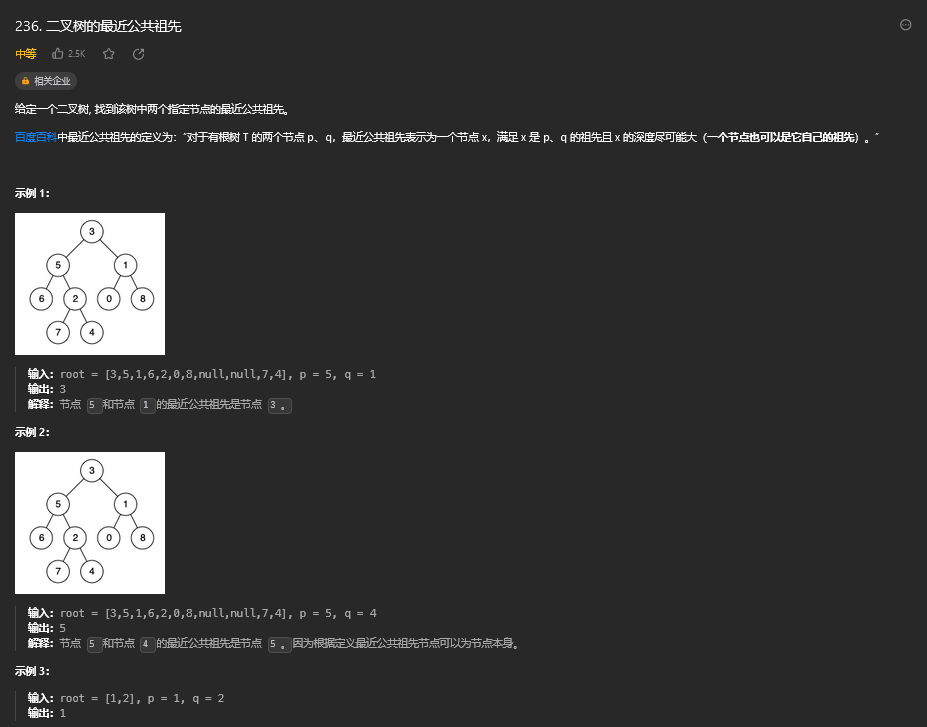
35.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归

class Solution {
private TreeNode ans;
public Solution() {
this.ans = null;
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return false;
boolean lson = dfs(root.left, p, q);
boolean rson = dfs(root.right, p, q);
if ((lson && rson) || ((root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val) && (lson || rson))) {
ans = root;
}
return lson || rson || (root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val);
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
this.dfs(root, p, q);
return this.ans;
}
}
方法二:存储父节点

class Solution {
Map<Integer, TreeNode> parent = new HashMap<Integer, TreeNode>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<Integer>();
public void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root.left != null) {
parent.put(root.left.val, root);
dfs(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
parent.put(root.right.val, root);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
dfs(root);
while (p != null) {
visited.add(p.val);
p = parent.get(p.val);
}
while (q != null) {
if (visited.contains(q.val)) {
return q;
}
q = parent.get(q.val);
}
return null;
}
}
36. 二叉树中的最大路径和(困难)
36.1. 题目描述
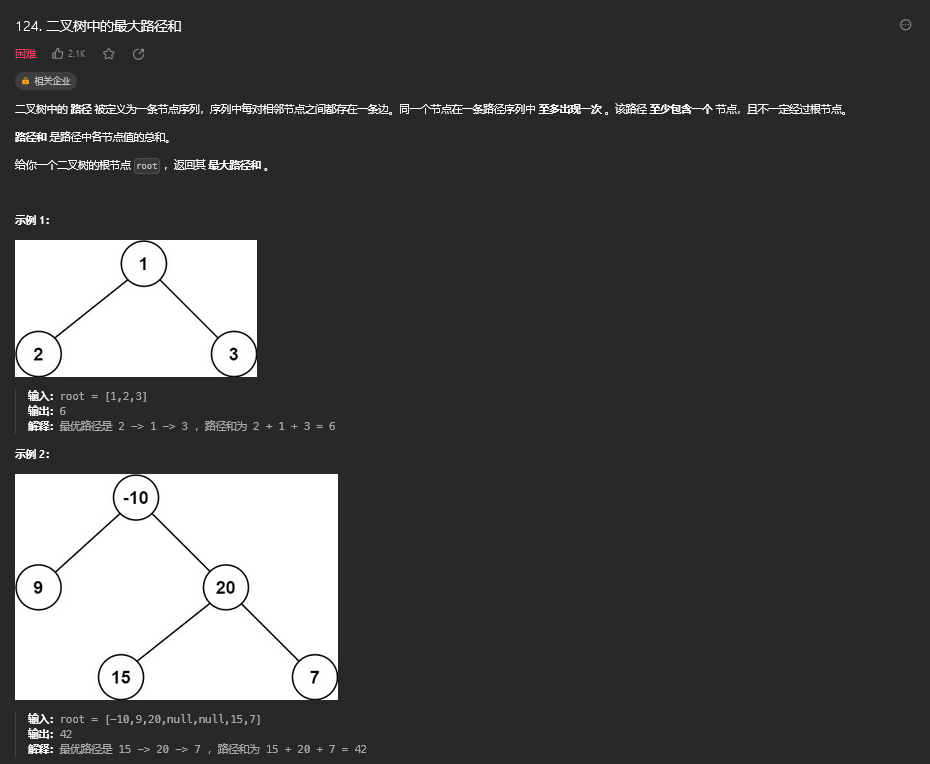

36.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归
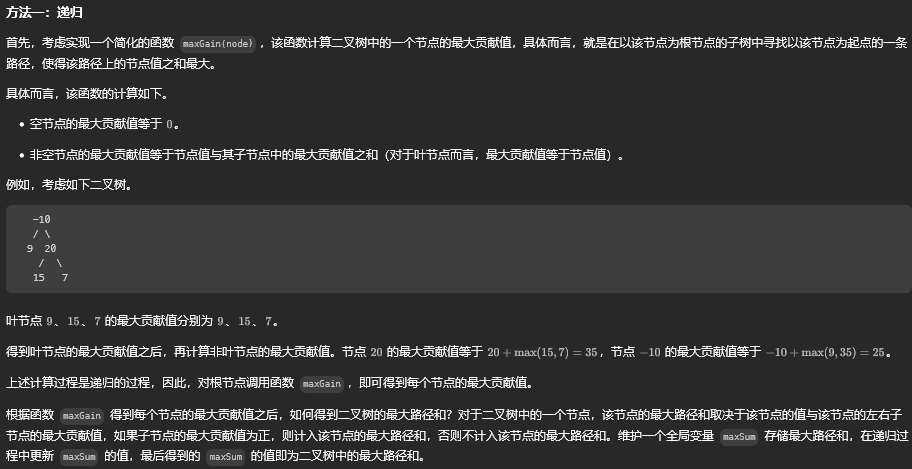
class Solution {
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
maxGain(root);
return maxSum;
}
public int maxGain(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
// 递归计算左右子节点的最大贡献值
// 只有在最大贡献值大于 0 时,才会选取对应子节点
int leftGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.left), 0);
int rightGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.right), 0);
// 节点的最大路径和取决于该节点的值与该节点的左右子节点的最大贡献值
int priceNewpath = node.val + leftGain + rightGain;
// 更新答案
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, priceNewpath);
// 返回节点的最大贡献值
return node.val + Math.max(leftGain, rightGain);
}
}
37. 叶子相似的树
37.1. 题目描述
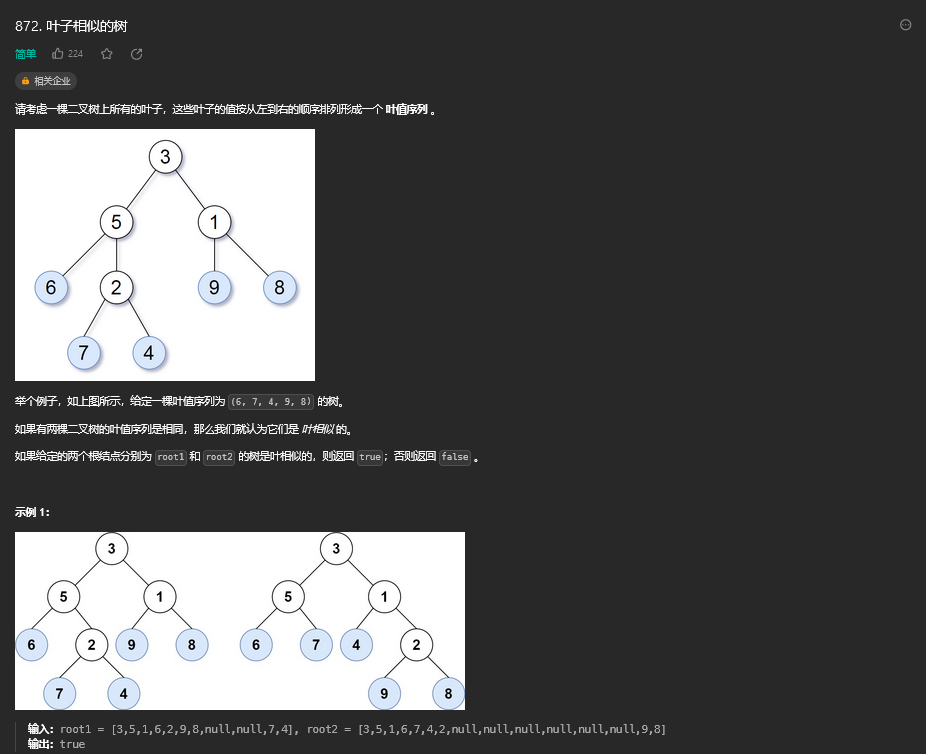
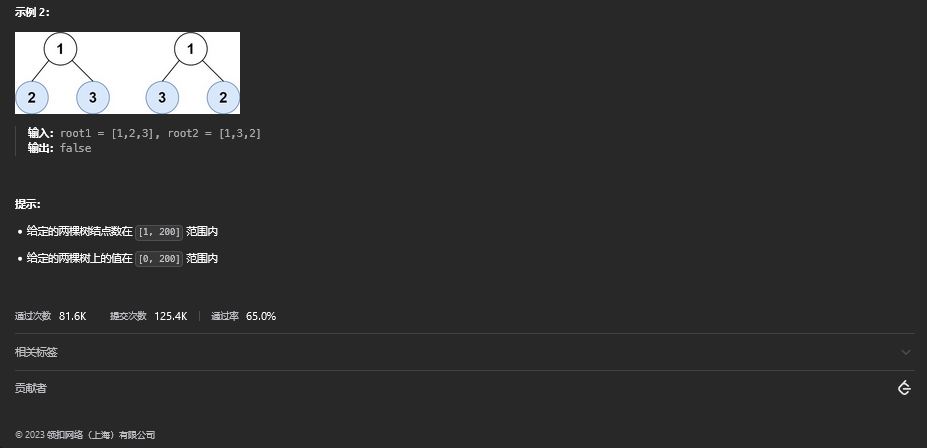
37.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先搜索

class Solution {
public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
List<Integer> seq1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root1 != null) {
dfs(root1, seq1);
}
List<Integer> seq2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root2 != null) {
dfs(root2, seq2);
}
return seq1.equals(seq2);
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, List<Integer> seq) {
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
seq.add(node.val);
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
dfs(node.left, seq);
}
if (node.right != null) {
dfs(node.right, seq);
}
}
}
}
38. 统计二叉树中好节点的数目
38.1. 题目描述
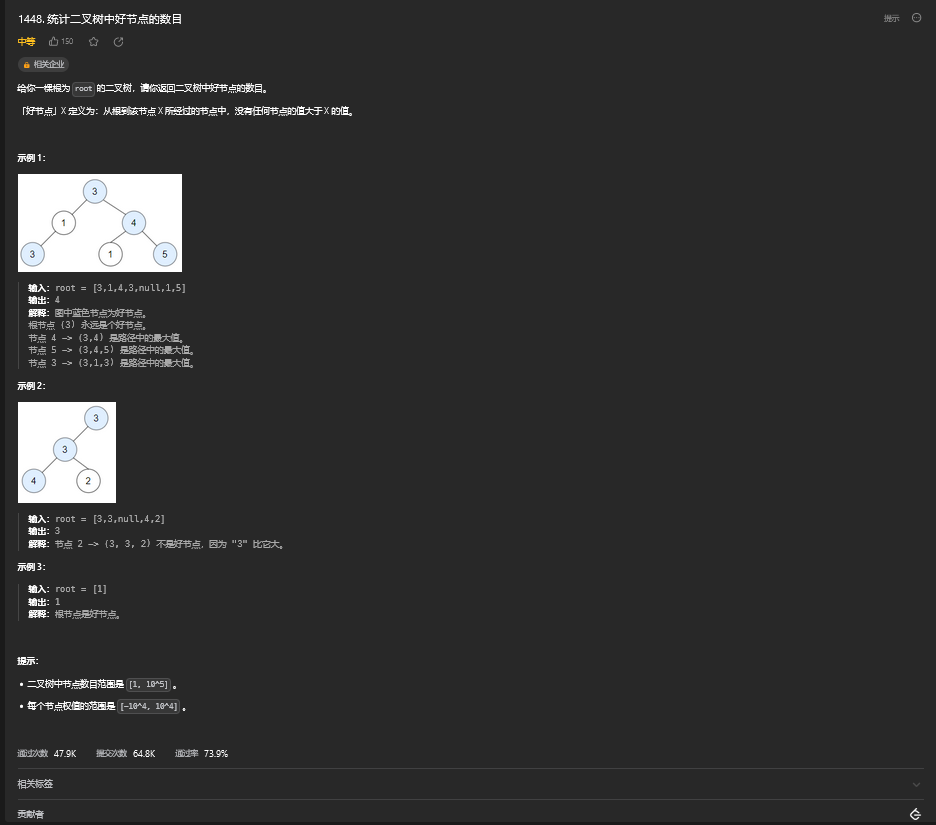
38.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先遍历

class Solution {
public int goodNodes(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, int pathMax) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int res = 0;
if (root.val >= pathMax) {
res++;
pathMax = root.val;
}
res += dfs(root.left, pathMax) + dfs(root.right, pathMax);
return res;
}
}
39. 二叉树中的最长交错路径
39.1. 题目描述
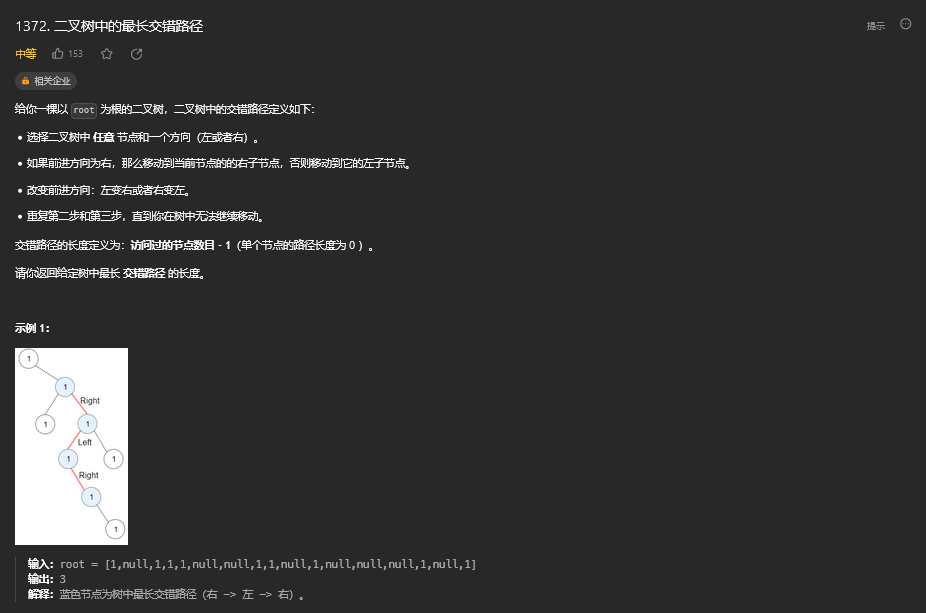
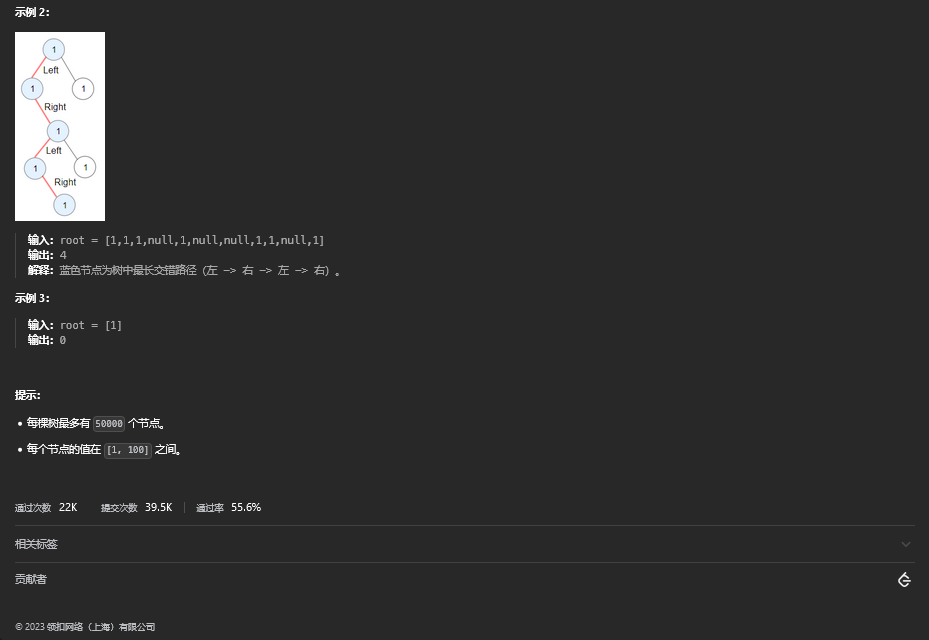
39.2. 解题思路
方法一:动态规划

class Solution {
Map<TreeNode, Integer> f = new HashMap<TreeNode, Integer>();
Map<TreeNode, Integer> g = new HashMap<TreeNode, Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode[]> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode[]>();
public int longestZigZag(TreeNode root) {
dp(root);
int maxAns = 0;
for (TreeNode u : f.keySet()) {
maxAns = Math.max(maxAns, Math.max(f.get(u), g.get(u)));
}
return maxAns;
}
public void dp(TreeNode o) {
f.put(o, 0);
g.put(o, 0);
q.offer(new TreeNode[]{o, null});
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode[] y = q.poll();
TreeNode u = y[0], x = y[1];
f.put(u, 0);
g.put(u, 0);
if (x != null) {
if (x.left == u) {
f.put(u, g.get(x) + 1);
}
if (x.right == u) {
g.put(u, f.get(x) + 1);
}
}
if (u.left != null) {
q.offer(new TreeNode[]{u.left, u});
}
if (u.right != null) {
q.offer(new TreeNode[]{u.right, u});
}
}
}
}
方法二:深度优先搜索

class Solution {
int maxAns;
public int longestZigZag(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
maxAns = 0;
dfs(root, false, 0);
dfs(root, true, 0);
return maxAns;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode o, boolean dir, int len) {
maxAns = Math.max(maxAns, len);
if (!dir) {
if (o.left != null) {
dfs(o.left, true, len + 1);
}
if (o.right != null) {
dfs(o.right, false, 1);
}
} else {
if (o.right != null) {
dfs(o.right, false, len + 1);
}
if (o.left != null) {
dfs(o.left, true, 1);
}
}
}
}
40. 最大层内元素和
40.1. 题目描述
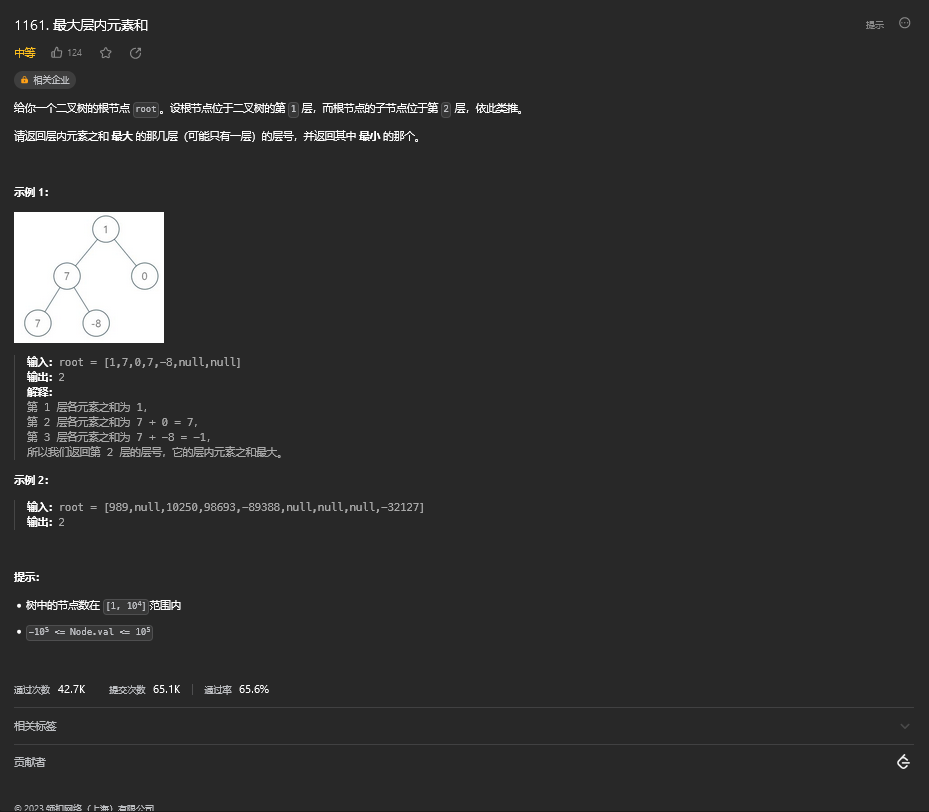
40.2. 解题思路
方法一:深度优先搜索

class Solution {
private List<Integer> sum = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public int maxLevelSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sum.size(); ++i) {
if (sum.get(i) > sum.get(ans)) {
ans = i;
}
}
return ans + 1; // 层号从 1 开始
}
private void dfs(TreeNode node, int level) {
if (level == sum.size()) {
sum.add(node.val);
} else {
sum.set(level, sum.get(level) + node.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
dfs(node.left, level + 1);
}
if (node.right != null) {
dfs(node.right, level + 1);
}
}
}
方法二:广度优先搜索

class Solution {
public int maxLevelSum(TreeNode root) {
int ans = 1, maxSum = root.val;
List<TreeNode> q = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
q.add(root);
for (int level = 1; !q.isEmpty(); ++level) {
List<TreeNode> nq = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
int sum = 0;
for (TreeNode node : q) {
sum += node.val;
if (node.left != null) {
nq.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
nq.add(node.right);
}
}
if (sum > maxSum) {
maxSum = sum;
ans = level;
}
q = nq;
}
return ans;
}
}
41. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
41.1. 题目描述

41.2. 解题思路
方法一:递归

class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (val == root.val) {
return root;
}
return searchBST(val < root.val ? root.left : root.right, val);
}
}
方法二:迭代

class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
while (root != null) {
if (val == root.val) {
return root;
}
root = val < root.val ? root.left : root.right;
}
return null;
}
}
42. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
42.1. 题目描述
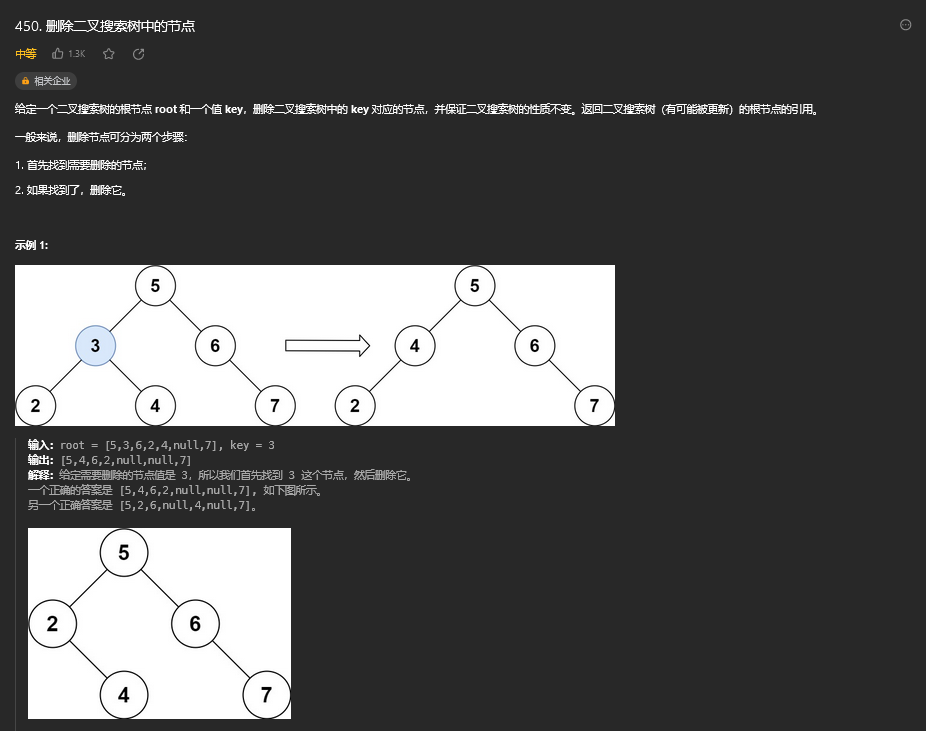

42.2 解题思路
方法一:递归

class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val > key) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
return root;
}
if (root.val < key) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
return root;
}
if (root.val == key) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return root.left;
}
if (root.left == null) {
return root.right;
}
TreeNode successor = root.right;
while (successor.left != null) {
successor = successor.left;
}
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, successor.val);
successor.right = root.right;
successor.left = root.left;
return successor;
}
return root;
}
}
方法二:迭代

class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
TreeNode cur = root, curParent = null;
while (cur != null && cur.val != key) {
curParent = cur;
if (cur.val > key) {
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = cur.right;
}
}
if (cur == null) {
return root;
}
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) {
cur = null;
} else if (cur.right == null) {
cur = cur.left;
} else if (cur.left == null) {
cur = cur.right;
} else {
TreeNode successor = cur.right, successorParent = cur;
while (successor.left != null) {
successorParent = successor;
successor = successor.left;
}
if (successorParent.val == cur.val) {
successorParent.right = successor.right;
} else {
successorParent.left = successor.right;
}
successor.right = cur.right;
successor.left = cur.left;
cur = successor;
}
if (curParent == null) {
return cur;
} else {
if (curParent.left != null && curParent.left.val == key) {
curParent.left = cur;
} else {
curParent.right = cur;
}
return root;
}
}
}
43. 数组中的第K个最大元素
43.1. 题目描述
43.2. 解题思路
方法一:基于快速排序的选择方法

class Solution {
int quickselect(int[] nums, int l, int r, int k) {
if (l == r) return nums[k];
int x = nums[l], i = l - 1, j = r + 1;
while (i < j) {
do i++; while (nums[i] < x);
do j--; while (nums[j] > x);
if (i < j){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
if (k <= j) return quickselect(nums, l, j, k);
else return quickselect(nums, j + 1, r, k);
}
public int findKthLargest(int[] _nums, int k) {
int n = _nums.length;
return quickselect(_nums, 0, n - 1, n - k);
}
}
方法二:基于堆排序的选择方法

class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int heapSize = nums.length;
buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize);
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= nums.length - k + 1; --i) {
swap(nums, 0, i);
--heapSize;
maxHeapify(nums, 0, heapSize);
}
return nums[0];
}
public void buildMaxHeap(int[] a, int heapSize) {
for (int i = heapSize / 2; i >= 0; --i) {
maxHeapify(a, i, heapSize);
}
}
public void maxHeapify(int[] a, int i, int heapSize) {
int l = i * 2 + 1, r = i * 2 + 2, largest = i;
if (l < heapSize && a[l] > a[largest]) {
largest = l;
}
if (r < heapSize && a[r] > a[largest]) {
largest = r;
}
if (largest != i) {
swap(a, i, largest);
maxHeapify(a, largest, heapSize);
}
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
44. 前 K 个高频元素
44.1. 题目描述
44.2. 解题思路
方法一:堆

class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> occurrences = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
occurrences.put(num, occurrences.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
// int[] 的第一个元素代表数组的值,第二个元素代表了该值出现的次数
PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<int[]>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] m, int[] n) {
return m[1] - n[1];
}
});
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : occurrences.entrySet()) {
int num = entry.getKey(), count = entry.getValue();
if (queue.size() == k) {
if (queue.peek()[1] < count) {
queue.poll();
queue.offer(new int[]{num, count});
}
} else {
queue.offer(new int[]{num, count});
}
}
int[] ret = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
ret[i] = queue.poll()[0];
}
return ret;
}
}
方法二:基于快速排序

class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> occurrences = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
occurrences.put(num, occurrences.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
// 获取每个数字出现次数
List<int[]> values = new ArrayList<int[]>();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : occurrences.entrySet()) {
int num = entry.getKey(), count = entry.getValue();
values.add(new int[]{num, count});
}
int[] ret = new int[k];
qsort(values, 0, values.size() - 1, ret, 0, k);
return ret;
}
public void qsort(List<int[]> values, int start, int end, int[] ret, int retIndex, int k) {
int picked = (int) (Math.random() * (end - start + 1)) + start;
Collections.swap(values, picked, start);
int pivot = values.get(start)[1];
int index = start;
for (int i = start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
// 使用双指针把不小于基准值的元素放到左边,
// 小于基准值的元素放到右边
if (values.get(i)[1] >= pivot) {
Collections.swap(values, index + 1, i);
index++;
}
}
Collections.swap(values, start, index);
if (k <= index - start) {
// 前 k 大的值在左侧的子数组里
qsort(values, start, index - 1, ret, retIndex, k);
} else {
// 前 k 大的值等于左侧的子数组全部元素
// 加上右侧子数组中前 k - (index - start + 1) 大的值
for (int i = start; i <= index; i++) {
ret[retIndex++] = values.get(i)[0];
}
if (k > index - start + 1) {
qsort(values, index + 1, end, ret, retIndex, k - (index - start + 1));
}
}
}
}
45. 数据流的中位数
45.1. 题目描述
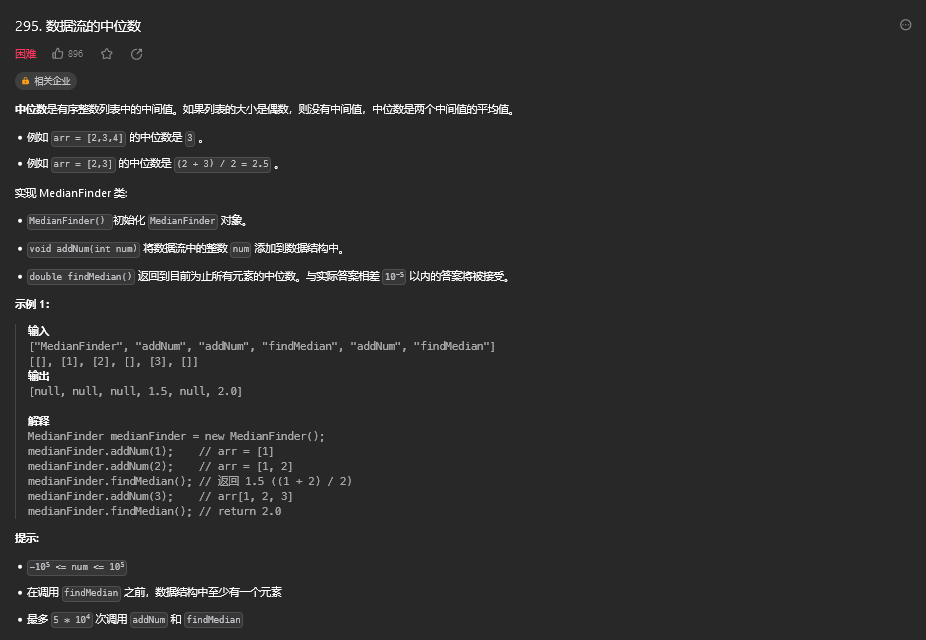
45.2. 解题思路
方法一:优先队列

class MedianFinder {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queMin;
PriorityQueue<Integer> queMax;
public MedianFinder() {
queMin = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((a, b) -> (b - a));
queMax = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((a, b) -> (a - b));
}
public void addNum(int num) {
if (queMin.isEmpty() || num <= queMin.peek()) {
queMin.offer(num);
if (queMax.size() + 1 < queMin.size()) {
queMax.offer(queMin.poll());
}
} else {
queMax.offer(num);
if (queMax.size() > queMin.size()) {
queMin.offer(queMax.poll());
}
}
}
public double findMedian() {
if (queMin.size() > queMax.size()) {
return queMin.peek();
}
return (queMin.peek() + queMax.peek()) / 2.0;
}
}
方法二:有序集合 + 双指针

class MedianFinder {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> nums;
int n;
int[] left;
int[] right;
public MedianFinder() {
nums = new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>();
n = 0;
left = new int[2];
right = new int[2];
}
public void addNum(int num) {
nums.put(num, nums.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
if (n == 0) {
left[0] = right[0] = num;
left[1] = right[1] = 1;
} else if ((n & 1) != 0) {
if (num < left[0]) {
decrease(left);
} else {
increase(right);
}
} else {
if (num > left[0] && num < right[0]) {
increase(left);
decrease(right);
} else if (num >= right[0]) {
increase(left);
} else {
decrease(right);
System.arraycopy(right, 0, left, 0, 2);
}
}
n++;
}
public double findMedian() {
return (left[0] + right[0]) / 2.0;
}
private void increase(int[] iterator) {
iterator[1]++;
if (iterator[1] > nums.get(iterator[0])) {
iterator[0] = nums.ceilingKey(iterator[0] + 1);
iterator[1] = 1;
}
}
private void decrease(int[] iterator) {
iterator[1]--;
if (iterator[1] == 0) {
iterator[0] = nums.floorKey(iterator[0] - 1);
iterator[1] = nums.get(iterator[0]);
}
}
}
46. 无限集中的最小数字
46.1. 题目描绘
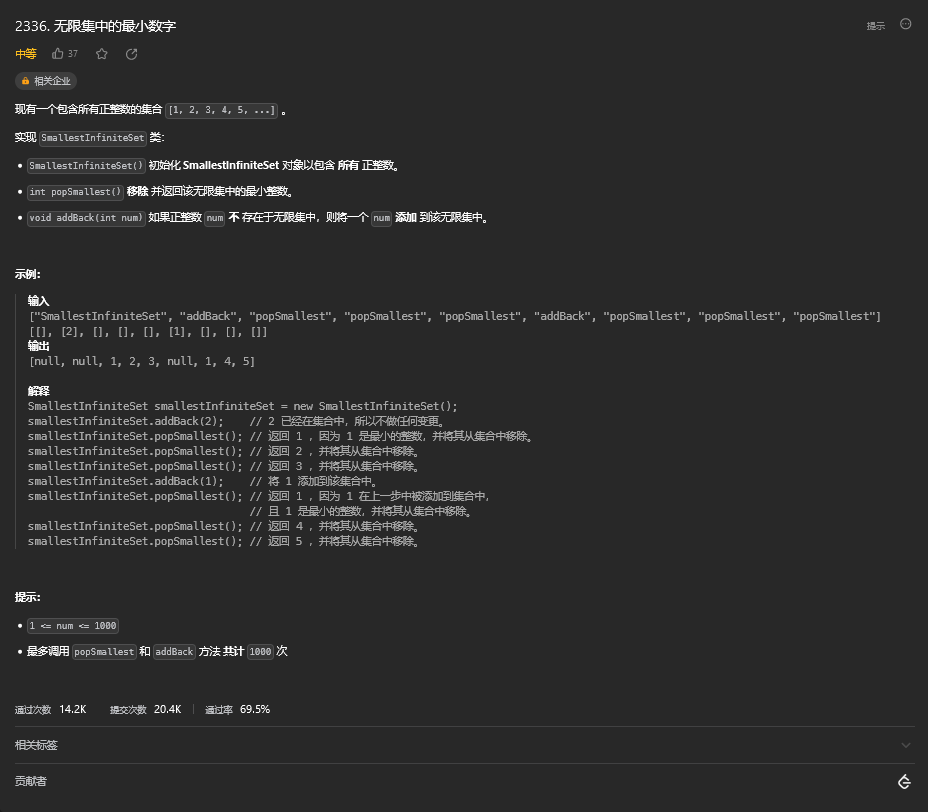
46.2. 解题思路
方法一:优先队列
用 index 记录正整数的取值进度,用优先队列保存后续加入的值
class SmallestInfiniteSet {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue;
int index;
public SmallestInfiniteSet() {
queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
index = 0;
}
public int popSmallest() {
if(!queue.isEmpty()){
return queue.peek() > index ? ++index: queue.poll();
}
return ++index;
}
public void addBack(int num) {
if (!queue.contains(num) && index >= num) {
queue.offer(num);
}
}
}
47. 最大子序列的分数
47.1. 题目描述
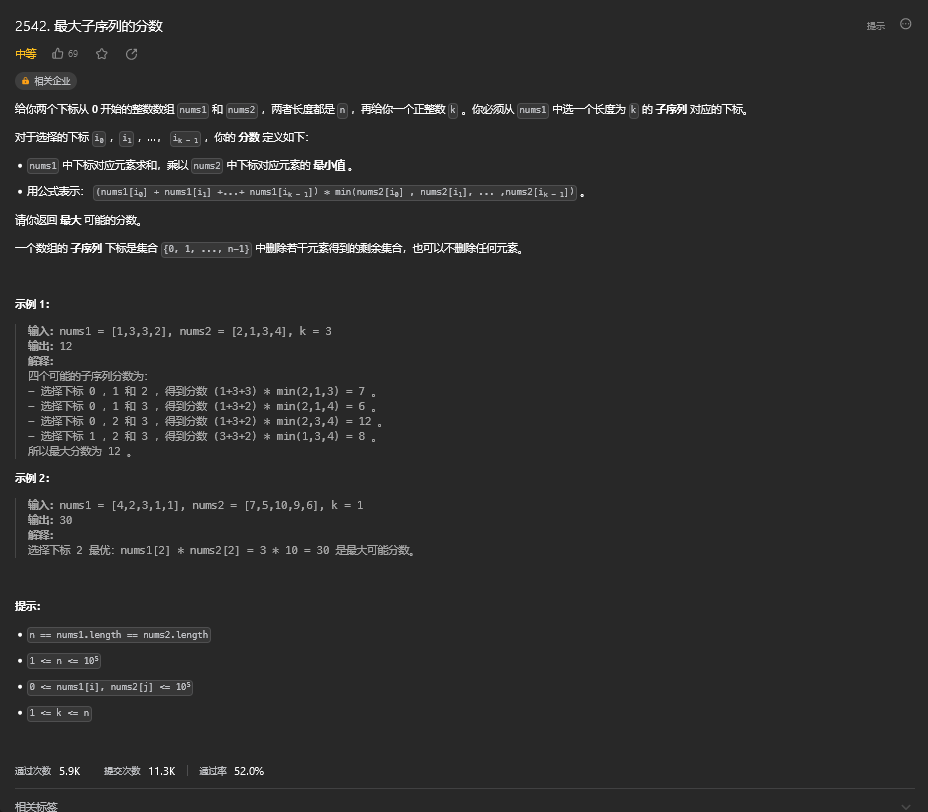
47.2. 解题思路
方法一:优先队列

class Solution {
public long maxScore(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
int n = nums1.length;
long ans = 0L;
Integer[] sorts = new Integer[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) sorts[i] = i;
Arrays.sort(sorts,(a,b)->nums2[b]-nums2[a]);
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
long sum = 0L;
for(int i = 0; i < k-1; i++){
sum += nums1[sorts[i]];
pq.offer(nums1[sorts[i]]);
}
for(int i = k-1; i < n; i++){
sum += nums1[sorts[i]];
pq.offer(nums1[sorts[i]]);
ans = Math.max(ans,nums2[sorts[i]]*sum);
sum -= pq.poll();
}
return ans;
}
}
}
48. 雇佣 K 位工人的总代价
48.1. 题目描述

48.2. 解题思路
方法一: 双堆简单模拟
class Solution {
public long totalCost(int[] costs, int k, int candidates) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> q1 = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
PriorityQueue<Integer> q2 = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
int l = candidates, n = costs.length, r = Math.max(l - 1, n - candidates - 1);
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < candidates; i++) q1.add(costs[i]);
for (int i = n - 1; i > r; i--) q2.add(costs[i]);
while (k-- > 0) {
if (!q1.isEmpty() && !q2.isEmpty()) {
if (q1.peek() <= q2.peek()) {
ans += q1.poll();
if (l <= r) q1.add(costs[l++]);
} else {
ans += q2.poll();
if (l <= r) q2.add(costs[r--]);
}
} else if(q2.isEmpty()) {
ans += q1.poll();
if (l <= r) q1.add(costs[l++]);
} else if (q1.isEmpty()) {
ans += q2.poll();
if (l <= r) q2.add(costs[r--]);
}
}
return ans;
}
}