目录
[1.1 静态变量](#1.1 静态变量)
[1.2 静态内存解析](#1.2 静态内存解析)
[1.3 static的应用与练习](#1.3 static的应用与练习)
[2.1 单例模式](#2.1 单例模式)
[2.2 如何实现单例模式](#2.2 如何实现单例模式)
[3.1 详解](#3.1 详解)
[3.2 练习,测试](#3.2 练习,测试)
[5.1 abstract](#5.1 abstract)
[5.2 练习](#5.2 练习)
[6.1 接口的理解](#6.1 接口的理解)
[6.2 接口的多态性](#6.2 接口的多态性)
[6.3 抽象类和接口对比](#6.3 抽象类和接口对比)
[6.4 接口的使用练习](#6.4 接口的使用练习)
[6.4.1 练习1](#6.4.1 练习1)
[1. 定义接口](#1. 定义接口)
[2. 实现接口](#2. 实现接口)
[3. 使用接口](#3. 使用接口)
[4. 测试支付系统](#4. 测试支付系统)
[6.4.2 练习2](#6.4.2 练习2)
[1. 接口](#1. 接口)
[2. Developer类](#2. Developer类)
[3. 父类Vehicle](#3. 父类Vehicle)
[4. 三个子类 Bicycle ElectricVhicle Car](#4. 三个子类 Bicycle ElectricVhicle Car)
[5. VehicleTest测试类](#5. VehicleTest测试类)
[6. 结果](#6. 结果)
一、static关键字
1.1 静态变量
static(静态的):用来修饰的结构、属性、方法;代码块、内部类
对比静态变量与实例变量:
①个数
- >静态变量:在内存空间中只有一份, 被类的多个对象所共享。
- >实例变量:类的每一个实例(或对象)都保存着一份实例变量。
②内存位置
- >静态变量: jdk6及之前:存放在方法区。jdk7及之后: 存放在堆空间
- >实例变量:存放在堆空间的对象实体中。
③加载时机
- >静态变量:随着类的加载而加载,由于类只会加载一次, 所以静态变量也只有一份。
- >实例变量:随着对象的创建而加载。每个对象拥有一份实例变量。
④调用者
- >静态变量:可以被类直接调用,也可以使用对象调用。
- >实例变量:只能使用对象进行调用。
⑤判断是否可以调用---> 从生命周期的角度解释
|----|-----|------|
| | 类变量 | 实例变量 |
| 类 | yes | no |
| 对象 | yes | yes |
⑥消亡时机.
- 静态变量:随着类的卸载而消亡
- 实例变量:随着对象的消亡而消亡
1.2 静态内存解析
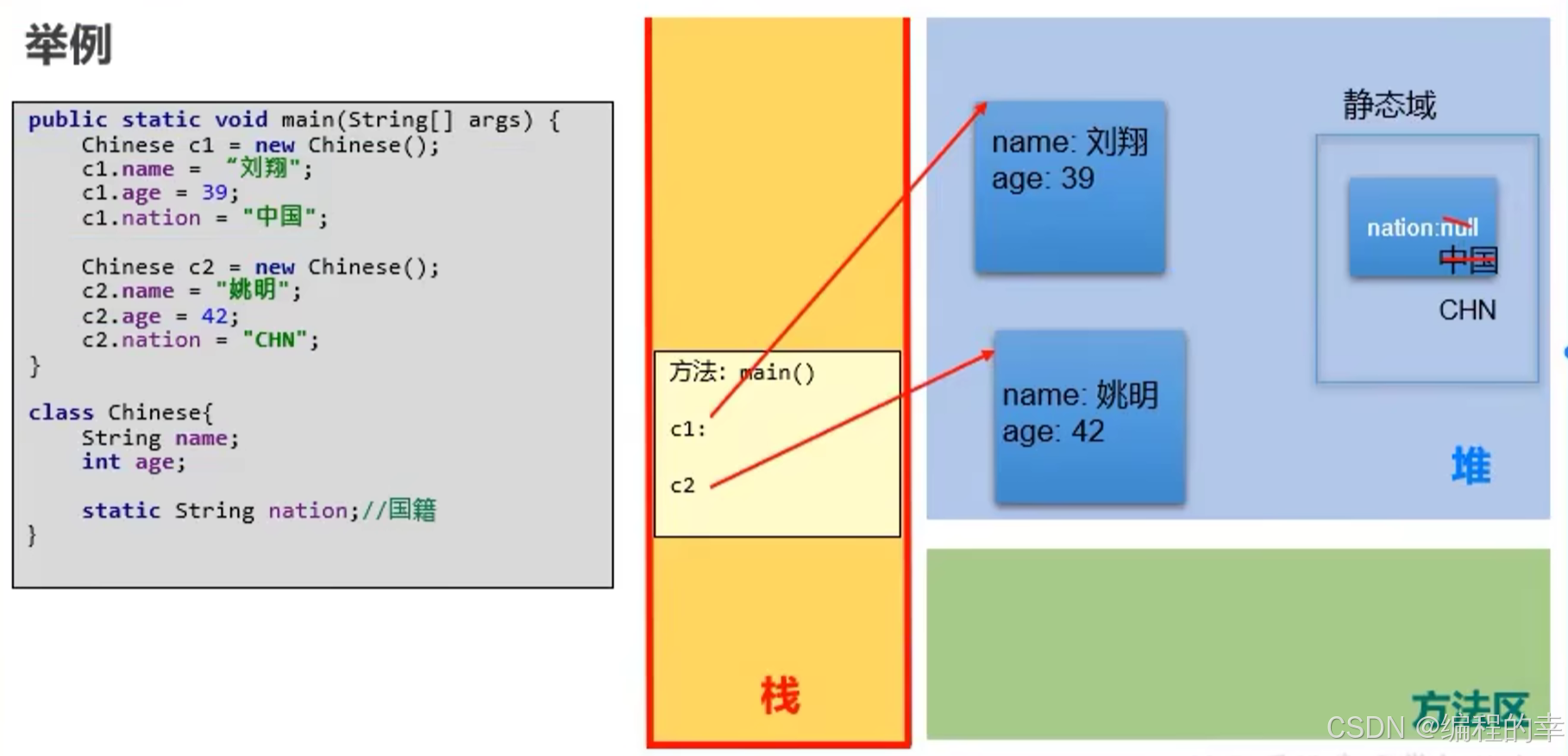
1.3 static的应用与练习
java
import java.util.Objects;
public class Account {
private int id;
private String password;//密码
private double balance;//金额
private static double interestRate;//利率
private static double minBalance = 1.0;
private static int init = 1001;
public Account(){
this.id = init;
init++;
password = "000000";
}
public Account(String password, double balance) {
this.password = password;
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public static double getInterestRate() {
return interestRate;
}
public static void setInterestRate(double interestRate) {
Account.interestRate = interestRate;
}
public static double getMinBalance() {
return minBalance;
}
public static void setMinBalance(double minBalance) {
Account.minBalance = minBalance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account acct1 = new Account();
System.out.println(acct1);
Account acct2 = new Account("123456",1155);
System.out.println(acct2);
Account.setInterestRate(0.0123);
Account.setMinBalance(10);
System.out.println("银行存款的利率:" + Account.getInterestRate());
System.out.println("银行最小存款: " + Account.getMinBalance());
}
}二、单例设计模式
2.1 单例模式
何为单例模式?
- 采取一定的办法保证在整个软件系统中,堆某个类只能存在一个对象实例,并且该类只提供一个取得其对象实例的方法。
经典设计模式:共23种
2.2 如何实现单例模式
1.饿汉式:
java
public class boyFirend {
private int age;
private String name;
//1.私有化构造器
private boyFirend(){
}
//2.创建对象私有化
private static boyFirend b1 = new boyFirend();
//3.
public static boyFirend getG1(){
return b1;
}
}2.懒汉式:
java
//懒汉式
public class GirlFirend {
private int age;
private String name;
//1.私有化构造器
private GirlFirend(){
}
//2.创建对象私有化
private static GirlFirend g1 = null;
//3.
public static GirlFirend getG1(){
if (g1 == null) {
g1 = new GirlFirend();
}
return g1;
}
}两种模式的对比:
特点:
- 饿汉式:"立即加载",随着类的加载,当前唯一的实例创建。
- 懒汉式:"延迟加载",在需要使用时,进行创建
优缺点:
- 饿汉式:(优点)写法简单,使用更快,线程安全(缺点)内存中占用时间长。
- 懒汉式:(优点)节省内存空间(缺点)线程不安全
三、代码块
3.1 详解
用来初始化类或对象的信息(即初始化类或对象的成员变量)
代码块修饰:只能使用static进行修饰
代码块分类:
- 静态代码块;使用static修饰
- 非静态代码块:不适用static修饰
格式:
{
//内容
}
static{
//内容
}
3.2 练习,测试
java
class User {
private String userName;
private String password;
private long registrationTime;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public long getRegistrationTime() {
return registrationTime;
}
{
System.out.println("新用户注册");
registrationTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public User() {
userName = System.currentTimeMillis() +"";
password = "123456";
}
public User(String userName, String password) {
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
}
public String getInfo() {
return
"用户名='" + userName +
", 密码='" + password +
", 注册时间=" + registrationTime ;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u1 = new User();
System.out.println(u1.getInfo());
User u2 = new User("张三","654321");
System.out.println(u2.getInfo());
}
}注意:运行上,由父及子,静态先行。记住:执行的先后顺序:默认-显式-代码块-构造器-对象
小测试:(请给出运行结果)
java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sub s = new Sub();
}
}
class Base{
Base(){
method(100);
}
{
System.out.println("base");
}
public void method(int i){
System.out.println("base :" + i);
}
}
class Sub extends Base{
Sub(){
super.method(70);
}
{
System.out.println("Sub");
}
public void method(int j){
System.out.println("sub :" + j);
}
}答案:

四、final关键字
final关键字: 修饰符,用于限制类、方法和变量的行为。
可在哪些位置赋值:
- 显示
- 代码块中
- 构造器中
final作用:
修饰类:表此类不能被继承
java
final class FinalClass {
void display() {
System.out.println("This is a final class.");
}
}
// class SubClass extends FinalClass { // 这行代码会导致编译错误
// }修饰方法:此方法不能被重写
java
class Parent {
final void show() {
System.out.println("This is a final method.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
// void show() { // 这行代码会导致编译错误
// System.out.println("Trying to override a final method.");
// }
}修饰变量:成员和局部变量都可修饰,此时"变量"其实变成了"常量",不可更改。
java
final int x = 10;
// x = 20; // 这行代码会导致编译错误
final StringBuilder a1 = new StringBuilder("Hello");
// a1 = new StringBuilder("World"); // 这行代码会导致编译错误
a1.append(", World!"); // 这行是允许的,因为a1引用的对象内容是可以改变的final搭配static使用:等于全局常量
java
class Constants {
static final int MAX_USERS = 100;
static final String APP_NAME = "MyApp";
}习题练习:

报错:++x导致x的值改变
五、抽象类与抽象方法
5.1 abstract
abstract:抽象的
abstract修饰类:
- 此类为抽象类。
- 抽象类不能实例化。
- 抽象类中包含构造器,因为子类实例化,直接或间接调用父类的构造器。
- 抽象类可无抽象方法,有抽象方法一定为抽象类。
abstract修饰方法
- 此方法为抽象方法。
- 抽象方法只有方法声明,没有方法体。
- 抽象方法的功能确定,不知具体实现。
- 抽象方法必须重写父类中的所有抽象方法,才能实例化,否则,此子类还是抽象类。
abstract不能使用的场景:属性,构造器,代码块
5.2 练习
场景:编写工资系统,不同类型的员工(多态)按月发工资,如果某个月是某个employee对象的生日,则当月的工资增加100


代码:
java
//Employee类
public abstract class Employee {
private String name;
private int number;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.number = number;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public abstract double earnings();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", number=" + number +
", birthday='" + birthday.toDateString() + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
//HourEmployee类
public class HourEmployee extends Employee{
private double wage;
private int hour;
public HourEmployee() {
}
public HourEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, double wage, int hour) {
super(name, number, birthday);
this.wage = wage;
this.hour = hour;
}
public double getWage() {
return wage;
}
public void setWage(double wage) {
this.wage = wage;
}
public int getHour() {
return hour;
}
public void setHour(int hour) {
this.hour = hour;
}
@Override
public double earnings() {
return wage * hour;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HourEmployee{" +
super.toString() +
'}';
}
}
//MyDate类
public class MyDate {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate() {
}
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public String toDateString(){
return year + "年" + month + "月" + day +"日";
}
}
//PayrollSystem类
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PayrollSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
Employee[] emps = new Employee[2];
emps[0] = new SalariedEmployee("张胜男", 1001,
new MyDate(1992, 12, 30), 2000);
emps[1] = new HourEmployee("李四", 1002,
new MyDate(1992, 10, 10),15 ,240);
System.out.println("请输入当前的月份: ");
int month = scan.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < emps.length; i++) {
System.out.println(emps[i].toString());
if (month == emps[i].getBirthday().getMonth()){
double a = 100.0;
double b =emps[i].earnings() + a;
System.out.println("工资为:"+ b);
System.out.println("生日快乐,加薪100");
}else{
System.out.println("工资为:"+emps[i].earnings());
}
scan.close();
}
}
}
//SalariedEmployee类
public class SalariedEmployee extends Employee{
private double monthlySalary;
public SalariedEmployee() {
}
@Override
public double earnings(){
return monthlySalary;
}
public SalariedEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, double monthlySalary) {
super(name, number, birthday);
this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary;
}
public double getMonthlySalary() {
return monthlySalary;
}
public void setMonthlySalary(double monthlySalary) {
this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SalariedEmployee{" +
super.toString() +
'}';
}
}六、接口
6.1 接口的理解
- 接口的本质是契约、标准、规范,就像我们的法律一样。制定好后大家都要遵守。
2.定义接口的关键字: interface
3.接口内部结构的说明:
可以声明:
- 属性:必须使用public static final修饰
- 方法: jdk8之前:声明抽象方法,修饰为public abstractjdk8 :声明静态方法、默认方法
- jdk9 :声明私有方法
不可以声明:构造器
4.接口与类的关系:实现关系
5.格式:
- class A extends SuperA implements B C{}
- A相较于SuperA来讲,叫做子类A相较于B, C来讲,叫做实现类。
6.满足此关系之后,说明:
- 类可以实现多个接口。
- 类针对于接口的多实现,一定程度上就弥补了类的单继承的局限性。
- 类必须将实现的接口中的所有的抽象方法都重写(或实现),方可实例化。否则,此实现类必须声明为抽象类。
7.接口与接口的关系:继承关系,且可以多继承
6.2 接口的多态性
接口名 变量名 = new 实现类对象;
以下为举例:Computer是类,transferData()方法,USB是接口,printer打印机
- 创建接口实现类的对象
Computer computer = new Computer();
Printer printer = new printer();
- 创建接口实现类的匿名对象
computer.transferData (new Computer);
- 创建接口匿名实现类的对象
USB usb1 = new USB(){
//重写接口中方法
}
computer.transferData (usb1);
- 创建接口匿名实现类的匿名对象
computer.transferData (new USB(){
//重写接口中方法
});
6.3 抽象类和接口对比
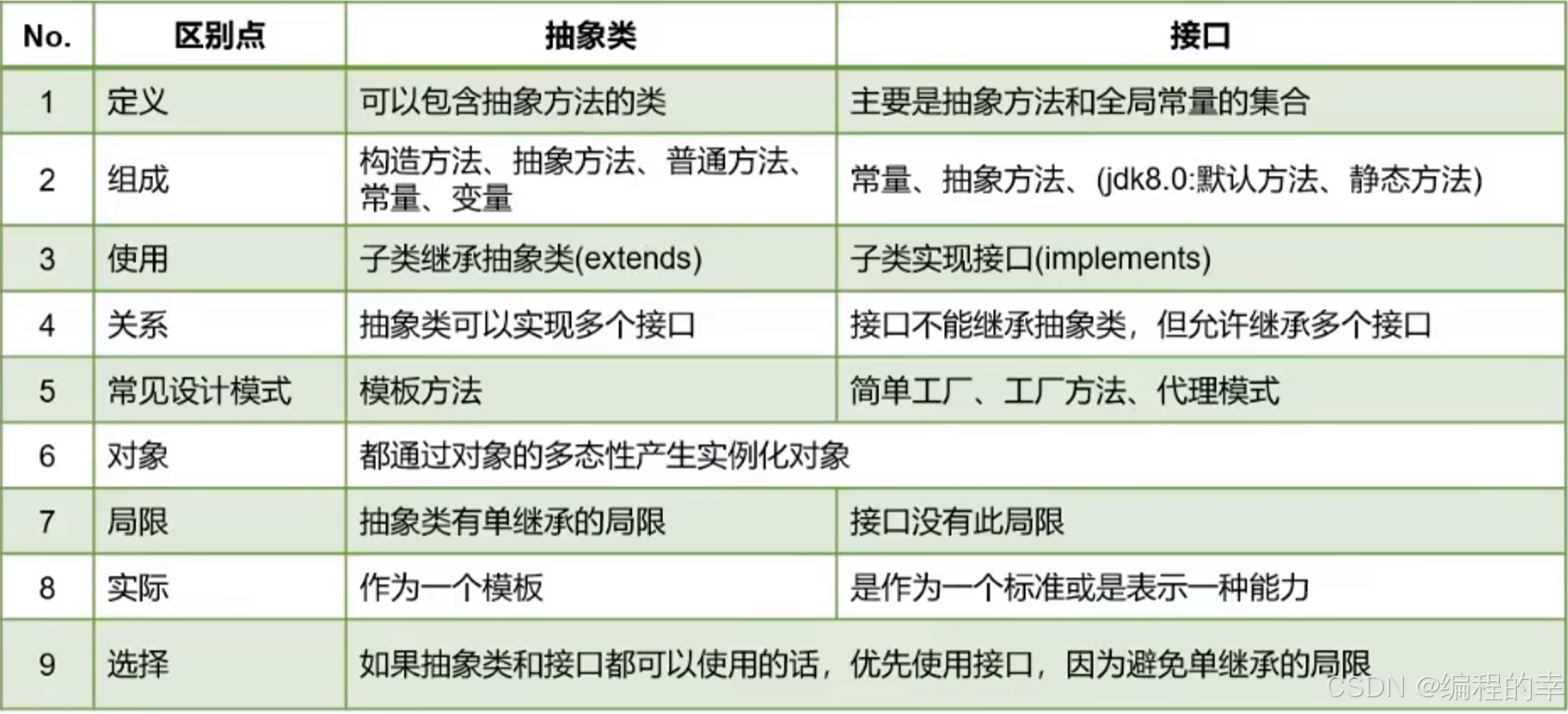
6.4 接口的使用练习
6.4.1 练习1
假设要创建一个,不同的支付方式(如信用卡、支付宝)需要实现相同的接口。
1. 定义接口
定义一个支付接口 Payment,包括方法 pay() 和 refund()。
java
public interface Payment {
void pay(double amount);
void refund(double amount);
}2. 实现接口
实现 CreditCardPayment 和 AliPay 两种支付方式。
java
public class CreditCardPayment implements Payment {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用信用卡支付 " + amount + "元");
}
@Override
public void refund(double amount) {
System.out.println("退款到信用卡" + amount + "元");
}
}
public class AliPay implements Payment {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用支付宝支付 " + amount + "元");
}
@Override
public void refund(double amount) {
System.out.println("退款到支付宝 " + amount + "元");
}
}3. 使用接口
创建一个简单的支付处理类,使用接口来处理支付逻辑。
java
public class PaymentProcessor {
private Payment payment;
public PaymentProcessor(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
}
public void processPayment(double amount) {
payment.pay(amount);
}
public void processRefund(double amount) {
payment.refund(amount);
}
}4. 测试支付系统
在主程序中,创建不同的支付方式并测试。
java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用信用卡支付
Payment creditCardPayment = new CreditCardPayment();
PaymentProcessor creditCardProcessor = new PaymentProcessor(creditCardPayment);
creditCardProcessor.processPayment(100.0);
creditCardProcessor.processRefund(50.0);
// 使用支付宝支付
Payment aliPayPayment = new AliPay();
PaymentProcessor aliPayProcessor = new PaymentProcessor(aliPayPayment);
aliPayProcessor.processPayment(200.0);
aliPayProcessor.processRefund(80.0);
}
}5.结果
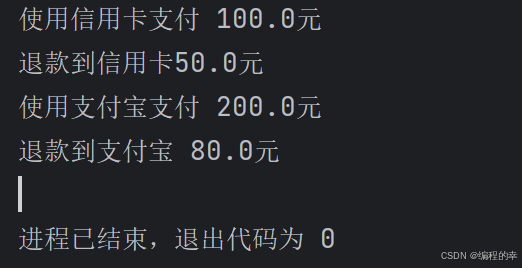
6.4.2 练习2
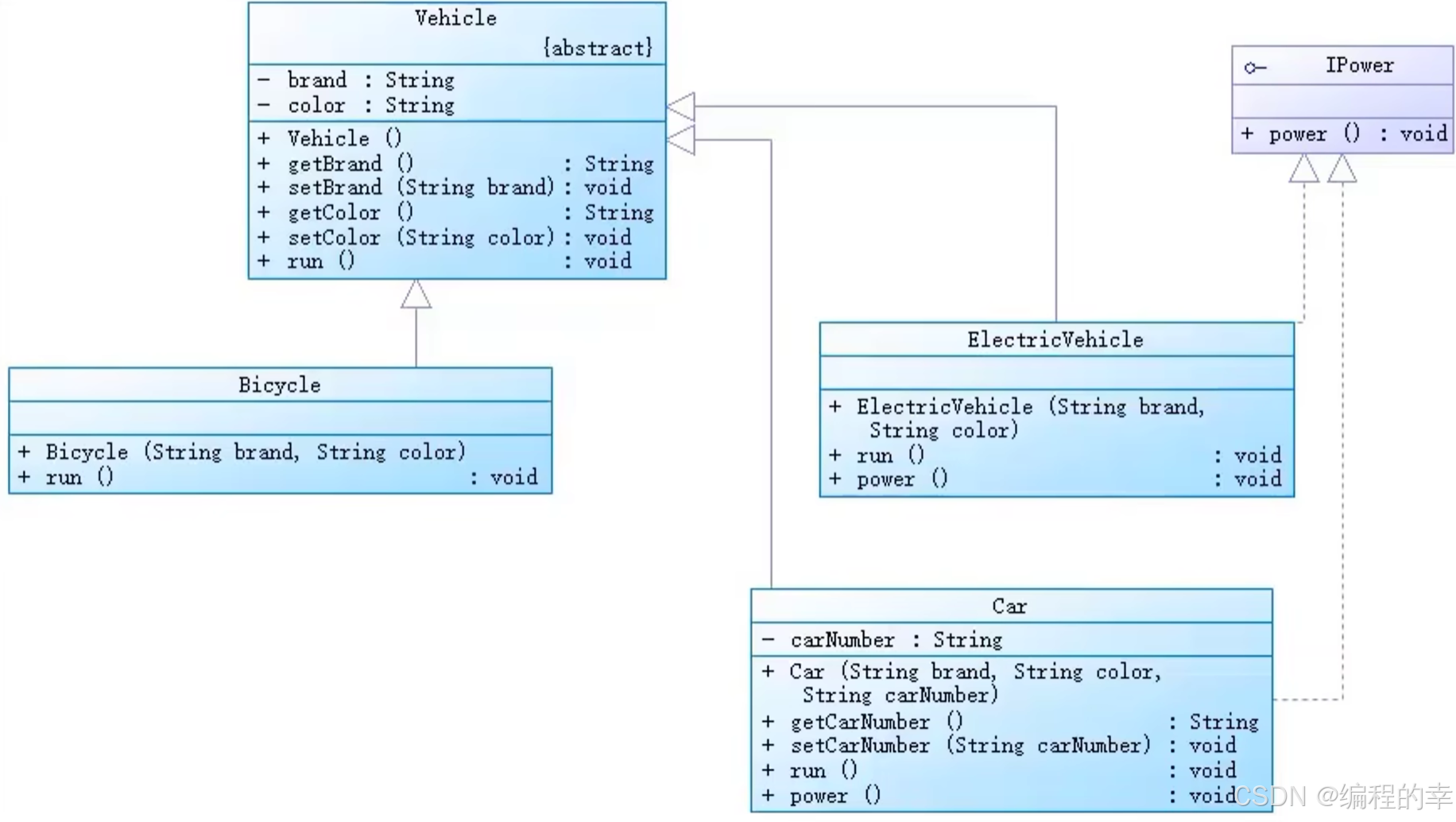
模拟场景:
UML类图:(UML类图讲解可跳转: 构造器和UML类图_类图中怎么创建加号-CSDN博客)

代码实现:
1. 接口
java
interface IPower {
public void power();
}2. Developer类
java
package test2;
public class Developer {
private int age;
public String name;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void takingVehicle(Vehicle vehicle){
vehicle.run();
}
}3. 父类Vehicle
java
package test2;
public abstract class Vehicle {
private String brand;
private String color;
public Vehicle() {
}
public Vehicle(String brand, String color) {
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public abstract void run();
}4. 三个子类
Bicycle-ElectricVhicle-Car
java
package test2;
public class Car extends Vehicle implements IPower{
private String carName;
public Car() {
}
public Car(String brand, String color, String carName) {
super(brand, color);
this.carName = carName;
}
public String getCarName() {
return carName;
}
public void setCarName(String carName) {
this.carName = carName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("汽车靠内燃机驱动");
}
@Override
public void power() {
System.out.println("动力来自汽油");
}
}
package test2;
public class ElectricVhicle extends Vehicle implements IPower{
public ElectricVhicle() {
}
public ElectricVhicle(String brand, String color) {
super(brand, color);
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("电动车电机驱动");
}
@Override
public void power() {
System.out.println("动力来自电力");
}
}
package test2;
public class Bicycle extends Vehicle{
public Bicycle() {
}
public Bicycle(String brand, String color) {
super(brand, color);
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("靠脚蹬骑自行车");
}
}5. VehicleTest测试类
java
package test2;
public class VehicleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Developer developer = new Developer();
Vehicle[] vehicles = new Vehicle[3];
vehicles[0] = new Bicycle("凤凰牌","黄色");
vehicles[1] = new ElectricVhicle("理想","蓝色");
vehicles[2] = new Car("奔驰","黑色","京A88888");
for (int i = 0; i < vehicles.length; i++) {
developer.takingVehicle(vehicles[i]);
if (vehicles[i] instanceof IPower) {
((IPower) vehicles[i]).power();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}6. 结果
